The Efficacy and Safety Herbal Medicine for Symptom Management After HIFU Treatment in Adenomyosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
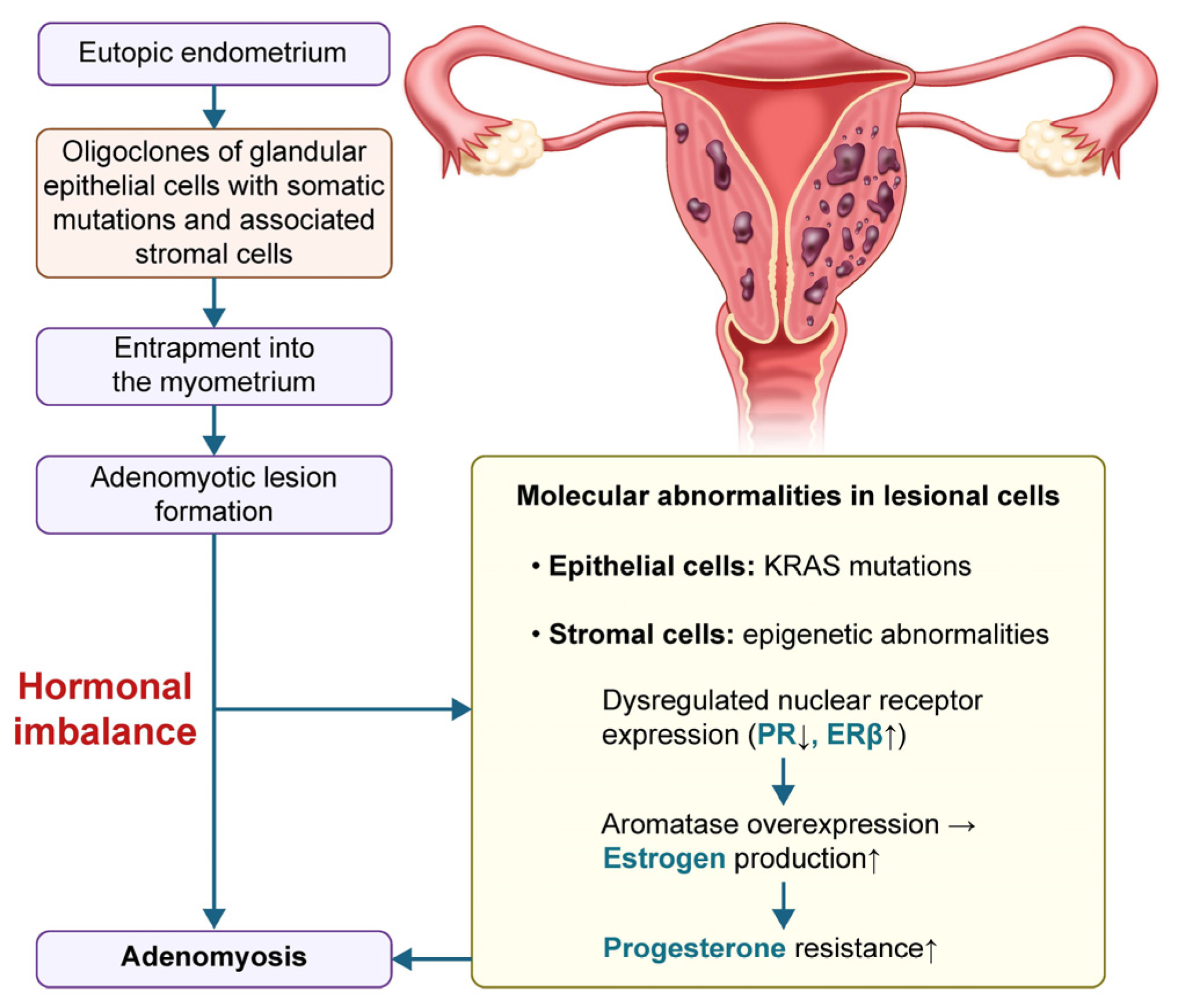
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Protocol and Registration
2.2. Eligibility Criteria
2.2.1. Types of Studies
2.2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.2.3. Types of Interventions
2.2.4. Types of Comparisons
2.2.5. Types of Outcome Measures
2.3. Data Sources and Search Strategy
2.4. Study Selection and Data Extraction
2.4.1. Study Selection
2.4.2. Data Extraction
2.5. RoB Assessment
2.6. Statistical Analysis
2.6.1. Heterogeneity Assessment
2.6.2. Reporting Bias Assessment
2.6.3. Subgroup and Sensitivity Analyses
2.7. Quality of Evidence
3. Results
3.1. Results of Literature Search
3.2. Study Characteristics
3.3. Interventions
3.4. Outcome Measures
3.5. Quality Assessment
3.6. Meta-Analysis
3.6.1. Uterine and Lesion Volumes
3.6.2. Serum Biomarkers
3.6.3. VAS Score for Dysmenorrhea
3.6.4. TER
3.6.5. PBAC Score for Menstrual Volume
3.6.6. Adverse Events
3.7. Publication Bias
3.8. Sensitivity Analyses
3.9. GRADE Certainty of Evidence
4. Discussion
4.1. Summary of This Review
4.2. Clinical Implication, Limitations and Suggestions
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AM | Adenomyosis |
| HIFU | High-intensity focused ultrasound |
| HM | Herbal medicine |
| RCTs | Randomized clinical trials |
| E2 | Estradiol |
| VAS | Visual analog scale |
| TER | Total effective rate |
| PBAC | Pictorial blood loss assessment chart |
| RoB | Risk of Bias |
| RR | Risk ratio |
| MD | Mean difference |
| SMD | Standardized mean difference |
| CI | Confidence interval |
| ROB | Risk of bias |
| GRADE | Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development, and Evaluation |
| GnRHa | Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone agonist |
| LNG-IUS | Levonorgestrel-Releasing Intrauterine System |
References
- Vannuccini, S.; Petraglia, F. Recent advances in understanding and managing adenomyosis. F1000Research 2019, 8, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulun, S.E.; Yildiz, S.; Adli, M.; Chakravarti, D.; Parker, J.B.; Milad, M.; Yang, L.; Chaudhari, A.; Tsai, S.; Wei, J.J.; et al. Endometriosis and adenomyosis: Shared pathophysiology. Fertil. Steril. 2023, 119, 746–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moawad, G.; Fruscalzo, A.; Youssef, Y.; Kheil, M.; Tawil, T.; Nehme, J.; Pirtea, P.; Guani, B.; Afaneh, H.; Ayoubi, J.M.; et al. Adenomyosis: An updated review on diagnosis and classification. