Unveiling the Polypharmacological Potency of FDA-Approved Rebamipide for Alzheimer’s Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
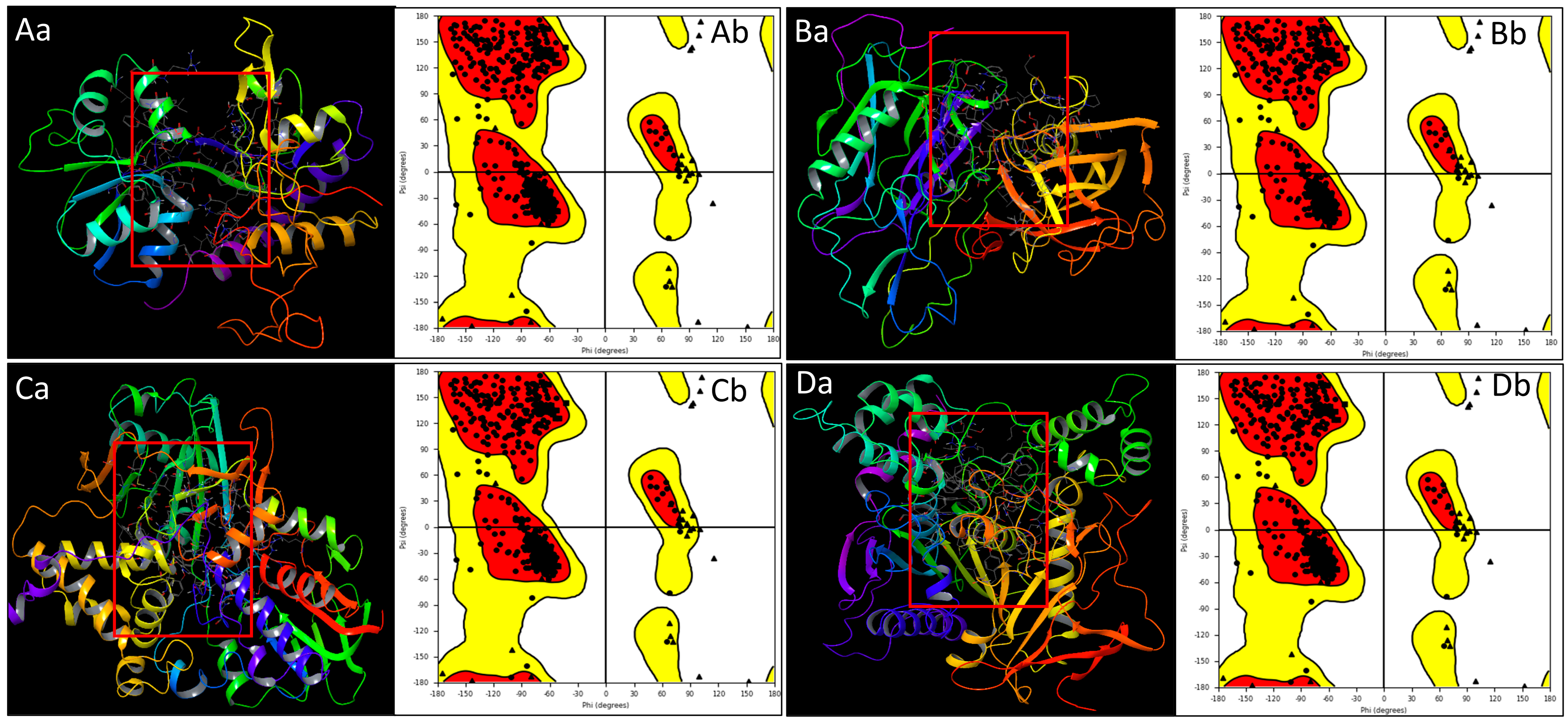
2.1. Prepared Protein Structure Analysis
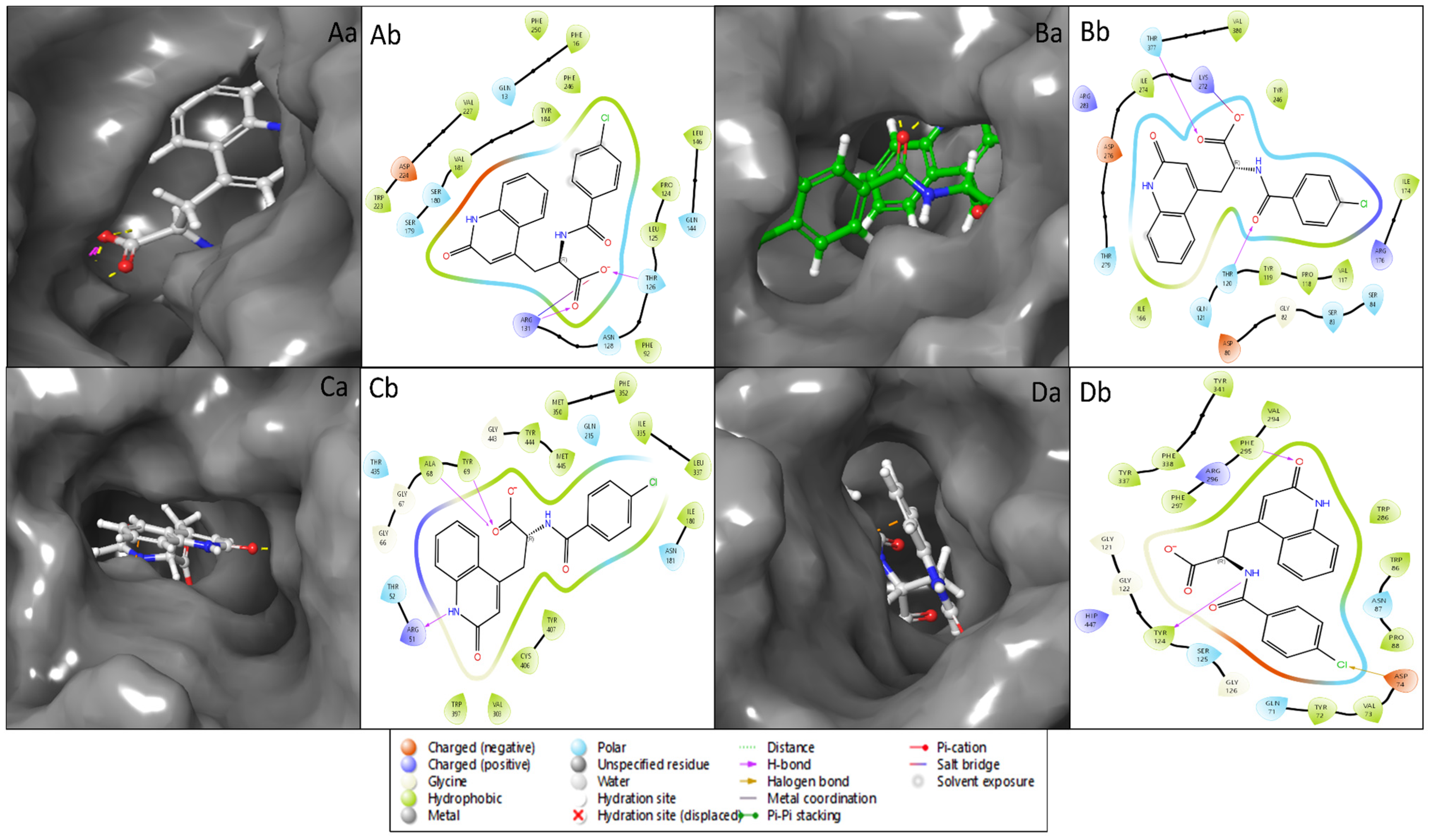
2.2. Molecular Interaction Studies
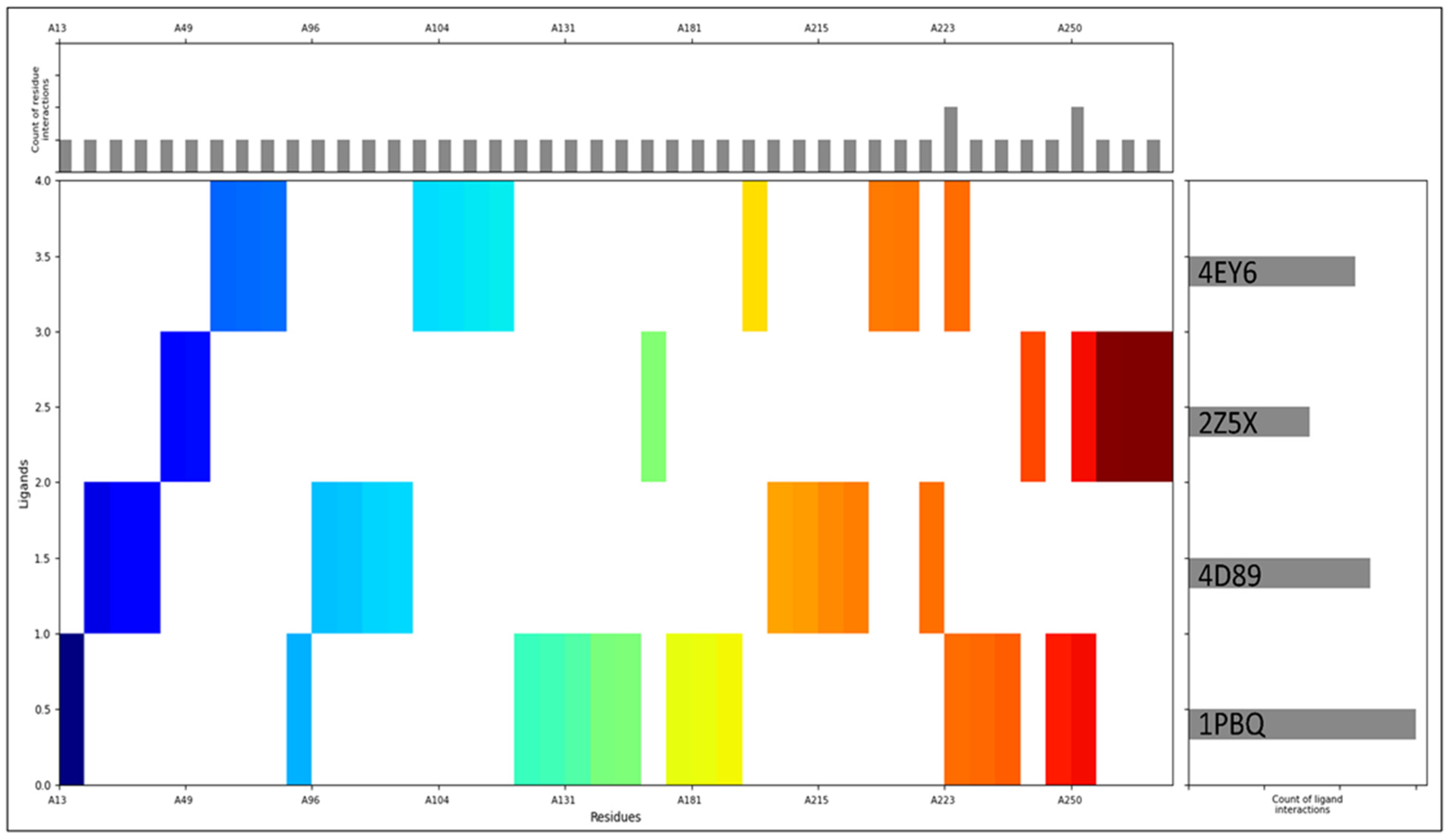
2.3. Pharmacokinetics Studies and Interaction Fingerprinting
2.4. WaterMap Analysis
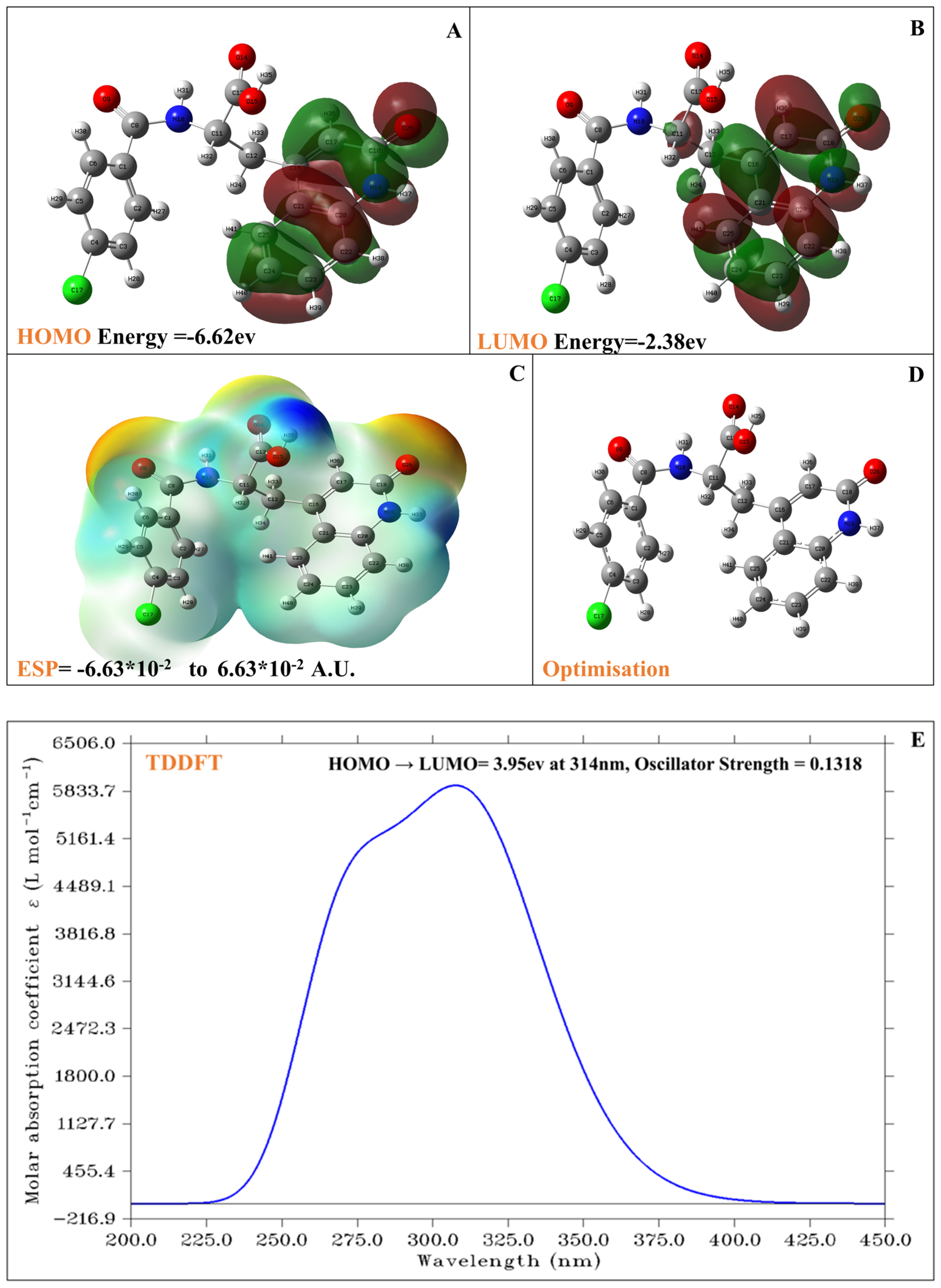
2.5. DFT and TDDFT Analysis of Rebamipide
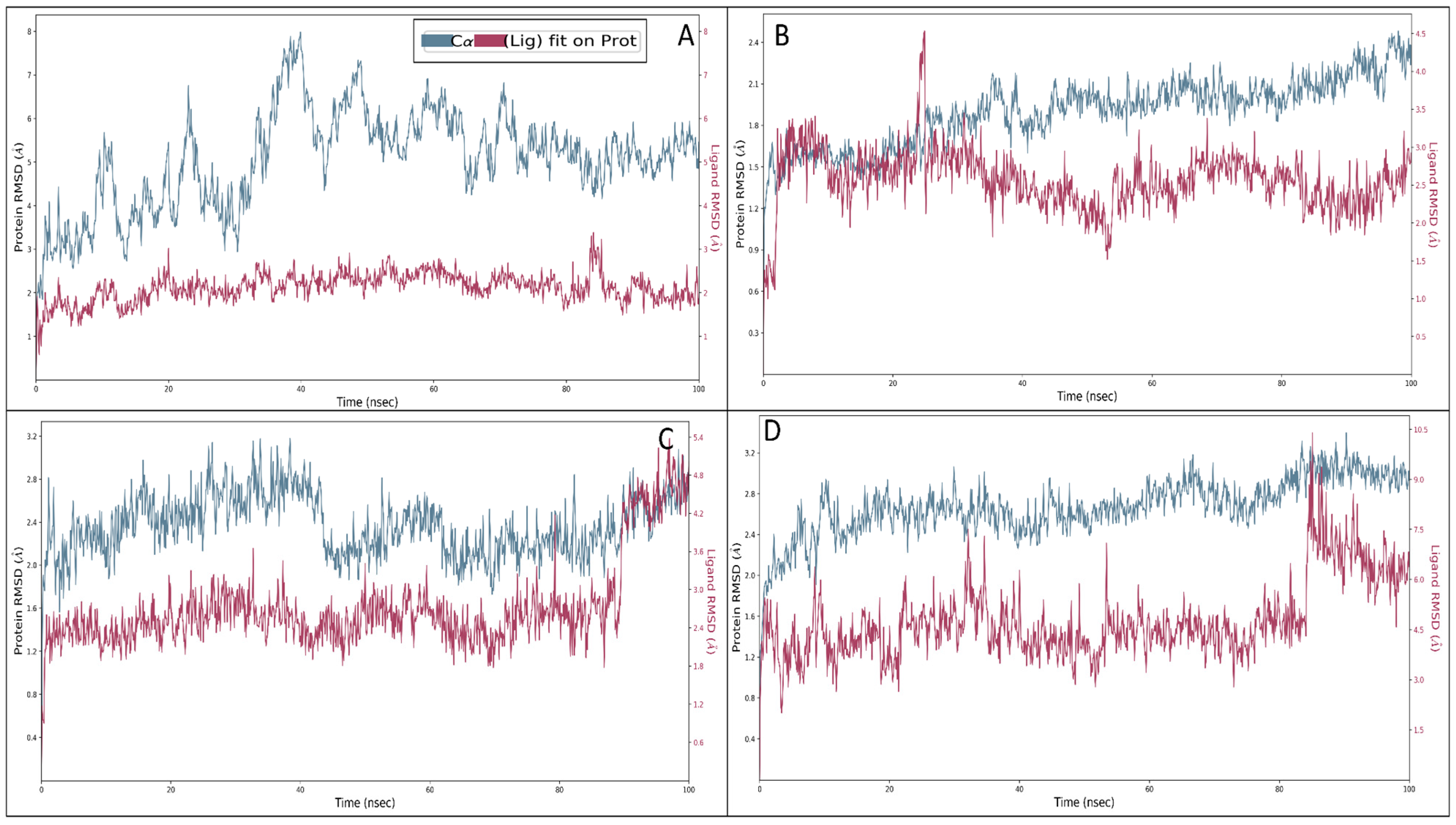
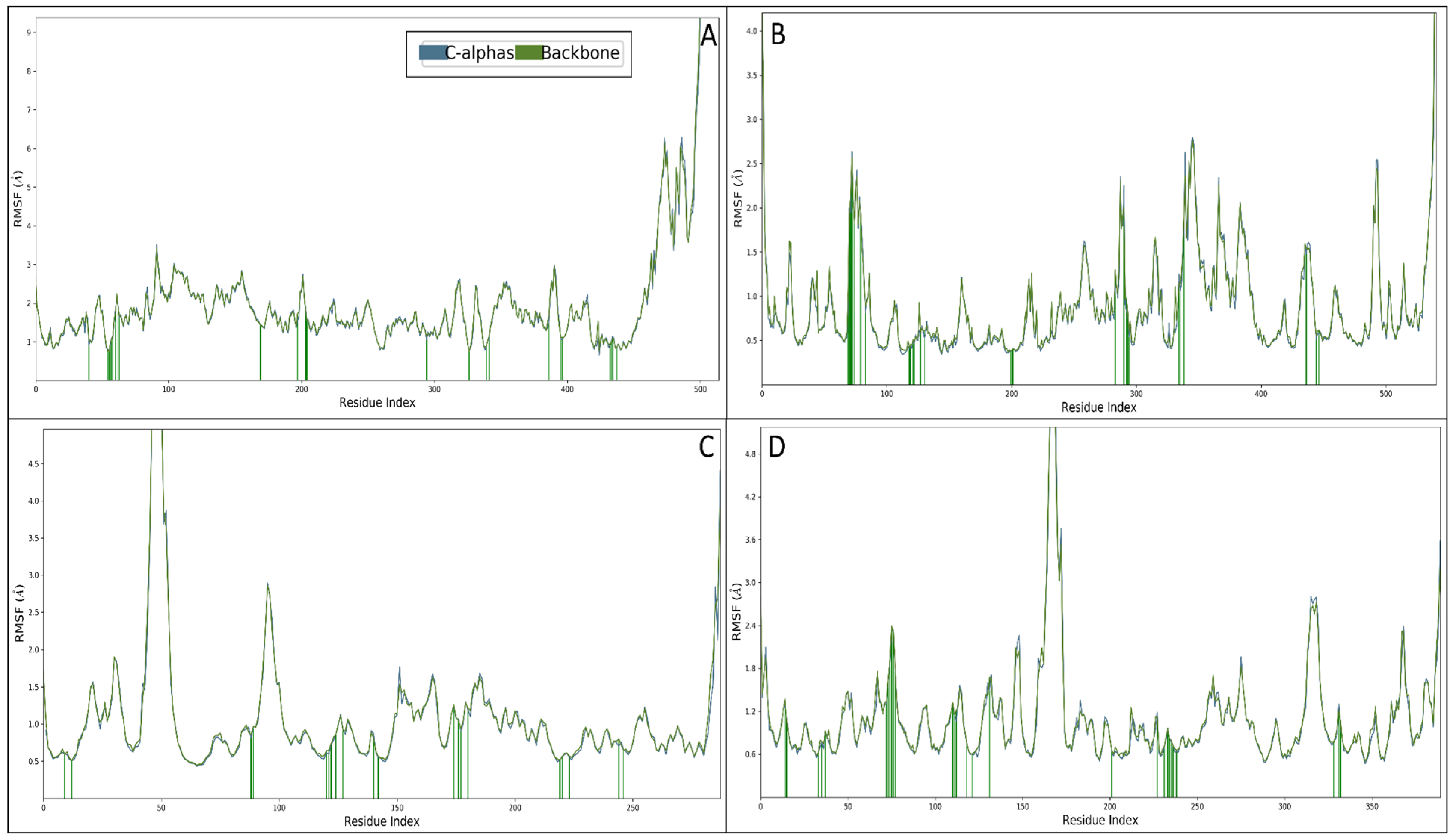
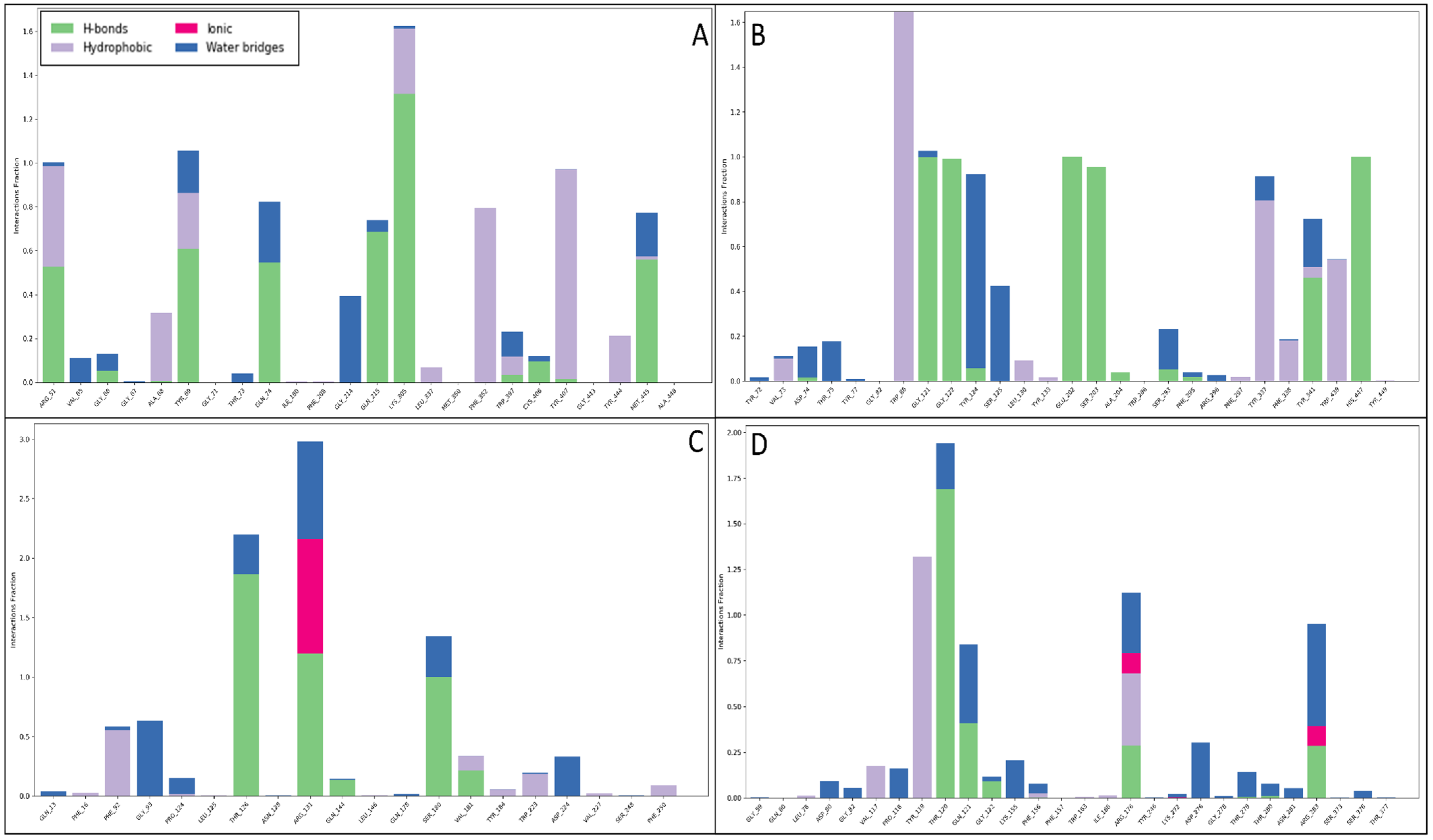
2.6. Molecular Dynamics Simulation Studies
2.6.1. Root Mean Square Deviation
2.6.2. Root Mean Square Fluctuations
2.6.3. Simulation Interaction Diagram
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Data Collection, Preparation, and Secondary Structure Analysis
4.2. Receptor Grid Generation and Molecular Interaction Analysis
4.3. Pharmacokinetics and Molecular Fingerprint Analysis
4.4. Water Thermodynamics (WaterMap Studies)
4.5. Density Functional Theory (DFT) and TDDFT Calculations
4.6. System Builder and Molecular Dynamics Simulation Studies
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Castellani, R.J.; Rolston, R.K.; Smith, M.A. Alzheimer disease. Dis.-A-Mon. DM 2010, 56, 484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Dyck, C.H.; Swanson, C.J.; Aisen, P.; Bateman, R.J.; Chen, C.; Gee, M.; Kanekiyo, M.; Li, D.; Reyderman, L.; Cohen, S. Lecanemab in early Alzheimer’s disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.A.; Alam, Q.; Haque, A.; Ashafaq, M.; Khan, M.J.; Ashraf, G.M.; Ahmad, M. Current progress on peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma agonist as an emerging therapeutic approach for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease: An update. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2019, 17, 232–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, Q.; ZubairAlam, M.; Karim, S.; Gan, S.H.; A Kamal, M.; Jiman-Fatani, A.; A Damanhouri, G.; M Abuzenadah, A.; G Chaudhary, A.; Haque, A. A nanotechnological approach to the management of Alzheimer disease and type 2 diabetes. CNS Neurol. Disord.-Drug Targets Former. Curr. Drug Targets-CNS Neurol. Disord. 2014, 13, 478–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anitha, K.; Singh, M.K.; Kohat, K.; Chenchula, S.; Padmavathi, R.; Amerneni, L.S.; Vardhan, V.; Chavan, M.R.; Bhatt, S. Recent insights into the neurobiology of Alzheimer’s disease and advanced treatment strategies. Mol. Neurobiol. 2025, 62, 2314–2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.; Dahiya, V.; Vibhuti, A.; Pandey, R.P.; Tripathi, M.K.; Yadav, M.K. Therapeutic Protein-Based Vaccines. In Protein-based Therapeutics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; pp. 355–384. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, S.; Singh, V.; Gautam, H.K.; Raza, K. Multisampling-based docking reveals Imidazolidinyl urea as a multitargeted inhibitor for lung cancer: An optimisation followed multi-simulation and in-vitro study. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2023, 42, 2494–2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alghamdi, Y.S.; Mashraqi, M.M.; Alzamami, A.; Alturki, N.A.; Ahmad, S.; Alharthi, A.A.; Alshamrani, S.; Asiri, S.A. Unveiling the multitargeted potential of N-(4-Aminobutanoyl)-S-(4-methoxybenzyl)-L-cysteinylglycine (NSL-CG) against SARS CoV-2: A virtual screening and molecular dynamics simulation study. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2023, 41, 6633–6642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alturki, N.A.; Mashraqi, M.M.; Alzamami, A.; Alghamdi, Y.S.; Alharthi, A.A.; Asiri, S.A.; Ahmad, S.; Alshamrani, S. In-silico screening and molecular dynamics simulation of drug bank experimental compounds against SARS-CoV-2. Molecules 2022, 27, 4391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzamami, A.; Alturki, N.A.; Alghamdi, Y.S.; Ahmad, S.; Alshamrani, S.; Asiri, S.A.; Mashraqi, M.M. Hemi-Babim and fenoterol as potential inhibitors of MPro and papain-like protease against SARS-CoV-2: An in-silico study. Medicina 2022, 58, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasubramanian, B.; Ahmad, S.; Alok, V.; Khan, F.N.; Anand, K.; Mehta, S.; Easwaran, M.; Meyyazhagan, A.; Saravanan, M. Exosomes as an emerging nanoplatform for functional therapeutics. Handb. Nanobio. Ther. Diagn. Appl. 2021, 483–498. [Google Scholar]
- Alam, Q.; Zubair Alam, M.; Mushtaq, G.; A Damanhouri, G.; Rasool, M.; Amjad Kamal, M.; Haque, A. Inflammatory process in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases: Central role of cytokines. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2016, 22, 541–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, N.; Li, H.; Peng, Y. A new deep belief network-based multi-task learning for diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. Neural Comput. Appl. 2023, 35, 11599–11610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedjadi, T.; Haque, A.; Alam, Q.; H Gan, S.; G Chaudhary, A.; M Abuzenadah, A.; A Damanhouri, G.; A Kamal, M. Genomic linkage between Alzheimer’s disease and type 2 diabetes. CNS Neurol. Disord.-Drug Targets Former. Curr. Drug Targets-CNS Neurol. Disord. 2014, 13, 203–212. [Google Scholar]
