Present and Future Perspectives in the Treatment of Liver Fibrosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Liver Fibrosis
3.1. Genetic Mechanisms of Liver Fibrosis
3.2. Epigenetic Mechanisms of Liver Fibrosis
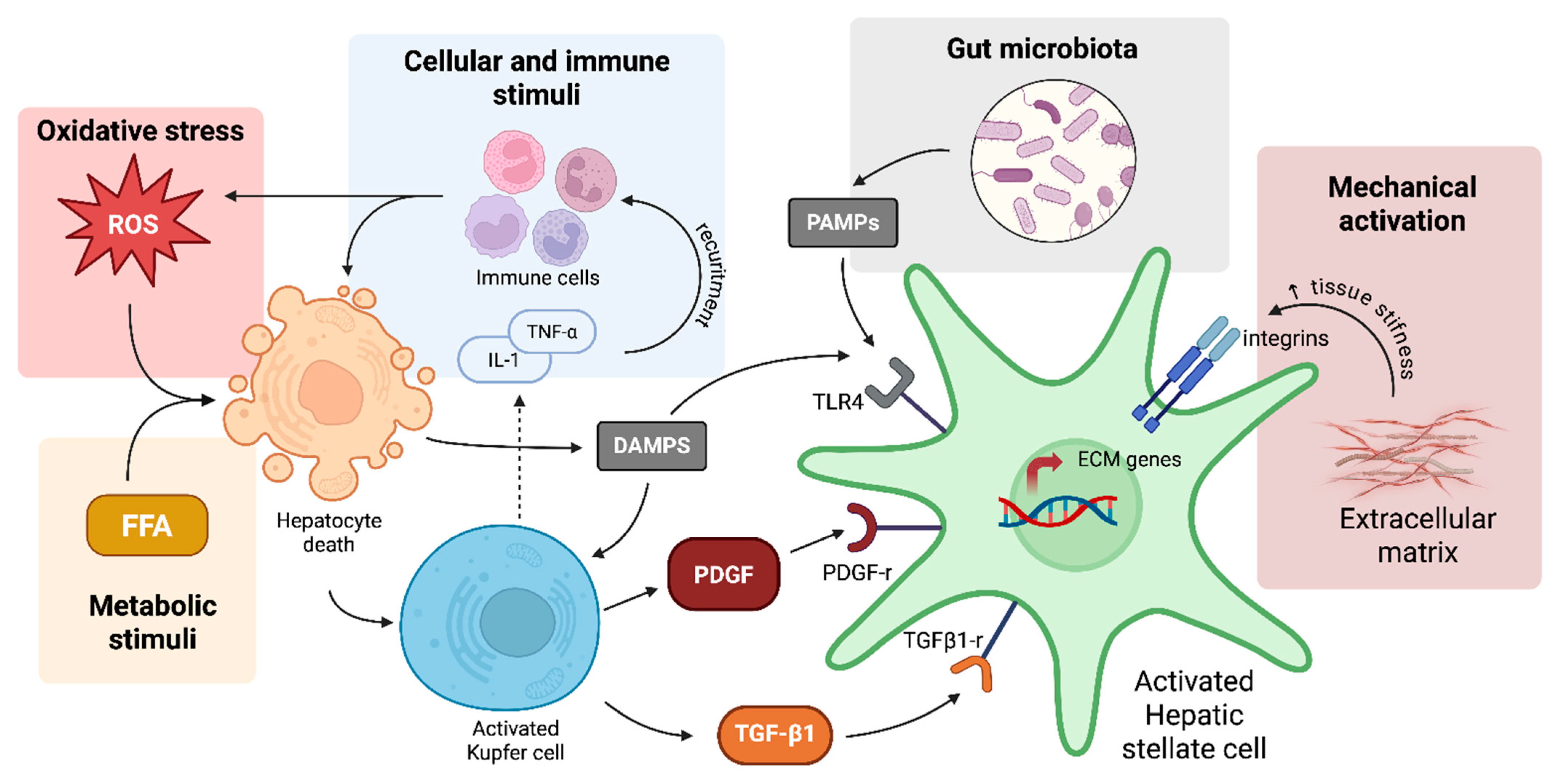
3.3. Hepatic Stellate Cells
3.3.1. Cellular and Immune Stimuli for HSC Activation
3.3.2. Oxidative Stress and HSC Activation
3.3.3. Metabolic Stimuli for HSC Activation
3.3.4. Mechanical and ECM-Driven Activation of HSCs in Liver Fibrosis
3.3.5. Gut Microbiota and HSC Activation
4. Fibrosis Quantification: Available Methodologies
5. Therapeutic Approaches for Liver Fibrosis
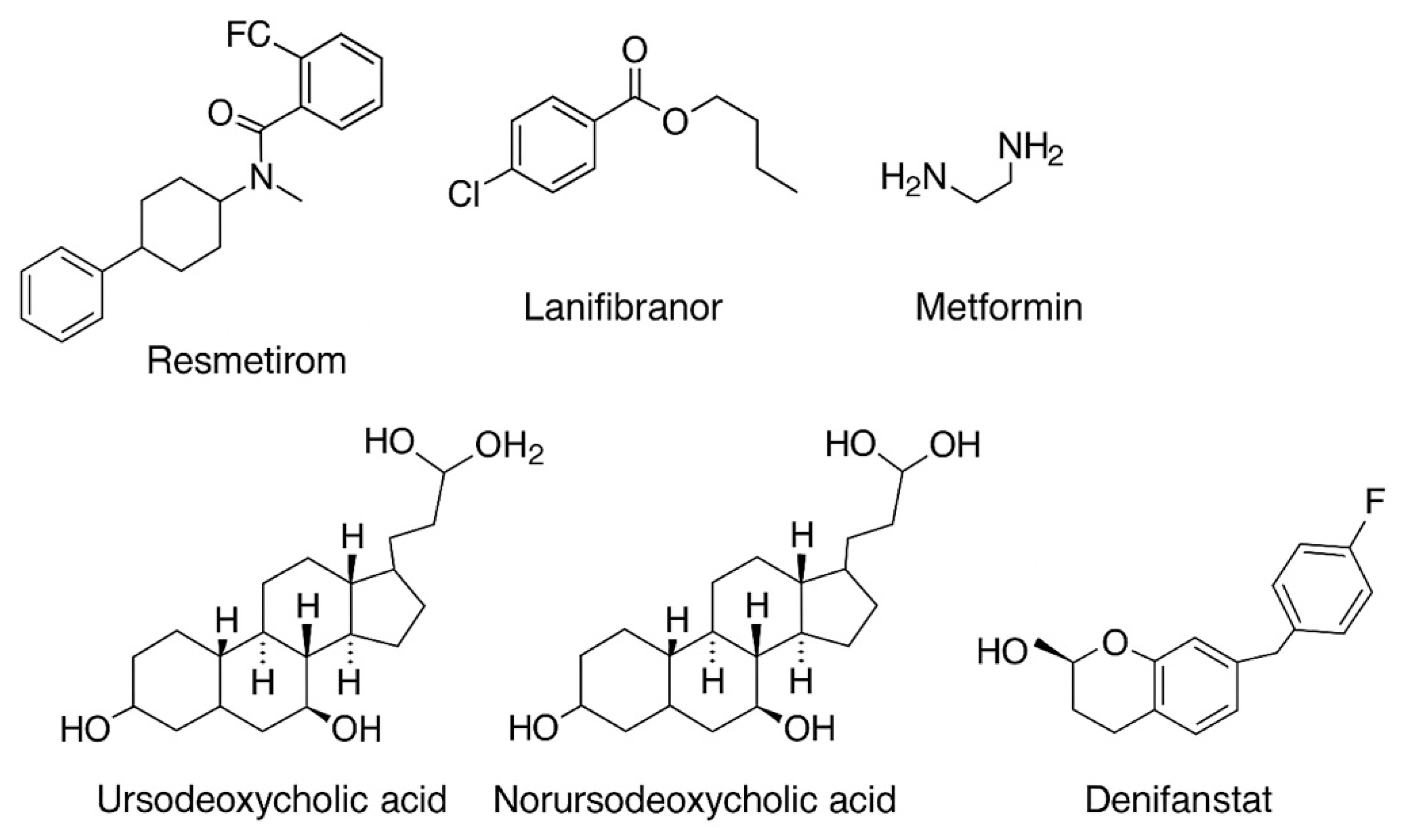
5.1. Liver-Directed Thyroid Hormone Receptor Agonists (THR)
5.2. Incretin Mimetics
5.3. Inhibitors of Sodium–Glucose Cotransporter 2 (SGLT2)
5.4. Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor Agonists
5.5. Metformin
5.6. Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 (FGF21) Analogues
5.7. Bile Acids
5.8. Agonists of the Farnesoid X Receptor
5.9. Inhibitors of the Fatty Acid Synthase
5.10. Inhibitors of the Renin–Angiotensin System
5.11. Other Medications
5.12. A Panoramic Overview on Anti-Fibrotic Medications
6. Microbiota-Targeted Therapies in Liver Fibrosis
7. Conclusions and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACLD | Advanced chronic liver disease |
| AIH | Autoimmune hepatitis |
| ARBs | Angiotensin-II type 1 receptor blockers |
| ASK1 | Apoptosis Signal-regulating Kinase 1 |
| Bambi | BMP and activin membrane-bound inhibitor |
| BDL | Bile duct ligation |
| CCl4 | Carbon tetrachloride |
| DAMPs | Damage-associated molecular patterns |
| DPP | Dipeptideyl peptidase 4 |
| ECM | Extracellular matrix |
| EZH2 | Enhancer of zeste homolog 2 |
| FFAs | Free fatty acids |
| FGF21 | Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 |
| FIB-4 | Fibrosis-4 |
| FMT | Faecal microbiome transplantation |
| FXR | Farnesoid X receptor |
| GLP-1 | Glucagon-like peptide 1 |
| GLP1RA | Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists |
| GLS1 | Glutaminase 1 |
| HBV | Hepatitis B virus |
| HCC | Hepatocellular carcinoma |
| HCV | Hepatitis C virus |
| HDACs | Histone deacetylases |
| HDV | Hepatitis D virus |
| HK2 | Hexokinase 2 |
| HMGB1 | High-mobility group box 1 |
| HSCs | Hepatic stellate cells |
| IFN-γ | Interferon-gamma |
| IL-1β | Interleukin-1 beta |
| IL-10 | Inteleukin-10 |
| ITT | Intention-to-treat population |
| KCs | Kupffer cells |
| KDM6B | Lysine demethylase 6B |
| kPa | Kilopascals |
| LDHA | Lactate dehydrogenase A |
| lncRNAs | Long non-coding RNAs |
| LPS | Lipopolysaccharide |
| MALAT1 | Metastasis Associated Lung Adenocarcinoma Transcript 1 |
| MASH | metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis |
| MASLD | Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease |
| MEG3 | Maternally Expressed 3 |
| miRNAs | MicroRNAs |
| mITT | Modified intention-to-treat population |
| ML NASH CRN | Machine Learning NASH Clinical Research Network |
| MRE | Magnetic resonance elastography |
| NASH | Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease |
| NF-κB | Nuclear factor kappa B |
| NFS | NAFLD fibrosis score |
| NK | Natural Killer |
| NKT | Natural Killer T |
| NOX | NADPH oxidase |
| OCA | Obeticholic acid |
| PAMPS | Pathogen Associated Molecular Patterns |
| PBC | Primary biliary cholangitis |
| PDGF | Platelet-derived growth factor |
| PKM2 | Pyruvate kinase M2 |
| PNPLA3 | Patatin-like phospholipase domain-containing 3 |
| PPAR | Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor |
| PRRs | Pattern recognition receptors |
| PSC | Primary sclerosing cholangitis |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| SAF | Steatosis Activity Fibrosis |
| SCD1 | Stearoyl-CoA desaturase |
| SCFAs | Short-chain fatty acids |
| SGLT-2 | Sodium–glucose cotransporter 2 |
| SIRT1 | Sirtuin 1 |
| SUCRA | Surface under the cumulative ranking curve |
| SWE | Shear wave elastography |
| TCA | Tricarboxylic acid |
| TE | Transient elastography |
| TGFβ1 | Transforming growth factor beta 1 |
| THR | Thyroid hormone receptor agonists |
| TLRs | Toll-like receptors |
| TM6SF2 | Transmembrane 6 superfamily member 2 |
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor alpha |
| VLDL | Very-low-density lipoproteins |
References
- Kisseleva, T.; Brenner, D. Molecular and cellular mechanisms of liver fibrosis and its regression. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 18, 151–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roehlen, N.; Crouchet, E.; Baumert, T.F. Liver Fibrosis: Mechanistic Concepts and Therapeutic Perspectives. Cells 2020, 9, 875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Taru, V.; Szabo, G.; Mehal, W.; Reiberger, T. Inflammasomes in chronic liver disease: Hepatic injury, fibrosis progression and systemic inflammation. J. Hepatol. 2024, 81, 895–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Tsuchida, T.; Friedman, S.L. Mechanisms of hepatic stellate cell activation. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 14, 397–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mederacke, I.; Hsu, C.C.; Troeger, J.S.; Huebener, P.; Mu, X.; Dapito, D.H.; Pradere, J.-P.; Schwabe, R.F. Fate tracing reveals hepatic stellate cells as dominant contributors to liver fibrosis independent of its aetiology. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyama, Y.; Brenner, D.A. Liver inflammation and fibrosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Blachier, M.; Leleu, H.; Peck-Radosavljevic, M.; Valla, D.C.; Roudot-Thoraval, F. The burden of liver disease in Europe: A review of available epidemiological data. J. Hepatol. 2013, 58, 593–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zatoński, W.A.; Sulkowska, U.; Mańczuk, M.; Rehm, J.; Boffetta, P.; Lowenfels, A.B.; La Vecchia, C. Liver cirrhosis mortality in europe, with special attention to central and eastern europe. Eur. Addict. Res. 2010, 16, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zakhari, S. Overview: How Is Alcohol Metabolized by the Body? Alcohol Res. Health 2006, 29, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Jeon, S.; Carr, R. Alcohol effects on hepatic lipid metabolism. J. Lipid Res. 2020, 61, 470–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ganem, D.; Prince, A.M. Hepatitis B Virus Infection—Natural History and Clinical Consequences. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 350, 1118–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guidotti, L.G.; Chisari, F.V. Immunobiology and pathogenesis of viral hepatitis. Annu. Rev. Pathol. Mech. Dis. 2006, 1, 23–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odenwald, M.A.; Paul, S. Viral hepatitis: Past, present, and future. World J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 28, 1405–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Rosen, H.R. Chronic hepatitis C infection. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 2429–2438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajarizadeh, B.; Grebely, J.; Dore, G.J. Epidemiology and natural history of HCV infection. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 10, 553–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadziyannis, S.J. Review: Hepatitis delta. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 1997, 12, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pouwels, S.; Sakran, N.; Graham, Y.; Leal, A.; Pintar, T.; Yang, W.; Kassir, R.; Singhal, R.; Mahawar, K.; Ramnarain, D. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): A review of pathophysiology, clinical management and effects of weight loss. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2022, 22, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ahmed, A.; Wong, R.J.; Harrison, S.A. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Review: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Outcomes. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 13, 2062–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machado, M.V.; Diehl, A.M. Pathogenesis of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 1769–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bandmann, O.; Weiss, K.H.; Kaler, S.G. Wilson’s disease and other neurological copper disorders. Lancet Neurol. 2015, 14, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Brissot, P.; Pietrangelo, A.; Adams, P.C.; de Graaff, B.; McLaren, C.E.; Loréal, O. Haemochromatosis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2018, 4, 18016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kane, S.F.; Roberts, C.; Paulus, R. Hereditary Hemochromatosis Rapid Evidence Review. Am. Fam. Physician 2021, 104, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Radford-Smith, D.E.; Powell, E.E.; Powell, L.W. Haemochromatosis: A clinical update for the practising physician. Intern. Med. J. 2018, 48, 509–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carbone, M.; Neuberger, J.M. Autoimmune liver disease, autoimmunity and liver transplantation. J. Hepatol. 2014, 60, 210–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pape, S.; Schramm, C.; Gevers, T.J. Clinical management of autoimmune hepatitis. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2019, 7, 1156–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lindor, K.D.; Gershwin, M.E.; Poupon, R.; Kaplan, M.; Bergasa, N.V.; Heathcote, E.J. American Association for Study of Liver Diseases. Primary biliary cirrhosis. Hepatology 2009, 50, 291–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karlsen, T.H.; Folseraas, T.; Thorburn, D.; Vesterhus, M. Primary sclerosing cholangitis—A comprehensive review. J. Hepatol. 