Computational Insights into the Polypharmacological Landscape of BCR-ABL Inhibitors: Emphasis on Imatinib and Nilotinib
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
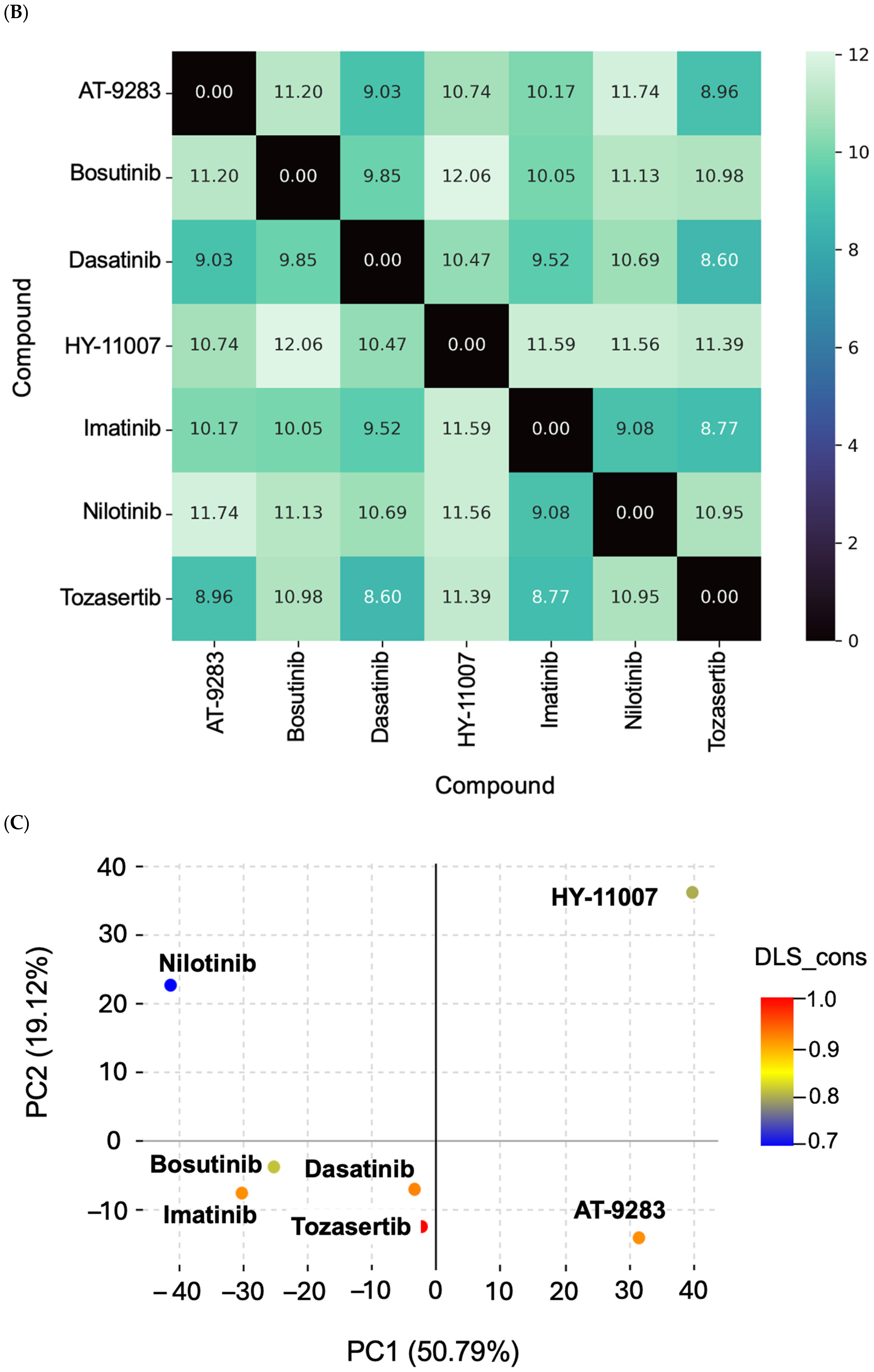
2.1. Chemical Dissimilarity
2.2. Biological Dissimilarity
2.3. Hypothesis Generation Polypharmacological Effects
2.3.1. Non-Cancer Indications of BCR-ABL Inhibitors
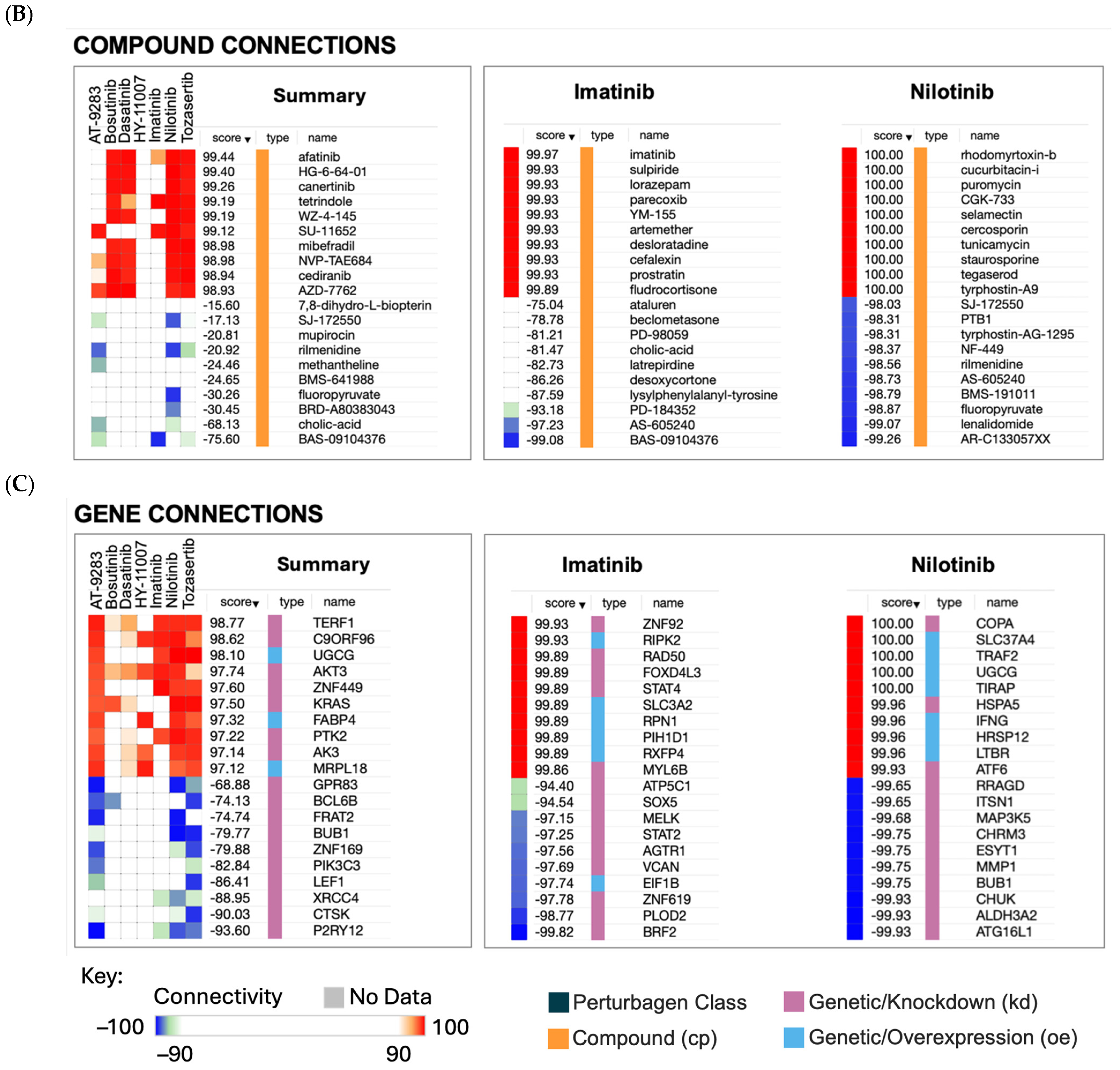
2.3.2. Non-Cancer Indications of Imatinib
| # | Perturbagen | Type | Score | Non-Cancer Indications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Mineralocorticoid Agonist | Class | 98.22 | Orthostatic Hypotension (FDA-approved); Addison Disease (FDA-approved). |
| 2 | PLK Inhibitor | Class | 97.63 | Inflammation (Preclinical) [58]; HIV Infections (Preclinical) [59]. |
| 3 | Dopamine Receptor Grp1 | Class | 96.93 | Parkinson’s Disease (Clinical) [60]; Depressive Disorder (Preclinical) [61]. |
| 4 | PKC Activator | Class | 95.54 | Alzheimer’s Disease (Clinical) [62]; HIV infection (Clinical) [62]. |
| 5 | VEGFR Inhibitor | Class | 95.45 | Uveitis (FDA-approved); Atherosclerosis (Preclinical) [63]. |
| 6 | Opioid Receptor Agonist | Class | 95.09 | Pain (FDA-approved); Cough (FDA-approved). |
| 7 | Dopamine Receptor Grp2 | Class | 92.62 | Schizophrenia (FDA-approved); Parkinson’s Disease (Clinical) [60]; Alzheimer’s Disease (Clinical) [64]. |
| 8 | ROCK Inhibitor | Class | 90.26 | Glaucoma (FDA-approved) [65]; Hypertension, Pulmonary (Clinical) [66]; Parkinson’s Disease (Clinical) [67]. |
| 9 | Na-K-Cl Transporter Inhibitor | Class | 89.83 | Kidney Diseases; Hypertension (FDA-approved for non-selective inhibitors); Epilepsy (Clinical for selective inhibitors) [68]; Autistic Disorder (Clinical for selective inhibitors) [69]. |
| 10 | Phosphodiesterase Inhibitor | Class | 89.61 | Erectile dysfunction (FDA-approved); Pulmonary Disease, Chronic Obstructive (FDA-approved); Heart Diseases (FDA-approved); Schizophrenia (Clinical) [70]. |
| 11 | Imatinib | Compound | 99.97 | Heart Diseases (Clinical) [3]; Asthma (Clinical) [71]; Insulin Resistance (Clinical) [72]. |
| 12 | Lorazepam | Compound | 99.61 | Anxiety Disorders (FDA-approved). |
| 13 | Parecoxib | Compound | 99.56 | Pain (FDA-approved); Inflammation (FDA-approved). |
| 14 | KUC103904N | Compound | 99.51 | Not detected. |
| 15 | Cefalexin | Compound | 99.51 | Surgical Wound Infection (FDA-approved); Urinary Tract Infections (FDA-approved); Respiratory Tract Infections (FDA-approved); Skin Diseases, Infectious (FDA-approved); Otitis Media (FDA-approved). |
| 16 | SNS-314 | Compound | 99.37 | Pulmonary Fibrosis (Clinical) [73]; Arthritis, Rheumatoid (Clinical) [74]; Alzheimer’s Disease (Preclinical) [13]; Psoriasis (Preclinical) [75]. |
| 17 | Pioglitazone | Compound | 99.28 | Diabetes Mellitus; Insulin Resistance (FDA-approved). |
| 18 | GSK-1904529A | Compound | 99.12 | None found. |
| 19 | BRD-A97035593 | Compound | 99.09 | None found. |
| 20 | Tandutinib | Compound | 99.07 | Parkinson’s Disease (Preclinical) [2]. |
| 21 | STAT4 | Gene (kd) | 99.34 | Autoimmune Diseases (Clinical) [76]; Inflammation (Clinical); (Preclinical) [77]; Hypersensitivity (Preclinical) [77]. |
| 22 | YTHDF2 | Gene (kd) | 99.29 | Alzheimer’s Disease (Preclinical) [78]. |
| 23 | ZNF92 | Gene (kd) | 99.21 | Alzheimer’s Disease (Preclinical) [79]; Parkinson’s Disease (Preclinical) [79]. |
| 24 | C2 | Gene (oe) | 99.12 | Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (Clinical) [80]; Sjögren’s Syndrome (Clinical) [80]. |
| 25 | CLPB | Gene (oe) | 99.07 | Neutropenia (Clinical) [81]; Parkinson’s Disease (Preclinical) [82]. |
| 26 | KIF5C | Gene (kd) | 99.03 | Neurodegenerative Diseases (Preclinical) [83]. |
| 27 | TKT | Gene (oe) | 98.98 | Diabetes Mellitus (Preclinical) [84]; Alzheimer’s Disease (Preclinical) [85]. |
| 28 | ACAT1 | Gene (kd) | 98.82 | Hypertension (Preclinical) [86]; Dementia (Preclinical) [87]. |
| 29 | SLC3A2 | Gene (oe) | 98.74 | Wound Healing (Preclinical) [88]. |
| 30 | YTHDF1 | Gene (kd) | 98.74 | Diabetes Mellitus (Clinical) [89]; Alzheimer’s Disease (Preclinical) [90]. |