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 4828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Lin, S.; Xie, X.; Yi, J.; Liu, X.; Guo, S.W. Systematic review and meta-analysis of reproductive outcomes after high-intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) treatment of adenomyosis. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2024, 92, 102433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szubert, M.; Koziróg, E.; Olszak, O.; Krygier-Kurz, K.; Kazmierczak, J.; Wilczynski, J. Adenomyosis and Infertility—Review of medical and surgical approaches. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loring, M.; Chen, T.Y.; Isaacson, K.B. A Systematic Review of Adenomyosis: It is time to reassess what we thought we knew about the disease. J. Minim. Invasive Gynecol. 2021, 28, 644–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.J.; Chung, J.P.W.; Wang, S.; Li, T.C.; Duan, H. The investigation and management of Adenomyosis in women who wish to improve or preserve fertility. Biomed. Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 6832685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.M.; Mpehle, C.R.; Olusola, E.; Ratshabedi, P.K.; Farag, E.A.H. How safe is high-intensity focused ultrasound? An intriguing solution for obstetric and gynecological diseases: A systematic review. Turk. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2024, 21, 190–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.X.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, L.L.; Ji, X.L.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Y.F.; Shi, L.; Wen, Y. Analysis of related factors influencing postoperative recurrence of adenomyosis treated with HIFU. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 2024, 309, 1765–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahutair, S.N.; Alhubaishi, L.Y. High-intensity focused ultrasound in adenomyosis treatment: Insights on safety, efficacy, and reproductive prospects. Womens Health 2024, 20, 17455057241295593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.N.; Pang, L.L.; Zhao, T.T.; Fan, L.X.; Zhou, Y.H. Study on the Efficacy and Safety of Traditional Chinese Medicine Combined with High Intensity Focused Ultrasound in the Treatment of Adenomyosis with Menorrhagia Based on the Real World. Master’s Thesis, Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chengdu, China, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Study Quality Assessment Tools. Available online: https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health-topics/study-quality-assessment-tools (accessed on 25 March 2025).
