Pharmacogenetic Biomarkers of Ibrutinib Response and Toxicity in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: Insights from an Observational Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Genotypic Frequencies
2.2. Ibrutinib Plasma Concentrations
2.3. Response Achieved
2.4. Analysis of Toxicity
2.5. Influence of Genotypes on Ibrutinib Plasma Concentrations, Response, and ADRs
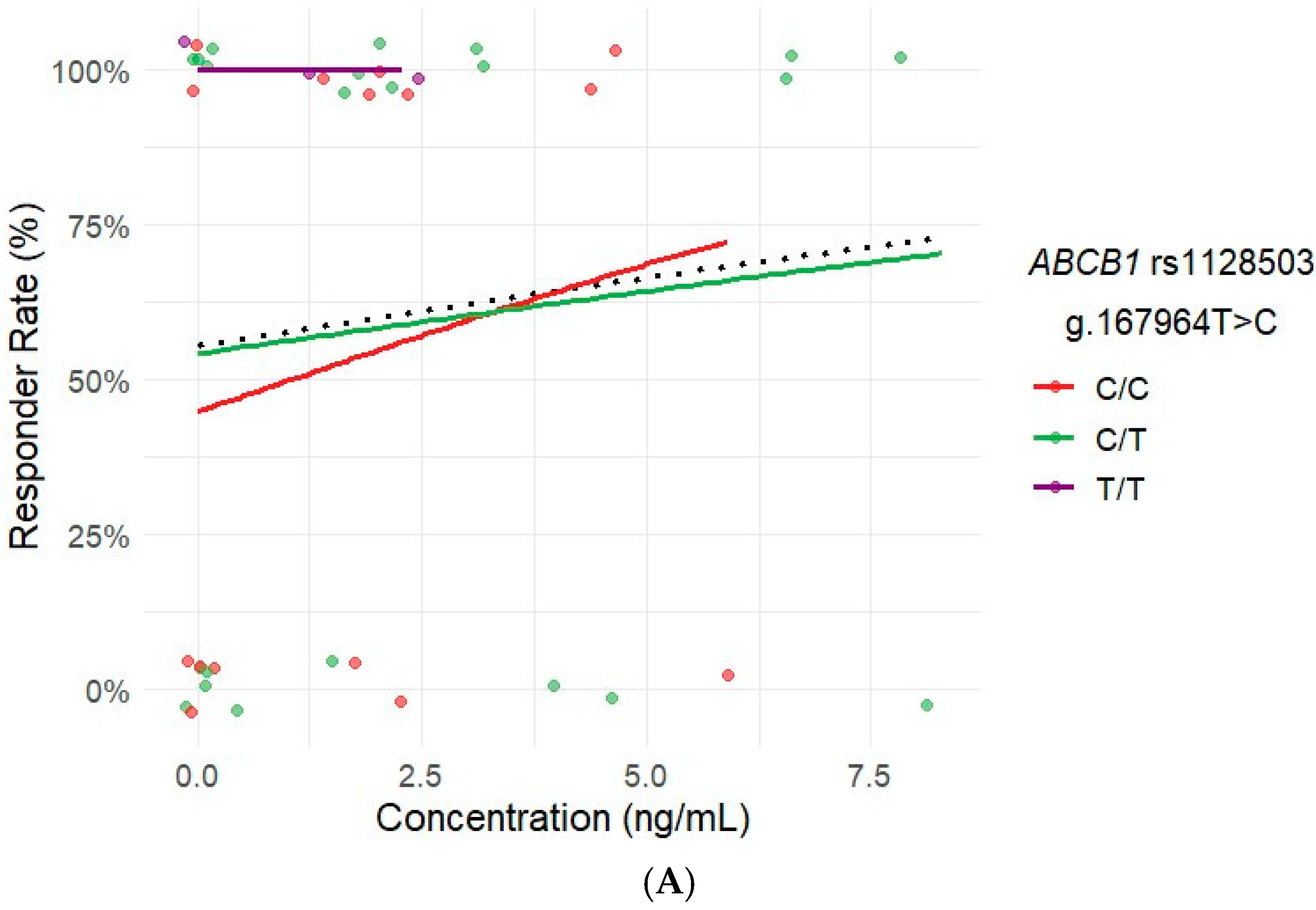
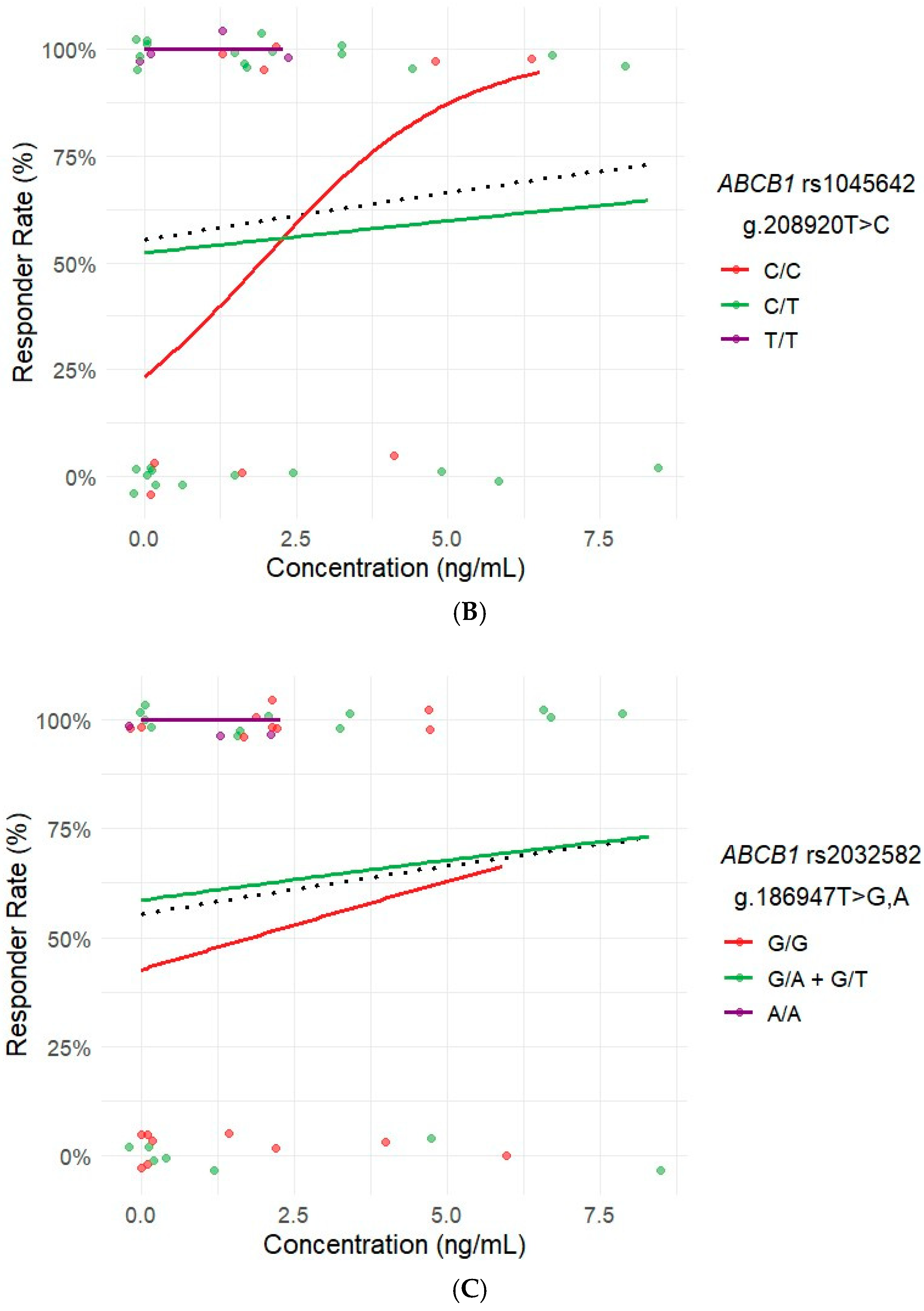
2.6. Influence of Ibrutinib Plasma Concentrations on Response and ADRs
2.7. Influence of Concomitant Medication on Response and ADRs
3. Discussion
Study Limitations
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Population, Design, and Procedures
4.2. Genotyping
4.3. Measurement of Ibrutinib Plasma Concentrations
4.4. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fuentes-Pananá, E.M.; Bannish, G.; Monroe, J.G. Basal B-cell receptor signaling in B lymphocytes: Mechanisms of regulation and role in positive selection, differentiation, and peripheral survival. Immunol. Rev. 2004, 197, 26–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Küppers, R. Mechanisms of B-cell lymphoma pathogenesis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2005, 5, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agencia Española de Medicamentos y Productos Sanitarios (AEMPS). Ficha Técnica del Ibrutinib. Ministerio de Sanidad. Available online: https://cima.aemps.es/cima/dochtml/ft/114945002/FT_114945002.html (accessed on 28 February 2025).
