Exploring the Therapeutic Potential of Bupleurum in Medical Treatment: A Comprehensive Overview
Abstract
1. Introduction

2. Review Methods
3. Chemical Composition
| Category | Chemical Name | Structural Formula | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Saponins | Saikosaponin A |  | [14] |
| Saikosaponin B1 |  | [14] | |
| Saikosaponin B2 |  | [14] | |
| Polysaccharides | Type I rhamnogalacturonan | 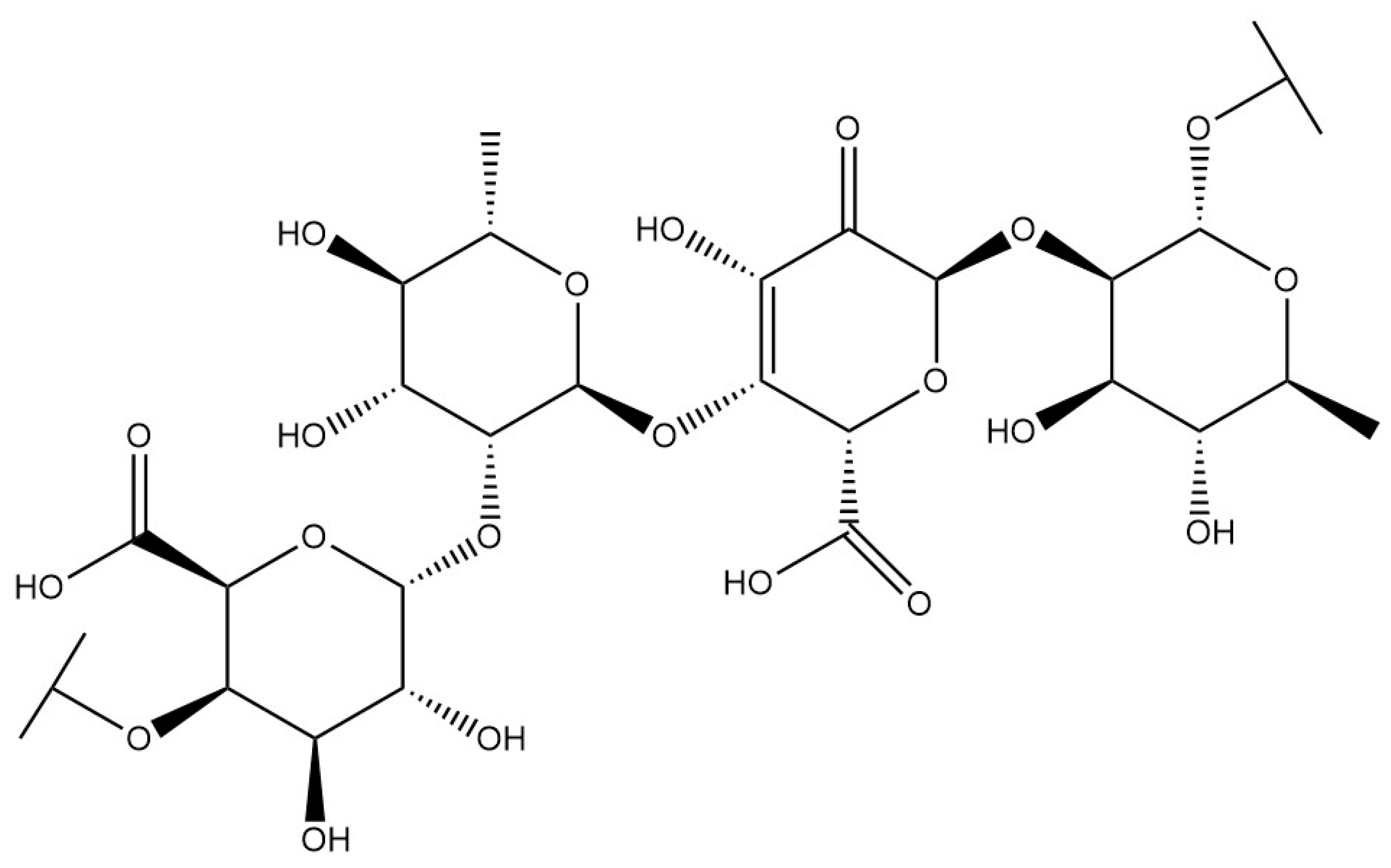 | [15] |
| Coumarins | Scopoletin | 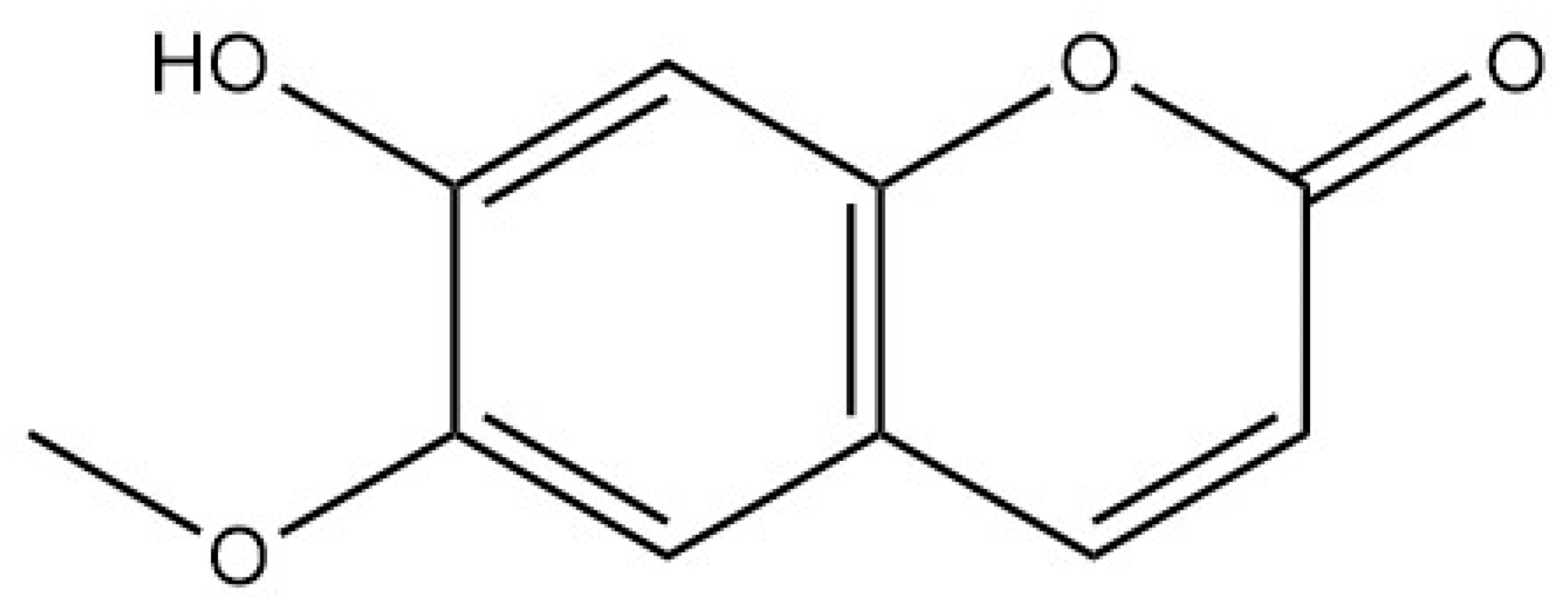 | [16] |
| Polyacetylenes | Bupleurynol |  | [17] |
4. Pharmacological Effect
4.1. Anti-Tumor
4.1.1. Anti-Liver Cancer
4.1.2. Anti-Gastric Cancer
4.1.3. Anti-Colon Cancer
4.1.4. Anti-Breast Cancer
4.1.5. Anti-Lung Cancer
4.1.6. Anti-Cervical Cancer
4.1.7. Anti-Melanoma
| Effect and Disease | Adopted Model | Main Mechanisms | Main Targets | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HCC | 1. PLC mice treated with SS-b2 or doxorubicin2. SMMC-7721 and HepG2 cells exposed to SS-d3. H22 hepatoma-bearing mice given BCP | SS-b2 raises STK4 expression, which in turn lowers IRAK1 and phosphorylated NF-κB p65, diminishes IL-1β/IL-6/TNF-α production and restrains tumor growth. SS-d blocks the p-STAT3/C-EBPβ axis, decreases COX-2 and reverses the Bax/Bcl-2 ratio, thereby activating caspase-3/9-mediated apoptosis. BCP arrests the cell cycle in the S phase and triggers apoptosis in tumors. | STK4, IRAK1, NF-κB p65, STAT3, COX-2, Bax, Bcl-2, caspase-3/9 | [36,38,40] |
| Gastric cancer | 1. HGC-27, AGS, MKN-28 cells treated with SS-a 2. AGS xenografts (including radio-resistant AGS-R and MKN-74-R) | SS-a blocks the PI3K–Akt–mTOR cascade, elevates Bax and lowers Bcl-2, leading to S-phase arrest and apoptosis. It simultaneously provokes ER stress (GRP78–PERK–eIF2α–ATF4–CHOP), activates caspase-3/8/9 and enhances radiosensitivity in resistant GC cells. | PI3K, Akt, mTOR, Bax, Bcl-2, GRP78, PERK, CHOP, caspase-3/8/9 | [31,51] |
| Colorectal cancer | 1. SW480 and SW620 cells exposed to TBSE 2. LoVo and SW480 cells and xenograft mice treated with SS-a | TBSE suppresses PI3K–Akt–mTOR signaling, shifts the Bax/Bcl-2 balance and activates caspase-9/3, culminating in apoptosis. SS-a sequentially activates caspase-4, then caspase-2/8/3, thereby inducing apoptosis and reducing tumor volume in vivo. | PI3K, Akt, mTOR, Bax, Bcl-2, caspase-4/2/8/3/9 | [33,42] |
| Breast cancer | 1. MCF-7 cells (SS-b2) 2. Adriamycin-resistant MCF-7/ADR cells (SS-a, SS-b) | SS-b2 inhibits STAT3 phosphorylation, down-regulates VASP and MMP-2/9, and thus curbs proliferation and migration. SS-a and SS-b repress MDR1 mRNA and P-gp, lowering the IC50 of doxorubicin in resistant cells. | STAT3, VASP, MMP-2/9, MDR1, P-gp | [35,37] |
| NSCLC | A549 and HCC827 cells treated with SS-d | SS-d accumulates ROS, acetylates NF-κB, and activates the NLRP3–caspase-1–GSDMD axis, leading to pyroptotic cell death. | ROS, NF-κB, NLRP3, caspase-1, GSDMD | [39] |
| Cervical cancer | HeLa cells treated with SS-a | SS-a decreases mitochondrial membrane potential, elevates ROS, and up-regulates Bax, caspase-3, and ER stress proteins (GRP78, CHOP, caspase-12), while suppressing PI3K/Akt, thereby inducing apoptosis. | Bax, Bcl-2, caspase-3/12, GRP78, CHOP, PI3K/Akt | [34] |
| Melanoma | A375 cells exposed to BCP | BCP disrupts β1-integrin binding to fibronectin, reduces phosphorylation of FAK and paxillin, and inhibits ECM-mediated adhesion, thereby impeding metastasis. | β1-integrin, FAK, paxillin | [41] |

4.2. Anti-Inflammatory
4.2.1. Anti-Rhinitis
4.2.2. Anti-Colitis
4.2.3. Anti-Osteoarthritis
4.2.4. Anti-Mastitis
| Condition | Adopted Model | Main Mechanisms | Main Targets | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Allergic rhinitis | 1. OVA-sensitized mice given SS-d 2. OVA-sensitized mice given BCE | SS-d and BCE both reduce sneezing and nasal rubbing, dampen eosinophil and mast-cell infiltration, lower IgE/IgG1 and Th2 cytokines, raise IgG2a and IL-10, and inhibit NF-κB signaling, improving nasal mucosal integrity. | NF-κB, IL-4/5/13, IgE, IgG1/2a, IL-10 | [65,70] |
| Ulcerative colitis | 1. DSS-induced zebrafish colitis (SS-b1, SS-d) 2. DSS-induced mouse colitis (SS-d) | SS-b1 and SS-d activate NRF2/HO-1, diminish lipid peroxidation and iron loading, and inhibit ferroptosis. SS-d also suppresses NF-κB, decreases TNF-α/IL-6/IL-1β, elevates IL-10, and recovers barrier proteins ZO-1, Claudin-1, Muc1/2. | NRF2, HO-1, TNF-α, IL-6/1β/10, ZO-1, Claudin-1, Muc1/2 | [66,69] |
| Osteoarthritis | IL-1β-stimulated human chondrocytes treated with SS-a | SS-a up-regulates LXRα, blocks NF-κB activation, and reduces NO, PGE2, and MMP-1/3/13, alleviating chondrocyte inflammation. | LXRα, NF-κB, MMP-1/3/13, NO, PGE2 | [67] |
| Mastitis | S. aureus-induced mouse mastitis treated with SS-a | SS-a activates SIRT1/Nrf2, raises HO-1, enhances tight-junction proteins, decreases Fe2+ and ferroptosis markers, and suppresses inflammatory cytokines, protecting the blood–milk barrier. | SIRT1, Nrf2, HO-1, ZO-1, Occludin, Claudin-3 | [68] |
4.3. Anti-Depression
| Effect | Adopted Model | Main Mechanisms | Main Targets | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antidepressant | 1. CUMS rats (Bupleurum extract) 2. CUMS mice (SS-d, SS-a) 3. Corticosterone-treated mice (TSS). | Bupleurum extract elevates cAMP/PKA/CREB, lowers CORT and inflammatory cytokines. SS-d fosters NLRP3 ubiquitination, inhibits inflammasome activation and hippocampal NF-κB/MAPK, while SS-a promotes hippocampal neurogenesis via Tet1–DLL3–Notch–BDNF. TSS activates AMPAR–mTOR signaling, improving depressive-like behavior. | cAMP, PKA, CREB, NLRP3, NF-κB, BDNF, mTOR, AMPAR | [90,91,92,94] |
4.4. Anti-Aging
