Comprehensive Identification and Mechanistic Evaluation of Novel DHODH Inhibitors as Potent Broad-Spectrum Antiviral Agents
Abstract
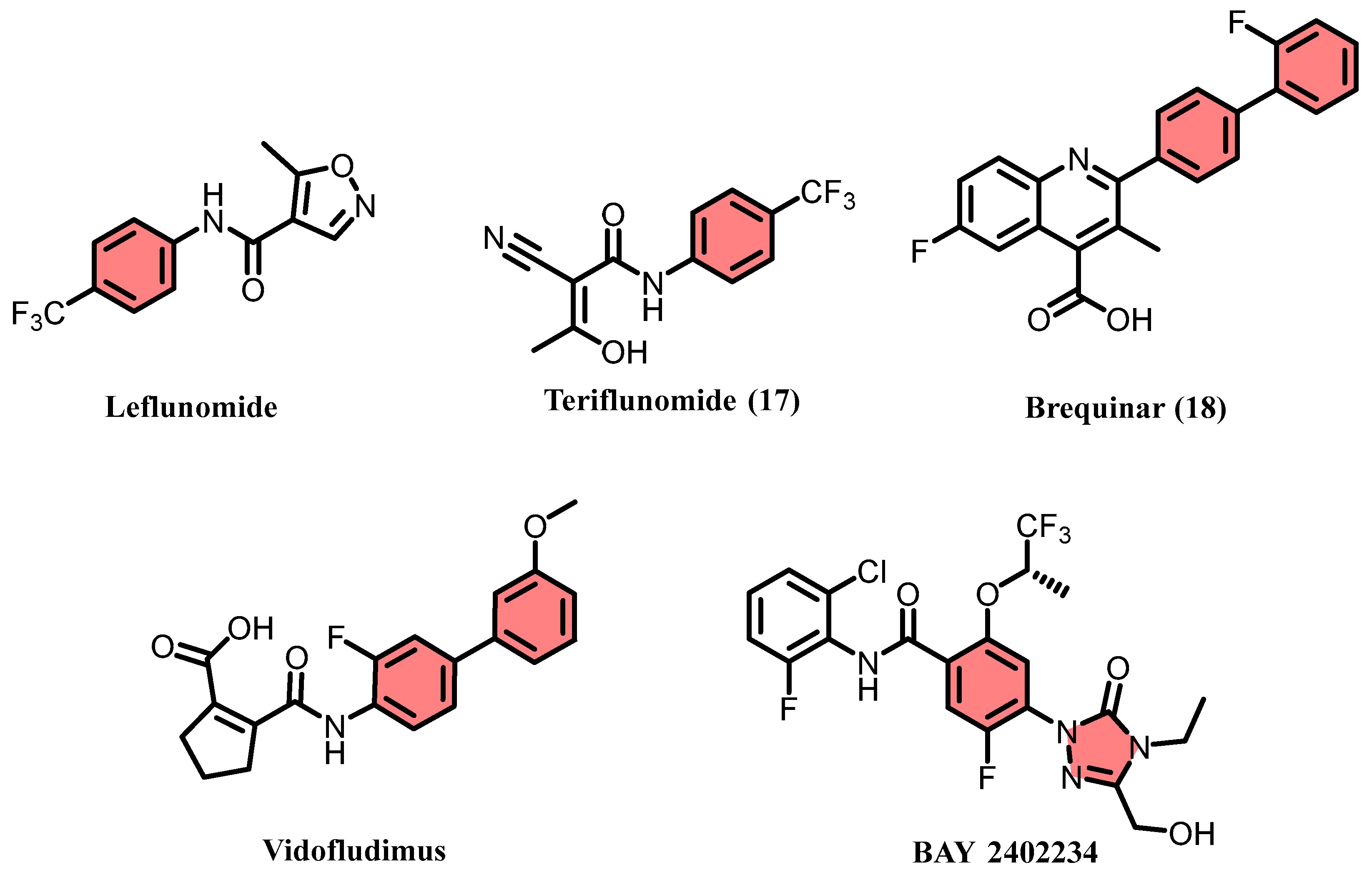
1. Introduction
2. Results
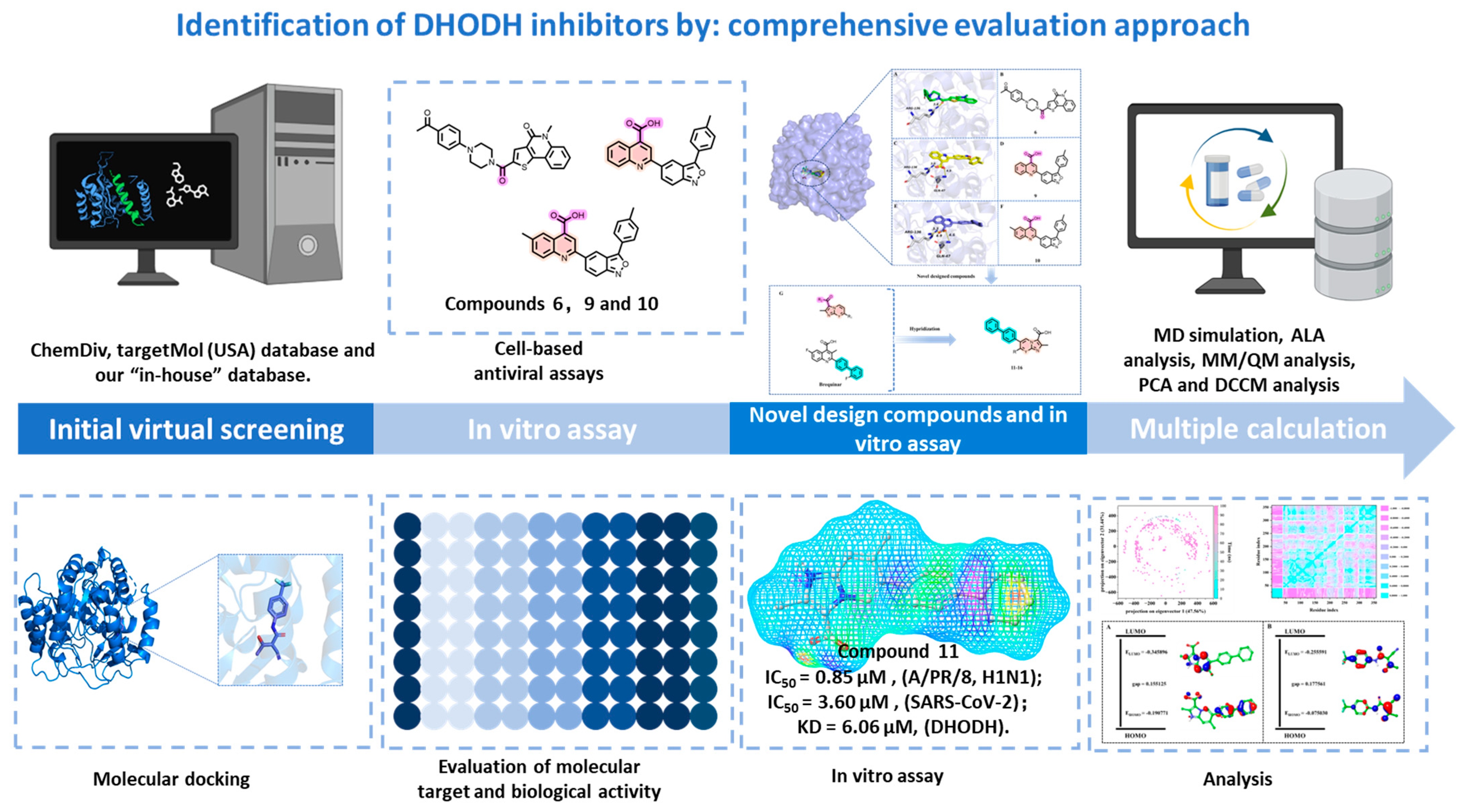
2.1. Virtual Screening
2.2. Biological Activity Assessment of the Candidate Compounds
2.3. Design of Novel Compounds
2.4. Biological Activity Assessment of the Novel Designed Compounds
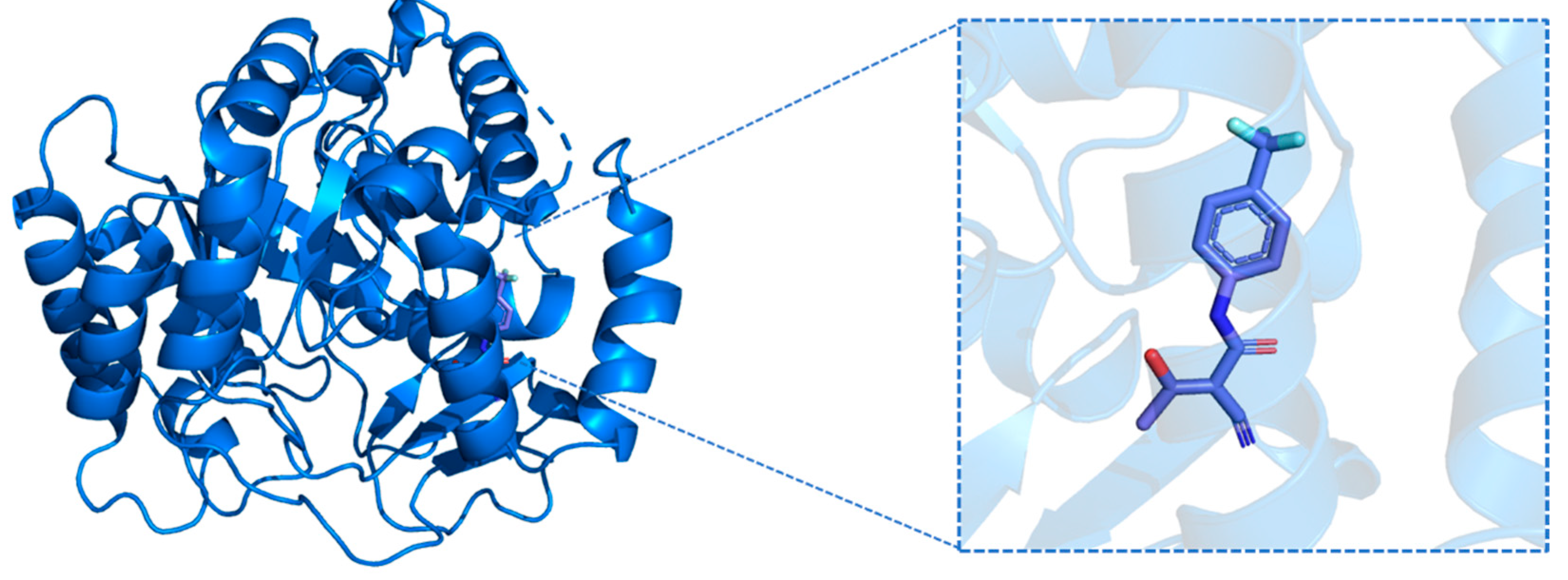
2.5. Validation of Molecular Target for Selected Compounds
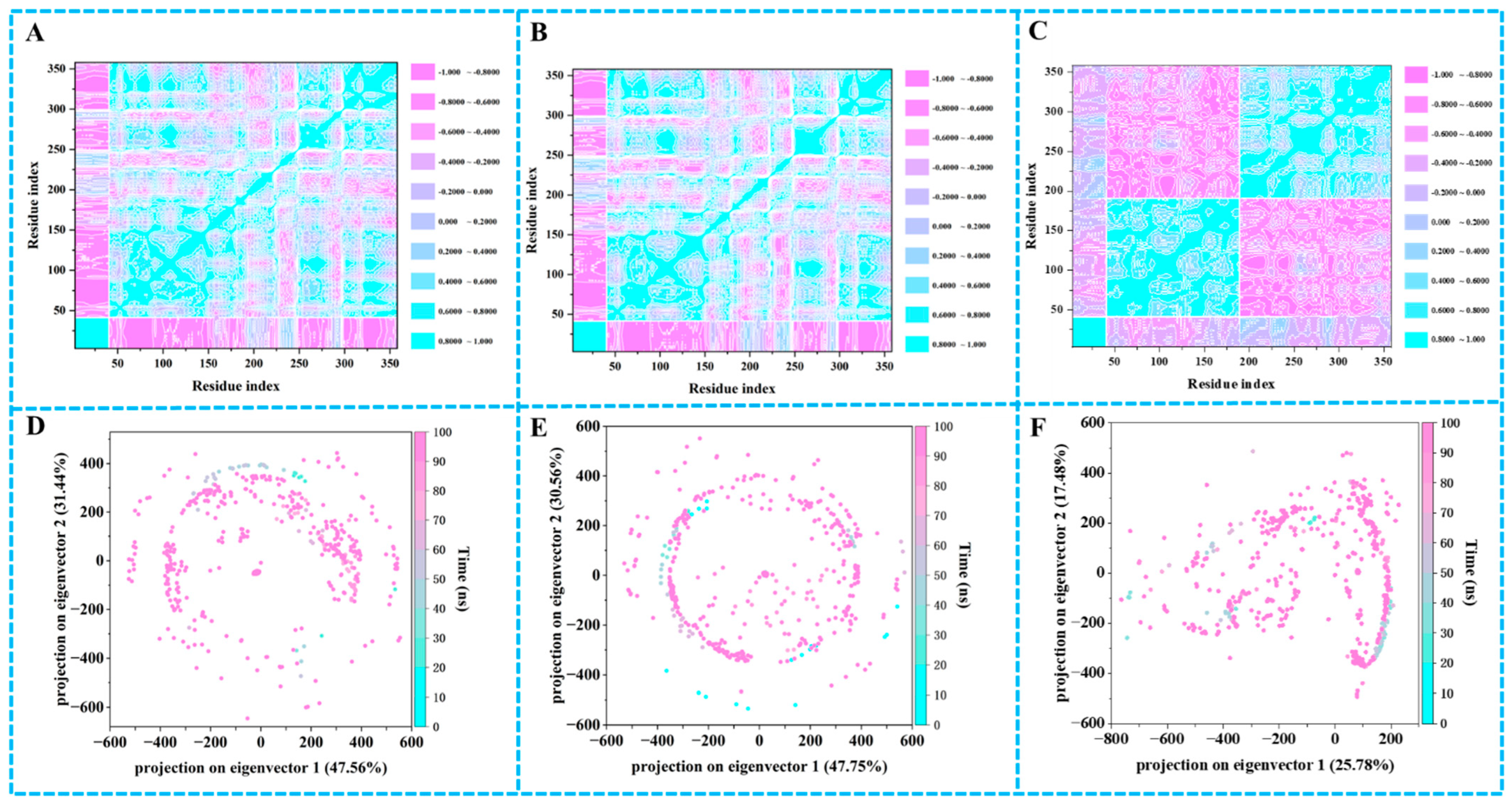
2.6. MD Simulation Analysis
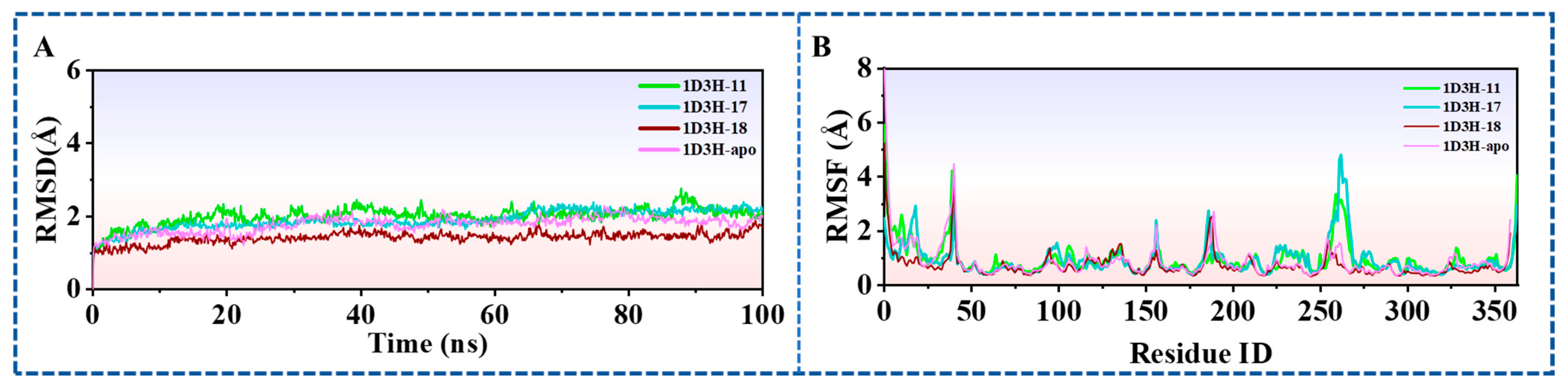
2.6.1. Stability of Dynamics Trajectory from RMSD Analysis
2.6.2. Analysis of Residue-Specific Mobility Derived from Root-Mean-Square Fluctuation (RMSF) Data
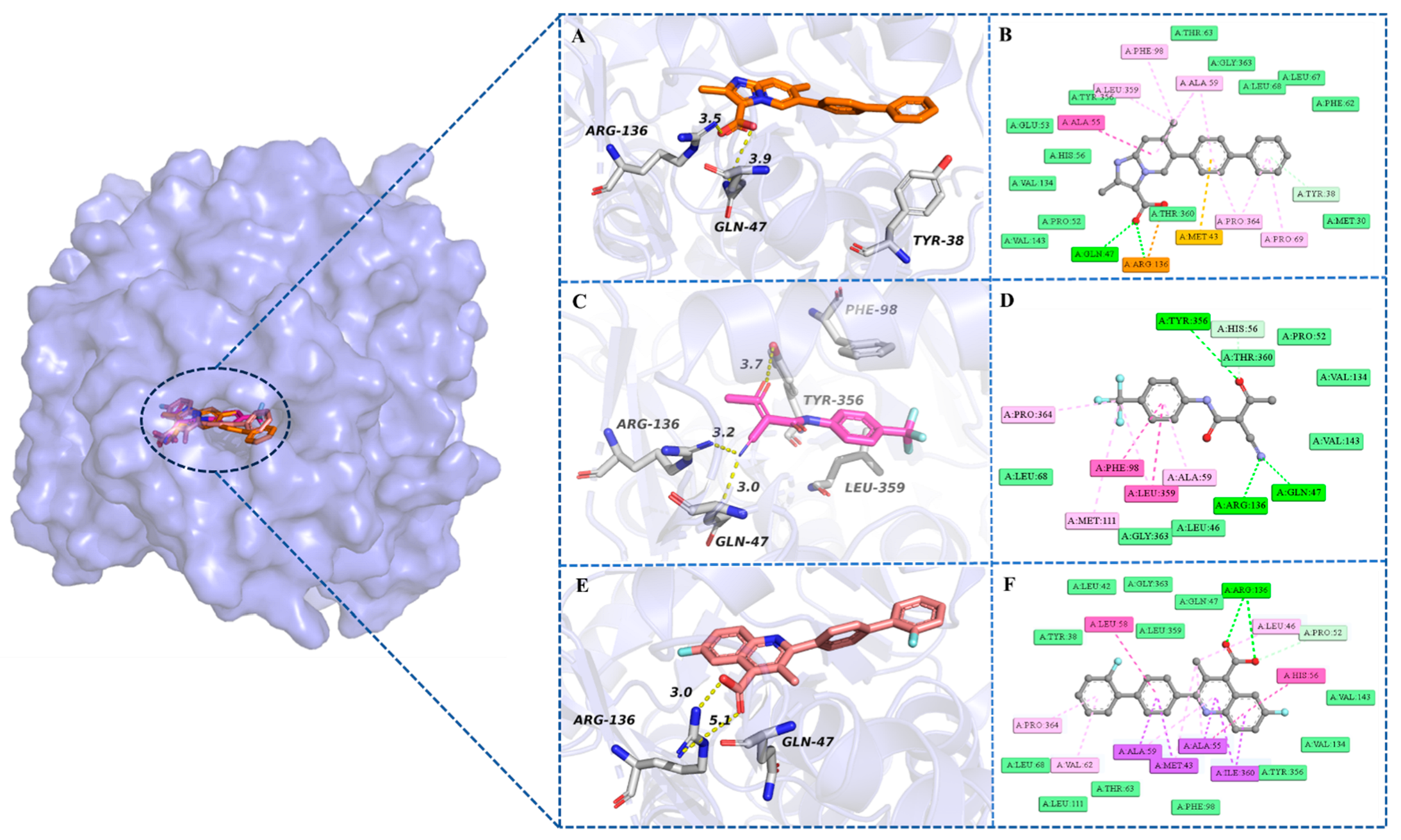
2.6.3. Analysis of Intermolecular Interactions Throughout the 100 ns MD Simulation
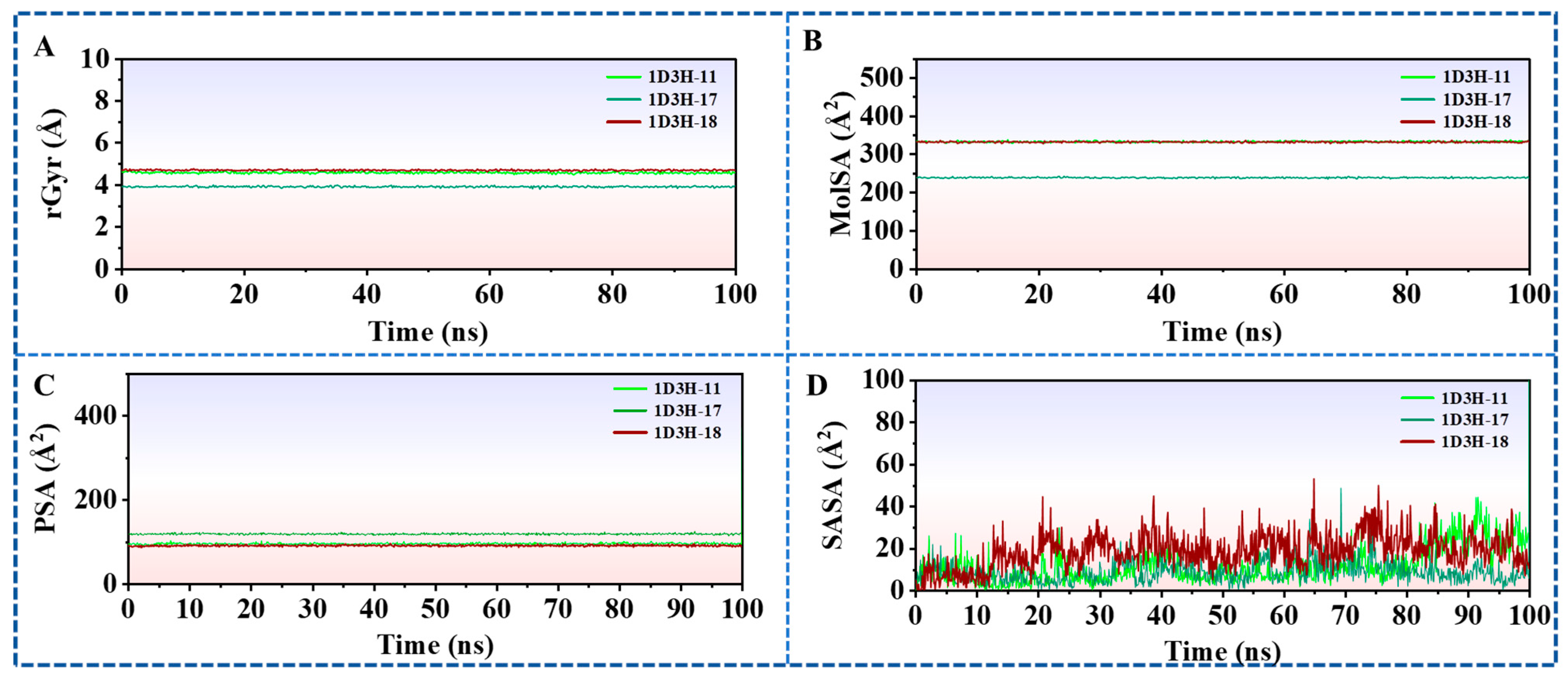
2.6.4. Ligands Properties Analysis Thorough the 100 ns MD Simulation
2.7. Alanine Scanning Mutagenesis (ASM)
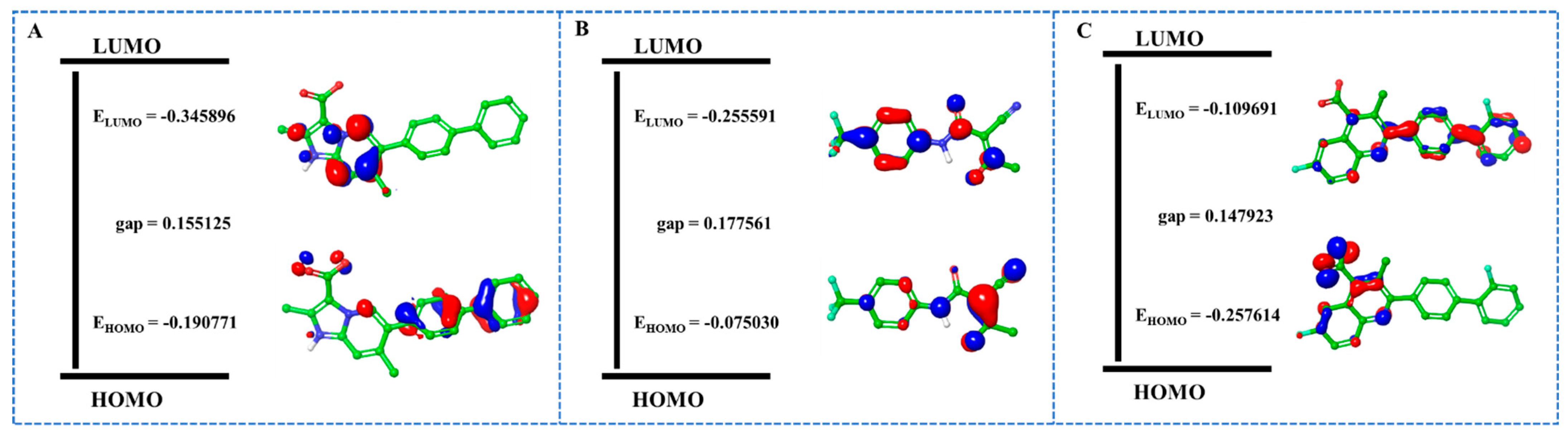
2.8. QM/MM Calculations
2.9. Principal Component Analysis (PCA) and Dynamic Cross-Correlation Matrices (DCCM) Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Virtual Screening
4.2. Prime/MM–GBSA Simulation
4.3. Lipinski’s Rule and ADMET Prediction
4.4. Materials
4.5. Cytotoxicity
4.6. Viral Titre Determination by Plaque Assay
4.7. Surface Plasmon Resonance Experiment
4.8. MD Simulations
4.9. ASM
4.10. QM/MM Calculations
4.11. DCCM Analysis and PCA
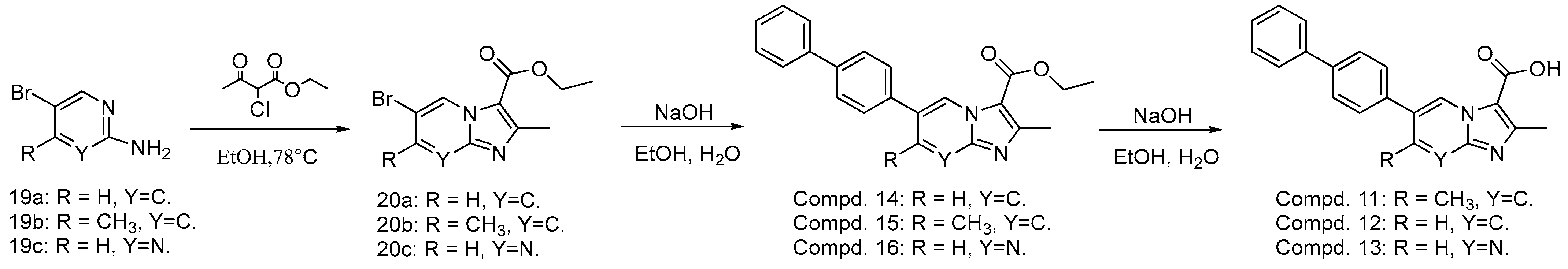
4.12. Chemistry
4.12.1. Preparation of Compounds 20a–20c
4.12.2. Preparation of Compounds 14–16
4.12.3. Preparation of Compounds 11–13
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DHODH | Dihydroorotate dehydrogenase |
| hDHODH | Human DHODH |
| DENV | Dengue viruses |
| ZIKV | Zika viruses |
| MD | Molecular dynamics |
| QM/MM | Quantum mechanics/molecular mechanics |
