Drugs Versus Microbiota: How Pharmacotherapy Affects Gut and Probiotic Bacteria
Abstract
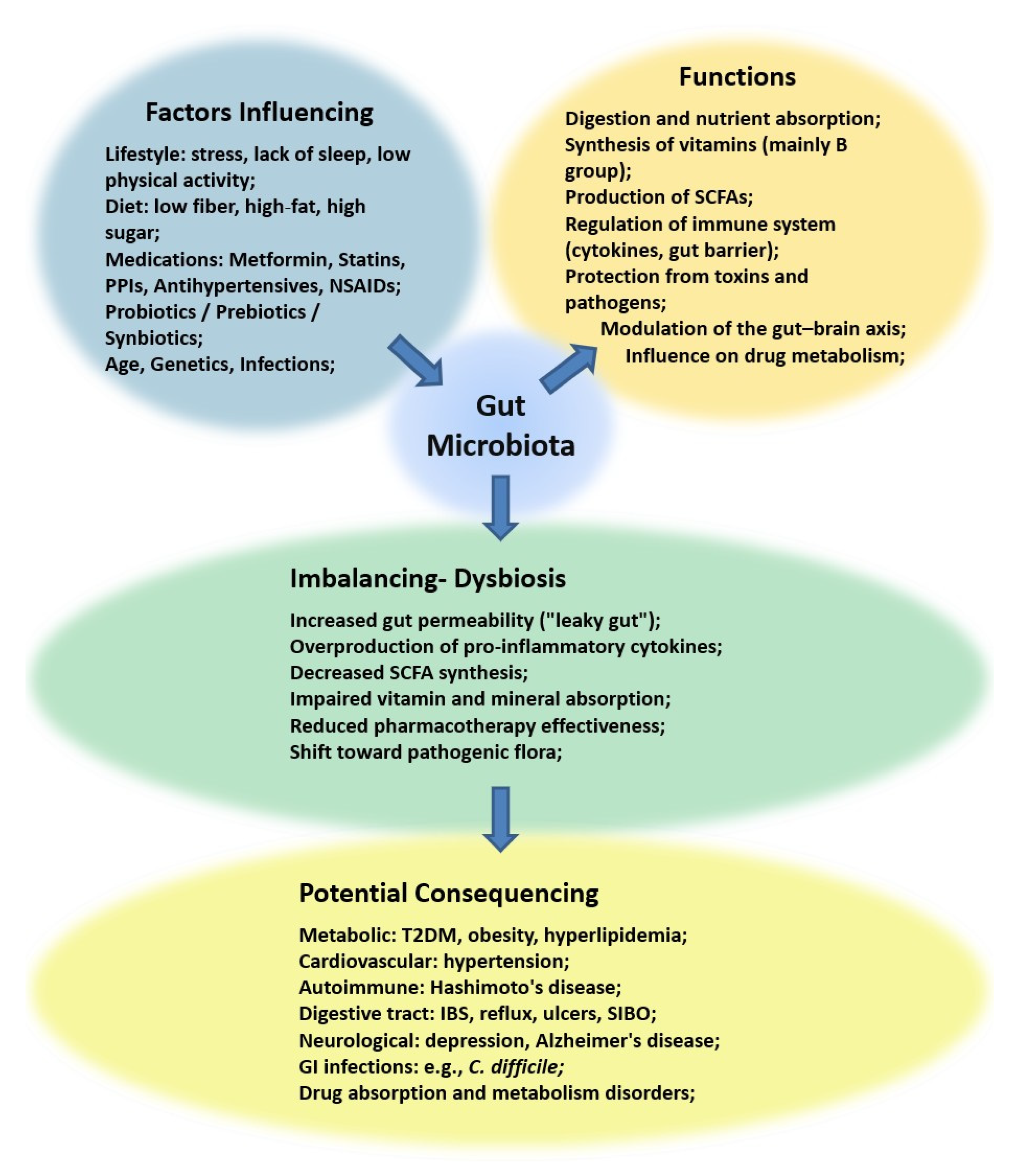
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
3. Selected Drugs Interaction with Microbiota
3.1. Medications Used in the Treatment of Diabetes
3.2. Medications Used in the Treatment of Hypothyroidism
3.3. Medications Used to Lower Cholesterol Level
3.4. Medications Used to Lower Blood Pressure
3.5. Medications Used to Reduce Gastric Acid Secretion
3.6. Summary
4. Perspectives
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shreiner, A.B.; Kao, J.Y.; Young, V.B. The gut microbiome in health and in disease. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 2015, 31, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Góralczyk-Bińkowska, A.; Szmajda-Krygier, D.; Kozłowska, E. The Microbiota–Gut–Brain Axis in Psychiatric Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petakh, P.; Kamyshna, I.; Kamyshnyi, A. Effects of metformin on the gut microbiota: A systematic review. Mol. Metab. 2023, 77, 101805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinninella, E.; Raoul, P.; Cintoni, M.; Franceschi, F.; Miggiano, G.A.D.; Gasbarrini, A.; Mele, M.C. What is the Healthy Gut Microbiota Composition? A Changing Ecosystem across Age, Environment, Diet, and Diseases. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhou, J.; Wang, L. Role and Mechanism of Gut Microbiota in Human Disease. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 625913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Li, T.; Liang, X.; Zhu, L.; Fang, Y.; Dong, L.; Zheng, Y.; Xu, X.; Li, M.; Cai, T.; et al. A decrease in Flavonifractor plautii and its product, phytosphingosine, predisposes individuals with phlegm-dampness constitution to metabolic disorders. Cell Discov. 2025, 11, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, T.; Wu, J.; Feng, F.; Wang, S.; Chi, Q.; Sha, Y.; Zha, S.; Shu, S.; et al. Gut microbiota-derived butyric acid regulates calcific aortic valve disease pathogenesis by modulating GAPDH lactylation and butyrylation. iMeta 2025, 4, e70048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zawistowska-Rojek, A.; Tyski, S. How to Improve Health with Biological Agents—Narrative Review. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruszewska, H.; Zawistowska-Rojek, A.; Tyski, S. Do NSAIDs and Other Pain Relief Drugs Can Inhibit the Growth of Lactobacillaceae? Pol. J. Microbiol. 2023, 72, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laudy, A.E.; Mrowka, A.; Krajewska, J.; Tyski, S. The influence of efflux pump inhibitors on the activity of non-antibiotic NSAIDs against Gram-negative rods. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0147131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Lee, H.; An, J.; Song, Y.; Lee, C.K.; Kim, K.; Kong, H. Alterations in Gut Microbiota by Statin Therapy and Possible Intermediate Effects on Hyperglycemia and Hyperlipidemia. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallianou, N.G.; Stratigou, T.; Tsagarakis, S. Metformin and gut microbiota: Their interactions and their impact on diabetes. Hormones 2019, 18, 141–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Memon, H.; Abdulla, F.; Reljic, T.; Alnuaimi, S.; Serdarevic, F.; Asimi, Z.V.; Kumar, A.; Semiz, S. Effects of combined treatment of probiotics and metformin in management of type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2023, 202, 110806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nabrdalik, K.; Drożdż, K.; Kwiendacz, H.; Skonieczna-Żydecka, K.; Łoniewski, I.; Kaczmarczyk, M.; Wijata, A.M.; Nalepa, J.; Holleman, F.; Nieuwdorp, M.; et al. Clinical Trial: Probiotics in Metformin Intolerant Patients with Type 2 Diabetes (ProGasMet). Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 168, 115650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jia, X.; Cong, B. Advances in the mechanism of metformin with wide-ranging effects on regulation of the intestinal microbiota. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1396031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palacios, T.; Vitetta, L.; Coulson, S.; Madigan, C.D.; Lam, Y.Y.; Manuel, R.; Briskey, D.; Hendy, C.; Kim, J.N.; Ishoey, T.; et al. Targeting the Intestinal Microbiota to Prevent Type 2 Diabetes and Enhance the Effect of Metformin on Glycaemia: A Randomised Controlled Pilot Study. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ermolenko, E.; Simanenkova, A.; Voropaeva, L.; Lavrenova, N.; Kotyleva, M.; Minasian, S.; Chernikova, A.; Timkina, N.; Gladyshev, N.; Dmitriev, A.; et al. Metformin Influence on the Intestinal Microbiota and Organism of Rats with Metabolic Syndrome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Cuesta-Zuluaga, J.; Mueller, N.T.; Corrales-Agudelo, V.; Velásquez-Mejía, E.P.; Carmona, J.A.; Abad, J.M.; Escobar, J.S. Metformin Is Associated with Higher Relative Abundance of Mucin-Degrading Akkermansia muciniphila and Several Short-Chain Fatty Acid-Producing Microbiota in the Gut. Diabetes Care 2017, 40, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forslund, K.; Hildebrand, F.; Nielsen, T.; Falony, G.; Le Chatelier, E.; Sunagawa, S.; Prifti, E.; Vieira-Silva, S.; Gudmundsdottir, V.; Pedersen, H.K.; et al. Disentangling type 2 diabetes and metformin treatment signatures in the human gut microbiota. Nature 2015, 528, 262–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.Y.; Yao, F.; Zhou, C.R.; Huang, X.Y.; Wang, Q.; Long, H.; Wu, Q.M. Role of gut microbiome in regulating the effectiveness of metformin in reducing colorectal cancer in type 2 diabetes. World J. Clin. Cases 2020, 8, 6213–6228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şahin, K.; Şahintürk, Y.; Köker, G.; Özçelik Köker, G.; Bostan, F.; Kök, M.; Uyar, S.; Çekin, A.H. Metformin with Versus without Concomitant Probiotic Therapy in Newly Diagnosed Patients with Type 2 Diabetes or Prediabetes: A Comparative Analysis in Relation to Glycemic Control, Gastrointestinal Side Effects, and Treatment Compliance. Turk. J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 33, 925–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hata, S.; Nakajima, H.; Hashimoto, Y.; Miyoshi, T.; Hosomi, Y.; Okamura, T.; Majima, S.; Nakanishi, N.; Senmaru, T.; Osaka, T.; et al. Effects of probiotic Bifidobacterium bifidum G9-1 on the gastrointestinal symptoms of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus treated with metformin: An open-label, single-arm, exploratory research trial. J. Diabetes Investig. 2022, 13, 489–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, S.A.; Mishra, S.; Dietsche, K.B.; Jain, S.; Mabundo, L.; Stagliano, M.; Krenek, A.; Courville, A.; Yang, S.; Turner, S.A.; et al. The effects of prebiotics on gastrointestinal side effects of metformin in youth: A pilot randomized control trial in youth-onset type 2 diabetes. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1125187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Available online: https://www.novonordisk.com/content/nncorp/global/en/news-and-media/news-and-ir-materials/news-details.html?id=667 (accessed on 6 March 2025).
