Weight Loss Effects of Once-Weekly Semaglutide 2.4 mg in Adults with and Without Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Information Sources and Search Strategy
2.2. Eligibility Criteria
2.3. Research Questions
- What is the efficacy of once-weekly subcutaneous semaglutide at 2.4 mg on body weight reduction in individuals with and without type 2 diabetes mellitus (DM)?
- Is there a difference in weight loss efficacy between individuals with and without DM receiving semaglutide?
2.4. Study Selection
2.5. Data Extraction
2.6. Outcome Measures
- The efficacy of once-weekly subcutaneous semaglutide at 2.4 mg on the percentage change in body weight in adults with and without DM.
- The difference in weight loss efficacy between individuals with and without DM was assessed as the weighted mean difference (WMD) in percentage body weight change.
2.7. Risk of Bias Assessment
2.8. Data Synthesis
3. Results
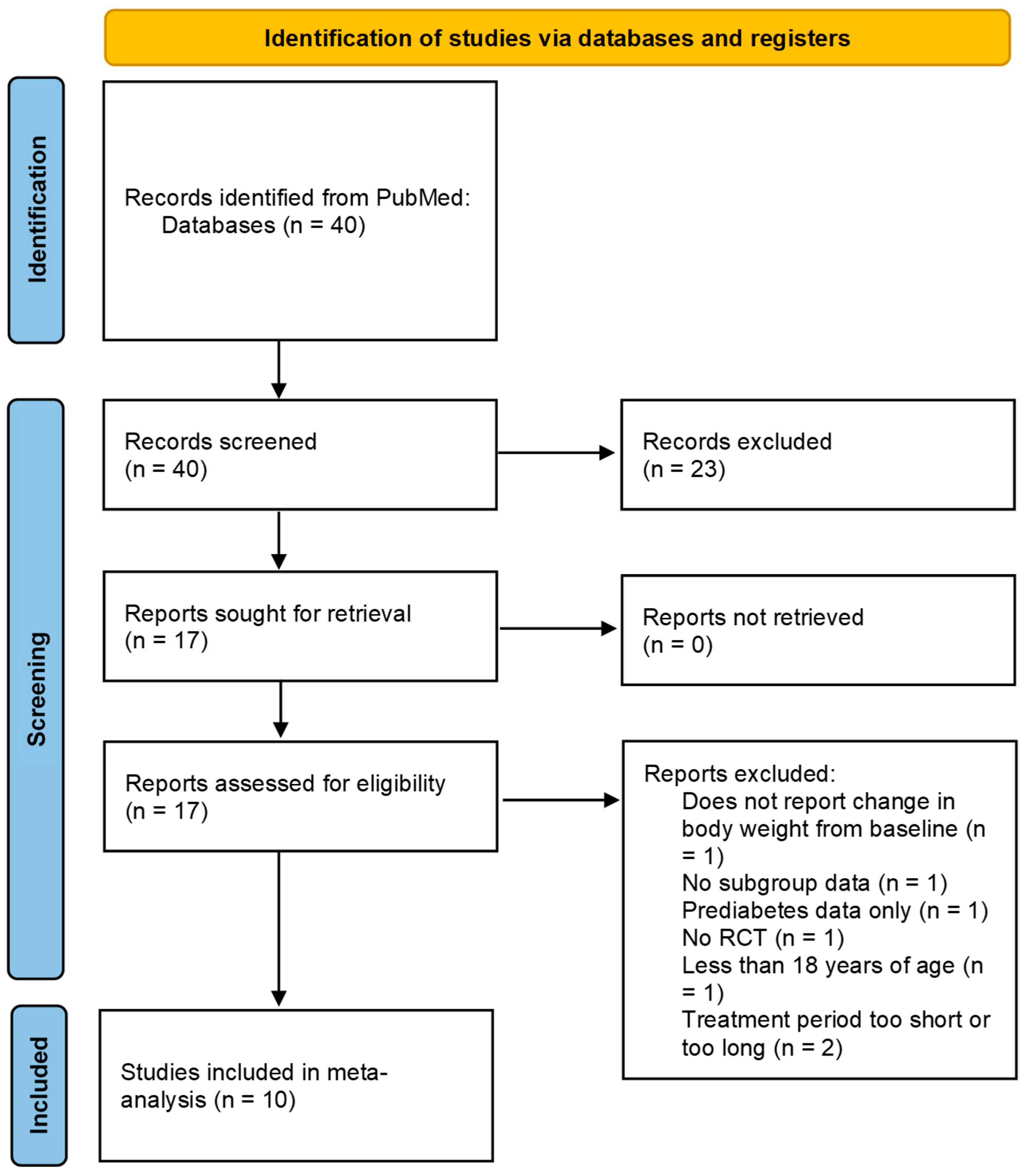
3.1. Study Selection
3.2. Study Characteristics
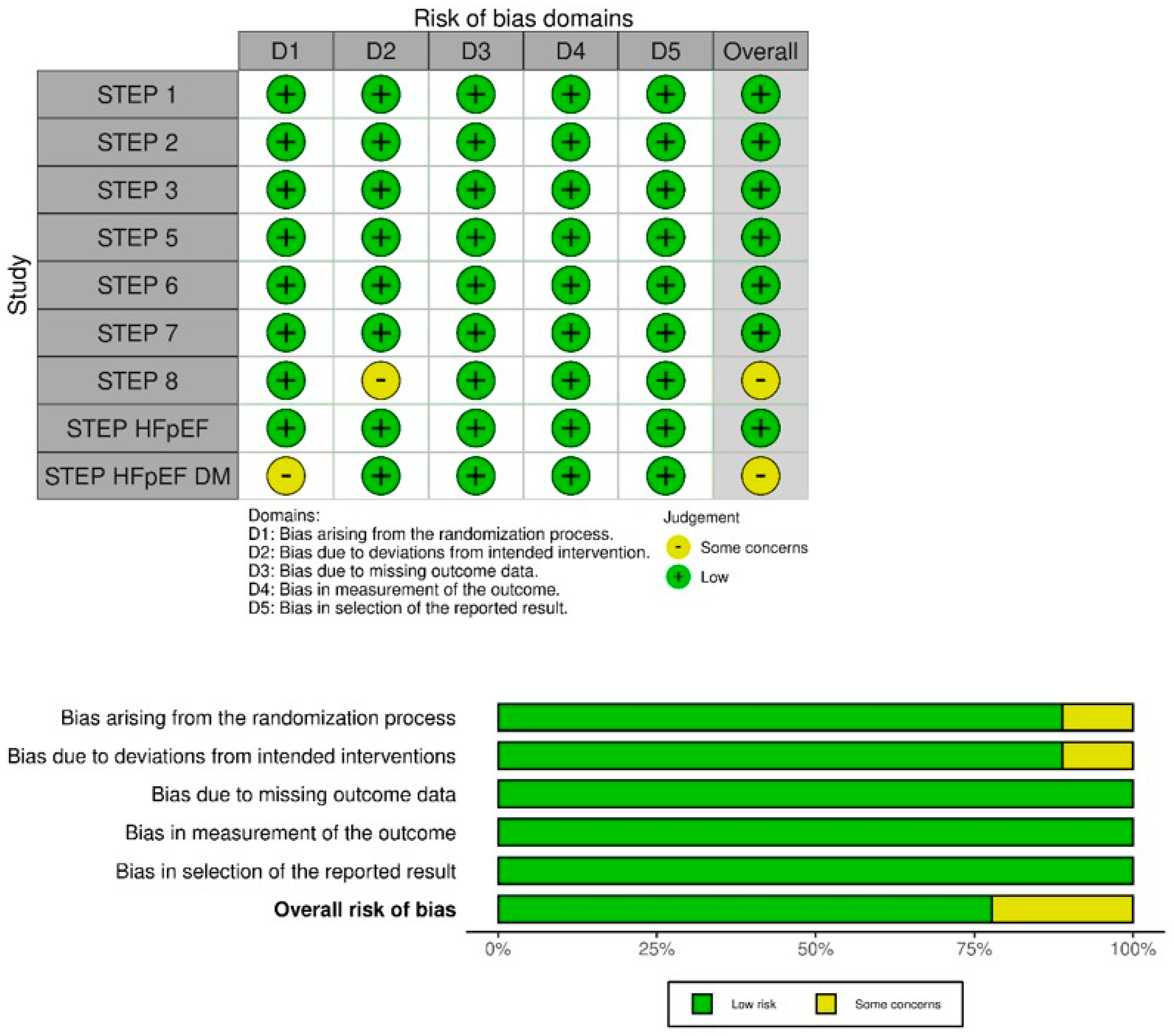
3.3. Risk of Bias
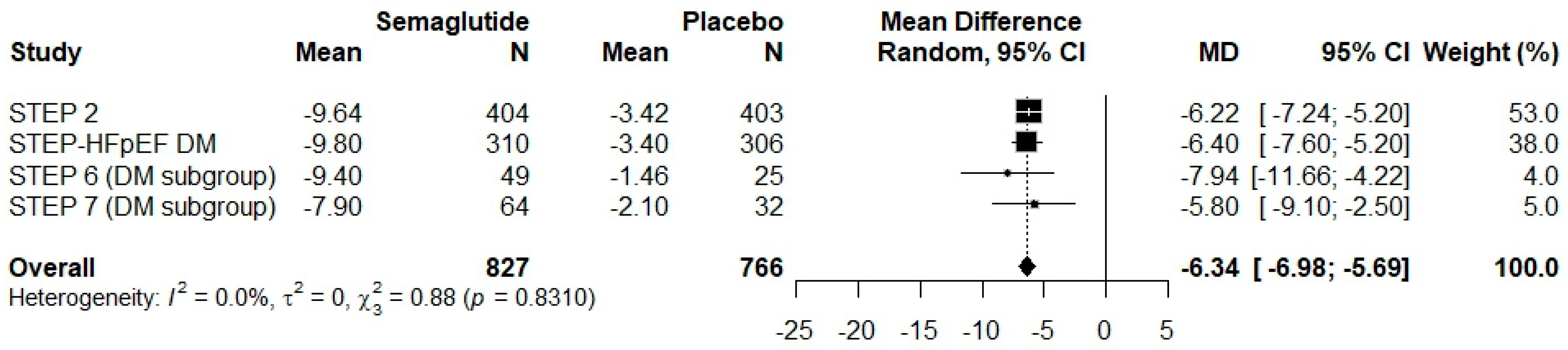
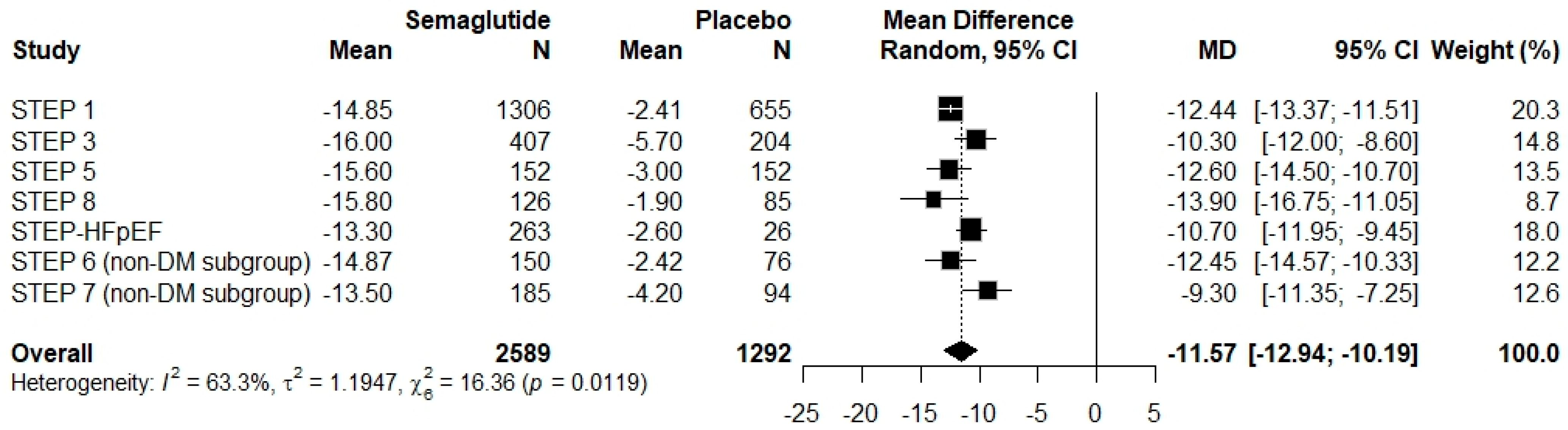
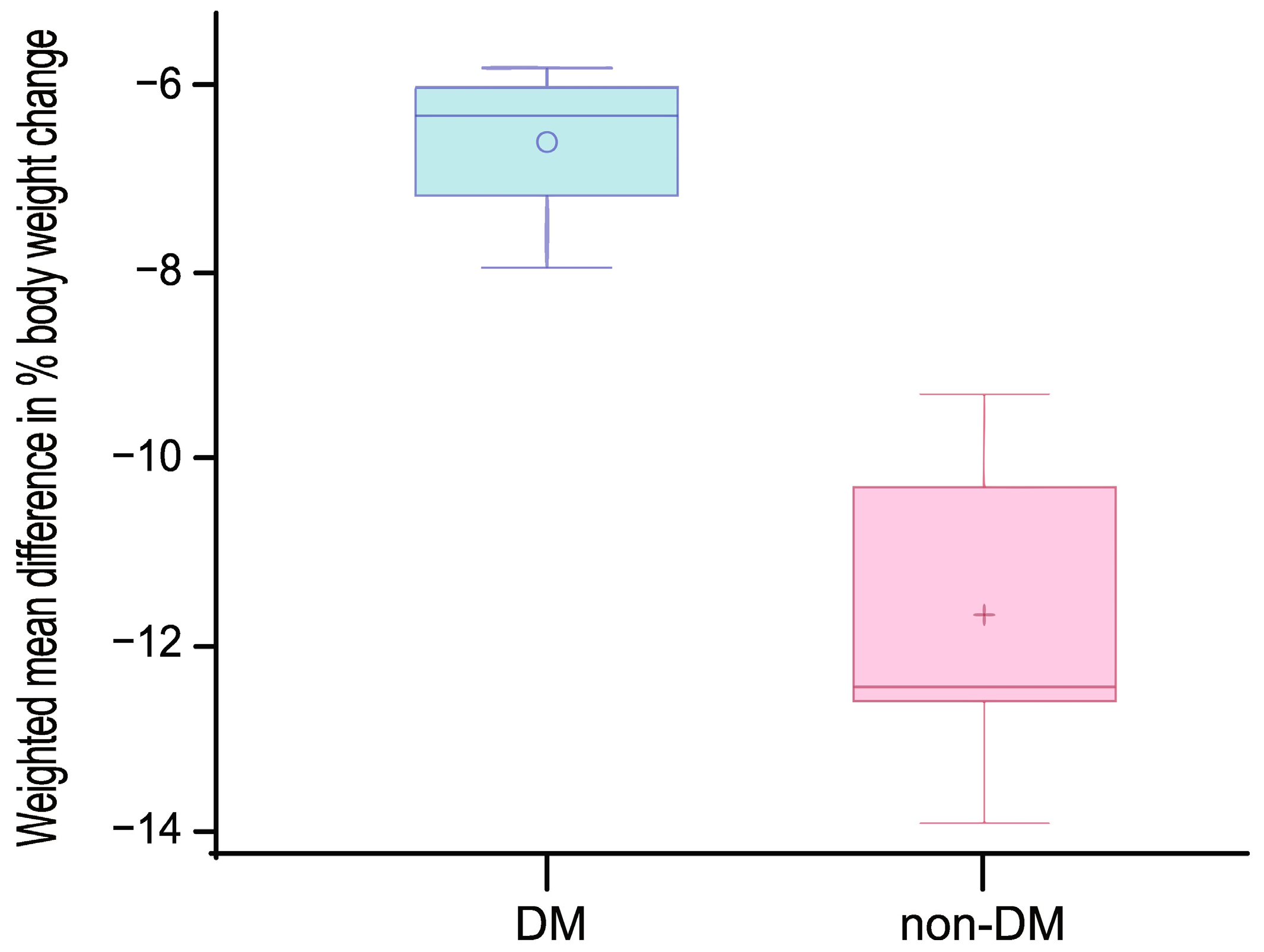
3.4. Results of Syntheses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Malik, V.S.; Popkin, B.M.; Bray, G.A.; Després, J.-P.; Willett, W.C.; Hu, F.B. Sugar-sweetened beverages, obesity, type 2 diabetes mellitus, and cardiovascular disease risk. Circulation 2010, 121, 1356–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedrosa, M.R.; Franco, D.R.; Gieremek, H.W.; Vidal, C.M.; Bronzeri, F.; de Cassia Rocha, A.; de Carvalho Cara, L.G.; Fogo, S.L.; Eliaschewitz, F.G. GLP-1 Agonist to Treat Obesity and Prevent Cardiovascular Disease: What Have We Achieved so Far? Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2022, 24, 867–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Obesity and Overweight. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight (accessed on 4 November 2024).
- Papamichou, D.; Panagiotakos, D.B.; Itsiopoulos, C. Dietary patterns and management of type 2 diabetes: A systematic review of randomised clinical trials. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2019, 29, 531–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magkos, F.; Fraterrigo, G.; Yoshino, J.; Luecking, C.; Kirbach, K.; Kelly, S.C.; de Las Fuentes, L.; He, S.; Okunade, A.L.; Patterson, B.W.; et al. Effects of moderate and subsequent progressive weight loss on metabolic function and adipose tissue biology in humans with obesity. Cell Metab. 2016, 23, 591–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvador, R.; Moutinho, C.G.; Sousa, C.; Vinha, A.F.; Carvalho, M.; Matos, C. Semaglutide as a GLP-1 Agonist: A Breakthrough in Obesity Treatment. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Q.; Wang, Y.; Hao, Q.; Vandvik, P.O.; Guyatt, G.; Li, J.; Chen, Z.; Xu, S.; Shen, Y.; Ge, L.; et al. Pharmacotherapy for adults with overweight and obesity: A systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Lancet 2024, 403, e21–e23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, J.; Bloch, P.; Schäffer, L.; Pettersson, I.; Spetzler, J.; Kofoed, J.; Madsen, K.; Knudsen, L.B.; McGuire, J.; Steensgaard, D.B.; et al. Discovery of the Once-Weekly Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 (GLP-1) Analogue Semaglutide. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 7370–7380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedrichsen, M.; Breitschaft, A.; Tadayon, S.; Wizert, A.; Skovgaard, D. The effect of semaglutide 2.4 mg once weekly on energy intake, appetite, control of eating, and gastric emptying in adults with obesity. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2021, 23, 754–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aroda, V.R.; Ahmann, A.; Cariou, B.; Chow, F.; Davies, M.J.; Jódar, E.; Mehta, R.; Woo, V.; Lingvay, I. Comparative efficacy, safety, and cardiovascular outcomes with once-weekly subcutaneous semaglutide in the treatment of type 2 diabetes: Insights from the SUSTAIN 1–7 trials. Diabetes Metab. 2019, 45, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aroda, V.R.; Rosenstock, J.; Terauchi, Y.; Altuntas, Y.; Lalic, N.M.; Morales Villegas, E.C.; Jeppesen, O.K.; Christiansen, E.; Hertz, C.L.; Haluzík, M. PIONEER 1: Randomized Clinical Trial of the Efficacy and Safety of Oral Semaglutide Monotherapy in Comparison With Placebo in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2019, 42, 1724–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilding, J.P.H.; Batterham, R.L.; Calanna, S.; Davies, M.; Van Gaal, L.F.; Lingvay, I.; McGowan, B.M.; Rosenstock, J.; Tran, M.T.D.; Wadden, T.A.; et al. Once-Weekly Semaglutide in Adults with Overweight or Obesity. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 989–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Y.; Shi, Y.; Guan, R.; Yan, S.; Liu, H.; Wang, Z.; Li, J.; Wang, T.; Cai, W.; Ma, G. Evaluation and comparison of efficacy and safety of tirzepatide and semaglutide in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A Bayesian network meta-analysis. Pharmacol. Res. 2024, 199, 107031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moiz, A.; Levett, J.Y.; Filion, K.B.; Peri, K.; Reynier, P.; Eisenberg, M.J. Long-term efficacy and safety of once-weekly semaglutide for weight loss in patients without diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Am. J. Cardiol. 2024, 222, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, M.; Færch, L.; Jeppesen, O.K.; Pakseresht, A.; Pedersen, S.D.; Perreault, L.; Rosenstock, J.; Shimomura, I.; Viljoen, A.; Wadden, T.A.; et al. Semaglutide 2·4 mg once a week in adults with overweight or obesity, and type 2 diabetes (STEP 2): A randomised, double-blind, double-dummy, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2021, 397, 971–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahn, S.E.; Hull, R.L.; Utzschneider, K.M. Mechanisms linking obesity to insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Nature 2006, 444, 840–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nauck, M.A.; Meier, J.J. Incretin hormones: Their role in health and disease. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2018, 20, 5–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kommu, S.; Berg, R.L. Efficacy and safety of once-weekly subcutaneous semaglutide on weight loss in patients with overweight or obesity without diabetes mellitus-A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Obes. Rev. 2024, 25, e13792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garvey, W.T.; Batterham, R.L.; Bhatta, M.; Buscemi, S.; Christensen, L.N.; Frias, J.P.; Jódar, E.; Kandler, K.; Rigas, G.; Wadden, T.A.; et al. Two-year effects of semaglutide in adults with overweight or obesity: The STEP 5 trial. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 2083–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wadden, T.A.; Bailey, T.S.; Billings, L.K.; Davies, M.; Frias, J.P.; Koroleva, A.; Lingvay, I.; O’Neil, P.M.; Rubino, D.M.; Skovgaard, D.; et al. Effect of subcutaneous semaglutide vs placebo as an adjunct to intensive behavioral therapy on body weight in adults with overweight or obesity: The STEP 3 randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2021, 325, 1403–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadowaki, T.; Isendahl, J.; Khalid, U.; Lee, S.Y.; Nishida, T.; Ogawa, W.; Tobe, K.; Yamauchi, T.; Lim, S.; STEP 6 Investigators. Semaglutide once a week in adults with overweight or obesity, with or without type 2 diabetes in an east Asian population (STEP 6): A randomised, double-blind, double-dummy, placebo-controlled, phase 3a trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2022, 10, 193–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadowaki, T.; Lee, S.Y.; Ogawa, W.; Nishida, T.; Overvad, M.; Tobe, K.; Yamauchi, T.; Lim, S.; STEP 6 Investigators. Clinical characteristics affecting weight loss in an East Asian population receiving semaglutide: A STEP 6 subgroup analysis. Obes. Res. Clin. Pract. 2024, 18, 457–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, Y.; Bao, X.; Eliaschewitz, F.G.; Hansen, M.R.; Kim, B.T.; Koroleva, A.; Ma, R.C.W.; Yang, T.; Zu, N.; Liu, M.; et al. Efficacy and safety of once weekly semaglutide 2.4 mg for weight management in a predominantly east Asian population with overweight or obesity (STEP 7): A double-blind, multicentre, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2024, 12, 184–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubino, D.M.; Greenway, F.L.; Kent, C.K.; Arslanian, S.; Tchang, B.G.; Pytlarz, G.; Gorfien, S.; Gumm, A.J.; Lin, W.; Nishida, T.; et al. Effect of weekly subcutaneous semaglutide vs daily liraglutide on body weight in adults with overweight or obesity without diabetes: The STEP 8 randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2022, 327, 138–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosiborod, M.N.; Abildstrøm, S.Z.; Borlaug, B.A.; Butler, J.; Rasmussen, S.; Davies, M.; Hovingh, G.K.; Kitzman, D.W.; Lindegaard, M.L.; Møller, D.V.; et al. Semaglutide in Patients with Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction and Obesity. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, 1069–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosiborod, M.N.; Petrie, M.C.; Borlaug, B.A.; Butler, J.; Davies, M.J.; Hovingh, G.K.; Kitzman, D.W.; Møller, D.V.; Treppendahl, M.B.; Verma, S.; et al. Semaglutide in Patients with Obesity-Related Heart Failure and Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 390, 1394–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssen, J.A.M.J.L. Hyperinsulinemia and its pivotal role in aging, obesity, type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease and cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssen, J.A.M.J.L. Overnutrition, hyperinsulinemia and ectopic fat: It is time for a paradigm shift in the management of type 2 diabetes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Arakawa, K.; Ueta, K.; Matsushita, Y.; Kuriyama, C.; Martin, T.; Du, F.; Liu, Y.; Xu, J.; Conway, W.; et al. Effect of canagliflozin on renal threshold for glucose, glycemia, and body weight in normal and diabetic animal models. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallon, V.; Thomson, S.C. Targeting renal glucose reabsorption to treat hyperglycaemia: The pleiotropic effects of SGLT2 inhibition. Diabetologia 2017, 60, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cersosimo, E.; Alatrach, M.; Solis-Herrera, C.; Baskoy, G.; Adams, J.; Hansis-Diarte, A.; Gastaldelli, A.; Chavez, A.; Triplitt, C.; DeFronzo, R.A. Emergence of a New Glucoregulatory Mechanism for Glycemic Control With Dapagliflozin/Exenatide Therapy in Type 2 Diabetes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2023, 109, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Candido, R.; Paccione, C.; Corbacelli, C.; Lichinchi, G.; Marcomigni, L.; Mattioli, C.; Pilla, R.; Sarais, C. Real-world retrospective study into the effects of oral semaglutide (as a switchover or add-on therapy) in type 2 diabetes. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 6052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samuel, V.T.; Shulman, G.I. Mechanisms for insulin resistance: Common threads and missing links. Cell 2012, 148, 852–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodish, I. Insulin therapy, weight gain and prognosis. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2018, 20, 2085–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bettadapura, S.; Dowling, K.; Jablon, K.; Al-Humadi, A.W.; le Roux, C.W. Changes in food preferences and ingestive behaviors after glucagon-like peptide-1 analog treatment: Techniques and opportunities. Int. J. Obes. 2025, 49, 418–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marso, S.P.; Bain, S.C.; Consoli, A.; Eliaschewitz, F.G.; Jódar, E.; Leiter, L.A.; Lingvay, I.; Rosenstock, J.; Seufert, J.; Warren, M.L.; et al. Semaglutide and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1834–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Husain, M.; Birkenfeld, A.L.; Donsmark, M.; Dungan, K.; Eliaschewitz, F.G.; Franco, D.R.; Jeppesen, O.K.; Lingvay, I.; Mosenzon, O.; Pedersen, S.D.; et al. Oral Semaglutide and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 841–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lincoff, A.M.; Brown-Frandsen, K.; Colhoun, H.M.; Deanfield, J.; Emerson, S.S.; Esbjerg, S.; Hardt-Lindberg, S.; Hovingh, G.K.; Kahn, S.E.; Kushner, R.F.; et