Thermosensitive Mucoadhesive Intranasal In Situ Gel of Risperidone for Nose-to-Brain Targeting: Physiochemical and Pharmacokinetics Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Preparation of RIS In Situ Thermosensitive Gel
2.2. Physical Appearance and pH
2.3. Gelation Temperature and Gelation Time
2.4. Drug Content of the Prepared In Situ Thermosensitive Gel
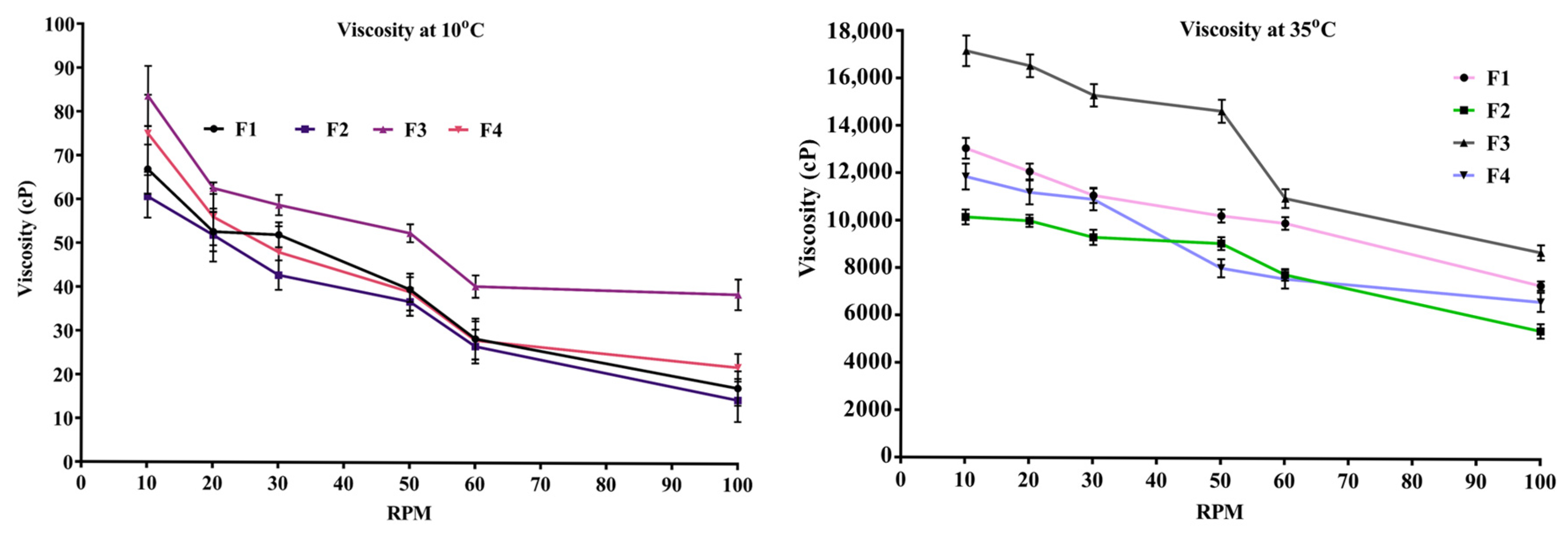
2.5. Viscosity of In Situ Thermosensitive Gel
2.6. Gelling Capacity and Spreadability
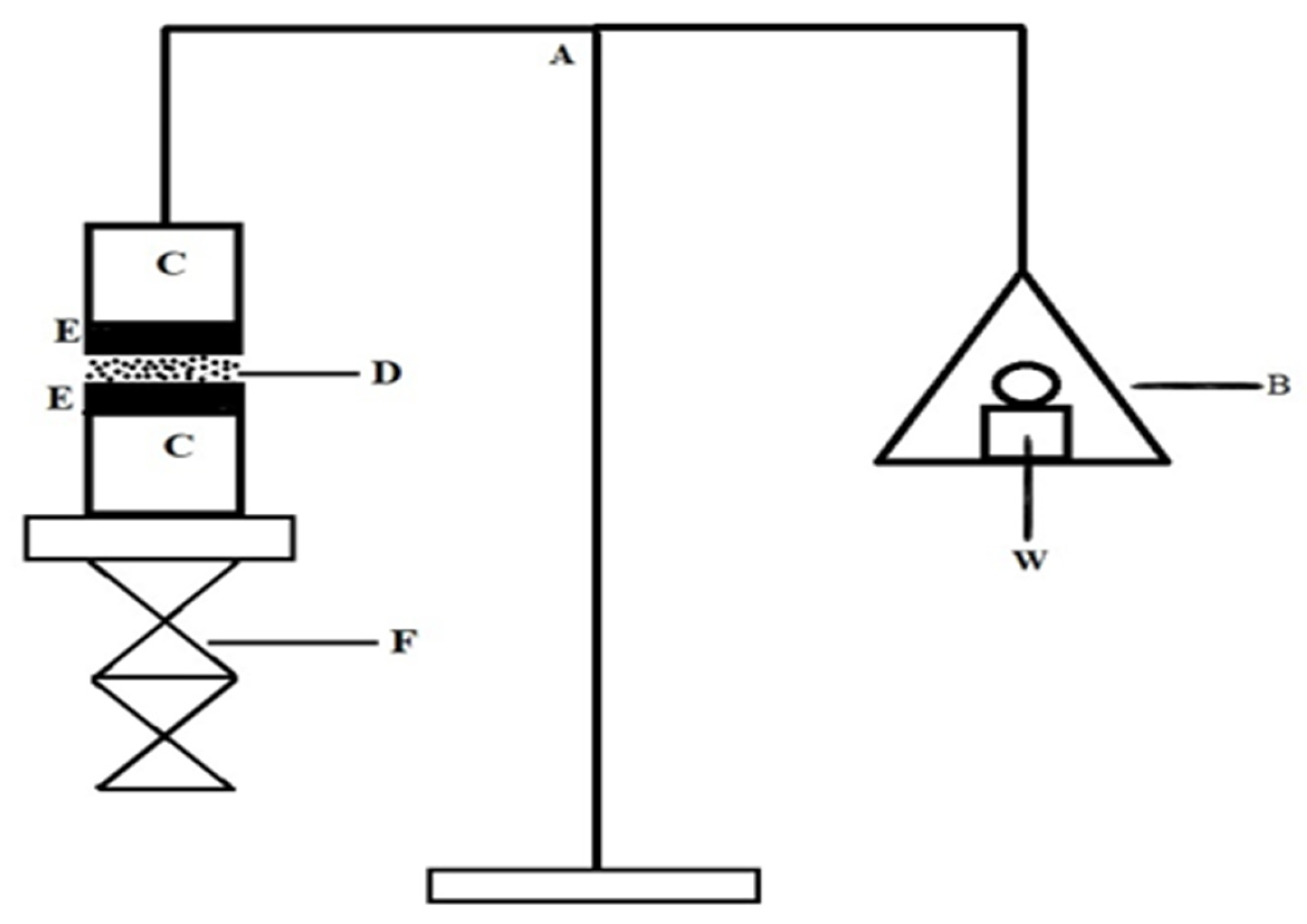
2.7. In Vitro Mucoadhesive Strength
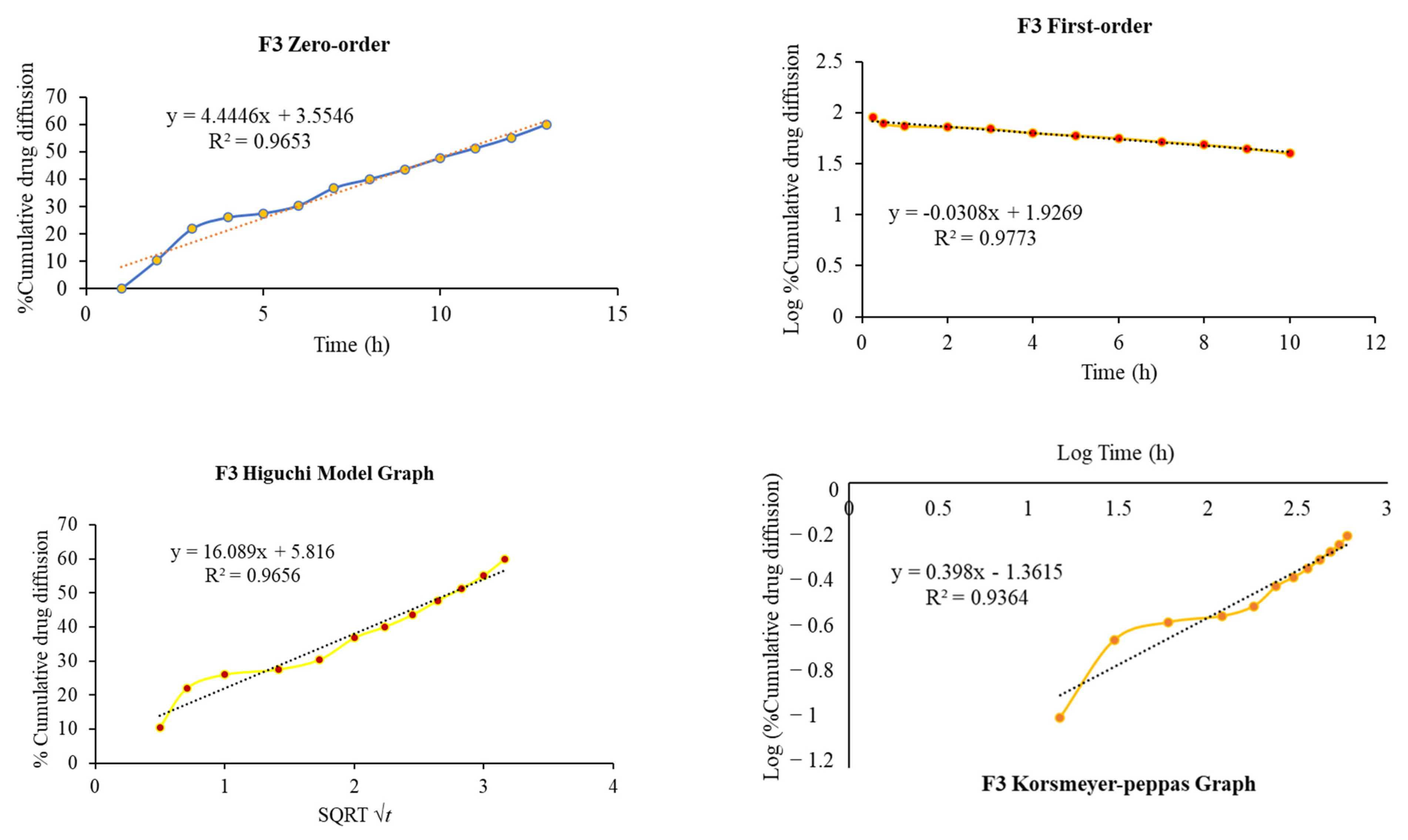
2.8. In Vitro Diffusion Study
2.9. FTIR Analysis
2.10. In Vivo Pharmacokinetics Studies
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Formulation of Thermosensitive Mucoadhesive In Situ Gel
4.3. Identification by FTIR
4.4. Appearance and pH Measurement
4.5. Gelation Time and Gelation Temperature
4.6. Drug Content Determination
4.7. Gelling Capacity and Spreadability
4.8. Determination of Viscosity
4.9. In Vitro Mucoadhesive Strength
4.10. In Vitro Diffusion Study
4.11. In Vitro Drug Release Kinetics Modeling
4.12. In Vivo Pharmacokinetics Studies
4.13. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shakeel, F.; Alanazi, F.K.; Alsarra, I.A.; Haq, N. Solubility of Antipsychotic Drug Risperidone in Transcutol+ Water Co-Solvent Mixtures at 298.15 to 333.15 K. J. Mol. Liq. 2014, 191, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, D.; Chakraborty, S.; Singh, S.; Mishra, B. Preparation and In-Vitro Characterization of Risperidone-Cyclodextrin Inclusion Complexes as a Potential Injectable Product. DARU 2009, 17, 226–235. [Google Scholar]
- Bavafa, A.; Sahab-Negah, S.; Forouzanfar, F. Nose-to-Brain Targeting of Resveratrol Nanoformulations. Curr. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, P.; Ren, C. Research Progress on Intranasal Treatment for Parkinson’s Disease. Neuroprotection 2024, 2, 79–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinkiewicz, M.; Pinkiewicz, M.; Walecki, J.; Zaczyński, A.; Zawadzki, M. Breaking Barriers in Neuro-Oncology: A Scoping Literature Review on Invasive and Non-Invasive Techniques for Blood–Brain Barrier Disruption. Cancers 2024, 16, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Yang, J.; Hou, Y.; Fang, Y.; Wu, K.; Song, Y.; Liu, K.; Zhu, J. Current Non-Invasive Strategies for Brain Drug Delivery: Overcoming Blood–Brain Barrier Transport. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2024, 51, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almahmoud, A.; Parekh, H.S.; Paterson, B.M.; Tupally, K.R.; Vegh, V. Intranasal Delivery of Imaging Agents to the Brain. Theranostics 2024, 14, 5022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Shukla, R. Current Strategic Arsenal and Advances in Nose to Brain Nanotheranostics for Therapeutic Intervention of Glioblastoma Multiforme. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2025, 36, 212–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teleanu, R.I.; Preda, M.D.; Niculescu, A.-G.; Vladâcenco, O.; Radu, C.I.; Grumezescu, A.M.; Teleanu, D.M. Current Strategies to Enhance Delivery of Drugs across the Blood–Brain Barrier. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Mental Health and COVID-19: Early Evidence of the Pandemic’s Impact: Scientific Brief, 2 March 2022; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Jiménez, A.; Estudillo, E.; Guzmán-Ruiz, M.A.; Herrera-Mundo, N.; Victoria-Acosta, G.; Cortés-Malagón, E.M.; López-Ornelas, A. Nanotechnology to Overcome Blood–Brain Barrier Permeability and Damage in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, T.; Dong, J.; Lu, Y. The Blood–Brain Barriers: Novel Nanocarriers for Central Nervous System Diseases. J. Nanobiotechnology 2025, 23, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adscheid, S.A.; Türeli, A.E.; Günday-Türeli, N.; Schneider, M. Nanotechnological Approaches for Efficient N2B Delivery: From Small-Molecule Drugs to Biopharmaceuticals. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2024, 15, 1400–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittal, V.; Yadav, K.S. Optimizing Nasal Drug Delivery for Peptides, Proteins, and Small Molecules: Strategic Use of Materials and Techniques to Target the CNS. Int. J. Polym. Mater. Polym. Biomater. 2024, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shringarpure, M.; Gharat, S.; Momin, M.; Omri, A. Management of Epileptic Disorders Using Nanotechnology-Based Strategies for Nose-to-Brain Drug Delivery. Expert. Opin. Drug Deliv. 2021, 18, 169–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montegiove, N.; Calzoni, E.; Emiliani, C.; Cesaretti, A. Biopolymer Nanoparticles for Nose-to-Brain Drug Delivery: A New Promising Approach for the Treatment of Neurological Diseases. J. Funct. Biomater. 2022, 13, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, M.; Roy, D.; Thakur, S.; Singh, A. Exploring the Potential of Nasal Drug Delivery for Brain Targeted Therapy: A Detailed Analysis. Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 2024, 45, 161–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adangale, S.; Singh, A.D.; Kulkarni, Y.A.; Wairkar, S. Brain-Targeted Nasal Chrysin Microemulsion for Reducing Oxidative Stress in Parkinson’s Disease: Pharmacodynamic, Biochemical Evaluation and Brain Distribution Studies. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2024, 97, 105756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadiri, M.; Young, P.M.; Traini, D. Strategies to Enhance Drug Absorption via Nasal and Pulmonary Routes. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sipos, B.; Katona, G.; Csóka, I. Risperidone-Loaded Nasal Thermosensitive Polymeric Micelles: Quality by Design-Based Formulation Study. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdallah, M.H.; El-Horany, H.E.-S.; El-Nahas, H.M.; Ibrahim, T.M. Tailoring Risperidone-Loaded Glycethosomal in Situ Gels Using Box–Behnken Design for Treatment of Schizophrenia-Induced Rats via Intranasal Route. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Ma, X.; Zong, S.; Su, Y.; Su, R.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.; Wang, C.; Li, Y. The Prescription Design and Key Properties of Nasal Gel for CNS Drug Delivery: A Review. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2024, 192, 106623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, S.J.; Zafar, S.; Shahzad, A.; Basit, M.; Mudassir, J.; Akhlaq, M.; Chohan, T.A.; Arshad, M.S. Preparation of Tamsulosin Hydrochloride-Loaded Mucoadhesive in Situ Gelling Polymeric Formulation for Nasal Delivery in Geriatrics. AAPS PharmSciTech 2023, 24, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, Z.; Li, W.; Liao, W.; Lv, Y.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, H.; Feng, Y. Fructus xanthii and Magnolia liliiflora Volatile Oils Liposomes-Loaded Thermosensitive in Situ Gel for Allergic Rhinitis Management. Int. J. Nanomedicine 2024, 19, 1557–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guarve, K.; Kriplani, P. HPMC-a Marvel Polymer for Pharmaceutical Industry-Patent Review. Recent. Adv. Drug Deliv. Formul. Former. Recent Pat. Drug Deliv. Formul. 2021, 15, 46–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clementino, A.; Climani, G.; Bianchera, A.; Buttini, F.; Sonvico, F. Polysaccharides: New Frontiers for Nasal Administration of Medicines. Polysaccharides 2025, 6, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodaverdi, K.; Bakhshi, A.; Mozafari, M.R.; Naghib, S.M. A Review of Chitosan-Based Nanocarriers as Drug Delivery Systems for Brain Diseases: Critical Challenges, Outlooks and Promises. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 278, 134962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B.; Liu, D.; Qin, X.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, P. Mucoadhesive-to-Mucopenetrating Nanoparticles for Mucosal Drug Delivery: A Mini Review. Int. J. Nanomedicine 2025, 20, 2241–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Sisi, A.M.; Eissa, E.M.; Hassan, A.H.E.; Bekhet, M.A.; El-Ela, F.I.A.; Roh, E.J.; Kharshoum, R.M.; Ali, A.A. Nose-to-Brain Delivery of Chitosan-Grafted Leciplexes for Promoting the Bioavailability and Antidepressant Efficacy of Mirtazapine: In Vitro Assessment and Animal Studies. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hisham, F.; Akmal, M.H.M.; Ahmad, F.; Ahmad, K.; Samat, N. Biopolymer Chitosan: Potential Sources, Extraction Methods, and Emerging Applications. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2024, 15, 102424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blebea, N.-M.; Pușcașu, C.; Vlad, R.-A.; Hancu, G. Chitosan-Based Gel Development: Extraction, Gelation Mechanisms, and Biomedical Applications. Gels 2025, 11, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Ma, Z.; Wu, X.; Wei, H.; Zhang, H.; Li, G.; Qian, Y.; Shahriari-Khalaji, M.; Hou, K.; Cao, R. Advances in Stimuli-responsive Chitosan Hydrogels for Drug Delivery Systems. Macromol. Biosci. 2024, 24, 2300399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edo, G.I.; Yousif, E.; Al-Mashhadani, M.H. Chitosan: An Overview of Biological Activities, Derivatives, Properties, and Current Advancements in Biomedical Applications. Carbohydr. Res. 2024, 109199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omidian, H.; Gill, E.J.; Dey Chowdhury, S.; Cubeddu, L.X. Chitosan Nanoparticles for Intranasal Drug Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazi-Chishti, M.; Shaikh, J.; Chishti, N.; Dehghan, M.H. Nasal Mucoadhesive in Situ Gelling Liquid Crystalline Fluid Precursor System of Polyene Antibiotic for Potential Treatment of Localized Sinuses Aspergillosis Post COVID Infection. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2024, 45, 1373–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjali, S.; Abhijeet, K.; Ajay, S.; Kulkarni, A. Nasal in Situ Gel: Novel Approach for Nasal Drug Delivery. J. Drug Deliv. Ther. 2020, 10, 183–197. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, L.; Cook, M.T.; Dreiss, C.A. In Situ Gels for Nasal Delivery: Formulation, Characterization and Applications. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2025, 2400356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Wu, W.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, W.; Li, Y.; Ding, T.; Fang, Z.; Jing, J.; He, X.; Huang, F. Enhanced Diabetic Foot Ulcer Treatment with a Chitosan-Based Thermosensitive Hydrogel Loaded Self-Assembled Multi-Functional Nanoparticles for Antibacterial and Angiogenic Effects. Carbohydr. Polym. 2025, 347, 122740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anggelia, M.R.; Cheng, H.; Lin, C. Thermosensitive Hydrogels as Targeted and Controlled Drug Delivery Systems: Potential Applications in Transplantation. Macromol. Biosci. 2024, 24, 2400064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Xue, K.; Loh, X.J. Thermo-Responsive Hydrogels: From Recent Progress to Biomedical Applications. Gels 2021, 7, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Xie, L.; Lv, L.; Chen, J.; Feng, F.; Liu, W.; Han, L.; Liu, F. Intranasally Administered Thermosensitive Gel for Brain-Targeted Delivery of Rhynchophylline to Treat Parkinson’s Disease. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2023, 222, 113065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Li, C.; Liu, Z.; Li, Q.; Yan, X.; Liu, Y.; Lu, W. Enhancement in Bioavailability of Ketorolac Tromethamine via Intranasal in Situ Hydrogel Based on Poloxamer 407 and Carrageenan. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 474, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soni, S.; Verma, A.; Ram, V. Evaluation of Chitosan-Hydroxy Propyl Methyl Cellulose as a Single Unit Hydrodynamically Balanced Sustained Release Matrices for Stomach Specific Delivery of Piroxicam. MOJ Bioequiv Availab. 2016, 2, 00014. [Google Scholar]
- Upadhyay, R.K. Drug Delivery Systems, CNS Protection, and the Blood Brain Barrier. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 869269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nance, E.; Pun, S.H.; Saigal, R.; Sellers, D.L. Drug Delivery to the Central Nervous System. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2022, 7, 314–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashyap, K.; Shukla, R. Drug Delivery and Targeting to the Brain through Nasal Route: Mechanisms, Applications and Challenges. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2019, 16, 887–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdő, F.; Bors, L.A.; Farkas, D.; Bajza, Á.; Gizurarson, S. Evaluation of Intranasal Delivery Route of Drug Administration for Brain Targeting. Brain Res. Bull. 2018, 143, 155–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, X.; Jasti, B.R. Role of Physicochemical Properties of Some Grades of Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose on in Vitro Mucoadhesion. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 609, 121218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Shi, X.; Tian, L. Design of Berberine Hydrochloride Sustained-Release Cold Sol Using Hydroxypropyl Methyl Cellulose K100M to Achieve Superior Drug Dissolution and Transdermal Absorption. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 275, 133611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Tong, J.; Zhang, L.; Wei, Y.; Tian, M. Recent Advances in Thermo-Sensitive Hydrogels for Drug Delivery. J. Mater. Chem. B 2021, 9, 2979–2992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdallah, M.H.; Shahien, M.M.; El-Horany, H.E.-S.; Ahmed, E.H.; El-Nahas, H.M.; Abdulla, N.A.; Ibrahim, T.M. Evaluation of Mucoadhesive Nano-Bilosomal In Situ Gels Containing Anti-Psychotic Clozapine for Treatment of Schizophrenia: In Vitro and In Vivo Studies. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkufi, H.K.; Kassab, H.J. Formulation and Evaluation of Sustained Release Sumatriptan Mucoadhesive Intranasal In-Situ Gel. Iraqi J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 28, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, E.; Qi, Z.; Cao, Y.; Li, R.; Wu, J.; Tang, R.; Gao, Y.; Du, R.; Liu, M. Gels as Promising Delivery Systems: Physicochemical Property Characterization and Recent Applications. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jagdale, S.; Shewale, N.; Kuchekar, B.S. Optimization of Thermoreversible in Situ Nasal Gel of Timolol Maleate. Scientifica 2016, 2016, 6401267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdeltawab, H.; Svirskis, D.; Hill, A.G.; Sharma, M. Increasing the Hydrophobic Component of Poloxamers and the Inclusion of Salt Extend the Release of Bupivacaine from Injectable In Situ Gels, While Common Polymer Additives Have Little Effect. Gels 2022, 8, 484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdeltawab, H.; Svirskis, D.; Sharma, M. Formulation Strategies to Modulate Drug Release from Poloxamer Based in Situ Gelling Systems. Expert. Opin. Drug Deliv. 2020, 17, 495–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novak, S.D.; Kuhelj, V.; Vrečer, F.; Baumgartner, S. The Influence of HPMC Viscosity as FRC Parameter on the Release of Low Soluble Drug from Hydrophylic Matrix Tablets. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2013, 18, 343–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahajan, H.S.; Tyagi, V.; Lohiya, G.; Nerkar, P. Thermally Reversible Xyloglucan Gels as Vehicles for Nasal Drug Delivery. Drug Deliv. 2012, 19, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galgatte, U.C.; Kumbhar, A.B.; Chaudhari, P.D. Development of in Situ Gel for Nasal Delivery: Design, Optimization, in Vitro and in Vivo Evaluation. Drug Deliv. 2014, 21, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, P.; Svirskis, D.; Waterhouse, G.I.N.; Wu, Z. Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose Bioadhesive Hydrogels for Topical Application and Sustained Drug Release: The Effect of Polyvinylpyrrolidone on the Physicomechanical Properties of Hydrogel. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, M.; Gharti, L.; Bansal, A.; Kaurav, H.; Sheth, S. Intranasal Mucoadhesive In Situ Gel of Glibenclamide-Loaded Bilosomes for Enhanced Therapeutic Drug Delivery to the Brain. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.A.; Oh, H.K.; Lee, J.C.; Choi, Y.H.; Jeong, S.H. Comparison of Solubility Enhancement by Solid Dispersion and Micronized Butein and Its Correlation with in Vivo Study. J. Pharm. Investig. 2021, 51, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajracharya, R.; Lee, S.H.; Song, J.G.; Kim, M.; Lee, K.; Han, H.