- Users’ Guides to the Medical Literature: Essentials of Evidence-Based Clinical Practice, 3rd ed.; McGraw-Hill Education: New York, NY, USA, 2015; Available online: https://jamaevidence.mhmedical.com/book.aspx?bookId=847#69031456 (accessed on 18 April 2025).
- An, F.; Wang, X.R.; Li, X.D.; Feng, J.; Yin, B.N.; Wang, W.L. Clinical observation of high-intensity focused ultrasound ablation combined with traditional Chinese medicine in the treatment of adenomyosis. J. Pract. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2022, 38, 946–947. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, R.; Li, L. The effects of Aifu nuangong decoction, acupoint application combined with personalized nursing on hormone levels in patients with dysmenorrhea caused by adenomyosis. Mod. Med. Health Res. J. 2020, 4, 102–104. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, S.X. Efficacy observation of comprehensive therapy of traditional Chinese medicine and high intensity focused ultrasound on adenomyosis-caused dysmenorrhea. Shanxi J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2024, 40, 18–20. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, Z.C. Analysis of effect of Neiyi pill combined with MR-guided HIFU in treating adenomyosis. Mod. Diagn. Treat. 2022, 33, 2380–2383. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, Q.L.; Huang, M. The effect of ultrasonic ablation combined with traditional Chinese medicine in the treatment of secondary dysmenorrhea caused by Adenomyosis. J. Med. Inf. 2021, 34, 157–159. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, S.; Jiang, H.; Li, Q.; Feng, Y.H.; He, J.H. Clinical study on High Intensity Focused Ultrasound Ablation Therapy (HIFU) combined with kidney tonifying and blood activating formula for the treatment of Adenomyosis. Prog. Mod. Biomed. 2023, 23, 4120–4124. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Huang, Y.F.; Wen, Y.; Shi, L.; Yin, X.L.; Yang, L.L.; Zhao, D. Effect of modified Sini Sijunzi Decoction combined with acupoint needle—Embedding on perioperative pain in patients with adenomyosis underwent high intensity focused ultrasound. Hebei J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2025, 47, 119–124. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.F.; Zhou, H.; Cai, Y.Y.; Xu, S.F. Clinical observation of HIFU combined with external application of traditional Chinese medicine in the treatment of adenomyosis. Zhejiang Clin. Med. J. 2019, 21, 190–192. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, Y.; Yang, Y.J.; Yan, J.; Qi, J. Efficacy of Bushen Huoxue Sanyu decoction combined with high-intensity focused ultrasound on adenomyosis and its influence on the immune function of patients. Anhui Med. Pharm. J. 2023, 27, 131–134. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, H.Y.; Liu, X.; Liu, X.G.; Zeng, L.; Zhang, X.H.; Hu, C.F. Observation on the curative effect of high intensity focused ultrasound combined with Wenjing Tongzu Formula in the treatment of adenomyosis. J. Shanxi Univ. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2024, 25, 655–660. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, S.N.; Liu, Y.; Wang, R.Y.; Yang, J.M. Clinical observation of 30 cases of adenomyoma treated with Chinese medicine enema combined with focused ultrasound. Chin. J. Ethnomed. Ethnopharm. 