2017, 67, 1298–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplan, D.E.; Teerlink, C.C.; Schwantes-An, T.-H.; Norden-Krichmar, T.M.; DuVall, S.L.; Morgan, T.R.; Tsao, P.S.; Voight, B.F.; Lynch, J.A.; Vujković, M.; et al. Clinical and genetic risk factors for progressive fibrosis in metabolic dysfunction–associated steatotic liver disease. Hepatol. Commun. 2024, 8, e0487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Unalp-Arida, A.; Ruhl, C.E. Patatin-Like Phospholipase Domain-Containing Protein 3 I148M and Liver Fat and Fibrosis Scores Predict Liver Disease Mortality in the U.S. Population. Hepatology 2019, 71, 820–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ericson, E.; Bergenholm, L.; Andréasson, A.; Dix, C.I.; Knöchel, J.; Hansson, S.F.; Lee, R.; Schumi, J.; Antonsson, M.; Fjellström, O.; et al. Hepatic patatin-like phospholipase domain-containing 3 levels are increased in I148M risk allele carriers and correlate with NAFLD in humans. Hepatol. Commun. 2022, 6, 2689–2701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Manchiero, C.; Nunes, A.K.d.S.; Magri, M.C.; Dantas, B.P.; Mazza, C.C.; Barone, A.A.; Tengan, F.M. The rs738409 polymorphism of the PNPLA3 gene is associated with hepatic steatosis and fibrosis in Brazilian patients with chronic hepatitis C. BMC Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, 780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Li, G.; Tang, L.-J.; Zhu, P.-W.; Huang, O.-Y.; Rios, R.S.; Zheng, K.I.; Chen, S.-D.; Ma, H.-L.; Targher, G.; Byrne, C.D.; et al. PNPLA3 rs738409 C>G Variant Influences the Association Between Visceral Fat and Significant Fibrosis in Biopsy-proven Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2021, 10, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Idilman, R.; Karatayli, S.C.; Kabacam, G.; Savas, B.; Elhan, A.H.; Bozdayi, A.M. The role of PNPLA3 (rs738409) c>g variant on histological progression of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatol. Forum 2020, 1, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Luo, F.; Oldoni, F.; Das, A. TM6SF2: A Novel Genetic Player in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver and Cardiovascular Disease. Hepatol. Commun. 2021, 6, 448–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kang, Q.; Xu, J.; Luo, H.; Tan, N.; Chen, H.; Cheng, R.; Pan, J.; Han, Y.; Yang, Y.; Liu, D.; et al. Evaluation of the association of a variant in PNPLA3 and TM6SF2 with fibrosis progression in patients with chronic hepatitis C infection after eradication: A retrospective study. Gene 2022, 820, 146235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Ginsberg, H.N.; Reyes-Soffer, G. Basic and translational evidence supporting the role of TM6SF2 in VLDL metabolism. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2024, 35, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Smagris, E.; Gilyard, S.; BasuRay, S.; Cohen, J.C.; Hobbs, H.H. Inactivation of Tm6sf2, a Gene Defective in Fatty Liver Disease, Impairs Lipidation but Not Secretion of Very Low Density Lipoproteins. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 10659–10676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Pant, A.; Chen, Y.; Kuppa, A.; Du, X.; Halligan, B.D.; Speliotes, E.K. Perturbation of TM6SF2 Expression Alters Lipid Metabolism in a Human Liver Cell Line. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- O’HAre, E.A.; Yang, R.; Yerges-Armstrong, L.M.; Sreenivasan, U.; McFarland, R.; Leitch, C.C.; Wilson, M.H.; Narina, S.; Gorden, A.; Ryan, K.A.; et al. TM6SF2 rs58542926 impacts lipid processing in liver and small intestine. Hepatology 2016, 65, 1526–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Njei, B.; Al-Ajlouni, Y.A.; Ugwendum, D.; Abdu, M.; Forjindam, A.; Mohamed, M.F. Genetic and epigenetic determinants of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) in lean individuals: A systematic review. Transl. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 9, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Raia, G.; Abdelsameea, E.; Taie, D.T.; Elshaarawy, O.; Bayomy, N.; Mostafa, R.; Alsharnoby, A.A.; Diab, K. The TM6SF2 variant as a risk factor for hepatocellular carcinoma development in chronic liver disease patients. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2022, 8, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Raksayot, M.; Chuaypen, N.; Khlaiphuengsin, A.; Pinjaroen, N.; Treeprasertsuk, S.; Poovorawan, Y.; Tanaka, Y.; Tangkijvanich, P. Independent and additive effects of PNPLA3 and TM6SF2 polymorphisms on the development of non-B, non-C hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 54, 427–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moran-Salvador, E.; Mann, J. Epigenetics and Liver Fibrosis. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 4, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Barchetta, I.; Zampieri, M.; Cimini, F.A.; Dule, S.; Sentinelli, F.; Passarella, G.; Oldani, A.; Karpach, K.; Bacalini, M.G.; Baroni, M.G.; et al. Association Between Active DNA Demethylation and Liver Fibrosis in Individuals with Metabolic-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhao, Q.; Fan, Y.-C.; Zhao, J.; Gao, S.; Zhao, Z.-H.; Wang, K. DNA methylation patterns of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma gene associated with liver fibrosis and inflammation in chronic hepatitis B. J. Viral Hepat. 2013, 20, 430–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardy, T.; Zeybel, M.; Day, C.P.; Dipper, C.; Masson, S.; McPherson, S.; Henderson, E.; Tiniakos, D.; White, S.; French, J.; et al. Plasma DNA methylation: A potential biomarker for stratification of liver fibrosis in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Gut 2016, 66, 1321–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yoshida, T.; Ogata, H.; Kamio, M.; Joo, A.; Shiraishi, H.; Tokunaga, Y.; Sata, M.; Nagai, H.; Yoshimura, A. SOCS1 is a suppressor of liver fibrosis and hepatitis-induced carcinogenesis. J. Exp. Med. 2004, 199, 1701–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhu, H.; Zhao, H.; Xu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, Y.; Li, J.; Huang, C.; Ma, T. Sennoside A alleviates inflammatory responses by inhibiting the hypermethylation of SOCS1 in CCl4-induced liver fibrosis. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 174, 105926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dewidar, B.; Meyer, C.; Dooley, S.; Meindl-Beinker, N. TGF-β in Hepatic Stellate Cell Activation and Liver Fibrogenesis—Updated 2019. Cells 2019, 8, 1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kim, K.K.; Sheppard, D.; Chapman, H.A. TGF-β1 Signaling and Tissue Fibrosis. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2017, 10, a022293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Akkız, H.; Gieseler, R.K.; Canbay, A. Liver Fibrosis: From Basic Science towards Clinical Progress, Focusing on the Central Role of Hepatic Stellate Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 7873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Liu, Y.; Wen, D.; Ho, C.; Yu, L.; Zheng, D.; O’rEilly, S.; Gao, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhang, Y. Epigenetics as a versatile regulator of fibrosis. J. Transl. Med. 2023, 21, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Grindheim, J.M.; Nicetto, D.; Donahue, G.; Zaret, K.S. Polycomb Repressive Complex 2 Proteins EZH1 and EZH2 Regulate Timing of Postnatal Hepatocyte Maturation and Fibrosis by Repressing Genes with Euchromatic Promoters in Mice. Gastroenterology 2019, 156, 1834–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Jiang, Y.; Xiang, C.; Zhong, F.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, J.; Ding, C.; Jin, L.; He, F.; et al. Histone H3K27 methyltransferase EZH2 and demethylase JMJD3 regulate hepatic stellate cells activation and liver fibrosis. Theranostics 2021, 11, 361–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Li, X.J.; Zhou, F.; Li, Y.J.; Xue, X.Y.; Qu, J.R.; Fan, G.F.; Liu, J.; Sun, R.; Wu, J.Z.; Zheng, Q.; et al. LncRNA H19-EZH2 interaction promotes liver fibrosis via reprogramming H3K27me3 profiles. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2023, 44, 2479–2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Claveria-Cabello, A.; Colyn, L.; Uriarte, I.; Latasa, M.U.; Arechederra, M.; Herranz, J.M.; Alvarez, L.; Urman, J.M.; Martinez-Chantar, M.L.; Banales, J.M.; et al. Dual Pharmacological Targeting of HDACs and PDE5 Inhibits Liver Disease Progression in a Mouse Model of Biliary Inflammation and Fibrosis. Cancers 2020, 12, 3748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Li, X.; Wu, X.-Q.; Xu, T.; Li, X.-F.; Yang, Y.; Li, W.-X.; Huang, C.; Meng, X.-M.; Li, J. Role of histone deacetylases(HDACs) in progression and reversal of liver fibrosis. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2016, 306, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Hong, W.; Hao, C.; Li, L.; Wu, D.; Shen, A.; Lu, J.; Zheng, Y.; Li, P.; Xu, Y. SIRT1 antagonizes liver fibrosis by blocking hepatic stellate cell activation in mice. FASEB J. 2017, 32, 500–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramadoss, S.; Chen, X.; Wang, C.-Y. Histone demethylase KDM6B promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 44508–44517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Gao, R.; Mao, J. Noncoding RNA-Mediated Epigenetic Regulation in Hepatic Stellate Cells of Liver Fibrosis. Non-Coding RNA 2024, 10, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ning, Z.-W.; Luo, X.-Y.; Wang, G.-Z.; Li, Y.; Pan, M.-X.; Yang, R.-Q.; Ling, X.-G.; Huang, S.; Ma, X.-X.; Jin, S.