Hawthorn (Crataegus spp.) Clinically Significantly Reduces Blood Pressure in Hypertension: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trials
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
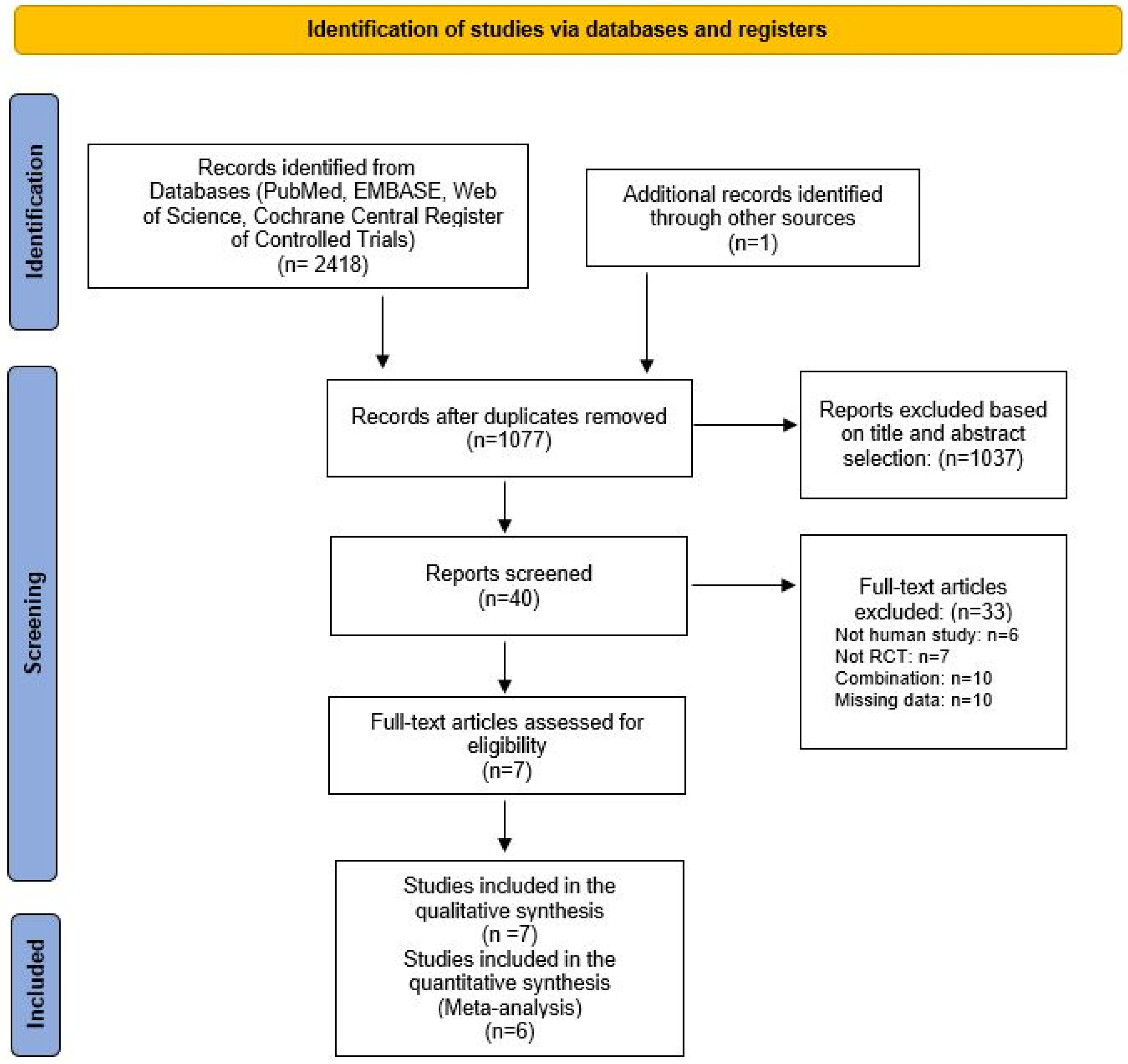
2.1. Literature Search and Study Selection
2.2. Risk of Bias Assessment
2.3. Study Characteristics
2.4. Patient Characteristics
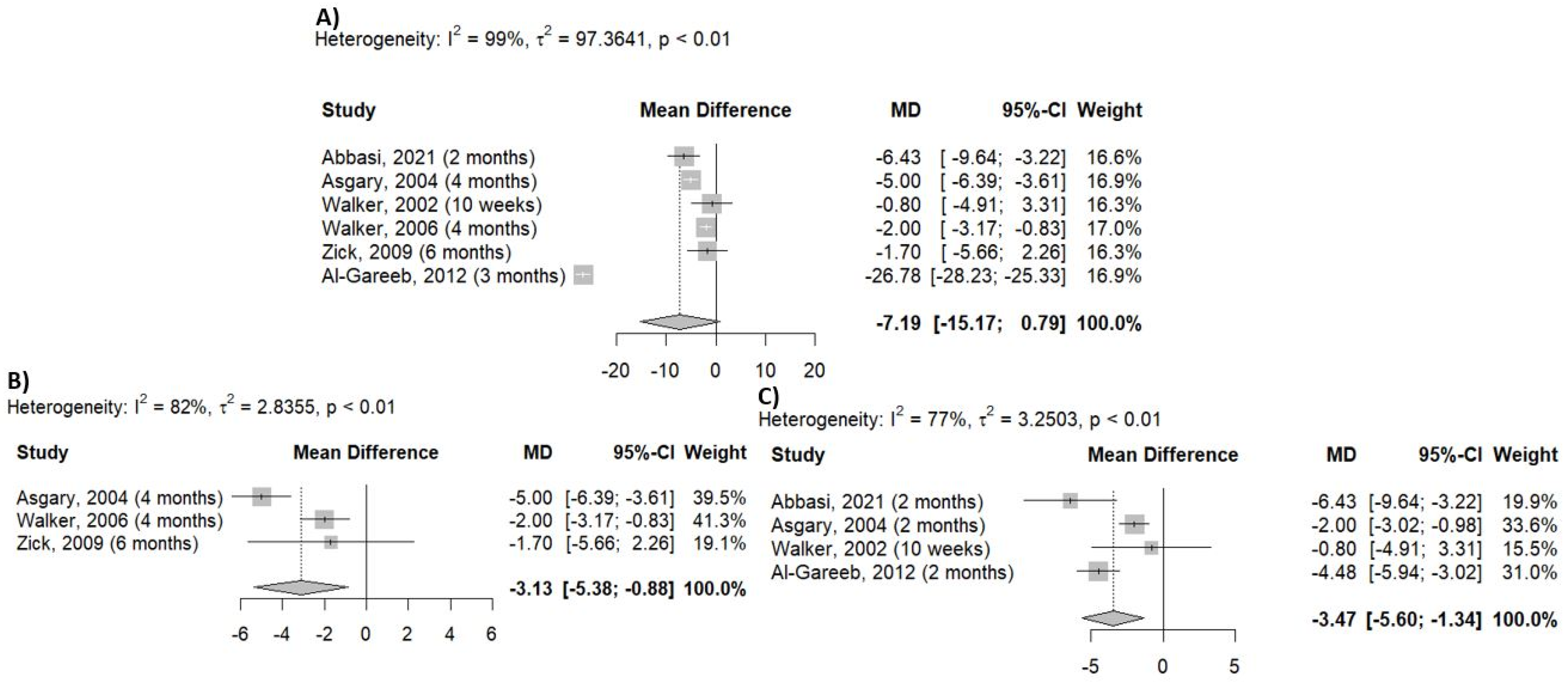