| Effect | Adopted Model | Main Mechanisms | Main Targets | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anti-ageing/antioxidant | 1. H2O2-induced senescent MLECs (S-BCP1-4, S-BCP1-8) 2. LPS-activated macrophages (BCP) | Sulfated BCP derivatives prevent G0/G1 arrest, down-regulate p53–p21 and p16–pRb pathways and favor S-phase entry. BCP lowers ROS, stabilizes mitochondrial membrane potential and represses NF-κB/p65, thereby reducing cellular senescence markers SA-β-gal and SAHF. | p53, p21, p16, NF-κB p65, ROS, SA-β-gal, SAHF | [103,104] |
4.5. Anti-Epileptic
| Effect | Adopted Model | Main Mechanisms | Main Targets | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antiepileptic | 1. KA-induced rat epilepsy (BCE-20, BCE-70) and LPS-BV-2 cells 2. KA-induced rats treated with BAO | BCE-20/70 enhance TREM2, suppress NF-κB/IκB signaling and pro-inflammatory cytokines, reducing seizures. BAO modulates Bcl-2/Bax/caspase-3 and GABAergic pathways (GAD65/67, GIRK1), protecting hippocampal neurons. | TREM2, NF-κB, IL-1β/6, TNF-α, Bcl-2, Bax, caspase-3, GAD65/67, GIRK1 | [107,108] |
4.6. Antipyretic Effect
| Effect | Adopted Model | Main Mechanisms | Main Targets | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antipyretic | LPS-induced fever rats and endotoxemic mice treated with BCE | BCE inhibits TNF-α release from peripheral monocytes, thereby lowering core body temperature in febrile animals. | TNF-α | [112] |
4.7. Anti-Hepatitis C Virus
| Effect | Adopted Model | Main Mechanisms | Main Targets | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HCV | Huh-7.5.1 cells infected with HCV and treated with SS-b2 | SS-b2 blocks HCV RNA translation and replication and suppresses Daclatasvir-resistant mutants, providing a potential combination therapy. | HCV RNA, NS5A pathway | [117] |
4.8. Other Pharmacological Effects
4.8.1. Anti-Alzheimer’s Disease
4.8.2. Anti-Cerebral Ischemic Injury
4.8.3. Anti-Allergic Asthma
4.8.4. Anti-Cardiovascular Disease
4.8.5. Liver Protection
4.8.6. Antidiabetics
5. VOSviewer
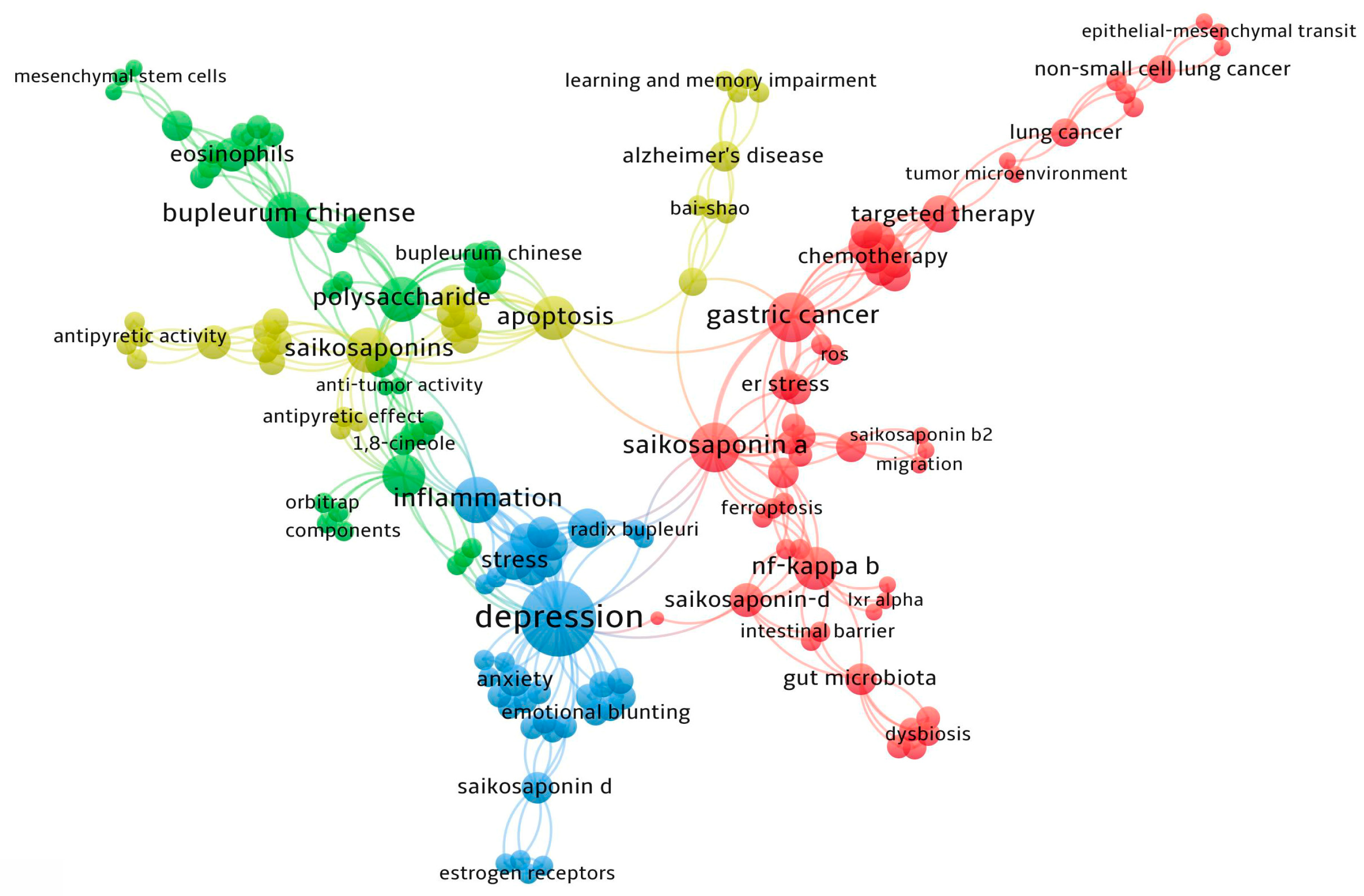

6. Conclusions
7. Challenges and Breakthrough Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nešić, M.D.; Nešić, M.S.; Dimitrijević, M.; Radulović, N.S. Essential Oil Composition of Bupleurum praealtum and Bupleurum affine: New Natural Constituents. Plants 2024, 13, 2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, L.; Guo, X.; Ma, Y.; Xu, L.; Wei, J.; Xiao, P. A comprehensive review on traditional and modern research of the genus Bupleurum (Bupleurum L., Apiaceae) in recent 10 years. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2023, 306, 116129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Jiang, Z.; Zhu, N.; Wang, D.; Guo, T.; Meng, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Tan, K.; Hu, M.; Tang, H.; et al. Exploring the multi-targeted mechanism of Saikosaponin A in prostate cancer treatment: A network pharmacology and molecular docking approach. Front. Pharmacol. 2025, 16, 1530715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, P.; Ma, R.; Liu, X.; Song, L.; Ma, B.; Zou, G. Saikosaponin-d Attenuates Irinotecan-Induced Intestinal Toxicity via TAK1/NF-κB Pathway and Enhances Antitumor Efficacy. J. Inflamm. Res. 2025, 18, 7973–7988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Xiao, L.; Chen, Q.; Shen, L.; Zhao, G.; Linghu, K.; Ma, Q.; Dar, P.; Yu, H. Bioactive Equivalent Combinatorial Compounds contributing to the holistic effect of traditional Chinese medicine Bupleuri chinense DC. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2025, 350, 120003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, X.; Huang, W. Exploring the mechanism of Radix Bupleuri in the treatment of depression combined with SARS-CoV-2 infection through bioinformatics, network pharmacology, molecular docking, and molecular dynamic simulation. Metab. Brain Dis. 2025, 40, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, Y.; Li, M.; Wang, Y.; Yao, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhuang, L.; Liu, S.; Li, Z.; Hao, Z.; et al. Saikosaponins from Bupleurum scorzonerifolium Willd. alleviates microglial pyroptosis in depression by binding and inhibiting P2X7 expression. Phytomedicine 2025, 136, 156240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, S.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, C.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, Y. Research progress on the molecular mechanisms of Saikosaponin D in various diseases (Review). Int. J. Mol. Med. 2025, 55, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.; Sui, Y.; Tang, X.Y.; Zhang, R.; Shu, Q.; Gong, T.; Wu, S.; Sun, Z.W.; Li, W.L.; Qu, Z.Y. Mechanism of Bupleurum scorzonerifolium and Paeonia lactiflora herbal pair against liver cancer: An exploration based on UPLC-Q-TOF-MS combined with network pharmacology. Zhongguo Zhongyao Zazhi/China J. Chin. Mater. Medica 2022, 47, 3597–3608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Shi, W.; He, X.Y.; Du, Q.Y.; Wang, F.; Guo, J. Saikosaponin D: Review on the antitumour effects, toxicity and pharmacokinetics. Pharm. Biol. 2021, 59, 1480–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, H.; Guo, Z.; Hu, B.; Zhang, G. Elucidation of the Anti-Inflammatory Mechanisms of Bupleuri and Scutellariae Radix Using System Pharmacological Analyses. Mediat. Inflamm. 2017, 2017, 3709874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cholet, J.; Decombat, C.; Vareille-Delarbre, M.; Gainche, M.; Berry, A.; Senejoux, F.; Ripoche, I.; Delort, L.; Vermerie, M.; Fraisse, D.; et al. In Vitro Anti-Inflammatory and Immunomodulatory Activities of an Extract from the Roots of Bupleurum rotundifolium. Medicines 2019, 6, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Wang, X.; Xu, H.; Zhao, R.; Hu, Q. Comparative Study on Volatile Oils among Bupleuri radix Species and Habitats: Yields, Chemical Characterization and Antipyretic Activities. Chem. Biodivers. 