2.3.3. Non-Cancer Indications of Nilotinib
| # | Perturbagen | Type | Score | Non-Cancer Indications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Aurora Kinase inhibitor Grp1 | Class | 99.90 | Alzheimer’s Disease (Preclinical) [13]; Liver Cirrhosis, Experimental (Preclinical) [92]; Pulmonary Fibrosis (Preclinical) [14]. |
| 2 | JAK inhibitor | Class | 99.28 | Alopecia Areata (FDA-approved); Colitis, Ulcerative (FDA-approved); Crohn’s Disease (FDA-approved); Vitiligo (FDA-approved); Arthritis, Rheumatoid (Clinical) [93]; Autoimmune Diseases (Clinical) [94]; Arthritis (Clinical) [95]; Psoriasis (Clinical) [95]; Dermatitis, Atopic (Clinical) [96]; Diabetes Mellitus (Clinical) [97]. |
| 3 | Vesicular transport | Class | 99.28 | None found. |
| 4 | EGFR inhibitor | Class | 99.09 | Psoriasis (Preclinical) [98]; Pulmonary Fibrosis (Preclinical) [99]; Atherosclerosis (Preclinical) [100]; Neovascularization, Pathologic (Preclinical) [101]. |
| 5 | BRAF RAF1 inhibitor | Class | 98.91 | Pulmonary Fibrosis (Preclinical) [28]; Arthritis, Rheumatoid (Preclinical) [27]. |
| 6 | EIF proteins | Class | 98.73 | Leukoencephalopathy (Preclinical) [102]; Diabetes Mellitus (In silico) [103]. |
| 7 | NFKB activation | Class | 98.57 | Inflammation (Clinical) [104]; Neurodegenerative Diseases (Preclinical) [105]. |
| 8 | BCL2 and related protein inhibitor | Class | 98.33 | Alzheimer’s Disease (Preclinical) [106]; Lupus Erythematosus, Cutaneous (Preclinical) [107]; |
| 9 | GSK3 inhibitor | Class | 98.23 | Psychiatric Disorders (Clinical) [108]; Alzheimer’s Disease (Preclinical) [109]; Diabetes Mellitus (Clinical) [110]; Inflammation (Preclinical) [111]. |
| 10 | RAR agonist Grp2 | Class | 98.21 | Acne Vulgaris (Clinical) [112]. |
| 11 | Nilotinib | Compound | 99.99 | Parkinson’s Disease (Clinical) [7]; Alzheimer’s Disease (Clinical) [113]; Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (Preclinical) [114]. |
| 12 | AT-9283 | Compound | 99.79 | Hypertension, Pulmonary (Preclinical) [115]; COVID-19 (In silico) [116]. |
| 13 | Alisertib | Compound | 99.68 | None found. |
| 14 | ZM-447439 | Compound | 99.61 | None found. |
| 15 | Avrainvillamide-analog-2 | Compound | 99.58 | Antibacterial Activity (Preclinical) [117]. |
| 16 | Tozasertib | Compound | 99.40 | Optic Nerve Injuries (Preclinical) [118]. |
| 17 | Crizotinib | Compound | 99.38 | None found. |
| 18 | Erastin | Compound | 99.30 | None found. |
| 19 | KI-8751 | Compound | 99.19 | Cystitis (Preclinical) [119]. |
| 20 | MK-5108 | Compound | 99.12 | Kidney Fibrosis (Preclinical) [120]. |
| 21 | HSPA5 | Gene (kd) | 99.84 | Fatty Liver, Nonalcoholic (Clinical) [121]; Alzheimer’s Disease (Preclinical) [122]; Parkinson’s Disease (Preclinical) [123]; Myositis (Preclinical) [124]; COVID-19 (Preclinical) [125]. |
| 22 | COPA | Gene (kd) | 99.84 | Autoimmune Diseases (Clinical) [126]. |
| 23 | GMDS | Gene (oe) | 99.81 | Glaucoma, Open-Angle (Preclinical) [127]. |
| 24 | SFPQ | Gene (oe) | 99.77 | HIV Infection (Clinical) [128]; Nervous System Diseases (Preclinical) [129]; Congenital Structural Myopathies (Preclinical) [130]; Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (Preclinical) [131]. |
| 25 | HSP90B1 | Gene (kd) | 99.73 | Tuberculosis (Preclinical) [132]; Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (Preclinical) [133]. |
| 26 | HRSP12 | Gene (oe) | 99.68 | Osteoarthritis (Preclinical) [134]; Diabetic Nephropathies (In silico) [135]. |
| 27 | EIF2B2 | Gene (kd) | 99.66 | Leukoencephalopathy (Preclinical) [136]; Nervous System Diseases (Preclinical) [137]. |
| 28 | NIT1 | Gene (kd) | 99.63 | None found. |
| 29 | NFE2L2 | Gene (oe) | 99.63 | Parkinson’s Disease (Preclinical) [138]; Heart Failure (Preclinical) [139]. |
| 30 | LYN | Gene (oe) | 99.63 | Autoimmune Diseases (Preclinical) [140]; Neurodegenerative Diseases (Preclinical) [140]; Alzheimer’s Disease (Preclinical) [141]. |
2.4. Supporting Evidence
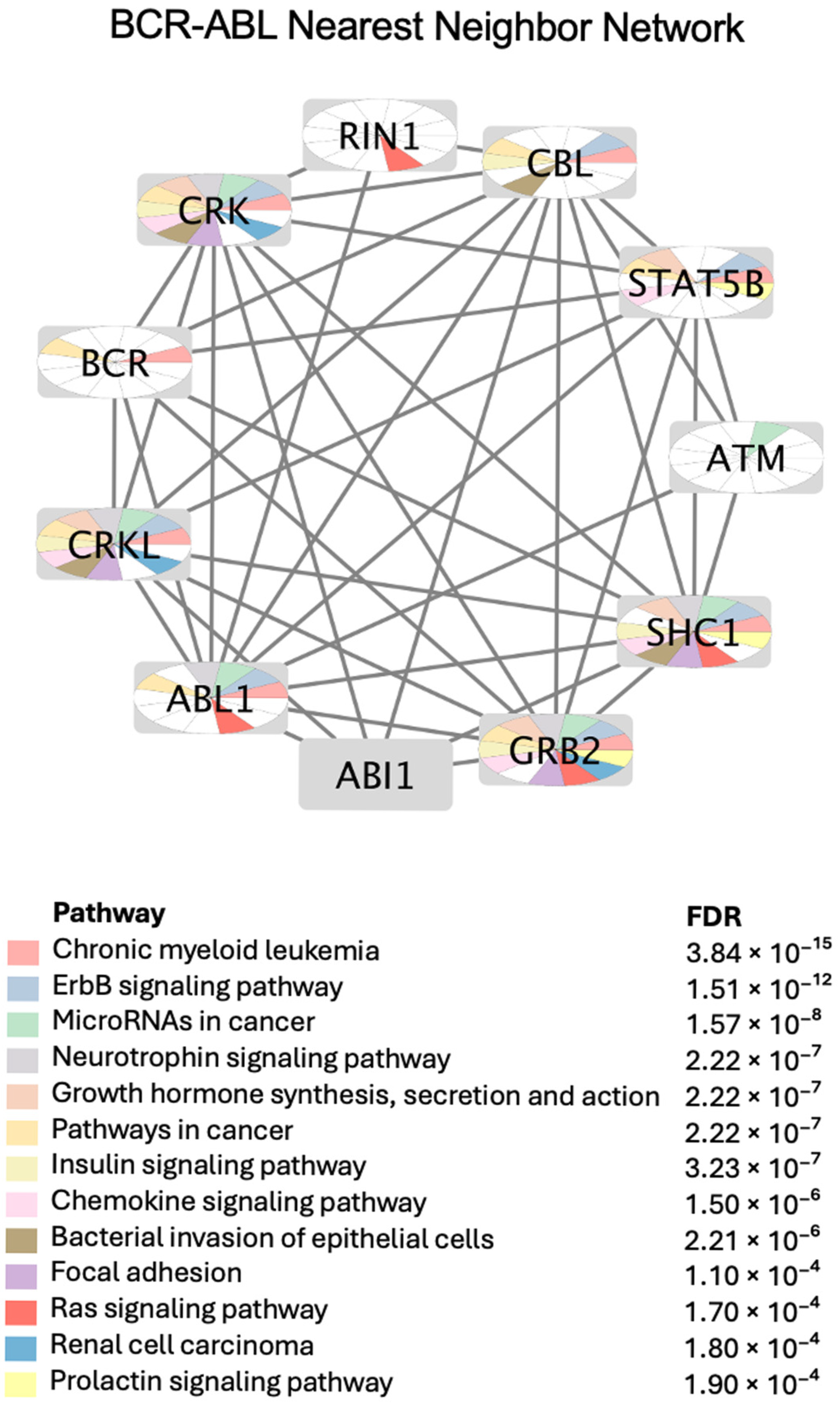
2.4.1. BCR-ABL PPI Network and Annotated Enriched Pathways
2.4.2. Literature-Based Validation