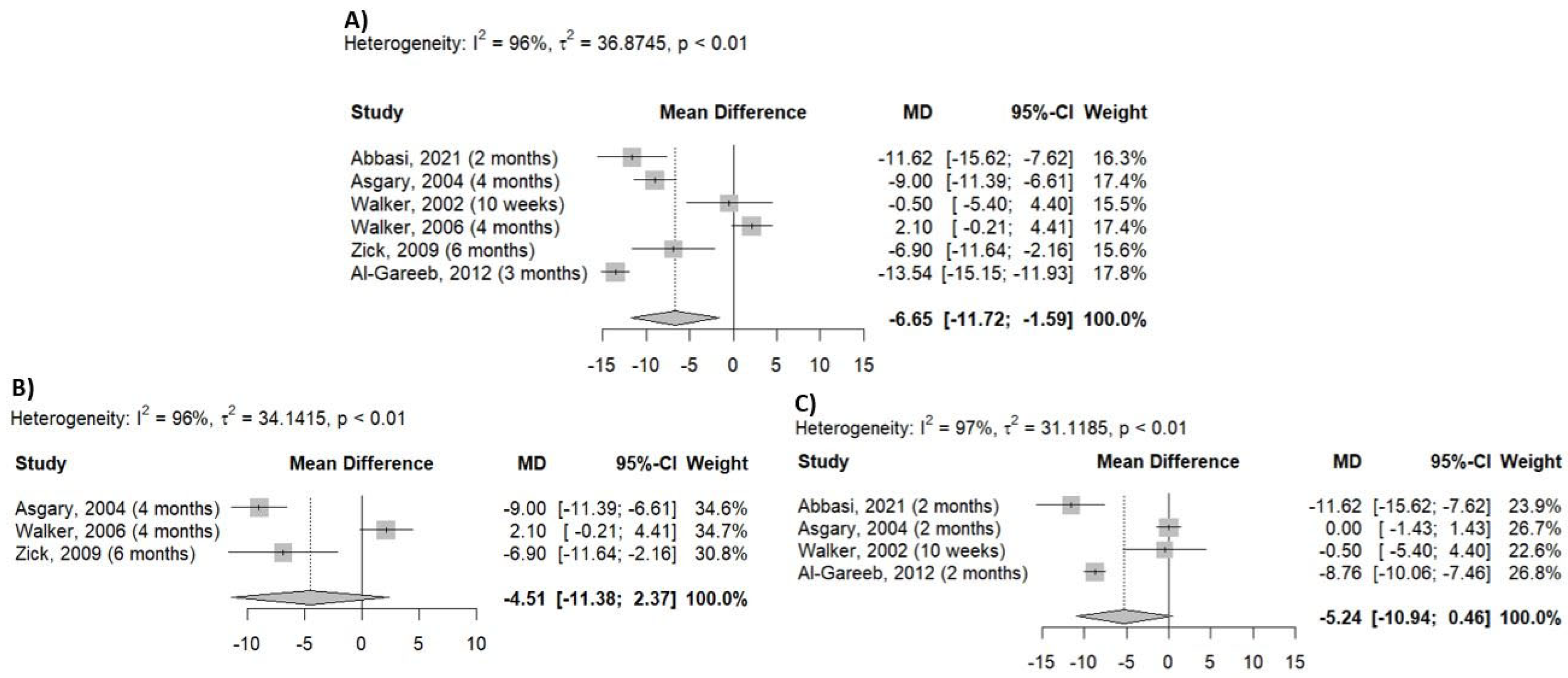
2.5. Outcome
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Information Sources and Search Strategy
4.2. Eligibility Criteria and Study Selection
4.3. Data Extraction and Synthesis of the Results
4.4. Risk of Bias Analysis
4.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACE | Angiotensin-converting enzyme |
| CAM | Complementary and alternative medicine |
| DBP | Diastolic blood pressure |
| FMD | Flow-mediated dilatation |
| MD | Mean difference |
| NO | Nitric oxide |
| NYHA | New York Heart Association |
| RCT | Randomized controlled trial |
| SBP | Systolic blood pressure |
References
- Global Report on Hypertension-the Race against a Silent Killer, WHO. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240081062 (accessed on 7 July 2025).