| MM/GBSA | Molecular Mechanics/Generalized Born Surface Area |
| SPR | Surface Plasmon Resonance |
| RMSD | Root-mean-square deviation |
| RMSF | Root-mean-square fluctuation |
| rGyr | Radius of gyration |
| MolSA | Molecular surface area |
| SASA | Solvent-accessible surface area |
| PSA | Polar surface area |
| HOMO | Highest occupied molecular orbital |
| LUMO | Lowest unoccupied molecular orbital |
| PCA | Principal component analysis |
| DCCM | Dynamic cross-correlation matrices |
| HTVS | High Throughput Virtual Screening |
| SP | Standard Precision |
| XP | Extra Precision |
| GB | Generalized Born |
| BBB | Blood–brain barrier |
| GI | Gastrointestinal |
| PPB | Plasma protein binding |
| DMEM | Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium |
| FBS | Fetal bovine serum |
| MTT | 3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide |
| MEM | Minimum essential medium |
| RU | Response unit |
| SPC | Simple Point Charge |
| ASM | Alanine scanning mutagenesis |
| PMFs | Potentials of mean force |
| WHAM | Weighted histogram analysis method |
| NBO | Natural Bond Orbital |
| TLC | Thin-layer chromatography |
| KD | Dissociation constants |
| MDCK | Madin–Darby Canine Kidney |
| SAR | Structure–activity relationship |
References
- Blackmore, N.J.; Reichau, S.; Jiao, W.; Hutton, R.D.; Baker, E.N.; Jameson, G.B.; Parker, E.J. Three sites and you are out: Ternary synergistic allostery controls aromatic amino acid biosynthesis in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J. Mol. Biol. 2013, 425, 1582–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Neidhardt, E.A.; Grossman, T.H.; Ocain, T.; Clardy, J. Structures of human dihydroorotate dehydrogenase in complex with antiproliferative agents. Structure 2000, 8, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purificação, A.D.; Benz, L.S.; Lima Silva, W.J.; Emery, F.S.; Andrade, C.H.; Weiss, M.S.; Nonato, M.C. Crystallographic structure of human dihydroorotate dehydrogenase in