2017, 26, 108–109. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Lin, B.; Ma, J.J.; Weng, X.C.; Zhang, Q.H.; Ai, X.Z. Effect of clearing heat and removing blood stasis traditional Chinese medicine on inflammation of patients with adenomyosis after operation of HIFU. Shanghai J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2021, 55, 58–60. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.L.; Zhang, L.J. Effect observation of High-Intensity Focused Ultrasound combined with traditional Chinese medicine in treating adenomyosis. Chin. Community Doctor. 2023, 39, 59–61. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Q. Efficacy of Xianrong Mixture combined with high-intensity focused ultrasound in the treatment of uterine adenomyosis and its effect on ovarian reserve function. Chin. J. Hum. Sex. 2021, 30, 105–108. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, X.; Kong, B.H.; Duan, T. Obstetrics and Gynecology, 9th ed.; People’s Medical Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2018; pp. 77–79. [Google Scholar]
- Chinese Medical Association of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of endometriosis (Third edition). Chin. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2021, 56, 812–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Evidence-based Healthcare Collaborating Agency. Radiofrequency Myolysis for Uterine Fibroids: Reassessment of Medical Technology NECA-R-23-001-23; NECA: Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2024; pp. 8–9. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Li, P.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, K. Study on the mechanism of the Danggui-Chuanxiong Herb pair on treating thrombus through network pharmacology and Zebrafish Models. ACS Omega 2021, 25, 14677–14691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.P.; Li, W.; Xiao, X.F.; Zhang, L.L.; Liu, C.X. Phytochemical and pharmacological studies on Radix Angelica sinensis. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2013, 11, 577–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bateman, H.R.; Liang, Q.; Fan, D.; Rodriguez, V.; Lessner, S.M. Sparstolonin B Inhibits Pro-Angiogenic Functions and Blocks Cell Cycle Progression in Endothelial Cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e70500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- d’Otreppe, J.; Patino-García, D.; Piekos, P.; de Codt, M.; Manavella, D.D.; Courtoy, G.E.; Orellana, R. Exploring the Endocrine Mechanisms in Adenomyosis: From Pathogenesis to Therapies. Endocrines 2024, 5, 46–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.Z.; Zhu, X.D.; Zhang, M.X.; Yu, J.; Jin, S.B.; Hu, X.L.; Piao, H.Z. The analgesic effect of paeoniflorin: A focused review. Open Life Sci. 2024, 19, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, E.S.; Yoon, J.J.; Han, B.H.; Jeong, D.H.; Lee, Y.J.; Kang, D.G.; Lee, H.S. Ligustilide attenuates vascular inflammation and activates Nrf2/HO-1 induction and, NO synthesis in HUVECs. Phytomedicine 2018, 38, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.G.; Liu, Q.; Guan, Z.J.; Liu, J.; Liu, H.J.; Yu, S.H. Study on analgesic activity of Corydalis Yanhusuo based on network pharmacology. J. Yichun Univ. 2022, 44, 18–24. [Google Scholar]