-Y.; et al. MicroRNA-21 Mediates Angiotensin II-Induced Liver Fibrosis by Activating NLRP3 Inflammasome/IL-1β Axis via Targeting Smad7 and Spry1. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2017, 27, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Li, H.; Liu, T.; Yang, Y.; Cho, W.C.; Flynn, R.J.; Harandi, M.F.; Song, H.; Luo, X.; Zheng, Y. Interplays of liver fibrosis-associated microRNAs: Molecular mechanisms and implications in diagnosis and therapy. Genes. Dis. 2023, 10, 1457–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Colaianni, F.; Zelli, V.; Compagnoni, C.; Miscione, M.S.; Rossi, M.; Vecchiotti, D.; Di Padova, M.; Alesse, E.; Zazzeroni, F.; Tessitore, A. Role of Circulating microRNAs in Liver Disease and HCC: Focus on miR-122. Genes 2024, 15, 1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Qin, R.; Huang, W.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Su, Y.; Chen, S.; Wang, H. lncRNA MEG3 modulates hepatic stellate cell activation by sponging miR-145 to regulate PPARγ. Mol. Med. Rep. 2021, 25, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wang, Y.; Mou, Q.; Zhu, Z.; Zhao, L.; Zhu, L. MALAT1 promotes liver fibrosis by sponging miR-181a and activating TLR4-NF-κB signaling. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2021, 48, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ganguly, N.; Chakrabarti, S. Role of long non-coding RNAs and related epigenetic mechanisms in liver fibrosis (Review). Int. J. Mol. Med. 2021, 47, 04856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Iredale, J.P.; Benyon, R.C.; Pickering, J.; McCullen, M.; Northrop, M.; Pawley, S.; Hovell, C.; Arthur, M.J. Mechanisms of spontaneous resolution of rat liver fibrosis. Hepatic stellate cell apoptosis and reduced hepatic expression of metalloproteinase inhibitors. J. Clin. Investig. 1998, 102, 538–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kisseleva, T.; A Brenner, D. Hepatic stellate cells and the reversal of fibrosis. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2006, 21 (Suppl. S3), S84–S87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwabe, R.F.; Luedde, T. Apoptosis and necroptosis in the liver: A matter of life and death. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 15, 738–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Woolbright, B.L.; Jaeschke, H. Role of the inflammasome in acetaminophen-induced liver injury and acute liver failure. J. Hepatol. 2017, 66, 836–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lee, U.E.; Friedman, S.L. Mechanisms of hepatic fibrogenesis. Best Pr. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2011, 25, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Braczkowski, M.J.; Kufel, K.M.; Kulińska, J.; Czyż, D.Ł.; Dittmann, A.; Wiertelak, M.; Młodzik, M.S.; Braczkowski, R.; Soszyński, D. Pleiotropic Action of TGF-Beta in Physiological and Pathological Liver Conditions. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wong, C.; Rougier-Chapman, E.M.; Frederick, J.P.; Datto, M.B.; Liberati, N.T.; Li, J.-M.; Wang, X.-F. Smad3-Smad4 and AP-1 Complexes Synergize in Transcriptional Activation of the c-Jun Promoter by Transforming Growth Factor β. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1999, 19, 1821–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ai, L.; Wang, Q.; Cheng, K. Key genes in the liver fibrosis process are mined based on single-cell transcriptomics. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2022, 598, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kikuchi, A.; Pradhan-Sundd, T.; Singh, S.; Nagarajan, S.; Loizos, N.; Monga, S.P. Platelet-Derived Growth Factor Receptor α Contributes to Human Hepatic Stellate Cell Proliferation and Migration. Am. J. Pathol. 2017, 187, 2273–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhao, M.; Wang, L.; Wang, M.; Zhou, S.; Lu, Y.; Cui, H.; Racanelli, A.C.; Zhang, L.; Ye, T.; Ding, B.; et al. Targeting fibrosis: Mechanisms and clinical trials. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sharip, A.; Kunz, J. Mechanosignaling via Integrins: Pivotal Players in Liver Fibrosis Progression and Therapy. Cells 2025, 14, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wright, J.H.; Johnson, M.M.; Shimizu-Albergine, M.; Bauer, R.L.; Hayes, B.J.; Surapisitchat, J.; Hudkins, K.L.; Riehle, K.J.; Johnson, S.C.; Yeh, M.M.; et al. Paracrine activation of hepatic stellate cells in platelet-derived growth factor C transgenic mice: Evidence for stromal induction of hepatocellular carcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 2013, 134, 778–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Papachristoforou, E.; Ramachandran, P. Macrophages as key regulators of liver health and disease. Int. Rev. Cell Mol. Biol. 2022, 368, 143–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palma, A.; Jarrah, A.S.; Tieri, P.; Cesareni, G.; Castiglione, F. Gene Regulatory Network Modeling of Macrophage Differentiation Corroborates the Continuum Hypothesis of Polarization States. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Jiang, Y.; Cai, R.; Huang, Y.; Zhu, L.; Xiao, L.; Wang, C.; Wang, L. Macrophages in organ fibrosis: From pathogenesis to therapeutic targets. Cell Death Discov. 2024, 10, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wei, Y.; Bingyu, W.; Lei, Y.; Xingxing, Y. The antifibrotic role of natural killer cells in liver fibrosis. Exp. Biol. Med. 2022, 247, 1235–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yang, M.; Vanderwert, E.; Kimchi, E.T.; Staveley-O’carroll, K.F.; Li, G. The Important Roles of Natural Killer Cells in Liver Fibrosis. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Seth, D.; Haber, P.S.; Syn, W.; Diehl, A.M.; Day, C.P. Pathogenesis of alcohol-induced liver disease: Classical concepts and recent advances. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011, 26, 1089–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Zhong, W.; Xu, W. Alcohol and the mechanisms of liver disease. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 38, 1233–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allameh, A.; Niayesh-Mehr, R.; Aliarab, A.; Sebastiani, G.; Pantopoulos, K. Oxidative Stress in Liver Pathophysiology and Disease. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Luedde, T.; Schwabe, R.F. NF-κB in the liver—Linking injury, fibrosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011, 8, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Banerjee, A.; Farci, P. Fibrosis and Hepatocarcinogenesis: Role of Gene-Environment Interactions in Liver Disease Progression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 8641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Paradies, G.; Paradies, V.; Ruggiero, F.M.; Petrosillo, G. Oxidative stress, cardiolipin and mitochondrial dysfunction in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 14205–14218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Mou, W.-L.; Chen, S.-R.; Wu, Z.-T.; Hu, L.-H.; Zhang, J.-Y.; Chang, H.-J.; Zhou, H.; Liu, Y. LPS-TLR4/MD-2–TNF-α signaling mediates alcohol-induced liver fibrosis in rats. J. Toxicol. Pathol. 2022, 35, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Liu, C.; Chen, X.; Yang, L.; Kisseleva, T.; Brenner, D.A.; Seki, E. Transcriptional repression of the transforming growth factor β (TGF-β) pseudo receptor BMP and activin membrane-bound inhibitor (BAMBI) by nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) p50 enhances TGF-β signaling in hepatic stellate cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 7082–7091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chen, X.; Li, J.; Xiang, A.; Guan, H.; Su, P.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, D.; Yu, Q. BMP and activin receptor membrane bound inhibitor: BAMBI has multiple roles in gene expression and diseases (Review). Exp. Ther. Med. 2023, 27, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zheng, H.; Sechi, L.A.; Navarese, E.P.; Casu, G.; Vidili, G. Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease and cardiovascular risk: A comprehensive review. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2024, 23, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- LeFort, K.R.; Rungratanawanich, W.; Song, B.-J. Contributing roles of mitochondrial dysfunction and hepatocyte apoptosis in liver diseases through oxidative stress, post-translational modifications, inflammation, and intestinal barrier dysfunction. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2024, 81, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hirsova, P.; Ibrabim, S.H.; Gores, G.J.; Malhi, H. Lipotoxic lethal and sublethal stress signaling in hepatocytes: Relevance to NASH pathogenesis. J. Lipid Res. 2016, 57, 1758–1770, Erratum in J. Lipid Res. 2017, 58, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Trivedi, P.; Wang, S.; Friedman, S.L. The Power of Plasticity—Metabolic Regulation of Hepatic Stellate Cells. Cell Metab. 2020, 33, 242–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Pan, M.; Li, H.; Shi, X. A New Target for Hepatic Fibrosis Prevention and Treatment: The Warburg Effect. Front. Biosci. 2024, 29, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paik, Y.H.; Kim, J.; Aoyama, T.; De Minicis, S.; Bataller, R.; Brenner, D.A. Role of NADPH oxidases in liver fibrosis. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2014, 20, 2854–2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bernard, K.; Logsdon, N.J.; Benavides, G.A.; Sanders, Y.; Zhang, J.; Darley-Usmar, V.M.; Thannickal, V.J. Glutaminolysis is required for transforming growth factor-β1–induced myofibroblast differentiation and activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 1218–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhao, Y.