complex with the natural product inhibitor lapachol. ACS Omega 2025, 10, 29087–29097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladds, M.J.G.W.; van Leeuwen, I.M.M.; Drummond, C.J.; Chu, S.; Healy, A.R.; Popova, G.; Pastor Fernández, A.; Mollick, T.; Darekar, S.; Sedimbi, S.K.; et al. A DHODH inhibitor increases p53 synthesis and enhances tumor cell killing by p53 degradation blockage. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J.; Ren, C.; Tang, P.; Ouyang, L.; Wang, Y. Recent advances of human dihydroorotate dehydrogenase inhibitors for cancer therapy: Current development and future perspectives. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 232, 114176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, J.; O’Connor, P.W. An update of teriflunomide for treatment of multiple sclerosis. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2013, 9, 177–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Cao, L.; Gao, H.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Fang, F.; Lan, T.; Lou, Z.; Rao, Y. Discovery, optimization, and target identification of novel potent broad-spectrum antiviral inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 4056–4073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hölper, J.E.; Grey, F.; Baillie, J.K.; Regan, T.; Parkinson, N.J.; Höper, D.; Thamamongood, T.; Schwemmle, M.; Pannhorst, K.; Wendt, L.; et al. A genome-wide CRISPR/Cas9 screen reveals the requirement of host sphingomyelin synthase 1 for infection with pseudorabies virus mutant gD–Pass. Viruses 2021, 13, 1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luganini, A.; Sibille, G.; Mognetti, B.; Sainas, S.; Pippione, A.C.; Giorgis, M.; Boschi, D.; Lolli, M.L.; Gribaudo, G. Effective deploying of a novel DHODH inhibitor against herpes simplex type 1 and type 2 replication. Antivir. Res. 2021, 189, 105057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stegmann, K.M.; Dickmanns, A.; Heinen, N.; Blaurock, C.; Karrasch, T.; Breithaupt, A.; Klopfleisch, R.; Uhlig, N.; Eberlein, V.; Issmail, L.; et