Effects of Angiotensin II Receptor 1 Inhibition by LCZ696 on the Acquisition and Relapse of Methamphetamine-Associated Contextual Memory
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
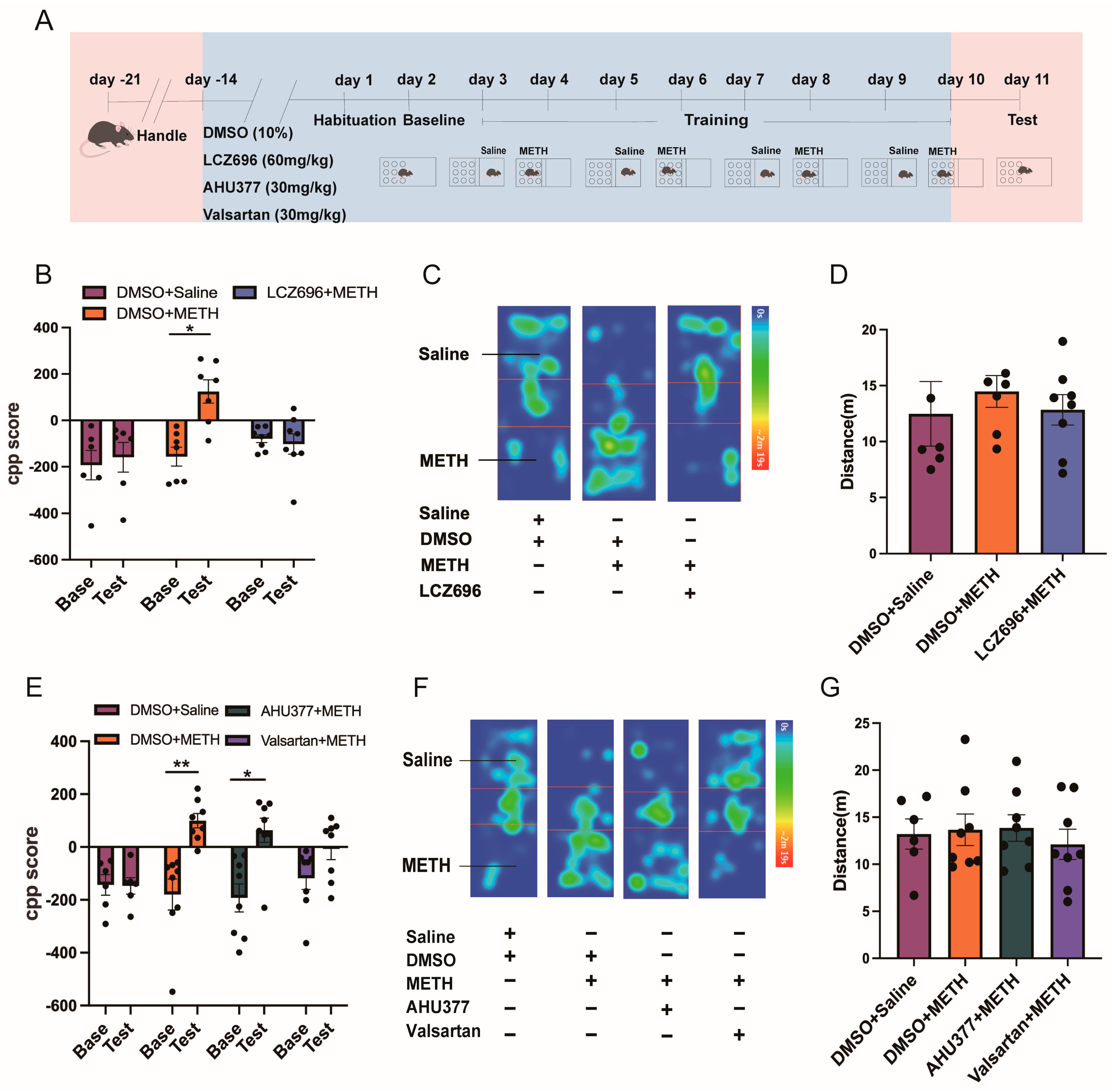
2.1. Experiment 1: The Effect of LCZ696, AHU337, and Valsartan on METH CPP
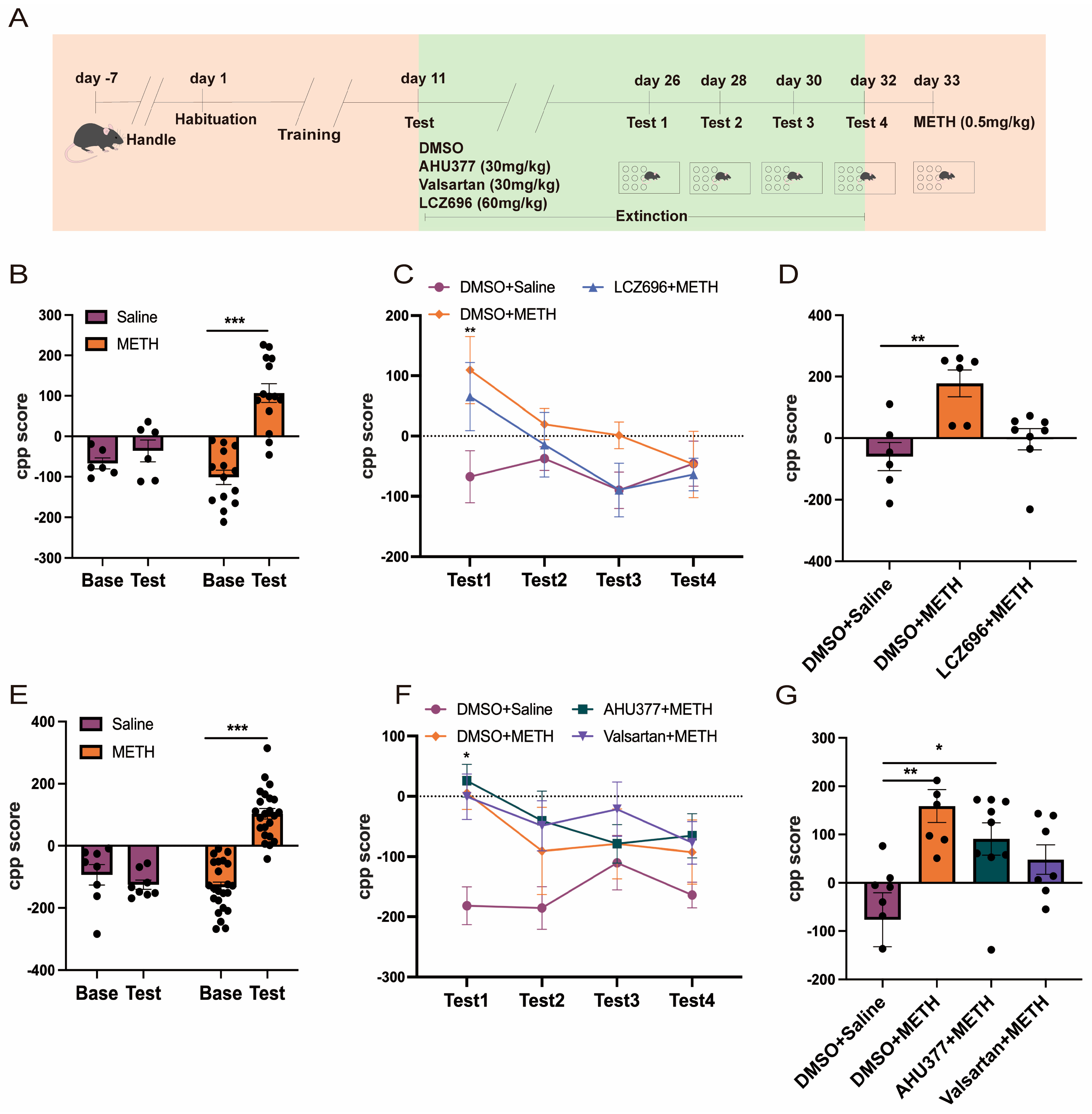
2.2. Experiment 2: The Effect of LCZ696, AHU337, and Valsartan on METH CPP Retrieval
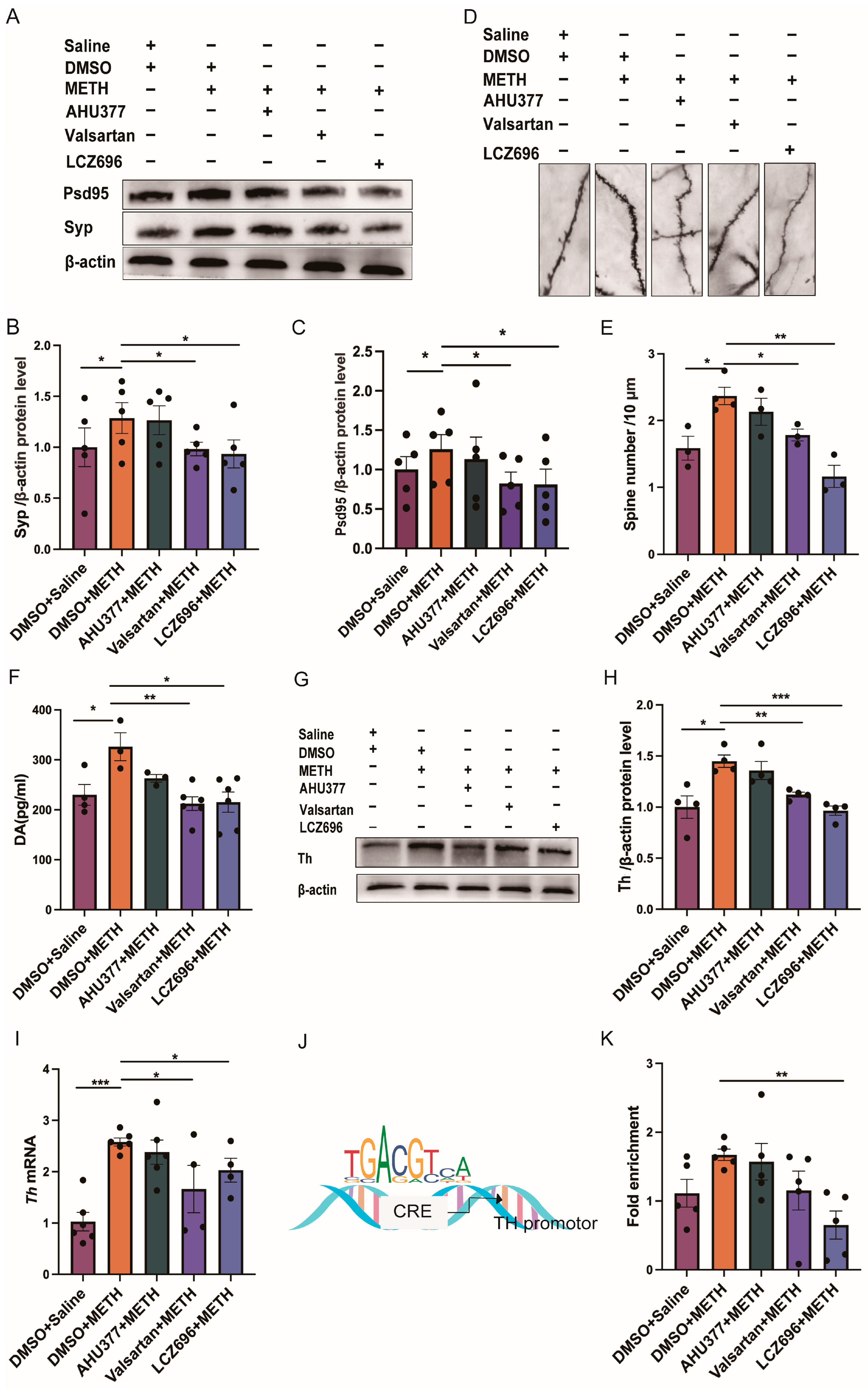
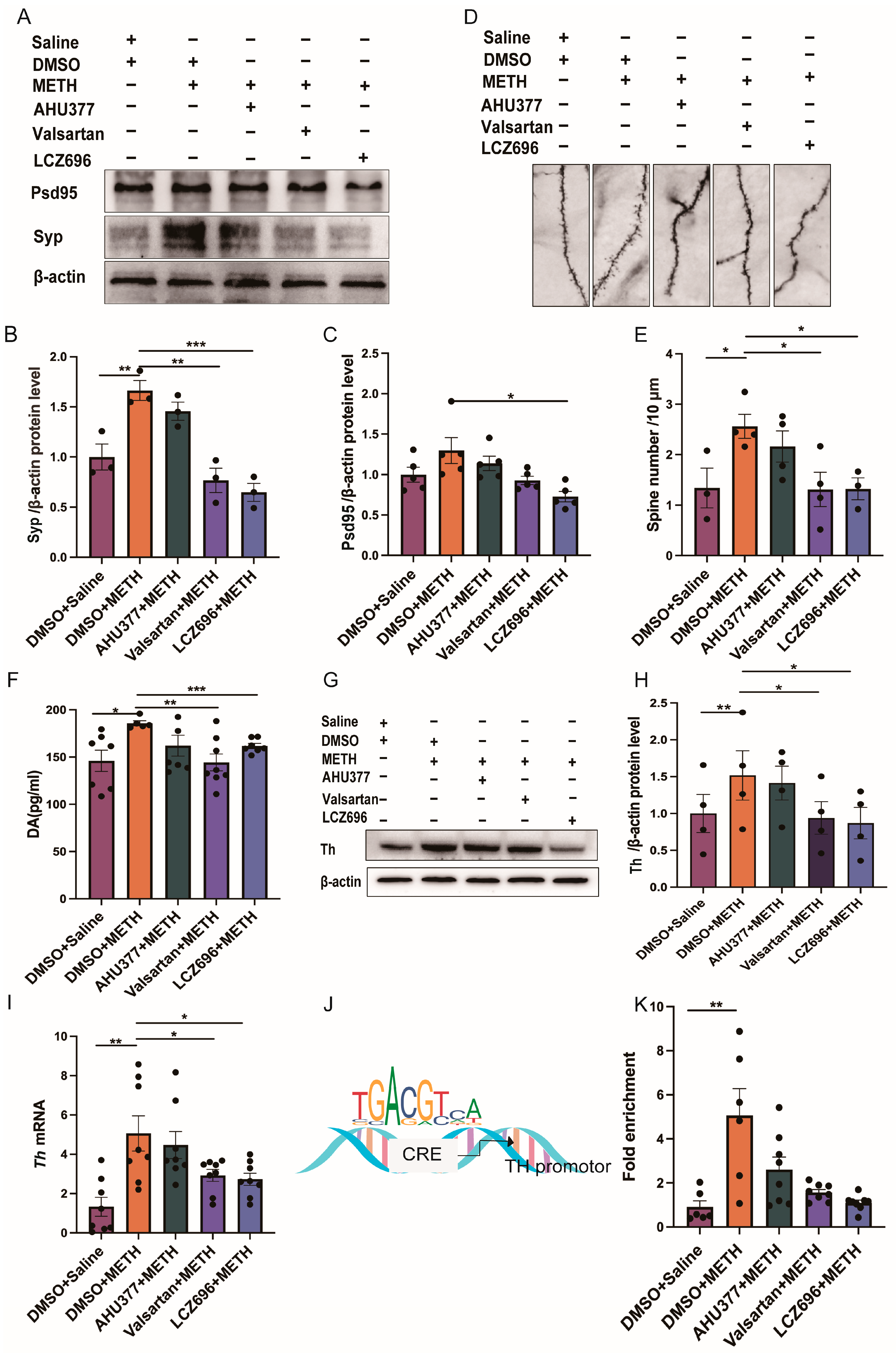
2.3. Experiment 3: The Effect of LCZ696, AHU337 and Valsartan on the Neuronal Plasticity and DA Level in METH CPP Mice
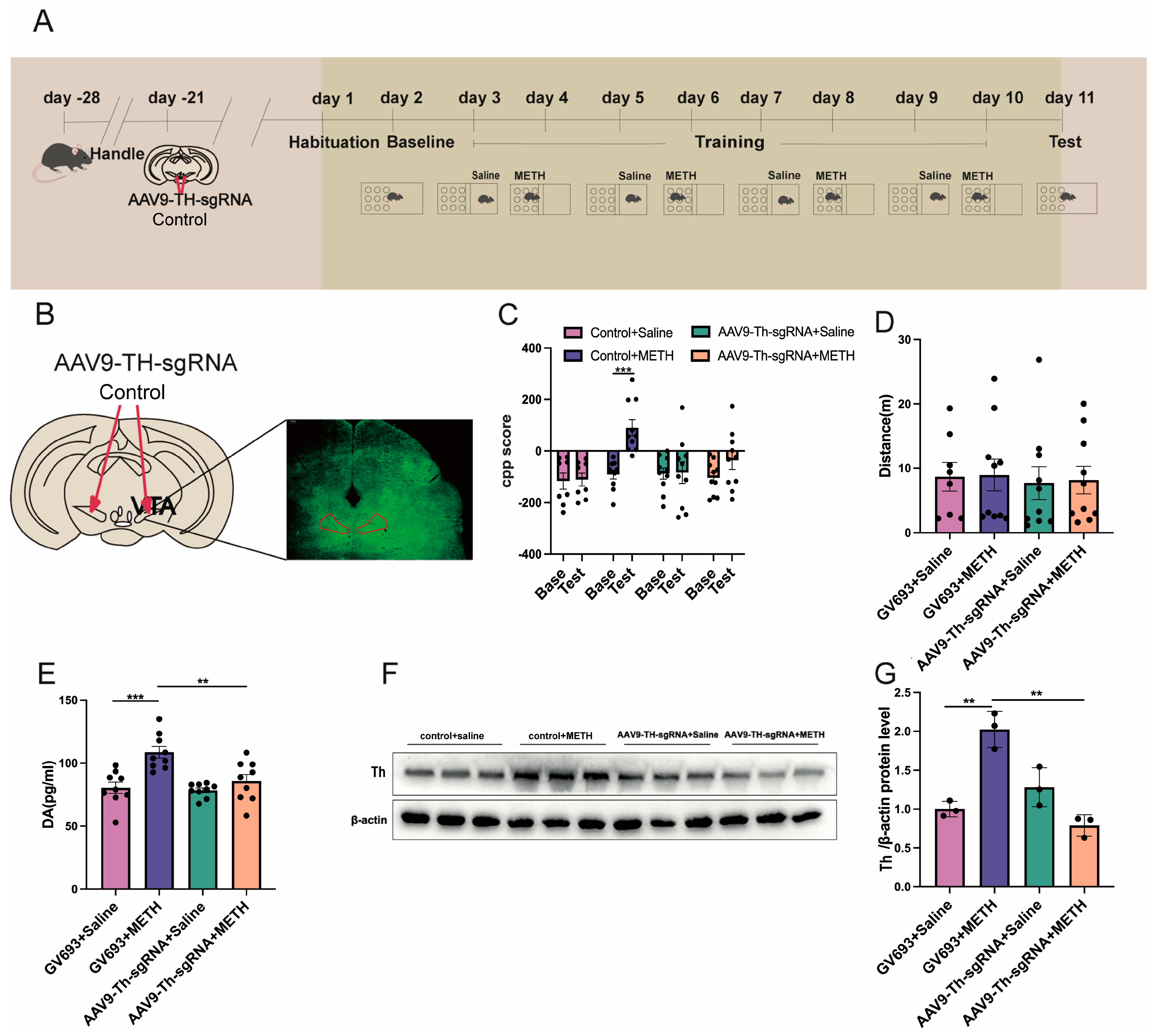
2.4. Experiment 4: The Effect of Cre Knockout in the Th Gene Promoter of VTA on METH CPP
