Targeting Hippo Signaling Pathway with a Boron Derivative, Sodium Pentaborate Pentahydrate (NaB): Therapeutic Strategies in Colorectal Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Exploring the Effects of NaB Treatment on Cell Survival
2.2. NaB-Induced Apoptosis and Caspase Activation in HCT-116, HT-29, and COLO-205 Colorectal Cancer Cell Lines
2.3. Mechanisms of NaB-Induced Growth Inhibition in HCT-116, HT-29, and COLO-205 Colorectal Cancer Cell Lines
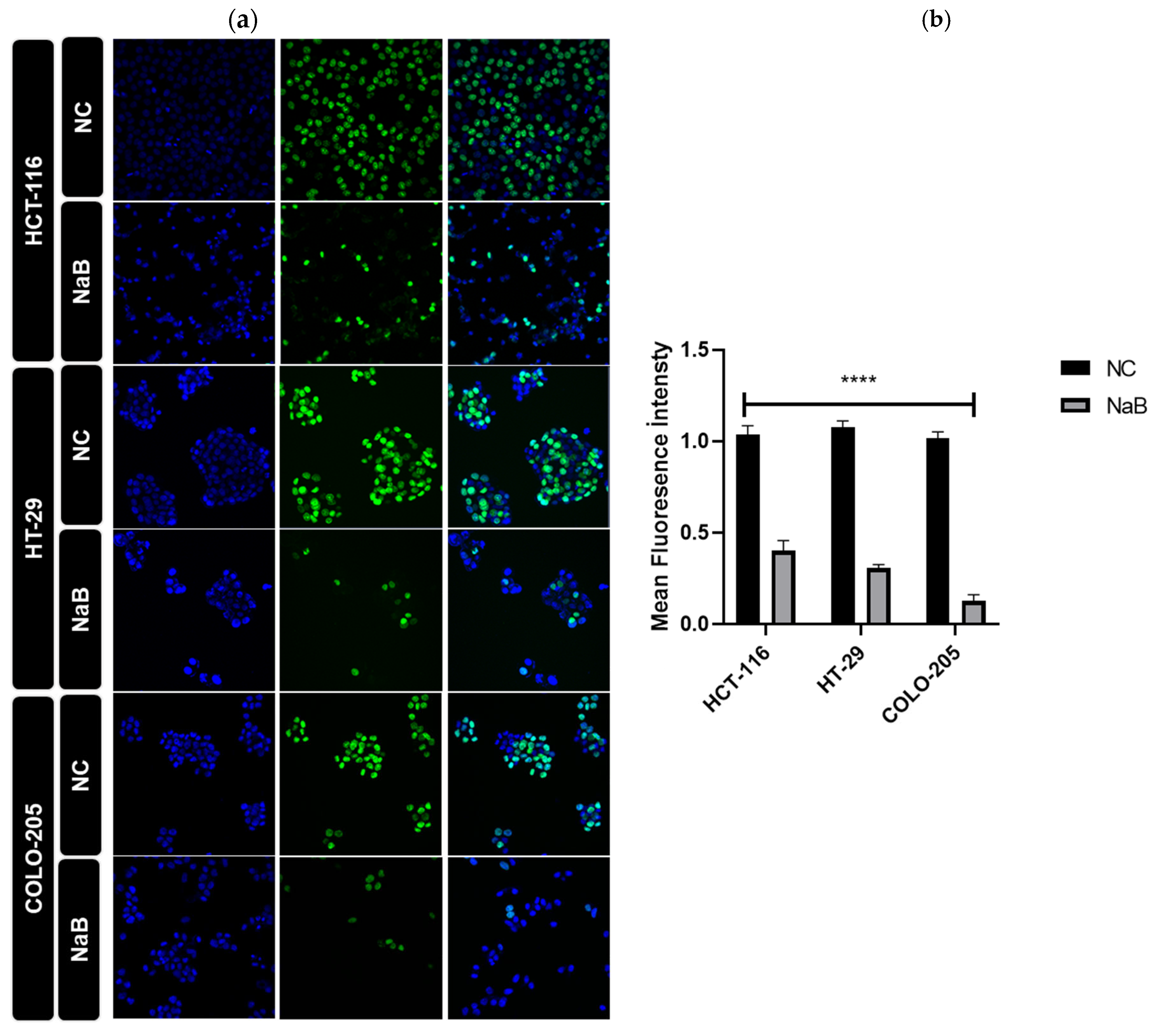
2.4. NaB Treatment Modulates Hippo Signaling Pathway and Expression of YAP1 Target Genes in HCT-116 and HT-29 Colorectal Cancer Cell Lines
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Lines and Cell Culture Conditions
4.2. Cell Viability Assay
4.3. Annexin V Assay
4.4. Cell Cycle Analysis
4.5. Real-Time PCR
4.6. Scratch Assay
4.7. Colony-Formation Assay
4.8. Caspase Activity Assay
4.9. Ethynyl-2′-Deoxyuridine Assay
4.10. Immunocytochemistry (ICC)
4.11. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CRC | Colorectal cancer |
| NaB | Sodium Pentaborate Pentahydrate |
| FDA | Food and Drug Administration |
| LATS1/2 | Large Tumor Suppressor Kinase 1/2 |
| MST1/2 | Mammalian STE20-like Kinase |
| SAV1 | Salvador Homologue 1 |
| MOB1A/B | MOB Kinase Activator 1 A |
| YAP | Yes-associated protein 1 |
| TAZ | WW-domain-containing transcription regulator 1 |
| TEAD | Transcriptional Enhanced Associated Domain |
| MTS | 3-(4,5-dimethyl-thiazol-2)-5-(3-carboxy-methoxy-phenyl)-2-(4-sulfo-phenyl)-2H-tetrazolium salt |
| PFA | Paraformaldehyde |
References
- Li, S.; Li, X.; Yang, X.; Lei, Y.; He, M.; Xiang, X.; Wu, Q.; Liu, H.; Wang, J.; Wang, Q. Corilagin enhances the anti-tumor activity of 5-FU by downregulating the expression of GRP 78. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 22661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fadlallah, H.; El Masri, J.; Fakhereddine, H.; Youssef, J.; Chemaly, C.; Doughan, S.; Abou-Kheir, W. Colorectal cancer: Recent advances in management and treatment. World J. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 15, 1136–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Guo, X.; Bai, P. Removal technology of boron dissolved in aqueous solutions—A review. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2014, 444, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, L.H. Boron, Elemental. Kirk-Othmer Encycl. Chem. Technol. 2011, 4, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messner, K.; Vuong, B.; Tranmer, G.K. The Boron Advantage: The Evolution and Diversification of Boron’s Applications in Medicinal Chemistry. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, S.J.; Ding, C.Z.; Akama, T.; Zhang, Y.K.; Hernandez, V.; Xia, Y. Therapeutic potential of boron-containing compounds. Future Med. Chem. 2009, 1, 1275–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirk, C.J.; Tuch, B.B.; Arastu-Kapur, S.; Boise, L.H. Proteasome inhibitors. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2015, 96, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, B.C.; Nandwana, N.K.; Das, S.; Nandwana, V.; Shareef, M.A.; Das, Y.; Saito, M.; Weiss, L.M.; Almaguel, F.; Hosmane, N.S.; et al. Boron Chemicals in Drug Discovery and Development: Synthesis and Medicinal Perspective. Molecules 2022, 27, 2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, E.E.; Türkel, N.; Yigit, U.M.; Dalan, A.B.; Sahin, F. Boron Derivatives Inhibit the Proliferation of Breast Cancer Cells and Affect Tumor-Specific T Cell Activity In Vitro by Distinct Mechanisms. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2023, 201, 5692–5707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turkez, H.; Arslan, M.E.; Tatar, A.; Mardinoglu, A. Promising potential of boron compounds against Glioblastoma: In Vitro antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and anticancer studies. Neurochem. Int. 2021, 149, 105137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cebeci, E.; Yüksel, B.; Şahin, F. Anti-cancer effect of boron derivatives on small-cell lung cancer. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2022, 70, 126923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Hanagata, N.; Wang, X.; Weng, Q.; Ito, A.; Bando, Y.; Golberg, D. Hollow boron nitride nanospheres as boron reservoir for prostate cancer treatment. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 13936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulu, Z.O.; Degirmenci, N.S.; Bolat, Z.B.; Sahin, F. Synergistic anti-cancer effect of sodium pentaborate pentahydrate, curcumin and piperine on hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 14404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doğan, A.; Demirci, S.; Apdik, H.; Bayrak, O.F.; Gulluoglu, S.; Tuysuz, E.C.; Gusev, O.; Rizvanov, A.A.; Nikerel, E.; Şahin, F. A new hope for obesity management: Boron inhibits adipogenesis in progenitor cells through the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Metabolism 2017, 69, 130–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demirci, S.; Doğan, A.; Aydın, S.; Dülger, E.Ç.; Şahin, F. Boron promotes streptozotocin-induced diabetic wound healing: Roles in cell proliferation and migration, growth factor expression, and inflammation. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2016, 417, 119–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aysan, E.; Idiz, U.O.; Elmas, L.; Saglam, E.K.; Akgun, Z.; Yucel, S.B. Effects of Boron-Based Gel on Radiation-Induced Dermatitis in Breast Cancer: A Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. J. Investig. Surg. 2017, 30, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, J.; Lin, L.; Othmer, H.G. A Model for the Hippo Pathway in the Drosophila wing disc. Biophys. J. 2018, 115, 737–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, M.; Hu, Y.; Lan, T.; Guan, K.L.; Luo, T.; Luo, M. The Hippo signalling pathway and its implications in human health and diseases. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Pratt, H.; Gao, M.; Wei, F.; Weng, Z.; Struhl, K. Yap and taz are transcriptional co-activators of ap-1 proteins and stat3 during breast cellular transformation. Elife 2021, 10, e67312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadpour, S.; Esfahani, A.T.; Sarpash, S.K.; Vakili, F.; Zafarjafarzadeh, N.; Mashaollahi, A.; Pardakhtchi, A.; Nazemalhosseini-Mojarad, E. Hippo Signaling Pathway in Colorectal Cancer: Modulation by Various Signals and Therapeutic Potential. Anal. Cell. Pathol. 2024, 2024, 5767535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patria, D.; Clin, J.E.; Res, C.; Di Patria, L.; Habel, N.; Olaso, R.; Fernandes, R.; Brenner, C. C-terminal binding protein-2 triggers CYR61-induced metastatic dissemination of osteosarcoma in a non-hypoxic microenvironment. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2025, 44, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Özyarım, S.C.; Çoban, F.K. Investigation of the apoptotic and antiproliferative effects of boron on CCL-233 human colon cancer cells. Cell J. 2021, 23, 429–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, D.; Pfannenstiel, L.; Demelash, A.; Phoon, Y.P.; Mayell, C.; Cabrera, C.; Liu, C.; Zhao, J.; Dermawan, J.; Patil, D.; et al. MCL1 nuclear translocation induces chemoresistance in colorectal carcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miele, E.; Abballe, L.; Spinelli, G.P.; Besharat, Z.M.; Catanzaro, G.; Chiacchiarini, M.; Vacca, A.; Po, A.; Capalbo, C.; Ferretti, E. BRAF mutant colorectal cancer: ErbB2 expression levels as predictive factor for the response to combined BRAF/ErbB inhibitors. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]














| IC-50 Values of Cell Lines | Treatment of NaB |
|---|---|
| HCT-116 | 1000 µg/mL |
| COLO-205 | 500 µg/mL |
| HT-29 | 500 µg/mL |
| CCD-18CO | 2500 µg/mL |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yüksel, B.; Şahin, F.; Türkel, N. Targeting Hippo Signaling Pathway with a Boron Derivative, Sodium Pentaborate Pentahydrate (NaB): Therapeutic Strategies in Colorectal Cancer. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 1171. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18081171
Yüksel B, Şahin F, Türkel N. Targeting Hippo Signaling Pathway with a Boron Derivative, Sodium Pentaborate Pentahydrate (NaB): Therapeutic Strategies in Colorectal Cancer. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(8):1171. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18081171
Chicago/Turabian StyleYüksel, Büşra, Fikrettin Şahin, and Nezaket Türkel. 2025. "Targeting Hippo Signaling Pathway with a Boron Derivative, Sodium Pentaborate Pentahydrate (NaB): Therapeutic Strategies in Colorectal Cancer" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 8: 1171. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18081171
APA StyleYüksel, B., Şahin, F., & Türkel, N. (2025). Targeting Hippo Signaling Pathway with a Boron Derivative, Sodium Pentaborate Pentahydrate (NaB): Therapeutic Strategies in Colorectal Cancer. Pharmaceuticals, 18(8), 1171. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18081171