-Q.; Deng, X.-W.; Xu, G.-Q.; Lin, J.; Lu, H.-Z.; Chen, J. Mechanical homeostasis imbalance in hepatic stellate cells activation and hepatic fibrosis. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2023, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Esnault, C.; Stewart, A.; Gualdrini, F.; East, P.; Horswell, S.; Matthews, N.; Treisman, R. Rho-actin signaling to the MRTF coactivators dominates the immediate transcriptional response to serum in fibroblasts. Genes. Dev. 2014, 28, 943–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Russell, J.O.; Camargo, F.D. Hippo signalling in the liver: Role in development, regeneration and disease. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 19, 297–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Xu, L.; Wettschureck, N.; Bai, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Wang, S. Myofibroblast YAP/TAZ is dispensable for liver fibrosis in mice. J. Hepatol. 2021, 75, 238–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Xiu, W.; Xu, J.; Chen, X.; Wang, G.; Duan, J.; Sun, L.; Liu, B.; Xie, W.; Pu, G.; et al. Increased CHCHD2 expression promotes liver fibrosis in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis via Notch/osteopontin signaling. J. Clin. Investig. 2022, 7, e162402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Monga, S.P.S. Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling in Liver Physiology and Disease. Hepatology 2015, 61, 597–606. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yu, F.; Jin, L.; Yang, G.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J. Wnt/β-catenin signaling in liver fibrosis: Concepts and therapeutic perspec-tives. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 990. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, A.-T.; Kim, Y.-O.; Yan, X.-Z.; Abe, H.; Aslam, M.; Park, K.-S.; Zhao, X.-Y.; Jia, J.-D.; Klein, T.; You, H.; et al. Fibroblast Activation Protein Activates Macrophages and Promotes Parenchymal Liver Inflammation and Fibrosis. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 15, 841–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Nalkurthi, C.; Schroder, W.A.; Melino, M.; Irvine, K.M.; Nyuydzefe, M.; Chen, W.; Liu, J.; Teng, M.W.; Hill, G.R.; Bertolino, P.; et al. ROCK2 inhibition attenuates profibrogenic immune cell function to reverse thioacetamide-induced liver fibrosis. JHEP Rep. 2021, 4, 100386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Liu, X.; Liu, D.; Tan, C.; Feng, W. Gut microbiome-based machine learning for diagnostic prediction of liver fibrosis and cirrhosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2023, 23, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Gudan, A.; Jamioł-Milc, D.; Hawryłkowicz, V.; Skonieczna-Żydecka, K.; Stachowska, E. The Prevalence of Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth in Patients with Non-Alcoholic Liver Diseases: NAFLD, NASH, Fibrosis, Cirrhosis—A Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis and Meta-Regression. Nutrients 2022, 14, 5261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Inoue, T.; Nakayama, J.; Moriya, K.; Kawaratani, H.; Momoda, R.; Ito, K.; Iio, E.; Nojiri, S.; Fujiwara, K.; Yoneda, M.; et al. Gut Dysbiosis Associated with Hepatitis C Virus Infection. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2018, 67, 869–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, F.; Zhang, Q.; Shi, K.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, B.; Bi, Y.; Wang, X. Gut microbiota dysbiosis with hepatitis B virus liver disease and association with immune response. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1152987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Saeed, H.; Díaz, L.A.; Gil-Gómez, A.; Burton, J.; Bajaj, J.S.; Romero-Gomez, M.; Arrese, M.; Arab, J.P.; Khan, M.Q. Microbiome-centered therapies for the management of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2025, 31, S94–S111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajaj, J.S.; Kakiyama, G.; Zhao, D.; Takei, H.; Fagan, A.; Hylemon, P.; Zhou, H.; Pandak, W.M.; Nittono, H.; Fiehn, O.; et al. Continued Alcohol Misuse in Human Cirrhosis is Associated with an Impaired Gut–Liver Axis. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2017, 41, 1857–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Yang, L.; Chu, H. Targeting Gut Microbiota for the Treatment of Primary Biliary Cholangitis: From Bench to Bedside. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2023, 11, 958–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maslennikov, R.; Poluektova, E.; Zolnikova, O.; Sedova, A.; Kurbatova, A.; Shulpekova, Y.; Dzhakhaya, N.; Kardasheva, S.; Nadinskaia, M.; Bueverova, E.; et al. Gut Microbiota and Bacterial Translocation in the Pathogenesis of Liver Fibrosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 16502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Liang, Q.; Zhang, M.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhu, P.; Chen, Y.; Xue, P.; Li, Q.; Wang, K. Gut Microbiome Contributes to Liver Fibrosis Impact on T Cell Receptor Immune Repertoire. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 571847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Liu, J.; Yang, W.; Ling, W. Lipopolysaccharide mediates hepatic stellate cell activation by regulating autophagy and retinoic acid signaling. Autophagy 2017, 13, 1813–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Fuchs, C.D.; Simbrunner, B.; Baumgartner, M.; Campbell, C.; Reiberger, T.; Trauner, M. Bile acid metabolism and signalling in liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2024, 82, 134–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.-L.; Zhu, L.; Tao, Y.; Lu, W.; Cheng, H. Role of targeting TLR4 signaling axis in liver-related diseases. Pathol.—Res. Pr. 2023, 244, 154410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awoniyi, M.; Wang, J.; Ngo, B.; Meadows, V.; Tam, J.; Viswanathan, A.; Lai, Y.; Montgomery, S.; Farmer, M.; Kummen, M.; et al. Protective and aggressive bacterial subsets and metabolites modify hepatobiliary inflammation and fibrosis in a murine model of PSC. Gut 2022, 72, 671–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Shen, B.; Gu, T.; Shen, Z.; Zhou, C.; Guo, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, B.; Xu, X.; Li, F.; Zhang, Q.; et al. Escherichia coli Promotes Endothelial to Mesenchymal Transformation of Liver Sinusoidal Endothelial Cells and Exacerbates Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Via Its Flagellin. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 16, 857–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ding, C.; Wang, Z.; Dou, X.; Yang, Q.; Ning, Y.; Kao, S.; Sang, X.; Hao, M.; Wang, K.; Peng, M.; et al. Farnesoid X receptor: From Structure to Function and Its Pharmacology in Liver Fibrosis. Aging Dis. 2023, 15, 1508–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Tian, S.-Y.; Chen, S.-M.; Pan, C.-X.; Li, Y. FXR: Structures, biology, and drug development for NASH and fibrosis diseases. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2022, 43, 1120–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Jung, K.; Kim, M.; So, J.; Lee, S.H.; Ko, S.; Shin, D. Farnesoid X Receptor Activation Impairs Liver Progenitor Cell-Mediated Liver Regeneration via the PTEN-PI3K-AKT-mTOR Axis in Zebrafish. Hepatology 2021, 74, 397–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wang, X.X.; Xie, C.; Libby, A.E.; Ranjit, S.; Levi, J.; Myakala, K.; Bhasin, K.; Jones, B.A.; Orlicky, D.J.; Takahashi, S.; et al. The role of FXR and TGR5 in reversing and preventing progression of Western diet–induced hepatic steatosis, inflammation, and fibrosis in mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2022, 298, 102530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sun, L.; Shao, Y.; Zhuang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Liu, M.; Qu, C.; Yang, H. Targeting TGR5 to mitigate liver fibrosis: Inhibition of hepatic stellate cell activation through modulation of mitochondrial fission. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 140, 112831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rurangirwa, F.R.; A Teitzel, C.; Cui, J.; French, D.M.; McDonough, P.L.; Besser, T. Streptococcus didelphis sp. nov., a streptococcus with marked catalase activity isolated from opossums (Didelphis virginiana) with suppurative dermatitis and liver fibrosis. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2000, 50 Pt 2, 759–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aliwa, B.; Horvath, A.; Traub, J.; Feldbacher, N.; Habisch, H.; Fauler, G.; Madl, T.; Stadlbauer, V. Altered gut microbiome, bile acid composition and metabolome in sarcopenia in liver cirrhosis. J. Cachex-Sarcopenia Muscle 2023, 14, 2676–2691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Shin, J.-H.; Lee, Y.; Song, E.-J.; Lee, D.; Jang, S.-Y.; Byeon, H.R.; Hong, M.-G.; Lee, S.-N.; Kim, H.-J.; Seo, J.-G.; et al. Faecalibacterium prausnitzii prevents hepatic damage in a mouse model of NASH induced by a high-fructose high-fat diet. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1123547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Badi, S.A.; Malek, A.; Seyedi, S.A.; Bereimipour, A.; Irian, S.; Shojaie, S.; Sohouli, M.H.; Rohani, P.; Masotti, A.; Khatami, S.; et al. Direct and macrophage stimulation mediated effects of active, inactive, and cell-free supernatant forms of Akkermansia muciniphila and Faecalibacterium duncaniae on hepcidin gene expression in HepG2 cells. Arch. Microbiol. 