Network Pharmacology-Driven Sustainability: AI and Multi-Omics Synergy for Drug Discovery in Traditional Chinese Medicine
Abstract
1. Introduction
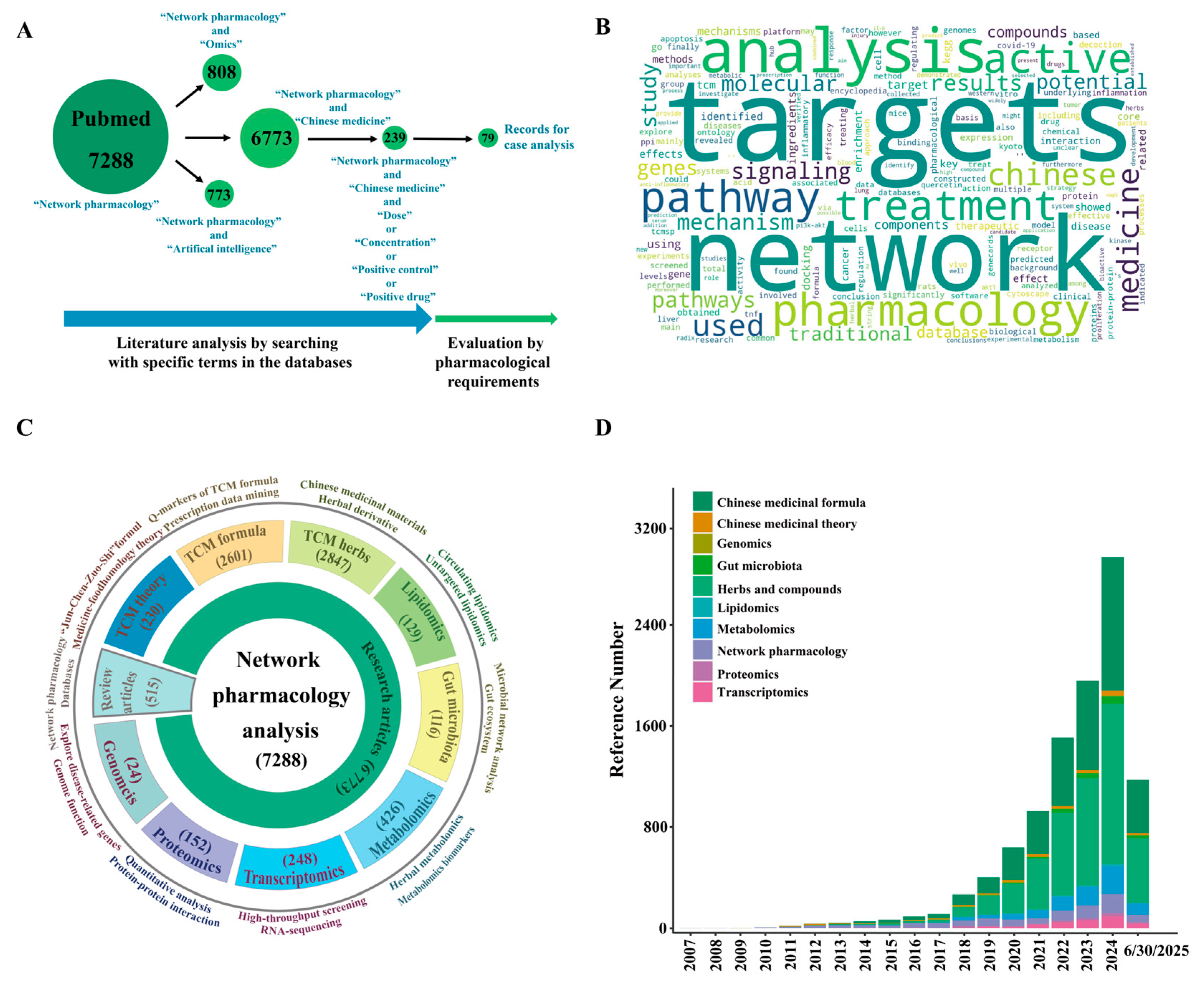
2. Data Collection and Analysis Processing
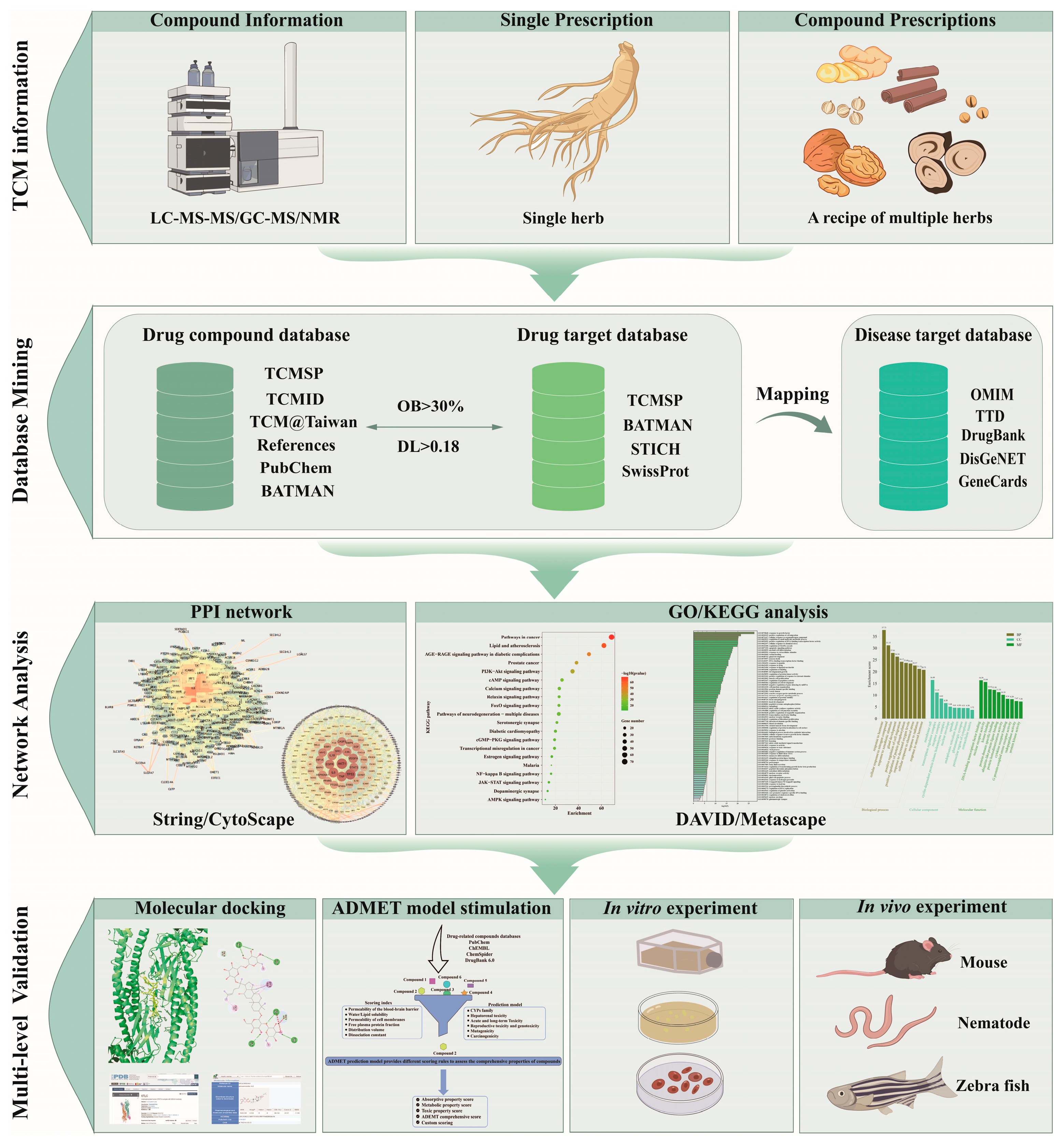
3. Summary of Processes and Resources in Network Pharmacology
3.1. Core Workflow
3.2. Screening Criteria and Network Analysis
3.3. Validation Experiments
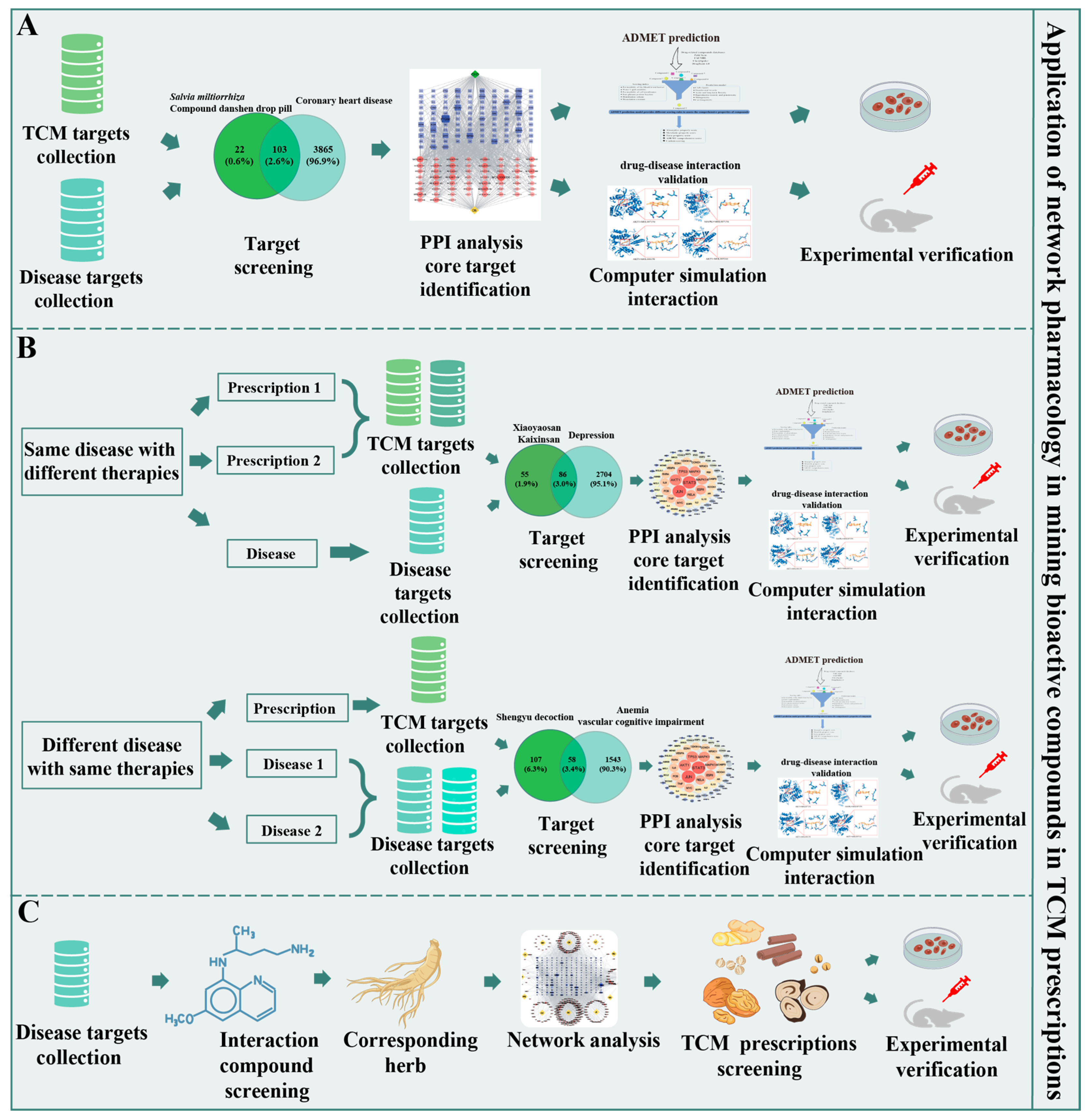
4. Application of Network Pharmacology in Mining Bioactive Compounds in TCM Prescriptions
4.1. Analyzing a Single Prescription
4.2. Analyzing Compound Prescriptions
4.3. Elucidating the Material Basis and Action Mechanisms of Chinese Medicine for Treating the Same Disease with Different Therapies and Different Diseases with the Same Therapy
4.4. Application to Reverse Pharmacology
5. Current Challenges of Applying Network Pharmacology to Drug Screening in TCM
5.1. Limitations in Data Resources and Screening Criteria
5.2. Reliability Gaps, Clinical Translation Barriers, and Trial Design Challenges
5.3. Discrepancies Between Predicted Bioactives and Quality Control
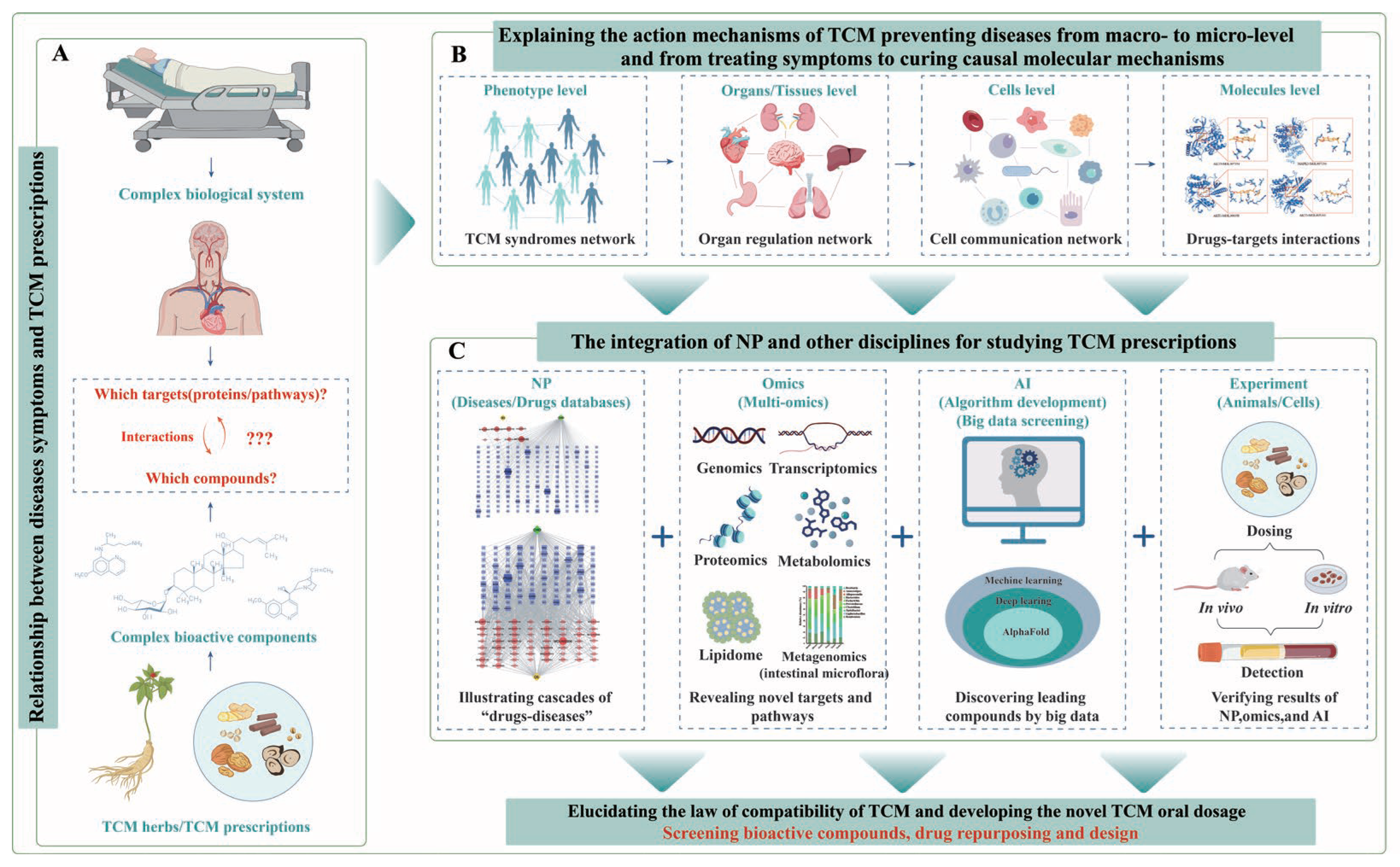
6. Synergizing Network Pharmacology, Multi-Omics, and AI to Revolutionize Drug Discovery
6.1. The Integration of NP with Multi-Omics
6.2. The Integration of NP with AI
6.3. The Integration of NP, Omcis, and AI Is Revolutionizing Drug Discovery
7. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Ma, D.; Wang, S.; Shi, Y.; Ni, S.; Tang, M.; Xu, A. The development of traditional Chinese medicine. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. Sci. 2021, 8, S1–S9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cyranoski, D. Why Chinese medicine is heading for clinics around the world. Nature 2018, 561, 448–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, R.; Li, J.; Yu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Martin, C. The yin and yang of traditional Chinese and Western medicine. Med. Res. Rev. 2021, 41, 3182–3200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Deng, Z.; Shi, C.; Cheng, K.; Zhai, R.; Li, X.; Fu, X. Tanshinone IIA, originated from Salvia miltiorrhiza, activated EPO/EPOR-JAK2-STAT5 pathway in rat blood deficiency therapy. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2024, 170, 105–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Zhang, X.; Xu, X.; Ke, Y.; Dai, J.; Cheng, H.; Mao, W. Compatibility principle in the Tanyu Tongzhi Formula revealed by a cell-based analysis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2019, 231, 507–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, Q.; Huang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Qin, Z.; Yang, Y.; Dai, Y.; Han, J.; Yao, X.; He, L.; et al. Five-layer-funnel filtering mode discovers effective components of Chinese medicine formulas: Zhishi-Xiebai-Guizhi decoction as a case study. Phytomedicine 2024, 129, 155678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, Y.; Liu, L.; Zhang, F.; Chen, X.; Wang, H.; Zhou, J.; Chai, K.; Liu, J.; Lei, H.; Lu, M.; et al. Network pharmacology: A crucial approach in traditional Chinese medicine research. Chin. Med. 2025, 20, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, S.; Duan, J.; Zeng, N.; Yu, B.; Yang, X.; Ning, H.; Rao, Y. Network pharmacology-based screening of the active ingredients and mechanisms of Huangqi against aging. Medicine 2021, 100, e25660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, L.; Li, X.; Miao, Y.; Li, D. Integrating network pharmacology, molecular docking and experimental validation to explore the pharmacological mechanisms of quercetin against diabetic wound. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2024, 21, 2837–2850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, H.; Wang, M.; Xu, K.; Peng, Q.; Zou, B.; Yin, S.; Yu, C.; Ren, L.; Li, P.; Tang, L.; et al. Effect of Fushengong Decoction on PTEN/PI3K/AKT/NF-κB pathway in rats with chronic renal failure via dual-dimension network pharmacology strategy. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 807651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besharatifard, M.; Vafaee, F. A review on graph neural networks for predicting synergistic drug combinations. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2024, 57, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krokidis, M.G.; Koumadorakis, D.E.; Lazaros, K.; Ivantsik, O.; Exarchos, T.P.; Vrahatis, A.G.; Kotsiantis, S.; Vlamos, P. AlphaFold3: An overview of applications and performance insights. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanenkov, Y.A.; Polykovskiy, D.; Bezrukov, D.; Zagribelnyy, B.; Aladinskiy, V.; Kamya, P.; Aliper, A.; Ren, F.; Zhavoronkov, A. Chemistry42: An AI-driven platform for molecular design and optimization. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2023, 63, 695–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazzara, F.; Conti, F.; Giuffrida, E.; Eandi, C.M.; Drago, F.; Platania, C.B.M.; Bucolo, C. Integrating network pharmacology: The next-generation approach in ocular drug discovery. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2024, 74, 102425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Su, L.; Shi, M.; Sun, L.; Chen, W.; Geng, J.; Li, J.; Zong, Y.; He, Z.; Du, R. Network pharmacology and transcriptomics to explore the pharmacological mechanisms of 20(S)-protopanaxatriol in the treatment of depression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 7574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Zhang, H.; Guo, J.; Ma, Y.; Bai, X.; Ma, N.; Ji, X.; Meng, Y.; Li, H.; Sangwanit, T.; et al. Exploring the therapeutic mechanism of Jianpi Zhidong Decoction on tourette syndrome based on proteomics and network pharmacology. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2025, 19, 3139–3158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qumu, D.; Tian, M.; Li, H.; Yang, X.; Han, B.; Wei, L.; Li, B.; Ma, M.; He, J.; Shao, X. Study on the mechanism of galangin on hyperuricemic nephropathy based on metabolomics and network pharmacology. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2025, 69, e70029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Luo, Y.; Hu, Y.; Li, S.; Li, G.; Zhang, W.; Gu, X.; Wang, J.; Li, S.; Cheng, H. Network pharmacology and multi-omics validation of the Jianpi-Yishen formula in the treatment of chronic kidney disease. Front. Immunol. 