al. Inhibitors of dihydroorotate dehydrogenase cooperate with molnupiravir and N4-hydroxycytidine to suppress SARS-CoV-2 replication. iScience 2022, 25, 104293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, D.C.; Johnson, R.M.; Ayyanathan, K.; Miller, J.; Whig, K.; Kamalia, B.; Dittmar, M.; Weston, S.; Hammond, H.L.; Dillen, C.; et al. Pyrimidine inhibitors synergize with nucleoside analogues to block SARS-CoV-2. Nature 2022, 604, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caburet, J.; Boucherle, B.; Bourdillon, S.; Simoncelli, G.; Verdirosa, F.; Docquier, J.D.; Moreau, Y.; Krimm, I.; Crouzy, S.; Peuchmaur, M. A fragment-based drug discovery strategy applied to the identification of NDM-1 β-lactamase inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 240, 114599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Li, S.; Song, K.; Ye, J.; Li, W.; Zhong, Y.; Feng, Z.; Liang, S.; Cai, Z.; Xu, K. A broad antiviral strategy: Inhibitors of human DHODH pave the way for host-targeting antivirals against emerging and re-emerging viruses. Viruses 2022, 14, 928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Li, J.B.; Zhang, Y.W.; Tang, Y.S.; Yu, X.F.; Zhang, Q.G.; Jin, Z.; Hou, S.C.; Shaw, P.C.; Hu, C. Novel benzamide derivatives with indole moiety as dual-target antiviral agents: Rational design, efficient synthesis, and potent anti-influenza activity through concurrent binding to PAC terminal domain and viral nucleoprotein. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2025, 293, 117681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, R.; Zhang, L.; Li, S.; Sun, Y.; Ding, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, Y.; Shang, W.; Jiang, X.; et al. Novel and potent inhibitors targeting DHODH are broad-spectrum antivirals against RNA viruses including newly-emerged coronavirus SARS-CoV-2. Protein Cell 2020, 11, 