2024, 206, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nor, M.H.M.; Ayob, N.; Mokhtar, N.M.; Ali, R.A.R.; Tan, G.C.; Wong, Z.; Shafiee, N.H.; Wong, Y.P.; Mustangin, M.; Nawawi, K.N.M. The Effect of Probiotics (MCP® BCMC® Strains) on Hepatic Steatosis, Small Intestinal Mucosal Immune Function, and Intestinal Barrier in Patients with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hizo, G.H.; Rampelotto, P.H. The Impact of Probiotic Bifidobacterium on Liver Diseases and the Microbiota. Life 2024, 14, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lee, D.-Y.; Shin, J.-W.; Shin, Y.-J.; Han, S.-W.; Kim, D.-H. Lactobacillus plantarum and Bifidobacterium longum Alleviate Liver Injury and Fibrosis in Mice by Regulating NF-κB and AMPK Signaling. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2023, 34, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Poynard, T.; Bedossa, P.; Opolon, P. Natural history of liver fibrosis progression in patients with chronic hepatitis C. The OBSVIRC, METAVIR, CLINIVIR, and DOSVIRC groups. Lancet 1997, 349, 825–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wendum, D.; Lacombe, K.; Chevallier, M.; Callard, P.; Valet, F.; Miailhes, P.; Bonnard, P.; Molina, J.-M.; Lascoux-Combe, C.; Fléjou, J.-F.; et al. Histological scoring of fibrosis and activity in HIV–chronic hepatitis B related liver disease: Performance of the METAVIR score assessed on virtual slides. J. Clin. Pathol. 2009, 62, 361–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Huang, C.; Xu, W.; Hu, Q.; Chen, L. Accuracy of FibroScan in analysis of liver fibrosis in patients with concomitant chronic Hepatitis B and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Medicine 2020, 99, e20616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Xu, X.; Jin, J.; Liu, Y. Performance of FibroScan in grading steatosis and fibrosis in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A meta-analysis. Arab. J. Gastroenterol. 2023, 24, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, D.R.; Levy, M.T. Liver transient elastography (Fibroscan®): A place in the management algorithms of chronic viral hepatitis. Antivir. Ther. 2010, 15, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosgrove, D.; Piscaglia, F.; Bamber, J.; Bojunga, J.; Correas, J.-M.; Gilja, O.H.; Klauser, A.S.; Sporea, I.; Calliada, F.; Cantisani, V.; et al. EFSUMB guidelines and recommendations on the clinical use of ultrasound elastography. Part 2: Clinical applications. Ultraschall der Med.—Eur. J. Ultrasound 2013, 34, 238–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deurdulian, C.; Grant, E.G.; Tchelepi, H.; Latterman, P.T.; Paluch, J.T.; Chopra, S.; Kazmierski, B.; Kahn, J.A.; Malhi, H.; Cen, S.Y. Assessment of Fibrosis in Liver Transplant Recipients: Diagnostic Performance of Shear Wave Elastography (SWE) and Correlation of SWE Findings with Biopsy Results. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2019, 213, W264–W271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaleska-Dorobisz, U.; Pawluś, A.; Kucharska, M.; Inglot, M. SWE elastography in assessment of liver fibrosis. Postepy Hig. I Med. Doswiadczalnej 2015, 69, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liguori, A.; Esposto, G.; Ainora, M.E.; Mignini, I.; Borriello, R.; Galasso, L.; Paratore, M.; Giustiniani, M.C.; Riccardi, L.; Garcovich, M.; et al. Liver Elastography for Liver Fibrosis Stratification: A Comparison of Three Techniques in a Biopsy-Controlled MASLD Cohort. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Xiao, H.; Shi, M.; Xie, Y.; Chi, X.; Bonino, F. Comparison of diagnostic accuracy of magnetic resonance elastography and Fibroscan for detecting liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis B patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0186660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Welle, C.L.; Olson, M.C.; Reeder, S.B.; Venkatesh, S.K. Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Liver Fibrosis, Fat, and Iron. Radiol. Clin. North Am. 2022, 60, 705–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Mallet, V.; Parlati, L.; Vallet-Pichard, A.; Terris, B.; Tsochatzis, E.; Sogni, P.; Pol, S. L’index FIB-4 pour faire le diagnostic de fibrose hépatique avancée au cours de la stéatose hépatique [FIB-4 index to rule-out advanced liver fibrosis in NAFLD patients]. Presse Med. 2019, 48, 1484–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravaioli, F.; Dajti, E.; Mantovani, A.; Newsome, P.N.; Targher, G.; Colecchia, A. Diagnostic accuracy of FibroScan-AST (FAST) score for the non-invasive identification of patients with fibrotic non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Gut 2023, 72, 1399–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, G.; Zhu, S.; Xiao, X.; Yan, L.; Yang, J.; Wu, G. Comparison of laboratory tests, ultrasound, or magnetic resonance elastography to detect fibrosis in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A meta-analysis. Hepatology 2017, 66, 1486–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, G.; Yang, J.; Yan, L. Comparison of diagnostic accuracy of aspartate aminotransferase to platelet ratio index and fibrosis-4 index for detecting liver fibrosis in adult patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection: A systemic review and meta-analysis. Hepatology 2014, 61, 292–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, T.; McQuaid, T.J.; Jacobson, I.M. HBV-Induced Carcinogenesis: Mechanisms, Correlation with Viral Suppression, and Implications for Treatment. Liver Int. 2025, 45, e16202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Flisiak, R.; Zarębska-Michaluk, D.; Dobrowolska, K.; Janocha-Litwin, J.; Dybowska, D.; Sitko, M.; Socha, Ł.; Lorenc, B.; Klapaczyński, J.; Brodowski, J. Treatment of HCV infection in patients with steatotic liver disease. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2024, 10, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Cabezas, J. Management of Alcohol-Related Liver Disease and Its Complications. Clin. Drug Investig. 2022, 42, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manikat, R.; Ahmed, A.; Kim, D. Current epidemiology of chronic liver disease. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2023, 12, goae069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Vilar-Gomez, E.; Martinez-Perez, Y.; Calzadilla-Bertot, L.; Torres-Gonzalez, A.; Gra-Oramas, B.; Gonzalez-Fabian, L.; Friedman, S.L.; Diago, M.; Romero-Gomez, M. Weight Loss Through Lifestyle Modification Significantly Reduces Features of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Gastroenterology 2015, 149, 367–378.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleiner, D.E.; Brunt, E.M.; Wilson, L.A.; Behling, C.; Guy, C.; Contos, M.; Cummings, O.; Yeh, M.; Gill, R.; Chalasani, N.; et al. Association of Histologic Disease Activity with Progression of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. JAMA Netw. Open 2019, 2, e1912565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tacke, F.; Horn, P.; Wong, V.W.-S.; Ratziu, V.; Bugianesi, E.; Francque, S.; Zelber-Sagi, S.; Valenti, L.; Roden, M.; Schick, F.; et al. EASL–EASD–EASO Clinical Practice Guidelines on the management of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD). J. Hepatol. 2024, 81, 492–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Kim, W.; Joo, S.K.; Bae, J.M.; Kim, J.H.; Ahmed, A. Subclinical Hypothyroidism and Low-Normal Thyroid Function Are Associated with Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis and Fibrosis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 16, 123–131.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso-Merino, E.; Orozco, R.M.; Ruíz-Llorente, L.; Martínez-Iglesias, O.A.; Velasco-Martín, J.P.; Montero-Pedrazuela, A.; Fanjul-Rodríguez, L.; Contreras-Jurado, C.; Regadera, J.; Aranda, A. Thyroid hormones inhibit TGF-β signaling and attenuate fibrotic responses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E3451–E3460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Harrison, S.A.; Bedossa, P.; Guy, C.D.; Schattenberg, J.M.; Loomba, R.; Taub, R.; Labriola, D.; Moussa, S.E.; Neff, G.W.; Rinella, M.E.; et al. A Phase 3, Randomized, Controlled Trial of Resmetirom in NASH with Liver Fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 390, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, S.A.; Ratziu, V.; Anstee, Q.M.; Noureddin, M.; Sanyal, A.J.; Schattenberg, J.M.; Bedossa, P.; Bashir, M.R.; Schneider, D.; Taub, R.; et al. Design of the phase 3 MAESTRO clinical program to evaluate resmetirom for the treatment of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2023, 59, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cusi, K. Selective agonists of thyroid hormone receptor beta for the treatment of NASH. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 390, 559–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drucker, D.J. GLP-1 physiology informs the pharmacotherapy of obesity. Mol. Metab. 2021, 57, 101351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newsome, P.N.; Ambery, P. Incretins (GLP-1 receptor agonists and dual/triple agonists) and the liver. J. Hepatol. 2023, 79, 1557–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newsome, P.N.; Buchholtz, K.; Cusi, K.; Linder, M.; Okanoue, T.; Ratziu, V.; Sanyal, A.J.; Sejling, A.-S.; Harrison, S.A. A Placebo-Controlled Trial of Subcutaneous Semaglutide in Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 1113–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phase 3 ESSENCE Trial: Semaglutide in Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatohepatitis. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, 20 (Suppl. S11), 6–7. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT04971785 (accessed on 20 December 2024).
