Synergistic Effect of Banaba Leaf Extract and Policosanol (Raydel®) Ameliorate High Cholesterol and High Galactose-Diet Induced Adverse Events in Zebrafish
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
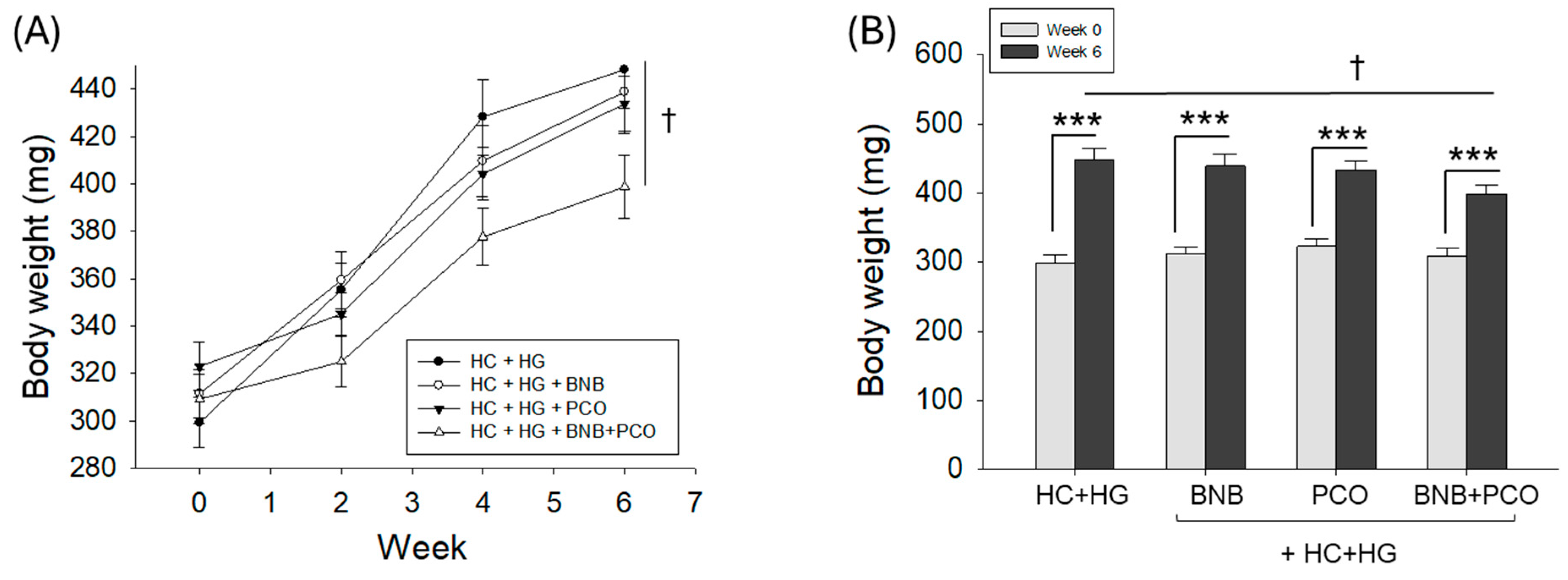
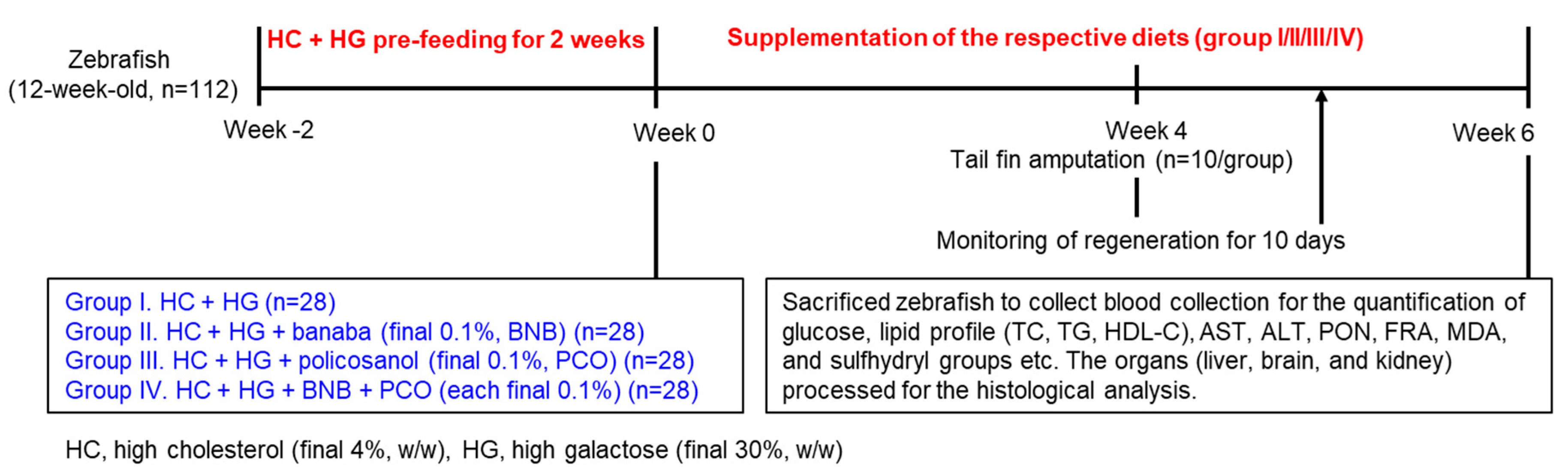
2.1. Survival Analysis and Variation in Body Weight
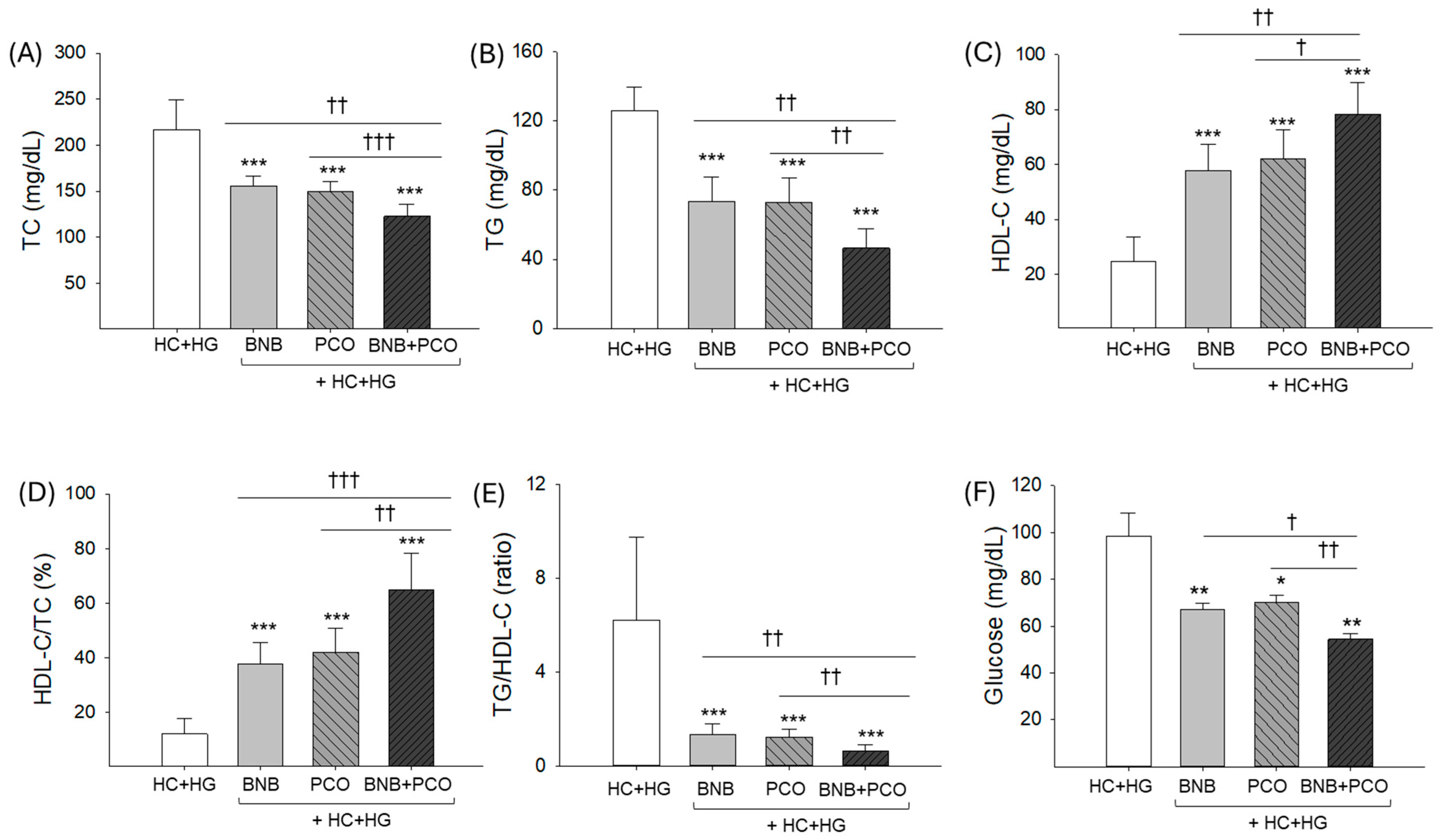
2.2. Lipid Profiles in Plasma
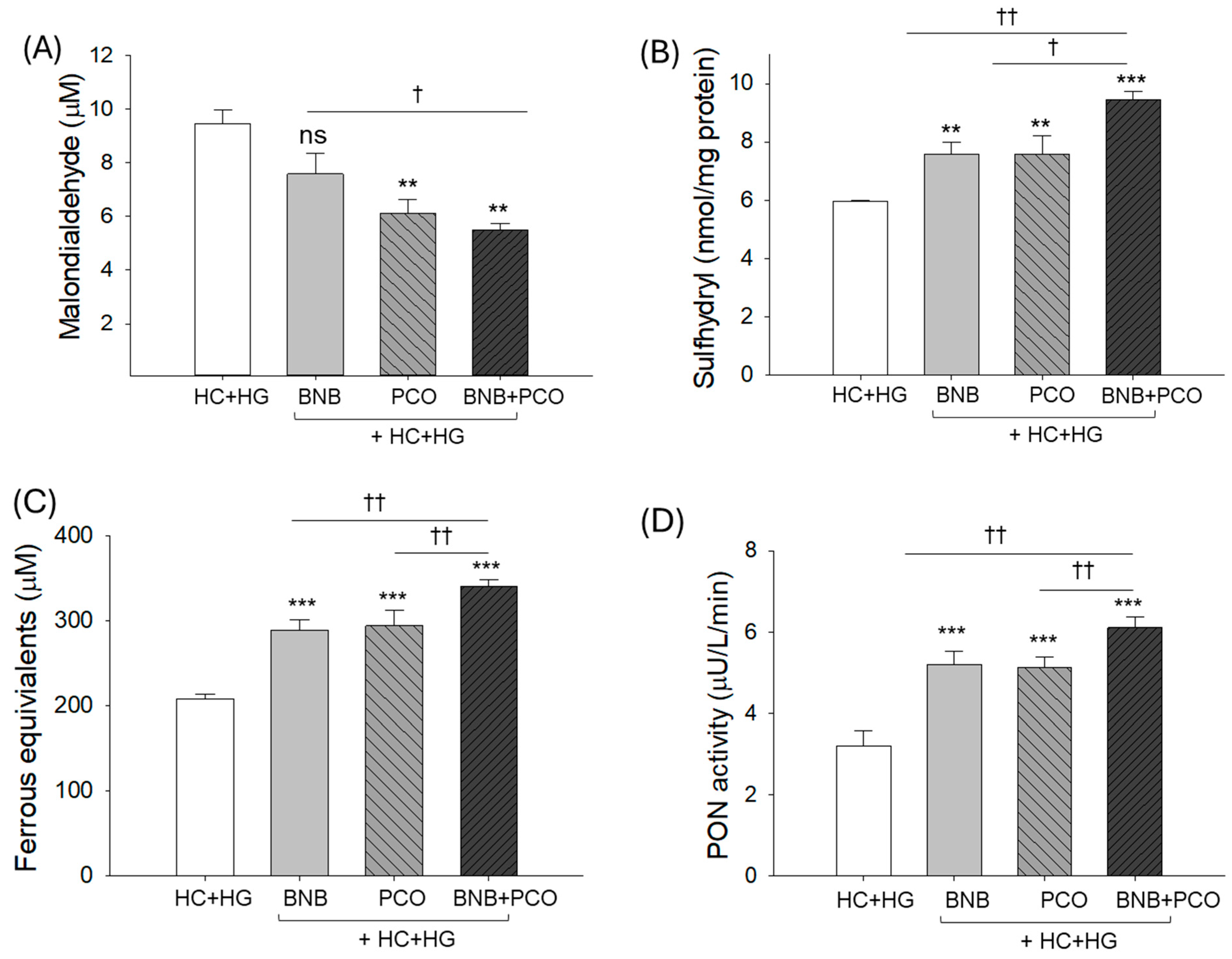
2.3. Plasma Antioxidant Capacity
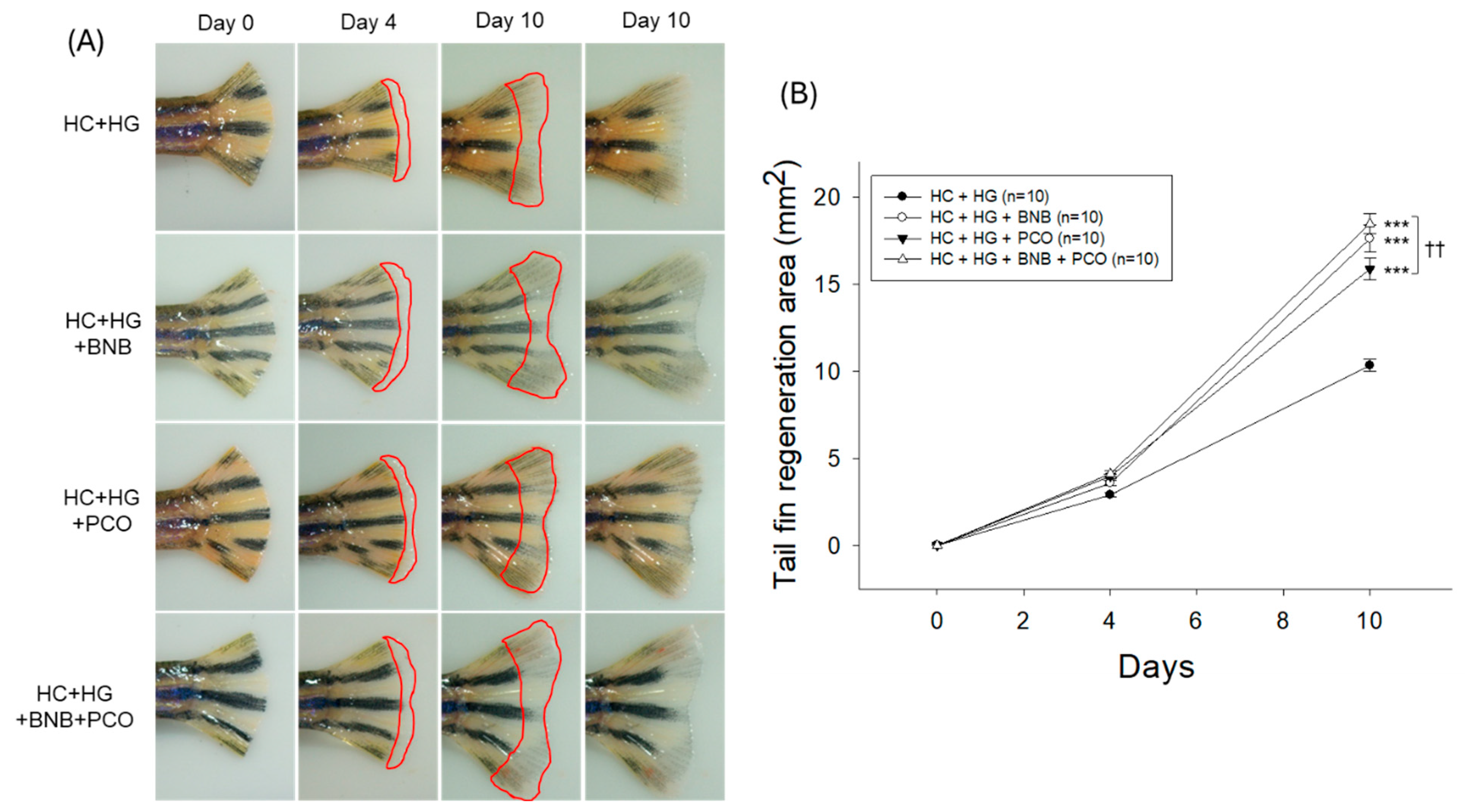
2.4. Tail Fin Regeneration Speed and Morphology
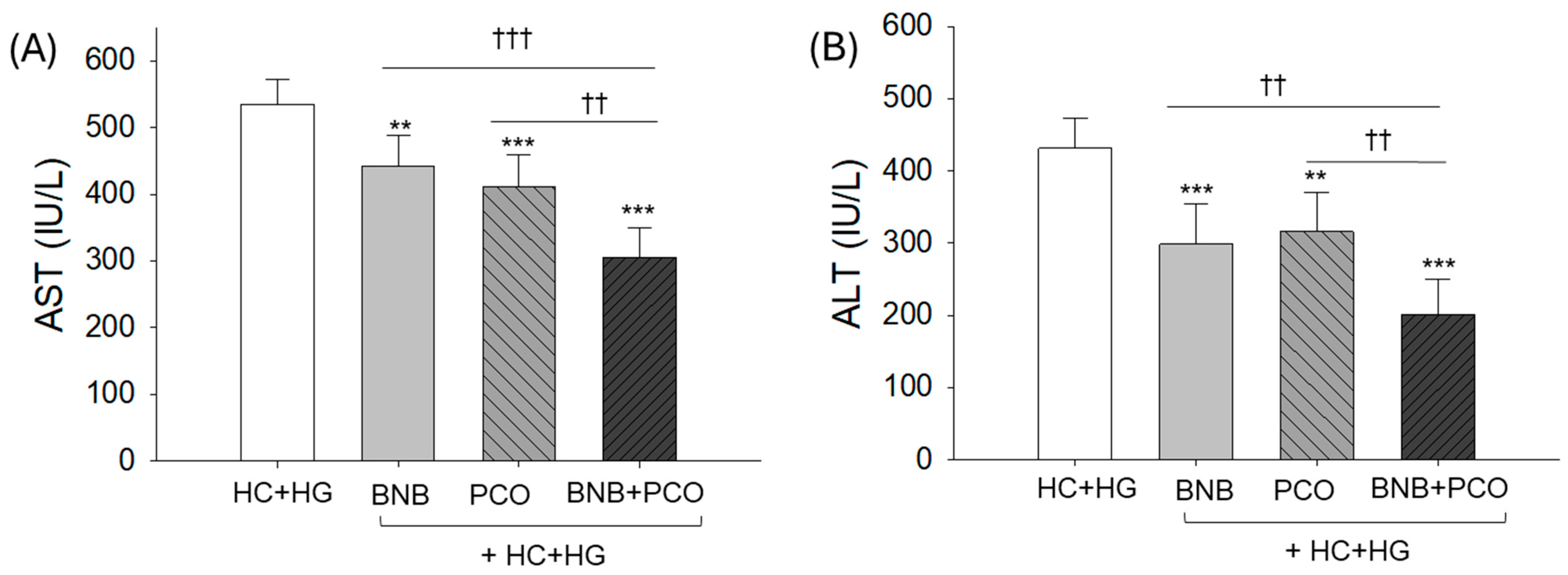
2.5. Hepatic Damage Markers in Plasma
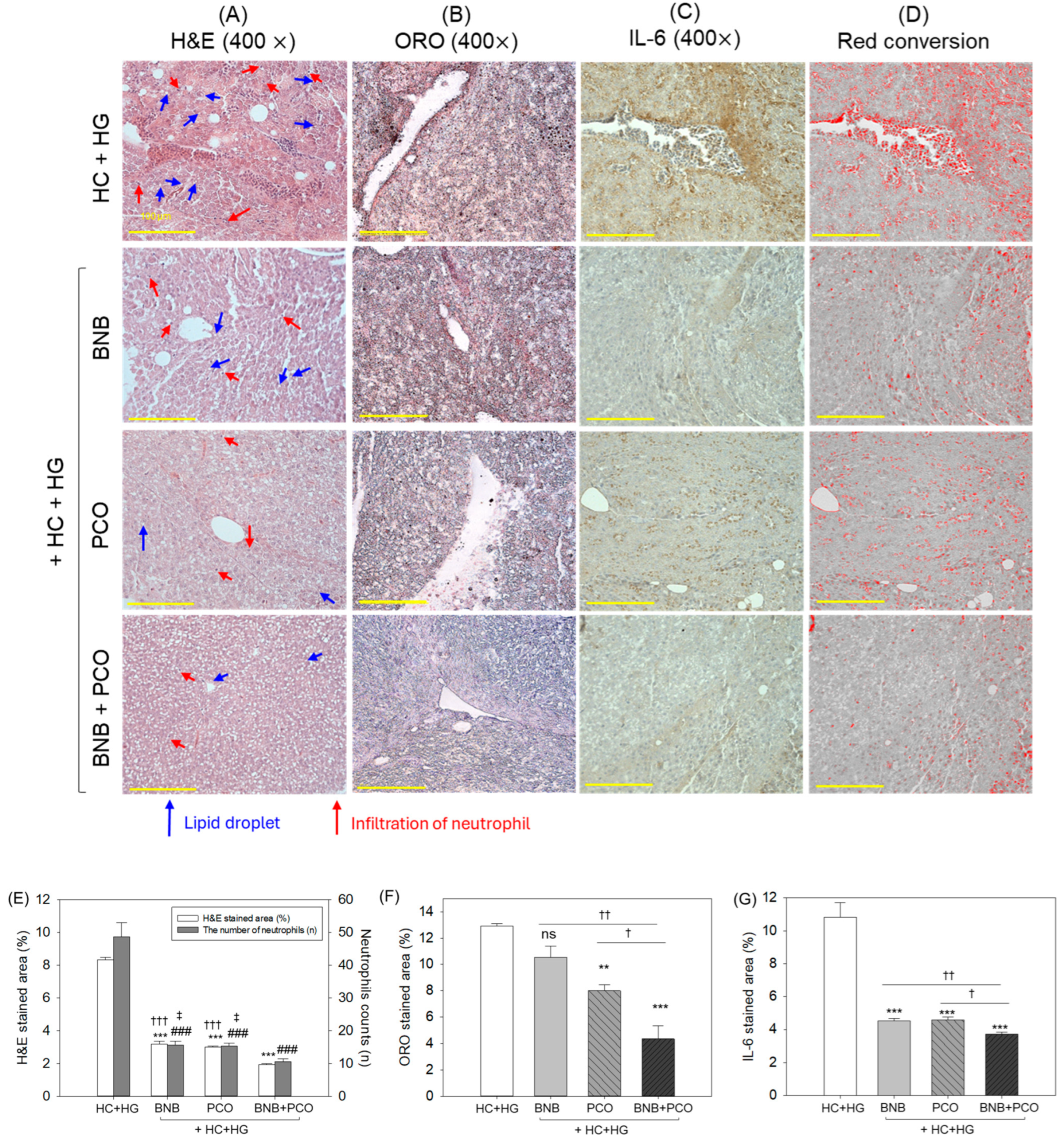
2.6. Histological and Immunohistochemical Analysis of Liver
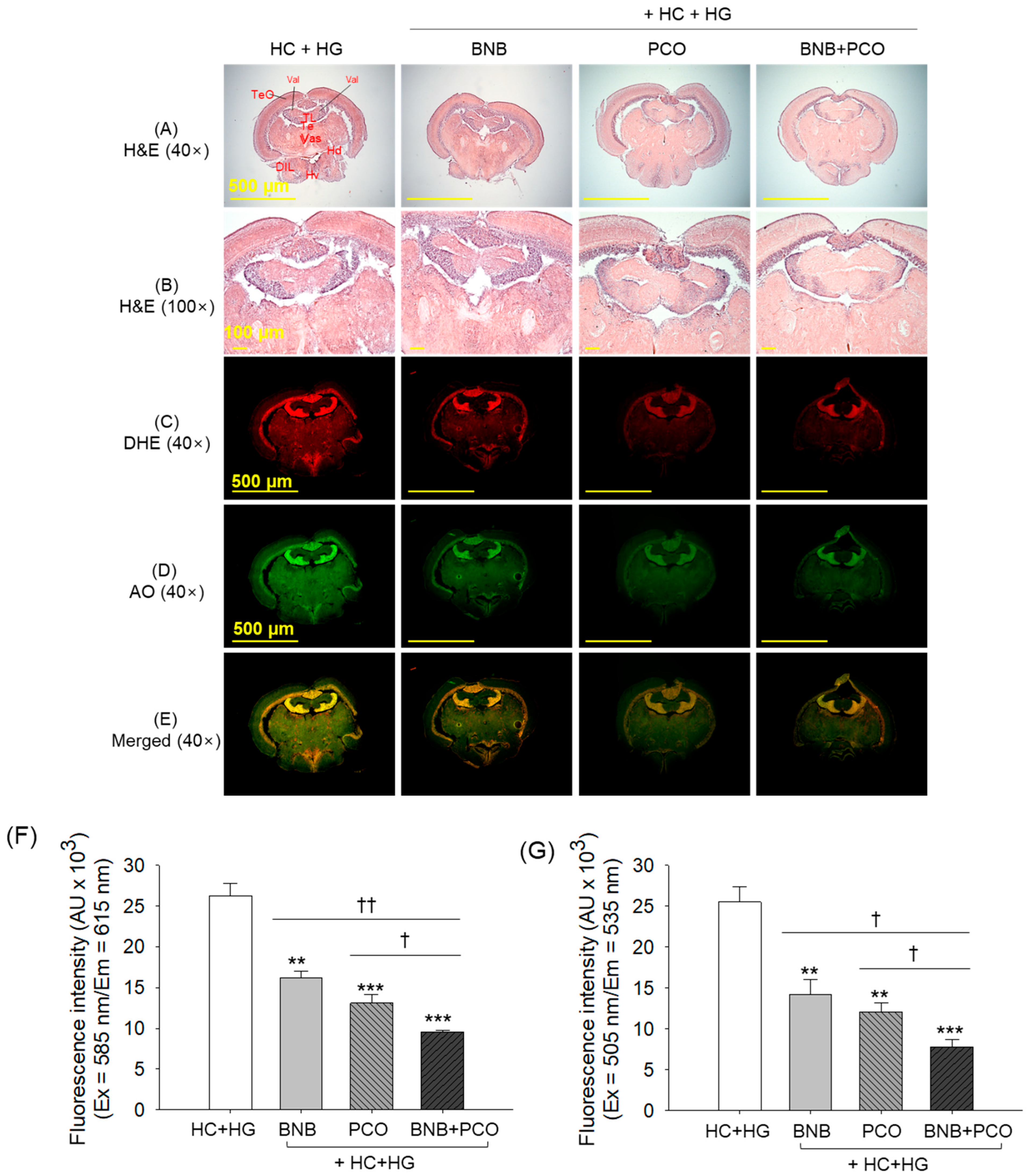
2.7. Histological Analysis of Brain
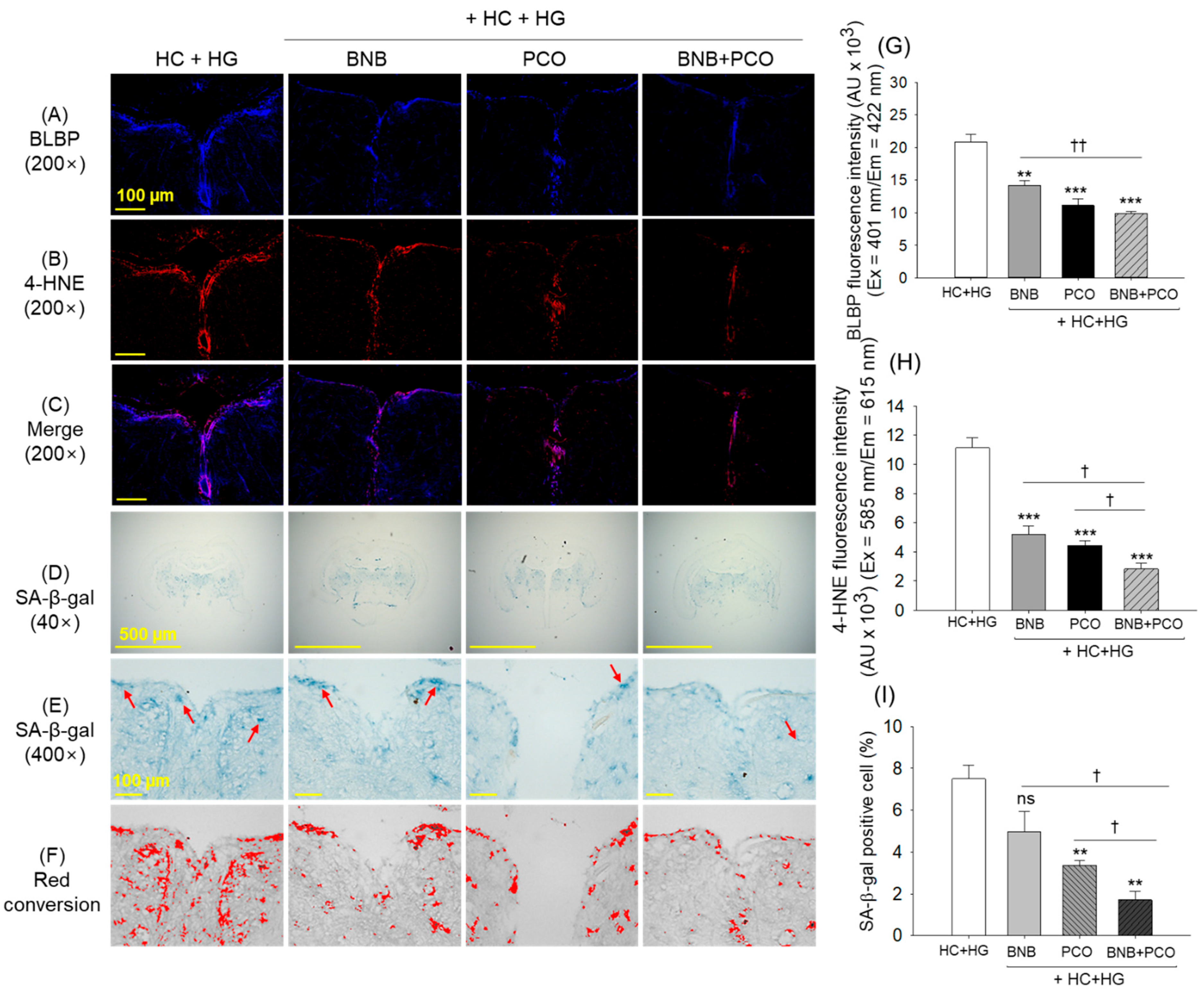
2.8. Cellular Senescence and Oxidative Stress in the Brain
2.9. Histological Analysis of Kidney, Ovary and Testis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials and Antibodies
4.2. Zebrafish Culturing
4.3. Specialized Diet Preparation
4.4. Feeding of the Zebrafish
4.5. Tail Fin Amputation
4.6. Collection of Blood and Organs
4.7. Blood Analysis for the Quantification of Lipoprotein, Hepatic Function Biomarkers and Glucose Level
4.8. Evaluation of Malondialdehyde (MDA), Sulfhydryl Content and Antioxidant Parameters
4.9. Histological Analysis
4.10. Immunohistochemical (IHC) Staining
4.11. Staining for Dihydroethidium (DHE), Acridine Orange (AO) and Cellular Senescence
4.12. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lai, K.; Elsas, L.J.; Wierenga, K.J. Galactose toxicity in animals. IUBMB Life 2009, 61, 1063–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bo-Htay, C.; Palee, S.; Apaijai, N.; Chattipakorn, S.C.; Chattipakorn, N. Effects of d-galactose-induced ageing on the heart and its potential interventions. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2018, 22, 1392–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conte, F.; van Buuringen, N.; Voermans, N.C.; Lefeber, D.J. Galactose in human metabolism, glycosylation and congenital metabolic diseases: Time for a closer look. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Gen. Subj. 2021, 1865, 129898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalid, M.; Petroianu, G.; Adem, A. Advanced glycation end products and diabetes mellitus: Mechanisms and perspectives. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.; Wang, T.; Wang, T.; Chen, H.; Deng, J.; Ye, H.; Li, W.; Ling, S. Characterization of an i.p. D-galactose-induced cataract model in rats. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods 2021, 107, 106891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udomkasemsab, A.; Prangthip, P. High fat diet for induced dyslipidemia and cardiac pathological alterations in Wistar rats compared to Sprague Dawley rats. Clin. Investig. Arterioscler. 2019, 31, 56–62. [Google Scholar]
