An Alternative Mechanism of Glutamate Dehydrogenase Inhibition by EGCG: Promotion of Protein Degradation
Abstract
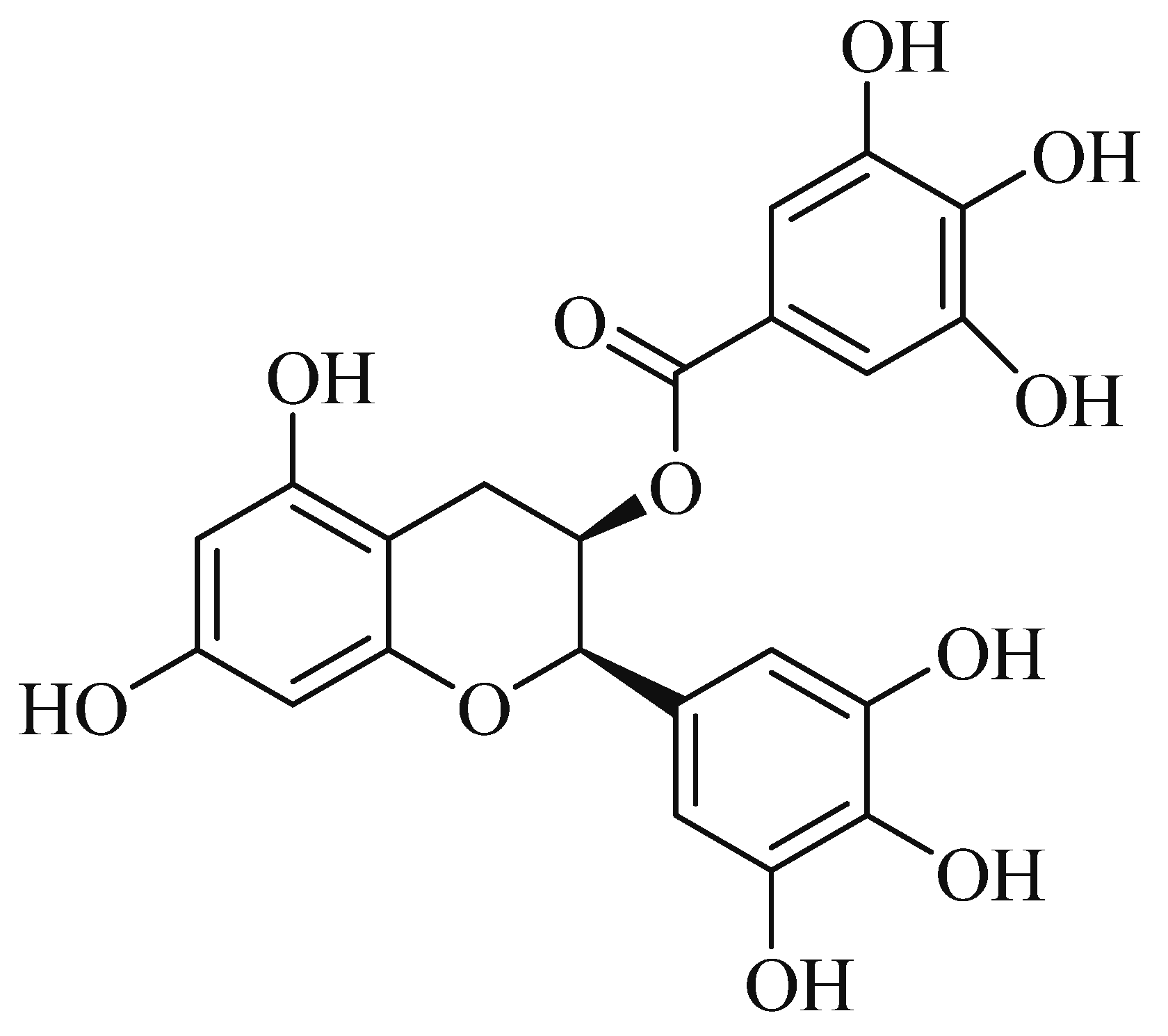
1. Introduction
2. Results
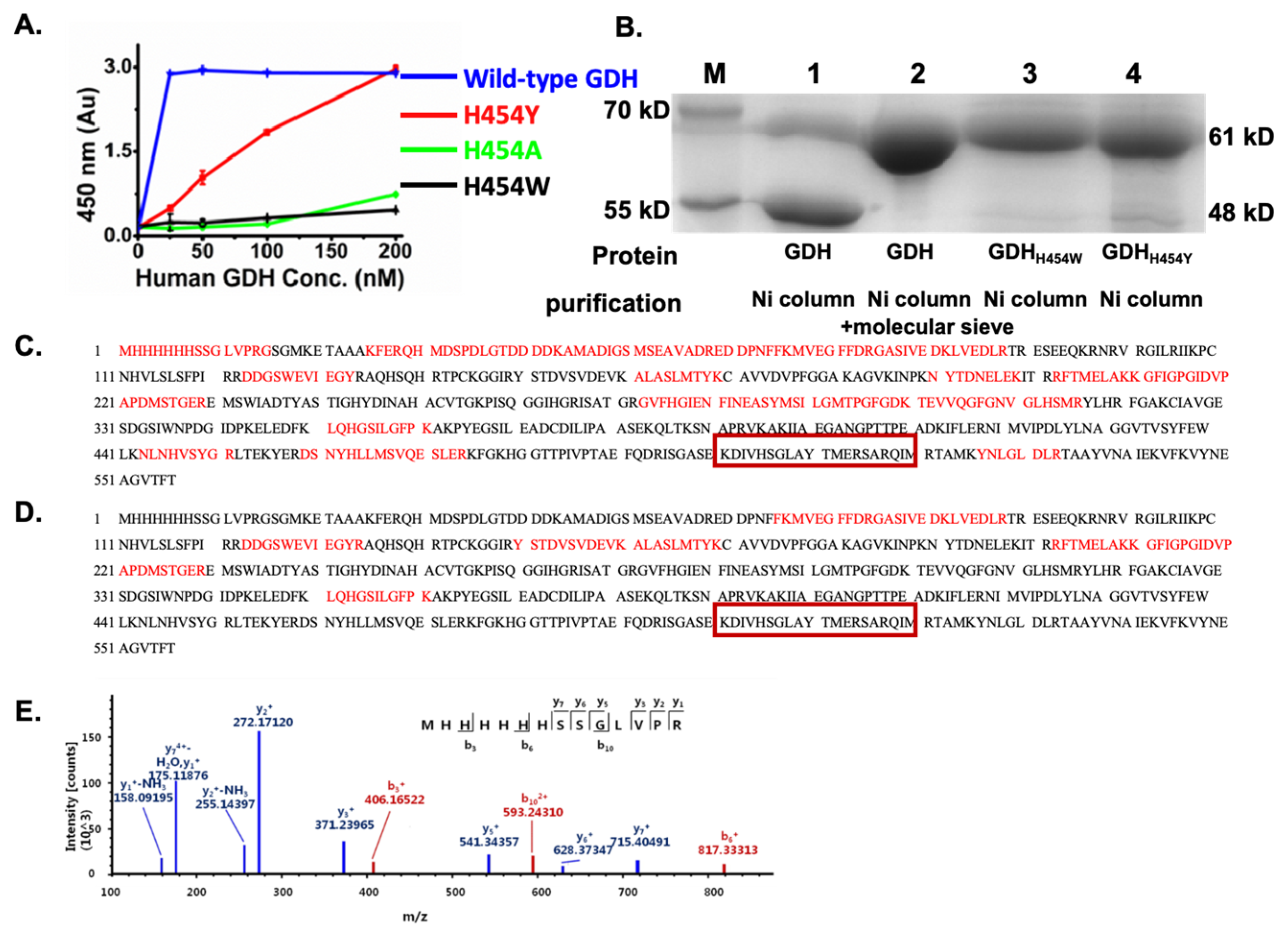
2.1. The GDH H454 Mutants Expressed in E. coli Showed Weaker Enzyme Activity and Greater Resistance to Proteolysis Compared to the Wild-Type
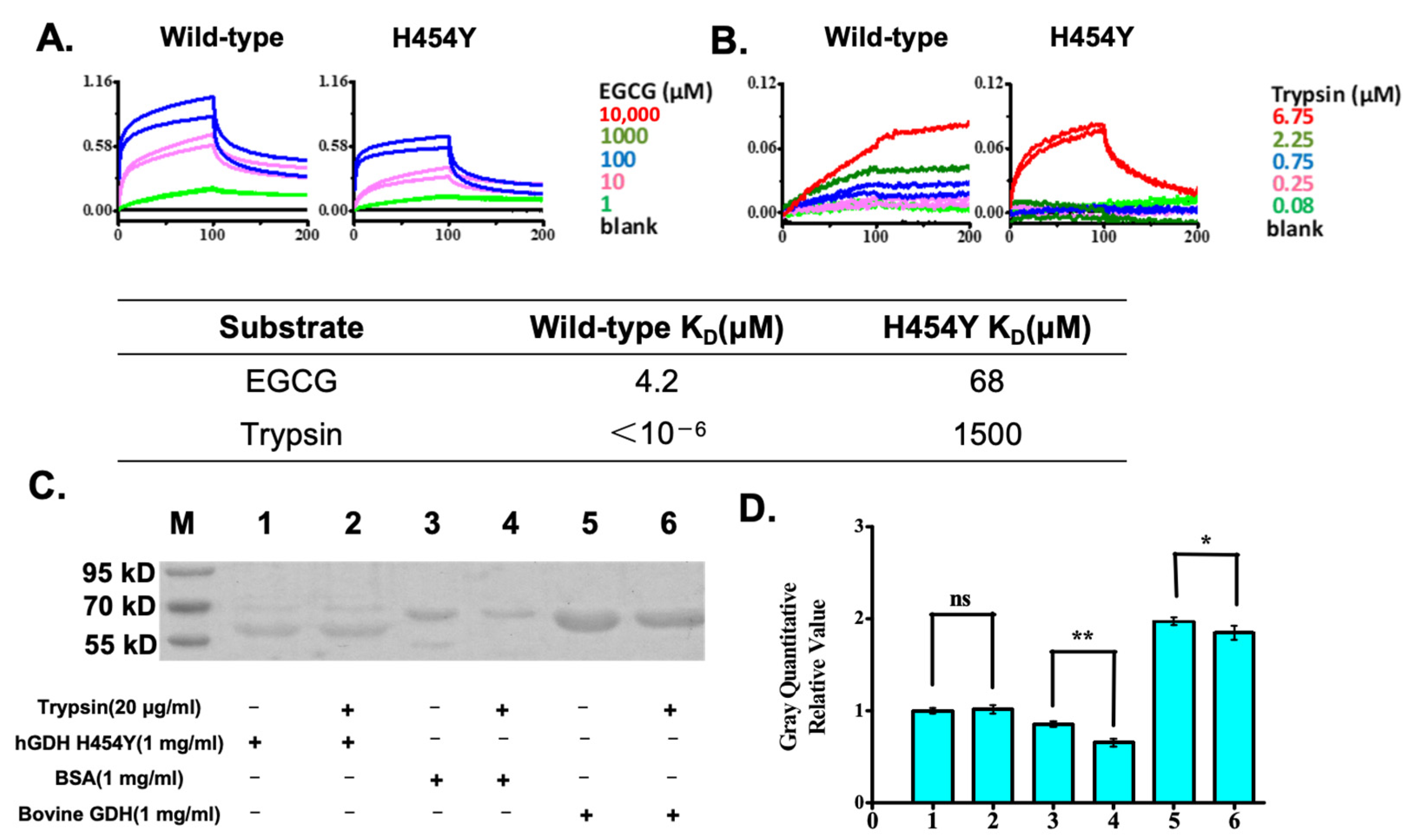
2.2. Biomolecular Interaction Analysis Demonstrated That the hGDHH454Y Mutant Greatly Reduced Its Affinity to a Protease, While EGCG Bound Well to Both GDHs
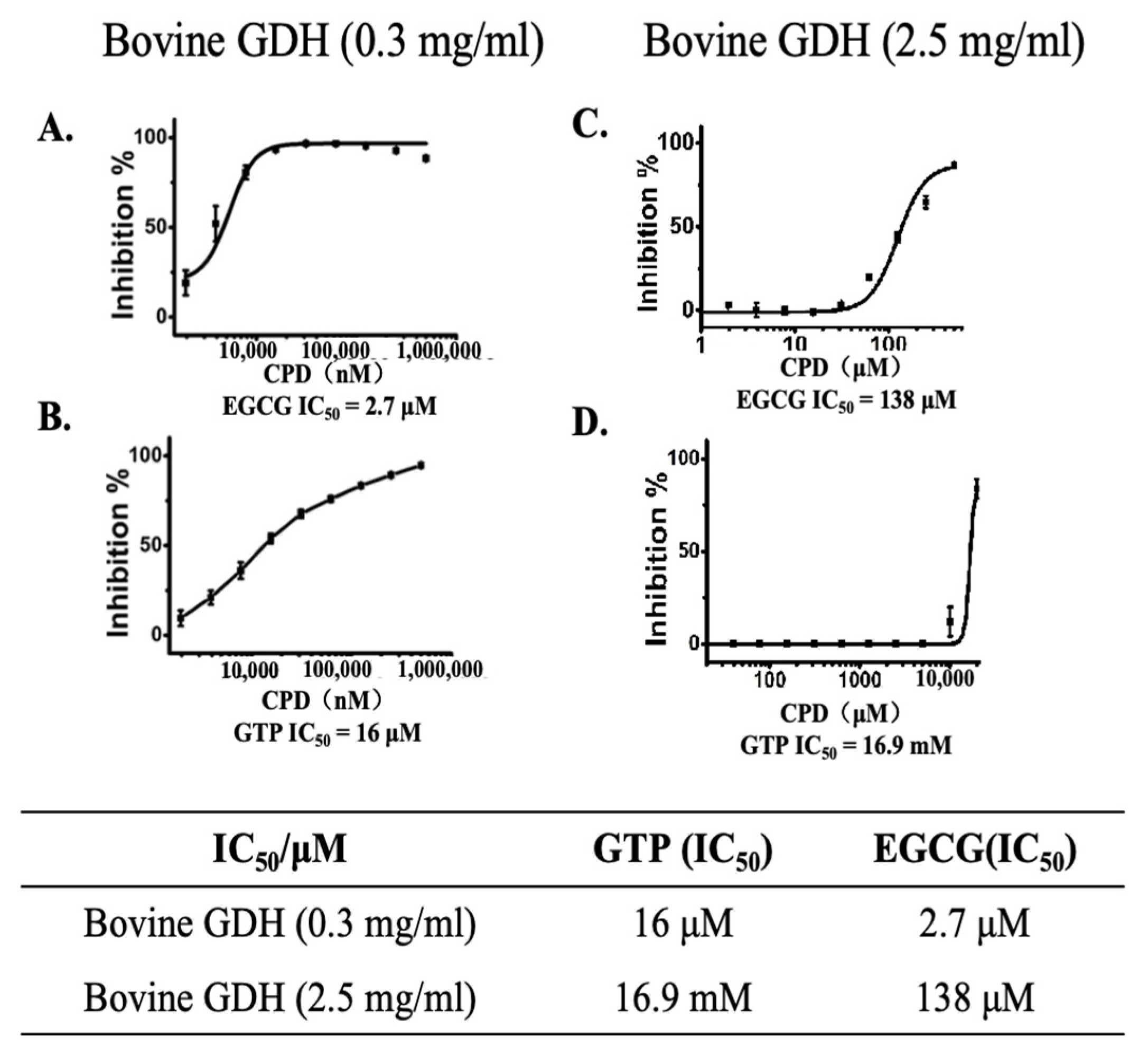
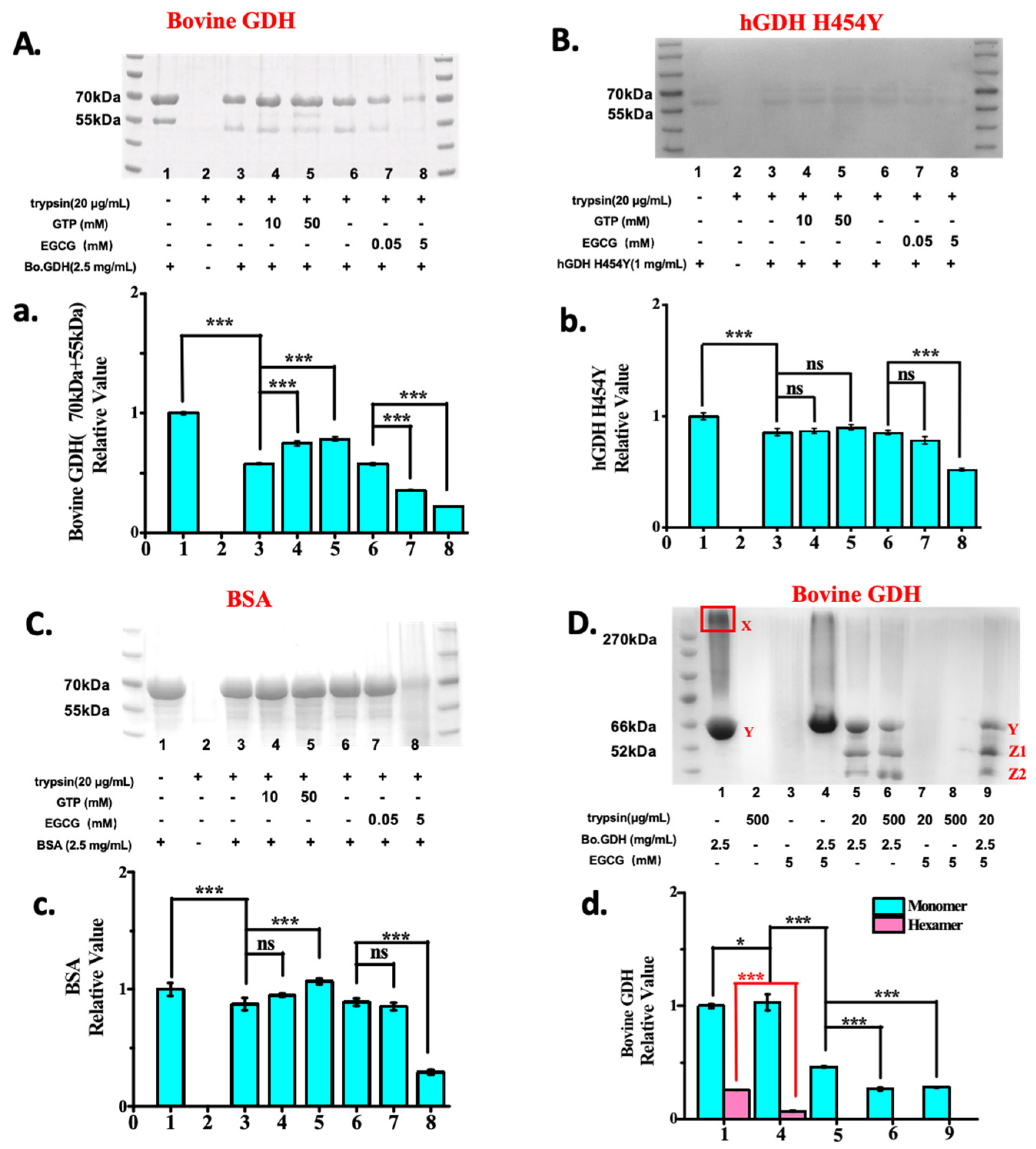
2.3. EGCG Is a Better Allosteric GDH Inhibitors than GTP and Promotes Protease Degradation of Both Wild-Type and hGDHH454Y Proteins
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Cloning and Purification of the Human GDH Mutants
4.3. Activity Assay of the Human GDH Mutants
4.4. Biomolecular Interaction Assay
4.5. GDH Inhibition Assay
4.6. Trypsin Degradation Assay of Bovine GDH, hGDHH454Y and BSA
4.7. Trypsin Degradation Assay of Bovine GDH and BSA in the Presence of EGCG and GTP
4.8. Gel Analysis and Proteomic Analysis
4.9. Gel Strip Analysis Assay
4.10. Statistical Analysis Assay
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pournourmohammadi, S.; Grimaldi, M.; Stridh, M.H.; Lavallard, V.; Waagepetersen, H.S.; Wollheim, C.B.; Maechler, P. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) activates AMPK through the inhibition of glutamate dehydrogenase in muscle and pancreatic ß-cells: A potential beneficial effect in the pre-diabetic state? Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2017, 88, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Y.; Li, D.; Lu, S.; Zhao, H.; Chen, Z.; Hou, W.; Ruan, B.H. Ebselen Reversibly Inhibits Human Glutamate Dehydrogenase at the Catalytic Site. Assay Drug Dev. Technol. 2018, 16, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Gao, J.; Su, S.; Shan, X.; Li, S.; Liu, H.; Yuan, Y.; Li, H. Regulation of the activity of maize glutamate dehydrogenase by ammonium and potassium. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2021, 85, 262–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.; Mao, S.; Xiong, Z.; Chen, Z.; Xu, N. Glutamate dehydrogenase: Potential therapeutic targets for neurodegenerative disease. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2023, 950, 175733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.; Sang, Y. Glutamate dehydrogenase hyperinsulinism: Mechanisms, diagnosis, and treatment. Orphanet. J. Rare Dis. 2023, 18, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdivielso, J.; Eritja, A.; Caus, M.; Bozic, M. Glutamate-Gated NMDA Receptors: Insights into the Function and Signaling in the Kidney. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenfeld, E.; Nanga, R.; Lucas, A.; Revell, A.Y.; Thomas, A.; Thomas, N.H.; Roalf, D.R.; Shinohara, R.T.; Reddy, R.; Davis, K.A.; et al. Characterizing the neurological phenotype of the hyperinsulinism hyperammonemia syndrome. Orphanet. J. Rare Dis. 2022, 17, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassar, O.; Li, C.; Stanley, C.; Pettitt, B.M.; Smith, T.J. Glutamate