PCSK9 Inhibitor and Potential Decreased Risk of Neoplasms, Especially in Females: A Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
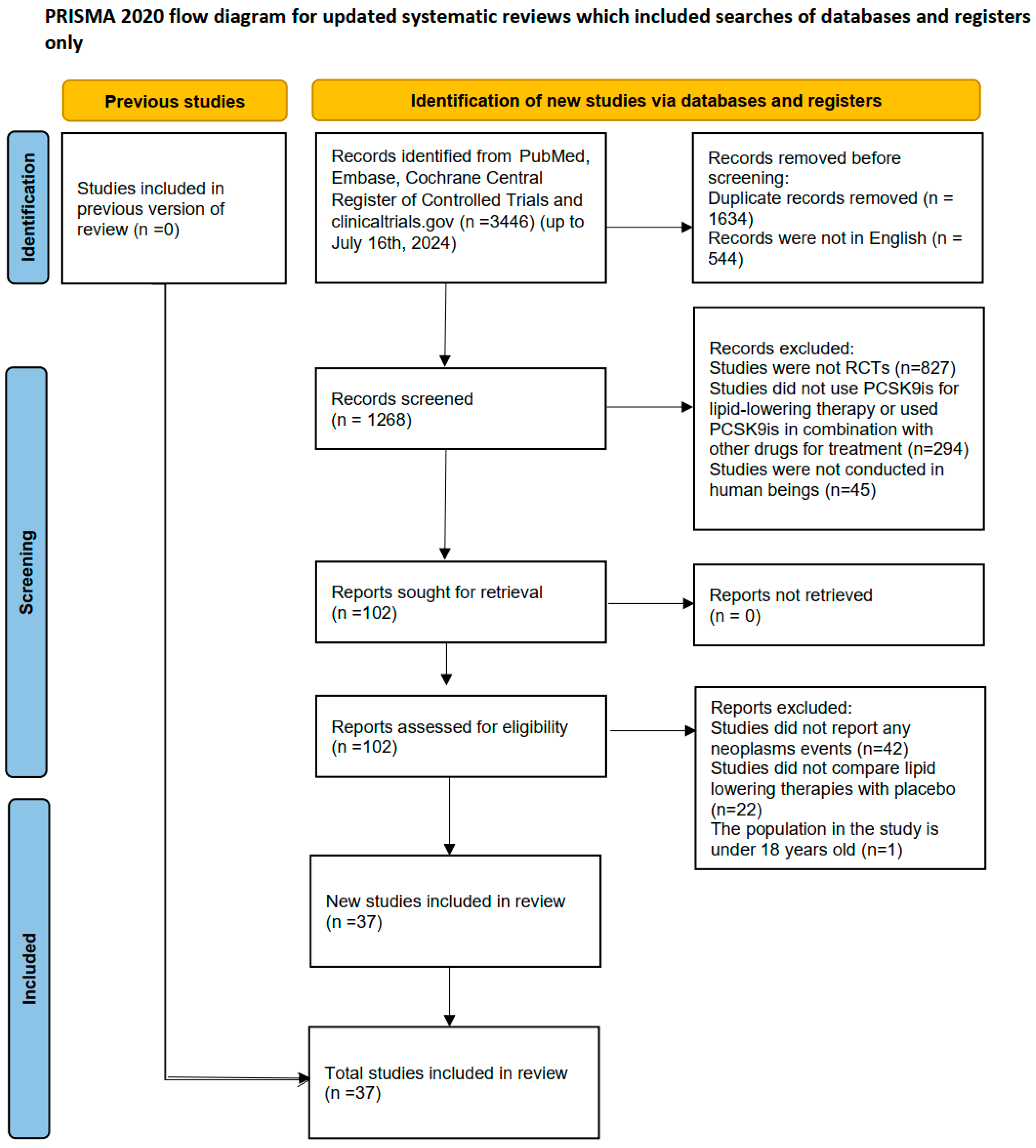
2.1. Characteristics and Quality Evaluation of Included Studies
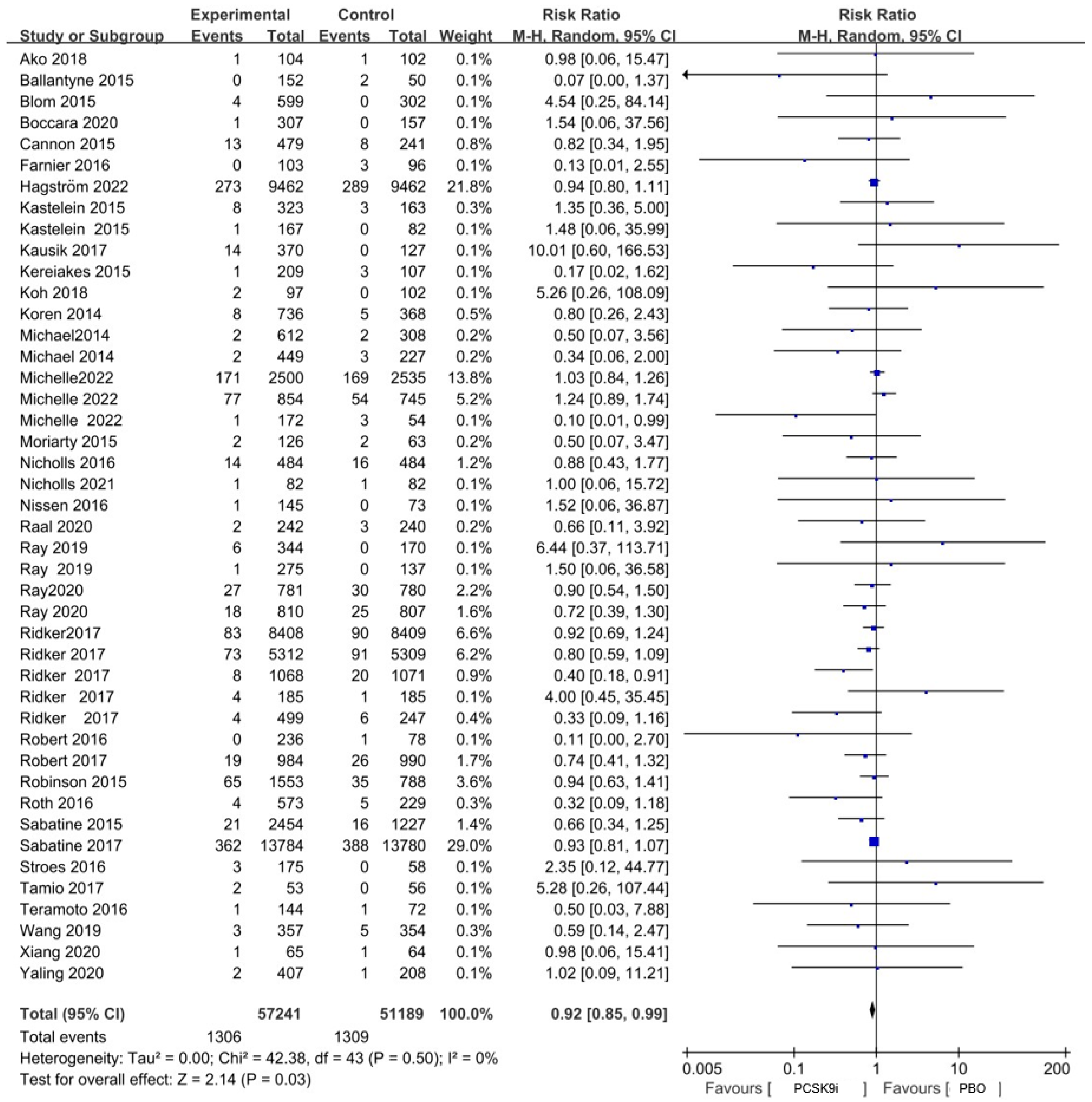
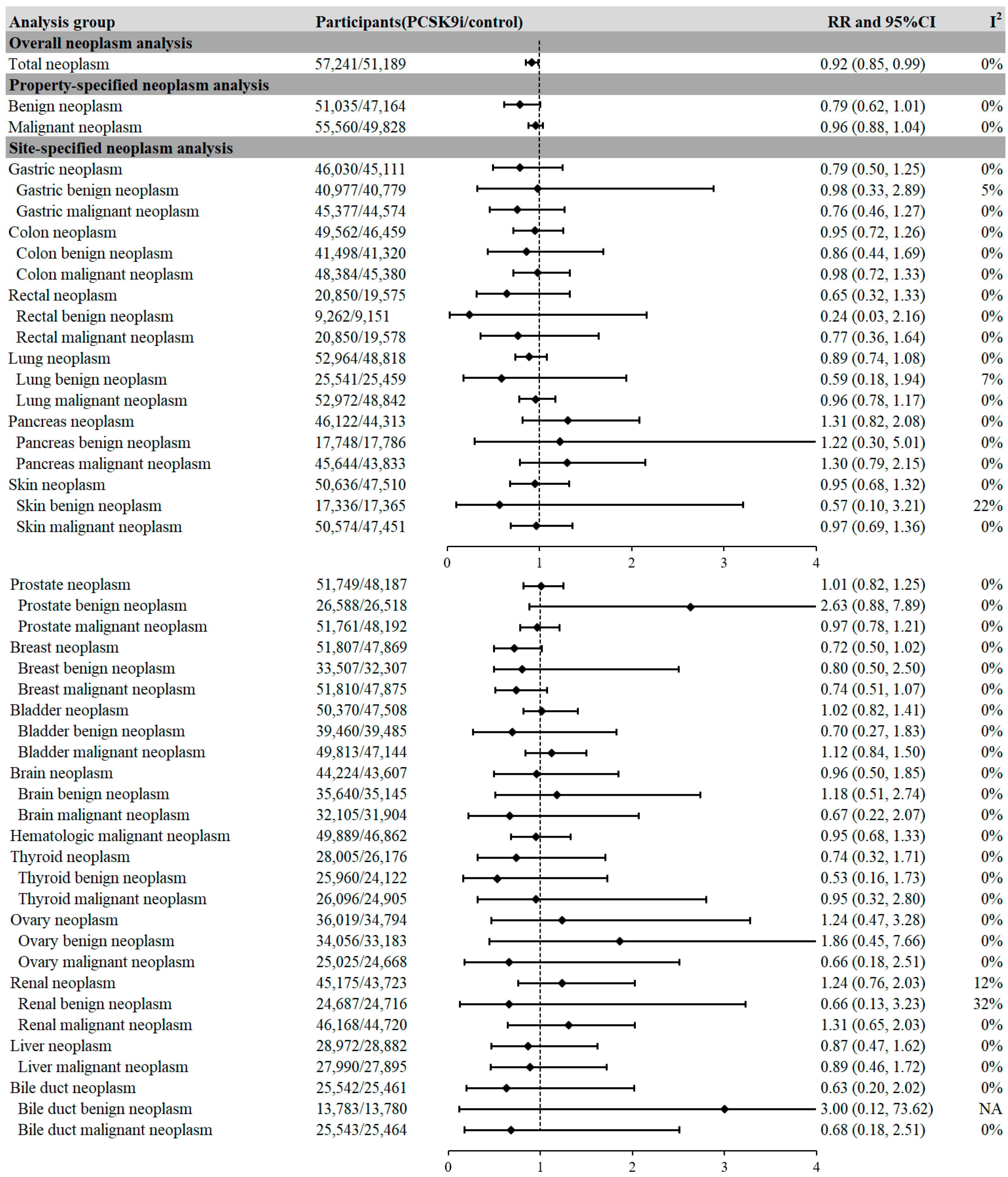
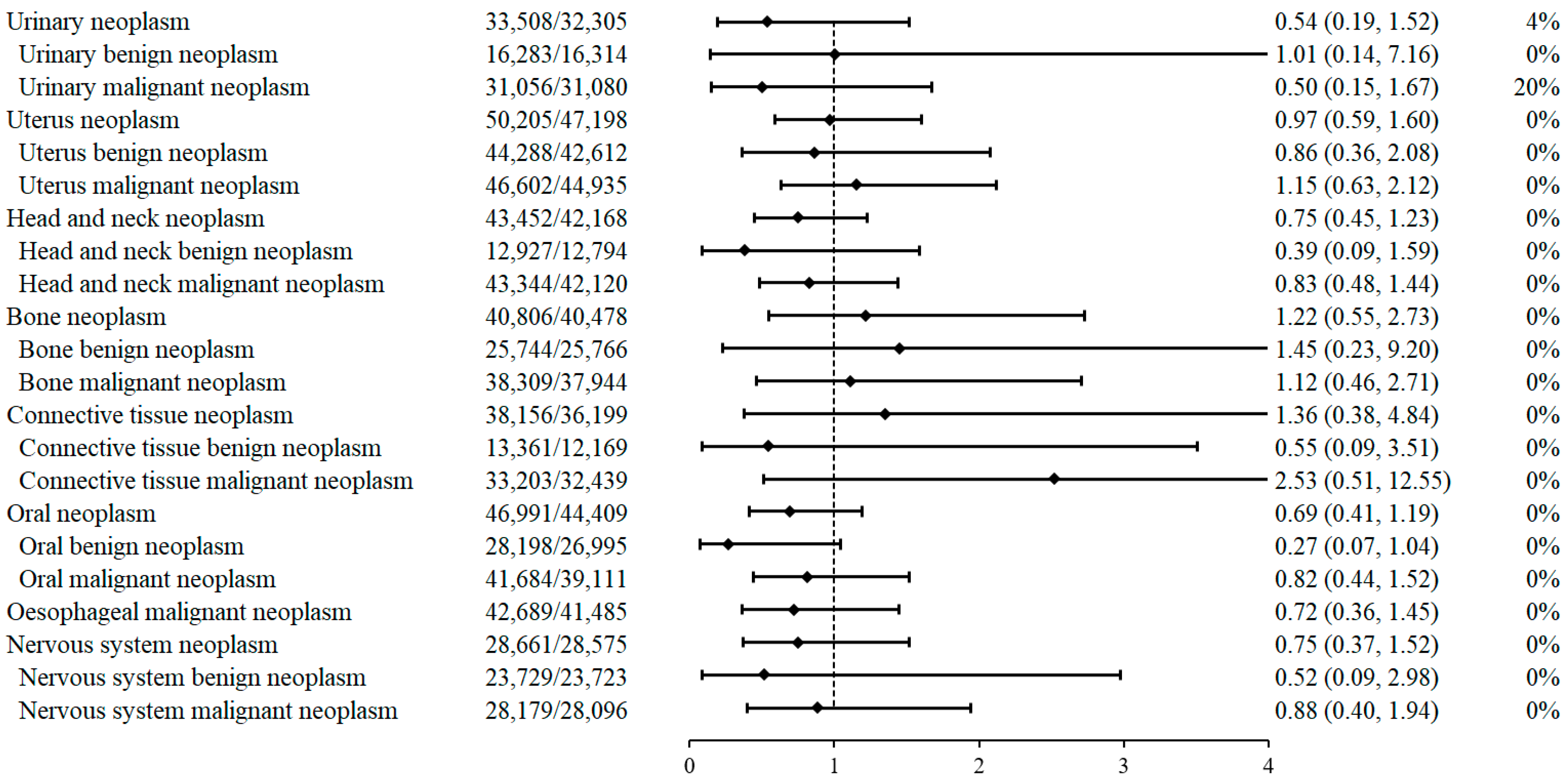
2.2. PCSK9i Treatment and the Risk of Neoplasms
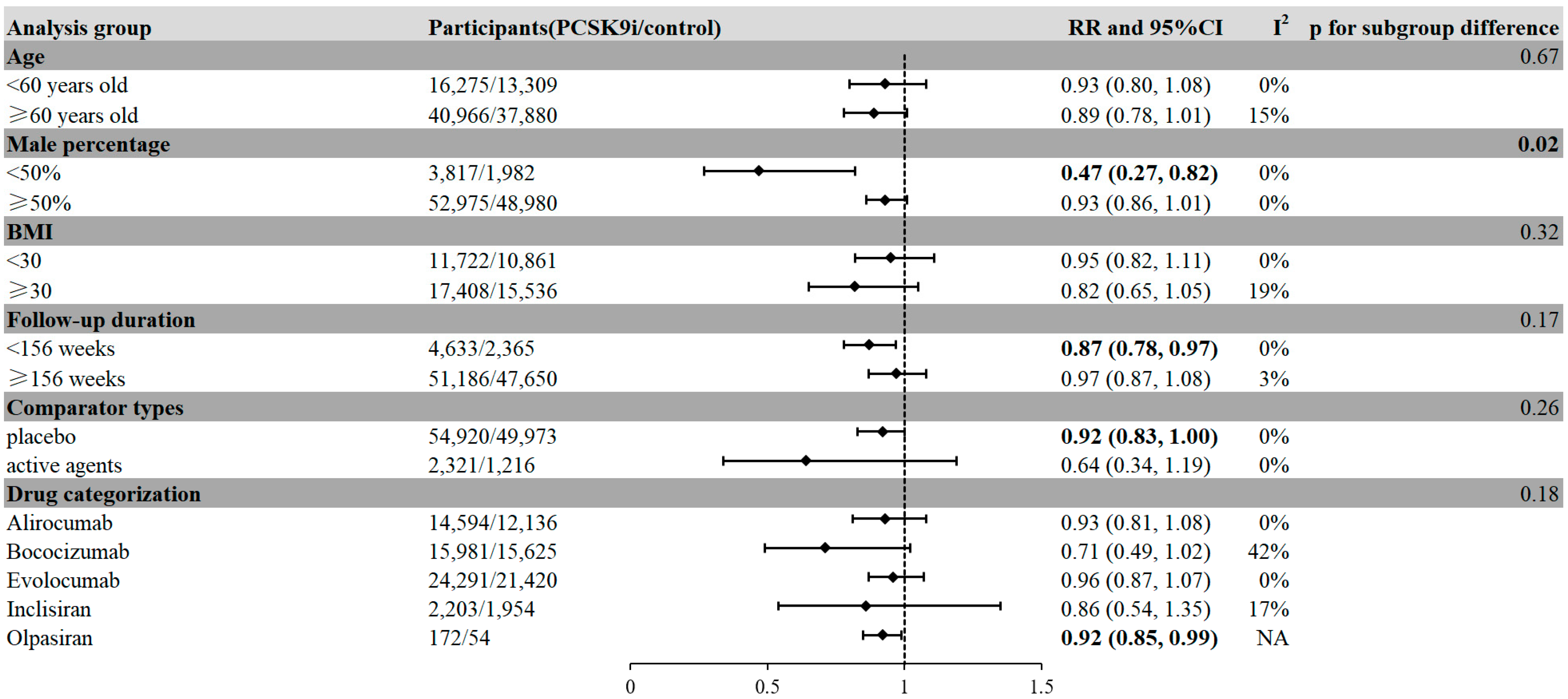
2.3. Factors Associated with Reduced Risk of Neoplasm in PCSK9i Treatment
2.4. Meta-Regression Analyses
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Design and Registration
4.2. Data Sources and Searches
4.3. Study Selection and Data Extraction
4.4. Data Synthesis and Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PCSK9i | proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 inhibitor |
| RCT | randomized controlled trial |
| LDL-c | low-density lipoprotein cholesterol |
| LDLR | low-density lipoprotein receptor |
| ASCVD | atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease |
| BMI | body mass index |
| MHC I | major histocompatibility complex class I |
| PD-1 | programmed cell death protein 1 |
| PD-L1 | programmed death-ligand 1 |
| Treg | regulatory T cell |
| IL-1α | interleukin-1 alpha |
| IL-6 | interleukin-6 |
| TNF-α | tumor necrosis factor alpha |
| NF-κB | nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells |
| THP-1 | human acute monocytic leukemia cell line |
| NK | natural killer (cell) |
| HR | hazard ratio |
| SEER | Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (program) |
| ICIs | immune checkpoint inhibitors |
| PRISMA | Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses |
| CI | confidence interval |
| RR | risk ratio |
References
- Hao, Q.; Aertgeerts, B.; Guyatt, G.; Bekkering, G.E.; Vandvik, P.O.; Khan, S.U.; Rodondi, N.; Jackson, R.; Reny, J.L.; Al Ansary, L.; et al. PCSK9 inhibitors and ezetimibe for the reduction of cardiovascular events: A clinical practice guideline with risk-stratified recommendations. Bmj 2022, 377, e069066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grundy, S.M.; Stone, N.J.; Bailey, A.L.; Beam, C.; Birtcher, K.K.; Blumenthal, R.S.; Braun, L.T.; de Ferranti, S.; Faiella-Tommasino, J.; Forman, D.E.; et al. 2018 AHA/ACC/AACVPR/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/ADA/AGS/APhA/ASPC/NLA/PCNA Guideline on the Management of Blood Cholesterol: Executive Summary: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 73, 3168–3209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.U.; Yedlapati, S.H.; Lone, A.N.; Hao, Q.; Guyatt, G.; Delvaux, N.; Bekkering, G.E.T.; Vandvik, P.O.; Riaz, I.B.; Li, S.; et al. PCSK9 inhibitors and ezetimibe with or without statin therapy for cardiovascular risk reduction: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Bmj 2022, 377, e069116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Onofrio, N.; Prattichizzo, F.; Marfella, R.; Sardu, C.; Martino, E.; Scisciola, L.; Marfella, L.; Grotta, R.; Frigé, C.; Paolisso, G.; et al. SIRT3 mediates the effects of PCSK9 inhibitors on inflammation, autophagy, and oxidative stress in endothelial cells. Theranostics 2023, 13, 531–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahboobnia, K.; Pirro, M.; Marini, E.; Grignani, F.; Bezsonov, E.E.; Jamialahmadi, T.; Sahebkar, A. PCSK9 and cancer: Rethinking the link. