Puerarin Inhibits Proliferation, Migration and Invasion of Colon Cancer Cells and Induces Apoptosis via Suppression of the PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Effects of Puerarin on the Viability and Proliferation of Colon Cancer Caco-2 Cells
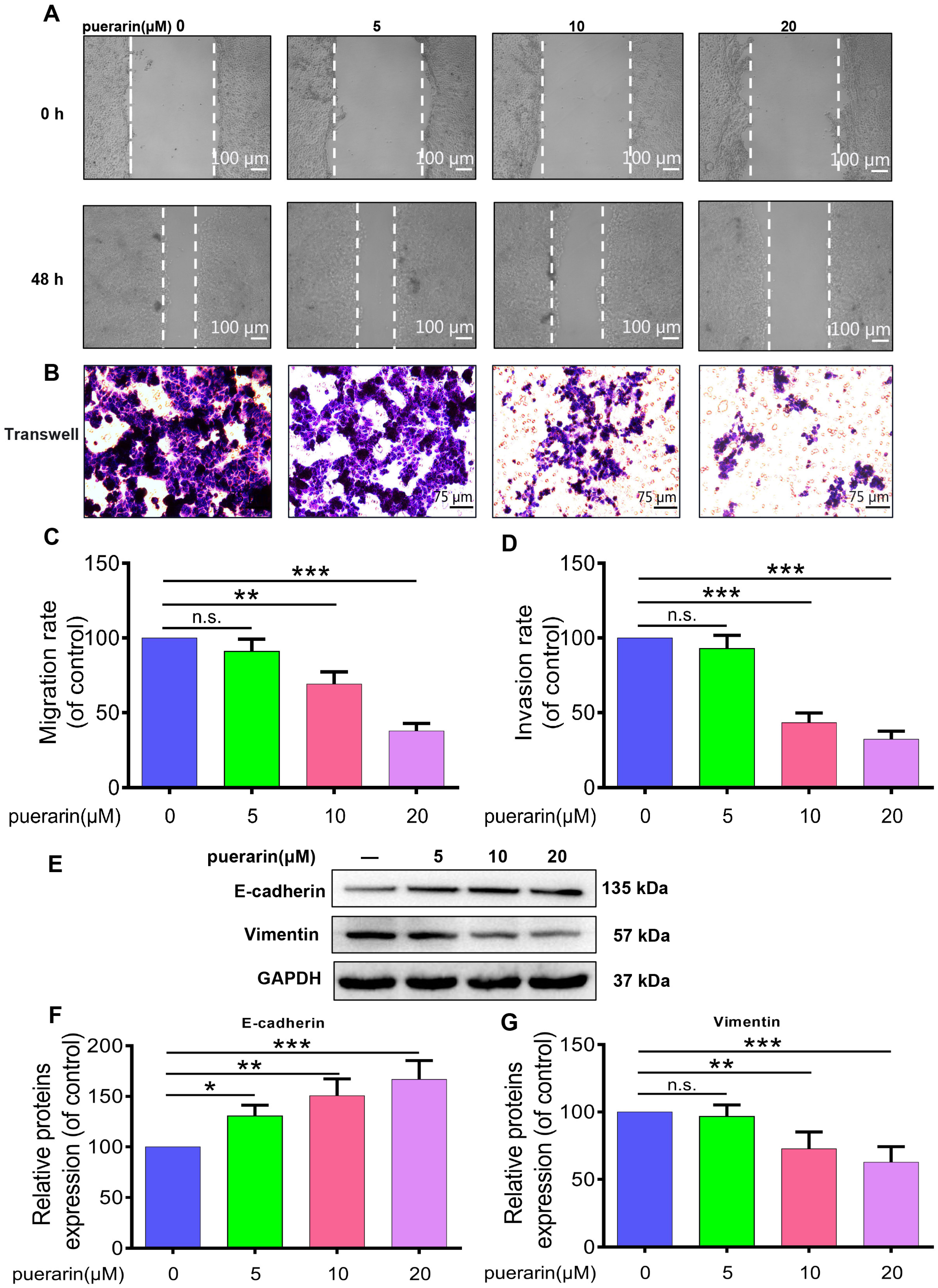
2.2. Effects of Puerarin on Migration, Invasion, and Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) in Caco-2 Cells
2.3. Effects of Puerarin on Apoptosis in Caco-2 Cells
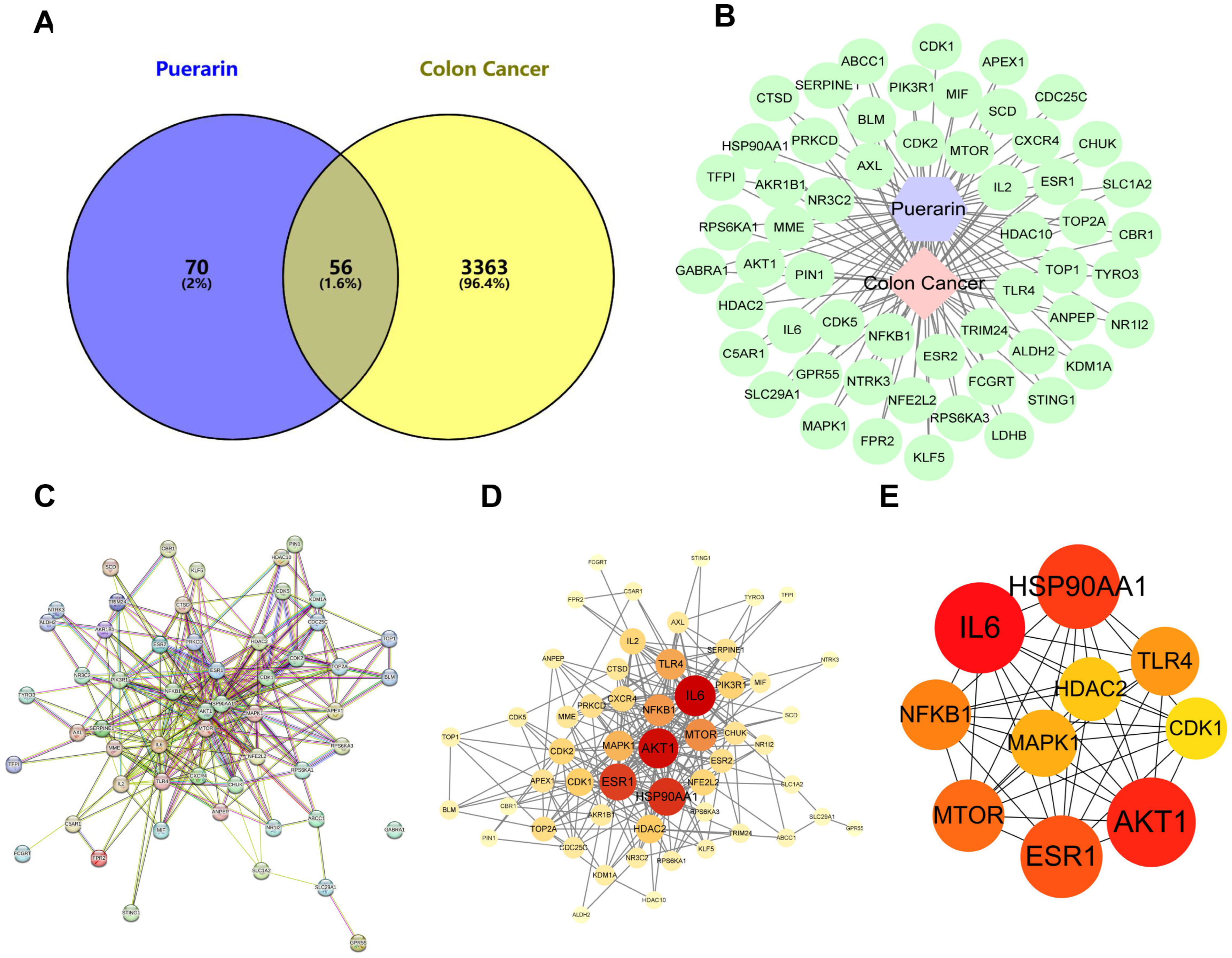
2.4. Network Pharmacology Investigation of the Anticancer Mechanism of Puerarin in Colon Cancer
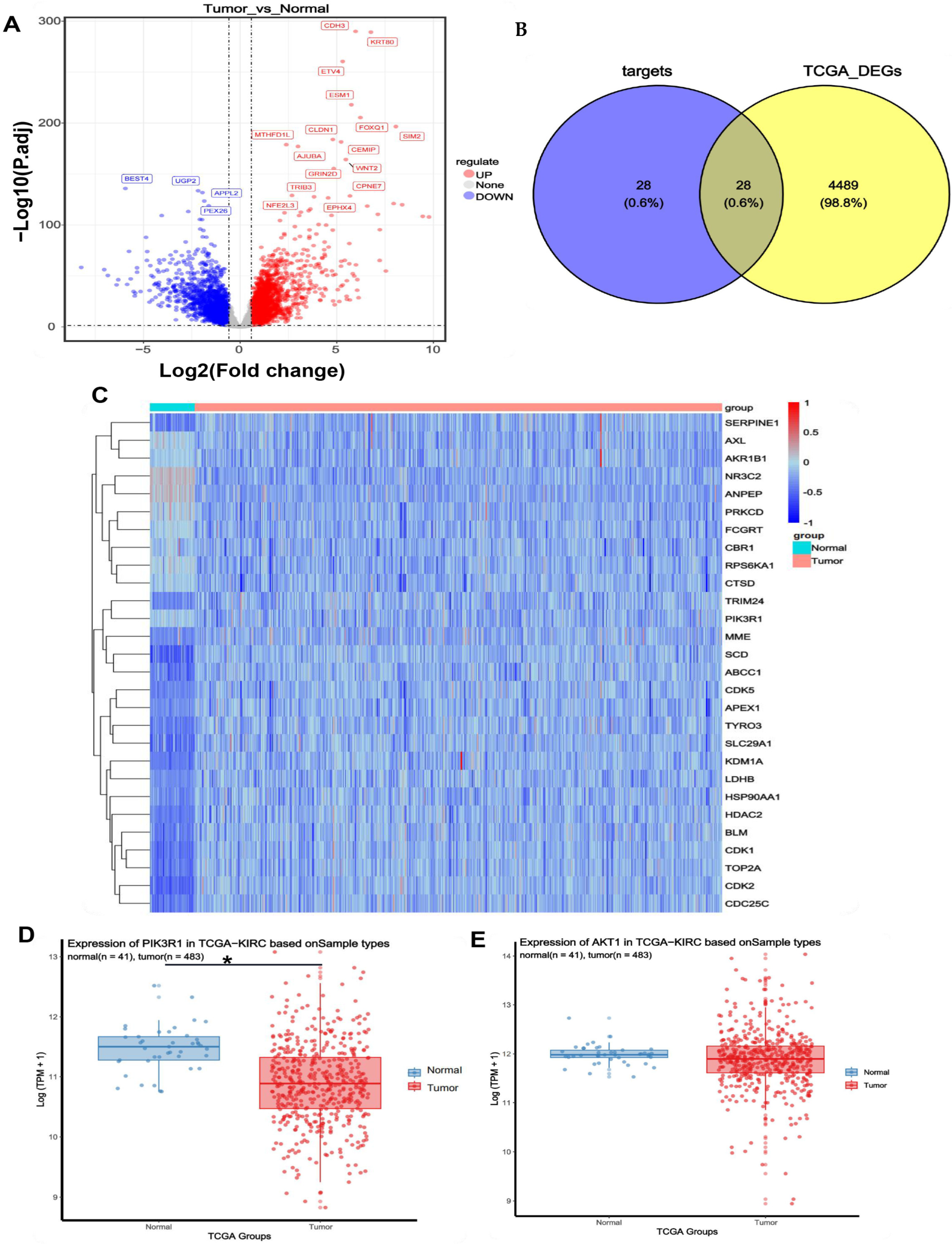
2.5. Identification of Colon Cancer Targets
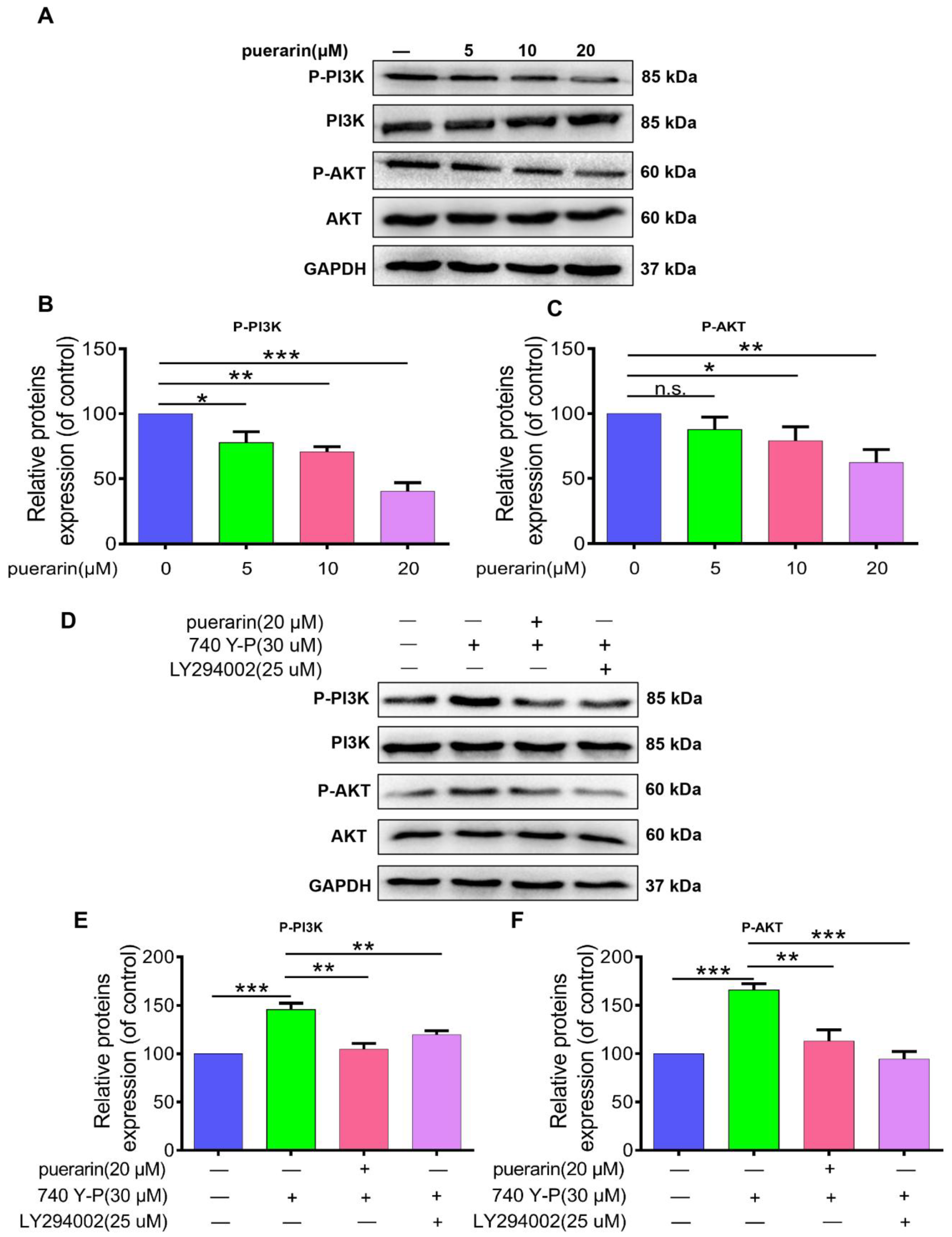
2.6. Effects of Puerarin on the PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway in Caco-2 Cells
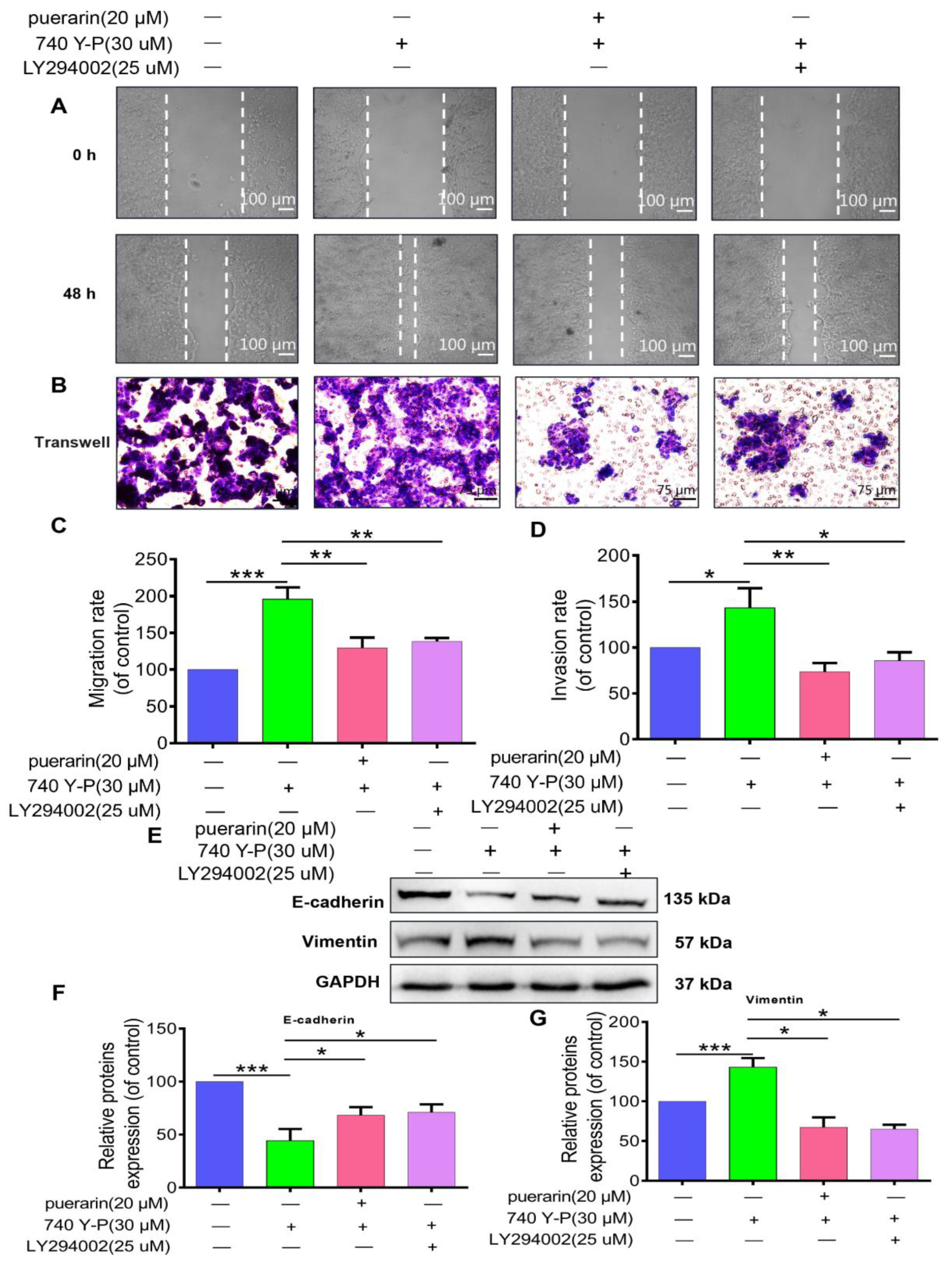
2.7. Effects of Puerarin on 740 Y-P-Induced Migration, Invasion, and EMT in Caco-2 Cells
2.8. Effects of Puerarin on 740 Y-P-Induced Apoptosis in Caco-2 Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents and Chemicals
4.2. Cell Culture and Proliferation Assay
4.3. Invasion and Wound Healing Assays
4.4. Western Blot Analysis
4.5. Immunofluorescence and Apoptosis Assays
4.6. Protein–Protein Interaction (PPI) Network Analysis
4.7. GO Enrichment and KEGG Pathway Analysis
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PI3K | Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase |
| AKT | Protein Kinase B |
| EMT | Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition |
| CCK-8 | Cell Counting Kit-8 |
| PI | Propidium Iodide |
| EGFP | Enhanced Green Fluorescent Protein |
| DAPI | 4′,6-Diamidino-2-Phenylindole |
| PPI | Protein–Protein Interaction |
| GO | Gene Ontology |