2025, 15, 1512519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinrich, M.; Appendino, G.; Efferth, T.; Fürst, R.; Izzo, A.A.; Kayser, O.; Pezzuto, J.M.; Vijoen, A. Best practice in research-overcoming common challenges in phytopharmacological research. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 246, 112230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ru, J.; Li, P.; Wang, J.; Zhou, W.; Li, B.; Huang, C.; Li, P.; Guo, Z.; Tao, W.; Yang, Y.; et al. TCMSP: A database of systems pharmacology for drug discovery from herbal medicines. J. Cheminform. 2014, 6, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Chen, J.; Cheng, T.; Gindulyte, A.; He, J.; He, S.; Li, Q.; Shoemaker, B.A.; Thiessen, P.A.; Yu, B.; et al. PubChem in 2021: New data content and improved web interfaces. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D1388–D1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stelzer, G.; Rosen, N.; Plaschkes, I.; Zimmerman, S.; Twik, M.; Fishilevich, S.; Stein, T.I.; Nudel, R.; Lieder, I.; Mazor, Y.; et al. The GeneCards Suite: From gene data mining to disease genome sequence analyses. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2016, 54, 30–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Shi, Y.; Chen, T.; Xu, Z.; Wang, P.; Yu, M.; Chen, W.; Li, B.; Jing, B.; et al. ETCM v2.0: An update with comprehensive resource and rich annotations for traditional Chinese medicine. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2023, 13, 2559–2571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Li, F.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, R.; Zhu, J.; Ren, Y.; Tan, Y.; et al. Therapeutic target database 2020: Enriched resource for facilitating research and early development of targeted therapeutics. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D1031–D1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otasek, D.; Morris, J.H.; Bouças, J.; Pico, A.R.; Demchak, B. Cytoscape automation: Empowering workflow-based network analysis. Genome Biol. 2019, 20, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, P.; Lang, J.; Li, H.; Lu, J.; Lin, H.; Tian, G.; Bai, H.; Yang, J.; Ning, K. TCM-Suite: A comprehensive and holistic platform for traditional Chinese medicine component identification and network pharmacology analysis. iMeta 2022, 1, e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Xu, J.; Yu, Z.; Chen, T.; Wang, N.; Du, X.; Wang, P.; Zhou, X.; Xu, H.; Zhang, Y. Ontology characterization, enrichment analysis, and similarity calculation-based evaluation of disease-syndrome-formula associations by applying SoFDA. iMeta 2023, 2, e80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Xu, J.; Li, H.; Zhang, L.; Xu, P. Network pharmacology-based investigation to explore the effect and mechanism of Erchen decoction against the nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Anat. Rec. 2021, 304, 2605–2619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Xie, D.; Yu, Y.; Liu, H.; Shi, Y.; Shi, T.; Wen, C. TCMID 2.0: A comprehensive resource for TCM. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D1117–D1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, Q.; Chen, G.; He, H.; Yang, Z.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, K.; Chen, C.Y.C. TCMBank-the largest TCM database provides deep learning-based Chinese-Western medicine exclusion prediction. STTT 2023, 8, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, S.; Dong, L.; Liu, L.; Guo, J.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, J.; Bu, D.; Liu, X.; Huo, P.; Cao, W.; et al. HERB: A high-throughput experiment- and reference-guided database of traditional Chinese medicine. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D1197–D1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, D.; Zheng, G.; Wang, C.; Chen, Z.; Mao, T.; Gao, J.; Yan, Y.; Chen, X.; Ji, X.; Yu, J.; et al. HIT 2.0: An enhanced platform for herbal ingredients targets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D1238–D1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, S.; Zhang, J.; Yuan, S.; Wang, Q.; Lv, C.; Wang, J.; Fang, J.; Fu, L.; Yang, J.; Zu, J.; et al. Exploring pharmacological active ingredients of traditional Chinese medicine by pharmacotranscriptomic map in ITCM. Brief. Bioinform. 2023, 24, bbad027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.; Huang, J.; Tang, R.; Li, M.; Yuan, H.; Wang, Y.; Wei, J.; Liu, J. CPMCP: A database of Chinese patent medicine and compound prescription. Database 2022, 2022, baac073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Zhang, F.; Yang, K.; Fang, S.; Bu, D.; Li, H.; Sun, L.; Hu, H.; Gao, K.; Wang, W.; et al. SymMap: An integrative database of traditional Chinese medicine enhanced by symptom mapping. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D1110–D1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendez, D.; Gaulton, A.; Bento, A.P.; Chambers, J.; Veij, M.D.; Félix, E.; Magariños, M.P.; Mosquera, J.F.; Mutowo, P.; Nowotka, M.; et al. ChEMBL: Towards direct deposition of bioassay data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D930–D940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pence, H.E.; Williams, A. ChemSpider: An online chemical information resource. J. Chem. Educ. 2010, 87, 1123–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wishart, D.S.; Feunang, Y.D.; Guo, A.C.; Lo, E.J.; Marcu, A.; Grant, J.R.; Sajed, T.; Johnson, D.; Li, C.; Sayeeda, Z.; et al. DrugBank 5.0: A major update to the DrugBank database for 2018. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D1074–D1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- UniProt, C. UniProt: The universal protein knowledgebase in 2023. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D480–D489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Licata, L.; Briganti, L.; Peluso, D.; Perfetto, L.; Lannuccelli, M.; Galeota, E.; Sacco, F.; Palma, A.; Nardozza, A.P.; Santonico, E.; et al. MINT, the molecular interaction database: 2012 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, D857–D861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gargano, M.A.; Matentzoglu, N.; Coleman, B.; Addo-Lartey, E.B.; Anagnostopoulos, A.V.; Anderton, J.; Avillach, P.; Bagley, A.M.; Bakštein, E.; Balhoff, J.P.; et al. The Human Phenotype Ontology in 2024: Phenotypes around the world. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, 52, D1207–D1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, A.P.; Wiegers, T.C.; Johnson, R.J.; Sciaky, D.; Wiegers, J.; Mattingly, C.J. Comparative Toxicogenomics Database (CTD): Update 2023. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D1257–D1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Lian, X.; Li, F.; Wang, C.; Zhu, F.; Qiu, Y.; Chen, Y. Therapeutic target database update 2022: Facilitating drug discovery with enriched comparative data of targeted agents. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D1398–D1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piñero, J.; Ramírez-Anguita, J.M.; Saüch-Pitarch, J.; Ronzano, F.; Centeno, E.; Sanz, F.; Furlong, L.I. The DisGeNET knowledge platform for disease genomics: 2019 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D845–D855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rappaport, N.; Twik, M.; Plaschkes, I.; Nudel, R.; Stein, T.I.; Levitt, J.; Gershoni, M.; Morrey, C.P.; Safran, M.; Lancet, D. MalaCards: An amalgamated human disease compendium with diverse clinical and genetic annotation and structured search. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D877–D887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Li, X.; Yang, J.; Liu, Y.; Fan, X.; Cheng, Y. CHD@ZJU: A knowledgebase providing network-based research platform on coronary heart disease. Database 2013, 2013, bat047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Nastou, K.; Koutrouli, M.; Kirsch, R.; Mehryary, F.; Hachilif, R.; Hu, D.; Peluso, M.E.; Huang, Q.; Fang, T.; et al. The STRING database in 2025: Protein networks with directionality of regulation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025, 53, D730–D737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oughtred, R.; Rust, J.; Chang, C.; Breitkreutz, B.J.; Stark, C.; Willems, A.; Boucher, L.; Leung, G.; Kolas, N.; Zhang, F.; et al. The BioGRID database: A comprehensive biomedical resource of curated protein, genetic, and chemical interactions. Protein Sci. 2021, 30, 187–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toro, N.D.; Shrivastava, A.; Ragueneau, E.; Meddal, B.; Combe, C.; Barrera, E.; Perfetto, L.; How, K.; Ratan, P.; Shirodkar, G.; et al. The IntAct database: Efficient access to fine-grained molecular interaction data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D648–D653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhou, B.; Pache, L.; Chang, M.; Khodabakhshi, A.H.; Tanaseichuk, O.; Benner, C.; Chanda, S.K. Metascape provides a biologist-oriented resource for the analysis of systems-level datasets. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, X.; Liu, C.; Zhang, Z.; Cheng, M.; Mei, Z.; Li, X.; Liu, P.; Diao, L.; Ma, Y.; Jiang, P.; et al. BATMAN-TCM 2.0: An enhanced integrative database for known and predicted interactions between traditional Chinese medicine ingredients and target proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, 52, D1110–D1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Ren, J.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, J.; Wu, J.; Sun, H.; Zhou, S.; Yan, K.; Yan, X.; et al. LTM-TCM: A comprehensive database for the linking of Traditional Chinese Medicine with modern medicine at molecular and phenotypic levels. Pharmacol. Res. 2022, 178, 106185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, W.; Liu, Y.; Lan, J.; Li, T.; He, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, T.; Ding, Y. Self-assembled nanoparticles from Xie-Bai-San decoction: Isolation, characterization and enhancing oral bioavailability. Int. J. Nanomed. 2024, 19, 3405–3421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Jin, M.; Jiang, S.; Shang, P.; Dong, X.; Li, L. Research progress on pharmacological effects and bioavailability of berberine. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 2024, 397, 8485–8514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huggins, D.J.; Venkitaraman, A.R.; Spring, D.R. Rational methods for the selection of diverse screening compounds. ACS Chem. Biol. 2011, 6, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talevi, A. Computer-aided drug discovery and design: Recent advances and future prospects. Methods Mol. Biol. 2024, 2714, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Ye, Y.; Xie, G.; Xu, Y.; Cheng, M.; Li, C.; Qu, M.; Zhu, F. Pharmacological mechanism of Sancao Yuyang decoction in the treatment of oral mucositis based on network pharmacology and experimental validation. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2023, 17, 55–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Q.; Zhu, L.; Ding, X.; Lou, Y. Integration of network pharmacology and experimental validation to explore the pharmacological mechanism of andrographolide against asthma. Bioresour. Bioprocess. 2025, 12, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, J.; Duan, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, H.; Wei, C.; Wang, J.; Qin, X.; Wang, X.; Li, Z. Metabolomics coupled with SystemsDock reveal the protective effect and the potential active components of Naozhenning granule against traumatic brain injury. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 246, 112247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mollazadeh, M.; Mohammadi-Khanaposhtani, M.; Valizadeh, Y.; Zonouzi, A.; Faramarzi, M.A.; Kiani, M.; Biglar, M.; Larijani, B.; Hamedifar, H.; Mahdavi, M.; et al. Novel coumarin containing dithiocarbamate derivatives as potent alpha-glucosidase inhibitors for management of type 2 diabetes. Med. Chem. 2021, 17, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.M.; Wang, D.; Lu, F.; Zhao, R.; Ye, X.; He, L.; Ai, L.; Wu, C.J. Identification of the active substances and mechanisms of ginger for the treatment of colon cancer based on network pharmacology and molecular docking. BioData Min. 2021, 14, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, L.L.G.; Andricopulo, A.D. ADMET modeling approaches in drug discovery. Drug Discov. Today. 