- Feng, J.; Teng, Z.; Yang, Y.; Liu, J.; Chen, S. Effects of semaglutide on gut microbiota, cognitive function and inflammation in obese mice. PeerJ 2024, 12, e17891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, T.; Zhang, C.; Yang, S.; Bi, Y.; Li, M.; Yu, J. Semaglutide alters gut microbiota and improves NAFLD in db/db mice. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2024, 710, 149882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Gong, W.; Yang, F.; Cheng, R.; Zhang, G.; Gan, L.; Zhu, Y.; Qin, W.; Gao, Y.; Li, X.; et al. Dual GIP and GLP-1 receptor agonist tirzepatide alleviates hepatic steatosis and modulates gut microbiota and bile acid metabolism in diabetic mice. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2025, 147, 113937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihnatowicz, P.; Drywień, M.; Wątor, P.; Wojsiat, J. The importance of nutritional factors and dietary management of Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2020, 27, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Virili, C.; Stramazzo, I.; Centanni, M. Gut microbiome and thyroid autoimmunity. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 35, 101506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osowiecka, K.; Skrypnik, D.; Myszkowska-Ryciak, J. Assessment of the Impact of Nutritional Intervention with the Probiotic Lactiplantibacillus plantarum 299v on Nutritional Status and Quality of Life of Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis Patients—A Randomized Double-Blind Study Protocol. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talebi, S.; Karimifar, M.; Heidari, Z.; Mohammadi, H.; Askari, G. The effects of synbiotic supplementation on thyroid function and inflammation in hypothyroid patients: A randomized, double blind, placebo controlled trial. Complement. Ther. Med. 2020, 48, 102234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, B.; Wang, C.; Meng, F.; Wang, H.; Song, B.; Yang, Y.; Shan, Z. Association Between Gut Microbiota and Autoimmune Thyroid Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 774362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zawadzka, K.; Kałuzińska, K.; Świerz, M.J.; Sawiec, Z.; Antonowicz, E.; Leończyk-Spórna, M.; Abadi, A.K.; Trofimiuk-Müldner, M.; Bała, M.M. Are probiotics, prebiotics, and synbiotics beneficial in primary thyroid diseases? A systematic review with meta-analysis. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2023, 30, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spaggiari, G.; Brigante, G.; De Vincentis, S.; Cattini, U.; Roli, L.; De Santis, M.C.; Baraldi, E.; Tagliavini, S.; Varani, M.; Trenti, T.; et al. Probiotics Ingestion Does Not Directly Affect Thyroid Hormonal Parameters in Hypothyroid Patients on Levothyroxine Treatment. Front. Endocrinol. 2017, 8, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramezani, M.; Reisian, M.; Sajadi Hezaveh, Z. The effect of synbiotic supplementation on hypothyroidism: A randomized double-blind placebo controlled clinical trial. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0277213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bargiel, P.; Szczuko, M.; Stachowska, L.; Prowans, P.; Czapla, N.; Markowska, M.; Petriczko, J.; Kledzik, J.; Jędrzejczyk-Kledzik, A.; Palma, J.; et al. Microbiome Metabolites and Thyroid Dysfunction. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virili, C.; Centanni, M. “With a little help from my friends”—The role of microbiota in thyroid hormone metabolism and enterohepatic recycling. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2017, 458, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.; Zhao, M.; Gong, Y.; Chen, W.; Wang, Q.; Fu, Y.; Guo, T.; Zhao, J.; Gao, L.; Bo, T. Relation of Gut Microbes and L-Thyroxine Through Altered Thyroxine Metabolism in Subclinical Hypothyroidism Subjects. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, Y.; Xu, Y.; Ban, Y.; Li, J.; Wu, B.; Ouyang, Q.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, M.; Cai, Y.; Wang, M.; et al. Efficacy evaluation of probiotics combined with prebiotics in patients with clinical hypothyroidism complicated with small intestinal bacterial overgrowth during the second trimester of pregnancy. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 983027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nolan, J.A.; Skuse, P.; Govindarajan, K.; Patterson, E.; Konstantinidou, N.; Casey, P.G.; MacSharry, J.; Shanahan, F.; Stanton, C.; Hill, C.; et al. The influence of rosuvastatin on the gastrointestinal microbiota and host gene expression profiles. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2017, 312, G488–G497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Chen, Y.; Huang, W.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, W. Drug-microbiota interactions: An emerging priority for precision medicine. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, H.H.T.; Lareu, R.R.; Dix, B.R.; Hughes, J.D. Statins: Antimicrobial resistance breakers or makers? PeerJ 2017, 5, e3952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, T.; Li, C.; Shen, L.; Wang, S.; Li, X.; Fu, C.; Li, T.; Liu, B.; Gu, Y.; Wang, W.; et al. The Intestinal Effect of Atorvastatin: Akkermansia muciniphila and Barrier Function. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 797062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kummen, M.; Solberg, O.G.; Storm-Larsen, C.; Holm, K.; Ragnarsson, A.; Trøseid, M.; Vestad, B.; Skårdal, R.; Yndestad, A.; Ueland, T.; et al. Rosuvastatin alters the genetic composition of the human gut microbiome. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 5397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhou, X.; Wei, X.; Xie, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, K.; Mu, J. The influence of the intestinal microflora to the efficacy of Rosuvastatin. Lipids Health Dis. 2018, 17, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Song, X.; Zhou, H.; Zhou, X.; Xia, Y.; Dong, X.; Zhong, W.; Tang, S.; Wang, L.; Wen, S.; et al. Gut Microbiome Associates with Lipid-Lowering Effect of Rosuvastatin In Vivo. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, T.J.; Ahmed, Y.M.; Zamzami, M.A.; Mohamed, S.A.; Khan, I.; Baothman, O.A.S.; Mehanna, M.G.; Yasir, M. Effect of atorvastatin on the gut microbiota of high fat diet-induced hypercholesterolemic rats. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Goel, R.; Kumar, A.; Qi, Y.; Lobaton, G.; Hosaka, K.; Mohammed, M.; Handberg, E.M.; Richards, E.M.; Pepine, C.J.; et al. Imbalance of gut microbiome and intestinal epithelial barrier dysfunction in patients with high blood pressure. Clin. Sci. 2018, 132, 701–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Wang, Z.; Hu, L.; Zhang, X.; Chen, J.; Yu, Z.; Liu, L.; Wu, M. Targets of statins intervention in LDL-C metabolism: Gut microbiota. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 972603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, J.; Sun, L.; Yu, Y.; Fan, H.; Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhuo, X.; Guo, M.; Liu, J.; Liu, P.; et al. A gut feeling of statin. Gut Microbes 2024, 16, 2415487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimizu, M.; Hashiguchi, M.; Shiga, T.; Tamura, H.O.; Mochizuki, M. Meta-Analysis: Effects of Probiotic Supplementation on Lipid Profiles in Normal to Mildly Hypercholesterolemic Individuals. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0139795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Zhou, B.; Zhou, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Jia, S.; Zhang, Z.; Chu, C.; Mu, J. Combined Lowering Effects of Rosuvastatin and L. acidophilus on Cholesterol Levels in Rat. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 29, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, F.; Roessler, J.; Schmidt, D.; Jasina, A.; Schumann, P.; Gast, M.; Poller, W.; Leistner, D.; Giral, H.; Kränkel, N.; et al. Impact of the Gut Microbiota on Atorvastatin Mediated Effects on Blood Lipids. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Hu, Y.; Chen, H.; Li, B.; Cao, L.; Xia, J.; Yin, Y. An in vitro evaluation of the effects of different statins on the structure and function of human gut bacterial community. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0230200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Wu, G.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, H.; Ren, M.; Song, X.; Chang, H.; Jing, Z. Probiotics combined with atorvastatin administration in the treatment of hyperlipidemia: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Medicine 2024, 103, e37883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Zhu, P.; Wang, Y.; Yang, H.; Zhou, R.; Shu, Y.; Zhou, H.; Li, Q. The Role of Gut Microbiota in Hypertension Pathogenesis and the Efficacy of Antihypertensive Drugs. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2021, 23, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Available online: https://world-heart-federation.org/what-we-do/hypertension/ (accessed on 27 October 2024).