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 140, 111758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, W.; Chen, L.; Xia, J.; Pei, B.; Song, B.; Li, X. Causal association between lipid-lowering drugs and cancers: A drug target Mendelian randomization study. Medicine 2024, 103, e38010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Li, W.; Zhang, D.; Mi, Y.; Zhang, J.; He, G. The Causal Relationship between PCSK9 Inhibitors and Malignant Tumors: A Mendelian Randomization Study Based on Drug Targeting. Genes 2024, 15, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadi, K.A.; Brackin, T.; Schwartz, G.G.; Steg, P.G.; Szarek, M.; Manvelian, G.; Pordy, R.; Fazio, S.; Geba, G.P. Effect of proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 inhibition on cancer events: A pooled, post hoc, competing risk analysis of alirocumab clinical trials. Cancer Med. 2023, 12, 16859–16868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayengbam, S.S.; Singh, A.; Pillai, A.D.; Bhat, M.K. Influence of cholesterol on cancer progression and therapy. Transl. Oncol. 2021, 14, 101043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, X.; Tian, Z. Dyslipidemia and colorectal cancer risk: A meta-analysis of prospective studies. Cancer Causes Control 2015, 26, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rice, K.R.; Koch, M.O.; Cheng, L.; Masterson, T.A. Dyslipidemia, statins and prostate cancer. Expert Rev. Anticancer Ther. 2012, 12, 981–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, B.; Yu, M.; Sang, C.; Bi, B.; Chen, J. Dyslipidemia and non-small cell lung cancer risk in Chinese population: A case-control study. Lipids Health Dis. 2018, 17, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, J.; Zhang, C.J.; Zhu, N.; Du, K.; Yin, Y.F.; Tan, X.; Liao, D.F.; Qin, L. Lipid metabolism and carcinogenesis, cancer development. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2018, 8, 778–791. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharya, A.; Chowdhury, A.; Chaudhury, K.; Shukla, P.C. Proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9): A potential multifaceted player in cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2021, 1876, 188581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Liu, H.; He, P.; An, D.; Guo, X.; Zhang, X.; Feng, M. Inhibition of PCSK9 enhances the antitumor effect of PD-1 inhibitor in colorectal cancer by promoting the infiltration of CD8(+) T cells and the exclusion of Treg cells. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 947756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Bao, X.; Hu, M.; Chang, H.; Jiao, M.; Cheng, J.; Xie, L.; Huang, Q.; Li, F.; Li, C.Y. Inhibition of PCSK9 potentiates immune checkpoint therapy for cancer. Nature 2020, 588, 693–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, C.C.; Wu, J.L.; Ji, F.; Kang, W.; Bian, X.; Chen, H.; Chan, L.S.; Luk, S.T.Y.; Tong, S.; Xu, J.; et al. The cholesterol uptake regulator PCSK9 promotes and is a therapeutic target in APC/KRAS-mutant colorectal cancer. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Essalmani, R.; Day, R.; Khatib, A.M.; Seidah, N.G.; Prat, A. Proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 deficiency reduces melanoma metastasis in liver. Neoplasia 2012, 14, 1122–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, K.; Zhu, J.; Luo, H.H.; Yu, S.W.; Wang, L. Pro-protein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 promotes intestinal tumor development by activating Janus kinase 2/signal transducer and activator of transcription 3/SOCS3 signaling in Apc(Min/+) mice. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2021, 35, 20587384211038345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ako, J.; Hibi, K.; Kozuma, K.; Miyauchi, K.; Morino, Y.; Shinke, T.; Tsujita, K.; Uno, K.; Kawabata, Y.; Hiro, T. Effect of alirocumab on coronary atheroma volume in Japanese patients with acute coronary syndromes and hypercholesterolemia not adequately controlled with statins: ODYSSEY J-IVUS rationale and design. J. Cardiol. 2018, 71, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballantyne, C.M.; Neutel, J.; Cropp, A.; Duggan, W.; Wang, E.Q.; Plowchalk, D.; Sweeney, K.; Kaila, N.; Vincent, J.; Bays, H. Results of bococizumab, a monoclonal antibody against proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9, from a randomized, placebo-controlled, dose-ranging study in statin-treated subjects with hypercholesterolemia. Am. J. Cardiol. 2015, 115, 1212–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blom, D.J.; Hala, T.; Bolognese, M.; Lillestol, M.J.; Toth, P.D.; Burgess, L.; Ceska, R.; Roth, E.; Koren, M.J.; Ballantyne, C.M.; et al. A 52-week placebo-controlled trial of evolocumab in hyperlipidemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 1809–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boccara, F.; Kumar, P.N.; Caramelli, B.; Calmy, A.; López, J.A.G.; Bray, S.; Cyrille, M.; Rosenson, R.S. Evolocumab in HIV-Infected Patients With Dyslipidemia: Primary Results of the Randomized, Double-Blind BEIJERINCK Study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 75, 2570–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cannon, C.P.; Cariou, B.; Blom, D.; McKenney, J.M.; Lorenzato, C.; Pordy, R.; Chaudhari, U.; Colhoun, H.M. Efficacy and safety of alirocumab in high cardiovascular risk patients with inadequately controlled hypercholesterolaemia on maximally tolerated doses of statins: The ODYSSEY COMBO II randomized controlled trial. Eur. Heart J. 2015, 36, 1186–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farnier, M.; Jones, P.; Severance, R.; Averna, M.; Steinhagen-Thiessen, E.; Colhoun, H.M.; Du, Y.; Hanotin, C.; Donahue, S. Efficacy and safety of adding alirocumab to rosuvastatin versus adding ezetimibe or doubling the rosuvastatin dose in high cardiovascular-risk patients: The ODYSSEY OPTIONS II randomized trial. Atherosclerosis 2016, 244, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagström, E.; Steg, P.G.; Szarek, M.; Bhatt, D.L.; Bittner, V.A.; Danchin, N.; Diaz, R.; Goodman, S.G.; Harrington, R.A.; Jukema, J.W.; et al. Apolipoprotein B, Residual Cardiovascular Risk After Acute Coronary Syndrome, and Effects of Alirocumab. Circulation 2022, 146, 657–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kastelein, J.J.; Ginsberg, H.N.; Langslet, G.; Hovingh, G.K.; Ceska, R.; Dufour, R.; Blom, D.; Civeira, F.; Krempf, M.; Lorenzato, C.; et al. ODYSSEY FH I and FH II: 78 week results with alirocumab treatment in 735 patients with heterozygous familial hypercholesterolaemia. Eur. Heart J. 2015, 36, 2996–3003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ray, K.K.; Landmesser, U.; Leiter, L.A.; Kallend, D.; Dufour, R.; Karakas, M.; Hall, T.; Troquay, R.P.; Turner, T.; Visseren, F.L.; et al. Inclisiran in Patients at High Cardiovascular Risk with Elevated LDL Cholesterol. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 1430–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kereiakes, D.J.; Robinson, J.G.; Cannon, C.P.; Lorenzato, C.; Pordy, R.; Chaudhari, U.; Colhoun, H.M. Efficacy and safety of the proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 inhibitor alirocumab among high cardiovascular risk patients on maximally tolerated statin therapy: The ODYSSEY COMBO I study. Am. Heart J. 2015, 169, 906–915.e913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koh, K.K.; Nam, C.W.; Chao, T.H.; Liu, M.E.; Wu, C.J.; Kim, D.S.; Kim, C.J.; Li, I.; Li, J.; Baccara-Dinet, M.T.; et al. A randomized trial evaluating the efficacy and safety of alirocumab in South Korea and Taiwan (ODYSSEY KT). J. Clin. Lipidol. 2018, 12, 162–172.e166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koren, M.J.; Giugliano, R.P.; Raal, F.J.; Sullivan, D.; Bolognese, M.; Langslet, G.; Civeira, F.; Somaratne, R.; Nelson, P.; Liu, T.; et al. Efficacy and safety of longer-term administration of evolocumab (AMG 145) in patients with hypercholesterolemia: 52-week results from the Open-Label Study of Long-Term Evaluation Against LDL-C (OSLER) randomized trial. Circulation 2014, 129, 234–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Donoghue, M.L.; Rosenson, R.S.; Gencer, B.; López, J.A.G.; Lepor, N.E.; Baum, S.J.; Stout, E.; Gaudet, D.; Knusel, B.; Kuder, J.F.; et al. Small Interfering RNA to Reduce Lipoprotein(a) in Cardiovascular Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 1855–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moriarty, P.M.; Thompson, P.D.; Cannon, C.P.; Guyton, J.R.; Bergeron, J.; Zieve, F.J.; Bruckert, E.; Jacobson, T.A.; Baccara-Dinet, M.T.; Zhao, J.; et al. Efficacy and safety of alirocumab in statin-intolerant patients over 3 years: Open-label treatment period of the ODYSSEY ALTERNATIVE trial. J. Clin. Lipidol. 2020, 14, 88–97.e82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicholls, S.J.; Puri, R.; Anderson, T.; Ballantyne, C.M.; Cho, L.; Kastelein, J.J.; Koenig, W.; Somaratne, R.; Kassahun, H.; Yang, J.; et al. Effect of Evolocumab on Progression of Coronary Disease in Statin-Treated Patients: The GLAGOV Randomized Clinical Trial. Jama 2016, 316, 2373–2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicholls, S.J.; Kataoka, Y.; Nissen, S.E.; Prati, F.; Windecker, S.; Puri, R.; Hucko, T.; Aradi, D.; Herrman, J.R.; Hermanides, R.S.; et al. Effect of Evolocumab on Coronary Plaque Phenotype and Burden in Statin-Treated Patients Following Myocardial Infarction. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2022, 15, 1308–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nissen, S.E.; Stroes, E.; Dent-Acosta, R.E.; Rosenson, R.S.; Lehman, S.J.; Sattar, N.; Preiss, D.; Bruckert, E.; Ceška, R.; Lepor, N.; et al. Efficacy and Tolerability of Evolocumab vs Ezetimibe in Patients With Muscle-Related Statin Intolerance: The GAUSS-3 Randomized Clinical Trial. Jama 2016, 315, 1580–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raal, F.J.; Kallend, D.; Ray, K.K.; Turner, T.; Koenig, W.; Wright, R.S.; Wijngaard, P.L.J.; Curcio, D.; Jaros, M.J.; Leiter, L.A.; et al. Inclisiran for the Treatment of Heterozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1520–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ray, K.K.; Leiter, L.A.; Müller-Wieland, D.; Cariou, B.; Colhoun, H.M.; Henry, R.R.; Tinahones, F.J.; Bujas-Bobanovic, M.; Domenger, C.; Letierce, A.; et al. Alirocumab vs usual lipid-lowering care as add-on to statin therapy in individuals with type 2 diabetes and mixed dyslipidaemia: The ODYSSEY DM-DYSLIPIDEMIA randomized trial. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2018, 20, 1479–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ray, K.K.; Wright, R.S.; Kallend, D.; Koenig, W.; Leiter, L.A.; Raal, F.J.; Bisch, J.A.; Richardson, T.; Jaros, M.; Wijngaard, P.L.J.; et al. Two Phase 3 Trials of Inclisiran in Patients with Elevated LDL Cholesterol. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1507–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridker, P.M.; Revkin, J.; Amarenco, P.; Brunell, R.; Curto, M.; Civeira, F.; Flather, M.; Glynn, R.J.; Gregoire, J.; Jukema, J.W.; et al. Cardiovascular Efficacy and Safety of Bococizumab in High-Risk Patients. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 1527–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridker, P.M.; Tardif, J.C.; Amarenco, P.; Duggan, W.; Glynn, R.J.; Jukema, J.W.; Kastelein, J.J.P.; Kim, A.M.; Koenig, W.; Nissen, S.; et al. Lipid-Reduction Variability and Antidrug-Antibody Formation with Bococizumab. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 1517–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giugliano, R.P.; Desai, N.R.; Kohli, P.; Rogers, W.J.; Somaratne, R.; Huang, F.; Liu, T.; Mohanavelu, S.; Hoffman, E.B.; McDonald, S.T.; et al. Efficacy, safety, and tolerability of a monoclonal antibody to proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 in combination with a statin in patients with hypercholesterolaemia (LAPLACE-TIMI 57): A randomised, placebo-controlled, dose-ranging, phase 2 study. Lancet 2012, 380, 2007–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giugliano, R.P.; Mach, F.; Zavitz, K.; Kurtz, C.; Im, K.; Kanevsky, E.; Schneider, J.; Wang, H.; Keech, A.; Pedersen, T.R.; et al. Cognitive Function in a Randomized Trial of Evolocumab. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 633–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, J.G.; Farnier, M.; Krempf, M.; Bergeron, J.; Luc, G.; Averna, M.; Stroes, E.S.; Langslet, G.; Raal, F.J.; El Shahawy, M.; et al. Efficacy and safety of alirocumab in reducing lipids and cardiovascular events. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 1489–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roth, E.M.; Moriarty, P.M.; Bergeron, J.; Langslet, G.; Manvelian, G.; Zhao, J.; Baccara-Dinet, M.T.; Rader, D.J. A phase III randomized trial evaluating alirocumab 300 mg every 4 weeks as monotherapy or add-on to statin: ODYSSEY CHOICE I. Atherosclerosis 2016, 254, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabatine, M.S.; Giugliano, R.P.; Wiviott, S.D.; Raal, F.J.; Blom, D.J.; Robinson, J.; Ballantyne, C.M.; Somaratne, R.; Legg, J.; Wasserman, S.M.; et al. Efficacy and safety of evolocumab in reducing lipids and cardiovascular events. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 1500–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabatine, M.S.; Giugliano, R.P.; Keech, A.C.; Honarpour, N.; Wiviott, S.D.; Murphy, S.A.; Kuder, J.F.; Wang, H.; Liu, T.; Wasserman, S.M.; et al. Evolocumab and Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Cardiovascular Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 1713–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stroes, E.; Guyton, J.R.; Lepor, N.; Civeira, F.; Gaudet, D.; Watts, G.F.; Baccara-Dinet, M.T.; Lecorps, G.; Manvelian, G.; Farnier, M. Efficacy and Safety of Alirocumab 150 mg Every 4 Weeks in Patients With Hypercholesterolemia Not on Statin Therapy: The ODYSSEY CHOICE II Study. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2016, 5, 3421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teramoto, T.; Kondo, A.; Kiyosue, A.; Harada-Shiba, M.; Ishigaki, Y.; Tobita, K.; Kawabata, Y.; Ozaki, A.; Baccara-Dinet, M.T.; Sata, M. Efficacy and safety of alirocumab in patients with hypercholesterolemia not adequately controlled with non-statin lipid-lowering therapy or the lowest strength of statin: ODYSSEY NIPPON study design and rationale. Lipids Health Dis. 2017, 16, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teramoto, T.; Kobayashi, M.; Tasaki, H.; Yagyu, H.; Higashikata, T.; Takagi, Y.; Uno, K.; Baccara-Dinet, M.T.; Nohara, A. Efficacy and Safety of Alirocumab in Japanese Patients With Heterozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia or at High Cardiovascular Risk With Hypercholesterolemia Not Adequately Controlled With Statins—ODYSSEY JAPAN Randomized Controlled Trial. Circ. J. 2016, 80, 1980–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, S.L.; Flanagan, K.L. Sex differences in immune responses. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 626–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Stiekema, L.C.A.; Stroes, E.S.G.; Groen, A.K. Metabolic effects of PCSK9 inhibition with Evolocumab in subjects with elevated Lp(a). Lipids Health Dis. 2020, 19, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Chen, J.; Chopra, V.K.; Zhang, S.; Su, G.; Ma, C.; Huang, Z.; Ma, Y.; Yao, Z.; Yuan, Z.; et al. ODYSSEY EAST: Alirocumab efficacy and safety vs ezetimibe in high cardiovascular risk patients with hypercholesterolemia and on maximally tolerated statin in China, India, and Thailand. J. Clin. Lipidol. 2020, 14, 98–108.e108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Z.; Jiang, L.; Peng, J.; Ren, Z.; Wei, D.; Wu, C.; Pan, L.; Jiang, Z.; Liu, L. PCSK9 siRNA suppresses the inflammatory response induced by oxLDL through inhibition of NF-κB activation in THP-1-derived macrophages. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2012, 30, 931–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alannan, M.; Seidah, N.G.; Merched, A.J. PCSK9 in Liver Cancers at the Crossroads between Lipid Metabolism and Immunity. Cells 2022, 11, 4132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Ma, J.; Li, S.; Liu, C.; Liu, Y.; Chen, J.; Liu, N.; Liu, S.; Huang, H. Sex difference in human diseases: Mechanistic insights and clinical implications. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Shao, X.; Wang, X.; Liu, L.; Liang, H. Sex disparities in cancer. Cancer Lett. 2019, 466, 35–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haupt, S.; Caramia, F.; Klein, S.L.; Rubin, J.B.; Haupt, Y. Sex disparities matter in cancer development and therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2021, 21, 393–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clocchiatti, A.; Cora, E.; Zhang, Y.; Dotto, G.P. Sexual dimorphism in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2016, 16, 330–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kesteloot, H. On the sex ratio of all-cause and disease-specific mortality rates worldwide. Verh. K. Acad. Geneeskd. Belg. 2007, 69, 105–130. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Benigni, R. Social sexual inequality and sex difference in cancer incidence. Environ. Res. 2007, 104, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oksuzyan, A.; Juel, K.; Vaupel, J.W.; Christensen, K. Men: Good health and high mortality. Sex differences in health and aging. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2008, 20, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, M.B.; Dawsey, S.M.; Freedman, N.D.; Inskip, P.D.; Wichner, S.M.; Quraishi, S.M.; Devesa, S.S.; McGlynn, K.A. Sex disparities in cancer incidence by period and age. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 2009, 18, 1174–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Dikshit, R.; Eser, S.; Mathers, C.; Rebelo, M.; Parkin, D.M.; Forman, D.; Bray, F. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 136, E359–E386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- OuYang, P.Y.; Zhang, L.N.; Lan, X.W.; Xie, C.; Zhang, W.W.; Wang, Q.X.; Su, Z.; Tang, J.; Xie, F.Y. The significant survival advantage of female sex in nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A propensity-matched analysis. Br. J. Cancer 2015, 112, 1554–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wisnivesky, J.P.; Halm, E.A. Sex differences in lung cancer survival: Do tumors behave differently in elderly women? J. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 25, 1705–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, F.; Fei, S.F.; Tong, D.B.; Xue, C.; Li, J.J. Sex difference in circulating PCSK9 and its clinical implications. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 953845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferri, N.; Ruscica, M.; Coggi, D.; Bonomi, A.; Amato, M.; Frigerio, B.; Sansaro, D.; Ravani, A.; Veglia, F.; Capra, N.; et al. Sex-specific predictors of PCSK9 levels in a European population: The IMPROVE study. Atherosclerosis 2020, 309, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, J.; Zhang, W.; Niu, Y.; Lin, N.; Li, X.; Zhang, H.; Hu, R.; Ning, G.; Fan, J.; Qin, L.; et al. Association of circulating proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 levels and the risk of incident type 2 diabetes in subjects with prediabetes: A population-based cohort study. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2020, 19, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Wei, T.F.; Zhao, B.; Yin, Z.; Shi, Q.X.; Liu, P.L.; Liu, L.F.; Liu, L.; Zhao, J.T.; Mao, S.; et al. Sex Differences Associated With Circulating PCSK9 in Patients Presenting With Acute Myocardial Infarction. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levenson, A.E.; Shah, A.S.; Khoury, P.R.; Kimball, T.R.; Urbina, E.M.; de Ferranti, S.D.; Maahs, D.M.; Dolan, L.M.; Wadwa, R.P.; Biddinger, S.B. Obesity and type 2 diabetes are associated with elevated PCSK9 levels in young women. Pediatr. Diabetes 2017, 18, 755–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Cowley, L.A.; Liu, X.S. Sex Differences in Cancer Immunotherapy Efficacy, Biomarkers, and Therapeutic Strategy. Molecules 2019, 24, 3214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pala, L.; De Pas, T.; Catania, C.; Giaccone, G.; Mantovani, A.; Minucci, S.; Viale, G.; Gelber, R.D.; Conforti, F. Sex and cancer immunotherapy: Current understanding and challenges. Cancer Cell 2022, 40, 695–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conforti, F.; Pala, L.; Bagnardi, V.; De Pas, T.; Martinetti, M.; Viale, G.; Gelber, R.D.; Goldhirsch, A. Cancer