| KEGG | Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes |
| TCGA | The Cancer Genome Atlas |
| COAD | Colon Adenocarcinoma |
| TPM | Transcripts Per Million |
| DEGs | Differentially Expressed Genes |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
| ANOVA | Analysis of Variance |
| BAX | Bcl-2-associated X protein |
| Bcl-2 | B-cell lymphoma-2 |
| mTOR | Mammalian Target of Rapamycin |
| HIF-1 | Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1 |
| FBS | Fetal Bovine Serum |
| HRP | Horseradish Peroxidase |
| RPMI | Roswell Park Memorial Institute medium |
| SMILES | Simplified Molecular Input Line Entry System |
| IC50 | Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration |
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2021. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.L.; Wagle, N.S.; Cercek, A.; Smith, R.A.; Jemal, A. Colorectal cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2023, 73, 233–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papamichael, D.; Audisio, R.A.; Glimelius, B.; De Gramont, A.; Glynne-Jones, R.; Haller, D.; Köhne, C.-H.; Rostoft, S.; Lemmens, V.; Mitry, E.; et al. Treatment of colorectal cancer in older patients: International Society of Geriatric Oncology (SIOG) consensus recommendations 2013. Ann. Oncol. 2015, 26, 463–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.; Xiao, Z.; Liu, X.; Wang, T.; Wang, Y.; Ye, F.; Su, J.; Yao, X.; Xiong, L.; Yang, D.-H. Natural products for combating multidrug resistance in cancer. Pharmacol. Res. 2024, 202, 107099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisol, Â.; De Campos, P.S.; Lamers, M.L. Flavonoids as anticancer therapies: A systematic review of clinical trials. Phytother. Res. 2020, 34, 