- Speliotes, E.K.; Balakrishnan, M.; Friedman, L.S.; Corey, K.E. Treatment of dyslipidemia in common liver diseases. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 16, 1189–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, S.H.; Kim, S.W. Dyslipidemia in patients with chronic kidney disease: An updated overview. Diabetes Metab. J. 2023, 47, 612–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Xie, Y.; Qu, L.; Zhang, M.; Mo, Z. Dyslipidemia involvement in the development of polycystic ovary syndrome. Taiwan. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2019, 58, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahalle, N.; Garg, M.; Naik, S.S.; Kulkarni, M.V. Study of pattern of dyslipidemia and its correlation with cardiovascular risk factors in patients with proven coronary artery disease. Indian J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 18, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bala, S.; Ganz, M.; Babuta, M.; Zhuang, Y.; Csak, T.; Calenda, C.D.; Szabo, G. Steatosis, inflammasome upregulation, and fibrosis are attenuated in miR-155 deficient mice in a high fat-cholesterol-sugar diet-induced model of NASH. Lab. Investig. 2021, 101, 1540–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paraskevas, K.I.; Gloviczki, P.; Antignani, P.L.; Comerota, A.J.; Dardik, A.; Davies, A.H.; Eckstein, H.-H.; Faggioli, G.; e Fernandes, J.F.; Fraedrich, G. Benefits and drawbacks of statins and non-statin lipid lowering agents in carotid artery disease. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2022, 73, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, N.C.; Watts, G.F.; Eckel, R.H. Statin toxicity. Circ. Res. 2019, 124, 328–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.-Y.; Jiao, R.; Ma, K.Y. Cholesterol—Lowering nutraceuticals and functional foods. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 8761–8773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Peng, J.; Zhang, K.; Wang, L.; Feng, T.; Nhamdriel, T.; Fan, G. Phytochemicals for the treatment of metabolic diseases: Evidence from clinical studies. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 165, 115274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olatunji, L.K.; Jimoh, A.O.; Tukur, U.M.; Imam, M.U. A review of the effects of policosanol on metabolic syndrome. Clin. Complement. Med. Pharmacol. 2022, 2, 100058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.; Qin, X.; Yuan, F.; Hu, M.; Chen, G.; Fang, K.; Wang, D.; Jiang, S.; Li, J.; Zhao, Y. Efficacy and safety of sugarcane policosanol on dyslipidemia: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2018, 62, 1700280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-Y.; Kim, S.-M.; Kim, S.-J.; Lee, E.-Y.; Kim, J.-R.; Cho, K.-H. Consumption of policosanol enhances HDL functionality via CETP inhibition and reduces blood pressure and visceral fat in young and middle-aged subjects. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2017, 39, 889–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crespo, N.; Illnait, J.; Mas, R.; Fernandez, L.; Fernandez, J.; Castano, G. Comparative study of the efficacy and tolerability of policosanol and lovastatin in patients with hypercholesterolemia and noninsulin dependent diabetes mellitus. Int. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Res. 1999, 29, 117–127. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.L.; Xu, R.X.; Zhu, C.G.; Wu, N.Q.; Cui, Z.P.; Li, J.J. Policosanol attenuates statin-induced increases in serum proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 when combined with atorvastatin. Evid. Based Compl. Alt. 2014, 2014, 926087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.-y.; Jiao, Q.-p.; Chen, S.-y.; Sheng, J.; Jiang, H.; Lu, J.; Zheng, S.-b.; Fang, N.-y. Efficacy and safety of policosanol plus fenofibrate combination therapy in elderly patients with mixed dyslipidemia: A randomized, controlled clinical study. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2018, 356, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canavaciolo, V.L.G.; Gómez, C.V. “Copycat-policosanols” versus genuine policosanol. Rev. CENIC Cienc. Quím. 2007, 38, 207–213. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, K.-H.; Baek, S.H.; Nam, H.-S.; Kim, J.-E.; Kang, D.-J.; Na, H.; Zee, S. Cuban sugar cane wax alcohol exhibited enhanced antioxidant, anti-glycation and anti-inflammatory activity in reconstituted high-density lipoprotein (rHDL) with improved structural and functional correlations: Comparison of various policosanols. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, K.-H.; Bahuguna, A.; Kim, J.-E.; Lee, S.H. Efficacy assessment of five policosanol brands and damage to vital organs in hyperlipidemic zebrafish by six-week supplementation: Highlighting the toxicity of red yeast rice and safety of Cuban policosanol (Raydel®). Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, D.-E.; Yun, J.-M.; Kim, D.; Kim, O.-K. Policosanol attenuates cholesterol synthesis via AMPK activation in hypercholesterolemic rats. J. Med. Food 2019, 22, 1110–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrabi, S.; Ferchichi, A.; Bacheli, A.; Fellah, H. Policosanol composition, antioxidant and anti-arthritic activities of milk thistle (Silybium marianum L.) oil at different seed maturity stages. Lipids Health Dis. 2018, 17, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stohs, S.J.; Miller, H.; Kaats, G.R. A review of the efficacy and safety of banaba (Lagerstroemia speciosa L.) and corosolic acid. Phytother. Res. 2012, 26, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousa, A.M.; El-Sammad, N.M.; Abdel-Halim, A.H.; Anwar, N.; Khalil, W.K.B.; Nawwar, M.; Hashim, A.N.; Elsayed, E.A.; Hassan, S.K. Lagerstroemia speciosa (L.) pers leaf extract attenuates lung tumorigenesis via alleviating oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, H.; Yuan, B.; Gothai, S.; Arulselvan, P.; Song, X.; Chen, L. Dietary triterpenes in the treatment of type 2 diabetes: To date. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 72, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, L.S.; Singh, W.S. Multifaceted therapeutic potential of corosolic acid: A novel bioactive compound. Obes. Med. 2024, 49, 100548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, K.-H.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, Y.; Bahuguna, A.; Kim, J.-E. Synergistic efficacy of policosanol (Raydel®) and banaba leaf extract to treat hyperglycemia and dyslipidemia in streptozotocin-induced diabetic and hyperlipidemic zebrafish (Danio rerio): Protection of liver and kidney with enhanced tissue regeneration. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patton, E.E.; Zon, L.I.; Langenau, D.M. Zebrafish disease models in drug discovery: From preclinical modelling to clinical trials. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021, 20, 611–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoo, J.Y.; Kumari, Y.; Shaikh, M.F.; Hue, S.M.; Goh, B.H. Zebrafish: A versatile animal model for fertility research. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 9732780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanni, O.; Fasemore, T.; Nkomozepi, P. Non-genetic-induced zebrafish model for type 2 diabetes with emphasis on tools in model validation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ka, J.; Jin, S.-W. Zebrafish as an emerging model for dyslipidemia and associated diseases. J. Lipid Atheroscler. 2021, 10, 42–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Willett, C.; Fremgen, T. Zebrafish: An animal model for toxicological studies. In Current Protocols in Toxicology; Unit 1.7; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, L.; Liu, C.; Miller, Y.I. Zebrafish models of dyslipidemia: Relevance to atherosclerosis and angiogenesis. Transl. Res. 2014, 163, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokgalaboni, K.; Lebelo, L.S.; Modjadji, P.; Ghaffary, S. Okra ameliorates hyperglycaemia in pre-diabetic and type 2 diabetic patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis of the clinical evidence. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1132650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokgalaboni, K.; Phoswa, W.N.; Mokgalabone, T.T.; Dlamini, S.; Ndhlala, A.R.; Modjadji, P.; Lebelo, S.L. Effect of Abelmoschus esculentus L. (Okra) on dyslipidemia: Systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical studies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 10922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, Y.; Kim, D.; Han, E.; Jung, J. Physiological activities of policosanol extracted from sugarcane wax. Nat. Prod. Sci. 2019, 25, 293–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira de Oliveira, D.; da Costa Fernandes, I.; Galdino de Sousa, G.; Pereira dos Santos, T.A.; Nogueira de Paiva, N.C.; Martins Carneiro, C.; Evangelista, E.A.; Rocha Barboza, N.; Guerra-Sá, R. High-sugar diet leads to obesity and metabolic diseases in ad libitum-fed rats irrespective of caloric intake. Arch. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 64, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aragno, M.; Mastrocola, R. Dietary sugars and endogenous formation of advanced glycation end products: Emerging mechanisms of disease. Nutrients 2017, 9, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cannarella, R.; Garofalo, V.; Calogero, A.E. Anti-dyslipidemic and anti-diabetic properties of corosolic acid: A narrative review. Endocrines 2023, 4, 616–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Throne Research. Monograph. Policosanol. Altern. Med. Rev. 2004, 9, 312–317. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.H.; Jia, Y.; Thach, T.T.; Han, Y.; Kim, B.; Wu, C.; Kim, Y.; Seo, W.D.; Lee, S.J. Hexacosanol reduces plasma and hepatic cholesterol by activating AMP-activated protein kinase and suppression of sterol regulatory element-binding protein-2 in HepG2 and C57BL/6J mice. Nutr. Res. 2017, 43, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imerb, N.; Thonusin, C.; Pratchayasakul, W.; Arunsak, B.; Nawara, W.; Ongnok, B.; Aeimlapa, R.; Charoenphandhu, N.; Chattipakorn, N.; Chattipakorn, S.C. D-galactose-induced aging aggravates obesity-induced bone dyshomeostasis. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 8580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajaj, S.; Khan, A. Antioxidants and diabetes. Indian J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 16, S267–S271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini, M.R.; Kazeminejad, S.; Jalalzadeh, M.; Majd, S.S.; Kavyani, Z.; Askari, G.; Hekmatdoost, A. The effects of policosanol supplementation on blood glucose: A systematic sreview and dose-response meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2024, 212, 111709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Leng, J.; Li, J.J.; Tang, J.F.; Li, Y.; Liu, B.L.; Wen, X.D. Corosolic acid inhibits adipose tissue inflammation and ameliorates insulin resistance via AMPK activation in high-fat fed mice. Phytomed. Int. J. Phytother. Phytopharm. 2016, 23, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottum, M.S.; Mistry, A.M. Advanced glycation end products: Modifiable environmental factors profoundly mediate insulin resistance. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2015, 57, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pareek, A.; Suthar, M.; Rathore, G.S.; Bansal, V.; Kumawat, T. In Vitro antioxidant studies of Lagerstroemia speciosa leaves. Pharmacogn. J. 2010, 2, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tidke, P.S.; Patil, C.R. Nrf2 activator corosolic acid meliorates alloxan induced diabetic nephropathy in mice. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2017, 7, 797–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saumya, S.M.; Basha, P.M. Antioxidant effect of Lagerstroemia speciosa Pers (Banaba) leaf extract in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Indian J. Exp. Biol. 2011, 49, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cho, K.