-K. Development of a Ternary Solid Dispersion Formulation of LW6 to Improve the in Vivo Activity as a BCRP Inhibitor: Preparation and in Vitro/in Vivo Characterization. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasconcelos, T.; Prezotti, F.; Araújo, F.; Lopes, C.; Loureiro, A.; Marques, S.; Sarmento, B. Third-Generation Solid Dispersion Combining Soluplus and Poloxamer 407 Enhances the Oral Bioavailability of Resveratrol. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 595, 120245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabir, S.A.; Rajab, N.A. Preparation, in-Vitro, Ex-Vivo, and Pharmacokinetic Study of Lasmiditan as Intranasal Nanoemulsion-Based in Situ Gel. Pharm. Nanotechnol. 2025, 13, 239–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, P.; Garg, T.; Rath, G.; Goyal, A.K. In Situ Nasal Gel Drug Delivery: A Novel Approach for Brain Targeting through the Mucosal Membrane. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2016, 44, 1167–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garala, K.; Joshi, P.; Shah, M.; Ramkishan, A.; Patel, J. Formulation and Evaluation of Periodontal in Situ Gel. Int. J. Pharm. Investig. 2013, 3, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Kanoujia, J.; Singh, P.; Parashar, P.; Arya, M.; Tripathi, C.B.; Sinha, V.R.; Saraf, S.A. Development of an α-Linolenic Acid Containing a Soft Nanocarrier for Oral Delivery-Part II: Buccoadhesive Gel. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 101602–101612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shikalgar, R.; Deshmukh, V.; Rathod, S.; Bangale, G.S.; Pore, Y.V.; Pawar, D.P. Fabrication of PF-127 Based Niosomal in Situ Gel for Intranasal Delivery of Lurasidone Hydrochloride and Optimization by Using 32 Factorial Design. Bionanoscience 2024, 14, 1318–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, F.; Ma, W.; Meng, G.; Wu, C.; Wang, Y. Preparation and in Vivo Evaluation of Gel-Based Nasal Delivery System for Risperidone. Acta Pharmaceutica 2016, 66, 555–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Name of Ingredients | Formulation Code | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | F2 | F3 | F4 | |
| Risperidone (mg) | 180.0 | 180.0 | 180.0 | 180.0 |
| Poloxamer 407 (%w/v) | 18.0 | 18.0 | 18.0 | 18.0 |
| HPMC K100M (%w/v) | 0.3 | - | 0.5 | - |
| HPMC K15M (%w/v) | - | 0.3 | - | 0.5 |
| Dichloromethane (mL) | 2.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 |
| Phosphate buffer (mL) | q.s. | q.s. | q.s. | q.s. |
| Benzalkonium chloride (%v/v) | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| Formulation Code | Gelation Temperature (°C) | Gelation Time (Minutes) | Drug Content (%) | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | 36.40 ± 0.95 | 2.05 ± 0.45 | 95.58 ± 2.37 | 6.37 ± 0.015 |