- Zong, C.X.; Sun, L.; Xu, X.; Xue, X.O. Huayu Sanjie Enema Liquid relieves pain in Endometriosis model rats by inhibiting inflammation, peripheral sensitization, and pelvic adhesion. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2022, 2022, 5256578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, E.B.; Kim, S.H.; Son, M.J. Common adverse events of herbal formulas for developing reporting forms for clinical practice and research: An overview of systematic reviews. Integr. Med. Res. 2025, 14, 101118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kongkaew, C.; Phan, D.T.A.; Janusorn, P.; Mongkhon, P. Estimating Adverse Events Associated with Herbal Medicines Using Pharmacovigilance Databases: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. JMIR Public Health Surveill. 2023, 9, e43310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niazi, A.; Moradi, M.; Askari, V.R.; Sharifi, N. Effect of complementary medicine on pain relief and wound healing after cesarean section: A Systematic Review. J. Pharmacopunct. 2021, 24, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, N.Y.; Lee, H.Y.; Hwang, S.I.; Sung, S.H.; Cho, S.J.; Yoon, Y.J.; Park, J.K. Herbal Medicine for postpartum pain: A systematic review of puerperal wind syndrome (Sanhupung). Healthcare 2023, 11, 2743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, D.; Liu, S.X.; Liu, F.Y.; Hao, S.L.; Zhang, C.L.; Shen, Y.; Wei, W.; Chen, Q.C.; Han, F.J. Exploring the role of Chinese herbal medicine in the long-term management of postoperative ovarian endometriotic cysts: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1376037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.B.; Wang, J.F.; Wang, M.X.; Peng, J.; Kong, X.D.; Tian, J. Nano-Based Drug Delivery Systems for Active Ingredients from Traditional Chinese Medicine: Harnessing the Power of Nanotechnology. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1405252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.H.; Li, M.; Liu, Z.W.; Luo, W.; Han, S.Q.; Xiao, F.; Tao, W.; Wu, Q.B.; Xie, T.; Kong, N. Unleashing the potential: Integrating nano-delivery systems with traditional Chinese medicine. Nanoscale 2024, 16, 8791–8806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| First Author (Year) | Sample Size (E/C) | Age Distribution (yr, Mean ± SD) | Duration of Illness (yr, Mean ± SD) | Experimental Intervention (E) | Total Treatment Periods | Follow Up Periods | Outcome Measurement | Adverse Events (n/N) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control Intervention (C) | ||||||||
| An (2022) [15] | 116 (58/58) | E: (34.72 ± 3.95) C: (35.26 ± 4.07) | E: (3.74 ± 0.85) C: (4.01 ± 0.96) | (C) + HM | 3 m | 6 m | (1)(2)(7)(8)(20) | E:4/58 C:7/58 |
| HIFU Treatment | ||||||||
| Cai (2020) [16] | 66 (33/33) | E: (37.93 ± 4.82) C: (38.30 ± 4.31) | E: (5.67 ± 2.13) C: (5.92 ± 1.67) | (C) + HM | 3 m | NR | (1)(2)(5)(8) | NR |
| HIFU Treatment | ||||||||
| Dong (2024) [17] | 130 (65/65) | E: (35.7 ± 12.8) C: (36.5 ± 13.1) | E: (4.5 ± 1.4) C: (5.3 ± 1.3) | (C) + HM + AC | 3 m | NR | (1)(3)(6)(9)(13) | NR |
| HIFU Treatment | ||||||||