| # | Perturbagen | Cancer Indications and Validity | Non-Cancer Effects and Validity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | AT-9283 | Leukemia, Lymphoid (Clinical) [142]; Multiple Myeloma (Clinical) [143]; Neoplasms (Clinical) [144]; Lymphoma, B-Cell (Preclinical) [145]. | Myeloproliferative Disorders (Preclinical) [146]. |
| 2 | Bosutinib | Leukemia, Myelogenous, Chronic, BCR-ABL Positive (FDA-approved). | Lewy Body Disease (Clinical) [147]. |
| 3 | Dasatinib | Leukemia, Myelogenous, Chronic, BCR-ABL Positive (FDA-approved). | Alzheimer’s Disease (Clinical) [148]; COVID-19 (Clinical) [149]; Hepatitis B, Chronic (Clinical) [150]; Pulmonary Fibrosis (Clinical) [151]; Obesity (Preclinical) [152]. |
| 4 | HY-1107 | Liver Neoplasms (Preclinical) | None found. |
| 5 | Imatinib | Leukemia, Lymphoid (FDA-approved); Mastocytosis (FDA-approved); Leukemia, Myelogenous, Chronic, BCR-ABL Positive (FDA-approved); Dermatofibrosarcoma Protuberans (FDA-approved); Hypereosinophilic Syndrome (FDA-approved); Leukemia, Eosinophilic, Chronic (FDA-approved); Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors (FDA-approved); Myeloproliferative Disorders (FDA-approved). | Anemia, Sickle Cell (Clinical) [153]; Diabetes Mellitus, Type 1 (Clinical) [154]; Pulmonary Fibrosis (Clinical) [155]; Stroke (Clinical) [156]; Liver Cirrhosis (Clinical) [157]. |
| 6 | Nilotinib | Leukemia, Myelogenous, Chronic, BCR-ABL Positive (FDA-approved). | Alzheimer’s Disease (Clinical) [158]; Parkinson’s Disease (Clinical) [7]. |
| 7 | Tozasertib | Glioma (Clinical) [159]; Melanoma (Preclinical) [160]. | Hypersensitivity (Preclinical) [161]; Neuralgia (Preclinical) [162]. |
| 8 | BCR-ABL | Leukemia, Myelogenous, Chronic, BCR-ABL Positive (Clinical) [163]. | None found. |
| 9 | BCR | None found. | Autoimmune Diseases (Clinical) [164]. |
| 10 | ABL | None found. | Developmental Disabilities (Preclinical) [165]; Parkinson’s Disease (Preclinical) [166]. |
2.5. Mechanistic Insight
3. Discussion
3.1. Translational and Safety Implications
3.2. Limitations
3.3. Future Perspectives
4. Methods
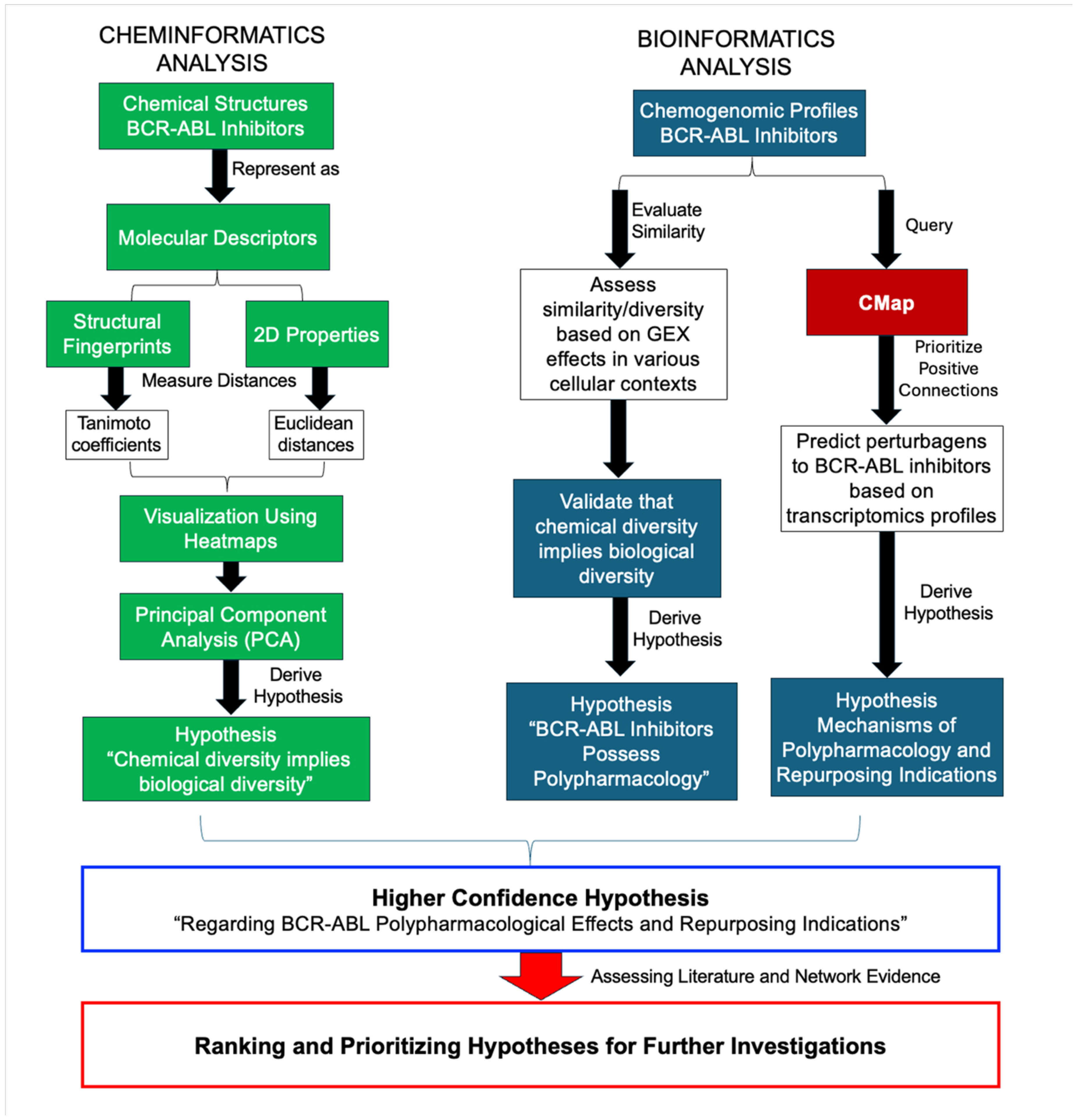
4.1. Chemical Biology Informatics Workflow
- Querying CMap: Gene expression signatures were retrieved using the search terms “mechanism = BCR ABL inhibitors”, “compound = imatinib”, and “compound = nilotinib”.
- Generating query signatures: The transcriptomic profiles of compounds identified from the initial search were used as input query signatures.
- Identifying similar perturbations: These signatures were used to search CMap for compounds and genetic perturbations exhibiting similar expression profiles.
- Prioritization of hits: Repurposing hypotheses were prioritized based on the top 10 gene and compound connections, all enriched pharmacological classes, and supporting preclinical or clinical evidence.
- Filtering by connectivity scores: The results were filtered using CMap connectivity scores, as previously described [8], to retain only relevant and strong associations.
- Pathway enrichment: High-confidence gene connections (CMap scores ≥ 90.00) were used for pathway enrichment analysis to gain mechanistic insights.
4.2. Bioinformatics Methods
4.2.1. The Connectivity Map (CMap)
4.2.2. Protein–Protein Interactions
4.2.3. Enrichment Analysis
4.3. Cheminformatics Methods
4.3.1. Molecular Descriptors
4.3.2. Similarity and Distance Matrix Calculation
4.4. Standardization of Condition Terms Using MeSH Vocabulary
4.5. Therapeutic Evidence
- FDA-approved: Interventions that are already approved for non-cancer indications. These reflect previously validated clinical uses and are not novel findings of this study but were included for benchmarking and validation purposes.
- Clinical: Candidates with reported efficacy in human studies or clinical trials but without formal regulatory approval. These are supported by clinical evidence yet still represent off-label or investigational use.
- Preclinical: Agents with supportive data from animal models or in vitro experiments but lacking human clinical validation.
- In silico/Hypothesis: Computational predictions generated in this study that have not yet been tested experimentally.