723–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gueiffier, A.; Lhassani, M.; Elhakmaoui, A.; Snoeck, R.; Andrei, G.; Chavignon, O.; Teulade, J.C.; Kerbal, A.; Essassi, E.M.; Debouzy, J.C.; et al. Synthesis of acyclo-C-nucleosides in the imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine and pyrimidine series as antiviral agents. J. Med. Chem. 1996, 39, 2856–2859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Hashem, A.A.; Al-Hussain, S.A. Design, synthesis, antimicrobial activity, and molecular docking of novel thiazoles, pyrazoles, 1,3-thiazepinones, and 1,2,4-triazolopyrimidines derived from quinoline-pyrido[2,3-d] pyrimidinones. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Argade, M.D.; Anirudhan, V.; Bradley, S.P.; Tomorowicz, Ł.; Bott, R.; Sownthirarajan, B.; Zielinski, C.A.; Sloan, J.P.; Nikolic, D.S.; Gaisin, A.M.; et al. Refinement of imidazo[2,1-a]pyrimidines in pursuit of potential drug candidates against group 2 influenza A viruses. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2025, 292, 117679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Tang, Y.S.; Meng, C.R.; Xu, J.; Zhang, D.L.; Wang, J.; Huang, E.F.; Shaw, P.C.; Hu, C. Design, synthesis, molecular docking analysis and biological evaluations of 4-[(quinolin-4-yl)amino]benzamide derivatives as novel anti-Influenza virus agents. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Zhou, Y.; Li, L.; Shen, X.; Chen, G.; Wang, X.; Liang, X.; Tan, M.; Huang, Z. Computational approaches in preclinical studies on drug discovery and development. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.S.; Zhang, C.; Lo, C.Y.; Jin, Z.; Kong, B.L.; Xiao, M.J.; Huang, E.F.; Hu, C.; Shaw, P.C. Anti-influenza virus activities and mechanism of antrafenine analogs. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 260, 115775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somarowthu, T.; Patekar, R.R.; Bharate, S.B. Identification of mitoxantrone as a potent inhibitor of CDK7/Cyclin H via structure-based virtual screening and in-vitro validation by ADP-Glo kinase assay. Bioorg. Chem. 2025, 155, 108111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bała, P.; Grochowski, P.; Nowiński, K.; Lesyng, B.; McCammon, J.A. Quantum-dynamical picture of a multistep enzymatic process: Reaction catalyzed by phospholipase A2. Biophys. J. 2000, 79, 1253–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Karwasra, R.; Ahmad, S.; Bano, N.; Qazi, S.; Raza, K.; Singh, S.; Varma, S. Macrophage-targeted punicalagin nanoengineering to alleviate methotrexate-induced neutropenia: A molecular docking, DFT, and MD simulation analysis. Molecules 2022, 27, 6034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, S.; Cheng, X.; Lee, J.; Kim, S.; Park, S.J.; Patel, D.S.; Beaven, A.H.; Lee, K.I.; Rui, H.; Park, S.; et al. CHARMM-GUI 10 years for biomolecular modeling and simulation. J. Comput. Chem. 2017, 38, 1114–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heydenreich, F.M.; Miljuš, T.; Milić, D.; Veprintsev, D.B. High-throughput site-directed scanning mutagenesis using a two-fragment PCR approach. Bio-Protoc. 2020, 10, e3484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.K.; Tao, Y.X. Alanine scanning mutagenesis of the DRYxxI motif and intracellular loop 2 of human melanocortin-4 receptor. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boukharta, L.; Gutiérrez-de-Terán, H.; Aqvist, J. Computational prediction of alanine scanning and ligand binding energetics in G-protein coupled receptors. PLoS Comp. Biol. 2014, 10, e1003585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marimuthu, P.; Singaravelu, K. Prediction of hot spots at myeloid cell leukemia-1-inhibitor interface using energy estimation and alanine scanning mutagenesis. Biochemistry 2018, 57, 1249–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, M.W.; Haider, S.Z.; Sun, X.; Al-Ghanim, K.A.; Nawaz, M.Z.; Yuan, Q. Leveraging deep learning and structure-based drug repurposing