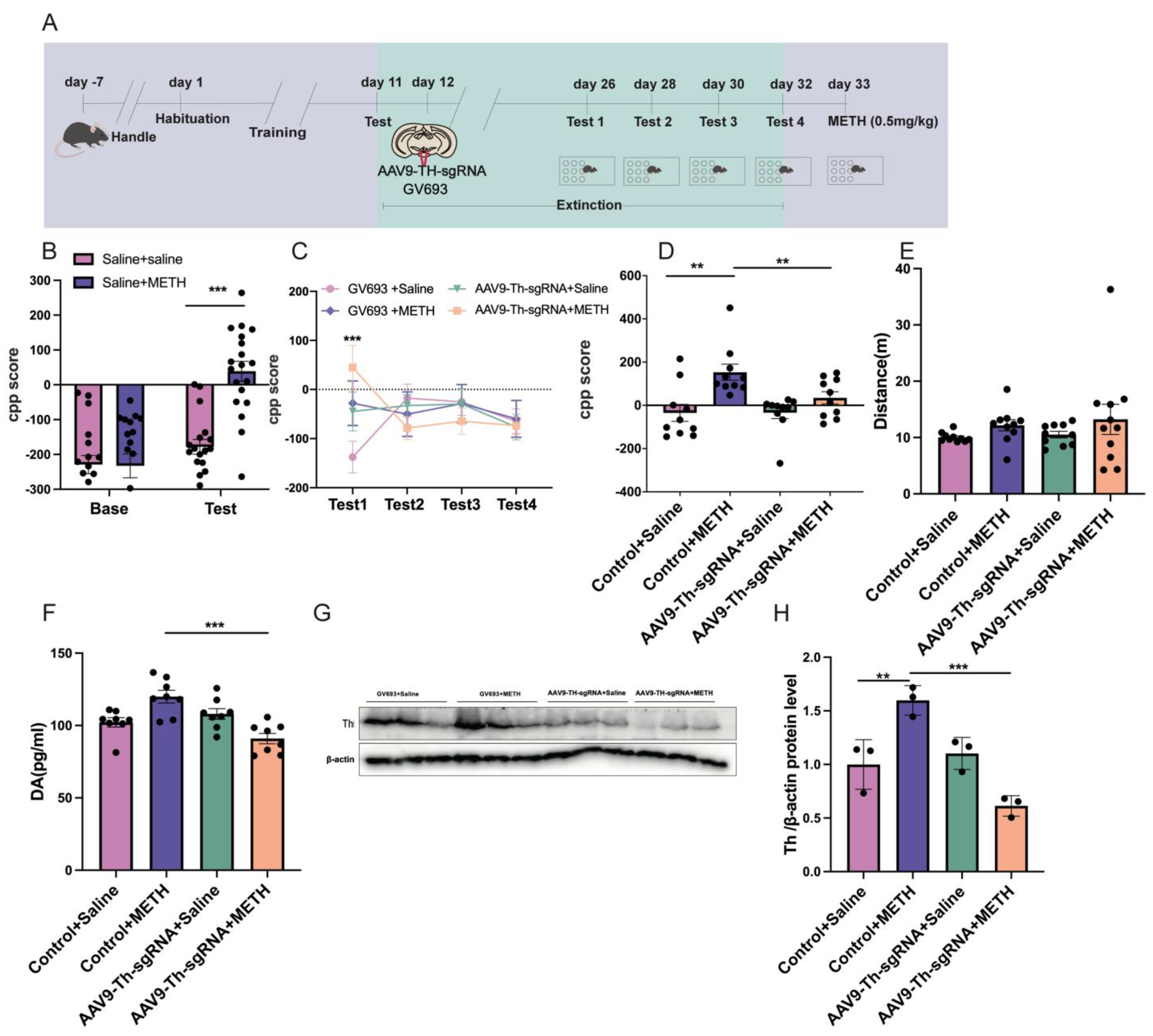
2.5. Experiment 5: The Effect of Cre Knockout in the Th Gene Promoter of VTA on METH CPP Retrieval
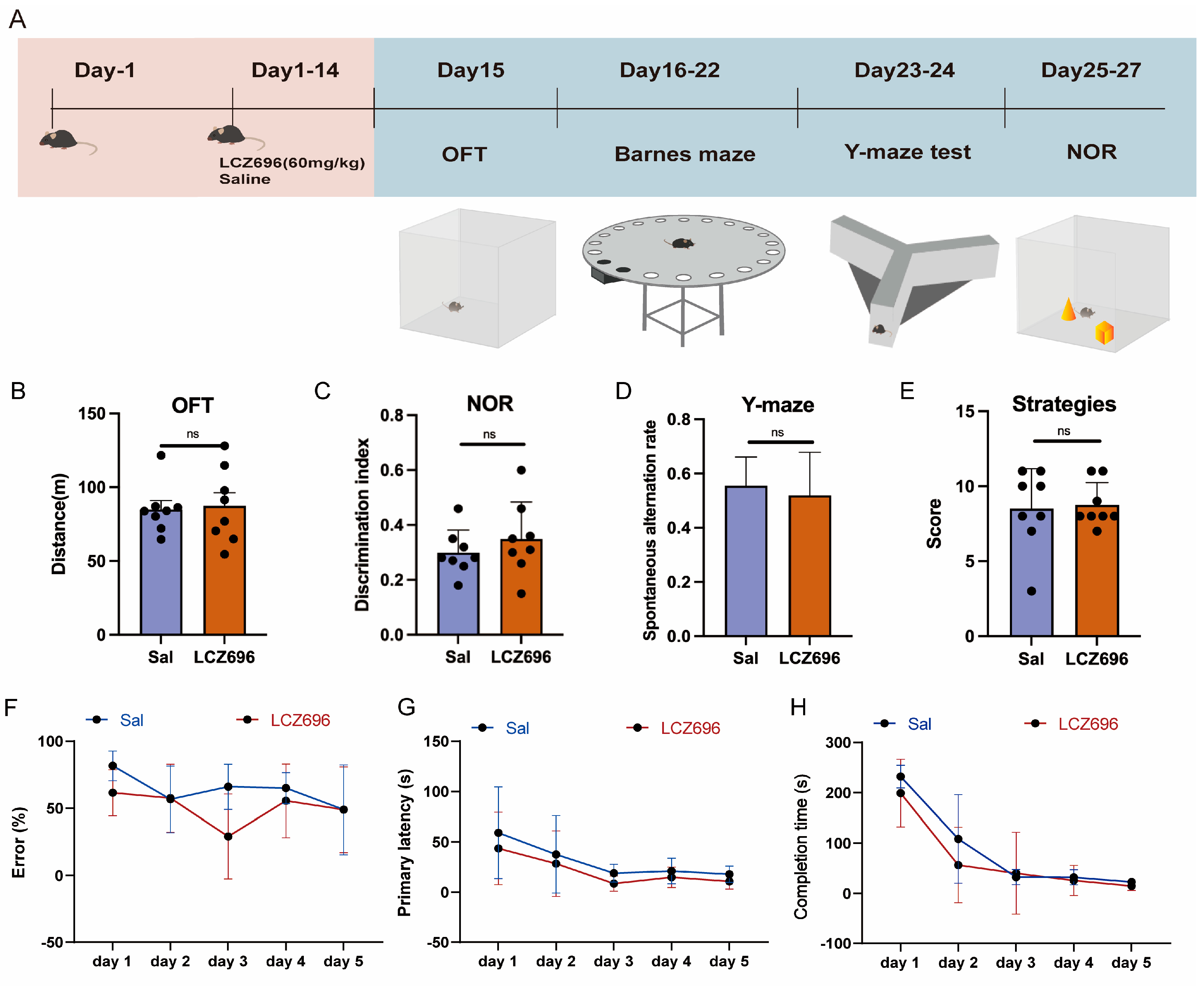
2.6. Experiment 6: The Effects of LCZ696 on the Other Behaviors of Mice
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Drugs
4.3. Conditioned Place Preference (CPP)
4.4. Locomotor Activity
4.5. Open Field Test (OFT)
4.6. Barnes Maze
4.7. Y-Maze Test
4.8. New Object Recognition (NOR)
4.9. Viral Injection
4.10. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
4.11. Western Blotting
4.12. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
4.13. Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (CHIP)