dehydrogenase: Structure of a hyperinsulinism mutant, corrections to the atomic model, and insights into a regulatory site. Proteins 2019, 87, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Li, C.; Allen, A.; Stanley, C.A.; Smith, T.J. Glutamate Dehydrogenase: Structure, Allosteric Regulation, and Role in Insulin Homeostasis. Neurochem. Res. 2012, 519, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, L.; Zhang, H.; Qi, R.; Tsao, R.; Mine, Y. Recent Advances in the Understanding of the Health Benefits and Molecular Mechanisms Associated with Green Tea Polyphenols. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 1029–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; McClements, D.; Liu, X.; Liu, F. EGCG-based nanoparticles: Synthesis, properties, and applications. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 65, 2177–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, N.; Mukhtar, H. Tea Polyphenols in Promotion of Human Health. Nutrients 2018, 11, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokotani, K.; Umegaki, K. Evaluation of plasma antioxidant activity in rats given excess EGCg with reference to endogenous antioxidants concentrations and assay methods. Free Radic. Res. 2017, 51, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Al, G.; Kwon, D. Antibacterial activity of epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) and its synergism with β-lactam antibiotics sensitizing carbapenem-associated multidrug resistant clinical isolates of Acinetobacter baumannii. Phytomed. Int. J. Phytother. Phytopharm. 