- Elliott, W.J. Systemic Hypertension. Curr. Probl. Cardiol. 2007, 32, 201–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nahas, R. Complementary and Alternative Medicine Approaches to Blood Pressure Reduction. Can. Fam. Physician 2008, 54, 1529–1533. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Al Disi, S.S.; Anwar, M.A.; Eid, A.H. Anti-Hypertensive Herbs and Their Mechanisms of Action: Part I. Front. Pharmacol. 2016, 6, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.; Liu, L.; Xing, Y.; Yang, S.; Li, H.; Cao, Y. Roles and Mechanisms of Hawthorn and Its Extracts on Atherosclerosis: A Review. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takó, M.; Tunali, F.; Zambrano, C.; Kovács, T.; Varga, M.; Szekeres, A.; Papp, T.; Tugay, O.; Kerekes, E.B.; Krisch, J.; et al. Phenolic Content, Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Properties of Hawthorn (Crataegus orientalis) Fruit Extracts Obtained via Carbohy-drase-Assisted Extraction. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 9790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabavi, S.; Habtemariam, S.; Ahmed, T.; Sureda, A.; Daglia, M.; Sobarzo-Sánchez, E.; Nabavi, S. Polyphenolic Composition of Crataegus monogyna Jacq.: From Chemistry to Medical Applications. Nutrients 2015, 7, 7708–7728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, J.; Deb, P.K.; Priya, S.; Medina, K.D.; Devi, R.; Walode, S.G.; Rudrapal, M. Dietary Flavonoids: Cardioprotective Potential with Antioxidant Effects and Their Pharmacokinetic, Toxicological and Therapeutic Concerns. Molecules 2021, 26, 4021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galleano, M.; Bernatova, I.; Puzserova, A.; Balis, P.; Sestakova, N.; Pechanova, O.; Fraga, C.G. (–)-Epicatechin Reduces Blood Pressure and Improves Vasorelaxation in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats by NO-mediated Mechanism. IUBMB. Life 2013, 65, 710–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Union Herbal Monograph on Crataegus spp., Folium Cum Flore. Available online: https://www.e-lactancia.org/media/papers/EspinoBlanco-DS-EMA2014.pdf (accessed on 7 July 2025).
- Wang, J.; Xiong, X.; Feng, B. Effect of Crataegus Usage in Cardiovascular Disease Prevention: An Evidence-Based Approach. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. ECAM 2013, 2013, 149363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.-T.; Dao, J.; Shao, Z.-H. Hawthorn: Potential Roles in Cardiovascular Disease. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2005, 33, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csupor, D.; Viczián, R.; Lantos, T.; Kiss, T.; Hegyi, P.; Tenk, J.; Czumbel, L.M.; Thanyaporn, S.-N.; Gyöngyi, Z.; Varga, G.; et al. The Combination of Hawthorn Extract and Camphor Significantly Increases Blood Pressure: A Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review. Phytomed. Int. J. Phytother. Phytopharm. 2019, 63, 152984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cloud, A.; Vilcins, D.; McEwen, B. The Effect of Hawthorn (Crataegus spp.) on Blood Pressure: A Systematic Review. Adv. Integr. Med. 2020, 7, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Gareeb, A.I.A. Effect of Hawthorn Extract on Blood Pressure and Lipid Profile in Patients with Stage I Hypertension: A Placebo-Controlled, Double-Blind Randomized Trial. Mustansiriya Med. J. 2012, 11, 52–57. [Google Scholar]
- Asher, G.N.; Viera, A.J.; Weaver, M.A.; Dominik, R.; Caughey, M.; Hinderliter, A.L. Effect of Hawthorn Standardized Extract on Flow Mediated Dilation in Prehypertensive and Mildly Hypertensive Adults: A Randomized, Controlled Cross-over Trial. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2012, 12, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, A.F.; Marakis, G.; Morris, A.P.; Robinson, P.A. Promising Hypotensive Effect of Hawthorn Extract: A Randomized Double-blind Pilot Study of Mild, Essential Hypertension. Phytother. Res. 2002, 16, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asgary, S.; Naderi, G.H.; Sadeghi, M.; Kelishadi, R.; Amiri, M. Antihypertensive Effect of Iranian Crataegus curvisepala Lind.: A Randomized, Double-Blind Study. Drugs Exp. Clin. Res. 2004, 30, 221–225. [Google Scholar]