al. Semaglutide and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Obesity without Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, 2221–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, D.H.; Lingvay, I.; Deanfield, J.; Kahn, S.E.; Barros, E.; Burguera, B.; Colhoun, H.M.; Cercato, C.; Dicker, D.; Horn, D.B.; et al. Long-term weight loss effects of semaglutide in obesity without diabetes in the SELECT trial. Nat. Med. 2024, 30, 2049–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, D.H.; Lingvay, I.; Colhoun, H.M.; Deanfield, J.; Emerson, S.S.; Kahn, S.E.; Kushner, R.F.; Marso, S.; Plutzky, J.; Brown-Frandsen, K.; et al. Semaglutide Effects on Cardiovascular Outcomes in People With Overweight or Obesity (SELECT) rationale and design. Am. Heart J. 2020, 229, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kristensen, S.L.; Rørth, R.; Jhund, P.S.; Docherty, K.F.; Sattar, N.; Preiss, D.; Køber, L.; Petrie, M.C.; McMurray, J.J.V. Cardiovascular, mortality, and kidney outcomes with GLP-1 receptor agonists in patients with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of cardiovascular outcome trials. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019, 7, 776–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perkovic, V.; Tuttle, K.R.; Rossing, P.; Mahaffey, K.W.; Mann, J.F.E.; Bakris, G.; Baeres, F.M.M.; Idorn, T.; Bosch-Traberg, H.; Lausvig, N.L.; et al. Effects of Semaglutide on Chronic Kidney Disease in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 391, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newsome, P.N.; Buchholtz, K.; Cusi, K.; Linder, M.; Okanoue, T.; Ratziu, V.; Sanyal, A.J.; Sejling, A.S.; Harrison, S.A. A Placebo-Controlled Trial of Subcutaneous Semaglutide in Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 1113–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wharton, S.; Calanna, S.; Davies, M.; Dicker, D.; Goldman, B.; Lingvay, I.; Mosenzon, O.; Rubino, D.M.; Thomsen, M.; Wadden, T.A.; et al. Gastrointestinal tolerability of once-weekly semaglutide 2.4 mg in adults with overweight or obesity, and the relationship between gastrointestinal adverse events and weight loss. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2022, 24, 94–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahrén, B.; Atkin, S.L.; Charpentier, G.; Warren, M.L.; Wilding, J.P.H.; Birch, S.; Holst, A.G.; Leiter, L.A. Semaglutide induces weight loss in subjects with type 2 diabetes regardless of baseline BMI or gastrointestinal adverse events in the SUSTAIN 1 to 5 trials. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2018, 20, 2210–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilding, J.P.H.; Batterham, R.L.; Davies, M.; Van Gaal, L.F.; Kandler, K.; Konakli, K.; Lingvay, I.; McGowan, B.M.; Oral, T.K.; Rosenstock, J.; et al. Weight regain and cardiometabolic effects after withdrawal of semaglutide: The STEP 1 trial extension. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2022, 24, 1553–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubino, D.; Abrahamsson, N.; Davies, M.; Hesse, D.; Greenway, F.L.; Jensen, C.; Lingvay, I.; Mosenzon, O.; Rosenstock, J.; Rubio, M.A.; et al. Effect of Continued Weekly Subcutaneous Semaglutide vs. Placebo on Weight Loss Maintenance in Adults With Overweight or Obesity: The STEP 4 Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2021, 325, 1414–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bray, G.A.; Kim, K.K.; Wilding, J.P.H. Obesity: A chronic relapsing progressive disease process. A position statement of the World Obesity Federation. Obes. Rev. 2017, 18, 715–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tzoulis, P.; Baldeweg, S.E. Semaglutide for weight loss: Unanswered questions. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1382814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knop, F.K.; Aroda, V.R.; do Vale, R.D.; Holst-Hansen, T.; Laursen, P.N.; Rosenstock, J.; Rubino, D.M.; Garvey, W.T. Oral semaglutide 50 mg taken once per day in adults with overweight or obesity (OASIS 1): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2023, 402, 705–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nauck, M.A.; Petrie, J.R.; Sesti, G.; Mannucci, E.; Courrèges, J.P.; Lindegaard, M.L.; Jensen, C.B.; Atkin, S.L. A Phase 2, Randomized, Dose-Finding Study of the Novel Once-Weekly Human GLP-1 Analog, Semaglutide, Compared With Placebo and Open-Label Liraglutide in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2016, 39, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Squire, P.; Naude, J.; Zentner, A.; Bittman, J.; Khan, N. Factors associated with weight loss response to GLP-1 analogues for obesity treatment: A retrospective cohort analysis. BMJ Open 2025, 15, e089477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| STEP-1 | STEP-2 | STEP-3 | STEP-5 | ||
| Location | 16 countries in Asia, Europe and North and South America | 12 countries across Europe, North America, South America, Middle East, South Africa, Asia | United States | Canada, Hungary, Italy, Spain and United States | |
| Population | STEP Program Population * | Adults (age ≥ 18 years) with BMI ≥ 27 kg/m2 and ≥1 weight-related comorbidity or BMI ≥ 30 kg/m2, with or without type 2 diabetes | STEP Program Population * | STEP Program Population * | |
| Sample Size | 1961 | 1210 | 611 | 304 | |
| Active Arm | Subcutaneous semaglutide 2.4 mg/week, lifestyle intervention and counseling | Subcutaneous semaglutide 2.4 mg/week, lifestyle intervention and counseling | Subcutaneous semaglutide 2.4 mg/week, lifestyle intervention and counseling | Subcutaneous semaglutide 2.4 mg/week, behavioral intervention | |
| Control | Matching subcutaneous placebo, lifestyle intervention and counseling | Matching subcutaneous placebo, lifestyle intervention and counseling | Matching subcutaneous placebo, lifestyle intervention and counseling | Matching subcutaneous placebo, behavioral intervention | |
| Extra Arm | Subcutaneous semaglutide 1.0 mg/week | ||||
| Treatment Period | 68 weeks | 68 weeks | 68 weeks | 104 weeks | |