2017, 24, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eng, Q.; Thanikachalam, P.; Ramamurthy, S. Molecular understanding of Epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) in cardiovascular and metabolic diseases. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 210, 296–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikoo, M.; Regenstein, J.; Gavlighi, H. Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Activities of (-)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) and its Potential to Preserve the Quality and Safety of Foods. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2018, 17, 732–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, S.; Keretsu, S.; Kang, S. Evaluation of decursin and its isomer decursinol angelate as potential inhibitors of human glutamate dehydrogenase activity through in silico and enzymatic assay screening. Comput. Biol. Med. 2022, 151, 106287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, W.; Lu, S.; Zhao, H.; Yu, Y.; Xu, H.; Yu, B.; Su, L.; Lin, C.; Ruan, B.H. Propylselen inhibits cancer cell growth by targeting glutamate dehydrogenase at the NADP+ binding site. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 509, 262–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Peng, J.; Gu, L.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Wu, J.; Xu, B.; Zhuge, Y.; Zhang, F. Targeting glutamine metabolism in hepatic stellate cells alleviates liver fibrosis. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Fang, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Xie, J.; Yu, Y.; Ruan, J.J.; Chen, Z.; Hou, W.; Yang, G.; et al. Biomolecular Interaction Assays Identified Dual Inhibitors of Glutaminase and Glutamate Dehydrogenase That Disrupt Mitochondrial Function and Prevent Growth of Cancer Cells. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 1689–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Ghanizadeh, H.; Li, X.; Han, Z.; Qiu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, A. A Study of the Interaction, Morphology, and Structure in Trypsin-Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate Complexes. Molecules 2021, 26, 4567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Chen, Y.; Xue, Z.; Gao, X.; Jia, Y.; Wang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, M.; Chen, H. Insight into the inactivation mechanism of soybean Bowman-Birk trypsin inhibitor (BBTI) induced by epigallocatechin gallate and epigallocatechin: Fluorescence, thermodynamics and docking studies. Food Chem. 2020, 303, 125380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boodhansingh, K.; Rosenfeld, E.; Lord, K.; Adzick, N.S.; Bhatti, T.; Ganguly, A.; De Leon, D.D.; Stanley, C.A. Mosaic GLUD1 mutations associated with hyperinsulinism hyperammonemia syndrome. Horm. Res. Paediatr. 2022, 95, 492–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.; Liang, X.J.; Li, W.J.; Wu, D.; Liu, M.; Cao, B.Y.; Chen, J.J.; Qin, M.; Meng, X.; Gong, C.X. Clinical and Molecular Spectrum of Glutamate Dehydrogenase Gene Defects in 26 Chinese Congenital Hyperinsulinemia Patients. J. Diabetes Res. 2018, 2018, 2802540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senniappan, S.; Shanti, B.; James, C.; Hussain, K. Hyperinsulinaemic hypoglycaemia: Genetic mechanisms, diagnosis and management. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2012, 35, 589–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, A.; Cheng, J.; Sheng, H.; Wen, Z.; Lin, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Zeng, C.; Shao, Y.; Li, C.; Liu, L.; et al. Clinical Management and Gene Mutation Analysis of Children with Congenital Hyperinsulinism in South China. J. Clin. Res. Pediatr. Endocrinol. 2019, 11, 400–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, H.Q.; Li, C.; Stanley, C.A.; Smith, T.J. Glutamate Dehydrogenase, a Complex Enzyme at a Crucial Metabolic Branch Point. Neurochem. Res. 2019, 44, 117–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, J.; Hsu, B.; Macmullen, C.M.; Poncz, M.; Smith, T.J.; Stanley, C.A. Expression, purification and characterization of human glutamate dehydrogenase (GDH) allosteric regulatory mutations. Biochem. J. 2002, 362, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurizi, M.; Rasulova, F. Degradation of L-glutamate dehydrogenase from Escherichia coli: Allosteric regulation of enzyme stability. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2002, 397, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.; Shin, S.; Cho, S.S.; Park, J.S. Purification and characterization of glutamate dehydrogenase as another isoprotein binding to the membrane of rough endoplasmic reticulum. J. Cell. Biochem. 1999, 76, 244–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molven, A.; Matre, G.E.; Duran, M.; Wanders, R.J.; Rishaug, U.; Njølstad, P.R.; Jellum, E.; Søvik, O. Familial hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia caused by a defect in the SCHAD enzyme of mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation. Diabetes 2004, 53, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zeng, Z.; Lin, C.; Pan, C.; Chen, Z.; Ruan, B.H. An Alternative Mechanism of Glutamate Dehydrogenase Inhibition by EGCG: Promotion of Protein Degradation. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 877. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18060877
Zeng Z, Lin C, Pan C, Chen Z, Ruan BH. An Alternative Mechanism of Glutamate Dehydrogenase Inhibition by EGCG: Promotion of Protein Degradation. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(6):877. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18060877
Chicago/Turabian StyleZeng, Ziying, Chenshui Lin, Chuqiao Pan, Zhao Chen, and Benfang Helen Ruan. 2025. "An Alternative Mechanism of Glutamate Dehydrogenase Inhibition by EGCG: Promotion of Protein Degradation" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 6: 877. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18060877
APA StyleZeng, Z., Lin, C., Pan, C., Chen, Z., & Ruan, B. H. (2025). An Alternative Mechanism of Glutamate Dehydrogenase Inhibition by EGCG: Promotion of Protein Degradation. Pharmaceuticals, 18(6), 877. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18060877