for the discovery of potent Trk-A inhibitors targeting CIPA. Bioorg. Chem. 2025, 163, 108680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, J.; Zhu, W. Molecular mechanism and energy basis of conformational diversity of antibody SPE7 revealed by molecular dynamics simulation and principal component analysis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| No. | Structure | Score (kcal/mol) | MM/GBSA (kcal/mol) | A/PR/8/34(H1N1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CC50 (μM) | IC50 (μM) | SI | ||||
| 1 | 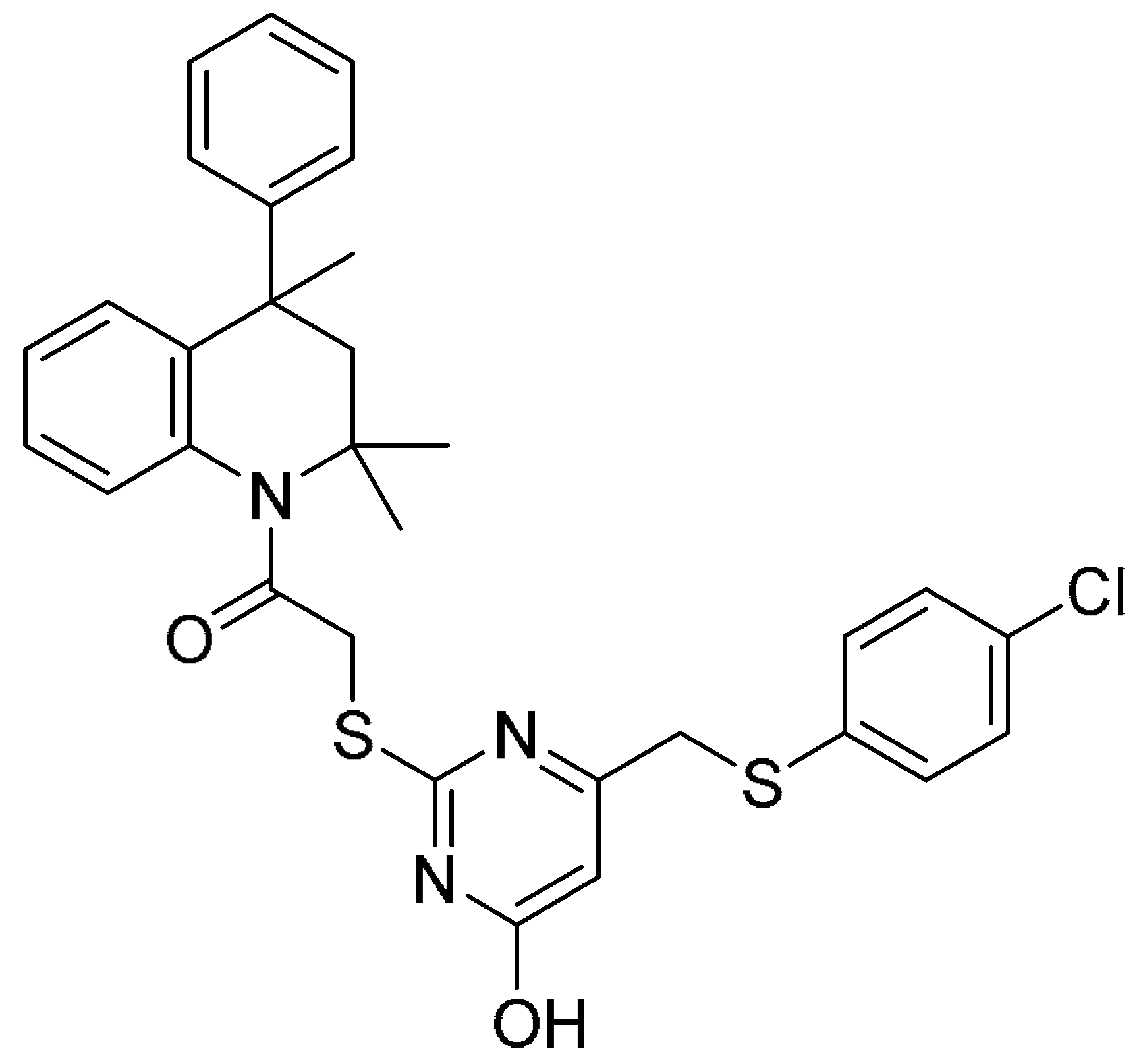 | −12.294 | −53.78 | 34.52 ± 1.58 | 36.83 ± 2.36 | 0.9 |
| 2 | 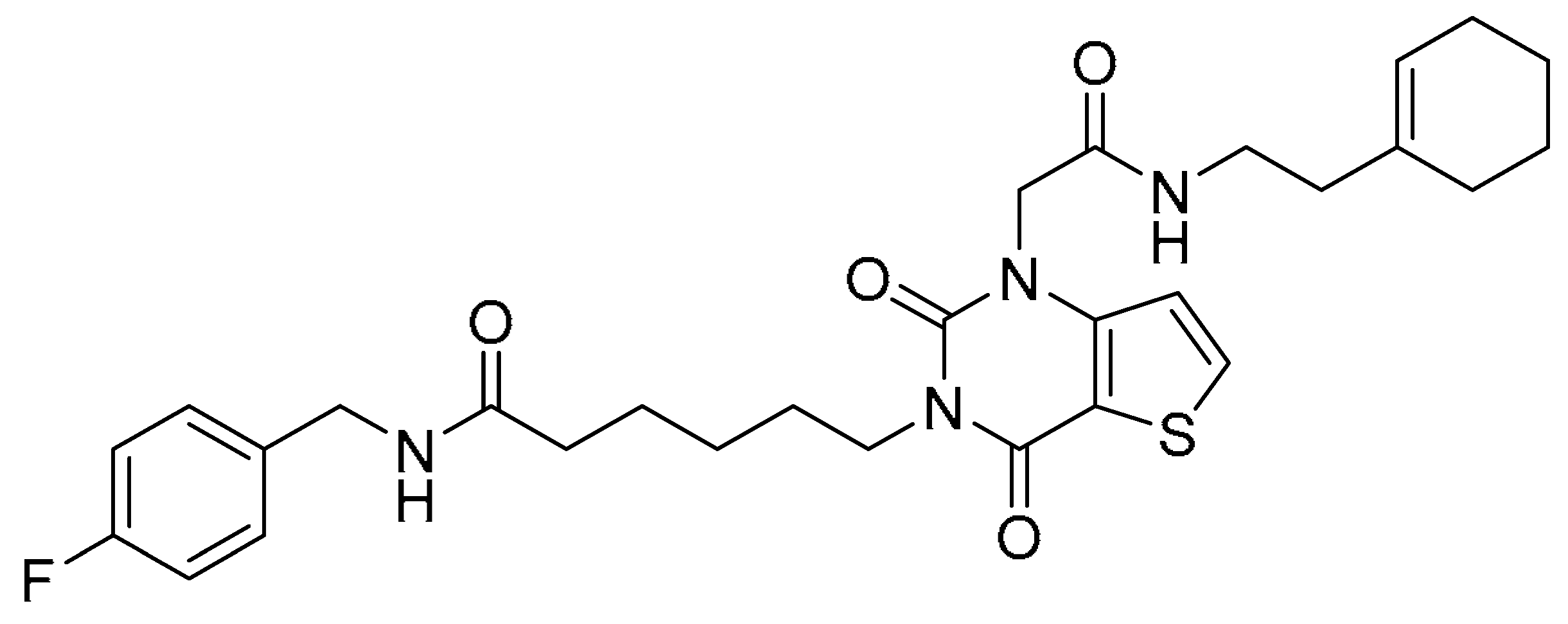 | −12.181 | −74.80 | >200 | >200 | - |
| 3 | 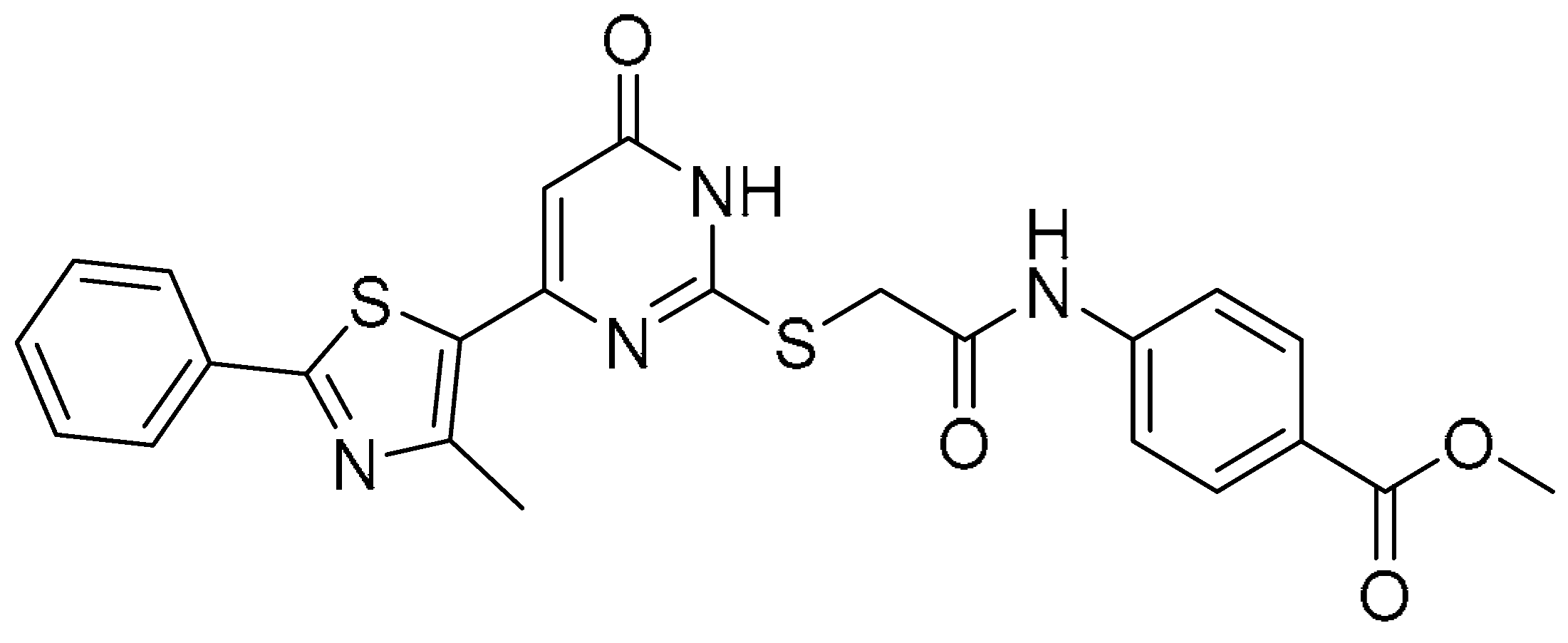 | −11.570 | −61.61 | >200 | >200 | - |
| 4 |  | −9.904 | −83.20 | >200 | 66.15 ± 6.29 | >3.0 |
| 5 |  | −10.351 | −67.08 | >200 | >200 | - |
| 6 | 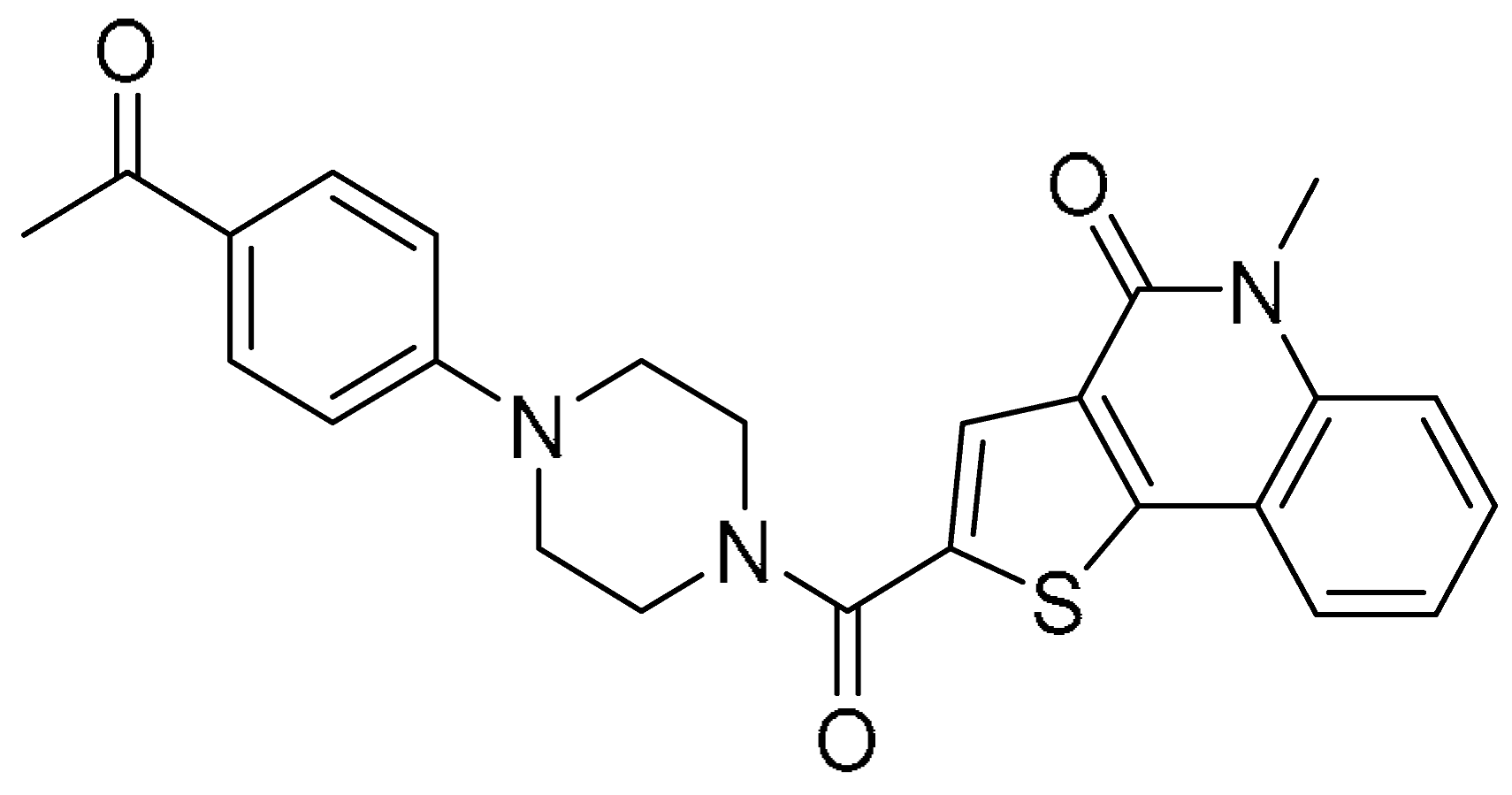 | −12.113 | −82.85 | >200 | 4.85 ± 0.58 | >41.2 |
| 7 | 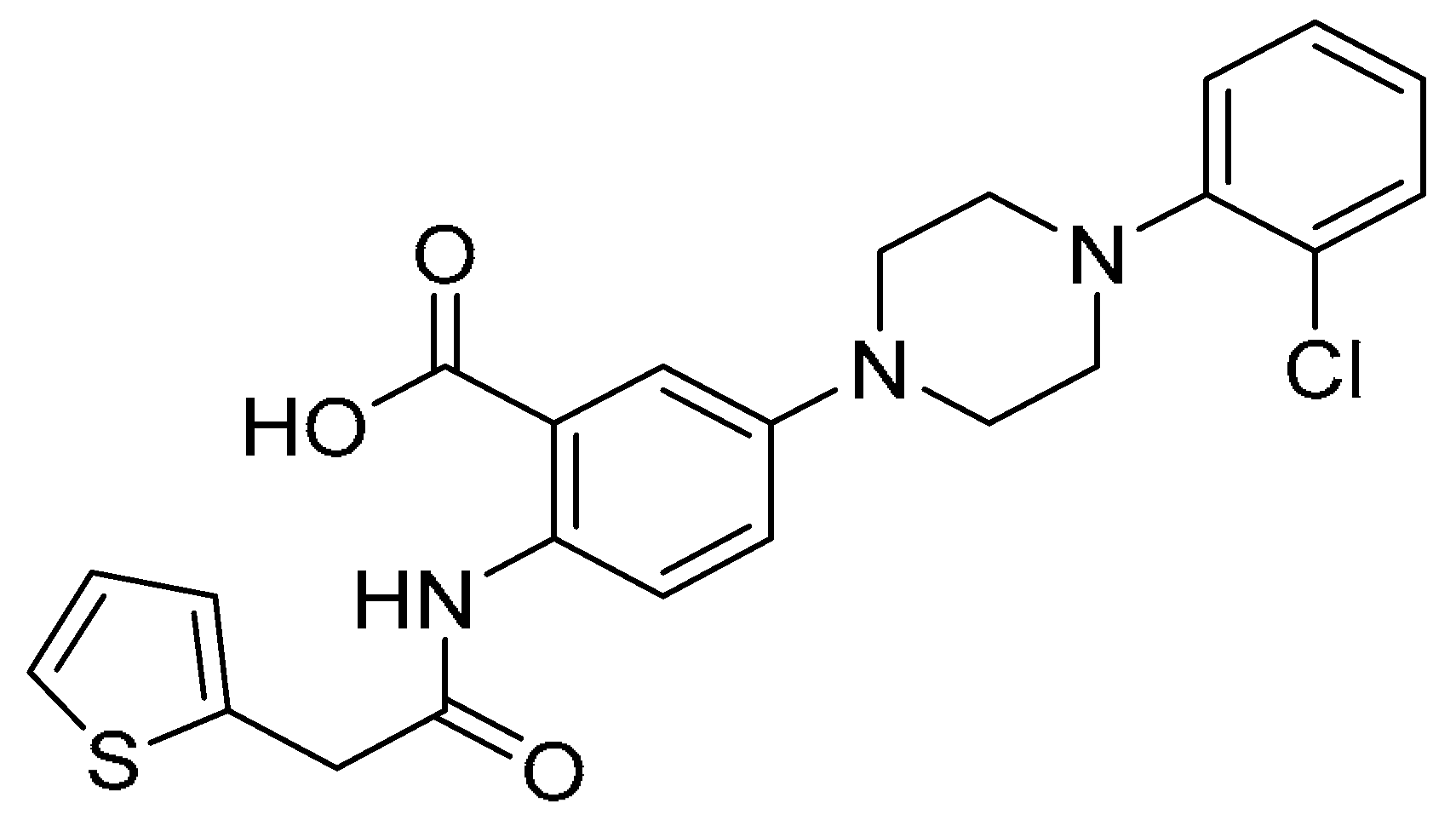 | −11.761 | −66.23 | >200 | 17.20 ± 1.19 | >11.6 |
| 8 | 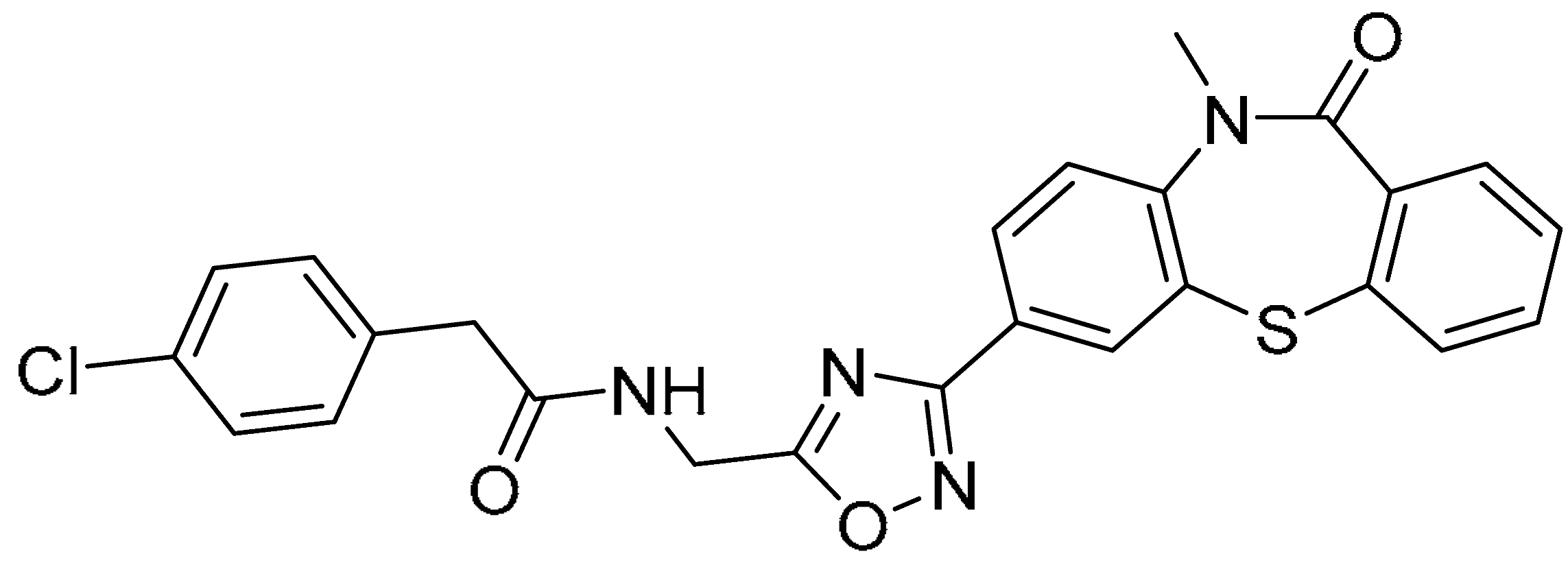 | −11.705 | −80.56 | >200 | 13.38 ± 2.45 | >14.9 |
| 9 |  | −13.497 | −73.06 | >200 | 7.35 ± 1.65 | >21.2 |
| 10 |  | −13.077 | −70.25 | >200 | 1.75 ± 0.28 | >114.3 |
| 17 | 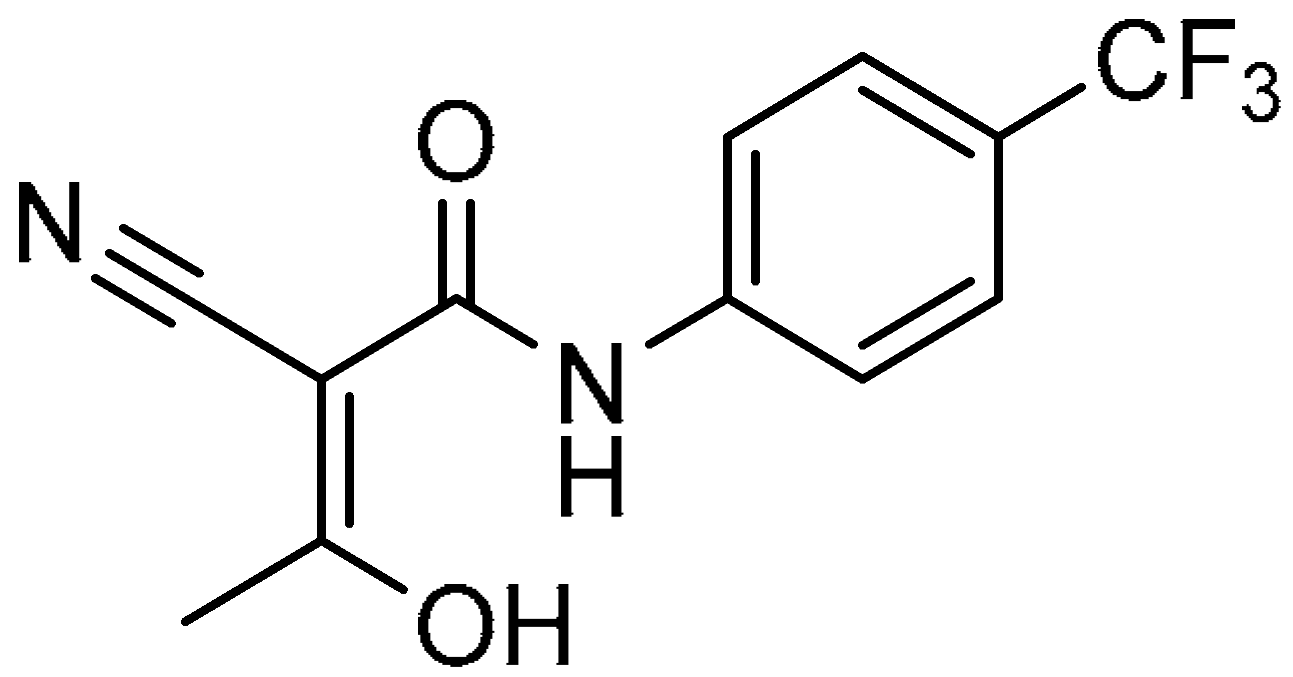 | −9.100 | −44.01 | 180.90 ± 16.45 | 35.02 ± 3.33 | 5.2 |
| No. | Structure | A/PR/8/34(H1N1) | SARS-CoV-2 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CC50 (μM) | IC50 (μM) | SI | CC50 (μM) | IC50 (μM) | SI | ||
| 11 | 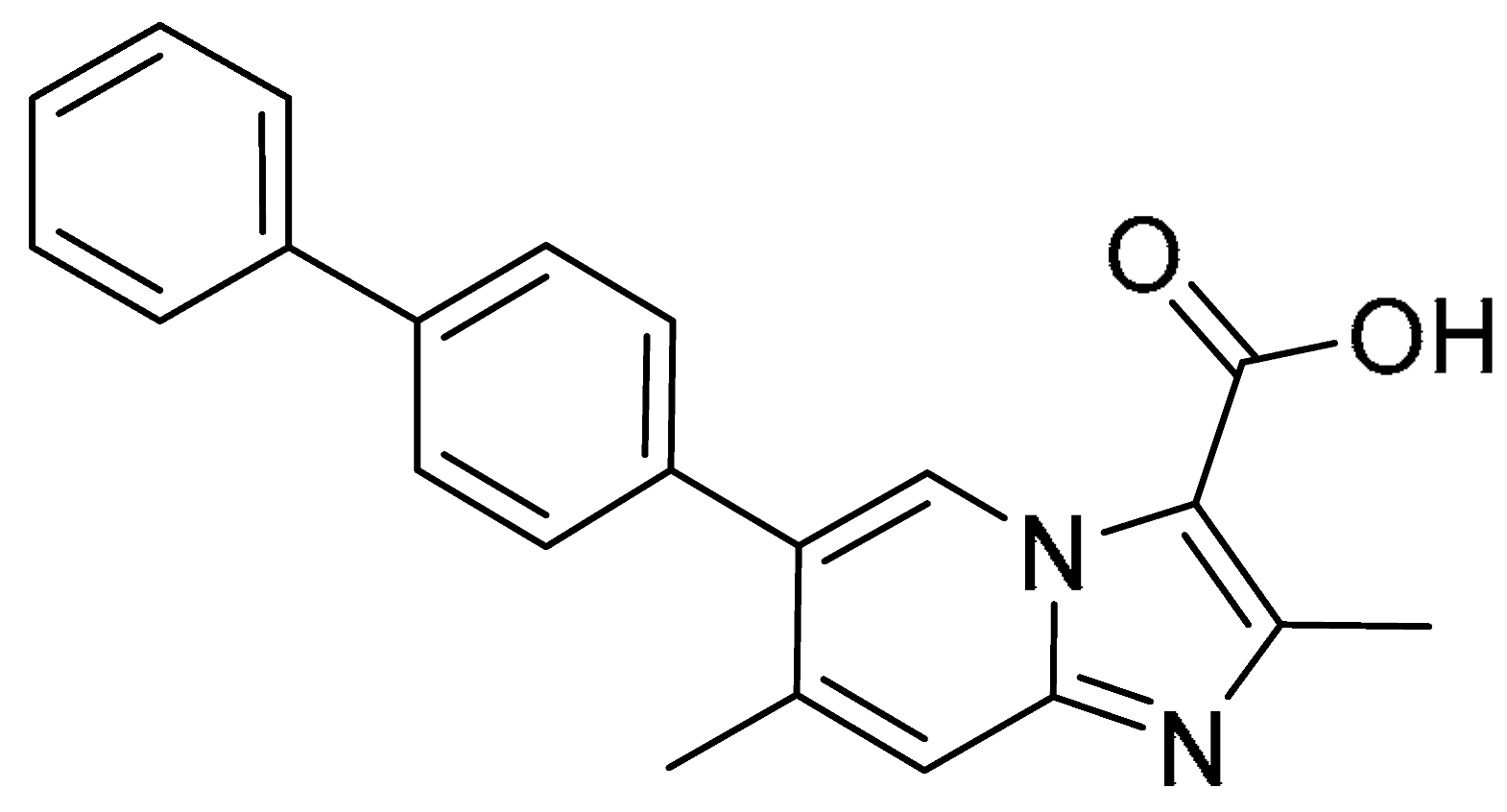 | >200 | 0.85 ± 0.05 | >235.3 | >200 | 3.60 ± 0.67 | >55.6 |
| 12 | 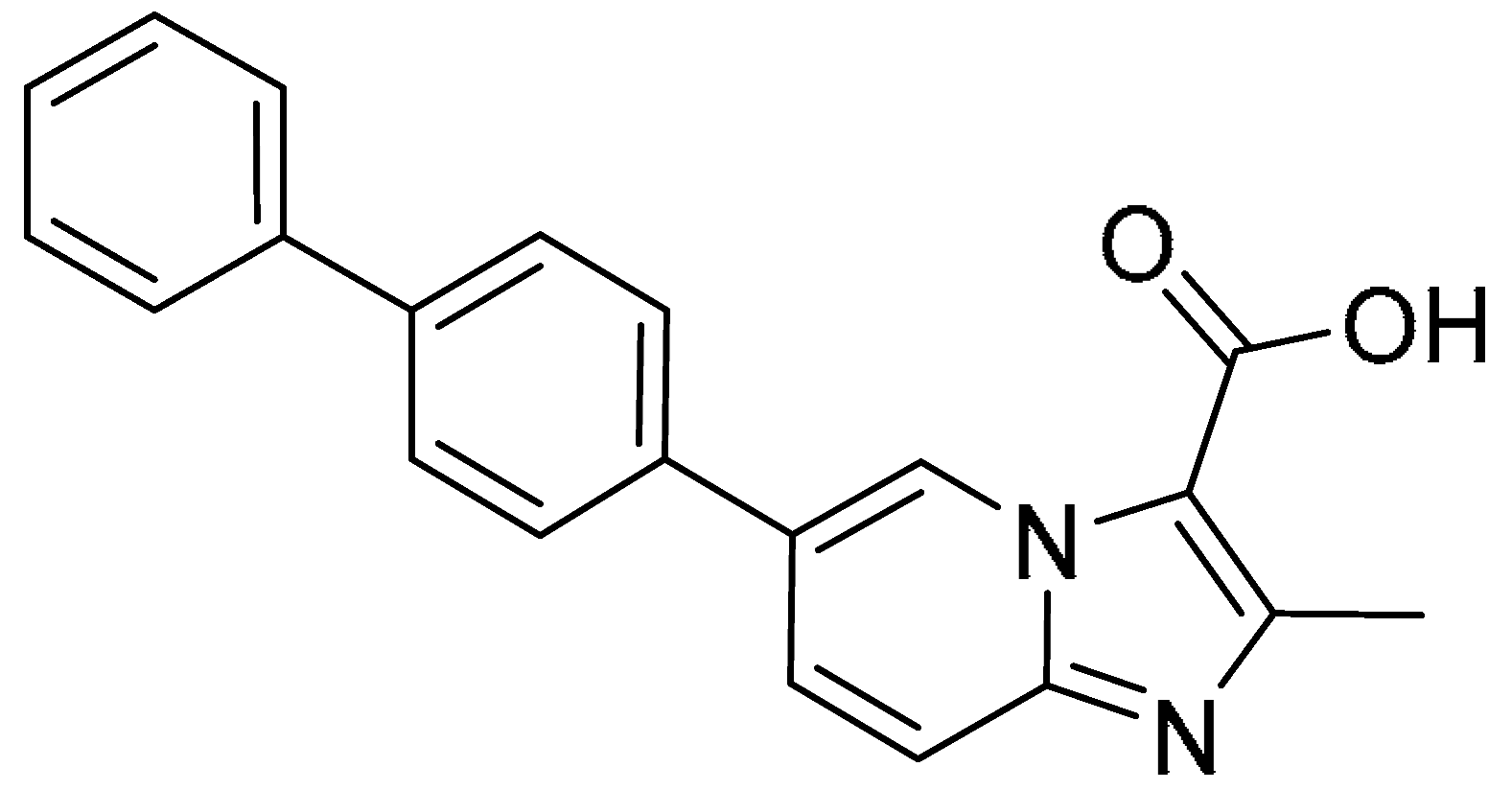 | >200 | 100 ± 1.13 | >2.0 | >200 | >200 | - |
| 13 | 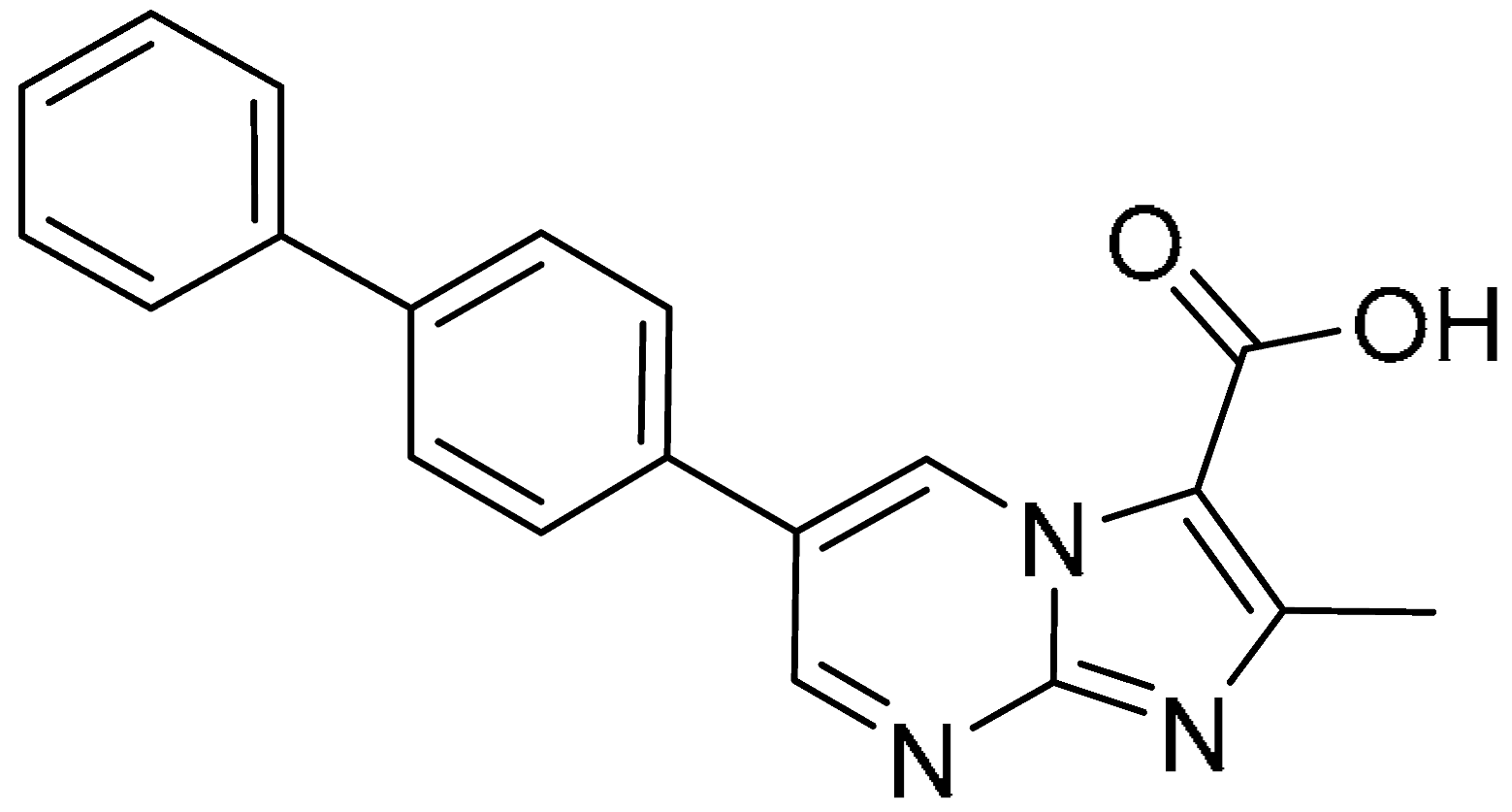 | >200 | 1.08 ± 0.26 | >185.2 | >200 | 104.84 ± 5.19 | >1.9 |
| 14 |  | >200 | >200 | - | >200 | >200 | - |