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ABL | Abelson Murine Leukemia Viral Oncogene |
| ALK | Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase |
| BCR-ABL | Breakpoint Cluster Region–Abelson Murine Leukemia Viral Oncogene Fusion Protein |
| BCR | Breakpoint Cluster Region |
| CML | Chronic Myeloid Leukemia |
| DCM | Dilated Cardiomyopathy |
| FDR | False Discovery Rate |
| MeSH | Medical Subject Headings |
| PPI | Protein–Protein Interaction |
| PCA | Principal Component Analysis |
| TAS | Transcriptional Activity Score |
| TKI | Tyrosine kinase inhibitor |
References
- Roskoski, R. Targeting BCR-Abl in the Treatment of Philadelphia-Chromosome Positive Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia. Pharmacol. Res. 2022, 178, 106156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansour, H.M.; El-Khatib, A.S. Repositioning of Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors: From Cancer to Neurodegenerative and Psychiatric Disorders. In Receptor Tyrosine Kinases in Neurodegenerative and Psychiatric Disorders; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2023; pp. 353–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, B.; Chen, D.F.; Bu, X.H.; Qin, H.B.; Xi, Y. Effect of Imatinib on DOCA-Induced Myocardial Fibrosis in Rats through P38 MAPK Signaling Pathway. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 2028–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tocci, D.; Fogel, M.; Gupta, V.; Kim, P.; Latimer, J.; Adlimoghaddam, A.; Robison, L.S.; Albensi, B.C. Beyond Expectations: Investigating Nilotinib’s Potential in Attenuating Neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s Disease. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 2025, 17, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Druker, B.J.; Talpaz, M.; Resta, D.J.; Peng, B.; Buchdunger, E.; Ford, J.M.; Lydon, N.B.; Kantarjian, H.; Capdeville, R.; Ohno-Jones, S.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of a Specific Inhibitor of the BCR-ABL Tyrosine Kinase in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 344, 1031–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, E.J. Asciminib: The First-in-Class Allosteric Inhibitor of BCR::ABL1 Kinase. Blood Res. 2023, 58, S29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Yuan, P.; Kou, L.; Chen, X.; Li, J.; Li, Y. Nilotinib in Parkinson’s Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2022, 14, 996217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, A.; Narayan, R.; Corsello, S.M.; Peck, D.D.; Natoli, T.E.; Lu, X.; Gould, J.; Davis, J.F.; Tubelli, A.A.; Asiedu, J.K.; et al. A Next Generation Connectivity Map: L1000 Platform and the First 1,000,000 Profiles. Cell 2017, 171, 1437–1452.e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajjo, R.; Tropsha, A. A Systems Biology Workflow for Drug and Vaccine Repurposing: Identifying Small-Molecule BCG Mimics to Reduce or Prevent COVID-19 Mortality. Pharm. Res. 2020, 37, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajjo, R.; Setola, V.; Roth, B.L.; Tropsha, A. Chemocentric Informatics Approach to Drug Discovery: Identification and Experimental Validation of Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulators as Ligands of 5-Hydroxytryptamine-6 Receptors and as Potential Cognition Enhancers. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 5704–5719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajjo, R.; Sabbah, D.A.; Bardaweel, S.K. Chemocentric Informatics Analysis: Dexamethasone Versus Combination Therapy for COVID-19. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 29765–29779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajjo, R.; Momani, E.; Sabbah, D.A.; Baker, N.; Tropsha, A. Identifying a Causal Link between Prolactin Signaling Pathways and COVID-19 Vaccine-Induced Menstrual Changes. NPJ Vaccines 2023, 8, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afghah, Z.; Khan, N.; Datta, G.; Halcrow, P.W.; Geiger, J.D.; Chen, X. Involvement of Endolysosomes and Aurora Kinase A in the Regulation of Amyloid β Protein Levels in Neurons. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 6200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Santos, D.M.; Pantano, L.; Knipe, R.; Abe, E.; Logue, A.; Pronzati, G.; Black, K.E.; Spinney, J.J.; Giacona, F.; et al. Screening for Inhibitors of YAP Nuclear Localization Identifies Aurora Kinase A as a Modulator of Lung Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2022, 67, 36–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsha, A.; Soutto, M.; Sehdev, V.; Peng, D.; Washington, M.K.; Piazuelo, M.B.; Tantawy, M.N.; Manning, H.C.; Lu, P.; Shyr, Y.; et al. Aurora Kinase A Promotes Inflammation and Tumorigenesis in Mice and Human Gastric Neoplasia. Gastroenterology 2013, 145, 1312–1322.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Du, X.; Wang, B.; Zhang, G. CircAKR1B10 Interacts with EIF4A3 to Stabilize AURKA and Promotes IL-22-Induced Proliferation, Migration and Invasion in Keratinocytes. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2024, 316, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czókolyová, M.; Hamar, A.; Pusztai, A.; Tajti, G.; Végh, E.; Pethő, Z.; Bodnár, N.; Horváth, Á.; Soós, B.; Szamosi, S.; et al. Effects of One-Year Tofacitinib Therapy on Lipids and Adipokines in Association with Vascular Pathophysiology in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.C.; Kang, D.; Ko, E.A. Roles of PDGF/PDGFR Signaling in Various Organs. Korean J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2024, 29, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Medley, S.C.; Hu, T.; Hinsdale, M.E.; Lupu, F.; Virmani, R.; Olson, L.E. PDGFRβ Signaling Regulates Local Inflammation and Synergizes with Hypercholesterolemia to Promote Atherosclerosis. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trempus, C.S.; Papas, B.N.; Sifre, M.I.; Bortner, C.D.; Scappini, E.; Tucker, C.J.; Xu, X.; Johnson, K.L.; Deterding, L.J.; Williams, J.G.; et al. Functional Pdgfra Fibroblast Heterogeneity in Normal and Fibrotic Mouse Lung. JCI Insight 2023, 8, e164380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schramm, F.; Schaefer, L.; Wygrecka, M. EGFR Signaling in Lung Fibrosis. Cells 2022, 11, 986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madan, V.; Ortiz-López, L.I.; Sakunchotpanit, G.; Chen, R.; Nayudu, K.; Nambudiri, V.E. Psoriasis in the Era of Targeted Cancer Therapeutics: A Systematic Review on De Novo and Pre-Existing Psoriasis in Oncologic Patients Treated with Emerging Anti-Neoplastic Agents. Dermatol. Ther. 2024, 14, 1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, D.; Xu, T.; Zhong, L.; Liang, Q.; Hu, Y.; Xiao, W.; Shi, J. Research Progress of VEGFR Small Molecule Inhibitors in Ocular Neovascular Diseases. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 257, 115535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, F.; Wang, M.Q.; Zhang, M.Y.; Gu, S.L.; Xie, Y.W.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, M.Y.; Li, F.L.; Yang, Y.C.; Zhang, P.P.; et al. CPD-002, a Novel VEGFR2 Inhibitor, Relieves Rheumatoid Arthritis by Reducing Angiogenesis through the Suppression of the VEGFR2/PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 131, 111850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Q.; Wu, G.; Chen, M.; Luo, G.; Wu, Z.; Huo, H.; Li, H.; Zheng, L.; Luo, M. Cediranib Ameliorates Portal Hypertensive Syndrome via Inhibition of VEGFR-2 Signaling in Cirrhotic Rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2024, 964, 176278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Tai, Z.; Zhu, C.; Yu, Q.; Zhu, Q.; Chen, Z. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor A VEGFA Inhibition: An Effective Treatment Strategy for Psoriasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Yuan, B.; Tao, X.; Guo, W.; Mao, X.; Wu, A.; Wang, Q.; Liu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Kong, X.; et al. Anti-Angiogenic Effect of YuXueBi Tablet in Experimental Rheumatoid Arthritis by Suppressing LOX/Ras/Raf-1 Signaling. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 298, 115611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, W.; Liu, K.; Jia, C.; Hou, Y.; Bai, G. Astragaloside IV Protects against Lung Injury and Pulmonary Fibrosis in COPD by Targeting GTP-GDP Domain of RAS and Downregulating the RAS/RAF/FoxO Signaling Pathway. Phytomedicine 2023, 120, 155066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Nie, X.; Lin, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Z.; Lin, M. Regulation of Keratinocyte Barrier Function and Inflammatory Response by the EGFR-STAT3 Pathway: Potential Therapeutic Implications of Osimertinib and Afatinib. Cytokine 2025, 185, 156802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clerk, A.; Meijles, D.N.; Hardyman, M.A.; Fuller, S.J.; Chothani, S.P.; Cull, J.J.; Cooper, S.T.E.; Alharbi, H.O.; Vanezis, K.; Felkin, L.E.; et al. Cardiomyocyte BRAF and Type 1 RAF Inhibitors Promote Cardiomyocyte and Cardiac Hypertrophy in Mice in Vivo. Biochemical Journal 2022, 479, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bano, S.; Copeland, M.A.; Stoops, J.W.; Orr, A.; Jain, S.; Paranjpe, S.; Mooli, R.G.R.; Ramakrishnan, S.K.; Locker, J.; Mars, W.M.; et al. Hepatocyte-Specific Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Deletion Promotes Fibrosis but Has No Effect on Steatosis in Fast-Food Diet Model of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, 18, 101380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korshunov, V.A.; Murashev, A.N.; Ivashev, M.N.; Dugin, S.F.; Medvedev, O.S. [Comparative Study of Hemodynamic Effects of Antidepressants (Tetrindole and Desipramine) during Immobilization Stress in Hypertensive Rats]. Eksperimental’naia i Klinicheskaia Farmakologiia 2000, 63, 18–20. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.L.; Tsaur, M.L.; Wang, S.W.; Wang, T.Y.; Hung, Y.C.; Lin, C.S.; Chang, Y.F.; Wang, Y.C.; Shiue, S.J.; Cheng, J.K. Chronic Intrathecal Infusion of Mibefradil, Ethosuximide and Nickel Attenuates Nerve Ligation-Induced Pain in Rats. Br. J. Anaesth. 2015, 115, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Choi, H.; Kim, Y.D.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, Y.; Gwon, Y.; Lee, D.Y.; Park, S.H.; Heo, W.D.; Jung, Y.K. Aberrant Role of ALK in Tau Proteinopathy through Autophagosomal Dysregulation. Mol. Psychiatry 2021, 26, 5542–5556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Chen, A.; Jalali, A.; Liu, S.; Guo, Y.; Na, S.; Nakshatri, H.; Li, B.Y.; Yokota, H. Effects of a Checkpoint Kinase Inhibitor, AZD7762, on Tumor Suppression and Bone Remodeling. Int. J. Oncol. 2018, 53, 1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanov, D.; Drobintseva, A.; Rodichkina, V. Inflammaging: Expanding the Molecular Palette of Cellular Immunophenotype. 2024; 2024040644, Preprints. [Google Scholar]