- Loomba, R.; Abdelmalek, M.F.; Armstrong, M.J.; Jara, M.; Kjær, M.S.; Krarup, N.; Lawitz, E.; Ratziu, V.; Sanyal, A.J.; Schattenberg, J.M.; et al. Semaglutide 2·4 mg once weekly in patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis-related cirrhosis: A randomised, placebo-controlled phase 2 trial. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 8, 511–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loomba, R.; Noureddin, M.; Kowdley, K.V.; Kohli, A.; Sheikh, A.; Neff, G.; Bhandari, B.R.; Gunn, N.; Caldwell, S.H.; Goodman, Z.; et al. Combination Therapies Including Cilofexor and Firsocostat for Bridging Fibrosis and Cirrhosis Attributable to NASH. Hepatology 2020, 73, 625–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, S.A.; Wong, V.W.-S.; Okanoue, T.; Bzowej, N.; Vuppalanchi, R.; Younes, Z.; Kohli, A.; Sarin, S.; Caldwell, S.H.; Alkhouri, N.; et al. Selonsertib for patients with bridging fibrosis or compensated cirrhosis due to NASH: Results from randomized phase III STELLAR trials. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 26–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loomba, R.; Hartman, M.L.; Lawitz, E.J.; Vuppalanchi, R.; Boursier, J.; Bugianesi, E.; Yoneda, M.; Behling, C.; Cummings, O.W.; Tang, Y.; et al. Tirzepatide for Metabolic Dysfunction–Associated Steatohepatitis with Liver Fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 391, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nahra, R.; Wang, T.; Gadde, K.M.; Oscarsson, J.; Stumvoll, M.; Jermutus, L.; Hirshberg, B.; Ambery, P. Effects of cotadutide on metabolic and hepatic parameters in adults with overweight or obesity and type 2 diabetes: A 54-week randomized phase 2b study. Diabetes Care 2021, 44, 1433–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanyal, A.J.; Bedossa, P.; Fraessdorf, M.; Neff, G.W.; Lawitz, E.; Bugianesi, E.; Anstee, Q.M.; Hussain, S.A.; Newsome, P.N.; Ratziu, V.; et al. A Phase 2 Randomized Trial of Survodutide in MASH and Fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 391, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, E.; Heerspink, H.J.L.; Cuthbertson, D.J.; Wilding, J.P.H. SGLT2 inhibitors and GLP-1 receptor agonists: Established and emerging indications. Lancet 2021, 398, 262–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.; Cheng, L.; Xu, M.; Wang, W.; Wan, Z.; Xiong, H.; Guo, W.; Cai, M.; Xu, F. SGLT2 inhibitor empagliflozin downregulates miRNA-34a-5p and targets GREM2 to inactivate hepatic stellate cells and ameliorate non-alcoholic fatty liver disease-associated fibrosis. Metabolism 2023, 146, 155657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimizu, M.; Suzuki, K.; Kato, K.; Jojima, T.; Iijima, T.; Murohisa, T.; Iijima, M.; Takekawa, H.; Usui, I.; Hiraishi, H.; et al. Evaluation of the effects of dapagliflozin, a sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitor, on hepatic steatosis and fibrosis using transient elastography in patients with type 2 diabetes and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2018, 21, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pradhan, R.; Yin, H.; Lu, S.; Sebastiani, G.; Yu, O.; Suissa, S.; Azoulay, L. Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonists and Sodium–Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors and the Prevention of Cirrhosis Among Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2025, 48, 444–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liss, K.H.H.; Finck, B.N. PPARs and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Biochimie 2017, 136, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Francque, S.; Szabo, G.; Abdelmalek, M.F.; Byrne, C.D.; Cusi, K.; Dufour, J.-F.; Roden, M.; Sacks, F.; Tacke, F. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: The role of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 18, 24–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Vilarrupla, A.; Laviña, B.; García-Calderó, H.; Russo, L.; Rosado, E.; Roglans, N.; Bosch, J.; García-Pagán, J.C. PPARα activation improves endothelial dysfunction and reduces fibrosis and portal pressure in cirrhotic rats. J. Hepatol. 2012, 56, 1033–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyer-Diaz, Z.; Aristu-Zabalza, P.; Andrés-Rozas, M.; Robert, C.; Ortega-Ribera, M.; Fernández-Iglesias, A.; Broqua, P.; Junien, J.-L.; Wettstein, G.; Bosch, J.; et al. Pan-PPAR agonist lanifibranor improves portal hypertension and hepatic fibrosis in experimental advanced chronic liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2021, 74, 1188–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francque, S.M.; Bedossa, P.; Ratziu, V.; Anstee, Q.M.; Bugianesi, E.; Sanyal, A.J.; Loomba, R.; Harrison, S.A.; Balabanska, R.; Mateva, L.; et al. A Randomized, Controlled Trial of the Pan-PPAR Agonist Lanifibranor in NASH. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 1547–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasmin, T.; Rahman, M.; Khan, F.; Kabir, F.; Nahar, K.; Lasker, S.; Islam, D.; Hossain, M.M.; Hasan, R.; Rana, S.; et al. Metformin treatment reverses high fat diet- induced non-alcoholic fatty liver diseases and dyslipidemia by stimulating multiple antioxidant and anti-inflammatory pathways. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2021, 28, 101168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lombardi, R.; Airaghi, L.; Targher, G.; Serviddio, G.; Maffi, G.; Mantovani, A.; Maffeis, C.; Colecchia, A.; Villani, R.; Rinaldi, L.; et al. Liver fibrosis by FibroScan® independently of established cardiovascular risk parameters associates with macrovascular and microvascular complications in patients with type 2 diabetes. Liver Int. 2019, 40, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, A.; Qian, F.; Li, Y.; Li, B.; Yang, F.; Hu, C.; Sun, W.; Huang, Y. Research progress of metformin in the treatment of liver fibrosis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2023, 116, 109738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.W.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, B.K.; Park, J.Y.; Kim, D.Y.; Ahn, S.H.; Kim, S.U. Evolution of liver fibrosis and steatosis markers in patients with type 2 diabetes after metformin treatment for 2 years. J. Diabetes its Complicat. 2021, 35, 107747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, K.; Wu, K.; Lin, L.; Ge, P.; Dai, J.; He, X.; Hu, K.; Zhang, L. Metformin mitigates carbon tetrachloride-induced TGF-β1/Smad3 signaling and liver fibrosis in mice. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 90, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shankaraiah, R.C.; Callegari, E.; Guerriero, P.; Rimessi, A.; Pinton, P.; Gramantieri, L.; Silini, E.M.; Sabbioni, S.; Negrini, M. Metformin prevents liver tumourigenesis by attenuating fibrosis in a transgenic mouse model of hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene 2019, 38, 7035–7045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilar-Gomez, E.; Vuppalanchi, R.; Desai, A.P.; Gawrieh, S.; Ghabril, M.; Saxena, R.; Cummings, O.W.; Chalasani, N. Long-term metformin use may improve clinical outcomes in diabetic patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis and bridging fibrosis or compensated cirrhosis. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 50, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujiwara, N.; Friedman, S.L.; Goossens, N.; Hoshida, Y. Risk factors and prevention of hepatocellular carcinoma in the era of precision medicine. J. Hepatol. 2018, 68, 526–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ma, S.; Zheng, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Zhou, P.; Tan, H. Meta-analysis of studies using metformin as a reducer for liver cancer risk in diabetic patients. Medicine 2017, 96, e6888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Falamarzi, K.; Malekpour, M.; Tafti, M.F.; Azarpira, N.; Behboodi, M.; Zarei, M. The role of FGF21 and its analogs on liver associated diseases. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 967375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loomba, R.; Sanyal, A.J.; Kowdley, K.V.; Bhatt, D.L.; Alkhouri, N.; Frias, J.P.; Bedossa, P.; Harrison, S.A.; Lazas, D.; Barish, R.; et al. Randomized, Controlled Trial of the FGF21 Analogue Pegozafermin in NASH. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, 998–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- A Study Evaluating the Efficacy and Safety of Pegozafermin in Participants with MASH and Fibrosis (ENLIGHTEN-Fibrosis). Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT06318169?cond=MASLD&intr=Pegozafermin&rank=1 (accessed on 8 July 2025).
- A Study to Evaluate the Efficacy and Safety of Pegozafermin in Participants with Compensated Cirrhosis Due to MASH. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT06419374?cond=MASLD&intr=Pegozafermin&rank=2 (accessed on 5 June 2025).
- Harrison, S.A.; Ruane, P.J.; Freilich, B.; Neff, G.; Patil, R.; Behling, C.; Hu, C.; Shringarpure, R.; de Temple, B.; Fong, E.; et al. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase IIa trial of efruxifermin for patients with compensated NASH cirrhosis. JHEP Rep. 2022, 5, 100563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puengel, T.; Tacke, F. Efruxifermin, an investigational treatment for fibrotic or cirrhotic nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2023, 32, 451–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- A Study Evaluating Efruxifermin in Subjects with Non-Cirrhotic Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH)/Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatohepatitis (MASH) and Fibrosis. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT06215716?intr=Efruxifermin%20&rank=2 (accessed on 19 August 2025).
- A Study Evaluating Efruxifermin in Subjects with Compensated Cirrhosis Due to NASH/MASH. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT06528314?intr=Efruxifermin%20&rank=1 (accessed on 30 July 2025).
- Loomba, R.; Sanyal, A.J.; Nakajima, A.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A.; Goodman, Z.D.; Harrison, S.A.; Lawitz, E.J.; Gunn, N.; Imajo, K.; Ravendhran, N.; et al. Pegbelfermin in Patients with Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis and Stage 3 Fibrosis (FALCON 1): A Randomized Phase 2b Study. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 22, 102–112.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- A Harrison, S.; Abdelmalek, M.F.; Neff, G.; Gunn, N.; Guy, C.D.; Alkhouri, N.; Bashir, M.R.; Freilich, B.; Kohli, A.; Khazanchi, A.; et al. Aldafermin in patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (ALPINE 2/3): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2b trial. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 7, 603–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, H.-L.; Zhang, J.-W.; Chen, X.-Z.; Wu, P.-B.; Chen, L.; Zhang, G. Ursodeoxycholic acid alleviates experimental liver fibrosis involving inhibition of autophagy. Life Sci. 2020, 242, 117175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buko, V.U.; Lukivskaya, O.Y.; Naruta, E.E.; Belonovskaya, E.B.; Tauschel, H.-D. Protective Effects of Norursodeoxycholic Acid Versus Ursodeoxycholic Acid on Thioacetamide-induced Rat Liver Fibrosis. J. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2014, 4, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Nevens, F.; Andreone, P.; Mazzella, G.; Strasser, S.I.; Bowlus, C.; Invernizzi, P.; Drenth, J.P.; Pockros, P.J.; Regula, J.; Beuers, U.; et al. A Placebo-Controlled Trial of Obeticholic Acid in Primary Biliary Cholangitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 631–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EMA Recommends Revoking Conditional Marketing Authorisation for Ocaliva. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/news/ema-recommends-revoking-conditional-marketing-authorisation-ocaliva (accessed on 28 June 2024).