-H.; Kim, J.-E.; Nam, H.-S.; Kang, D.-J.; Baek, S.-H. Comparison of policosanols via incorporation into reconstituted high-density lipoproteins: Cuban policosanol (Raydel®) exerts the highest antioxidant, anti-glycation, and anti-inflammatory activity. Molecules 2023, 28, 6715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Ge, Y.; Yang, Y.; Li, Z.; Liu, J.; Xue, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Pang, X.; Ngan, A.H.W.; Tang, B. Vascular endothelial cellular mechanics under hyperglycemia and its role in tissue regeneration. Regen. Biomater. 2024, 11, rbae004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Accipe, L.; Abadie, A.; Neviere, R.; Bercion, S. Antioxidant activities of natural compounds from caribbean plants to enhance diabetic wound healing. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azman, K.F.; Safdar, A.; Zakaria, R. D-galactose-induced liver aging model: Its underlying mechanisms and potential therapeutic interventions. Exp. Gerontol. 2021, 150, 111372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Cui, R.; Zhao, J.; Mo, R.; Peng, L.; Yan, M. Corosolic acid protects hepatocytes against ethanol-induced damage by modulating mitogen-activated protein kinases and activating autophagy. Eur. J. Pharm. 2016, 791, 578–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahadevan, M.; Kasiske, B.L. Hyperlipidemia in kidney disease causes and consequences. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2002, 11, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.-Y.; Chang, T.-C.; Lin, S.-H.; Wu, S.-T.; Cha, T.-L.; Tsao, C.-W. Metformin ameliorates testicular function and spermatogenesis in male mice with high-fat and high-cholesterol diet-induced obesity. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; Lin, L.; Xiao, W.; Li, Y. L-theanine protects rat kidney from D-galactose-induced injury via inhibition of the AGEs/RAGE signaling pathway. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2022, 927, 175072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Yang, C.Y.; Zhang, M.; Lu, X.M.; Cao, W.S.; Xie, C.F.; Li, X.T.; Wu, J.S.; Zhong, C.Y.; Geng, S.S. Protective effects of ginseng stem-leaf saponins on D-galactose-induced reproductive injury in male mice. Aging 2021, 13, 8916–8928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamagishi, S.; Matsui, T. Advanced glycation end products, oxidative stress and diabetic nephropathy. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2010, 3, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; Yu, Y.H.; Wang, S.T.; Ren, J.; Camer, D.; Hua, Y.Z.