4.14. Golgi-Cox
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wise, R.A.; Robble, M.A. Dopamine and Addiction. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2020, 71, 79–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, X.; Wang, H.; Yang, X.; Yu, Z.; Lin, S.; Zou, Z.; Lv, J.; Qian, L.; Ruan, Y.; Si, Z.; et al. The Effect of Paeoniflorin on the Rewarding Effect of Methamphetamine and the Associated Cognitive Impairment in Mice. Metab. Brain Dis. 2024, 40, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Bai, J.; Fan, Y.; Sun, T.; Du, Y.; Li, Y.; Wei, Z.; Chen, T.; Guo, X.; Yun, K. The Distinct Roles of Various Neurotransmitters in Modulating Methamphetamine-Induced Conditioned Place Preference in Relevant Brain Regions in Mice. NeuroReport 2022, 33, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christoffel, D.J.; Walsh, J.J.; Hoerbelt, P.; Heifets, B.D.; Llorach, P.; Lopez, R.C.; Ramakrishnan, C.; Deisseroth, K.; Malenka, R.C. Selective Filtering of Excitatory Inputs to Nucleus Accumbens by Dopamine and Serotonin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2106648118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurokawa, K.; Shibasaki, M.; Kiyokage, E.; Mizuno, K.; Toida, K.; Ohkuma, S. Involvement of NMDA Receptors in Ryanodine Receptor Expression in Dopaminergic Neurons in the Ventral Tegmental Area of Mice with Intermittent Methamphetamine Treatment. Synapse 2011, 65, 