- Abellanas, M.A.; Purnapatre, M.; Burgaletto, C.; Schwartz, M. Monocyte-derived macrophages act as reinforcements when microglia fall short in Alzheimer’s disease. Nat. Neurosci. 2025, 28, 436–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.; Bano, N.; Qazi, S.; Yadav, M.K.; Ahmad, N.; Raza, K. Multitargeted molecular dynamic understanding of butoxypheser against SARS-CoV-2: An in silico study. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2022, 17, 1934578X221115499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.; Pasha Km, M.; Raza, K.; Rafeeq, M.M.; Habib, A.H.; Eswaran, M.; Yadav, M.K. Reporting dinaciclib and theodrenaline as a multitargeted inhibitor against SARS-CoV-2: An in-silico study. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2023, 41, 4013–4023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.; Raza, K. Identification of 5-nitroindazole as a multitargeted inhibitor for CDK and transferase kinase in lung cancer: A multisampling algorithm-based structural study. Mol. Divers. 2023, 28, 1189–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, S.; Sayeed, S.; Bano, N.; Sheikh, K.; Raza, K. In-silico analysis reveals Quinic acid as a multitargeted inhibitor against cervical cancer. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2022, 41, 9770–9786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.; Sheikh, K.; Bano, N.; Rafeeq, M.M.; Mohammed, M.R.S.; Yadav, M.K.; Raza, K. Illustrious Implications of Nature-Inspired Computing Methods in Therapeutics and Computer-Aided Drug Design. In Nature-Inspired Intelligent Computing Techniques in Bioinformatics; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2022; pp. 293–308. [Google Scholar]
- Z Alam, M.; Alam, Q.; A Kamal, M.; M Abuzenadah, A.; Haque, A. A possible link of gut microbiota alteration in type 2 diabetes and Alzheimer’s disease pathogenicity: An update. CNS Neurol. Disord.-Drug Targets Former. Curr. Drug Targets-CNS Neurol. Disord. 2014, 13, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, F.; Asghar Ansari, J.; Eqbal Ansari, Z.; Alam, Q.; Hua Gan, S.; A Kamal, M.; Ahmad, E. A molecular bridge: Connecting type 2 diabetes and Alzheimer’s disease. CNS Neurol. Disord.-Drug Targets Former. Curr. Drug Targets-CNS Neurol. Disord. 2014, 13, 312–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furukawa, H.; Gouaux, E. Mechanisms of activation, inhibition and specificity: Crystal structures of the NMDA receptor NR1 ligand-binding core. EMBO J. 2003, 22, 2873–2885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mertaş, B.; Boşgelmez, İ.İ. The Role of Genetic, Environmental, and Dietary Factors in Alzheimer’s Disease: A Narrative Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rueeger, H.; Lueoend, R.; Rogel, O.; Rondeau, J.-M.; Möbitz, H.; Machauer, R.; Jacobson, L.; Staufenbiel, M.; Desrayaud, S.; Neumann, U. Discovery of cyclic sulfone hydroxyethylamines as potent and selective β-site APP-cleaving enzyme 1 (BACE1) inhibitors: Structure-based design and in vivo reduction of amyloid β-peptides. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 3364–3386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zazeri, G.; Povinelli, A.P.R.; Le Duff, C.S.; Tang, B.; Cornelio, M.L.; Jones, A.M. Synthesis and spectroscopic analysis of piperine-and piperlongumine-inspired natural product scaffolds and their molecular docking with IL-1β and NF-κB proteins. Molecules 2020, 25, 2841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, S.-Y.; Ma, J.; Kondou, Y.; Yoshimura, M.; Yamashita, E.; Tsukihara, T. Structure of human monoamine oxidase A at 2.2-Å resolution: The control of opening the entry for substrates/inhibitors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 5739–5744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhati, R.; Nigam, A.; Ahmad, S.; Raza, K.; Singh, R. Structural–functional analysis and molecular characterization of arsenate reductase from Enterobacter cloacae RSC3 for arsenic biotransformation. 3 Biotech 2023, 13, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Famuyiwa, S.O.; Ahmad, S.; Fakola, E.G.; Olusola, A.J.; Adesida, S.A.; Obagunle, F.O.; Raza, K.; Ugwo, J.P.; Oyelekan, E.I.; Faloye, K.O. Comprehensive computational studies of naturally occurring kuguacins as antidiabetic agents by targeting visfatin. Chem. Afr. 2023, 6, 1415–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karwasra, R.; Ahmad, S.; Bano, N.; Qazi, S.; Raza, K.; Singh, S.; Varma, S. Macrophage-targeted punicalagin nanoengineering to alleviate methotrexate-induced neutropenia: A molecular docking, DFT, and MD simulation analysis. Molecules 2022, 27, 6034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karwasra, R.; Khanna, K.; Singh, S.; Ahmad, S.; Verma, S. The Incipient Role of Computational Intelligence in Oncology: Drug Designing, Discovery, and Development. In Computational Intelligence in Oncology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; Volume 1016, pp. 369–384. [Google Scholar]
- Mateev, E.; Georgieva, M.; Mateeva, A.; Zlatkov, A.; Ahmad, S.; Raza, K.; Azevedo, V.; Barh, D. Structure-Based Design of Novel MAO-B Inhibitors: A Review. Molecules 2023, 28, 4814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, J.; Rudolph, M.J.; Burshteyn, F.; Cassidy, M.S.; Gary, E.N.; Love, J.; Franklin, M.C.; Height, J.J. Structures of human acetylcholinesterase in complex with pharmacologically important ligands. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 10282–10286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zazeri, G.; Povinelli, A.P.R.; Pavan, N.M.; Jones, A.M.; Ximenes, V.F. Solvent-Induced Lag Phase during the Formation of Lysozyme Amyloid Fibrils Triggered by Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate: Biophysical Experimental and In Silico Study of Solvent Effects. Molecules 2023, 28, 6891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bansal, N.; Parvez, M.K.; Babu, M.A.; Al-Dosari, M.S.; Singh, T.G.; Ali, N.; Tyagi, Y.; Dadwal, A.; Yadav, U.; Dwivedi, A.R. Identification and investigation of hits targeting the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor via drug repurposing: A plausible approach for anti-Alzheimer drugs discovery. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 2025, 138, 109036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Q.; Wang, X. Alzheimer’s disease: Insights into pathology, molecular mechanisms, and therapy. Protein Cell 2025, 16, 83–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burley, S.K.; Berman, H.M.; Kleywegt, G.J.; Markley, J.L.; Nakamura, H.; Velankar, S. Protein Data Bank (PDB): The single global macromolecular structure archive. Protein Crystallogr. Methods Protoc. 2017, 1607, 627–641. [Google Scholar]
- Arakawa, T.; Kobayashi, K.; Yoshikawa, T.; Tarnawski, A. Rebamipide: Overview of its mechanisms of action and efficacy in mucosal protection and ulcer healing. Dig. Dis. Sci. 1998, 43, 5S–13S. [Google Scholar]
- Naito, Y.; Yoshikawa, T. Rebamipide: A gastrointestinal protective drug with pleiotropic activities. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2010, 4, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.; Bano, N.; Raza, K. Evaluating the polypharmacological potency of FEDPN from ChEMBL BioAssays against lung cancer EGFR, ALK, TrkA and KRAS proteins. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 306, 141703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.; Bano, N.; Raza, K. RCSB Protein Data Bank: Revolutionising drug discovery and design for over five decades. Med. Data Min. 2025, 8, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maestro, S. Maestro; Schrödinger LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Protein Preparation Wizard Schrödinger; Schrödinger LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2019.
- Epik; Schrödinger LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2018.
- Prime, S. Release, Schrödinger; Schrödinger, LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Rana, M.; Ahmedi, S.; Fatima, A.; Ahmad, S.; Siddiqui, N.; Raza, K.; Manzoor, N.; Javed, S. Synthesis, single crystal, TD-DFT, molecular dynamics simulation and DNA binding studies of carbothioamide analog. J. Mol. Struct. 2023, 1287, 135701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.A.; Ahmad, S.; Yadav, M.K.; Raza, K.; Kamal, M.A.; Akhtar, S. Structure-based virtual screening, molecular docking, molecular dynamics simulation, and metabolic reactivity studies of quinazoline derivatives for their anti-EGFR activity against tumor angiogenesis. Curr. Med. Chem. 2023, 31, 595–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, K.; Sayeed, S.; Asif, A.; Siddiqui, M.F.; Rafeeq, M.M.; Sahu, A.; Ahmad, S. Consequential Innovations in Nature-Inspired Intelligent Computing Techniques for Biomarkers and Potential Therapeutics Identification. In Nature-Inspired Intelligent Computing Techniques in Bioinformatics; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2022; pp. 247–274. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, A.P.; Ahmad, S.; Raza, K.; Gautam, H.K. Computational screening and MM/GBSA-based MD simulation studies reveal the high binding potential of FDA-approved drugs against Cutibacterium acnes sialidase. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2023, 42, 6245–6255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripathi, M.K.; Ahmad, S.; Tyagi, R.; Dahiya, V.; Yadav, M.K. Fundamentals of molecular modeling in drug design. In Computer Aided Drug Design (CADD): From Ligand-Based Methods to Structure-Based Approaches; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 125–155. [Google Scholar]
- Yadav, M.K.; Ahmad, S.; Raza, K.; Kumar, S.; Eswaran, M.; Pasha KM, M. Predictive modeling and therapeutic repurposing of natural compounds against the receptor-binding domain of SARS-CoV-2. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2022, 41, 1527–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jorgensen, W.L.; Tirado-Rives, J. The OPLS [optimized potentials for liquid simulations] potential functions for proteins, energy minimizations for crystals of cyclic peptides and crambin. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1988, 110, 1657–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramlal, A.; Ahmad, S.; Kumar, L.; Khan, F.N.; Chongtham, R. From molecules to patients: The clinical applications of biological databases and electronic health records. In Translational Bioinformatics in Healthcare and Medicine; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021; pp. 107–125. [Google Scholar]
- Schrödinger LLC. LigPrep; Schrödinger LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Schrödinger LLC. Receptor Grid Generation; Schrödinger LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Friesner, R.A.; Murphy, R.B.; Repasky, M.P.; Frye, L.L.; Greenwood, J.R.; Halgren, T.A.; Sanschagrin, P.C.; Mainz, D.T. Extra precision glide: Docking and scoring incorporating a model of hydrophobic enclosure for protein−ligand complexes. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 6177–6196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrödinger LLC. QikProp; Schrödinger LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Lipinski, C.A. Lead-and drug-like compounds: The rule-of-five revolution. Drug Discov. Today Technol. 2004, 1, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abel, R.; Young, T.; Farid, R.; Berne, B.J.; Friesner, R.A. Role of the active-site solvent in the thermodynamics of factor Xa ligand binding. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 2817–2831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.; Bano, N.; Khanna, K.; Gupta, D.; Raza, K. Reporting multitargeted potency of Tiaprofenic acid against lung cancer: Molecular fingerprinting, MD simulation, and MTT-based cell viability assay studies. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 276, 133872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.; Singh, A.P.; Bano, N.; Raza, K.; Singh, J.; Medigeshi, G.R.; Pandey, R.; Gautam, H.K. Integrative analysis discovers Imidurea as dual multitargeted inhibitor of CD69, CD40, SHP2, lysozyme, GATA3, cCBL, and S-cysteinase from SARS-CoV-2 and M. tuberculosis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 270, 132332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frisch, M. Gaussian 09; Revision d. 01; Gaussian Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Becke, A.D. Density-functional thermochemistry. III. The role of exact exchange. J. Chem. Phys. 1993, 98, 5648–5652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Yang, W.; Parr, R.G. Development of the Colle-Salvetti correlation-energy formula into a functional of the electron density. Phys. Rev. B 1988, 37, 785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, R.; Binkley, J.S.; Seeger, R.; Pople, J.A. Self-consistent molecular orbital methods. XX. A basis set for correlated wave functions. J. Chem. Phys. 1980, 72, 650–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, T.; Chandrasekhar, J.; Spitznagel, G.W.; Schleyer, P.V.R. Efficient diffuse function-augmented basis sets for anion calculations. III. The 3-21+ G basis set for first-row elements, Li–F. J. Comput. Chem. 1983, 4, 294–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, D.; Pavanello, M.; Shao, X.; Ihara, M.; Ayers, P.W.; Matta, C.F.; Jenkins, S.; Manzhos, S. The analysis of electron densities: From basics to emergent applications. Chem. Rev. 2024, 124, 12661–12737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, M.P.; Uvdal, P. New scale factors for harmonic vibrational frequencies using the B3LYP density functional method with the triple-ζ basis set 6-311+ G (d, p). J. Phys. Chem. A 2005, 109, 2937–2941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laane, J. Experimental determination of vibrational potential energy surfaces and molecular structures in electronic excited states. J. Phys. Chem. A 2000, 104, 7715–7733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aihara, J.