- Mahady, L.J.; He, B.; Malek-Ahmadi, M.; Mufson, E.J. Telomeric Alterations in the Default Mode Network during the Progression of Alzheimer’s Disease: Selective Vulnerability of the Precuneus. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2021, 47, 428–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmak, H.; Redouane, S.; Charoute, H.; Aniq Filali, O.; Barakat, A.; Rouba, H. In Silico Exploration and Molecular Dynamics of Deleterious SNPs on the Human TERF1 Protein Triggering Male Infertility. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2023, 41, 14665–14688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ain, N.U.; Saith, A.; Ruan, A.; Yang, R.; Burton, A.; Mistry, P.K. Eliglustat and Cardiac Comorbidities in Gaucher Disease: A Pharmacogenomic Approach to Safety and Efficacy. Front. Med. 2025, 12, 1535099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, C.; Liu, Y.; Chen, H. The Sphingolipids Metabolism Mechanism and Associated Molecular Biomarker Investigation in Keloid. Comb. Chem. High Throughput Screen. 2022, 26, 2003–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, W.; Jiao, R.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, T.; Chai, D.; Meng, L.; Yang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wu, H.; et al. Miglustat Ameliorates Isoproterenol-Induced Cardiac Fibrosis via Targeting UGCG. Mol. Med. 2025, 31, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Wang, Y.; Kong, L.; Ji, Y.; Cui, J.; Shen, W. Role of UDP-Glucose Ceramide Glucosyltransferase in Venous Malformation. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2023, 11, 1178045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brazdis, R.M.; von Zimmermann, C.; Lenz, B.; Kornhuber, J.; Mühle, C. Peripheral Upregulation of Parkinson’s Disease-Associated Genes Encoding α-Synuclein, β-Glucocerebrosidase, and Ceramide Glucosyltransferase in Major Depression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 3219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alcantara, D.; Timms, A.E.; Gripp, K.; Baker, L.; Park, K.; Collins, S.; Cheng, C.; Stewart, F.; Mehta, S.G.; Saggar, A.; et al. Mutations of AKT3 Are Associated with a Wide Spectrum of Developmental Disorders Including Extreme Megalencephaly. Brain 2017, 140, 2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerau-de-Arellano, M.; Piedra-Quintero, Z.L.; Tsichlis, P.N. Akt Isoforms in the Immune System. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 990874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howell, K.R.; Floyd, K.; Law, A.J. PKBγ/AKT3 Loss-of-Function Causes Learning and Memory Deficits and Deregulation of AKT/MTORC2 Signaling: Relevance for Schizophrenia. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0175993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Peng, P.; Peng, J. The Phenotypic and Genetic Spectrum of AKT3-Related Neurodevelopmental Condition. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 7484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, S.; Dai, H.; Zhao, X.; Gui, C.; Gui, J. AKT3 Deficiency in M2 Macrophages Impairs Cutaneous Wound Healing by Disrupting Tissue Remodeling. Aging 2020, 12, 6928–6946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, K.; Fukai, A.; Mori, D.; Hosaka, Y.; Yano, F.; Chung, U.I.; Kawaguchi, H.; Tanaka, S.; Ikeda, T.; Saito, T. Identification of SCAN Domain Zinc-Finger Gene ZNF449 as a Novel Factor of Chondrogenesis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e115169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newbury, L.J.; Wang, J.H.; Hung, G.; Hendry, B.M.; Sharpe, C.C. Inhibition of Kirsten-Ras Reduces Fibrosis and Protects against Renal Dysfunction in a Mouse Model of Chronic Folic Acid Nephropathy. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laryushina, Y.; Parakhina, V.; Turmukhambetova, A.; Turgunova, L.; Ibraeva, L.; Amirkhanova, D.; Nildibayeva, F. The Relationship between the Level Fabp4, Risks of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus, and Cardiovascular Events. Open Access Maced. J. Med. Sci. 2020, 8, 762–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.W.; Chang, T.T.; Chang, C.C.; Chen, J.W. Fatty-Acid-Binding Protein 4 as a Novel Contributor to Mononuclear Cell Activation and Endothelial Cell Dysfunction in Atherosclerosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taguchi, K.; Chen, L.; Usawachintachit, M.; Hamamoto, S.; Kang, M.; Sugino, T.; Unno, R.; Tzou, D.T.; Sherer, B.A.; Okada, A.; et al. Fatty Acid–Binding Protein 4 Downregulation Drives Calcification in the Development of Kidney Stone Disease. Kidney Int. 2020, 97, 1042–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Başarır Sivri, F.N.; Çiftçi, S. A New Insight into Fatty Acid Binding Protein 4 Mechanisms and Therapeutic Implications in Obesity-Associated Diseases: A Mini Review. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2024, 68, 2300840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Sun, C.-K.; Tang, L.; Tan, M.-S. Microglia PTK2B/Pyk2 in the Pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s Disease. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2023, 20, 692–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ionescu, M.I. Adenylate Kinase: A Ubiquitous Enzyme Correlated with Medical Conditions. Protein J. 2019, 38, 120–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thawanaphong, S.; Nair, A.; Volfson, E.; Nair, P.; Mukherjee, M. IL-18 Biology in Severe Asthma. Front. Med. 2024, 11, 1486780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldrighi, M.; Doreth, C.; Li, Y.; Zhao, X.; Warner, E.; Chenoweth, H.; Kishore, K.; Umrania, Y.; Minde, D.-P.; Thome, S.; et al. PLK1 Inhibition Dampens NLRP3 Inflammasome–Elicited Response in Inflammatory Disease Models. J. Clin. Investig. 2023, 133, e162129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Hayashi, T.; Jean, M.; Kong, W.; Fiches, G.; Biswas, A.; Liu, S.; Yosief, H.O.; Zhang, X.; Bradner, J.; et al. Inhibition of Polo-like Kinase 1 (PLK1) Facilitates the Elimination of HIV-1 Viral Reservoirs in CD4+ T Cells Ex Vivo. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaba1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latif, S.; Jahangeer, M.; Maknoon Razia, D.; Ashiq, M.; Ghaffar, A.; Akram, M.; El Allam, A.; Bouyahya, A.; Garipova, L.; Ali Shariati, M.; et al. Dopamine in Parkinson’s Disease. Clin. Chim. Acta 2021, 522, 114–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desormeaux, C.; Demars, F.; Davenas, E.; Jay, T.M.; Lavergne, F. Selective Activation of D1 Dopamine Receptors Exerts Antidepressant-like Activity in Rats. J. Psychopharmacol. 2020, 34, 1443–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawano, T.; Inokuchi, J.; Eto, M.; Murata, M.; Kang, J.H. Activators and Inhibitors of Protein Kinase C (PKC): Their Applications in Clinical Trials. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dabravolski, S.A.; Khotina, V.A.; Omelchenko, A.V.; Kalmykov, V.A.; Orekhov, A.N. The Role of the VEGF Family in Atherosclerosis Development and Its Potential as Treatment Targets. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Cheng, Z.Y.; Li, Y.F.; Liu, C.; Wang, C.; Gong, X.J.; He, L. Dopamine D2 Receptor Agonist Bromocriptine Ameliorates Aβ1-42-Induced Memory Deficits and Neuroinflammation in Mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2023, 938, 175443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.B.; Harris, J.M.; Baldwin, G.; Goss, D.; Margeta, M.A. Ocular Effects of Rho Kinase (ROCK) Inhibition: A Systematic Review. Eye 2024, 38, 3418–3428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montagnoli, T.L.; da Silva, J.S.; Sudo, S.Z.; Santos, A.D.; Gomide, G.F.; de Sá, M.P.L.; Zapata-Sudo, G. ROCK Inhibition as Potential Target for Treatment of Pulmonary Hypertension. Cells 2021, 10, 1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quadir, H.; Hakobyan, K.; Gaddam, M.; Ojinnaka, U.; Ahmed, Z.; Kannan, A.; Mostafa, J.A. Role of Rho-Associated Protein Kinase Inhibition As Therapeutic Strategy for Parkinson’s Disease: Dopaminergic Survival and Enhanced Mitophagy. Cureus 2021, 13, e16973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampel, P.; Römermann, K.; Gailus, B.; Johne, M.; Gericke, B.; Kaczmarek, E.; Löscher, W. Effects of the NKCC1 Inhibitors Bumetanide, Azosemide, and Torasemide Alone or in Combination with Phenobarbital on Seizure Threshold in Epileptic and Nonepileptic Mice. Neuropharmacology 2021, 185, 108449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savardi, A.; Patricelli Malizia, A.; De Vivo, M.; Cancedda, L.; Borgogno, M. Preclinical Development of the Na-K-2Cl Co-Transporter-1 (NKCC1) Inhibitor ARN23746 for the Treatment of Neurodevelopmental Disorders. ACS Pharmacol. Transl. Sci. 2023, 6, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilleen, J.; Nottage, J.; Yakub, F.; Kerins, S.; Valdearenas, L.; Uz, T.; Lahu, G.; Tsai, M.; Ogrinc, F.; Williams, S.C.; et al. The Effects of Roflumilast, a Phosphodiesterase Type-4 Inhibitor, on EEG Biomarkers in Schizophrenia: A Randomised Controlled Trial. J. Psychopharmacol. 2021, 35, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahill, K.N.; Katz, H.R.; Cui, J.; Lai, J.; Kazani, S.; Crosby-Thompson, A.; Garofalo, D.; Castro, M.; Jarjour, N.; DiMango, E.; et al. KIT Inhibition by Imatinib in Patients with Severe Refractory Asthma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pichavaram, P.; Shawky, N.M.; Hartney, T.J.; Jun, J.Y.; Segar, L. Imatinib Improves Insulin Resistance and Inhibits Injury-Induced Neointimal Hyperplasia in High Fat Diet-Fed Mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 890, 173666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasam, R.K.; Ghandikota, S.; Soundararajan, D.; Reddy, G.B.; Huang, S.K.; Jegga, A.G.; Madala, S.K. Inhibition of Aurora Kinase B Attenuates Fibroblast Activation and Pulmonary Fibrosis. EMBO Mol. Med. 2020, 12, e12131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glant, T.T.; Besenyei, T.; Kádár, A.; Kurkó, J.; Tryniszewska, B.; Gál, J.; Soós, G.; Szekanecz, Z.; Hoffmann, G.; Block, J.A.; et al. Differentially Expressed Epigenome Modifiers, Including Aurora Kinases A and B, in Immune Cells in Rheumatoid Arthritis in Humans and Mouse Models. Arthritis Rheum. 2013, 65, 1725–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Tang, X.; Guo, Z.; Cheng, H.; Zheng, X.; Chen, G.; Huang, H.; Wang, W.; Gao, J.; Sheng, Y.; et al. AURKA Facilitates the Psoriasis-Related Inflammation by Impeding Autophagy-Mediated AIM2 Inflammasome Suppression. Immunol. Lett. 2021, 240, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baghdassarian, H.; Blackstone, S.A.; Clay, O.S.; Philips, R.; Matthiasardottir, B.; Nehrebecky, M.; Hua, V.K.; McVicar, R.; Liu, Y.; Tucker, S.M.; et al. Variant STAT4 and Response to Ruxolitinib in an Autoinflammatory Syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 2241–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolomeo, M.; Cascio, A. STAT4 and STAT6, Their Role in Cellular and Humoral Immunity and in Diverse Human Diseases. Int. Rev. Immunol. 2024, 43, 394–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasaki, S.; Avey, D.R.; Kearns, N.A.; Iatrou, A.; Yu, C.; De Tissera, S.; Vyas, H.; Xu, J.; Flood, D.J.; Rothamel, K.; et al. The YTHDF Proteins Shape the Brain Gene Signatures of Alzheimer’s Disease. bioRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, H.Z.; Cheng, Y.; Zhou, Z.W.; Luo, H.Y.; Wen, D.D.; Gao, L.C. PI3K/AKT Signal Pathway: A Target of Natural Products in the Prevention and Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease and Parkinson’s Disease. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 648636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundtoft, C.; Sjöwall, C.; Rantapää-Dahlqvist, S.; Bengtsson, A.A.; Jönsen, A.; Pucholt, P.; Wu, Y.L.; Lundström, E.; Eloranta, M.L.; Gunnarsson, I.; et al. Strong Association of Combined Genetic Deficiencies in the Classical Complement Pathway With Risk of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022, 74, 1842–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, J.T.; Cupo, R.R.; Wattanasirakul, P.; Spencer, D.H.; Locke, A.E.; Makaryan, V.; Bolyard, A.A.; Kelley, M.L.; Kingston, N.L.; Shorter, J.; et al. Heterozygous Variants of CLPB Are a Cause of Severe Congenital Neutropenia. Blood 2022, 139, 779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cupo, R.R.; Shorter, J. Skd3 (Human Clpb) Is a Potent Mitochondrial Protein Disaggregase That Is Inactivated by 3-Methylglutaconic Aciduria-Linked Mutations. Elife 2020, 9, e55279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berth, S.H.; Lloyd, T.E. Disruption of Axonal Transport in Neurodegeneration. J. Clin. Investig. 2023, 133, e168554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, T.; Yang, J.; Zhou, S.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Tong, X. The Role of the Pentose Phosphate Pathway in Diabetes and Cancer. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibson, G.E.; Feldman, H.H.; Zhang, S.; Flowers, S.A.; Luchsinger, J.A. Pharmacological Thiamine Levels as a Therapeutic Approach in Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 1033272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Yang, H.; Wang, H.; Luo, N.; Xia, Y.; Jiang, X. Association between ACAT1 Rs1044925 and Increased Hypertension Risk in Tongdao Dong. Medicine 2022, 101, e32196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alavez-Rubio, J.S.; Martínez-Rodríguez, N.; Escobedo-de-la-Peña, J.; Garrido-Acosta, O.; Juárez-Cedillo, T. Relationship Between Genetic Variants of ACAT1 and APOE with the Susceptibility to Dementia (SADEM Study). Mol. Neurobiol. 2021, 58, 905–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Lin, Y.; Shi, L.; Zhai, A.; Wu, C.; Zhu, Q.Y. Disulfidptosis-Related Gene SLC3A2: A Novel Prognostic Biomarker in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma and Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2025, 15, 1451034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yang, Y.; Chen, Z. Downregulation of the M6A Reader Protein YTHDC1 Leads to Islet β-Cell Failure and Diabetes. Metabolism 2023, 138, 155339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Technology—YTH Domain-Containing Family Protein 1 (YTHDF1): A Novel Therapeutic Target for Alzheimer’s Disease. Available online: https://usf.technologypublisher.com/technology/56448 (accessed on 21 April 2025).