2022, 19, e202200549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N. Study on the Bioactive Components of the Above-Ground Parts of Bupleurum Chinensis. Master’s Thesis, Shenyang Pharmaceutical University, Shenyang, China, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, Z.; Liu, X. Research Progress on Chemical Composition and Quality Control Methods of Bupleurum chinense. Mod. Chin. Med. 2021, 23, 940–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.Y.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Liu, Z.M.; Chen, T.; Lv, C.Y.; Tang, S.H.; Zhang, X.B.; Zhang, W.; Li, Z.Y.; Zhou, R.R.; et al. ETCM: An encyclopaedia of traditional Chinese medicine. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D976–D982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Y.; Zhang, F.; Liu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Tian, J.; Qin, X.; Gao, X. Isolation and quantitative determination of polyacetylenes in Bupleuri Radix. Zhongcaoyao 2015, 46, 2365–2370. [Google Scholar]
- Sui, C.; Han, W.J.; Zhu, C.R.; Wei, J.H. Recent Progress in Saikosaponin Biosynthesis in Bupleurum. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2021, 22, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Li, Q. Simultaneous Extraction and Analysis of Seven Major Saikosaponins from Bupleuri Radix and the Exploration of Antioxidant Activity and Its Mechanism. Molecules 2023, 28, 5872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Xiao, Z.; Jin, H.; Kuang, H.; Yang, B. Chemical Constituents from the Aerial Parts of Bupleurum chinense. Zhongyaocai 2021, 44, 1620–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wan, P.; Wang, J.; Li, P.; Hu, Q.; Zhao, R. Polysaccharide from vinegar baked radix bupleuri as efficient solubilizer for water-insoluble drugs of Chinese medicine. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 229, 115473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Dong, X.; Yin, X.; Wang, W.; You, L.; Ni, J. Radix Bupleuri: A Review of Traditional Uses, Botany, Phytochemistry, Pharmacology, and Toxicology. Biomed. Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 7597596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wo, Y.; Yao, L.; Sun, S. Progress of Chemical Constituents of Bupleurum Chinese. Heilongjiang Med. J. 2011, 24, 215–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuzarte, M.; Correia, P.M.P.; Alves-Silva, J.M.; Gonçalves, M.J.; Cavaleiro, C.; Cruz, T.; Salgueiro, L. Antifungal and Anti-Inflammatory Potential of Bupleurum rigidum subsp. paniculatum (Brot.) H.Wolff Essential Oil. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Chen, X.; Yang, W.; Song, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Yang, X.; Yang, Z. Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry analysis of essential oils from five parts of Chaihu (Radix Bupleuri Chinensis). J. Tradit. Chin. Med./Chung I Tsa Chih Ying Wen Pan 2014, 34, 741–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Li, Y.; Wei, S.; Zhao, T.; Wang, Y.; Song, C.; Xue, L.; Wang, F.; Xiao, L.; Wu, J.; et al. Pharmacological Effects and Chemical Constituents of Bupleurum. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2019, 19, 34–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Weiderpass, E.; Soerjomataram, I. The ever-increasing importance of cancer as a leading cause of premature death worldwide. Cancer 2021, 127, 3029–3030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coussens, N.P.; Braisted, J.C.; Peryea, T.; Sittampalam, G.S.; Simeonov, A.; Hall, M.D. Small-Molecule Screens: A Gateway to Cancer Therapeutic Agents with Case Studies of Food and Drug Administration-Approved Drugs. Pharmacol. Rev. 2017, 69, 479–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Q.; Cao, H.; Qi, X.; Li, H.; Ye, P.; Wang, Z.; Wang, D.; Sun, M. Research Progress in Reversal of Tumor Multi-drug Resistance via Natural Products. Anti Cancer Agents Med. Chem. 2017, 17, 1466–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.C.; Liu, S.Y.; Liu, J.; Yang, P.Y.; Lin, H.S.; Zhang, Y. Lung Cancer Treatment in Traditional Chinese Medicine: History, Current Status, and Development. World J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2023, 9, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, R.; Chen, X.; Yuan, M.; Wu, J.; Sun, Q.; Miao, C.; Jing, Y. The potential effect and mechanism of Saikosaponin A against gastric cancer. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2023, 23, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.W. Targeting ER Stress with Saikosaponin A to Overcome Resistance under Radiation in Gastric Cancer Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.J.; Lee, Y.J.; Kang, S.G.; Cho, S.; Yoon, W.; Lim, J.H.; Min, S.H.; Lee, T.H.; Kim, B.M. Caspase-4 is essential for saikosaponin a-induced apoptosis acting upstream of caspase-2 and γ-H2AX in colon cancer cells. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 100433–100448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Song, D.; Cao, T.; Li, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, B.; Li, L. Saikosaponin-A induces apoptosis of cervical cancer through mitochondria- and endoplasmic reticulum stress-dependent pathway in vitro and in vivo: Involvement of PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Cell Cycle 2021, 20, 2221–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Ji, D.-C.; Wu, D.; Wang, L.; Yu, C.; Li, C.H.; Gai, X. Reversal Effect of Saikosaponin A and Saikosaponin B on Doxorubicin-resistant Breast Cancer Cells and its Mechanism. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2023, 19, 700–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, C.; Gao, Z.; Lv, X.; Zhu, Y.; Li, R.; Li, S. Saikosaponin-b2 Inhibits Primary Liver Cancer by Regulating the STK4/IRAK1/NF-κB Pathway. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Q.; Gao, F.F.; He, X.; Li, K.; Gao, Y.; Xu, X.L.; Jiang, N.H.; Ding, L.; Song, W.J.; He, Y.Q.; et al. Antitumor effects of saikosaponin b2 on breast cancer cell proliferation and migration. Mol. Med. Rep. 2019, 20, 1943–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, M.; McGowan, E.; Li, Y.; Zhu, X.; Lu, X.; Zhu, Z.; Lin, Y.; He, S. Saikosaponin-d Suppresses COX2 Through p-STAT3/C/EBPβ Signaling Pathway in Liver Cancer: A Novel Mechanism of Action. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Hu, C.; Yang, L.; Guo, Q.; Liang, Y.; Wang, W. Saikosaponin-D induces the pyroptosis of lung cancer by increasing ROS and activating the NF-κB/NLRP3/caspase-1/GSDMD pathway. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2023, 37, e23444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, S.; Chang, M.; Liu, H.; Ding, S.; Yan, Z.; Si, K.; Gong, T. The Structural Characteristics of an Acidic Water-Soluble Polysaccharide from Bupleurum chinense DC and Its In Vivo Anti-Tumor Activity on H22 Tumor-Bearing Mice. Polymers 2022, 14, 1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, H.; Jiang, G.; Qi, D.; Bi, J.; Tian, D.; Guan, X.; Zheng, S.; Sun, X. Bupleurum chinense polysaccharide inhibit adhesion of human melanoma cells via blocking β1 integrin function. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 156, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, Z.; Chen, S.; Li, H.; Dong, L.; Fu, X. A new discovery: Total Bupleurum saponin extracts can inhibit the proliferation and induce apoptosis of colon cancer cells by regulating the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 283, 114742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Serag, H.B. Epidemiology of viral hepatitis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2012, 142, 1264–1273.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, H.A.; Shigle, T.L.; Hammoudi, N.; Link, J.T.; Samaniego, F.; Kaseb, A.; Mallet, V. The oncologic burden of hepatitis C virus infection: A clinical perspective. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2017, 67, 411–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadolny, C.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Q.; Hashmi, S.F.; Ali, W.; Hemme, C.; Ahsan, N.; Chen, Y.; Deng, R. Dysregulation and activities of ubiquitin specific peptidase 2b in the pathogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2021, 11, 4746–4767. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Qian, M.; Li, J.; Ruan, L.; Wang, Y.; Cai, C.; Gu, S.; Zhao, X. The role of tumor-associated macrophages in lung cancer: From mechanism to small molecule therapy. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 170, 116014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin, R.A.; Li, M.O. Ontogeny of Tumor-associated Macrophages and Its Implication in Cancer Regulation. Trends Cancer 2016, 2, 20–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guardiario, D.L.P.; Dy, C. 128P Survival outcome of gastric cancer patients in a tertiary care center: A 10-year single center retrospective study. Ann. Oncol. 2022, 33, S1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smyth, E.C.; Nilsson, M.; Grabsch, H.I.; van Grieken, N.C.; Lordick, F. Gastric cancer. Lancet 2020, 396, 635–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.H.; Zhang, X.T.; Tang, L.; Wu, Q.; Cai, M.Y.; Li, Y.F.; Qu, X.J.; Qiu, H.; Zhang, Y.J.; Ying, J.E.; et al. The Chinese Society of Clinical Oncology (CSCO): Clinical guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of gastric cancer, 2023. Cancer Commun. 2024, 44, 127–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.W. Paeoniflorin Induces ER Stress-Mediated Apoptotic Cell Death by Generating Nox4-Derived ROS under Radiation in Gastric Cancer. Nutrients 2023, 15, 5092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morii, Y.; Tsubaki, M.; Takeda, T.; Otubo, R.; Seki, S.; Yamatomo, Y.; Imano, M.; Satou, T.; Shimomura, K.; Nishida, S. Perifosine enhances the potential antitumor effect of 5-fluorourasil and oxaliplatin in colon cancer cells harboring the PIK3CA mutation. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 898, 173957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavoro, A.; Scalisi, A.; Candido, S.; Zanghì, G.N.; Rizzo, R.; Gattuso, G.; Caruso, G.; Libra, M.; Falzone, L. Identification of the most common BRCA alterations through analysis of germline mutation databases: Is droplet digital PCR an additional strategy for the assessment of such alterations in breast and ovarian cancer families? Int. J. Oncol. 2022, 60, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harbeck, N.; Gnant, M. Breast cancer. Lancet 2017, 389, 1134–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasim, F.; Sabath, B.F.; Eapen, G.A. Lung Cancer. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2019, 103, 463–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Yuan, W.Q.; Li, J.; Luo, Y.Q. Knockdown of METTL14 suppresses the malignant progression of non-small cell lung cancer by reducing Twist expression. Oncol. Lett. 2021, 22, 847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- del Carmen, M.G.; Rice, L.W.; Schmeler, K.M. Global health perspective on gynecologic oncology. Gynecol. Oncol. 2015, 137, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schadendorf, D.; Hauschild, A. Melanoma in 2013: Melanoma--the run of success continues. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 11, 75–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damsky, W.E.; Theodosakis, N.; Bosenberg, M. Melanoma metastasis: New concepts and evolving paradigms. Oncogene 2014, 33, 2413–2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwamoto, D.V.; Calderwood, D.A. Regulation of integrin-mediated adhesions. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2015, 36, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giraulo, C.; Turiello, R.; Orlando, L.; Leonardelli, S.; Landsberg, J.; Belvedere, R.; Rolshoven, G.; Müller, C.E.; Hölzel, M.; Morello, S. The CD73 is induced by TGF-β1 triggered by nutrient deprivation and highly expressed in dedifferentiated human melanoma. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 165, 115225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, R.S.; Ortiz, B.L.S.; Pereira, A.C.M.; Keita, H.; Carvalho, J.C.T. Rosmarinus officinalis essential oil: A review of its phytochemistry, anti-inflammatory activity, and mechanisms of action involved. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2019, 229, 29–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, B.; Sharopov, F.; Boyunegmez Tumer, T.; Ozleyen, A.; Rodríguez-Pérez, C.; Ezzat, S.M.; Azzini, E.; Hosseinabadi, T.; Butnariu, M.; Sarac, I.; et al. Symphytum Species: A Comprehensive Review on Chemical Composition, Food Applications and Phytopharmacology. Molecules 2019, 24, 2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraenkel, L.; Buta, E.; Suter, L.; Dubreuil, M.; Levy, C.; Najem, C.; Brennan, M.; Corn, B.; Kerns, R.; Goulet, J. Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs vs Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Arthritis Pain: A Randomized Withdrawal Trial. JAMA Intern. Med. 2020, 180, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piaoa, C.H.; Zou, S.C.; Bui, T.T.; Song, C.H.; Chai, O.H. Saikosaponin D inhibits nasal inflammation by regulating the transcription factors T-box protein expressed in T cells/GATA-3 and retinoic acid-related orphan nuclear receptor γt in a murine model of allergic rhinitis. Heliyon 2023, 9, e17319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Wu, M.; Xiong, W.; Li, J.; An, Y.; Ren, J.; Xie, Y.; Xue, H.; Yan, D.; Li, M.; et al. Saikosaponin-d ameliorates dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis by suppressing NF-κB activation and modulating the gut microbiota in mice. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 81, 106288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Song, Y.; Li, D.; Feng, W.; Liu, J. Saikosaponin A inhibits IL-1β-induced inflammatory mediators in human osteoarthritis chondrocytes by activating LXRα. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 88941–88950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Jin, L.; Yang, B. Saikosaponin A alleviates Staphylococcus aureus-induced mastitis in mice by inhibiting ferroptosis via SIRT1/Nrf2 pathway. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2023, 27, 3443–3450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huimei, H.; Kangdi, Z.; Xiaoying, X.; Boyi, L.; Qiuxiong, Y.; Haizhou, Z.; Yupeng, J.; Zhao, Z.; Shengsuo, M.; Tao, C.; et al. Saikosaponin B1/D alleviate dextran sulfate sodium- induced colitis via regulating the NRF2/HO-1 pathway to inhibit the ferroptosis in zebrafish. Res. Sq. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, T.T.; Piao, C.H.; Hyeon, E.; Fan, Y.; Choi, D.W.; Jung, S.Y.; Jang, B.H.; Shin, H.S.; Song, C.H.; Chai, O.H. Preventive Effect of Bupleurum chinense on Nasal Inflammation via Suppressing T Helper Type 2, Eosinophil and Mast Cell Activation. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2019, 47, 405–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, W.; Zhang, J.; Li, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, S.; Liu, G. A novel therapeutic approach for allergic rhinitis by exosome-mimetic nanovesicles derived from mesenchymal stem cells to restore nasal mucosal epithelial barrier. Med. Hypotheses 2023, 173, 111046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.I.; Kim, J.H.; Nam, K.E.; Lee, W.; Rhee, D.K. Pneumococcal Δpep27 Immunization Attenuates TLRs and NLRP3 Expression and Relieves Murine Ovalbumin-Induced Allergic Rhinitis. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 32, 709–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Fu, Q.; Wang, S.; Jin, X.; Tan, J.; Ding, K.; Zhang, Q.; Li, X. Association between air pollution and the prevalence of allergic rhinitis in Chinese children: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2022, 43, e47–e57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Ji, Q.; Liao, C.; Tian, L. A systematic review and meta-analysis of loratadine combined with montelukast for the treatment of allergic rhinitis. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1287320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upasana, K.; Sunil, S.; Meenakshi, B. Levo Cetirizine—the Drug with Numerous Plus to Cure Allergic Syndrome Compared to other Treatment Systems. Europe 2022, 16, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Berre, C.; Honap, S.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L. Ulcerative colitis. Lancet 2023, 402, 571–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eom, T.; Kim, Y.S.; Choi, C.H.; Sadowsky, M.J.; Unno, T. Current understanding of microbiota- and dietary-therapies for treating inflammatory bowel disease. J. Microbiol. 2018, 56, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levine, J.; McKibbin, J.; Ham, R.; Cohen-Mekelburg, S.; Bishu, S.; Tang, K.; Higgins, P.D.R.; Berinstein, J.A. Use of Upadacitinib in 16 Tofacitinib-refractory Ulcerative Colitis Patients: A Single-center Case 2Series. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2024, 30, 2232–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Oliveira, N.M.T.; Schneider, V.S.; Bueno, L.R.; de Mello Braga, L.L.V.; da Silva, K.S.; Malaquias da Silva, L.C.; Souza, M.L.; da Luz, B.B.; Lima, C.D.; Bastos, R.S.; et al. CPW partially attenuates DSS-induced ulcerative colitis in mice. Food Res. Int. 2023, 173, 113334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Tang, Y.; Ye, Y.; Zuo, M.; Lu, Q. Potential of natural flavonols and flavanones in the treatment of ulcerative colitis. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1120616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockwell, B.R.; Jiang, X. The Chemistry and Biology of Ferroptosis. Cell Chem. Biol. 2020, 27, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Lyu, C.; Teng, L.; Wu, A.; Zhu, Z.; He, Y.; Lu, J. Glycopolypeptide hydrogels with adjustable enzyme-triggered degradation: A novel proteoglycans analogue to repair articular-cartilage defects. Mater. Today Bio 2023, 20, 100659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tee, C.A.; Han, J.; Hui, J.H.P.; Lee, E.H.; Yang, Z. Perspective in Achieving Stratified Articular Cartilage Repair Using Zonal Chondrocytes. Tissue Eng. Part B Rev. 2023, 29, 310–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, A.; Imran, M. Causes, types, etiological agents, prevalence, diagnosis, treatment, prevention, effects on human health and future aspects of bovine mastitis. Anim. Health Res. Rev. 2020, 21, 36–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dean, J.; Keshavan, M. The neurobiology of depression: An integrated view. Asian J. Psychiatr. 2017, 27, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, T.; Yu, C.; Mao, Q.; Han, F.; Yang, Z.; Yang, Z.; Pires, N.; Wei, X.; Jing, W.; Lin, Q.; et al. Advances in biosensors for major depressive disorder diagnostic biomarkers. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2024, 258, 116291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bschor, T.; Kilarski, L.L. Are antidepressants effective? A debate on their efficacy for the treatment of major depression in adults. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2016, 16, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagiolini, A.; Florea, I.; Loft, H.; Christensen, M.C. Effectiveness of Vortioxetine on Emotional Blunting in Patients with Major Depressive Disorder with inadequate response to SSRI/SNRI treatment. J. Affect. Disord. 2021, 283, 472–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fajemiroye, J.O.; da Silva, D.M.; de Oliveira, D.R.; Costa, E.A. Treatment of anxiety and depression: Medicinal plants in retrospect. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 2016, 30, 198–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, B.; Liu, Y.; Hu, J.; Tang, Z.; Qiu, Z.; Song, Z.; Jia, A.; Zhang, Y. Bupleurum chinense DC improves CUMS-induced depressive symptoms in rats through upregulation of the cAMP/PKA/CREB signalling pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 289, 115034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Li, X.; Pan, R.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Song, M. Total Saikosaponins of Bupleurum yinchowense reduces depressive, anxiety-like behavior and increases synaptic proteins expression in chronic corticosterine-treated mice. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 18, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, T.; Wang, T.; Wu, L.; Tong, Y.; Tian, J.; Zhao, K.; Wang, H. Saikosaponin-d alleviates depression by promoting NLRP3 ubiquitination and inhibiting inflammasome activation. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 127, 111324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.Y.; Zhao, Y.H.; Zeng, M.J.; Fang, F.; Li, M.; Qin, T.T.; Ye, L.Y.; Li, H.W.; Qu, R.; Ma, S.P. Saikosaponin D relieves unpredictable chronic mild stress induced depressive-like behavior in rats: Involvement of HPA axis and hippocampal neurogenesis. Psychopharmacology 2017, 234, 3385–3394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Y.; Zhao, G.; Shuang, R.; Wang, H.; Zeng, N. Saikosaponin a activates tet1/dll3/notch1 signalling and promotes hippocampal neurogenesis to improve depression-like behavior in mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 319, 117289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halaris, A. Inflammation and depression but where does the inflammation come from? Curr. Opin. Psychiatry 2019, 32, 422–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gałecka, M.; Bliźniewska-Kowalska, K.; Orzechowska, A.; Szemraj, J.; Maes, M.; Berk, M.; Su, K.P.; Gałecki, P. Inflammatory versus Anti-inflammatory Profiles in Major Depressive Disorders-The Role of IL-17, IL-21, IL-23, IL-35 and Foxp3. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, A.E.; Wouk, K.; Grewen, K.; Gottfredson, N.C.; Meltzer-Brody, S.; Propper, C.; Mills-Koonce, R.; Pearson, B.; Whitley, J.; Stuebe, A.M.; et al. 70: Prenatal depression and anxiety is associated with Hypothalamic Pituitary Adrenal (HPA) axis dysregulation—ScienceDirect. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2020, 222, S59–S60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanes, S.J.; Dennie, L.; Perera, P. Targeting the Arginine Vasopressin V(1b) Receptor System and Stress Response in Depression and Other Neuropsychiatric Disorders. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2023, 19, 811–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santiago, E.; Moreno, D.F.; Acar, M. Modeling aging and its impact on cellular function and organismal behavior. Exp. Gerontol. 2021, 155, 111577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, C.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Y.; Qian, P.; Huang, H. Inflammation and aging: Signaling pathways and intervention therapies. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, L.P.; Teixeira, V.R.; Alencar-Silva, T.; Simonassi-Paiva, B.; Pereira, R.W.; Pogue, R.; Carvalho, J.L. Hallmarks of aging and immunosenescence: Connecting the dots. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2021, 59, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, N.; Kim, D.; Swamy, K.M.K.; Yoon, J. Metal-coordinated fluorescent and luminescent probes for reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reactive nitrogen species (RNS). Coord. Chem. Rev. 2021, 427, 213581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, H.; Zheng, X.; Song, J.; Liu, J.; Ren, T.; Zhang, X.; Huang, L.; Wu, M. Radical scavenging activity of sulfated Bupleurum chinense polysaccharides and their effects against oxidative stress-induced senescence. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 192, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Sun, S.; Ge, J.; Shen, Y.; Li, T.; Sun, X. Bupleurum chinense Polysaccharide Improves LPS-Induced Senescence of RAW264.7 Cells by Regulating the NF-κB Signaling Pathway. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. Ecam 2020, 2020, 7060812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, A.J.B. 15-Pgdh Inhibition Alternatively Activates Macrophages to Promote Hematopoietic Function during Aging. Blood 2023, 142, 5610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundap, U.P.; Paudel, Y.N.; Shaikh, M.F. Animal Models of Metabolic Epilepsy and Epilepsy Associated Metabolic Dysfunction: A Systematic Review. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, S.; Guan, W.; Pan, J.; Kuang, H.; Yang, B. Identification and potential mechanism of different components from the aerial part of Bupleurum chinense DC. for epileptic treatment. Nat. Prod. Res. 2022, 36, 6137–6142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, S.; Jiang, Y.; Algradi, A.M.; Zhou, Y.; Pan, J.; Guan, W.; Kuang, H.; Yang, B. The Aerial Parts of Bupleurum Chinense DC. Aromatic Oil Attenuate Kainic Acid-Induced Epilepsy-Like Behavior and Its Potential Mechanisms. Biomed. Res. Int. 2022, 2022, 1234612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; Wei, Z.H.; Liu, C.; Li, G.Y.; Qiao, X.Z.; Gan, Y.J.; Zhang, C.C.; Deng, Y.C. Genetic variations in GABA metabolism and epilepsy. Seizure 2022, 101, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choo, B.K.M.; Shaikh, M.F. The Role of Neurotransmitters in Epileptogenesis: Focus on GABA and Glutamate. In Handbook of Neurodegenerative Disorders; Springer: Singapore, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Czapski, G.A.; Strosznajder, J.B. Glutamate and GABA in Microglia-Neuron Cross-Talk in Alzheimer’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Li, X.; Guo, X.; Liu, Z.; Li, W.; Wei, J.; Qi, Y. Bupleurum chinense exerts a mild antipyretic effect on LPS-induced pyrexia rats involving inhibition of peripheral TNF-α production. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2023, 310, 116375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neufeldt, C.J.; Cortese, M.; Acosta, E.G.; Bartenschlager, R. Rewiring cellular networks by members of the Flaviviridae family. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 125–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torrents de la Peña, A.; Sliepen, K.; Eshun-Wilson, L.; Newby, M.L.; Allen, J.D.; Zon, I.; Koekkoek, S.; Chumbe, A.; Crispin, M.; Schinkel, J.; et al. Structure of the hepatitis C virus E1E2 glycoprotein complex. Science 2022, 378, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Applegate, T.L.; Fajardo, E.; Sacks, J.A. Hepatitis C Virus Diagnosis and the Holy Grail. Infect. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2018, 32, 425–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heffernan, A.; Cooke, G.S.; Nayagam, S.; Thursz, M.; Hallett, T.B. Scaling up prevention and treatment towards the elimination of hepatitis C: A global mathematical model. Lancet 2019, 393, 1319–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.P.; Lan, K.L.; Liao, S.X.; Huang, Y.H.; Hou, M.C.; Lan, K.H. Antiviral effect of saikosaponin B2 in combination with daclatasvir on NS5A resistance-associated substitutions of hepatitis C virus. J. Chin. Med. Assoc. 2019, 82, 368–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jinwen, X.; Minglu, L.; Jintao, W.; Xingyu, Z.; Wei, C.; Guoping, P.; Hua, H.; Huayan, L.; Junping, L.; Sheng, L.; et al. 2023 China Alzheimer’s disease: Facts and figures. Hum. Brain 2023, 2, 1598–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.; Kim, H.; Jedrychowski, M.P.; Bakiasi, G.; Park, J.; Kruskop, J.; Choi, Y.; Kwak, S.S.; Quinti, L.; Kim, D.Y.; et al. Irisin reduces amyloid-β by inducing the release of neprilysin from astrocytes following downregulation of ERK-STAT3 signaling. Neuron 2023, 111, 3619–3633.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.H.; Li, J.; Zhao, X.X.; Yang, X.H.; Li, J.; Zou, B.; Zang, W.B.; Ma, R.X.; Wang, Y.F.; Yao, Y. Saikogenin F From Bupleurum smithii Ameliorates Learning and Memory Impairment via Antiinflammation Effect in an Alzheimer’s Disease Mouse Model. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2022, 17, 1934578X221111029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.-H.; Fang, Y.; Yu, Q.; Wang, T. Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking Analysis of the Mechanisms of Combined Radix Bupleuri (Chai-Hu) and Radix Paeoniae Alba (Bai-Shao) Treatment in the Prevention and Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease. World J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2024, 10, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Zhou, T.; Yuan, J.J.; Xiong, X.Y.; Liu, X.H.; Qiu, Z.M.; Hu, L.L.; Lu, H.; He, Q.; Liu, C.; et al. Metabolomics profiling to characterize cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in mice. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1091616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Yang, G. Saikosaponin A attenuates neural injury caused by ischemia/reperfusion. Transl. Neurosci. 