568–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopustinskiene, D.M.; Jakstas, V.; Savickas, A.; Bernatoniene, J. Flavonoids as anticancer agents. Nutrients 2020, 12, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Peng, Y.; Qiao, Y.; Huang, Y.; Song, F.; Zhang, M.; Song, F. Consumption of flavonoids and risk of hormone-related cancers: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Nutr. J. 2022, 21, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, B.; Khan, S.; Liu, Y.; Xue, M.; Nabi, G.; Kumar, S.; Alshwmi, M.; Qarluq, A.W. Molecular mechanisms of anticancer activities of puerarin. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, X.; Liu, T.; Zou, Z.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, G. Effects and mechanisms of puerarin against neuroblastoma: Insights from bioinformatics and in vitro experiments. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2024, 24, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.-Q.; Zhang, H.-B.; Wang, G.-F.; Xu, D.; Zhang, W.-Y.; Wang, Q.-S.; Cui, Y.-L. Colon-specific microspheres loaded with puerarin reduce tumorigenesis and metastasis in colitis-associated colorectal cancer. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 570, 118644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, S.; Ma, T.; Long, Q.; Chen, L.; Xu, K.; Cao, Y. Promotion of apoptosis in melanoma cells by taxifolin through the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway: Screening of natural products using WGCNA and CMAP platforms. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 138, 112517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Qing, J.; Xiao, Y.; Huang, X.; Chi, Y.; Chen, Z. TIM-1 promotes proliferation and metastasis, and inhibits apoptosis, in cervical cancer through the PI3K/AKT/p53 pathway. BMC Cancer 2022, 22, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Liu, C.; Shi, J.; Wen, K.; Wang, X. AIM2 inhibits the proliferation; invasion; migration, and promotes the apoptosis of osteosarcoma cells by inactivating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. Mol. Med. Rep. 2021, 25, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemi, M.; Khosroshahi, E.M.; Asadi, S.; Tanha, M.; Mohseni, F.G.; Sagha, R.A.; Taheri, E.; Vazayefi, P.; Shekarriz, H.; Habibi, F.; et al. Emerging roles of non-coding RNAs in modulating the PI3K/AKT pathway in cancer. Non Coding RNA Res. 2025, 10, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narayanankutty, A. PI3K/AKT/mTOR Pathway as a Therapeutic Target for Colorectal Cancer: A Review of Preclinical and Clinical Evidence. Curr. Drug Targets 2019, 20, 1217–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayer, I.A.; Arteaga, C.L. The PI3K/AKT Pathway as a Target for Cancer Treatment. Annu. Rev. Med. 2016, 67, 11–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danielsen, S.A.; Eide, P.W.; Nesbakken, A.; Guren, T.; Leithe, E.; Lothe, R.A. Portrait of the PI3K/AKT pathway in colorectal cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1855, 104–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, I.; Gaykalova, D.A. Unveiling the role of PIK3R1 in cancer: A comprehensive review of regulatory signaling and therapeutic implications. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2024, 106–107, 58–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, S.; Wang, J.; Weng, F.; Xiang, D.; Sun, G. Extracellular matrix protein 1 regulates colorectal cancer cell proliferative, migratory, invasive and epithelial-mesenchymal transition activities through the PI3K/AKT/GSK3β/Snail signaling axis. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 889159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, S.; Chavan, P.; Dufossé, L. Hidden treasure: Halophilic fungi as a repository of bioactive lead compounds. J. Fungi 2024, 10, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, A.; Ghorbani, A. Cancer therapy with phytochemicals: Evidence from clinical studies. Avicenna J. Phytomed. 2015, 5, 84–97. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.; Shin, M.-H.; Park, K.-Y.; Lee, K.-T.; Jung, H.-J.; Lee, M.-S.; Park, H.-J. Effect of kaikasaponin III obtained from Pueraria thunbergiana flowers on serum and hepatic lipid peroxides and tissue factor activity in the streptozotocin-induced diabetic rat. J. Med. Food 2004, 7, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benlhabib, E.; Baker, J.I.; Keyler, D.E.; Singh, A.K. Kudzu root extract suppresses voluntary alcohol intake and alcohol withdrawal symptoms in P rats receiving free access to water and alcohol. J. Med. Food 2004, 7, 168–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Xue, R.; Wang, J.; Ren, H. Puerarin inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma invasion and metastasis through miR-21-mediated PTEN/AKT signaling to suppress the epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2020, 53, e8882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, C.; Ma, X.; Yang, L.; Ren, H. Identification of the potential mechanism of radix pueraria in colon cancer based on network pharmacology. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 3765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Liu, F.; Cai, Q.; Deng, L.; Ouyang, Q.; Zhang, X.H.-F.; Zheng, J. Invasion and metastasis in cancer: Molecular insights and therapeutic targets. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2025, 10, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Zhou, J.; Kong, W. Extracellular matrix in vascular homeostasis and disease. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2025, 22, 333–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falanga, A.; Russo, L.; Milesi, V.; Vignoli, A. Mechanisms and risk factors of thrombosis in cancer. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2017, 118, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.L.; Wang, W.; Lan, X.L.; Zeng, Z.C.; Liang, Y.S.; Yan, Y.R.; Song, F.Y.; Wang, F.F.; Zhu, X.H.; Liao, W.J.; et al. CAFs secreted exosomes promote metastasis and chemotherapy resistance by enhancing cell stemness and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in colorectal cancer. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, W.; Yang, L.; Chen, C.; Ashrafizadeh, M.; Tian, Y.; Sun, R. Wnt/β-catenin-driven EMT regulation in human cancers. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2024, 81, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Xu, J.; Zhu, J.; Pu, Y.; Bao, Y. Study on the physicochemical properties and immunomodulatory anti-tumor effect of the Pholiota adiposa polysaccharide. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 5153–5165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Li, J.; Chen, X.; Kou, M. Puerarin attenuates cisplatin-induced apoptosis of hair cells through the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Mol. Cell Res. 2022, 1869, 119208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, X.; Ge, X.; Zhang, F. Puerarin attenuates neurological deficits via Bcl-2/Bax/cleaved caspase-3 and Sirt3/SOD2 apoptotic pathways in subarachnoid hemorrhage mice. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 109, 726–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czabotar, P.E.; Lessene, G.; Strasser, A.; Adams, J.M. Control of apoptosis by the BCL-2 protein family: Implications for physiology and therapy. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 15, 49–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llambi, F.; Green, D.R. Apoptosis and oncogenesis: Give and take in the BCL-2 family. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2011, 21, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Shen, Q.; Li, J. Traditional Chinese medicine targeting apoptotic mechanisms for esophageal cancer therapy. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2016, 37, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, P.; Liu, F.; Lei, F.; Peng, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Gao, Z.; Gao, Q.; Gu, J. Breviscapine regulates the proliferation, migration, invasion, and apoptosis of colorectal cancer cells via the PI3K/AKT pathway. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 9674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefani, C.; Miricescu, D.; Stanescu-Spinu, I.-I.; Nica, R.I.; Greabu, M.; Totan, A.R.; Jinga, M. Growth factors, PI3K/AKT/mTOR and MAPK signaling pathways in colorectal cancer pathogenesis: Where are we now? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okkenhaug, K.; Graupera, M.; Vanhaesebroeck, B. Targeting PI3K in cancer: Impact on tumor cells, their protective stroma, angiogenesis, and immunotherapy. Cancer Discov. 2016, 6, 1090–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Chen, Y.; Dai, C.; Xing, Y.; Qiu, Z.; Zhao, J.; Ye, J.; Yu, C.; Lin, P.; Zhang, W.; et al. Huachansu suppresses colorectal cancer via inhibiting PI3K/AKT and glycolysis signaling pathways: Systems biology and network pharmacology. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2025, 343, 119479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y. The role of HM13 expression and its relationship to PI3K/AKT and p53 signaling pathways in colorectal cancer. Tissue Cell 2025, 93, 102702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, L.; Li, X.; Zhao, S.; Hao, M.; Wang, H.; Zhou, Z.; Xiong, X.; Yuan, D.; Luo, P.; Wang, L.; et al. Puerarin Inhibits Proliferation, Migration and Invasion of Colon Cancer Cells and Induces Apoptosis via Suppression of the PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 1378. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18091378
Chen L, Li X, Zhao S, Hao M, Wang H, Zhou Z, Xiong X, Yuan D, Luo P, Wang L, et al. Puerarin Inhibits Proliferation, Migration and Invasion of Colon Cancer Cells and Induces Apoptosis via Suppression of the PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(9):1378. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18091378
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Lin, Xuhong Li, Shijie Zhao, Mengyu Hao, Heng Wang, Zhi Zhou, Xinyu Xiong, Die Yuan, Piao Luo, Luwen Wang, and et al. 2025. "Puerarin Inhibits Proliferation, Migration and Invasion of Colon Cancer Cells and Induces Apoptosis via Suppression of the PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 9: 1378. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18091378
APA StyleChen, L., Li, X., Zhao, S., Hao, M., Wang, H., Zhou, Z., Xiong, X., Yuan, D., Luo, P., Wang, L., Pan, D., Shen, X., Zhang, Y., & Chen, Y. (2025). Puerarin Inhibits Proliferation, Migration and Invasion of Colon Cancer Cells and Induces Apoptosis via Suppression of the PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway. Pharmaceuticals, 18(9), 1378. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18091378