- Honigberg, L.A.; Smith, A.M.; Sirisawad, M.; Verner, E.; Loury, D.; Chang, B.; Li, S.; Pan, Z.; Thamm, D.H.; Miller, R.A.; et al. The Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor PCI-32765 blocks B-cell activation and is efficacious in models of autoimmune disease and B-cell malignancy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 13075–13080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vries, R.; Smit, J.W.; Hellemans, P.; Jiao, J.; Murphy, J.; Skee, D.; Snoeys, J.; Sukbuntherng, J.; Vliegen, M.; de Zwart, L.; et al. Stable isotope-labelled intravenous microdose for absolute bioavailability and effect of grapefruit juice on ibrutinib in healthy adults. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2016, 81, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanger, U.M.; Klein, K.; Thomas, M.; Rieger, J.K.; Tremmel, R.; A Kandel, B.; Klein, M.; Magdy, T. Genetics, Epigenetics, and Regulation of Drug-Metabolizing Cytochrome P450 Enzymes. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 95, 258–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apellaniz-Ruiz, M.; Inglada, L.; Naranjo, M.E.G.; Sanchez, L.P.M.; Mancikova, V.; Currasfreixes, M.; de Cubas, A.A.; Comino-Mendez, I.; Triki, S.; Rebai, A.; et al. High frequency and founder effect of the CYP3A4*20 loss-of-function allele in the Spanish population classifies CYP3A4 as a polymorphic enzyme. Pharm. J. 2015, 15, 288–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuehl, P.; Zhang, J.; Lin, Y.; Lamba, J.; Assem, M.; Schuetz, J.; Watkins, P.B.; Daly, A.; Wrighton, S.A.; Hall, S.D.; et al. Sequence diversity in CYP3A promoters and characterization of the genetic basis of polymorphic CYP3A5 expression. Nat. Genet. 2001, 27, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jong, J.; Skee, D.; Murphy, J.; Sukbuntherng, J.; Hellemans, P.; Smit, J.; de Vries, R.; Jiao, J.J.; Snoeys, J.; Mannaert, E. Effect of CYP3A perpetrators on ibrutinib exposure in healthy participants. Pharmacol. Res. Perspect. 2015, 3, e00156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rood, J.J.M.; Jamalpoor, A.; van Hoppe, S.; van Haren, M.J.; Wasmann, R.E.; Janssen, M.J.; Schinkel, A.H.; Masereeuw, R.; Beijnen, J.H.; Sparidans, R.W. Extrahepatic metabolism of ibrutinib. Investig. New Drugs 2021, 39, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senagore, A.J.; Champagne, B.J.; Dosokey, E.; Brady, J.; Steele, S.R.; Reynolds, H.L.; Stein, S.L.; Delaney, C.P. Pharmacogenetics-guided analgesics in major abdominal surgery: Further benefits within an enhanced recovery protocol. Am. J. Surg. 2017, 213, 467–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dessilly, G.; Panin, N.; Elens, L.; Haufroid, V.; Demoulin, J.B. Impact of ABCB1 1236C > T-2677G > T-3435C > T polymorphisms on the anti-proliferative activity of imatinib, nilotinib, dasatinib and ponatinib. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 29559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schinkel, A.; Smit, J.; van Tellingen, O.; Beijnen, J.; Wagenaar, E.; van Deemter, L.; Mol, C.; van der Valk, M.; Robanus-Maandag, E.; Riele, H.T.; et al. Disruption of the mouse mdr1a P-glycoprotein gene leads to a deficiency in the blood-brain barrier and to increased sensitivity to drugs. Cell 1994, 77, 491–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schinkel, A.H.; Mayer, U.; Wagenaar, E.; Mol, C.A.A.M.; van Deemter, L.; Smit, J.J.M.; van der Valk, M.A.; Voordouw, A.C.; Spits, H.; van Tellingen, O.; et al. Normal viability and altered pharmacokinetics in mice lacking mdr1-type (drug-transporting) P-glycoproteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 4028–4033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.H.; Wang, Y.H.; Li, Y.; Yang, L. MDR1 gene polymorphisms and clinical relevance. Yi Chuan Xue Bao 2006, 33, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Hoppe, S.; Rood, J.J.; Buil, L.; Wagenaar, E.; Sparidans, R.W.; Beijnen, J.H.; Schinkel, A.H. P-Glycoprotein (MDR1/ABCB1) Restricts Brain Penetration of the Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Ibrutinib, While Cytochrome P450-3A (CYP3A) Limits Its Oral Bioavailability. Mol. Pharm. 2018, 15, 5124–5134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.M.; Choi, K.H.; Lee, H.H.; Gwak, H.S. Association between SLCO1B1 polymorphism and methotrexate-induced hepatotoxicity: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Anti-Cancer Drugs 2022, 33, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.P.S.; McMullen, J.; Tam, C. Cardiac side effects of bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitors. Leuk. Lymphoma 2018, 59, 1554–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mato, A.R.; Nabhan, C.; Thompson, M.C.; Lamanna, N.; Brander, D.M.; Hill, B.; Howlett, C.; Skarbnik, A.; Cheson, B.D.; Zent, C.; et al. Toxicities and outcomes of 616 ibrutinib-treated patients in the United States: A real-world analysis. Haematologica 2018, 103, 874–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuttall, E.; Tung, J.; Trounce, E.; Johnston, R.; Chevassut, T. Real-world experience of ibrutinib therapy in relapsed chronic lymphocytic leukemia: Results of a single-center retrospective analysis. J. Blood Med. 2019, 10, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, J.-E.; Manouchehri, A.; Bretagne, M.; Lebrun-Vignes, B.; Groarke, J.D.; Johnson, D.B.; Yang, T.; Reddy, N.M.; Funck-Brentano, C.; Brown, J.R.; et al. Cardiovascular Toxicities Associated With Ibrutinib. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 74, 1667–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genomes Project Consortium; Auton, A.; Brooks, L.D.; Durbin, R.M.; Garrison, E.P.; Kang, H.M.; Korbel, J.O.; Marchini, J.L.; McCarthy, S.; McVean, G.A.; et al. A global reference for human genetic variation. Nature 2015, 526, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Prajapati, P.; Patel, A.; Desai, A.; Shah, P.; Pulusu, V.S.; Haque, A.; Kalam, M.A.; Shah, S. In-vivo pharmacokinetic study of ibrutinib-loaded nanostructured lipid carriers in rat plasma by sensitive spectrofluorimetric method using harmonized approach of quality by design and white analytical chemistry. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2024, 321, 124731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barr, P.M.; Robak, T.; Owen, C.; Tedeschi, A.; Bairey, O.; Bartlett, N.L.; Burger, J.A.; Hillmen, P.; Coutre, S.; Devereux, S.; et al. Sustained efficacy and detailed clinical follow-up of first-line ibrutinib treatment in older patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia: Extended phase 3 results from RESONATE-2. Haematologica 2018, 103, 1502–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marini, B.L.; Samanas, L.; Perissinotti, A.J. Expanding the armamentarium for chronic lymphocytic leukemia: A review of novel agents in the management of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. J. Oncol. Pharm. Pract. 2017, 23, 502–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardy-Abeloos, C.; Pinotti, R.; Gabrilove, J. Ibrutinib dose modifications in the management of CLL. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 13, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguirre, C.; García, M. Evaluación de la causalidad en las comunicaciones de reacciones adversas a medicamentos. Algoritmo del Sistema Español de Farmacovigilancia. Med. Clínica 2016, 147, 461–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlson, M.E.; Pompei, P.; Ales, K.L.; MacKenzie, C.R. A new method of classifying prognostic comorbidity in longitudinal studies: Development and validation. J. Chronic Dis. 1987, 40, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saiz-Rodríguez, M.; Almenara, S.; Navares-Gómez, M.; Ochoa, D.; Román, M.; Zubiaur, P.; Koller, D.; Santos, M.; Mejía, G.; Borobia, A.M.; et al. Effect of the Most Relevant CYP3A4 and CYP3A5 Polymorphisms on the Pharmacokinetic Parameters of 10 CYP3A Substrates. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, T. Omeprazole Drug Interaction Studies. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 1991, 21, 195–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grupo Español de Leucemia Linfocítica Cronica. Clinical Practice Guide for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Chronic Lympocytic Leukemia and Small Cell Lympocytic Lymphoma. Available online: https://www.gellc.es/guias-clinicas/24-guia-gellc-2024-pdf/file (accessed on 18 June 2025).
- Koller, D.; Vaitsekhovich, V.; Mba, C.; Steegmann, J.L.; Zubiaur, P.; Abad-Santos, F.; Wojnicz, A. Effective quantification of 11 tyrosine kinase inhibitors and caffeine in human plasma by validated LC-MS/MS method with potent phospholipids clean-up procedure. Application to therapeutic drug monitoring. Talanta 2020, 208, 120450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotta, V.; Widmer, N.; Montemurro, M.; Leyvraz, S.; Haouala, A.; Decosterd, L.A.; Csajka, C.; Buclin, T. Therapeutic Drug Monitoring of Imatinib: Bayesian and Alternative Methods to Predict Trough Levels. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2012, 51, 187–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variable | N (%) or Mean (SD) |
|---|---|
| Sex | |
| Men | 35 (71) |
| Women | 14 (29) |
| Age | 70 (9) |
| Weight | 72 (13.0) |
| Height | 1.67 (0.08) |
| BMI | 26.5 (3.6) |
| CCI score (median) | 5 (3–15) |
| 10-year survival (median of CCI calculated percentage) | 21.36 (0–77.48) |
| Line of therapy | |
| First-line therapy | 24 (49) |
| ≥Second-line therapy | 25 (51) |