- Walker, A.F.; Marakis, G.; Simpson, E.; Hope, J.L.; Robinson, P.A.; Hassanein, M.; Simpson, H.C.R. Hypotensive Effects of Hawthorn for Patients with Diabetes Taking Prescription Drugs: A Randomised Controlled Trial. Br. J. Gen. Pract. 2006, 56, 437–443. [Google Scholar]
- Zick, S.M.; Vautaw, B.M.; Gillespie, B.; Aaronson, K.D. Hawthorn Extract Randomized Blinded Chronic Heart Failure (HERB CHF) Trial. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2009, 11, 990–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, M.; Gohari, S.; Ahangar, H.; Bahrami, M.; Kamalinejad, M.; Reshadmanesh, T.; Nazari, S.S. Efficacy of Hawthorn Fruit Extract on Blood Pressure and Quality of Sleep in Patients with Hypertension along with Sleep Disorders: A Randomized Double-Blind Controlled Trial. J. Contemp. Med. Sci. 2021, 7, 196–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostchega, Y.; Nguyen, D.T. Hypertension Prevalence Among Adults Aged 18 and Over: United States, 2017–2018. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/databriefs/db364-h.pdf (accessed on 7 July 2025).
- Woerdenbag, H.J.; Ursidae, M.; Ekhart, C.; Schmidt, M.; Vitalone, A.; Van Hunsel, F.P.A.M. Analysis of Adverse Reactions Associated with the Use of Crataegus-Containing Herbal Products. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assessment Report on Crataegus spp., Folium Cum Flore. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/herbal-report/final-assessment-report-crataegus-spp-folium-cum-flore_en.pdf (accessed on 7 July 2025).
- Birman, H.; Dar, K.A.; Kapucu, A.; Olgaç, V.; Gürel, E. Effects of crataegus tanacetifolia and hyperoside on salivary gland and kidney tissue and relation to nitric oxide (NO) in experimental hypertensive rats. Nobel Med. 2011, 7, 17–22. [Google Scholar]
- Nazhand, A.; Lucarini, M.; Durazzo, A.; Zaccardelli, M.; Cristarella, S.; Souto, S.B.; Silva, A.M.; Severino, P.; Souto, E.B.; Santini, A. Hawthorn (Crataegus spp.): An Updated Overview on Its Beneficial Properties. Forests 2020, 11, 564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alirezalu, A.; Ahmadi, N.; Salehi, P.; Sonboli, A.; Alirezalu, K.; Mousavi Khaneghah, A.; Barba, F.J.; Munekata, P.E.S.; Lorenzo, J.M. Physicochemical Characterization, Antioxidant Activity, and Phenolic Compounds of Hawthorn (Crataegus spp.) Fruits Species for Potential Use in Food Applications. Foods 2020, 9, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, B.; Zhang, M.; Sun, L.; Liu, H.; Tian, Z. Study on the Hypotensive Effect and Mechanism of Hawthorn (Crataegus pinnatifida) Fruits and Hyperoside in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. Food Funct. 2024, 15, 5627–5640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, T.; Sinha, M.; Bansal, N.; Yadav, S.R.; Shah, K.; Chauhan, N.S. Plants Used as Antihypertensive. Nat. Prod. Bioprospect. 2021, 11, 155–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz, M.A.; de-La-Sierra, A.; Sáez, M.; Barceló, M.A.; Rodríguez, J.J.; Castro, S.; Lagarón, C.; Garrido, J.M.; Vera, P.; Coll-de-Tuero, G. Treatment Efficacy of Anti-Hypertensive Drugs in Monotherapy or Combination: ATOM Systematic Review and Me-ta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials According to PRISMA Statement. Medicine 2016, 95, e4071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemi, E.; Mansoursamaei, A.; Bijan, M.; Hosseinzadeh, A.; Namavar, H.; Masroor, M.J.; Sheibani, H. Effect of Crataegus Oxyacantha on High Blood Pressure: A Randomized Single-Blind Controlled Trial. Adv. Integr. Med. 2024, S2212958824001228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagnier, J.J.; Boon, H.; Rochon, P.; Moher, D.; Barnes, J.; Bombardier, C.; for the CONSORT Group*. Reporting Randomized, Controlled Trials of Herbal Interventions: An Elaborated CONSORT Statement. Ann. Intern. Med. 2006, 144, 364–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions (current version) Version 6.5. 2024. Available online: https://www.cochrane.org/authors/handbooks-and-manuals/handbook/current/chapter-10#section-10-10 (accessed on 7 July 2025).