- Tripathi, V.B.; Baskaran, P.; Shaw, C.E.; Guthrie, S. Tar DNA-Binding Protein-43 (TDP-43) Regulates Axon Growth in Vitro and in Vivo. Neurobiol. Dis. 2014, 65, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, G.; Lin, J.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, X.; Chen, P.; Zhang, Y.; Song, Z.; Zhuang, X.; Cong, J.; Li, Y.; et al. Aurora Kinase A Promotes Hepatic Stellate Cell Activation and Liver Fibrosis through the Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway. Front. Oncol. 2024, 14, 1517226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Important Safety Information for Janus Kinase (JAK) Inhibitors | Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA). Available online: https://www.tga.gov.au/news/safety-updates/important-safety-information-janus-kinase-jak-inhibitors (accessed on 20 April 2025).
- Benucci, M.; Bernardini, P.; Coccia, C.; De Luca, R.; Levani, J.; Economou, A.; Damiani, A.; Russo, E.; Amedei, A.; Guiducci, S.; et al. JAK Inhibitors and Autoimmune Rheumatic Diseases. Autoimmun. Rev. 2023, 22, 103276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarabia, S.; Ranjith, B.; Koppikar, S.; Wijeratne, D.T. Efficacy and Safety of JAK Inhibitors in the Treatment of Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. BMC Rheumatol. 2022, 6, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chovatiya, R.; Paller, A.S. JAK Inhibitors in the Treatment of Atopic Dermatitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2021, 148, 927–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, M.; Shen, Q.; Li, B. JAK Inhibitors: A New Choice for Diabetes Mellitus? Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2025, 17, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furue, K.; Ito, T.; Tanaka, Y.; Hashimoto-Hachiya, A.; Takemura, M.; Murata, M.; Kido-Nakahara, M.; Tsuji, G.; Nakahara, T.; Furue, M. The EGFR-ERK/JNK-CCL20 Pathway in Scratched Keratinocytes May Underpin Koebnerization in Psoriasis Patients. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangamesh, V.C.; Alagundagi, D.B.; Jayaswamy, P.K.; Kuriakose, N.; Shetty, P. Targeting AnxA2-EGFR Signaling: Hydroxychloroquine as a Therapeutic Strategy for Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 2024, 398, 2015–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abulizi, A.; Simayi, J.; Nuermaimaiti, M.; Han, M.; Hailati, S.; Talihati, Z.; Maihemuti, N.; Nuer, M.; Khan, N.; Abudurousuli, K.; et al. Quince Extract Resists Atherosclerosis in Rats by Down-Regulating the EGFR/PI3K/Akt/GSK-3β Pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 160, 114330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, J.; Yu, J.; Zhu, X.; Liang, S. MiR-335 Promotes Corneal Neovascularization by Targeting EGFR. BMC Ophthalmol. 2022, 22, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Knaap, M.S.; Bugiani, M.; Abbink, T.E.M. Vanishing White Matter. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2024, 204, 77–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, G.A.; Schooling, C.M. Causal Association between MTOR-Dependent EIF-4E and EIF-4A Circulating Protein Levels and Type 2 Diabetes: A Mendelian Randomization Study. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 15737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Ma, C.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Hu, H. NF-ΚB Signaling in Inflammation and Cancer. MedComm 2021, 2, 618–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaltschmidt, B.; Helweg, L.P.; Greiner, J.F.W.; Kaltschmidt, C. NF-ΚB in Neurodegenerative Diseases: Recent Evidence from Human Genetics. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2022, 15, 954541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuovo, G.J.; Rice, M.; Zanesi, N.; Sawant, D.; Crilly, C.; Tili, E. The Prevention of Fatal Tauopathy in a Mouse Model of Alzheimer Disease by Blocking BCL2. Appl. Immunohistochem. Mol. Morphol. 2025, 33, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Zhu, H.; Yang, M.; Yang, B.; Wu, H.; Lu, Q. Topical Administration of a BCL-2 Inhibitor Alleviates Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 142, 113132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snitow, M.E.; Bhansali, R.S.; Klein, P.S. Lithium and Therapeutic Targeting of GSK-3. Cells 2021, 10, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Wei, M.; Guo, M.; Wang, M.; Niu, H.; Xu, T.; Zhou, Y. GSK3: A Potential Target and Pending Issues for Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2024, 30, e14818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bala, A.; Roy, S.; Das, D.; Marturi, V.; Mondal, C.; Patra, S.; Haldar, P.K.; Samajdar, G. Role of Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3 in the Etiology of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Review. Curr. Diabetes Rev. 2021, 18, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandar, C.C.; Sen, D.; Maity, A. Anti-Inflammatory Potential of GSK-3 Inhibitors. Curr. Drug Targets 2021, 22, 1464–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassir, M.; Karagaiah, P.; Sonthalia, S.; Katsambas, A.; Galadari, H.; Gupta, M.; Lotti, T.; Wollina, U.; Abdelmaksoud, A.; Grabbe, S.; et al. Selective RAR Agonists for Acne Vulgaris: A Narrative Review. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2020, 19, 1278–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobili, A.; D’Amelio, M.; Viscomi, M.T. Nilotinib: From Animal-Based Studies to Clinical Investigation in Alzheimer’s Disease Patients. Neural Regen. Res. 2023, 18, 803–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myszczyńska, M.A. Uncovering Novel Drug Therapies and Targets for Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) Using Artificial Intelligence (AI). Ph.D. Thesis, University of Sheffield, Sheffield, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, H.; Li, X.; Cai, M.; Zhang, C.; Mao, W.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Q.; Chen, M.; Wang, L.; Huang, X. Integrated Bioinformatic Analysis Reveals the Underlying Molecular Mechanism of and Potential Drugs for Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. Aging 2021, 13, 14234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kandwal, S.; Fayne, D. Repurposing Drugs for Treatment of SARS-CoV-2 Infection: Computational Design Insights into Mechanisms of Action. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2022, 40, 1316–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myers, A.G.; Herzon, S.B.; Wulff, J.E.; Siegrist, R.; Svenda, J.; Zajac, M.A. Synthesis of Avrainvillamide, Stephacidin b, and Analogues Thereof. US Patent US20110166170A1, 7 July 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, C.; Huang, G.F.; Sun, X.C.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, J.H. Tozasertib Attenuates Neuronal Apoptosis via DLK/JIP3/MA2K7/JNK Pathway in Early Brain Injury after SAH in Rats. Neuropharmacology 2016, 108, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beca, K. Mediators of Bladder Dysfunction in a Rat Model of Mediators of Bladder Dysfunction in a Rat Model of Cyclophosphamide-Induced Cystitis Cyclophosphamide-Induced Cystitis; The University of Vermont and State Agricultural College: Burlington, VT, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, M.; Bai, M.; Xu, S.; Wang, T.; Lei, J.; Xu, M.; Huang, S.; Jia, Z.; Zhang, A. Blocking AURKA with MK-5108 Attenuates Renal Fibrosis in Chronic Kidney Disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Basis Dis. 2021, 1867, 166227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehati, A.; Abuduaini, B.; Liang, Z.; Chen, D.; He, F. Identification of Heat Shock Protein Family A Member 5 (HSPA5) Targets Involved in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Genes Immun. 2023, 24, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Li, H.; Xiong, W.; Li, X.; Duan, S.; Yang, C.; Shi, C. Proteomic Alteration in Catalpol Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease by Regulating HSPA5/ GPX4. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2025, 987, 177075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enogieru, A.B.; Omoruyi, S.I.; Hiss, D.C.; Ekpo, O.E. GRP78/BIP/HSPA5 as a Therapeutic Target in Models of Parkinson’s Disease: A Mini Review. Adv. Pharmacol. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 2019, 2706783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, F.; Tan, J.Z.; Xu, X.Y.; Wang, X.F. Increased Levels of HSPA5 in the Serum of Patients with Inflammatory Myopathies—Preliminary Findings. Clin. Rheumatol. 2015, 34, 715–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Fu, J.; Cheng, J.; Elfiky, A.A.; Wei, C.; Fu, J. New Progresses on Cell Surface Protein HSPA5/BiP/GRP78 in Cancers and COVID-19. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1166680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.T.N.; Salman, R.; Vogel, T.P.; Silva-Carmona, M.; DeGuzman, M.; Guillerman, R.P. Imaging Findings of COPA Syndrome. Pediatr. Radiol. 