2019, 24, 1157–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Wang, D.; Hao, X.; Li, Y.; Gao, H.; Fan, Y.; Fang, B.; Guo, Y. Exploring the high-quality ingredients and mechanisms of Da chuanxiong formula in the treatment of neuropathic pain based on network pharmacology, molecular docking, and molecular dynamics simulation. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 178, 117195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pant, J.; Mittal, P.; Singh, L.; Marwah, H. Canthaxanthin downregulates EGFR in NSCLC: Network pharmacology, molecular docking, dynamics simulations, ADMET, and in-vitro analysis. Mol. Divers. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, X.; Li, B.; Omarini, A.B.; Gand, M.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J. Discovery of TCMs and derivatives against the main protease of SARS-CoV-2 via high throughput screening, ADMET analysis, and inhibition assay in vitro. J. Mol. Struct. 2022, 1268, 133709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Wu, Q.; Wu, Q.; Zhong, G.; Liang, Y.; Gu, Y.; Hu, Y.; Wang, W.; Hao, N.; Hao, N.; et al. Modulating endoplasmic reticulum stress in APP/PS1 mice by gomisin B and osthole in Bushen-Yizhi formula: Synergistic effects and therapeutic implications for Alzheimer’s disease. Phytomedicine 2023, 119, 155023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cádiz-Gurrea, M.L.; Sinan, K.I.; Zengin, G.; Bene, K.; Etienne, O.K.; Leyva-Jiménez, F.J.; Fernández-Ochoa, Á.; Villegas-Aguilar, M.D.C.; Mahomoodally, M.F.; Lobine, D.; et al. Bioactivity assays, chemical characterization, ADMET predictions and network analysis of khaya senegalensis A. juss (Meliaceae) extracts. Food Res. Int. 2021, 139, 109970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, J.; Wang, N.N.; Yao, Z.J.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Y.; Ouyang, D.; Lu, A.P.; Cao, D.S. ADMETlab: A platform for systematic ADMET evaluation based on a comprehensively collected ADMET database. J. Cheminform. 2018, 10, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.; Li, S.; Li, Z.; Wang, Z.; Lin, J. Interpretable-ADMET: A web service for ADMET predition and optimization based on deep neural representation. Bioinformatics 2022, 38, 2863–2871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sander, T.; Freyss, J.; Korff, M.V.; Rufener, C. DataWarrior: An open-source program for chemistry aware data visualization and analysis. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2015, 55, 460–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudik, A.V.; Bezhentsev, V.M.; Dmitriev, A.V.; Druzhilovskiy, D.S.; Lagunin, A.A.; Filimonov, D.A.; Poroikov, V. MetaTox: Web application for predicting structure and toxicity of xenobiotics’ metabolites. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2017, 57, 638–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, N.; Zhai, M.; Su, Z.; Chu, F.; Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liao, M.; Li, P.; Bo, R.; Meng, X.; et al. Pharmacodynamics and pharmacological mechanism of moluodan concentrated pill in the treatment of atrophic gastritis: A network pharmacological study and in vivo experiments. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 318, 116937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Li, J.; Hu, M. Mechanism analysis of Buyang huanwu decoction in treating atherosclerosis based on network pharmacology and in vitro experiments. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2024, 103, e14447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Zhang, X.; Kong, Y.; Su, B.; Wu, L.; Liu, D.; Wang, X. Therapeutic effects of Panax notoginseng saponins in rheumatoid arthritis: Network pharmacology and experimental validation. Bioengineered 2022, 13, 14438–14449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, X.; Zhang, W.; Peng, C.; Yan, J.; Chen, P.; Jiang, C.; Yuan, Y.; Chen, D.; Zhu, W.; Yao, M. In vitro anti-bacterial activity and network pharmacology analysis of Sanguisorba officinalis L. against Helicobacter pylori infection. Chin. Med. 2021, 16, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Li, H.; Wang, T.; Zhao, Y.; Shao, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Z. Network pharmacology-based analysis of the mechanism of Saposhnikovia divaricate for the treatment of type I allergy. Pharm. Biol. 2022, 60, 1224–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Zhou, F.; Xiao, K.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Wang, S.; Yang, S. Mechanism of Sijunzi decoction in the treatment of colorectal cancer based on network pharmacology and experimental validation. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2023, 302, 115876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, W.; Deng, J.; He, J.; Yin, L.; You, R.; Zhang, L.; Shen, J.; Han, Z.; Xie, F.; He, J.; et al. Integration of molecular docking, molecular dynamics and network pharmacology to explore the multi-target pharmacology of fenugreek against diabetes. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2023, 27, 1959–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Gao, H.; Wei, Y.; Wang, Y. Traditional Chinese medicine in the prevention of diabetes mellitus and cardiovascular complications: Mechanisms and therapeutic approaches. Front. Pharmacol. 2025, 16, 1511701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, K.; Cao, W.; He, Z.; Liu, L.; Guo, J.; Dong, L.; Song, J.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, Y. Network medicine analysis for dissecting the therapeutic mechanism of consensus TCM formulae in treating hepatocellular carcinoma with different TCM syndromes. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1373054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, X.; Shu, Z.; Wang, X.; Yan, D.; Li, J.; Ofaim, S.; Albert, P.; Li, X.; Liu, B.; Zhou, X.; et al. Network medicine framework reveals generic herb-symptom effectiveness of traditional Chinese medicine. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eadh0215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, J.; Chen, X.; Hou, M.; Yang, K.; Yang, B.; Wang, P.; Du, Y.; Yu, Q.; Ren, J.; Liu, J. The TCM preparation Feilike mixture for the treatment of pneumonia: Network analysis, pharmacological assessment and silico simulation. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 794405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, L.; Zhang, X.; Li, S.; Sun, Y.; Jin, H.; Yan, S.; Han, C. Network pharmacological investigation into the mechanism of Kaixinsan powder for the treatment of depression. Metab. Brain Dis. 2022, 37, 2903–2914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Wei, F.; Lv, M.; Qu, P.; Chen, S.; Li, S.; Qin, X. The synergistic anti-depression effects of different efficacy groups of Xiaoyaosan as demonstrated by the integration of network pharmacology and serum metabolomics. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2021, 197, 113949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Z.; Jiao, H.; Chen, J.; Zhang, K.; Wang, X.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xue, Z.; Ma, Q.; Li, X.; et al. Antidepressant mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine formula Xiaoyaosan in CUMS-Induced depressed mouse model via RIPK1-RIPK3-MLKL mediated necroptosis based on network pharmacology analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 773562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bo, M.; Zhang, H.; Xu, J.; Zhao, H.; Jia, X.; Wang, G.; Lu, Z. Systematic review of Kaixinsan in treating depression: Efficacy and pharmacological mechanisms. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 1061877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Sun, H.; Yan, G.; Zhang, X.; Guan, Y.; Li, D.; Wang, X. Combination of ultra-performance liquid chromatography-quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry and network pharmacology to reveal the mechanism of Shengyu decoction for treating anemia. J. Sep. Sci. 2023, 46, e2200678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, C.; Liu, J.; Feng, M.; Jia, Z.; Li, Y.; Dai, Y.; Zhu, M.; Huang, B.; Liu, L.; Wei, Z.; et al. Shengyu decoction treating vascular cognitive impairment by promoting AKT/HIF-1α/VEGF related cerebrovascular generation and ameliorating MAPK/NF-kB mediated neuroinflammation. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 296, 115441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Su, H.; Wang, H.; Lu, F.; Nie, K.; Wang, Z.; Huang, W.; Dong, H. The effect and mechanism of Jiao-tai-wan in the treatment of diabetes mellitus with depression based on network pharmacology and experimental analysis. Mol. Med. 2021, 27, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, S.; Jing, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, W.; Gao, W. Network pharmacology and the experimental findings of Bushenhuoxue formula for improving hippocampal neuron injury in vascular demented rats. J. Integr. Neurosci. 2021, 20, 847–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, S.; Cai, Y.; Cai, X.; Zheng, X.; Cao, D.; Ye, F.; Xiang, Z. A network pharmacology approach to understanding the mechanisms of action of traditional medicine: Bushenhuoxue formula for treatment of chronic kidney disease. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, 89123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Li, S.; Xu, R.; Fang, L.; Xu, H.; Tong, P. Predication of the underlying mechanism of Bushenhuoxue formula acting on knee osteoarthritis via network pharmacology-based analyses combined with experimental validation. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 263, 113217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, P.; Lu, J.; Han, X.; She, J. Network pharmacology and experimental validation to explore the molecular mechanisms of Bushen huoxue for the treatment of premature ovarian insufficiency. Bioengineered 2021, 12, 10345–10362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sudhakar, K.; Mishra, V.; Hemani, V.; Verma, A.; Jain, A.; Jain, S.; Charyulu, R.N. Reverse pharmacology of phytoconstituents of food and plant in the management of diabetes: Current status and perspectives. Trends Food Sci. Tech. 2021, 110, 594–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhang, B.; Jiang, D.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, N. Herb network construction and co-module analysis for uncovering the combination rule of traditional Chinese herbal formulae. BMC Bioinform. 2010, 11, S6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Bai, L.; Lu, J.; Dong, Q.; Cao, B. Study on medication rules of traditional Chinese medicine in treating constipation through data mining and network pharmacology. Biomed. Res. Int. 2022, 15, 6733851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, L.Q.; Xu, J.; Chen, S.D. In silico screening of potential Chinese herbal medicine against COVID-19 by targeting SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro and angiotensin converting enzyme II using molecular docking. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 2020, 26, 527–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagunin, A.A.; Ivanov, S.M.; Gloriozova, T.A.; Pogodin, P.V.; Filimonov, D.A.; Kumar, S.; Goel, R.K. Combined network pharmacology and virtual reverse pharmacology approaches for identification of potential targets to treat vascular dementia. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tai, Y.; Tian, H.; Yang, X.; Feng, S.; Chen, S.; Zhong, C.; Gao, T.; Gang, X.; Liu, M. Identification of hub genes and candidate herbal treatment in obesity through integrated bioinformatic analysis and reverse network pharmacology. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 17113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Wang, J.; Zhou, W.; Wang, Y.; Yang, L. Systems approaches and polypharmacology for drug discovery from herbal medicines: An example using licorice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2013, 146, 773–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Jiang, C.; Lin, Q. Entropy analysis and grey cluster analysis of multiple indexes of 5 kinds of genuine medicinal materials. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 6618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, Y.; Cai, X.; Wang, Y.; Ban, L.; Mei, M.; Chen, S.; Xu, Q.; Chen, B.; Liang, S.; Wang, X. Utilizing network pharmacology and experimental validation to investigate the underlying mechanism of Denglao qingguan decoction against HCoV-229E. Heliyon 2024, 10, E27829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, X.; Li, H.; Jin, J.; Ju, X.; Gao, J.; Chen, X.; Yuan, F.; Gu, J.; Xu, D.; Ju, G. Network pharmacology and experimental validation to explore the role and potential mechanism of Liuwei dihuang decoction in prostate cancer. BMC Complement. Med. 2024, 24, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Chen, Y.; Yang, Z.; Xiang, H.; Kang, P.; Li, J. Active substances and molecular mechanisms of the anti-myocardial ischemia effects of Carthami flos by network pharmacology and in vitro experiments. Heliyon 2023, 9, E13877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Song, H.; Zhang, C.; Wang, A.; Zhang, B.; Xiong, C.; Zhuang, X.; Zang, Y.; Li, C.; Fang, Q.; et al. Efficacy and safety of Panax notoginseng saponins in the treatment of adults with ischemic stroke in China: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA Netw. Open 2023, 6, e2317574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Li, X.; Chen, G.; Xian, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wu, J.; Wang, C.; He, S.; et al. Traditional Chinese medicine compound (Tongxinluo) and clinical outcomes of patients with acute myocardial infarction: The CTS-AMI randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2023, 330, 1534–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, Y.; Chen, H.; Li, J.; Wu, Q. Efficacy, chemical constituents, and pharmacological actions of Radix Paeoniae Rubra and Radix Paeoniae Alba. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, Y.; Chen, K.; Quan, D.; Kang, L.; Yang, D.; Hu, H.; Yan, M.; Wu, S.; Lv, L.; Zhang, G. The combination of Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi and Sophora japonica L. ameliorate renal function by regulating gut microbiota in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 11, 575294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Wang, Z.; Shi, K.; Shen, Y.; Yu, X.; Cheng, C.; Xia, Y.; Dai, G.; Zhao, Z.; Xiong, Y.; et al. Using network pharmacology and transcriptome sequencing to investigate the mechanism of action of luteolin and quercetin in treating obesity. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2025, 105, e70061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; Shi, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, R.; Wu, X.; Zhao, W.; Chen, Z.; Ye, G. Network pharmacology and single-cell transcriptomic analysis with molecular docking to elucidate the potential compounds and targets of Polygonum cuspidatum Sieb.et Zucc. for hepatocellular carcinoma. iLIVER 2024, 3, 100115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Cheng, C.; Wu, Z. Mechanisms underlying the therapeutic effects of cinobufagin in treating melanoma based on network pharmacology, single-cell RNA sequencing data, molecular docking, and molecular dynamics simulation. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 14, 1315965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Wu, H.; Jiang, X.; Ou, Q.; Gan, Z.; Han, F.; Cai, Y. Single-cell RNA sequencing, cell communication, and network pharmacology reveal the potential mechanism of Senecio scandens Buch.-Ham in hepatocellular carcinoma inhibition. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Li, H.; Wang, X.; Sun, P.; Zhang, H.; Yin, W.; Fan, K.; Yang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Zhong, J.; et al. The effect and mechanism of sanguinarine against PCV2 based on the analysis of network pharmacology and TMT quantitative proteomics. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 296, 139767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, J.; Zhan, Y.; Huang, K.; Han, S.; Lin, Z.; Chen, R.; Luo, Q.; Li, Z.; Chen, B.; Li, S. Integration of network pharmacology and proteomics analysis to identify key target pathways of ginsenoside Re for myocardial ischemia. Phytomedicine 2024, 132, 155728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, D.; Wang, X.; Huang, D.; Chen, B.; Lin, X.; Huang, J. Disclosing targets and pharmacological mechanisms of total bioflavonoids extracted from Selaginella doederleinii against non-small cell lung cancer by combination of network pharmacology and proteomics. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 286, 114836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Wu, Y.; Huang, T.; Huang, D.; Zeng, Q.; Wang, Z.; Hu, Y.; Liang, P.; Chen, H.; Zheng, Z.; et al. Licorice flavonoid ameliorates ethanol-induced gastric ulcer in rats by suppressing apoptosis via PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 325, 117739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Li, Q. Study on the anti-inflammatory mechanism of coumarins in Peucedanum decursivum based on spatial metabolomics combined with network pharmacology. Molecules 2024, 29, 3346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, D.; Min, J.; Chen, J.; Yan, D.; Han, J.; Liu, H.; Yu, X.; Nie, Z.; Li, B. Study on the material basis and mechanisms of Achyrocline satureioides in the treatment of nonsmall cell lung cancer based on network pharmacology and spatial metabolomics. Anal. Chem. 2025, 97, 5688–5697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, M.; Shi, J.; Wu, C.; Xu, Y.; Liu, Y. Integrating lipidomics, metabolomics, and network pharmacology to reveal the mechanism of cannabidiol against inflammation in high-fat, high-cholesterol diet-induced mice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 19246–19256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Zhu, J.; Zhou, T.; Jin, Z. Exploring the mechanisms of Yinchenhao decoction against ANIT-induced cholestatic liver injury by lipidomics, metabolomics and network pharmacology. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2025, 258, 116736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Tan, Y.; Huang, J.; Wu, C.; Fan, X.; Stalin, A.; Lu, S.; Wang, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, F.; et al. Revealing the mechanism of huazhi rougan granule in the treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver through intestinal flora based on 16S rRNA, metagenomic sequencing and network pharmacology. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 13, 875700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Guo, M.; Li, X.; Zhao, D.; Wang, M. Microbiota, co-metabolites, and network pharmacology reveal the alteration of the ginsenoside fraction on inflammatory bowel disease. J. Ginseng Res. 2023, 47, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muthamil, S.; Muthuramalingam, P.; Kim, H.Y.; Jang, H.J.; Lyu, J.H.; Shin, U.C.; Go, Y.; Park, S.H.; Lee, H.G.; Shin, H.; et al. Unlocking prognostic genes and multi-targeted therapeutic bioactives from herbal medicines to combat cancer-associated cachexia: A transcriptomics and network pharmacology approach. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 25, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muthuramalingama, P.; Akasshc, S.; Rithigac, S.B.; Prithika, S.; Gunasekaran, R.; Shin, H.; Kumar, R.; Baskar, V.; Kim, J. Integrated omics profiling and network pharmacology uncovers the prognostic genes and multi-targeted therapeutic bioactives to combat lung cancer. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2023, 940, 175479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Chang, L.; Wu, W.; Jing, M.; Li, H.; Niu, C.; Wei, S.; Zhu, S.; Zhao, Y. Multi-omics analysis combined with network pharmacology revealed the mechanisms of rutaecarpine in chronic atrophic gastritis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2025, 339, 119151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Zhang, D.; Zhou, W.; Wang, L.; Wang, B.; Zhang, T.; Li, S. Network pharmacology: Towards the artificial intelligence-based precision traditional Chinese medicine. Brief. Bioinform. 2024, 25, bbad518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Z.; Chen, G.; Chen, C.Y.C. AI empowering traditional Chinese medicine? Chem. Sci. 2024, 15, 16844–16886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noorain; Srivastava, V.; Parveen, B.; Parveen, R. Artificial intelligence in drug formulation and development: Applications and future prospects. Curr. Drug Metab. 2023, 24, 622–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noor, F.; Asif, M.; Ashfaq, U.A.; Qasim, M.; Qamar, M.T.U. Machine learning for synergistic network pharmacology: A comprehensive overview. Brief. Bioinform. 2023, 24, bbad120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huo, K.; Yang, Y.; Yang, T.; Zhang, W.; Shao, J. Identification of drug targets and agents associated with ferroptosis-related osteoporosis through integrated network pharmacology and molecular docking technology. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2024, 30, 1103–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Zheng, Y.; Shao, M.; Chen, A.; Liu, M.; Sun, W.; Li, T.; Fang, Y.; Dong, Y.; Zhao, S.; et al. AlphaFold-based AI docking reveals AMPK/SIRT1-TFEB pathway modulation by traditional Chinese medicine in metabolic-associated fatty liver disease. Pharmacol. Res. 2025, 212, 107617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Wei, P.; Xu, X.; Dong, R.; Deng, X.; Zhang, F.; Sun, M.; Li, M.; Liu, W.; Yao, W.; et al. Machine learning-assisted analysis of serum metabolomics and network pharmacology reveals the effective compound from herbal formula against alcoholic liver injury. Chin. Med. 2025, 20, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, P.; Huang, H.; Li, D. Combining bioinformatics, network pharmacology, and artificial intelligence to predict the mechanism of resveratrol in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Heliyon 2024, 10, e37371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.; Guo, J.; Lin, H.; Wei, W.; Fan, L.; Chen, H.; Gong, Y. Machine learning-enhanced network pharmacology in TCM: Mechanistic insights into Chai hu gui zhi tang for allergic rhinitis. Chem. Biodivers. 2025, 10, e202500214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Wang, S.; Gao, Y.; Hu, Y.; Zeng, X.; Liu, S.; Li, P.; Lan, T.; Shen, Q.; Tong, Y.Y.; et al. Yi-qi-yang-yin decoction ameliorates diabetic retinopathy: New and comprehensive evidence from network pharmacology, machine learning, molecular docking and molecular biology experiment. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2025, 260, 116794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Type | Name | Description | Website (Access Date) | Release | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TCM-related databases | TCMSP | Chinese herbal medicine action mechanism analysis platform and database, including 499 kinds of herbal medicines, providing herbal ingredients and key pharmacokinetic properties, and obtaining the relationship between Chinese herbal medicines, targets, and diseases. | https://tcmsp-e.com/tcmsp.php (1 June 2025) | Monthly | [20] |
| ETCM 2.0 | This database includes comprehensive information on TCM formulas and their ingredients and provides predictive targets for TCM formulas and their ingredients. It can systematically establish a network of relationships among ingredients, herbs, formulas, targets, and diseases. | http://www.tcmip.cn/ETCM/ (1 June 2025) | 2023 | [23] | |
| TCMID 2.0 | A comprehensive database with the goal of the modernization and standardization of TCM, including 46,929 prescriptions, 8159 herbal medicines, 43,413 total ingredients, 8182 drugs, and 4633 diseases. | https://bidd.group/TCMID/about.html (1 June 2025) | 2017 | [29] | |
| TCMBanK | The largest TCM database. It provides deep learning-based Chinese–Western medicine exclusion prediction. | http://tcm.cmu.edu.tw (1 June 2025, not accessible) | 2023 | [30] | |
| HERB | A reference guide database for high-throughput experiments of traditional Chinese medicine, including 12,933 targets, 28,212 diseases, 7263 herbs, and 49,258 ingredients. | http://herb.ac.cn (1 June 2025) | 2020 | [31] | |
| HIT 2.0 | Comprehensive Chinese herbal medicine ingredient index database; molecular target information, including proteins that are directly/indirectly activated/inhibited; protein conjugates and substrates; products which are the enzymes of these compounds. | http://hit2.badd-cao.net/ (1 June 2025) | 2021 | [32] | |
| ITCM | The largest-to-date online TCM active ingredient-based pharmacotranscriptomic platform on integrated TCM for effective screening of bioactive compounds. | http://itcm.biotcm.net (1 June 2025) | 2022 | [33] | |
| CPMCP | A TCM-related database collecting components, indications, and contraindications originating from TCM. | http://cpmcp.top/ (2 Nov 2022, not accessible) | 2022 | [34] | |
| SymMap | An integrative database of TCM enhanced by symptom mapping. | http://www.symmap.org/ (1 June 2025) | 2019 | [35] | |
| Drug-related databases | PubChem | Public chemical information resources to analyze the biological activity of small chemical molecules. | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov (1 June 2025) | 2021 | [21] |