- Borenstein, M.; Hedges, L.V.; Higgins, J.P.T.; Rothstein, H.R. A Basic Introduction to Fixed-Effect and Random-Effects Models for Meta-Analysis. Res. Synth. Methods 2010, 1, 97–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| First Author (Year) | Country | Group | Dose | Duration | Patient Characteristics | Outcome Measure |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ann F. Walker (2002) [17] | UK | Crataegus spp. Placebo | 500 mg capsule /daily | 10 weeks | mild hypertension (DBP: 85–100 mmHg) | Changes in blood pressure |
| Asgary S. (2004) [18] | Iran | Crataegus curvisepala Placebo | 250 mg drops /daily | 4 months | mild hypertension (SBP: 140–159 mmHg; DBP: 90–95 mmHg) | Changes in blood pressure |
| Ann F. Walker (2006) [19] | UK | Crataegus laevigata Placebo | 600 mg tablet/twice daily | 4 months | hypertension (SBP: 145–165 mmHg; DBP: 85–95 mmHg) type 2 diabetes mellitus | Changes in blood pressure |
| Suzanna M. Zick (2009) [20] | USA | Crataegus spp. Placebo | 450 mg Crataegutt forte tablet /twice daily | 6 months | NYHA class II–III chronic heart failure | Changes in blood pressure |
| Al-Gareeb (2012) [15] | Iraq | Crataegus spp. Placebo | 450 mg capsule/twice daily | 3 months | first stage of hypertension (SBP: 140–159 mmHg; DBP: 90–99 mmHg) | Changes in blood pressure |
| Masumeh Abbasi (2021) [21] | Iran | Crataegus monogyna Placebo | 250 mg capsule/twice daily | 2 months | first stage of hypertension (SBP: 140–159 mmHg; DBP: 90–99 mmHg) sleep disorders | Changes in blood pressure |
| First Author (year) | Duration | Group | Systolic Blood Pressure Before Treatment (Mean ± SD, mmHg; p Value) | Systolic Blood Pressure After Treatment (Mean ± SD, mmHg; p Value) | Diastolic Blood Pressure Before Treatment (Mean ± SD, mmHg; p Value) | Diastolic Blood Pressure After Treatment (Mean ± SD, mmHg; p Value) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ann. F. Walker (2002) [17] | 10 weeks | Crataegus | 146.3 ± 6; N.A. | 139.1 ± 5.5; N.A. | 93.1 ± 3.8; N.A. | 91.4 ± 4.6; N.A. |
| placebo | 154.5 ± 4.1; N.A. | 139.6 ± 4.4; N.A | 100 ± 4.5; N.A. | 92.2 ± 3.7; N.A. | ||
| Asgary (2004) [18] | 2 months | Crataegus | 146 ± 16.23; 0.8 | 140 ± 3.49; 0.95 | 92 ± 6.03; 0.2 | 88 ± 2.49; 0.09 |
| placebo | 148 ± 12.5; 0.8 | 140 ± 3.53; 0.95 | 95 ± 5.03; 0.2 | 90 ± 2.51; 0.09 | ||
| 4 months | Crataegus | 146 ± 16.23; 0.8 | 135 ± 6.95; 0.002 | 92 ± 6.03; 0.2 | 87 ± 3.74; 0.003 | |
| placebo | 148 ± 12.5; 0.8 | 142 ± 5.98; 0.002 | 95 ± 5.03; 0.2 | 91 ± 3.66; 0.003 | ||