| 15 | 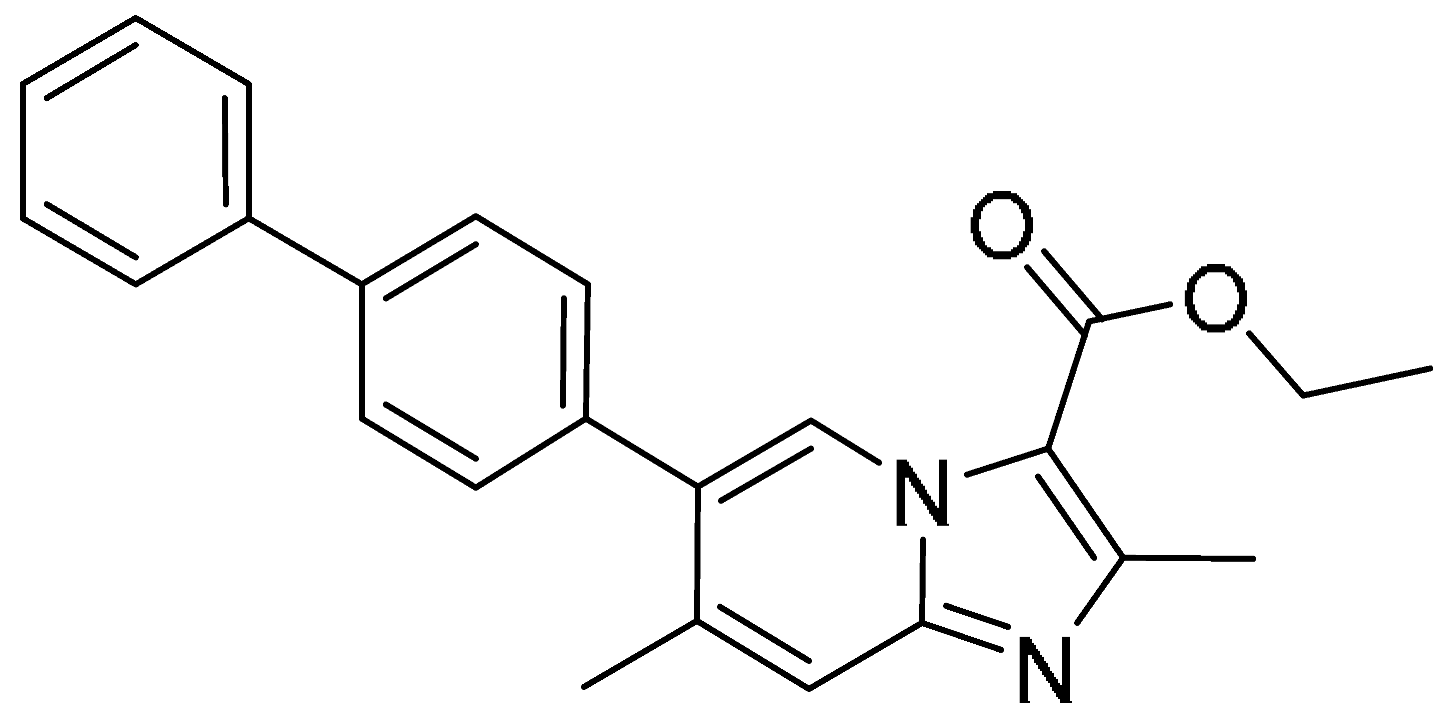 | >200 | >200 | - | >200 | >200 | - |
| 16 | 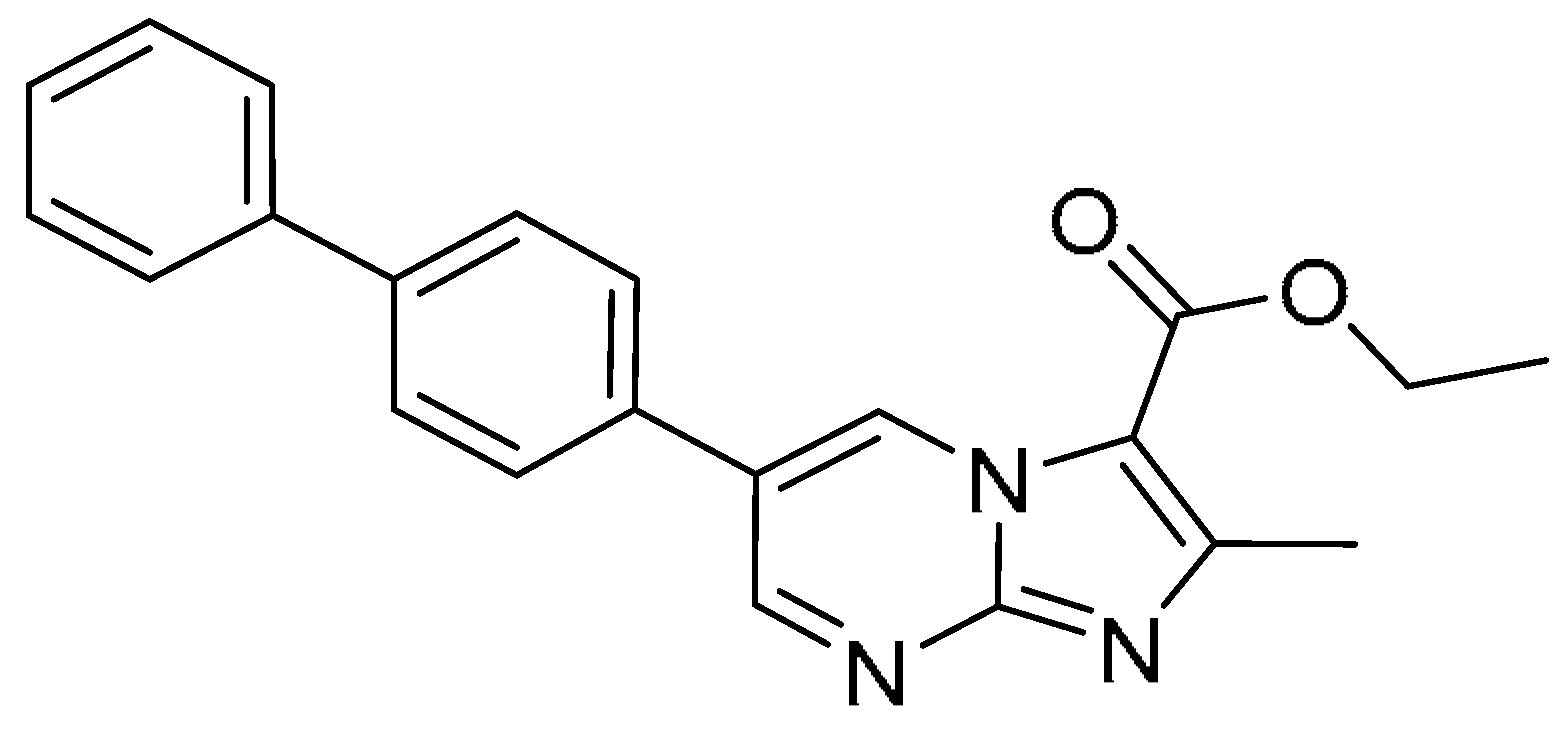 | >200 | >200 | - | >200 | >200 | - |
| 17 | 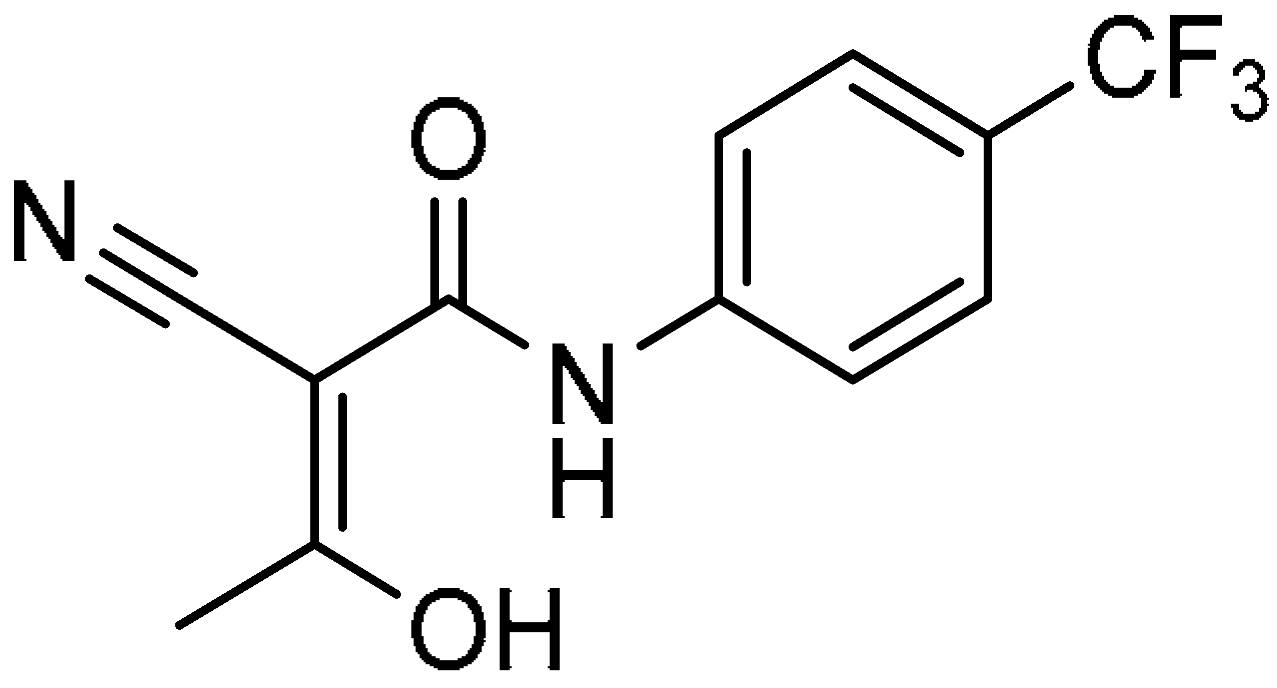 | 180.90 ± 16.45 | 35.02 ± 3.33 | 5.2 | >200 | 26.06 ± 4.32 | >7.7 |
| Baloxavir marboxil |  | - | 9.67 ± 1.12 nM | - | - | - | - |
| Remdesivir | 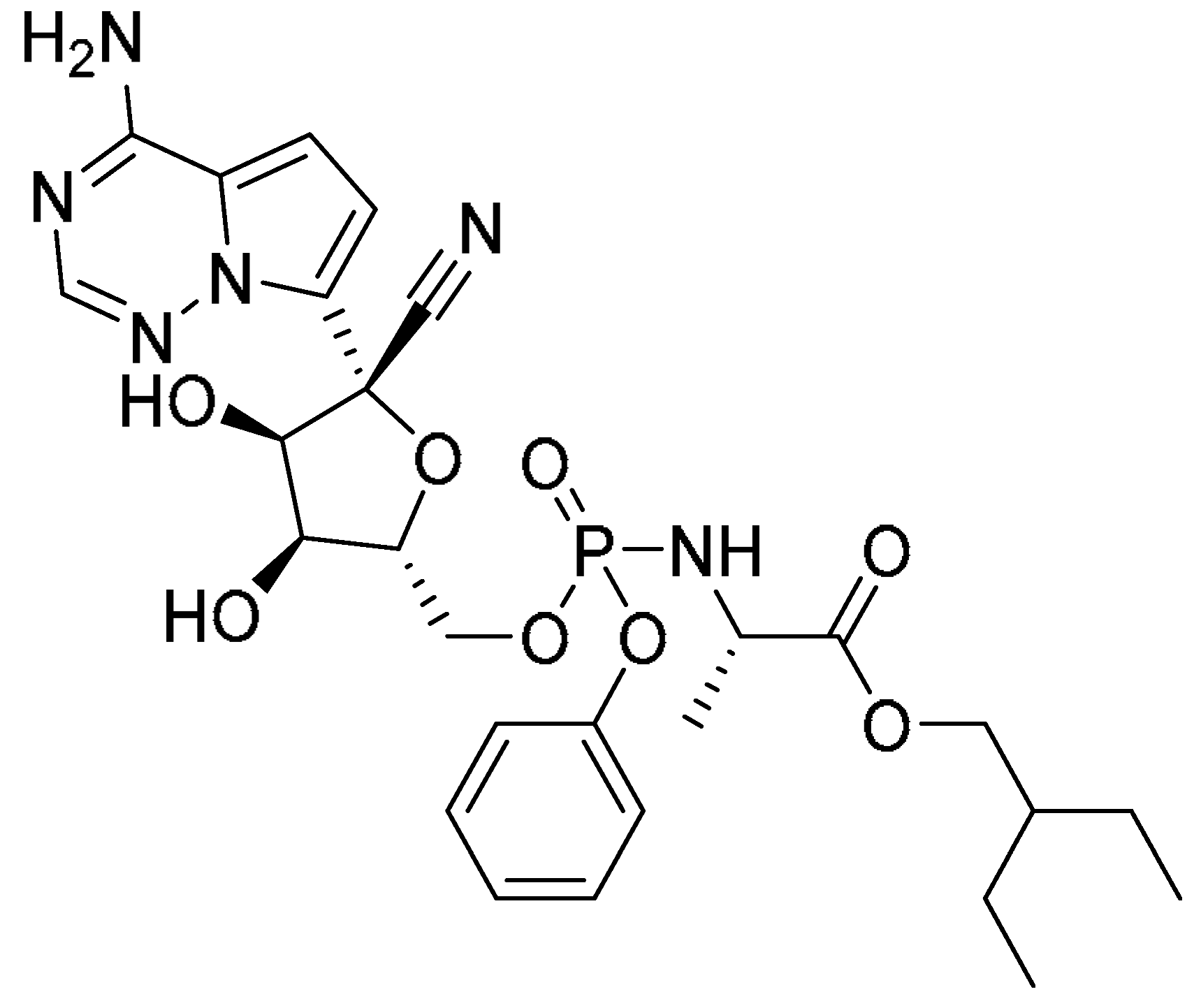 | - | - | - | - | 4.95 ± 0.78 | - |
| No. | Ka (M−1S−1) | Kdis (S−1) | KD (M) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 11 | 4.83 × 106 | 2.93 × 101 | 6.06 × 106 |
| 17 | 3.36 × 109 | 8.04 × 104 | 2.39 × 105 |
| 18 | 1.31 × 106 | 8.02 × 100 | 6.13 × 106 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, C.; Sun, S.; Xie, H.; Ding, Y.; Hu, C.; Guo, J.; Xiao, J. Comprehensive Identification and Mechanistic Evaluation of Novel DHODH Inhibitors as Potent Broad-Spectrum Antiviral Agents. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 1416. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18091416
Zhang C, Sun S, Xie H, Ding Y, Hu C, Guo J, Xiao J. Comprehensive Identification and Mechanistic Evaluation of Novel DHODH Inhibitors as Potent Broad-Spectrum Antiviral Agents. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(9):1416. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18091416
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Chao, Shiyang Sun, Huiru Xie, Yongzhao Ding, Chun Hu, Jialin Guo, and Junhai Xiao. 2025. "Comprehensive Identification and Mechanistic Evaluation of Novel DHODH Inhibitors as Potent Broad-Spectrum Antiviral Agents" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 9: 1416. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18091416
APA StyleZhang, C., Sun, S., Xie, H., Ding, Y., Hu, C., Guo, J., & Xiao, J. (2025). Comprehensive Identification and Mechanistic Evaluation of Novel DHODH Inhibitors as Potent Broad-Spectrum Antiviral Agents. Pharmaceuticals, 18(9), 1416. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18091416