| Primary Endpoint | Percentage change in body weight and weight loss of ≥5% from baseline at week 68 | Percentage change in body weight and weight loss of ≥5% from baseline at week 68 | Percentage change in body weight and weight loss of ≥5% from baseline at week 68 | Percentage change in body weight and weight loss of ≥5% from baseline at week 104 | |
| Maximum Follow-up | 75 weeks | 75 weeks | 75 weeks | 111 weeks | |
| STEP-6 | STEP-7 | STEP-8 | STEP-HFpEF | STEP-HFpEF DM | |
| Location | Japan and South Korea | China, Hong Kong, Brazil, South Korea | United States | 13 countries in Asia, Europe and North and South America | 16 countries in Asia, Europe and North and South America |
| Population | Adults (age ≥ 18 years in South Korea, ≥20 years in Japan) with BMI ≥ 27 kg/m2 and ≥2 comorbidities, or BMI ≥ 35 kg/m2 and ≥1 comorbidity (including hypertension, dyslipidaemia, or type 2 diabetes in Japan) | Adults (age ≥ 18 years) with BMI ≥ 30 kg/m2, or BMI ≥ 27 kg/m2 with ≥1 weight-related comorbidity (eg, hypertension, dyslipidaemia, OSA, CVD), with or without type 2 diabetes | STEP Program Population * | Persons 18 years of age or older, with a left ventricular ejection fraction of at least 45% and BMI ≥ 30 kg/m2 | Adults (age ≥ 18 years) with HFpEF (LVEF ≥ 45%), BMI ≥ 30 kg/m2, and type 2 diabetes (diagnosed ≥ 90 days before screening, HbA1c ≤ 10%) |
| Sample Size | 401 | 375 | 338 | 529 | 616 |
| Active Arm | Subcutaneous semaglutide 2.4 mg/week, lifestyle intervention and counseling | Subcutaneous semaglutide 2.4 mg/week, lifestyle intervention and counseling | Subcutaneous semaglutide 2.4 mg/week, lifestyle intervention and counseling | Subcutaneous semaglutide 2.4 mg/week | Subcutaneous semaglutide 2.4 mg/week |
| Control | Matching subcutaneous placebo, lifestyle intervention and counseling | Matching subcutaneous placebo, lifestyle intervention and counseling | Matching subcutaneous placebo, lifestyle intervention and counseling | Matching subcutaneous placebo | Matching subcutaneous placebo |
| Extra Arm | Subcutaneous semaglutide 1.7 mg/week, lifestyle intervention and counseling | Subcutaneous liraglutide 3.0 mg/day, lifestyle intervention, and counseling | |||
| Treatment Period | 68 weeks | 44 weeks | 68 weeks | 52 weeks | 52 weeks |
| Primary Endpoint | Percentage change in body weight and weight loss of ≥5% from baseline at week 68 | Percentage change in body weight and weight loss of ≥5% from baseline at week 44 | Percentage change in body weight from baseline at week 68 | Change from baseline to week 52 in KCCQ-CSS and percentage change in body weight | Change from baseline to week 52 in KCCQ-CSS and percentage change in body weight |
| Maximum Follow-up | 75 weeks | 51 weeks | 75 weeks | 57 weeks | 57 weeks |
| Study | Sample Size | Age (mean) | Female (%) | Body Weight (kg, mean) | Body Mass Index (kg/m2) | Waist Circumference | Blood Pressure (mmHg, mean) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | <30 (%) | ≥30 (%) | Systolic | Diastolic | ||||||
| STEP-2 | ||||||||||
| Semaglutide | 404 | 55.0 | 55.2 | 99.9 | 35.9 | 16.8 | 83.2 | 114.5 | 130 | 80 |
| Placebo | 403 | 55.0 | 47.1 | 100.5 | 35.9 | 19.1 | 80.9 | 115.5 | 130 | 80 |
| STEP-HFpEF DM | ||||||||||