| Ann. F. Walker (2006) [19] | 4 months | Crataegus | 152.3 ± N.A.; 0.096 | 148.7 ± N.A.; 0.096 | 85.6 ± N.A.; 0.016 | 83 ± N.A.; 0.016 |
| placebo | 147.4 ± N.A.; N.A. | 146.6 ± N.A.; N.A. | 84.5 ± N.A.; N.A. | 85 ± N.A.; N.A. | ||
| Suzanna M. Zick (2009) [20] | 6 months | Crataegus | 109 ± 15; 0.25 | 106.9 ± 13.3; 0.26 | 66 ± 10; 0.76 | 65.2 ± 10.7; 0.45 |
| placebo | 113 ± 19; 0.25 | 113.8 ± 13.2; 0.26 | 66 ± 10; 0.76 | 66.9 ± 11.4; 0.45 | ||
| Al-Gareeb (2012) [15] | 2 months | Crataegus | 153.95 ± 3.14; N.A. | 139.88 ± 2.81; N.A. | 93.8 ± 2.19; N.A. | 86.4 ± 2.54; N.A. |
| placebo | 153.08 ± 2.25; N.A. | 148.64 ± 2.30; N.A. | 92.11 ± 2.37; N.A. | 90.88 ± 3.21; N.A. | ||
| 3 months | Crataegus | 153.95 ± 3.14; N.A. | 136.8 ± 3.32; N.A. | 93.8 ± 2.19; N.A. | 86.4 ± 1.92; N.A. | |
| placebo | 153.08 ± 2.25; N.A. | 150.34 ± 3.05; N.A. | 92.11 ± 2.37; N.A. | 91.38 ± 3.56; N.A. | ||
| Abbasi (2021) [21] | 2 months | Crataegus | 133.43 ± 6.5; N.A | 118.14 ± 6.76; N.A. | 90.71 ± 7.39; N.A. | 77.14 ± 5.32; N.A. |
| placebo | 131.43 ± 6.73; N.A. | 129.76 ± 8.28. N.A. | 89.76 ± 4.32; N.A. | 83.57 ± 6.73; N.A. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Szikora, Z.; Mátyus, R.O.; Szabó, B.V.; Csupor, D.; Tóth, B. Hawthorn (Crataegus spp.) Clinically Significantly Reduces Blood Pressure in Hypertension: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trials. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 1027. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18071027
Szikora Z, Mátyus RO, Szabó BV, Csupor D, Tóth B. Hawthorn (Crataegus spp.) Clinically Significantly Reduces Blood Pressure in Hypertension: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trials. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(7):1027. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18071027
Chicago/Turabian StyleSzikora, Zsóka, Rebeka Olga Mátyus, Bettina Vargáné Szabó, Dezső Csupor, and Barbara Tóth. 2025. "Hawthorn (Crataegus spp.) Clinically Significantly Reduces Blood Pressure in Hypertension: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trials" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 7: 1027. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18071027
APA StyleSzikora, Z., Mátyus, R. O., Szabó, B. V., Csupor, D., & Tóth, B. (2025). Hawthorn (Crataegus spp.) Clinically Significantly Reduces Blood Pressure in Hypertension: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trials. Pharmaceuticals, 18(7), 1027. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18071027