| Gene | Genotype | Total Frequency (n = 49) N (%) | Frequency in Men (n = 35) N (%) | Frequency in Women (n = 14) N (%) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ABCB1 rs1045642 g.208920T>C | C/C | 11 (22.9) | 8 (23.5) | 3 (21.4) | 0.5 |
| C/T | 31 (64.6) | 23 (67.7) | 8 (57.2) | ||
| T/T | 6 (12.5) | 3 (8.8) | 3 (21.4) | ||
| ABCB1 rs1128503 g.167964T>C | C/C | 17 (35.4) | 14 (41.2) | 3 (21.4) | 0.062 |
| C/T | 27 (56.3) | 19 (55.9) | 8 (57.2) | ||
| T/T | 4 (8.3) | 1 (2.9) | 3 (21.4) | ||
| ABCB1 rs2032582 g.186947T>G,A | G/G | 19 (39.6) | 15 (44.1) | 4 (28.6) | 0.12 |
| G/A + G/T | 25 (52.1) | 18 (53.0) | 7 (50.0) | ||
| A/A | 4 (8.3) | 1 (2.9) | 3 (21.4) | ||
| ABCG2 rs2231137 g.89061114C>T | C/C | 44 (91.7) | 30 (88.2) | 14 (100.0) | 0.3 |
| C/T | 4 (8.3) | 4 (11.8) | 0 | ||
| ABCG2 rs2231142 g.89052323G>T | G/G | 43 (91.5) | 31 (93.9) | 12 (85.7) | 0.6 |
| G/T | 4 (8.5) | 2 (6.1) | 2 (14.3) | ||
| SLCO1B1 rs4149056 g.21331549T>C | T/T | 35 (72.9) | 25 (73.5) | 10 (71.4) | >0.9 |
| C/T | 13 (27.1) | 9 (26.5) | 4 (28.6) | ||
| CYP3A4 | *1/*1 | 42 (91.3) | 28 (87.5) | 14 (100.0) | 0.3 |
| *1/*22 | 4 (8.7) | 4 (12.5) | 0 | ||
| CYP3A5 | *1/*3 | 2 (4.3) | 1 (3.0) | 1 (7.2) | 0.5 |
| *3/*3 | 45 (95.7) | 32 (97.0) | 13 (92.8) |
| Type of Adverse Reaction | Total Frequency (n = 49) N (%) | Frequency in Men (n = 35) N (%) | Frequency in Women (n = 14) N (%) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Infections and infestations | 13 (26.5) | 11 (31.4) | 2 (14.3) | 0.3 |
| Neoplasms | 4 (8.2) | 4 (11.4) | 0 | 0.3 |
| Nervous system disorders | 5 (10.2) | 4 (11.4) | 1 (7.1) | >0.9 |
| Cardiac disorders | 3 (6.1) | 2 (5.7) | 1 (7.1) | >0.9 |
| Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders | 2 (4.1) | 2 (5.7) | 0 | >0.9 |
| Blood and lymphatic system disorders | 4 (8.2) | 2 (5.7) | 2 (14.3) | 0.6 |
| Metabolism and nutritional disorders | 3 (6.1) | 2 (5.7) | 1 (7.1) | >0.9 |
| Gastrointestinal disorders | 4 (8.2) | 1 (2.9) | 3 (21.4) | 0.065 |
| Hepatobiliary disorders | 1 (2.0) | 1 (2.9) | 0 | >0.9 |
| Musculoskeletal disorders | 5 (10.2) | 4 (11.4) | 1 (7.1) | >0.9 |
| Vascular disorders | 19 (38.8) | 13 (37.1) | 6 (42.9) | 0.7 |
| General disorders | 2 (4.1) | 2 (5.7) | 0 | >0.9 |
| Gene | Genotype | Mean Ibrutinib Concentration (ng/mL) | SD | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ABCB1 rs1045642 g.208920T>C | C/C (n = 11) | 2.50 | 2.17 | 0.527 |
| C/T (n = 31) | 2.14 | 2.58 | ||
| T/T (n = 6) | 0.87 | 1.10 | ||
| ABCB1 rs1128503 g.167964T>C | C/C (n = 17) | 1.77 | 1.94 | 0.560 |
| C/T (n = 27) | 2.44 | 2.76 | ||
| T/T (n = 4) | 1.16 | 1.14 | ||
| ABCB1 rs2032582 g.186947T>G,A | G/G (n = 19) | 1.82 | 1.90 | 0.546 |
| G/A + G/T (n = 25) | 2.50 | 2.90 | ||
| A/A (n = 4) | 1.16 | 1.14 | ||
| ABCG2 rs2231137 g.89061114C>T | C/C (n = 44) | 2.11 | 2.35 | 0.996 |
| C/T (n = 4) | 2.16 | 3.16 | ||
| ABCG2 rs2231142 g.89052323G>T | G/G (n = 43) | 2.30 | 2.43 | 0.249 |
| G/T (n = 4) | 0.828 | 1.66 | ||
| SLCO1B1 rs4149056 g.21331549T>C | C/T (n = 13) | 2.48 | 1.74 | 0.615 |
| T/T (n = 35) | 2.00 | 2.54 | ||
| CYP3A4 | *1/*1 (n = 42) | 2.08 | 2.35 | 0.287 |
| *1/*22 (n = 4) | 3.29 | 2.88 | ||