1156–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adaptive Changes in Group 2 Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors Underlie the Deficit in Recognition Memory Induced by Methamphetamine in Mice—PubMed. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38969501/ (accessed on 31 May 2025).
- Hopkins, J.L.; Goldsmith, S.T.; Wood, S.K.; Nelson, K.H.; Carter, J.S.; Freels, D.L.; Lewandowski, S.I.; Siemsen, B.M.; Denton, A.R.; Scofield, M.D.; et al. Perirhinal to Prefrontal Circuit in Methamphetamine Induced Recognition Memory Deficits. Neuropharmacology 2023, 240, 109711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, R.J.; Parvaz, M.A.; Wakabayashi, K.T.; Blair, R.J.R.; Hubbard, N.A. Methamphetamine-Related Working Memory Difficulties Underpinned by Reduced Frontoparietal Responses. Addict. Biol. 2024, 29, e13444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukla, M.; Vincent, B. Methamphetamine Abuse Disturbs the Dopaminergic System to Impair Hippocampal-Based Learning and Memory: An Overview of Animal and Human Investigations. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2021, 131, 541–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Methamphetamine-Induced Impairment of Memory and Fleeting Neuroinflammation: Profiling mRNA Changes in Mouse Hippocampus Following Short-Term and Long-Term Exposure—PubMed. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/39357738/ (accessed on 31 May 2025).