| Semaglutide | 310 | 69.0 (median) | 41.3 | 103.8 (median) | 36.9 (median) | 0 | 100 | 122.0 (median) | 132 (median) | 79 (median) |
| Placebo | 306 | 70.0 (median) | 47.4 | 101.7 (median) | 36.9 (median) | 0 | 100 | 118.5 (median) | 137 (median) | 78 (median) |
| STEP-6 (DM Subgroup) | ||||||||||
| Semaglutide | 49 | 54.0 | 42.9 | 83.3 | 31.4 | 51.0 | 49.0 | 102.5 | ||
| Placebo * | 25 | 51.0 | 20.0 | 95.1 | 33.3 | 28.0 | 72.0 | 108.1 | ||
| TOTAL † | 1497 | 54.8 | 47.6 | 99.1 | 35.6 | 11.8 | 88.2 | 114.1 | 130.0 | 80.0 |
| Study | Sample Size | Age (mean) | Female (%) | Body Weight (kg, mean) | Body Mass Index (kg/m2) | Waist Circumference | Blood Pressure (mmHg, mean) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | <30 (%) | ≥30 (%) | Systolic | Diastolic | ||||||
| STEP-1 | ||||||||||
| Semaglutide | 1306 | 46.0 | 73.1 | 105.4 | 37.8 | 6.2 | 93.8 | 114.6 | 126 | 80 |
| Placebo | 655 | 47.0 | 76.0 | 105.2 | 38.0 | 5.5 | 94.5 | 114.8 | 127 | 80 |
| STEP-3 | ||||||||||
| Semaglutide | 407 | 46.0 | 77.4 | 106.9 | 38.1 | 5.7 | 94.3 | 113.6 | 124 | 80 |
| Placebo | 204 | 46.0 | 88.2 | 103.7 | 37.8 | 7.4 | 92.6 | 111.8 | 124 | 81 |
| STEP-5 | ||||||||||
| Semaglutide | 152 | 47.3 | 80.9 | 105.6 | 38.6 | 115.8 | 126 | 80 | ||
| Placebo * | 152 | 47.4 | 74.3 | 106.5 | 38.5 | 115.7 | 125 | 80 | ||
| STEP-8 | ||||||||||
| Semaglutide | 126 | 48.0 | 81.0 | 102.5 | 37.0 | 7.1 | 92.9 | 111.8 | 125 | 81 |
| Placebo ‡ | 85 | 51.0 | 77.6 | 108.8 | 38.8 | 4.7 | 95.3 | 115.4 | 123 | 79 |
| STEP-HFpEF | ||||||||||
| Semaglutide | 263 | 70.0 (median) | 56.7 | 104.7 (median) | 37.2 (median) | 0 | 100 | 119.0 (median) | 133.0 (median) | 78.0 (median) |
| Placebo | 266 | 69.0 (median) | 55.6 | 105.3 (median) | 36.9 (median) | 0 | 100 | 120.0 (median) | 132.0 (median) | 78.0 (median) |
| STEP-6 (Non-DM Subgroup) | ||||||||||
| Semaglutide | 150 | 51.0 | 42.7 | 88.1 | 32.3 | 104.2 | ||||
| Placebo * | 76 | 49.0 | 27.6 | 88.6 | 31.5 | 102.4 | ||||
| TOTAL † | 3842 | 46.8 | 71.1 | 104.3 | 37.5 | 5.1 | 94.9 | 113.6 | 125.6 | 80.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hong, B.; Kim, H.; Lee, D.; Kim, K. Weight Loss Effects of Once-Weekly Semaglutide 2.4 mg in Adults with and Without Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 1058. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18071058
Hong B, Kim H, Lee D, Kim K. Weight Loss Effects of Once-Weekly Semaglutide 2.4 mg in Adults with and Without Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(7):1058. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18071058
Chicago/Turabian StyleHong, Boram, Haesoo Kim, Daeun Lee, and Kisok Kim. 2025. "Weight Loss Effects of Once-Weekly Semaglutide 2.4 mg in Adults with and Without Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 7: 1058. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18071058
APA StyleHong, B., Kim, H., Lee, D., & Kim, K. (2025). Weight Loss Effects of Once-Weekly Semaglutide 2.4 mg in Adults with and Without Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Pharmaceuticals, 18(7), 1058. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18071058