| Pang (2022) [18] | 60 (30/30) | E: (39.82 ± 2.75) C: (40.09 ± 2.72) | E: (2.16 ± 0.49) C: (2.21 ± 0.46) | (C) + HM | 6 m | NR | (1)(2)(4)(5)(6)(10)(11)(20) | E:3/30 C:5/30 |
| HIFU Treatment | ||||||||
| Peng (2021) [19] | 124 (62/62) | E: (35.02 ± 6.84) C: (34.87 ± 7.90) | E: (5.14 ± 1.05) C: (5.03 ± 0.83) | (C) + HM | 3 m | 6 m, 12 m | (1)(2)(3)(4)(6)(7)(20)(21) | E:7/62 C:12/62 |
| HIFU Treatment + LNG-IUS | ||||||||
| Shi (2023) [20] | 100 (50/50) | E: (34.73 ± 6.24) C: (34.25 ± 6.83) | E: (5.52 ± 1.35) C: (5.25 ± 1.20) | (C) + HM | 3 m | 6 m | (1)(2)(3)(4)(5)(7) | NR |
| HIFU Treatment | ||||||||
| Wang (2025) [21] | 77 (38/39) | E: (40.71 ± 6.34) C: (40.18 ± 6.41) | NR | (C) + HM + AC | 3 d | NR | (14)(15)(16)(17)(20) | E:15/38 C:34/39 |
| HIFU Treatment | ||||||||
| Xu (2019) [22] | 120 (50/70) | E: (42.70 ± 5.04) C: (43.49 ± 4.42) | NR | (C) + HM | 7 d | 3 m, 6 m | (1)(3)(4)(9)(20) | NR |
| HIFU Treatment | ||||||||
| Xue (2023) [23] | 110 (55/55) | E: (37.89 ± 3.69) C: (38.46 ± 3.78) | E: (2.49 ± 0.69) C: (2.43 ± 0.65) | (C) + HM | 3 m | NR | (1)(2)(4)(5)(6)(20) | E:10/55 C:14/55 |
| HIFU Treatment | ||||||||
| Yi (2024) [24] | 66 (33/33) | E: (38.600 ± 4.073) C: (38.530 ± 4.216) | E: (224.667 ± 195.525) wk C: (331.367 ± 342.319) wk | (C) + HM | 3 m | 6 m | (1)(3)(4)(5)(6)(7)(12)(20) | E:3/30 C:12/30 |
| HIFU Treatment + GnRHa | ||||||||
| Yu (2017) [25] | 60 (30/30) | E: (34.2 ± 2.86) C: (35.6 ± 3.12) | NR | (C) + HM | 7 d | 3 m | (1)(7)(20) | E:2/30 C:1/30 |
| HIFU Treatment | ||||||||
| Zhang (2021) [26] | 60 (30/30) | E: (38.96 ± 1.13) C: (38.41 ± 1.90) | E: (5.87 ± 2.08) C: (6.02 ± 1.98) | (C) + HM | 7 d | NR | (2)(3)(5) | NR |
| HIFU Treatment + GnRHa | ||||||||
| Zhang (2023) [27] | 110 (55/55) | E: (38.96 ± 1.13) C: (38.41 ± 1.90) | E: (2.11 ± 0.68) C: (2.09 ± 0.95) | (C) + HM | 3 m | NR | (1)(2)(3)(5)(8)(18)(20) | E:5/55 C:7/55 |
| HIFU Treatment | ||||||||
| Zhou (2021) [28] | 60 (30/30) | E: (43.47 ± 4.71) C: (42.98 ± 4.11) | E: (3.22 ± 0.78) C: (3.18 ± 0.74) | (C) + HM | 3 m | 6 m | (2)(3)(6)(7)(19) | NR |
| HIFU Treatment |
| First Author (Year) | Type of Formulation/Composition | Dosage | Frequency (per Day) |
|---|---|---|---|
| An (2022) [15] | Decoction Astragali radix 15 g, Poria sclerotium 10 g, Cinnamomi ramulus 10 g, Paeoniae radix 10 g, Moutan radicis cortex 10 g, Persicae semen 6 g, Sparganii rhizoma 6 g, Curcumae rhizoma 6 g | 200 mL | 2 times |
| Cai (2020) [16] | Aifu Nuangong Decoction Astragali radix, Leonuri herba 20 g, Cyperi rhizoma, Cnidii rhizoma, Paeoniae radix alba, Morindae radix, Corydalis tuber, Linderae radix, Typhae pollen 15 g, Angelicae gigantis radix, Angelicae dahuricae radix, Artemisiae argyi folium, Dipsaci radix, Cinnamomi ramulus 10 g | 150 mL | 2 times |
| External application Astragali radix, Cyperi rhizoma, Cnidii rhizoma, Morindae radix, Corydalis tuber, Linderae radix, Typhae pollen, Artemisiae argyi folium, Dipsaci radix, Cinnamomi ramulus 10 g, Paeoniae radix alba, Leonuri herba, Angelicae gigantis radix, Angelicae dahuricae radix 15 g | 4~6 h | 1 time | |
| Dong (2024) [17] | Bushen Huoxue Decoction Hominis placenta, Cuscutae semen, Ligustri fructus, Angelicae gigantis radix, Cnidii rhizoma, Paeoniae radix 15 g, Olibanum, Myrrha 10 g | 200 mL | 2 times |