- Sanyal, A.J.; Ratziu, V.; Loomba, R.; Anstee, Q.M.; Kowdley, K.V.; Rinella, M.E.; Sheikh, M.Y.; Trotter, J.F.; Knapple, W.; Lawitz, E.J.; et al. Results from a new efficacy and safety analysis of the REGENERATE trial of obeticholic acid for treatment of pre-cirrhotic fibrosis due to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. J. Hepatol. 2023, 79, 1110–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anstee, Q.M.; Lucas, K.J.; Francque, S.; Abdelmalek, M.F.; Sanyal, A.J.; Ratziu, V.; Gadano, A.C.; Rinella, M.; Charlton, M.; Loomba, R.; et al. Tropifexor plus cenicriviroc combination versus monotherapy in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: Results from the phase 2b TANDEM study. Hepatology 2023, 78, 1223–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Loomba, R.; Bedossa, P.; Grimmer, K.; Kemble, G.; Martins, E.B.; McCulloch, W.; O’FArrell, M.; Tsai, W.-W.; Cobiella, J.; Lawitz, E.; et al. Denifanstat for the treatment of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis: A multicentre, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 2b trial. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, 9, 1090–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- A Phase 3 Study Evaluating the Safety and Efficacy of Denifanstat in Patients with MASH and F2/F3 Fibrosis (FASCINATE-3). Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT06594523?intr=Denifanstat%20&rank=1 (accessed on 15 May 2025).
- Yokohama, S.; Yoneda, M.; Haneda, M.; Okamoto, S.; Okada, M.; Aso, K.; Hasegawa, T.; Tokusashi, Y.; Miyokawa, N.; Nakamura, K. Therapeutic efficacy of an angiotensin II receptor antagonist in patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology 2004, 40, 1222–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rimola, A.; Londoño, M.-C.; Guevara, G.; Bruguera, M.; Navasa, M.; Forns, X.; García-Retortillo, M.; García-Valdecasas, J.-C.; Rodes, J. Beneficial effect of angiotensin-blocking agents on graft fibrosis in hepatitis C recurrence after liver transplantation. Transplantation 2004, 78, 686–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, L.; Zhu, Y.; Lee, M.; Nguyen, A.; Ryujin, N.T.; Huang, J.Y.; Pandit, S.K.; Chamseddine, S.; Xiao, L.; Mohamed, Y.I.; et al. Angiotensin II receptor inhibition ameliorates liver fibrosis and enhances hepatocellular carcinoma infiltration by effector T cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2300706120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okanoue, T.; Sakamoto, M.; Harada, K.; Inagaki, M.; Totsuka, N.; Hashimoto, G.; Kumada, H. Efficacy and safety of apararenone (MT-3995) in patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: A randomized controlled study. Hepatol. Res. 2021, 51, 943–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Argo, C.K.; Patrie, J.T.; Lackner, C.; Henry, T.D.; de Lange, E.E.; Weltman, A.L.; Shah, N.L.; Al-Osaimi, A.M.; Pramoonjago, P.; Jayakumar, S.; et al. Effects of n-3 fish oil on metabolic and histological parameters in NASH: A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. J. Hepatol. 2015, 62, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sanyal, A.J.; Abdelmalek, M.F.; Suzuki, A.; Cummings, O.W.; Chojkier, M.; EPE-A Study Group. No significant effects of ethyl-eicosapentanoic acid on histologic features of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in a phase 2 trial. Gastroenterology 2014, 147, 377–384.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraser, D.A.; Wang, X.; Lund, J.; Nikolić, N.; Iruarrizaga-Lejarreta, M.; Skjaeret, T.; Alonso, C.; Kastelein, J.J.; Rustan, A.C.; Kim, Y.O.; et al. A structurally engineered fatty acid, icosabutate, suppresses liver inflammation and fibrosis in NASH. J. Hepatol. 2022, 76, 800–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratziu, V.; de Guevara, L.; Safadi, R.; Poordad, F.; Fuster, F.; Flores-Figueroa, J.; Arrese, M.; Fracanzani, A.L.; Ben Bashat, D.; Lackner, K.; et al. Aramchol in patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 2b trial. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 1825–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scorletti, E.; Creasy, K.T.; Vujkovic, M.; Vell, M.; Zandvakili, I.; Rader, D.J.; Schneider, K.M.; Schneider, C.V. Dietary Vitamin E Intake Is Associated with a Reduced Risk of Developing Digestive Diseases and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 117, 927–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chen, Y.; Huang, Y.; Huang, R.; Chen, Z.; Wang, X.; Chen, F.; Huang, Y. Interleukin-10 gene intervention ameliorates liver fibrosis by enhancing the immune function of natural killer cells in liver tissue. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2023, 127, 111341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naffaa, M.E.; Hassan, F.; Jeries, H.; Dror, D.; Rozenberg, V.; Chodick, G.; Carmiel, M. Long-term use of colchicine is associated with incident cirrhosis: A real-world cohort study. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2025, 60, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarro, V.J.; Belle, S.H.; D’Amato, M.; Adfhal, N.; Brunt, E.M.; Fried, M.W.; Reddy, K.R.; Wahed, A.S.; Harrison, S.; Silymarin in NASH and C Hepatitis (SyNCH) Study Group. Silymarin in non-cirrhotics with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: A randomized, dou-ble-blind, placebo controlled trial. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0223915, Erratum in PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0221683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Nguyen, V.H.; Przybyszewski, E.; Song, J.; Carroll, A.; Michta, M.; Almazan, E.; Simon, T.G.; Chung, R.T. Statin Use and Risk of Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Liver Fibrosis in Chronic Liver Disease. JAMA Intern. Med. 2025, 185, 522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ayada, I.; van Kleef, L.A.; Zhang, H.; Liu, K.; Li, P.; Abozaid, Y.J.; Lavrijsen, M.; Janssen, H.L.; van der Laan, L.J.; Ghanbari, M.; et al. Dissecting the multifaceted impact of statin use on fatty liver disease: A multidimensional study. EBioMedicine 2023, 87, 104392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Cusi, K.; Orsak, R.B.; Bril, F.; Lomonaco, R.; Hecht, R.J.; Ortiz-Lopez, C.; Tio, F.; Hardies, J.; Darland, R.C.; Musi, N.; et al. Long-Term Pioglitazone Treatment for Patients with Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis and Prediabetes or Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Ann. Intern. Med. 2016, 165, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza, M.; Al-Sharif, L.; Antunes, V.L.; Huang, D.Q.; Loomba, R. Comparison of pharmacological therapies in metabolic dysfunction–associated steatohepatitis for fibrosis regression and MASH resolution: Systematic review and network meta-analysis. Hepatology 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramachandran, G.; Pottakkat, B. Probiotics—A Promising Novel Therapeutic Approach in the Management of Chronic Liver Diseases. J. Med. Food 2024, 27, 467–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawada, Y.; Kawaratani, H.; Kubo, T.; Fujinaga, Y.; Furukawa, M.; Saikawa, S.; Sato, S.; Seki, K.; Takaya, H.; Okura, Y.; et al. Combining probiotics and an angiotensin-II type 1 receptor blocker has beneficial effects on hepatic fibrogenesis in a rat model of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatol. Res. 2018, 49, 284–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alisi, A.; Bedogni, G.; Baviera, G.; Giorgio, V.; Porro, E.; Paris, C.; Giammaria, P.; Reali, L.; Anania, F.; Nobili, V. Randomised clinical trial: The beneficial effects of VSL#3 in obese children with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 39, 1276–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wong, V.W.; Won, G.L.; Chim, A.M.; Chu, W.C.; Yeung, D.K.; Li, K.C.; Chan, H.L. Treatment of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis with probi-otics. A proof-of-concept study. Ann. Hepatol. 2013, 12, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solga, S.F.; Buckley, G.; Clark, J.M.; Horska, A.; Diehl, A.M. The Effect of a Probiotic on Hepatic Steatosis. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2008, 42, 1117–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Niu, Z.; Zou, M.; Liu, S.; Wang, M.; Gu, X.; Lu, H.; Tian, H.; Jha, R. Probiotics, prebiotics, and synbiotics regulate the intestinal microbiota differentially and restore the relative abundance of specific gut microorganisms. J. Dairy. Sci. 2020, 103, 5816–5829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dewulf, E.M.; Cani, P.D.; Claus, S.P.; Fuentes, S.; Puylaert, P.G.; Neyrinck, A.M.; Bindels, L.B.; de Vos, W.M.; Gibson, G.R.; Thissen, J.-P.; et al. Insight into the prebiotic concept: Lessons from an exploratory, double blind intervention study with inulin-type fructans in obese women. Gut 2012, 62, 1112–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ferolla, S.M.; Couto, C.A.; Costa-Silva, L.; Armiliato, G.N.A.; Pereira, C.A.S.; Martins, F.S.; Ferrari, M.D.L.A.; Vilela, E.G.; Torres, H.O.G.; Cunha, A.S.; et al. Beneficial Effect of Synbiotic Supplementation on Hepatic Steatosis and Anthropometric Parameters, But Not on Gut Permeability in a Population with Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Nutrients 2016, 8, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mofidi, F.; Poustchi, H.; Yari, Z.; Nourinayyer, B.; Merat, S.; Sharafkhah, M.; Malekzadeh, R.; Hekmatdoost, A. Synbiotic supplementation in lean patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A pilot, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, clinical trial. Br. J. Nutr. 2017, 117, 662–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Guo, G.; Sun, C. Therapeutic potential of rifaximin in liver diseases. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 178, 117283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du Plessis, J.; Vanheel, H.; Janssen, C.E.; Roos, L.; Slavik, T.; Stivaktas, P.I.; Nieuwoudt, M.; van Wyk, S.G.; Vieira, W.; Pretorius, E.; et al. Activated intestinal macrophages in patients with cirrhosis release NO and IL-6 that may disrupt intestinal barrier function. J. Hepatol. 2013, 58, 1125–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sikorska, K.; Bernat, A.; Wróblewska, A. Molecular pathogenesis and clinical consequences of iron overload in liver cirrhosis. Hepatobiliary Pancreat. Dis. Int. 2016, 15, 461–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Israelsen, M.; Madsen, B.S.; Torp, N.; Johansen, S.; Hansen, C.D.; Detlefsen, S.; Andersen, P.; Hansen, J.K.; Lindvig, K.P.; Rasmussen, D.N.; et al. Rifaximin-α for liver fibrosis in patients with alcohol-related liver disease (GALA-RIF): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2 trial. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 8, 523–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajaj, J.S.; Gavis, E.A.; Fagan, A.; Wade, J.B.; Thacker, L.R.; Fuchs, M.; Patel, S.; Davis, B.; Meador, J.; Puri, P.; et al. A Randomized Clinical Trial of Fecal Microbiota Transplant for Alcohol Use Disorder. Hepatology 2020, 73, 1688–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, S.C.; Xu, Z.; Mak, J.W.Y.; Yang, K.; Liu, Q.; Zuo, T.; Tang, W.; Lau, L.; Lui, R.N.; Tse, Y.K.; et al. Microbiota engraftment after faecal microbiota transplantation in obese subjects with type 2 diabetes: A 24-week, double-blind, randomised controlled trial. Gut 2021, 71, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oguri, N.; Miyoshi, J.; Nishinarita, Y.; Wada, H.; Nemoto, N.; Hibi, N.; Kawamura, N.; Miyoshi, S.; Lee, S.T.M.; Matsuura, M.; et al. Akkermansia muciniphila in the small intestine improves liver fibrosis in a murine liver cirrhosis model. Npj Biofilms Microbiomes 2024, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zazueta, A.; Valenzuela-Pérez, L.; Ortiz-López, N.; Pinto-León, A.; Torres, V.; Guiñez, D.; Aliaga, N.; Merino, P.; Sandoval, A.; Covarrubias, N.; et al. Alteration of Gut Microbiota Composition in the Progression of Liver Damage in Patients with Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