- Mishima, E.; Abe, T. Role of the microbiota in hypertension and antihypertensive drug metabolism. Hypertens. Res. 2022, 45, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyoung, J.; Atluri, R.R.; Yang, T. Resistance to Antihypertensive Drugs: Is Gut Microbiota the Missing Link? Hypertension 2022, 79, 2138–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Wang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Ge, Z.; Li, Z.; Feng, S.; Wu, C. Gut microbiota and hypertension: Association, mechanisms and treatment. Clin. Exp. Hypertens. 2023, 45, 2195135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.; Gu, Y.; Li, X.; Yang, W.; Jia, L.; Chen, C.; Han, X.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Li, P.; et al. Alterations of the Gut Microbiome in Hypertension. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhao, F.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Tao, J.; Tian, G.; Wu, S.; Liu, W.; Cui, Q.; Geng, B.; et al. Gut microbiota dysbiosis contributes to the development of hypertension. Microbiome 2017, 5, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinakis, E.; Nakai, M.; Gill, P.; Ribeiro, R.; Yiallourou, S.; Sata, Y.; Muir, J.; Carrington, M.; Head, G.A.; Kaye, D.M.; et al. Association Between the Gut Microbiome and Their Metabolites with Human Blood Pressure Variability. Hypertension 2022, 79, 1690–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmu, J.; Salosensaari, A.; Havulinna, A.S.; Cheng, S.; Inouye, M.; Jain, M.; Salido, R.A.; Sanders, K.; Brennan, C.; Humphrey, G.C.; et al. Association Between the Gut Microbiota and Blood Pressure in a Population Cohort of 6953 Individuals. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2020, 9, e016641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, H.H.; Kim, I.S.; Yoo, D.H.; Kim, D.H. Effects of orally administered antibiotics on the bioavailability of amlodipine: Gut microbiota-mediated drug interaction. J. Hypertens. 2016, 34, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.Q.; Gong, J.Y.; Xing, K.; Liu, M.Z.; Ren, H.; Luo, J.Q. Pharmacomicrobiomics: Exploiting the Drug-Microbiota Interactions in Antihypertensive Treatment. Front. Med. 2022, 8, 742394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dharmarathne, G.; Kazi, S.; King, S.; Jayasinghe, T.N. The Bidirectional Relationship Between Cardiovascular Medications and Oral and Gut Microbiome Health: A Comprehensive Review. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, T.; Marques, F.Z. Gut Microbiota: Friends or Foes for Blood Pressure-Lowering Drugs. Hypertension 2022, 79, 1602–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M.S.; Yu, J.S.; Yoo, H.H.; Kim, D.H. The role of gut microbiota in the pharmacokinetics of antihypertensive drugs. Pharmacol. Res. 2018, 130, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruszewska, H.; Zareba, T.; Kociszewska, A.; Tyski, S. Activity of selected non-antibiotic medicinal preparations against standard microorganisms including bacterial probiotic strains. Acta Pol. Pharm. Drug Res. 2021, 78, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhao, D.; Qian, M.; Liu, J.; Pan, C.; Zhang, X.; Duan, X.; Zhang, Y.; Jia, W.; Wang, L. Amlodipine, an anti-hypertensive drug, alleviates non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by modulating gut microbiota. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2022, 179, 2054–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saputri, F.A.; Kang, D.; Kusuma, A.S.W.; Rusdiana, T.; Hasanah, A.N.; Mutakin; Surono, I.S.; Koyama, H.; Abdulah, R. Lactobacillus plantarum IS-10506 probiotic administration increases amlodipine absorption in a rabbit model. J. Int. Med. Res. 2018, 46, 5004–5010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, T.; Aquino, V.; Lobaton, G.O.; Li, H.; Colon-Perez, L.; Goel, R.; Qi, Y.; Zubcevic, J.; Febo, M.; Richards, E.M.; et al. Sustained Captopril-Induced Reduction in Blood Pressure Is Associated with Alterations in Gut-Brain Axis in the Spontaneously Hypertensive Rat. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2019, 8, e010721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Correa, C.; Moleón, J.; Miñano, S.; Robles-Vera, I.; Toral, M.; Barranco, A.M.; Martín-Morales, N.; O’Valle, F.; Guerra-Hernández, E.; Sánchez, M.; et al. Differing contributions of the gut microbiota to the blood pressure lowering effects induced by first-line antihypertensive drugs. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2024, 181, 3420–3444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robles-Vera, I.; Toral, M.; de la Visitación, N.; Sánchez, M.; Gómez-Guzmán, M.; Muñoz, R.; Algieri, F.; Vezza, T.; Jiménez, R.; Gálvez, J.; et al. Changes to the gut microbiota induced by losartan contributes to its antihypertensive effects. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 177, 2006–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, A.; Ericson, U.; Jönsson, D.; Miari, M.; Athanasiadis, P.; Baldanzi, G.; Brunkwall, L.; Hellstrand, S.; Klinge, B.; Melander, O.; et al. New connections of medication use and polypharmacy with the gut microbiota composition and functional potential in a large population. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 23723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, L.; Li, Y.; Chen, M.; Xue, L.; Wang, J.; Ding, Y.; Gu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Yang, R.; Zhao, H.; et al. Effects of probiotics on hypertension. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2023, 107, 1107–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hata, Y.; Yamamoto, M.; Ohni, M.; Nakajima, K.; Nakamura, Y.; Takano, T. A placebo-controlled study of the effect of sour milk on blood pressure in hypertensive subjects. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1996, 64, 767–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agerholm-Larsen, L.; Raben, A.; Haulrik, N.; Hansen, A.S.; Manders, M.; Astrup, A. Effect of 8 week intake of probiotic milk products on risk factors for cardiovascular diseases. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2000, 54, 288–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naruszewicz, M.; Johansson, M.L.; Zapolska-Downar, D.; Bukowska, H. Effect of Lactobacillus plantarum 299v on cardiovascular disease risk factors in smokers. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2002, 76, 1249–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiecka, A.; Szczepanik, M. Proton pump inhibitor-induced gut dysbiosis and immunomodulation: Current knowledge and potential restoration by probiotics. Pharmacol. Rep. 2023, 75, 791–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imhann, F.; Vich Vila, A.; Bonder, M.J.; Lopez Manosalva, A.G.; Koonen, D.P.Y.; Fu, J.; Wijmenga, C.; Zhernakova, A.; Weersma, R.K. The influence of proton pump inhibitors and other commonly used medication on the gut microbiota. Gut Microbes 2017, 8, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, M.A.; Goodrich, J.K.; Maxan, M.E.; Freedberg, D.E.; Abrams, J.A.; Poole, A.C.; Sutter, J.L.; Welter, D.; Ley, R.E.; Bell, J.T.; et al. Proton pump inhibitors alter the composition of the gut microbiota. Gut 2016, 65, 749–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemmens, A.S.; Huysentruyt, K.; Vandenplas, Y. Why think twice before prescribing proton pump inhibitors. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2025, 184, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kostrzewska, M.; Świdnicka-Siergiejko, A.; Olszańska, D.; Jurkowska, G.; Garley, M.; Ratajczak-Wrona, W.; Jabłońska, E.; Jamiołkowski, J.; Dabrowski, A. The effect of omeprazole treatment on the gut microflora and neutrophil function. Clin. Res. Hepatol. Gastroenterol. 2017, 41, 575–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Yan, H.; Xing, X.; Yang, J. Proton pump inhibitors alter gut microbiota by promoting oral microbiota translocation: A prospective interventional study. Gut 2024, 73, 1098–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvath, A.; Leber, B.; Feldbacher, N.; Steinwender, M.; Komarova, I.; Rainer, F.; Blesl, A.; Stadlbauer, V. The effects of a multispecies synbiotic on microbiome-related side effects of long-term proton pump inhibitor use: A pilot study. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Li, Q.; Xia, S.; He, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yang, J.; Xiao, X. Proton Pump Inhibitors and Oral-Gut Microbiota: From Mechanism to Clinical Significance. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, G.; Zaccari, P.; Rocco, G.; Scalese, G.; Panetta, C.; Porowska, B.; Pontone, S.; Severi, C. Proton pump inhibitors and dysbiosis: Current knowledge and aspects to be clarified. World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 2706–2719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hojo, M.; Asahara, T.; Nagahara, A.; Takeda, T.; Matsumoto, K.; Ueyama, H.; Matsumoto, K.; Asaoka, D.; Takahashi, T.; Nomoto, K.; et al. Gut Microbiota Composition Before and After Use of Proton Pump Inhibitors. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2018, 63, 2940–2949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amir, I.; Konikoff, F.M.; Oppenheim, M.; Gophna, U.; Half, E.E. Gastric microbiota is altered in oesophagitis and Barrett’s oesophagus and further modified by proton pump inhibitors. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 16, 2905–2914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, M.A.; Verdi, S.; Maxan, M.E.; Shin, C.M.; Zierer, J.; Bowyer, R.C.E.; Martin, T.; Williams, F.M.K.; Menni, C.; Bell, J.T.; et al. Gut microbiota associations with common diseases and prescription medications in a population-based cohort. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Piano, M.; Anderloni, A.; Balzarini, M.; Ballarè, M.; Carmagnola, S.; Montino, F.; Orsello, M.; Pagliarulo, M.; Tari, R.; Soattini, L.; et al. The innovative potential of Lactobacillus rhamnosus LR06, Lactobacillus pentosus LPS01, Lactobacillus plantarum LP01, and Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. delbrueckii LDD01 to restore the “gastric barrier effect” in patients chronically treated with PPI: A pilot study. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2012, 46, S18–S26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belei, O.; Olariu, L.; Dobrescu, A.; Marcovici, T.; Marginean, O. Is It Useful to Administer Probiotics Together with Proton Pump Inhibitors in Children with Gastroesophageal Reflux? J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2018, 24, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwak, D.S.; Jun, D.W.; Seo, J.G.; Chung, W.S.; Park, S.E.; Lee, K.N.; Khalid-Saeed, W.; Lee, H.L.; Lee, O.Y.; Yoon, B.C.; et al. Short-term probiotic therapy alleviates small intestinal bacterial overgrowth, but does not improve intestinal permeability in chronic liver disease. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 26, 1353–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, G.; Haileselassie, Y.; Briscoe, L.; Bai, L.; Patel, A.; Sanjines, E.; Hendler, S.; Singh, P.K.; Garud, N.R.; Limketkai, B.N.; et al. The effect of gastric acid suppression on probiotic colonization in a double blinded randomized clinical trial. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2022, 47, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Drug | Effect on Gut Microbiota | Interaction with Probiotics | References |
|---|---|---|---|
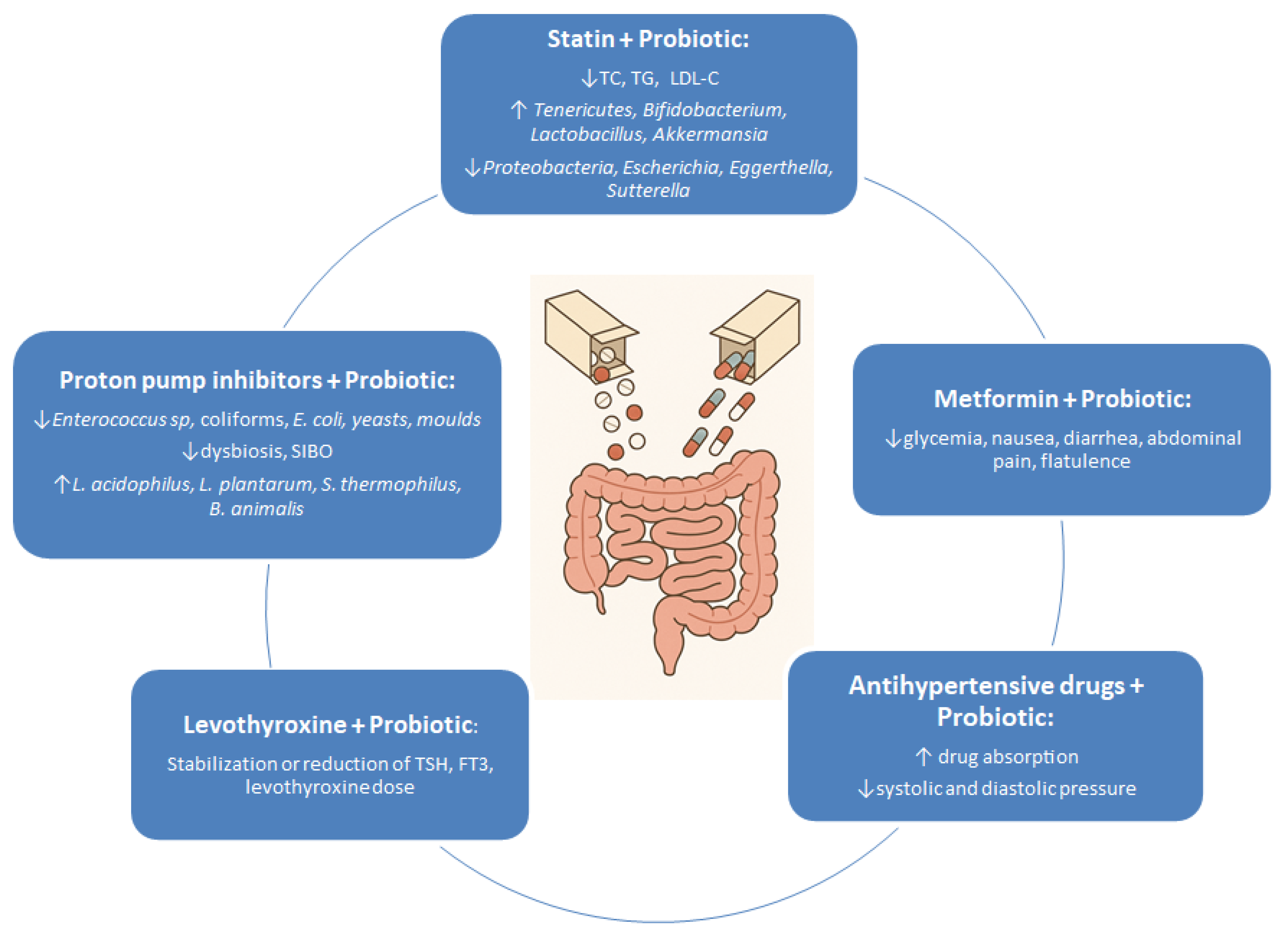
| Metformin | Microbiota changes: ↑ Bacteroidetes, ↑ Actinobacteria, ↑ Proteobacteria; ↓ Firmicutes, ↓ Verrucomicrobia; At genus level: ↑ Bacteroides, ↑ Streptococcus, ↑ Collinsella, ↑ Escherichia, ↑ Clostridium, ↑ Subdoligranulum,↑ Akkermansia, ↓ Faecalibacterium, ↓ Ruminococcus, ↓ Roseburia; ↑ SCFA-producing bacteria (Butyrivibrio, Bifidobacterium, Megasphaera, Prevotella, Lactobacillus spp); | Probiotics reduce gastrointestinal side effects and improve glycaemic (HbA1c, glucose) and insulin control; | [14,15,16,17,18,20,21,22] |