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, J.; Xue, D.L.; Zhang, X.F.; et al. Chlorogenic acid protects D-galactose-induced liver and kidney injury via antioxidation and anti-inflammation effects in mice. Pharm. Biol. 2016, 54, 1027–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garavaglia, M.L.; Giustarini, D.; Colombo, G.; Reggiani, F.; Finazzi, S.; Calatroni, M.; Landoni, L.; Portinaro, N.M.; Milzani, A.; Badalamenti, S.; et al. Blood thiol redox state in chronic kidney disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, J.; Ding, N.; Wang, D.; Ge, X.; Ma, J.; Ma, R.; Hung, X.; Jueraitetibaike, K.; Liang, K.; Wang, S.; et al. Oxidized-LDL inhibits testosterone biosynthesis by affecting mitochondrial function and the p38 MAPK/COX-2 signaling pathway in Leydig cells. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoshdel, F.; Golmohammadi, M.G.; Dost, M.J.; Najafzade, N.; Salimnejad, R. Impact of caffeic acid on the testicular damages in D-galactose-induced aging model in mice. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2022, 25, 1190. [Google Scholar]
- Pandey, A.K.; Gupta, A.; Tiwari, M.; Prasad, S.; Pandey, A.N.; Yadav, P.K.; Sharma, A.; Sahu, K.; Asrafuzzaman, S.; Vengayil, D.T.; et al. Impact of stress on female reproductive health disorders: Possible beneficial effects of shatavari (Asparagus racemosus). Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 103, 46–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.L.; Cai, Y.Q.; Long, S.L.; Chen, Z.; Mo, Z.C. The role of advanced glycation end products in human infertility. Life Sci. 2020, 255, 117830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Cunha, N.M.; Sergi, D.; Lane, M.M.; Naumovski, N.; Gamage, E.; Rajendran, A.; Kouvari, M.; Gauci, S.; Dissanayka, T.; Marx, W.; et al. The effects of dietary advanced glycation end-products on neurocognitive and mental disorders. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budni, J.; Pacheco, R.; da Silva, S.; Garcez, M.L.; Mina, F.; Bellettini-Santos, T.; de Medeiros, J.; Voss, B.C.; Steckert, A.V.; Valvassori, S.d.S.; et al. Oral administration of D-galactose induces cognitive impairments and oxidative damage in rats. Behav. Brain Res. 2016, 302, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Yang, H.; Huo, L.; Gao, J.; Chen, H.; Gao, W. Protective effect of tetrahydropalmatine against d-galactose induced memory impairment in rat. Physiol. Behav. 2016, 154, 114–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Q.; Kawahata, I.; Cheng, A.; Jia, W.; Wang, H.; Fukunaga, K. Fatty acid-binding proteins: Their roles in ischemic stroke and potential as drug targets. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.-X.; Li, H.-Y.; Li, Y.-Q.; Kong, L.-D. Can medicinal plants and bioactive compounds combat lipid peroxidation product 4-HNE-induced deleterious effects? Biomolecules 2020, 10, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, M.; Man, S.; Sun, B.; Ma, L.; Guo, L.; Huang, L.; Gao, W. Gut liver brain axis in diseases: The implications for therapeutic interventions. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, A.S.; Cordeiro, T.M.; Dos Santos Lacerda Soares, T.M.; Ferreira, R.N.; Simões e Silva, A.C. Kidney-brain axis inflammatory crosstalk: From bench to bedside. Clin. Sci. 2017, 131, 1093–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- How Does the Liver Affect Brain Health? Available online: https://www.alzdiscovery.org/cognitive-vitality/blog/how-does-the-liver-affect-brain-health#ref-4 (accessed on 11 November 2024).