- Jiang, L.; Zhu, R.; Bu, Q.; Li, Y.; Shao, X.; Gu, H.; Kong, J.; Luo, L.; Long, H.; Guo, W.; et al. Brain Renin-Angiotensin System Blockade Attenuates Methamphetamine-Induced Hyperlocomotion and Neurotoxicity. Neurotherapeutics 2018, 15, 500–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, T.F.; De La Garza, R.; Grasing, K. The Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitor Perindopril Treatment Alters Cardiovascular and Subjective Effects of Methamphetamine in Humans. Psychiatry Res. 2010, 179, 96–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosarderelioglu, C.; Nidadavolu, L.S.; George, C.J.; Marx-Rattner, R.; Powell, L.; Xue, Q.-L.; Tian, J.; Salib, J.; Oh, E.S.; Ferrucci, L.; et al. Higher Angiotensin II Type 1 Receptor Levels and Activity in the Postmortem Brains of Older Persons with Alzheimer’s Dementia. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2022, 77, 664–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjbar, H.; Aghaei, I.; Moosazadeh, M.; Shabani, M. Angiotensin II Type 1 Receptor Blocker Losartan Attenuates Locomotor, Anxiety-like Behavior, and Passive Avoidance Learning Deficits in a Sub-Chronic Stress Model. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2018, 21, 856–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horiuchi, M.; Mogi, M. Role of Angiotensin II Receptor Subtype Activation in Cognitive Function and Ischaemic Brain Damage. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 163, 1122–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valenzuela, R.; Barroso-Chinea, P.; Villar-Cheda, B.; Joglar, B.; Muñoz, A.; Lanciego, J.L.; Labandeira-Garcia, J.L. Location of Prorenin Receptors in Primate Substantia Nigra: Effects on Dopaminergic Cell Death. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2010, 69, 1130–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trieu, B.H.; Remmers, B.C.; Toddes, C.; Brandner, D.D.; Lefevre, E.M.; Kocharian, A.; Retzlaff, C.L.; Dick, R.M.; Mashal, M.A.; Gauthier, E.A.; et al. Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Gates Brain Circuit-Specific Plasticity via an Endogenous Opioid. Science 2022, 375, 1177–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Pan, J.; Li, X.; Cui, Y.; Mao, Z.; Wu, B.; Xu, H.; Zhou, W.; Liu, Y. Inhibition of Methamphetamine Self-Administration and Reinstatement by Central Blockade of Angiotensin II Receptor in Rats. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2019, 369, 244–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Fan, R.; Ruan, Y.; Xu, M.; He, J.; Cao, M.; Li, X.; Zhou, W.; Liu, Y. Inhibition of PLCβ1 Signaling Pathway Regulates Methamphetamine Self-Administration and Neurotoxicity in Rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2021, 149, 111970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, L.; Ruan, Y.; Gong, X.; Yu, Z.; Lin, S.; Li, X.; Shen, Y.; Luo, H.; Si, Z.; Liu, Y. The Neuroprotective Effect of LCZ696 on Methamphetamine-Induced Cognitive Impairment in Mice. Neurosci. Lett. 2024, 823, 137630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontremoli, R.; Borghi, C.; Perrone Filardi, P. Renal Protection in Chronic Heart Failure: Focus on Sacubitril/Valsartan. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacother. 2021, 7, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammadi, S.H.; Hassan, M.A.; Allam, E.A.; Elsharkawy, A.M.; Shams, S.S. Effect of Sacubitril/Valsartan on Cognitive Impairment in Colchicine-Induced Alzheimer’s Model in Rats. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 2023, 37, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacciatore, F.; Amarelli, C.; Maiello, C.; Pratillo, M.; Tosini, P.; Mattucci, I.; Salerno, G.; Curcio, F.; Elia, F.; Mercurio, V.; et al. Effect of Sacubitril-Valsartan in Reducing Depression in Patients with Advanced Heart Failure. J. Affect. Disord. 2020, 272, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannon, J.A.; Shen, L.; Jhund, P.S.; Kristensen, S.L.; Køber, L.; Chen, F.; Gong, J.; Lefkowitz, M.P.; Rouleau, J.L.; Shi, V.C.; et al. Dementia-Related Adverse Events in PARADIGM-HF and Other Trials in Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2017, 19, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vecchis, R.; Ariano, C.; Di Biase, G.; Noutsias, M. Cognitive Performance of Patients with Chronic Heart Failure on Sacubitril/Valsartan: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Herz 2019, 44, 534–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perlman, A.; Hirsh Raccah, B.; Matok, I.; Muszkat, M. Cognition- and Dementia-Related Adverse Effects with Sacubitril-Valsartan: Analysis of the FDA Adverse Event Report System Database. J. Card. Fail. 2018, 24, 533–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oros-González, A.; Gallardo-Ortíz, I.A.; Montes, S.; Del Valle-Mondragón, L.; Páez-Martínez, N. Captopril and Losartan Attenuate Behavioural Sensitization in Mice Chronically Exposed to Toluene. Behav. Brain Res. 2022, 418, 113640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaeidi, A.; Amirteimoury, M.; Zare, M.-S.; Nazari, A.; Hakimizadeh, E.; Hassanshahi, J.; Fatemi, I. Effects of Valsartan on Morphine Tolerance and Dependence in Rats. Res. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 16, 286–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Wu, C.; Liu, L.; Gu, L.; Wang, Z.; Xu, F.; Zhu, D. Interplay between the Renin Angiotensin System and Oxidative Stress Contributes to Alcohol Addiction by Stimulating Dopamine Accumulation in the Mesolimbic Pathway. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2023, 212, 115578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Xu, T.; Zeng, Y.; Zhang, R.; Qi, Z.; Zhao, W.; Kendrick, K.M.; Becker, B. The Angiotensin Antagonist Losartan Modulates Social Reward Motivation and Punishment Sensitivity via Modulating Midbrain-Striato-Frontal Circuits. J. Neurosci. 2023, 43, 472–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nago-Iwashita, Y.; Moriya, Y.; Hara, S.; Ogawa, R.; Aida, R.; Miyajima, K.; Shimura, T.; Muramatsu, S.; Ide, S.; Ikeda, K.; et al. Overexpression of Tyrosine Hydroxylase in Dopaminergic Neurons Increased Sensitivity to Methamphetamine. Neurochem. Int. 2023, 164, 105491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aurelian, L.; Warnock, K.T.; Balan, I.; Puche, A.; June, H. TLR4 Signaling in VTA Dopaminergic Neurons Regulates Impulsivity through Tyrosine Hydroxylase Modulation. Transl. Psychiatry 2016, 6, e815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logan, R.W.; Parekh, P.K.; Kaplan, G.N.; Becker-Krail, D.D.; Williams, W.P.; Yamaguchi, S.; Yoshino, J.; Shelton, M.A.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, H.; et al. NAD+ Cellular Redox and SIRT1 Regulate the Diurnal Rhythms of Tyrosine Hydroxylase and Conditioned Cocaine Reward. Mol. Psychiatry 2019, 24, 1668–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalivaeva, N.N.; Zhuravin, I.A.; Turner, A.J. Neprilysin Expression and Functions in Development, Ageing and Disease. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2020, 192, 111363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valentino, R.J.; Volkow, N.D. Untangling the Complexity of Opioid Receptor Function. Neuropsychopharmacology 2018, 43, 2514–2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roques, B.P. Contribution of Delta-Opioid Receptors to Pathophysiological Events Explored by Endogenous Enkephalins. In Opioid Receptor Pharmacology and Therapeutic Applications; Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 247, pp. 53–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaulden, A.D.; Burson, N.; Sadik, N.; Ghosh, I.; Khan, S.J.; Brummelte, S.; Kallakuri, S.; Perrine, S.A. Effects of Fentanyl on Acute Locomotor Activity, Behavioral Sensitization, and Contextual Reward in Female and Male Rats. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2021, 229, 109101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yates, J.R.; Campbell, H.L.; Hawley, L.L.; Horchar, M.J.; Kappesser, J.L.; Wright, M.R. Effects of the GluN2B-Selective Antagonist Ro 63-1908 on Acquisition and Expression of Methamphetamine Conditioned Place Preference in Male and Female Rats. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2021, 225, 108785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, T.A.; Bardo, M.T. Opposite Regulation of Conditioned Place Preference and Intravenous Drug Self-Administration in Rodent Models: Motivational and Non-Motivational Examples. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2020, 116, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yates, J.R. Quantifying Conditioned Place Preference: A Review of Current Analyses and a Proposal for a Novel Approach. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1256764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzschentke, T.M. REVIEW ON CPP: Measuring Reward with the Conditioned Place Preference (CPP) Paradigm: Update of the Last Decade. Addict. Biol. 2007, 12, 227–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Yan, C.; Yang, X.; Zhou, X.; Lv, W.; Guo, N.; Li, Y.; Bai, J. Thioredoxin-1 Downregulation in the Nucleus Accumbens Promotes Methamphetamine-Primed Reinstatement in Mice. Neuropharmacology 2018, 139, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boivin, J.R.; Piscopo, D.M.; Wilbrecht, L. Brief Cognitive Training Interventions in Young Adulthood Promote Long-Term Resilience to Drug-Seeking Behavior. Neuropharmacology 2015, 97, 404–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Zou, Z.; Yang, X.; Lü, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, J.; Zhu, D.; Gong, X.; Lin, S.; Yu, Z.; et al. Effects of Angiotensin II Receptor 1 Inhibition by LCZ696 on the Acquisition and Relapse of Methamphetamine-Associated Contextual Memory. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 1016. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18071016
Li X, Zou Z, Yang X, Lü J, Zhang X, Zhou J, Zhu D, Gong X, Lin S, Yu Z, et al. Effects of Angiotensin II Receptor 1 Inhibition by LCZ696 on the Acquisition and Relapse of Methamphetamine-Associated Contextual Memory. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(7):1016. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18071016
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xiaofang, Zhiting Zou, Xiangdong Yang, Jinnan Lü, Xiaoyu Zhang, Jiahui Zhou, Dan Zhu, Xinshuang Gong, Shujun Lin, Zhaoying Yu, and et al. 2025. "Effects of Angiotensin II Receptor 1 Inhibition by LCZ696 on the Acquisition and Relapse of Methamphetamine-Associated Contextual Memory" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 7: 1016. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18071016
APA StyleLi, X., Zou, Z., Yang, X., Lü, J., Zhang, X., Zhou, J., Zhu, D., Gong, X., Lin, S., Yu, Z., Si, Z., Wei, W., Xie, Y., & Liu, Y. (2025). Effects of Angiotensin II Receptor 1 Inhibition by LCZ696 on the Acquisition and Relapse of Methamphetamine-Associated Contextual Memory. Pharmaceuticals, 18(7), 1016. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18071016