immunotherapy efficacy and patients’ sex: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2018, 19, 737–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. Ann. Intern. Med. 2009, 151, 264–269, w64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leiter, L.A.; Cariou, B.; Müller-Wieland, D.; Colhoun, H.M.; Del Prato, S.; Tinahones, F.J.; Ray, K.K.; Bujas-Bobanovic, M.; Domenger, C.; Mandel, J.; et al. Efficacy and safety of alirocumab in insulin-treated individuals with type 1 or type 2 diabetes and high cardiovascular risk: The ODYSSEY DM-INSULIN randomized trial. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2017, 19, 1781–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, G.G.; Bessac, L.; Berdan, L.G.; Bhatt, D.L.; Bittner, V.; Diaz, R.; Goodman, S.G.; Hanotin, C.; Harrington, R.A.; Jukema, J.W.; et al. Effect of alirocumab, a monoclonal antibody to PCSK9, on long-term cardiovascular outcomes following acute coronary syndromes: Rationale and design of the ODYSSEY outcomes trial. Am. Heart J. 2014, 168, 682–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Donoghue, M.L.; Giugliano, R.P.; Wiviott, S.D.; Atar, D.; Keech, A.; Kuder, J.F.; Im, K.; Murphy, S.A.; Flores-Arredondo, J.H.; López, J.A.G.; et al. Long-Term Evolocumab in Patients With Established Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease. Circulation 2022, 146, 1109–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koren, M.J.; Lundqvist, P.; Bolognese, M.; Neutel, J.M.; Monsalvo, M.L.; Yang, J.; Kim, J.B.; Scott, R.; Wasserman, S.M.; Bays, H. Anti-PCSK9 monotherapy for hypercholesterolemia: The MENDEL-2 randomized, controlled phase III clinical trial of evolocumab. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2014, 63, 2531–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, J.G.; Nedergaard, B.S.; Rogers, W.J.; Fialkow, J.; Neutel, J.M.; Ramstad, D.; Somaratne, R.; Legg, J.C.; Nelson, P.; Scott, R.; et al. Effect of evolocumab or ezetimibe added to moderate- or high-intensity statin therapy on LDL-C lowering in patients with hypercholesterolemia: The LAPLACE-2 randomized clinical trial. Jama 2014, 311, 1870–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wei, T.; Li, Z.; Lin, C.; Yang, Y.; Tie, C.; Cai, X.; Lv, F.; Yang, W.; Ji, L. PCSK9 Inhibitor and Potential Decreased Risk of Neoplasms, Especially in Females: A Meta-Analysis. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 1095. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18081095
Wei T, Li Z, Lin C, Yang Y, Tie C, Cai X, Lv F, Yang W, Ji L. PCSK9 Inhibitor and Potential Decreased Risk of Neoplasms, Especially in Females: A Meta-Analysis. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(8):1095. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18081095
Chicago/Turabian StyleWei, Tingyang, Zonglin Li, Chu Lin, Yuteng Yang, Changjie Tie, Xiaoling Cai, Fang Lv, Wenjia Yang, and Linong Ji. 2025. "PCSK9 Inhibitor and Potential Decreased Risk of Neoplasms, Especially in Females: A Meta-Analysis" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 8: 1095. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18081095
APA StyleWei, T., Li, Z., Lin, C., Yang, Y., Tie, C., Cai, X., Lv, F., Yang, W., & Ji, L. (2025). PCSK9 Inhibitor and Potential Decreased Risk of Neoplasms, Especially in Females: A Meta-Analysis. Pharmaceuticals, 18(8), 1095. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18081095