| Mechanism | Key Points |
|---|---|
| Genetic Factors | PNPLA3 (rs738409 C>G): Impaired lipid hydrolysis → HSC activation → ECM deposition. TM6SF2 (rs58542926 C>T): Disrupted VLDL secretion → Lipid accumulation → Steatosis & fibrosis. MBOAT7 (rs641738): Increased fibrosis risk in chronic liver diseases. |
| DNA Methylation | Hypermethylation: Silences anti-fibrotic genes (e.g., PPARγ, SOCS1), preventing fibrosis resolution. Hypomethylation: Activates pro-fibrotic genes (e.g., TGFβ1), promoting fibrosis. |
| Epigenetic Regulators | EZH2: Gene silencing → HSC activation. HDACs/SIRT1: Histone acetylation → Drives fibrosis. KDM6B: Removes repressive marks → Activates fibrogenic genes. |
| Non-Coding RNAs | miR-21: Promotes HSC activation. miR-29: Downregulated → Excessive ECM accumulation. miR-122: Downregulated → Link to fibrosis and HCC. H19/MEG3/MALAT1: Regulate chromatin and fibrosis pathways. |
| Drug | Drug Type | Mechanism of Action | Key Clinical Trial and Population | Main Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Resmetirom [157,158,159,160,161] | Liver-directed THR agonist | THR-β agonist; reduces hepatic lipogenesis and TGF-β activity | MAESTRO-NASH, Phase III, non-cirrhotic MASH F2–F3 | Reduced inflammation, slower fibrosis progression; AEs: nausea 22%, diarrhea 33%, vomiting 11% |
| Semaglutide [162,163,164,165,166] | GLP-1 RA | Mimics GLP-1 → glycemic control, appetite/weight reduction | ESSENCE, Phase III, MASH patients | MASH resolution 62.9% vs. 34.1%; fibrosis improvement 37% vs. 22.5%; GI AEs common |
| Tirzepatide [169] | Dual GLP-1/GIP RA | Dual GLP-1 and GIP agonist | Phase II, dose-finding, MASH | ≥1-stage fibrosis improvement 51–55% vs. 30% placebo; GI AEs dose-related |
| Cotadutide [170] | Dual GLP-1/Glucagon RA | Dual GLP-1/glucagon receptor agonist | Phase II, MASH | Reduction in fibrosis scores (FIB-4/NFS, p = 0.010) |
| Liraglutide [170] | GLP-1 RA | GLP-1 receptor agonist | Various trials in MASH | No significant fibrosis improvement; well tolerated |
| Survodutide [171] | Dual GLP-1/Glucagon RA | Dual GLP-1/glucagon receptor agonist | Phase II, MASH | ≥1-stage fibrosis reduction: 34–36% vs. 22% placebo; study not powered for fibrosis |
| Dapagliflozin/Empagliflozin/Licogliflozin [156,172,173,174,175] | SGLT2 inhibitors | Block renal glucose reabsorption; modulate HSC-activating microRNAs | Small studies & large cohort analyses, T2DM | Potential fibrosis reduction in advanced fibrosis; lower risk of cirrhosis vs. DPP-4 inhibitors; effects may be weight-mediated |
| Lanifibranor [176,177,178,179,180] | Pan-PPAR agonist | Activates PPAR-α, -β/δ, -γ → modulates lipid metabolism, inflammation, fibrogenesis | Phase II, MASH | ≥1-stage fibrosis improvement 48% (1200 mg), 34% (800 mg), vs. 29% placebo; AEs: weight gain, edema |
| Metformin [156,181,182,183,184,185,186,187,188,189] | Biguanide | Glucose-lowering, anti-inflammatory, anti-fibrotic | Observational/animal studies, MASLD/T2DM | >50% regression in fibrosis; inhibits TGF-β, SMAD3, HSC activation; improves transplant-free survival; reduces HCC risk |
| Pegozafermin [191,192,193,223] | FGF21 analogue | Hormone-like factor → reduces lipogenesis, increases insulin sensitivity | Phase 2b, non-cirrhotic MASH F2–F3 | ≥1-stage fibrosis improvement 22–27% vs. 7% placebo; well tolerated; phase 3 ongoing |
| Efruxifermin [194,195,196,197] | FGF21 analogue | Same as above | Phase 2, MASH F2–F3 | ≥1-stage fibrosis improvement 39–41% vs. 20% placebo; MASH resolution; good tolerability |
| Pegbelfermin/Aldafermin [198,199] | FGF21 analogues | Same | Phase 2b, MASH | Failed to show significant fibrosis improvement |
| Obeticholic acid (OCA) [156,202,203,204] | FXR agonist | Farnesoid X receptor agonist → modulates bile acid metabolism, inflammation, fibrosis | Regenerate, Phase III, MASH | ≥1-stage fibrosis improvement 22.4% vs. 9.6%; AEs: pruritus, LDL ↑; approval withdrawn for NASH |
| Tropifexor ± Cenicriviroc [205] | FXR agonist ± CCR2/5 inhibitor | Same | Phase 2b | No significant antifibrotic effect |
| Denifanstat [206,207] | Fatty acid synthase inhibitor | Blocks lipogenesis → prevents lipotoxicity-driven fibrosis | Phase 2b, F2–F3 fibrosis | ≥1-stage fibrosis improvement 41% mITT vs. 18% placebo; mild AEs; phase 3 ongoing |
| Losartan/Apararenone [208,209,210,211] | Renin-angiotensin system inhibitors | Inhibit RAAS; reduce TGF-β signaling and fibroblast activation | Small clinical studies, MASLD/HCC | Experimental antifibrotic effects; results inconsistent or non-significant |
| Pioglitazone/Thiazolidinediones [222] | PPARγ agonist | Improves steatohepatitis histologically | Various trials | No clear long-term fibrosis regression; adverse events limit use |
| Vitamin E (±Pioglitazone) [223] | Antioxidant/anti-inflammatory | Reduce oxidative stress and inflammation | Various trials | Modest/inconsistent effect on fibrosis |
| Statins [220,221] | HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors | Lipid-lowering; potential anti-inflammatory | Small clinical studies | Possible fibrosis reduction and lower HCC risk; larger trials needed |
| Icosabutate/Omega-3 PUFA [212,213,214] | Fatty acids | Anti-inflammatory | Preclinical/small trials | Icosabutate reduces inflammation and improves fibrosis in mice; omega-3 PUFA no significant effect |
| Aramchol [215] | SCD1 partial inhibitor | Reduces lipogenesis | Preclinical | Potential fibrosis benefit in mice; no human phase 3 data |
| IL-10 [217] | Immunomodulator | Activates NK cells → antifibrotic | Preclinical | Reduces fibrosis in mice; requires further in vivo research |
| Colchicine [218] | Anti-inflammatory | Inhibits microtubule polymerization | Observational | Long-term use linked to cirrhosis; limited clinical use |
| Silymarin [219] | Antioxidant/anti-inflammatory | Free radical scavenger | Various small studies | No significant histological improvement in fibrosis |
| Therapy | Type | Mechanism of Action | Main Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Probiotics (VSL#3, Lepicol, others) [224,225,226,227] | Live microorganisms | Restore intestinal epithelial barrier, modulate gut microbiome, reduce intestinal permeability, anti-inflammatory | Reduced BMI and fatty liver severity; reduced liver inflammation and fat levels; variable results across studies; small trials |
| Prebiotics (inulin, lactulose) [230] | Indigestible oligosaccharides | Promote beneficial bacteria growth, reduce intestinal permeability | Increased Faecalibacterium prausnitzii and Bifidobacterium; decreased LPS, Bacteroides and Propionibacterium; reduced fat mass |
| Symbiotics [231,232] | Combination of prebiotics and probiotics | Selective growth of beneficial bacteria, reduce pro-inflammatory factors | Potential reduction in MASH activity index; direct effect on liver fibrosis not well established |
| Antibiotics (Rifaximin) [233,234,235,236] | Non-absorbable antibiotic | Modulate gut microbiota, reduce inflammation, inhibit HSC activation | Potential suppression of fibrosis progression, reduced inflammatory burden; further studies needed due to limited statistical significance |
| Fecal Microbiota Transplantation (FMT) [237,238] | Microbiome transfer | Restore intestinal barrier, modulate gut microbiota | Reiterated FMT plus lifestyle changes improved microbiota engraftment and liver stiffness compared to FMT alone or lifestyle alone |
| Akkermansia muciniphila supplementation [239] | Commensal bacteria | Reduce fibrosis, improve hyperammonemia | Significant reduction in fibrosis area (p = 0.0012) |
| Gut microbiota composition markers [240] | Microbiome profiling | Predict MASLD severity and fibrosis progression | Higher abundance of Sellimonas and lower Ruminococcaceae UCG 013/Ruminoclostridium linked with fibrosis and MASLD progression |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cerrito, L.; Galasso, L.; Iaccarino, J.; Pizzi, A.; Termite, F.; Esposto, G.; Borriello, R.; Ainora, M.E.; Gasbarrini, A.; Zocco, M.A. Present and Future Perspectives in the Treatment of Liver Fibrosis. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 1321. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18091321
Cerrito L, Galasso L, Iaccarino J, Pizzi A, Termite F, Esposto G, Borriello R, Ainora ME, Gasbarrini A, Zocco MA. Present and Future Perspectives in the Treatment of Liver Fibrosis. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(9):1321. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18091321
Chicago/Turabian StyleCerrito, Lucia, Linda Galasso, Jacopo Iaccarino, Alessandro Pizzi, Fabrizio Termite, Giorgio Esposto, Raffaele Borriello, Maria Elena Ainora, Antonio Gasbarrini, and Maria Assunta Zocco. 2025. "Present and Future Perspectives in the Treatment of Liver Fibrosis" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 9: 1321. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18091321
APA StyleCerrito, L., Galasso, L., Iaccarino, J., Pizzi, A., Termite, F., Esposto, G., Borriello, R., Ainora, M. E., Gasbarrini, A., & Zocco, M. A. (2025). Present and Future Perspectives in the Treatment of Liver Fibrosis. Pharmaceuticals, 18(9), 1321. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18091321