| Semaglutide | Microbiota changes: ↑ Akkermansia, ↑ Alloprevotella, ↑ Alistipes, ↑ Muribaculaceae, ↑ Coriobacteriaceae; ↓ Romboutsia, ↓ Dubosiella, ↓ Lactobacillus, ↓ Ligilactobacillus, ↓ Enterorhabdus; | No conclusive data on interactions with probiotics; | [25,26,27] |
| Levothyroxine | Microbiota changes: ↑ Odoribacter, ↑ Enterococcus; Dysbiosis observed in Hashimoto’s patients; ↓ Lactobacillus, ↓ Bifidobacterium; microbiota affects T3/T4 and micronutrient absorption; | Probiotics may stabilise TSH, improve thyroid function, and reduce drug dosage; | [31,32,34,35,38,39] |
| Atorvastatin | Microbiota changes: ↑ Oscillibacter, ↑ Turicibacter, ↑ Anaerovorax, ↑ Parvibacter, ↑ Anaerotruncus, ↑ Bacteroides, ↑ Butyricimonas, ↑ Dorea, ↑ Mucispirillum, ↓ Parabacteroides,↓ Akkermansia, ↓ Rikenella, ↓ Christensensellaceae, ↓ Bifidobacterium, ↓ Tyzzerella, ↓ Lactobacillus; intestinal barrier disruption; reduced effectiveness in poor microbiota; | Probiotics enhance effectiveness (↓ LDL-C, ↓ TC, ↓ TG); Changes in gut microbiota diversity: ↑ Tenericutes, ↑ Bifidobacterium, ↑ Lactobacillus, ↑ Akkermansia, ↓ Proteobacteria, ↓ Escherichia, ↓ Eggerthella, ↓ Sutterella; | [11,43,54,55] |
| Rosuvastatin | Microbiota changes: ↑ Bacteroides,↑ Butyricimonas, ↑ Clostridium, ↑ Mucispirillum, ↑ Ruminococcaceae, ↑ Lachnospiraceae; ↓ Bacteroidetes; | L. acidophilus enhances lipid-lowering effect; increased faecal levels in rats after combined therapy; | [11,46,52] |
| Amlodipine | Microbiota changes: ↑ Akkermansia, ↑ Bacteroides, ↑ Lactobacillus, ↑ Ruminoclostridium,↑ Lachnospiraceae, ↑ Verrucomicrobia | L. plantarum increases plasma drug levels—potential enhancement of absorption and bioavailability; | [71,72] |
| Captopril | Microbiota changes: ↑ Tenericutes, ↑ Actinobacteria, ↑ Firmicutes, ↓ Bacteroidetes, impacts gut permeability and CNS function; | No data on probiotic use with captopril; | [73,74] |
| Losartan | Restores F/B balance; Microbiota changes: ↑ Verrucomicrobiaceae, ↑ Akkermansia, ↑ Pedobacter; ↓ Lactobacillaceae; improves gut integrity and defensin production; | No specific data, but microbiota improvement may enhance therapeutic effect; | [75] |
| Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs: omeprazole, esomeprazole, etc.) | Microbiota changes: oral cavity: ↑ Fusobacteriaceae, ↑ Leptotrichiaceae, ↓ Neisseriaceae, ↓ Veillonellaceae; oesophageal: ↓ Comamonadaceae, ↑ Clostridiaceae, ↑ Lachnospiraceae, ↑ Micrococaceae, ↑ Actinomycetaceae, ↑ Lactobacillales, ↑ Gemellales; gastric: ↓ Moraxellaceae, ↓ Flavobacteriaceae, ↓ Comamonadaceae, ↓ Methylobacteriaceae, ↑ Erysipelotrichaceae, ↑ Clostridiales; stomach: ↑ Streptococcaceae, ↓ Prevotellaceae; small intestine: ↑ Streptococcaceae, ↑ Staphylococcaceae, ↑ Enterobacteriaceae, ↑ Bacteroidaceae, ↑ Lactobacillaceae, ↑ Veillonellaceae, ↑ Clostridiaceae, ↓ Bifidobacteriaceae; colon: ↑ Enterobacteriaceae, ↑ Enterococcaceae, ↑ Lactobacillaceae, ↓ Ruminococcaceae, ↓ Bifidobacteriaceae; | Decreases SIBO prevalence, reduces pathogenic bacteria, improves gut barrier function, and alleviates gastrointestinal side effects of long-term PPI use; | [87,89,91,92,93,94,95,96] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zawistowska-Rojek, A.; Tyski, S. Drugs Versus Microbiota: How Pharmacotherapy Affects Gut and Probiotic Bacteria. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 1372. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18091372
Zawistowska-Rojek A, Tyski S. Drugs Versus Microbiota: How Pharmacotherapy Affects Gut and Probiotic Bacteria. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(9):1372. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18091372
Chicago/Turabian StyleZawistowska-Rojek, Anna, and Stefan Tyski. 2025. "Drugs Versus Microbiota: How Pharmacotherapy Affects Gut and Probiotic Bacteria" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 9: 1372. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18091372
APA StyleZawistowska-Rojek, A., & Tyski, S. (2025). Drugs Versus Microbiota: How Pharmacotherapy Affects Gut and Probiotic Bacteria. Pharmaceuticals, 18(9), 1372. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18091372