2023, 53, 844–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.J.; Zhao, A.G.; Wang, X.L. Correlations of AFAP1, GMDS and PTGFR Gene Polymorphisms with Intra-Ocular Pressure Response to Latanoprost in Patients with Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 2017, 42, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kikhai, T.; Agapkina, Y.; Silkina, M.; Prikazchikova, T.; Gottikh, M. The Cellular SFPQ Protein as a Positive Factor in the HIV-1 Integration. Biochimie 2024, 222, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeuchi, A.; Iida, K.; Tsubota, T.; Hosokawa, M.; Denawa, M.; Brown, J.B.; Ninomiya, K.; Ito, M.; Kimura, H.; Abe, T.; et al. Loss of Sfpq Causes Long-Gene Transcriptopathy in the Brain. Cell Rep. 2018, 23, 1326–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosokawa, M.; Takeuchi, A.; Tanihata, J.; Iida, K.; Takeda, S.; Hagiwara, M. Loss of RNA-Binding Protein Sfpq Causes Long-Gene Transcriptopathy in Skeletal Muscle and Severe Muscle Mass Reduction with Metabolic Myopathy. iScience 2019, 13, 229–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neeves, J. Examining the Role of SFPQ and Intron Retention in Physiology and Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Doctoral Thesis, UCL (University College London), London, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Graustein, A.D.; Misch, E.A.; Musvosvi, M.; Shey, M.; Shah, J.A.; Seshadri, C.; Aguoju, A.; Bowman, K.; Mulenga, H.; Veldsman, A.; et al. Toll-like Receptor Chaperone HSP90B1 and the Immune Response to Mycobacteria. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0208940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Mo, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Peng, X.; Luo, X. The Role of Heat Shock Protein 90B1 in Patients with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0152837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Lin, Y.; Wei, B.; Hu, X.; Xu, L.; Zhang, W.; Lu, J. N6-Methyladenosine-Modified CircRNA RERE Modulates Osteoarthritis by Regulating β-Catenin Ubiquitination and Degradation. Cell Prolif. 2023, 56, e13297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Liu, F.; Li, H.; Yuan, Y.; Lu, F. Cuproptosis Gene Characterizes the Immune Microenvironment of Diabetic Nephropathy. Transpl. Immunol. 2025, 89, 102175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escobar-Pacheco, M.; Luna-Álvarez, M.; Dávila-Ortiz De Montellano, D.; Yescas-Gómez, P.; Ramírez-García, M.Á. Ovarioleukodystrophy Due to EIF2B Genes: Systematic Review and Case Report. Cureus 2024, 16, e64497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, S.L.; Sonenberg, N.; Parker, R. Neuronal Regulation of EIF2α Function in Health and Neurological Disorders. Trends Mol. Med. 2018, 24, 575–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, Y.X.; Zhang, L.S.; Lv, W.; Zhang, W.M.; Zhao, J.J.; Hu, X.Y. NFE2L2 Variations Reduce Antioxidant Response in Patients with Parkinson Disease. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 10756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, J.J.; Porter, C.; Garg, N.J. Inhibition of NFE2L2-Antioxidant Response Element Pathway by Mitochondrial Reactive Oxygen Species Contributes to Development of Cardiomyopathy and Left Ventricular Dysfunction in Chagas Disease. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2017, 27, 550–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weerawarna, P.M.; Richardson, T.I. Lyn Kinase Structure, Regulation, and Involvement in Neurodegenerative Diseases: A Mini Review. Kinases Phosphatases 2023, 1, 23–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, R.; Choudhary, H.H.; Zhang, F.; Mehta, H.; Yoshida, J.; Thomas, A.J.; Hanafy, K. Microglial TLR4-Lyn Kinase Is a Critical Regulator of Neuroinflammation, Aβ Phagocytosis, Neuronal Damage, and Cell Survival in Alzheimer’s Disease. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 11368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vormoor, B.; Veal, G.J.; Griffin, M.J.; Boddy, A.V.; Irving, J.; Minto, L.; Case, M.; Banerji, U.; Swales, K.E.; Tall, J.R.; et al. A Phase I/II Trial of AT9283, a Selective Inhibitor of Aurora Kinase in Children with Relapsed or Refractory Acute Leukemia: Challenges to Run Early Phase Clinical Trials for Children with Leukemia. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2017, 64, e26351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hay, A.E.; Murugesan, A.; DiPasquale, A.M.; Kouroukis, T.; Sandhu, I.; Kukreti, V.; Bahlis, N.J.; Lategan, J.; Reece, D.E.; Lyons, J.F.; et al. A Phase II Study of AT9283, an Aurora Kinase Inhibitor, in Patients with Relapased or Refractory Multiple Myloma; NCIC Clinical Trials Group IND.191. Blood 2014, 124, 5734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, L.; Marshall, L.V.; Pearson, A.D.J.; Morland, B.; Elliott, M.; Campbell-Hewson, Q.; Makin, G.; Halford, S.E.R.; Acton, G.; Ross, P.; et al. A Phase I Trial of AT9283 (a Selective Inhibitor of Aurora Kinases) in Children and Adolescents with Solid Tumors: A Cancer Research UK Study. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, K.; Bai, L.; Wang, C.; Xiao, X.; Cheng, Z.; Peng, H.; Liu, S. The Aurora Kinase Inhibitor AT9283 Inhibits Burkitt Lymphoma Growth by Regulating Warburg Effect. PeerJ 2023, 11, e16581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, M.A.; Curry, J.E.; Barber, K.; Beer, P.A.; Graham, B.; Lyons, J.F.; Richardson, C.J.; Scott, M.A.; Smyth, T.; Squires, M.S.; et al. AT9283, a Potent Inhibitor of the Aurora Kinases and Jak2, Has Therapeutic Potential in Myeloproliferative Disorders. Br. J. Haematol. 2010, 150, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagan, F.L.; Torres-Yaghi, Y.; Hebron, M.L.; Wilmarth, B.; Turner, R.S.; Matar, S.; Ferrante, D.; Ahn, J.; Moussa, C. Safety, Target Engagement, and Biomarker Effects of Bosutinib in Dementia with Lewy Bodies. Alzheimers Dement. 2022, 8, e12296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millar, C.L.; Iloputaife, I.; Baldyga, K.; Norling, A.M.; Boulougoura, A.; Vichos, T.; Tchkonia, T.; Deisinger, A.; Pirtskhalava, T.; Kirkland, J.L.; et al. A Pilot Study of Senolytics to Improve Cognition and Mobility in Older Adults at Risk for Alzheimer’s Disease. EBioMedicine 2025, 113, 105612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, T.; Konishi, I. Cancer Therapy with Decreased SARS-CoV-2 Infection Rates in Cancer Patients. Br. J. Cancer 2022, 126, 521–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, T.; Li, W.; Yu, T. Management of Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia with COVID-19 and Hepatitis B. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1217023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Justice, J.N.; Nambiar, A.M.; Tchkonia, T.; LeBrasseur, N.K.; Pascual, R.; Hashmi, S.K.; Prata, L.; Masternak, M.M.; Kritchevsky, S.B.; Musi, N.; et al. Senolytics in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Results from a First-in-Human, Open-Label, Pilot Study. EBioMedicine 2019, 40, 554–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.T.; Tuday, E.; Allen, S.; Kim, J.; Trott, D.W.; Holland, W.L.; Donato, A.J.; Lesniewski, L.A. Senolytic Drugs, Dasatinib and Quercetin, Attenuate Adipose Tissue Inflammation, and Ameliorate Metabolic Function in Old Age. Aging Cell 2023, 22, e13767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, M.; Bahadoram, M.; Mafakher, L.; Rastegar, M. Impact of Imatinib on Reducing the Painful Crisis in Patients with Sickle Cell Disease. Hematol. Transfus. Cell Ther. 2024, 46, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gitelman, S.E.; Bundy, B.N.; Ferrannini, E.; Lim, N.; Blanchfield, J.L.; DiMeglio, L.A.; Felner, E.I.; Gaglia, J.L.; Gottlieb, P.A.; Long, S.A.; et al. Imatinib Therapy for Patients with Recent-Onset Type 1 Diabetes: A Multicentre, Randomised, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Phase 2 Trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2021, 9, 502–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Li, W.; Luo, Z.; Chen, Y. A Comprehensive Comparison of the Safety and Efficacy of Drugs in the Treatment of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: A Network Meta-Analysis Based on Randomized Controlled Trials. BMC Pulm. Med. 2024, 24, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahlgren, N.; Thorén, M.; Höjeberg, B.; Käll, T.-B.; Laska, A.-C.; Sjöstrand, C.; Höijer, J.; Almqvist, H.; Holmin, S.; Lilja, A.; et al. Randomized Assessment of Imatinib in Patients with Acute Ischaemic Stroke Treated with Intravenous Thrombolysis. J. Intern. Med. 2017, 281, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Study Details | Effect of Imatinib in Advance Liver Fibrosis Patients | ClinicalTrials.Gov. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT05224128 (accessed on 1 June 2025).