| Acupuncture Sameumgyo(SP6)(Bilateral), Gwanwon(CV4), Jigi(SP8), Sinsu(BL23), Yoyanggwan(GV3)(Unilateral) | 30 min | 1 time | |
| Pang (2022) [18] | Nei Yi Pill * Draconis sanguis, Salviae miltiorrhizae radix, Angelicae gigantis radix, Notoginseng radix et rhizoma, Persicae semen, Curcumae rhizoma, Sparganii rhizoma, Cyperi rhizoma, Cinnamomi ramulus, Achyranthis radix | 10 g | 2 times |
| Peng (2021) [19] | Danggui Shaoyao San Pill Paeoniae radix alba 20 g, Angelicae gigantis radix 10 g, Atractylodis rhizoma alba 10 g, Cnidii rhizoma 10 g, Alismatis rhizoma 20 g, Poria sclerotium 30 g | 1 pill | 3 times |
| Shi (2023) [20] | Bushen Huoxue Decoction Cuscutae semen 30 g, Cistanchis herba, Poria sclerotium, Lycii fructus, Eucommiae cortex, Rehmanniae radix preparata 20 g, Curcumae rhizoma, Sparganii rhizoma, Myrrha, Angelicae gigantis radix 15 g, Carthami flos 10 g Menstrual period: Corni fructus, Psoraleae semen 20 g Non-Menstrual period: Typhae pollen 20 g, Crataegi fructus, Trogopterorum faeces 15 g, Notoginseng radix et rhizoma 10 g | NR | 2 times |
| Wang (2025) [21] | Jiawei Sini Sijunzi Decotion Bupleuri radix 10 g, Aurantii fructus immaturus 10 g, Paeoniae radix alba 10 g, Glycyrrhizae radix et rhizoma Praeparata cum melle 5 g, Codonopsis pilosulae radix 10 g, Poria sclerotium 10 g, Atractylodis rhizoma alba praeparata 10 g, Dioscoreae rhizoma 20 g, Massa medicata fermentata 15 g, Corydalis tuber 10 g | 150 mL | 3 times |
| Acupuncture and Auricular acupuncture Shenmen(TF4), Sympathetic autonomic(AH6a), Sameumgyo(SP6)(Bilateral) | NR | NR | |
| Xu (2019) [22] | External application Angelicae gigantis radix 10 g, Paeoniae radix 10 g, Artemisiae argyi folium 30 g, Acanthopanacis cortex 15 g, Osterici seu notopterygii radix et rhizoma 15 g, Speranskiae tuberculatae herba 15 g, Angelicae dahuricae radix 10 g, Foeniculi fructus 30 g, Spatholobi caulis 15 g, Carthami flos 15 g, Araliae continentalis radix 15 g | NR | 1 time |
| Xue (2023) [23] | Bushen Huoxue Sanyu Decoction Euonymi ramuli suberalatum, Corydalis tuber, Paeoniae radix, Cnidii rhizoma, Angelicae gigantis radix, Hominis placenta, Cuscutae semen 10 g, Citri unshius pericarpium immaturus 6 g | 200 mL | 2 times |
| Yi (2024) [24] | Enema: Wenjing Tongzu Decoction Cinnamomi ramulus, Paeoniae radix, Linderae radix, Sparganii rhizoma, Curcumae rhizoma, Cyperi rhizoma, Corydalis tuber, Artemisiae anomalae herba, Lycopi herba, Cnidi fructus, Spatholobi caulis, Cynanchi paniculati radix et rhizoma, Speranskiae tuberculatae herba 30 g, Ephedrae herba, Poria sclerotium, Morindae radix 20 g, Hirudo, Asiasari radix et rhizoma, Olibanum, Myrrha 15 g | 100 mL | 1 time |
| Yu (2017) [25] | Enema Ilicis pubescentis radix, Lonicerae folium et caulis, Rhei radix et rhizoma, Prunellae spica, Gleditsiae spina, Liquidambaris fructus, Sparganii rhizoma, Curcumae rhizom, Salviae miltiorrhizae radix, et al. | 100 mL | 1 time |
| Zhang (2021) [26] | Decoction Rhei radix et rhizoma 3 g, Cnidii rhizoma 9 g, Lonicerae flos 9 g, Trogopterorum faeces 12 g, Angelicae gigantis radix 15 g, Scrophulariae radix 15 g, Taraxaci herba 15 g, Typhae pollen 15 g, Sargentodoxae caulis 18 g, Paeoniae radix alba 30 g, Patriniae radix 30 g, Notoginseng radix et rhizoma 3 g | NR | 1 time |