- Fischer, A.H.; Jacobson, K.A.; Rose, J.; Zeller, R. Hematoxylin and eosin staining of tissue and cell sections. Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2008, 2008, prot4986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| HC+HG | HC+HG +BNB | HC+HG +PCO | HC+HG +BNB+PCO | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Survivability (%) at week 6 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| BW at week 0 (mg, n = 28) | 299 ± 11 | 312 ± 10 | 323 ± 10 | 309 ± 10 |
| BW at week 6 (mg, n = 28) | 448 ± 16 *** | 439 ± 17 *** | 434 ± 12 *** | 399 ± 13 ***,† |
| Net increase in BW (mg) | 149 ± 16 | 127 ± 17 | 111 ± 12 | 90 ± 13 † |
| Net increase in BW (%) | 50 | 41 | 34 | 29 † |
| Dietary Components (mg) | HC+HG | HC+HG +BNB | HC+HG +PCO | HC+HG +BNB+PCO |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tetrabits (ND) | 6.60 | 6.59 | 6.59 | 6.58 |
| Cholesterol (final 4%, w/w) | 0.40 | 0.40 | 0.40 | 0.40 |
| Galactose (final 30%, w/w) | 3.00 | 3.00 | 3.00 | 3.00 |
| Banaba (final 0.1%, w/w) | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| Policosanol (final 0.1%, w/w) | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| Total mixture (mg) | 10.00 | 10.00 | 10.00 | 10.00 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cho, K.-H.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, Y.; Bahuguna, A.; Kim, J.-E.; Djayanti, K.; Jeon, C. Synergistic Effect of Banaba Leaf Extract and Policosanol (Raydel®) Ameliorate High Cholesterol and High Galactose-Diet Induced Adverse Events in Zebrafish. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 860. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18060860
Cho K-H, Lee SH, Lee Y, Bahuguna A, Kim J-E, Djayanti K, Jeon C. Synergistic Effect of Banaba Leaf Extract and Policosanol (Raydel®) Ameliorate High Cholesterol and High Galactose-Diet Induced Adverse Events in Zebrafish. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(6):860. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18060860
Chicago/Turabian StyleCho, Kyung-Hyun, Sang Hyuk Lee, Yunki Lee, Ashutosh Bahuguna, Ji-Eun Kim, Krismala Djayanti, and Cheolmin Jeon. 2025. "Synergistic Effect of Banaba Leaf Extract and Policosanol (Raydel®) Ameliorate High Cholesterol and High Galactose-Diet Induced Adverse Events in Zebrafish" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 6: 860. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18060860
APA StyleCho, K.-H., Lee, S. H., Lee, Y., Bahuguna, A., Kim, J.-E., Djayanti, K., & Jeon, C. (2025). Synergistic Effect of Banaba Leaf Extract and Policosanol (Raydel®) Ameliorate High Cholesterol and High Galactose-Diet Induced Adverse Events in Zebrafish. Pharmaceuticals, 18(6), 860. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18060860