2020, 11, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humaidy, R.S.; Subkhan, M.; Yuliyanasari, N.; Ambar, N.S. Analysis of eosinophil and lymphocyte concentrations on the incidence of mild and severe acute asthma exacerbations. Gac. Méd. Caracas 2021, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inniss, L.J. Independent prescribing for a child with a first diagnosis of asthma: A case study. Emerg. Nurse 2023, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iordache, A.; Balica, N.C.; Horhat, I.D.; Morar, R.; Tischer, A.A.; Milcu, A.I.; Salavat, M.C.; Borugă, V.M. A Review Regarding the Connections between Allergic Rhinitis and Asthma—Epidemiology, Diagnosis and Treatment. Curr. Health Sci. J. 2023, 49, 5–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Ruan, G.; Su, Q.; Li, L.; Zheng, N.; Hong, Y. Therapeutic effect of saikosaponin-d on airway allergy in asthma. Mater. Express 2024, 14, 370–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, T.T.; Piao, C.H.; Song, C.H.; Shin, H.S.; Chai, O.H. Bupleurum chinense extract ameliorates an OVA-induced murine allergic asthma through the reduction of the Th2 and Th17 cytokines production by inactivation of NFκB pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 91, 1085–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergmark, B.A.; Mathenge, N.; Merlini, P.A.; Lawrence-Wright, M.B.; Giugliano, R.P. Acute coronary syndromes. Lancet 2022, 399, 1347–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Șoșdean, R.; Dănilă, M.D.; Ionică, L.N.; Pescariu, A.S.; Mircea, M.; Ionac, A.; Mornoș, C.; Luca, C.T.; Feier, H.B.; Muntean, D.M.; et al. Monoamine Oxidase Contributes to Valvular Oxidative Stress: A Prospective Observational Pilot Study in Patients with Severe Mitral Regurgitation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 10307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.; Liu, X.; Ouyang, W.; Zhu, H.; Ding, X.-J.; Tang, J.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, Y.M. Effect of polysaccharide from the root of Bupleurum Chinese DC and Bupleurum scorzonerifolium Willd on hydrogen peroxide-induced myocardial apoptosis. Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 2020, 19, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y.J.; Zhao, R.Z.; Xiang, F.J. Vinegar amount in the process affected the components of vinegar-baked Radix Bupleuri and its hepatoprotective effect. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 16, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, L.; Cheng, Y.M.; Zhu, S.L.J. Xiao Chai Hu Tang for Liver Diseases: A Literature Review. World J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2017, 3, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gevrenova, R.; Kondeva-Burdina, M.; Denkov, N.; Zheleva-Dimitrova, D. Flavonoid profiles of three Bupleurum species and in vitro hepatoprotective of activity Bupleurum flavum Forsk. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2015, 11, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Lin, L.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, N.; Zhou, M.; Li, Y. Saikosaponin d Alleviates Liver Fibrosis by Negatively Regulating the ROS/NLRP3 Inflammasome Through Activating the ERβ Pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 894981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeyanthi, K.A. Determining the Effect of Cassia fistula (L) Flower Extract on Antioxidant Defense in Streptozotocin Induced Diabetic Rats. Chall. Adv. Pharm. Res. 2022, 8, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshpande, J.; Jadhao, P.R. Ultrasound Guided Femorosciatic Block for Diabetic Foot Ulcer in a Psychiatric Patient with Sepsis, Anaemia and Coagulation Defect. Arch. Anesth. Crit. Care 2022, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, D.; Song, Y.; Zhang, B.; Cao, G.; Zhou, H.; Li, H.; Sun, H.; Deng, M.; Qiu, Y.; Yi, W.; et al. Progress and application of adipose-derived stem cells in the treatment of diabetes and its complications. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2024, 15, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakhar, K.; Vaishnavi, S.; Kaur, P.; Singh, P.; Munshi, A. Pharmacogenomics of GLP-1 receptor agonists: Focus on pharmacological profile. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2022, 936, 175356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, P.; Behera, B.S.; Singh, S.; Munshi, A. “The pharmacological profile of SGLT2 inhibitors: Focus on mechanistic aspects and pharmacogenomics”. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 904, 174169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Weng, H.; Li, H.; Liu, Z.; Xu, Y.; Zhou, C.; Lu, X.; Su, X.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, D. Therapeutic Effects of Bupleurum Polysaccharides in Streptozotocin Induced Diabetic Mice. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0133212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Pan, J.; Shen, N.; Zhang, H.; Zou, L.; Miao, H.; Xing, L. Development of Saikosaponin D Liposome Nanocarrier with Increased Hepatoprotective Effect Against Alcoholic Hepatitis Mice. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2021, 17, 627–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tian, Y.; Guo, J.; Jiang, X.; Lu, H.; Xie, J.; Zhang, F.; Du, Z.; Hao, E. Exploring the Therapeutic Potential of Bupleurum in Medical Treatment: A Comprehensive Overview. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 1331. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18091331
Tian Y, Guo J, Jiang X, Lu H, Xie J, Zhang F, Du Z, Hao E. Exploring the Therapeutic Potential of Bupleurum in Medical Treatment: A Comprehensive Overview. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(9):1331. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18091331
Chicago/Turabian StyleTian, Yu, Jiageng Guo, Xinya Jiang, Hongyu Lu, Jinling Xie, Fan Zhang, Zhengcai Du, and Erwei Hao. 2025. "Exploring the Therapeutic Potential of Bupleurum in Medical Treatment: A Comprehensive Overview" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 9: 1331. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18091331
APA StyleTian, Y., Guo, J., Jiang, X., Lu, H., Xie, J., Zhang, F., Du, Z., & Hao, E. (2025). Exploring the Therapeutic Potential of Bupleurum in Medical Treatment: A Comprehensive Overview. Pharmaceuticals, 18(9), 1331. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18091331