| Zhang (2023) [27] | Granules Rehmanniae radix preparata 15 g, Codonopsis pilosulae radix 15 g, Sparganii rhizoma 10 g, Curcumae rhizoma 10 g, Olibanum praeparata cum aceto 10 g, myrrha praeparata cum aceto 10 g, Liquidambaris fructus 15 g, Ephedrae herba 6 g, Cinnamomi cortex 10 g, Hirudo praeparata 3 g, Crataegi fructus 15 g | NR | 2 times |
| Zhou (2021) [28] | Epimedii Herba Mixture Decoction Epimedii herba 15 g, Cistanchis herba 15 g, Polygoni multiflori radix praeparata 10 g, Cuscutae semen 15 g, Codonopsis pilosulae radix 15 g, Astragali radix 20 g, Curcumae rhizoma 15 g, Salviae miltiorrhizae radix 15 g, Paeoniae radix 15 g, Corydalis tuber 15 g, Meliae fructus 15 g, Persicae semen 10 g, Olibanum 10 g, Myrrha 10 g, Achyranthis radix 10 g | NR | 2 times |
| Outcomes | No. Participants (Studies) | Anticipated Absolute Effects (95% CI) | Relative Effect (95% CI) | Heterogeneity (I2) | Quality of Evidence (GRADE) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Risk with Control Group | Risk with Intervention Group | |||||
| Uterine volume | 304 (4 RCTs) | - | MD 11.84 lower (13.74 lower to 9.95 lower) | - | 24 | ⨁⨁◯◯ Low a,b |
| Adenomyotic lesion volume | 420 (5 RCTs) | - | MD 2.86 lower (3.29 lower to 2.43 lower) | - | 42 | ⨁⨁◯◯ Low a,b |
| CA125 | 616 (7 RCTs) | - | SMD 1.49 lower (2.41 lower to 0.58 lower) | - | 96 | ⨁⨁◯◯ Low a,b,c |
| E2 | 294 (3 RCTs) | - | SMD 1.28 lower (1.54 lower to 1.03 lower) | - | 0 | ⨁⨁◯◯ Low a,b |
| VAS scores of dysmenorrhea | 990 (10 RCTs) | - | MD 1.51 lower (2.02 lower to 1 lower) | - | 96 | ⨁⨁⨁◯ Moderate c,d |
| Total effective rate | 764 (8 RCTs) | 793 per 1000 | 119 more per 1000 (63 more to 175 more) | RR 1.15 (1.08 to 1.22) | 26 | ⨁⨁⨁◯ Moderate d |
| PBAC score for menstrual volume | 350 (4 RCTs) | - | MD 8.75 lower (11.51 lower to 5.99 lower) | - | 14 | ⨁⨁◯◯ Low b,d |
| Adverse effect | 717 (8 RCTs) | 256 per 1000 | 118 fewer per 1000 (154 fewer to 72 fewer) | RR 0.54 (0.40 to 0.72) | 0 | ⨁⨁⨁◯ Moderate a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, E.-J.; Shim, Y.-S.; Sung, H.-K.; Min, S.-Y. The Efficacy and Safety Herbal Medicine for Symptom Management After HIFU Treatment in Adenomyosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 843. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18060843
Kim E-J, Shim Y-S, Sung H-K, Min S-Y. The Efficacy and Safety Herbal Medicine for Symptom Management After HIFU Treatment in Adenomyosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(6):843. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18060843
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Eun-Jin, Young-Shin Shim, Hyun-Kyung Sung, and Sang-Yeon Min. 2025. "The Efficacy and Safety Herbal Medicine for Symptom Management After HIFU Treatment in Adenomyosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 6: 843. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18060843
APA StyleKim, E.-J., Shim, Y.-S., Sung, H.-K., & Min, S.-Y. (2025). The Efficacy and Safety Herbal Medicine for Symptom Management After HIFU Treatment in Adenomyosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Pharmaceuticals, 18(6), 843. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18060843