- Turner, R.S.; Hebron, M.L.; Lawler, A.; Mundel, E.E.; Yusuf, N.; Starr, J.N.; Anjum, M.; Pagan, F.; Torres-Yaghi, Y.; Shi, W.; et al. Nilotinib Effects on Safety, Tolerability, and Biomarkers in Alzheimer’s Disease. Ann. Neurol. 2020, 88, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jane, E.P.; Premkumar, D.R.; Rajasundaram, D.; Thambireddy, S.; Reslink, M.C.; Agnihotri, S.; Pollack, I.F. Reversing Tozasertib Resistance in Glioma through Inhibition of Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Kinases. Mol. Oncol. 2021, 16, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Liu, W.; Zhou, H.; Lai, W.; Hu, C.; Dai, Y.; Li, G.; Zhang, R.; Zhao, Y. Tozasertib Activates Anti-Tumor Immunity through Decreasing Regulatory T Cells in Melanoma. Neoplasia 2024, 48, 100966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Ji, K.; Sun, Y.; Hou, Y.; Chen, J. Aurora Kinase Inhibitor Tozasertib Suppresses Mast Cell Activation in Vitro and in Vivo. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 177, 2848–2859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uniyal, A.; Shantanu, P.A.; Vaidya, S.; Belinskaia, D.A.; Shestakova, N.N.; Kumar, R.; Singh, S.; Tiwari, V. Tozasertib Attenuates Neuropathic Pain by Interfering with Aurora Kinase and KIF11 Mediated Nociception. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2021, 12, 1948–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, H.; Lei, X.; Tang, G.; Cao, X.; Peng, J. Recent Advances in Bcr-Abl Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors for Overriding T315I Mutation. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2021, 97, 649–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Jing, Y.; Yang, L.; Kang, D.; Jiang, P.; Li, N.; Cheng, J.; Li, J.; Li, X.; Peng, Z.; et al. The Regulators of BCR Signaling during B Cell Activation. Blood Sci. 2019, 1, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blakes, A.J.M.; Gaul, E.; Lam, W.; Shannon, N.; Knapp, K.M.; Bicknell, L.S.; Jackson, M.R.; Wade, E.M.; Robertson, S.; White, S.M.; et al. Pathogenic Variants Causing ABL1 Malformation Syndrome Cluster in a Myristoyl-Binding Pocket and Increase Tyrosine Kinase Activity. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2021, 29, 593–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, D.; Chandía-Cristi, A.; Yáñez, M.; Zanlungo, S.; Álvarez, A. C-Abl Kinase at the Crossroads of Healthy Synaptic Remodeling and Synaptic Dysfunction in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Neural Regen. Res. 2023, 18, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajkumar, V.S.; Shiwen, X.; Bostrom, M.; Leoni, P.; Muddle, J.; Ivarsson, M.; Gerdin, B.; Denton, C.P.; Bou-Gharios, G.; Black, C.M.; et al. Platelet-Derived Growth Factor-β Receptor Activation Is Essential for Fibroblast and Pericyte Recruitment during Cutaneous Wound Healing. Am. J. Pathol. 2006, 169, 2254–2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, M.; Valent, P.; Galli, S.J. KIT as a Master Regulator of the Mast Cell Lineage. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2022, 149, 1845–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blair, L.J.; Sabbagh, J.J.; Dickey, C.A. Targeting Hsp90 and Its Co-Chaperones to Treat Alzheimer’s Disease. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2014, 18, 1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, F.; Liu, X.; Cai, H.; Le, W. Autophagy in Neurodegenerative Diseases: Pathogenesis and Therapy. Brain Pathol. 2017, 28, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shelton, L.B.; Baker, J.D.; Zheng, D.; Sullivan, L.E.; Solanki, P.K.; Webster, J.M.; Sun, Z.; Sabbagh, J.J.; Nordhues, B.A.; Koren, J.; et al. Hsp90 Activator Aha1 Drives Production of Pathological Tau Aggregates. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 9707–9712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ou, J.R.; Tan, M.S.; Xie, A.M.; Yu, J.T.; Tan, L. Heat Shock Protein 90 in Alzheimer’s Disease. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 796869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Liao, C.; Yu, L. Molecules for COVID-19 Treatment. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2024, 35, 109349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, R. NLRP3 Inflammasome in Neuroinflammation and Central Nervous System Diseases. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2025, 22, 341–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; He, J.; Zhang, X.; Cai, Y.; Liu, J.; Nie, X.; Shi, L. Cardiovascular Adverse Events in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Patients Treated with Nilotinib or Imatinib: A Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis and Integrative Bioinformatics Analysis. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 966182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.W.; Shinagare, A.B.; Krajewski, K.M.; Pyo, J.; Tirumani, S.H.; Jagannathan, J.P.; Ramaiya, N.H. Fluid Retention Associated with Imatinib Treatment in Patients with Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor: Quantitative Radiologic Assessment and Implications for Management. Korean J. Radiol. 2015, 16, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doncheva, N.T.; Morris, J.H.; Gorodkin, J.; Jensen, L.J. Cytoscape StringApp: Network Analysis and Visualization of Proteomics Data. J. Proteome Res. 2019, 18, 623–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvascience. AlvaDesc (Software for Molecular Descriptors Calculation) Version 1.0.18. 2020. Available online: https://www.alvascience.com (accessed on 7 April 2025).
- RDKit. Available online: https://www.rdkit.org/ (accessed on 2 May 2025).
- Medical Subject Headings RDF. Available online: https://id.nlm.nih.gov/mesh/ (accessed on 1 May 2025).



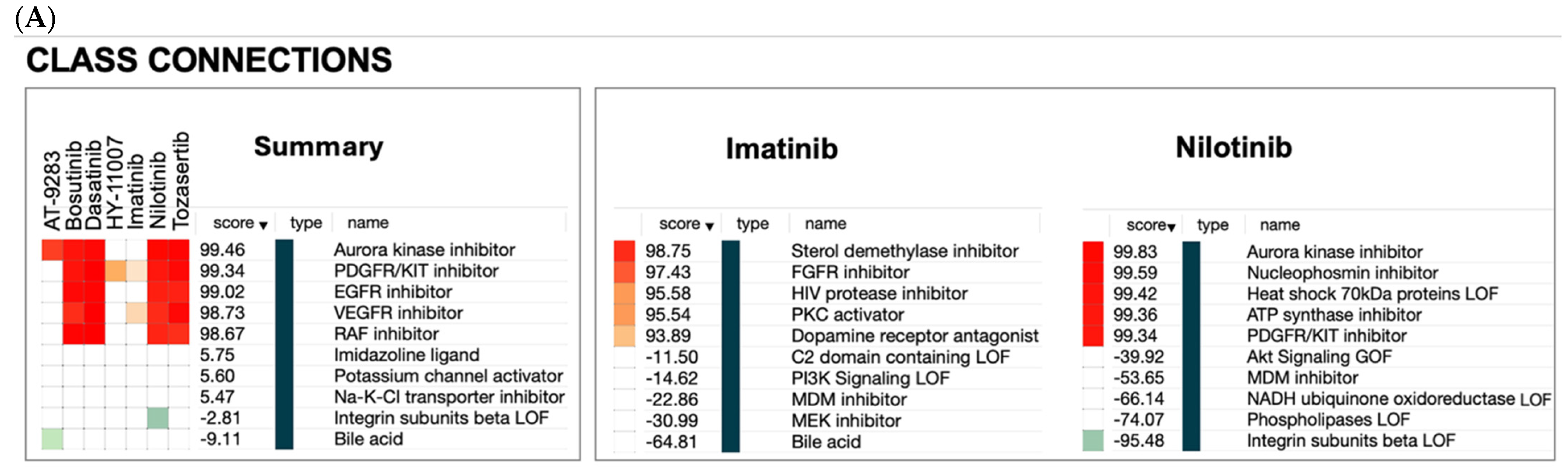

| # | Perturbagen | Type | Score | Non-Cancer Indications and Validity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Aurora kinase inhibitor | Class | 99.46 | Alzheimer’s Disease (Preclinical) [13]; Pulmonary Fibrosis (Preclinical) [14]; Inflammatory Bowel Diseases (Preclinical but weak) [15]; Arthritis, Psoriasis (Preclinical) [16]; Arthritis, Rheumatoid (In silico) [17]. |
| 2 | PDGFR\KIT inhibitor | Class | 99.34 | Alzheimer’s Disease (Preclinical) [18]; Atherosclerosis (Preclinical) [19]; Gastrointestinal Diseases (Preclinical) [18]; Liver Cirrhosis, Experimental (Preclinical) [18] Pulmonary Fibrosis (Preclinical) [20]; Wound Healing (Preclinical) [18]. |
| 3 | EGFR inhibitor | Class | 99.02 | Pulmonary Fibrosis (Preclinical) [21]; Psoriasis (Preclinical) [22]. |
| 4 | VEGFR inhibitor | Class | 98.73 | Eye Diseases (Clinical/Approved) [23]; Arthritis, Rheumatoid (Preclinical) [24]; Hypertension, Portal [25]; Psoriasis (Preclinical) [26]. |
| 5 | RAF inhibitor | Class | 98.67 | Arthritis, Rheumatoid (Preclinical) [27]; Lung Injury and Pulmonary Fibrosis (Preclinical) [28]. |
| 6 | Afatinib | Compound | 99.44 | Skin Diseases (Preclinical) [29]. |
| 7 | HG-6-64-01 | Compound | 99.40 | Heart failure (Preclinical) [30]. |
| 8 | Carnertinib | Compound | 99.26 | Liver Cirrhosis, Experimental (Preclinical) [31]. |
| 9 | Tetrindole | Compound | 99.19 | Depression (Preclinical/Early clinical) [32]. |
| 10 | WZ-4-145 | Compound | 99.19 | Unknown. |
| 11 | SU-11652 | Compound | 99.12 | Unknown. Multi-targeted TKI. |
| 12 | Mibefradil | Compound | 98.98 | Pain, Neuropathic (Preclinical) [33]. |
| 13 | NVP-TAE684 | Compound | 99.98 | Neuroprotection; Alzheimer Disease (Preclinical) [34]. |
| 14 | Cediranib | Compound | 98.94 | Liver Cirrhosis, Experimental (Preclinical) [25]. |
| 15 | AZD-7762 | Compound | 98.93 | Osteoporosis (Preclinical) [35]. |
| 16 | TERF1 | Gene (kd) | 98.77 | Aging (Preclinical) [36]; Alzheimer’s Disease (Preclinical) [37]; Infertility, Male (Preclinical) [38]. |
| 17 | C9ORF96 | Gene (kd) | 98.62 | Unknown. |
| 18 | UGCG | Gene (oe) | 98.10 | Gaucher Disease (Clinical) [39]; Keloid (Preclinical) [40]; Myocardial Fibrosis (Preclinical) [41]; Vascular Malformations (Preclinical) [42]; Parkinson’s Disease (Preclinical) [43], Depressive Disorder (Preclinical) [43]. |
| 19 | AKT3 | Gene (kd) | 97.47 | Brain Malformations (Clinical) [44]; Autoimmunity (Preclinical) [45]; Cognitive Dysfunction (Preclinical) [46]; Hemimegaloencephaly (Preclinical) [47]; Wound Healing (Preclinical) [48]. |
| 20 | ZNF449 | Gene (kd) | 97.60 | Chondrogenesis/Cartilage (Preclinical) [49]. |
| 21 | KRAS | Gene (kd) | 97.50 | Kidney Fibrosis (Preclinical) [50]. |
| 22 | FABP4 | Gene (oe) | 97.32 | Diabetes Mellitus (Clinical) [51]; Atherosclerosis (Preclinical) [52]; Kidney Stones (Preclinical) [53]; Obesity (Preclinical) [54]. |
| 23 | PTK2 | Gene (kd) | 97.22 | Alzheimer’s Disease (Preclinical) [55]. |
| 24 | AK3 | Gene (kd) | 97.14 | Alzheimer’s Disease (In silico) [56]. |
| 25 | MRP1L18 | Gene (oe) | 97.12 | Asthma (Preclinical) [57]. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hajjo, R.; Sabbah, D.A.; Alhaded, R.; Alquabe’h, A.; Bardaweel, S.K. Computational Insights into the Polypharmacological Landscape of BCR-ABL Inhibitors: Emphasis on Imatinib and Nilotinib. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 936. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18070936
Hajjo R, Sabbah DA, Alhaded R, Alquabe’h A, Bardaweel SK. Computational Insights into the Polypharmacological Landscape of BCR-ABL Inhibitors: Emphasis on Imatinib and Nilotinib. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(7):936. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18070936
Chicago/Turabian StyleHajjo, Rima, Dima A. Sabbah, Raghad Alhaded, Aye Alquabe’h, and Sanaa K. Bardaweel. 2025. "Computational Insights into the Polypharmacological Landscape of BCR-ABL Inhibitors: Emphasis on Imatinib and Nilotinib" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 7: 936. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18070936
APA StyleHajjo, R., Sabbah, D. A., Alhaded, R., Alquabe’h, A., & Bardaweel, S. K. (2025). Computational Insights into the Polypharmacological Landscape of BCR-ABL Inhibitors: Emphasis on Imatinib and Nilotinib. Pharmaceuticals, 18(7), 936. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18070936