| ChEMBL | Open large-scale biological activity database, including target annotation and drug metabolism pathways. | https://www.ebi.ac.uk/chembl (1 June 2025) | 2019 | [36] | |
| ChemSpider | Free chemical structure database, providing fast text and structure search of 67 million structures. | http://www.chemspider.com (1 June 2025) | 2024 | [37] | |
| DrugBank 6.0 | This database provides detailed drug data and drug target information, as well as comprehensive molecular information about their mechanisms. | https://go.drugbank.com (1 June 2025) | 2023 | [38] | |
| Protein-related databases | UniProt | The protein database with the most information and resources, providing protein sequences with functional information annotations. | https://www.uniprot.org (1 June 2025) | 2023 | [39] |
| MINT | Public repository of protein interactions. | https://mint.bio.uniroma2.it (1 June 2025) | 2012 | [40] | |
| HPO | This database provides phenotypic information about human diseases, containing more than 13,000 terms and more than 156,000 notes on genetic diseases. | https://hpo.jax.org (1 June 2025) | 2021 | [41] | |
| Disease-related databases | GeneCards | This database provides comprehensive annotated and predicted human genes, including genome, transcriptome, proteome, and related functional information. | https://www.genecards.org (1 June 2025) | 2024 | [22] |
| CTD | This database provides information on chemical–gene/protein interactions, chemical–disease and gene–disease relationships and helps elucidate potential mechanisms of environmental impact on diseases. | https://ctdbase.org (1 June 2025) | 2023 | [42] | |
| TTD | This database provides information about the main targets of drugs. | http://db.idrblab.net/ttd/ (1 June 2025) | 2022 | [43] | |
| DisGeNET | This database includes 1,134,942 gene–disease associations (GDAs) and 369,554 variant–disease associations (VDAs). | https://www.disgenet.org (1 June 2025) | 2020 | [44] | |
| MalaCards | An integrated database of human maladies and their annotations. | https://www.malacards.org (1 June 2025) | 2023 | [45] | |
| CHD@ZJU | This database provides a network-based study platform on coronary heart disease. | http://tcm.zju.edu.cn/chd/ (not accessible) | 2023 | [46] | |
| Protein interaction database | STRING v12 | Protein networks with directionality of regulation. | https://string-db.org (1 June 2025) | 2024 | [47] |
| BioGRID | Archive of genetic and protein interaction data from model organisms and humans. | https://thebiogrid.org/ (1 June 2025) | 2021 | [48] | |
| IntAct | An open-source database and analysistool for molecular interaction data. | https://www.ebi.ac.uk/intact/home (1 June 2025) | 2022 | [49] | |
| Software or platform | Cytoscape | This database integrates bio-molecular interaction networks with high-throughput expression data and other molecular states into a unified conceptual framework. | https://cytoscape.org (1 June 2025) | 2024 | [25] |
| TCM-Suite | A comprehensive and holistic platform for traditional Chinese medicine component identification and network pharmacology analysis. | http://TCM-Suite.AImicrobiome.cn (1 June 2025) | 2022 | [26] | |
| SoFDA | Ontology characterization, enrichment analysis, and similarity calculation-based evaluation of disease–syndrome–formula associations. | http://www.tcmip.cn/Syndrome/front/ (1 June 2025) | 2023 | [27] | |
| Metascape | This database is able to perform GO/KEGG enrichment analysis of genes, including a large number of databases and tools for gene annotation and gene enrichment analysis. | https://metascape.org/ (1 June 2025) | 2019 | [50] | |
| BATMAN- TCM 2.0 | The first online bioinformatics analysis platform specially designed for studying the molecular mechanisms of TCM. | http://bionet.ncpsb.org.cn/batman-tcm/index.php (1 June 2025) | 2024 | [51] | |
| LTM-TCM | A standardized platform for studying TCM mechanisms, providing reverse docking and ADME prediction analyses. | http://cloud.tasly.com/#/tcm/home (not accessible) | 2022 | [52] |
| Name | Description | Website (Access Date) | Release | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ADMETlab 2.0 | An integrated online platform for accurate and comprehensive predictions of ADMET properties. | https://admetmesh.scbdd.com/ (1 June 2025) | 2021 | [68] |
| Interpretable-ADMET | A web service for ADMET prediction and optimization based on deep neural representation. | http://cadd.pharmacy.nankai.edu.cn/interpretableadmet/ (1 June 2025) | 2022 | [69] |
| DataWarrior | Explores the compound space in an interactive way by visualizing the spatial structure of compounds or pharmacophores based on vector or non-vector descriptors. | http://www.openmolecules.org/datawarrior/download.html (1 June 2025) | 2019 | [70] |
| MetaTox 2.0 | Predicts the toxicity of metabolites in the body based on the structure of the compound. | https://www.way2drug.com/metatox (1 June 2025) | 2023 | [71] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, L.; Wang, H.; Zhu, Z.; Yang, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Cui, X.; Liu, Y. Network Pharmacology-Driven Sustainability: AI and Multi-Omics Synergy for Drug Discovery in Traditional Chinese Medicine. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 1074. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18071074
Yang L, Wang H, Zhu Z, Yang Y, Xiong Y, Cui X, Liu Y. Network Pharmacology-Driven Sustainability: AI and Multi-Omics Synergy for Drug Discovery in Traditional Chinese Medicine. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(7):1074. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18071074
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Lifang, Hanye Wang, Zhiyao Zhu, Ye Yang, Yin Xiong, Xiuming Cui, and Yuan Liu. 2025. "Network Pharmacology-Driven Sustainability: AI and Multi-Omics Synergy for Drug Discovery in Traditional Chinese Medicine" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 7: 1074. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18071074
APA StyleYang, L., Wang, H., Zhu, Z., Yang, Y., Xiong, Y., Cui, X., & Liu, Y. (2025). Network Pharmacology-Driven Sustainability: AI and Multi-Omics Synergy for Drug Discovery in Traditional Chinese Medicine. Pharmaceuticals, 18(7), 1074. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18071074