| CYP3A5 | *1/*3 (n = 0) | NA | NA | NA * |
| *3/*3 (n = 25) | 2.15 | 2.39 |
| Gene | Variant | rs Number | Reference | RefSeq Reference Allele | RefSeq Alternative Allele | Consequence | MAF in European Population |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ABCB1 | g.167964T>C | rs1128503 | C___7586662_10 | A | G | Synonymous variant | 0.584 |
| ABCB1 | g.208920T>C | rs1045642 | C___7586657_20 | A | G | Missense Variant | 0.482 |
| ABCB1 | g.186947T>G,A | rs2032582 | C_11711720C_30 | A | G | Missense Variant | 0.573 |
| ABCB1 | g.186947T>G,A | rs2032582 | C_11711720D_40 | A | T | Missense Variant | 0.001 |
| ABCG2 | g.89061114C>T | rs2231137 | ANXG6CY | C | T | Missense Variant | 0.16 |
| ABCG2 | g.89052323G>T | rs2231142 | C__15854163_70 | G | T | Stop Gained | 0.12 |
| CYP3A4 | *20 | rs67666821 | ANNKRXD | TTTTT | TTTTTT | Frameshift Variant | 0.0001 |
| CYP3A4 | *22 | rs35599367 | C__59013445_10 | G | A | Intron Variant | 0.05 |
| CYP3A5 | *3 | rs776746 | C__26201809_30 | T | C | Splice Acceptor Variant | 0.943 |
| SLCO1B1 | g.21331549T>C | rs4149056 | C__30633906_10 | T | C | Missense Variant | 0.22 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pérez-Gómez, N.; Sanz-Solas, A.; Cuevas, B.; Cuevas, M.V.; Alonso-Madrigal, C.; Loscertales, J.; Álvarez-Nuño, R.; García, C.; Zubiaur, P.; Villapalos-García, G.; et al. Pharmacogenetic Biomarkers of Ibrutinib Response and Toxicity in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: Insights from an Observational Study. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 996. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18070996
Pérez-Gómez N, Sanz-Solas A, Cuevas B, Cuevas MV, Alonso-Madrigal C, Loscertales J, Álvarez-Nuño R, García C, Zubiaur P, Villapalos-García G, et al. Pharmacogenetic Biomarkers of Ibrutinib Response and Toxicity in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: Insights from an Observational Study. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(7):996. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18070996
Chicago/Turabian StylePérez-Gómez, Noelia, Antonio Sanz-Solas, Beatriz Cuevas, María Victoria Cuevas, Cristina Alonso-Madrigal, Javier Loscertales, Rodolfo Álvarez-Nuño, Covadonga García, Pablo Zubiaur, Gonzalo Villapalos-García, and et al. 2025. "Pharmacogenetic Biomarkers of Ibrutinib Response and Toxicity in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: Insights from an Observational Study" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 7: 996. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18070996
APA StylePérez-Gómez, N., Sanz-Solas, A., Cuevas, B., Cuevas, M. V., Alonso-Madrigal, C., Loscertales, J., Álvarez-Nuño, R., García, C., Zubiaur, P., Villapalos-García, G., Parra-Garcés, R. M., Mejía-Abril, G., Alcaraz, R., Vinuesa, R., Díaz-Gálvez, F. J., González-Oter, M., García-Sancha, N., Azibeiro-Melchor, R., González-López, T. J., ... Saiz-Rodríguez, M. (2025). Pharmacogenetic Biomarkers of Ibrutinib Response and Toxicity in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: Insights from an Observational Study. Pharmaceuticals, 18(7), 996. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18070996