| F2 | 37.50 ± 1.05 | 2.50 ± 0.55 | 97.12 ± 1.59 | 6.24 ± 0.011 |
| F3 | 34.25 ± 1.10 | 1.65 ± 0.30 | 98.03 ± 1.68 | 6.25 ± 0.020 |
| F4 | 35.80 ± 0.85 | 1.95 ± 0.60 | 96.14 ± 1.95 | 6.20 ± 0.026 |
| Formulation Code | Spreadability Range (gm/s) | Gelling Capacity (h) | In Vitro Mucoadhesive Strength (dyne/cm2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | 28.33 ± 1.52 | 9.13 ± 0.321 | 780.08 ± 3.92 |
| F2 | 33.66 ± 2.08 | 8.35 ± 0.348 | 708.21 ± 4.52 |
| F3 | 18.24 ± 2.15 | 9.52 ± 0.513 | 1110.65 ± 6.87 |
| F4 | 27.41 ± 3.05 | 8.86 ± 0.264 | 943.41 ± 4.82 |
| Formulation Code | Zero-Order R2 | First-Order R2 | Higuchi R2 | Korsymer–Peppas | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | n Value | ||||
| F1 | 0.988 | 0.979 | 0.994 | 0.990 | 0.827 |
| F2 | 0.913 | 0.821 | 0.846 | 0.920 | 0.412 |
| F3 | 0.965 | 0.977 | 0.965 | 0.936 | 0.398 |
| F4 | 0.993 | 0.960 | 0.974 | 0.986 | 0.512 |
| Parameters | Brain | Blood | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Formulation | F3 | Marketed | F3 | Marketed |
| Route | Nasal | Oral | Nasal | Oral |
| tmax (h) | 1.00 | 2.00 | 2.00 | 2.00 |
| Cmax (ng/g, ng/mL) | 1523.56 ± 122.14 * | 329.78 ± 35.08 | 696.13 ± 77.56 | 1556.32 ± 225.53 |
| t1/2 (h) | 1.49 ± 0.15 | 2.06 ± 0.19 | 2.08 ± 0.42 | 4.10 ± 1.03 |
| AUC0–∞ (ng.h/mL) | 4612 ± 316.53 * | 848 ± 110.45 | 1425 ± 151.32 | 6432 ± 462.64 |
| AUCbrain/AUCplasma | 3.236 | 0.132 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Singh, M.; Kumar, S.; Vinayagam, R.; Samivel, R. Thermosensitive Mucoadhesive Intranasal In Situ Gel of Risperidone for Nose-to-Brain Targeting: Physiochemical and Pharmacokinetics Study. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 871. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18060871
Singh M, Kumar S, Vinayagam R, Samivel R. Thermosensitive Mucoadhesive Intranasal In Situ Gel of Risperidone for Nose-to-Brain Targeting: Physiochemical and Pharmacokinetics Study. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(6):871. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18060871
Chicago/Turabian StyleSingh, Mahendra, Sanjay Kumar, Ramachandran Vinayagam, and Ramachandran Samivel. 2025. "Thermosensitive Mucoadhesive Intranasal In Situ Gel of Risperidone for Nose-to-Brain Targeting: Physiochemical and Pharmacokinetics Study" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 6: 871. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18060871
APA StyleSingh, M., Kumar, S., Vinayagam, R., & Samivel, R. (2025). Thermosensitive Mucoadhesive Intranasal In Situ Gel of Risperidone for Nose-to-Brain Targeting: Physiochemical and Pharmacokinetics Study. Pharmaceuticals, 18(6), 871. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18060871