-i. Reduced HOMO− LUMO gap as an index of kinetic stability for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. J. Phys. Chem. A 1999, 103, 7487–7495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minsky, A.; Meyer, A.Y.; Rabinovitz, M. Paratropicity and antiaromaticity: Role of the homo-lumo energy gap. Tetrahedron 1985, 41, 785–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dennington, R.; Keith, T.; Millam, J. GaussView, Version 5; Semichem Inc: Shawnee Mission, KS, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Stratmann, R.E.; Scuseria, G.E.; Frisch, M.J. An efficient implementation of time-dependent density-functional theory for the calculation of excitation energies of large molecules. J. Chem. Phys. 1998, 109, 8218–8224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauernschmitt, R.; Ahlrichs, R. Treatment of electronic excitations within the adiabatic approximation of time dependent density functional theory. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1996, 256, 454–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.; Chen, F. Multiwfn: A multifunctional wavefunction analyzer. J. Comput. Chem. 2012, 33, 580–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, R.A.; Stevenson, K.J. Software review of Origin 8. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowers, K.J.; Chow, E.; Xu, H.; Dror, R.O.; Eastwood, M.P.; Gregersen, B.A.; Klepeis, J.L.; Kolossvary, I.; Moraes, M.A.; Sacerdoti, F.D. Scalable algorithms for molecular dynamics simulations on commodity clusters. In Proceedings of the 2006 ACM/IEEE Conference on Supercomputing, Tampa, FL, USA, 11–17 November 2006; pp. 84–es. [Google Scholar]
- Mark, P.; Nilsson, L. Structure and dynamics of the TIP3P, SPC, and SPC/E water models at 298 K. J. Phys. Chem. A 2001, 105, 9954–9960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Kim, E.; Lee, S.; Kim, J.S.; Lee, S. New method for constant-npt molecular dynamics. J. Phys. Chem. A 2019, 123, 1689–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| S No | PDB | Docking Score | MMGBSA | Prime Hbond | Prime vdW |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 4EY6 | −10.738 | −24.6 | −289.16 | −2945.74 |
| 2 | 2Z5X | −11.022 | −14.25 | −305.76 | −2747.19 |
| 3 | 4D89 | −4.581 | −34.97 | −189.86 | −1895.04 |
| 4 | 1PBQ | −9.321 | −50.07 | −152.29 | −1403.84 |
| Properties | Standard Values | Rebamipide | Properties | Standard Values | Rebamipide |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QPlogS | −6.5–0.5 | −5.575 | donorHB | 0.0–6.0 | 2.25 |
| CIQPlogS | −6.5–0.5 | −5.164 | QPlogPo/w | −2.0–6.5 | 3.421 |
| QPlogHERG | concern below −5 | −4.89 | #rotor | 0–15 | 5 |
| QPlogKp | −8.0–−1.0 | −3.625 | #NandO | 2–15 | 6 |
| CNS | −2 (inactive), +2 (active) | −2 | accptHB | 2.0–20.0 | 6.25 |
| QPlogBB | −3.0–1.2 | −1.813 | dipole | 1.0–12.5 | 8.096 |
| #amidine | 0 | 0 | IP(eV) | 7.9–10.5 | 9.208 |
| #amine | 0–1 | 0 | QPlogPw | 4.0–45.0 | 13.562 |
| #amide | 0–1 | 0 | QPlogPC16 | 4.0–18.0 | 13.867 |
| #rtvFG | 0–2 | 0 | #ringatoms | N/A | 16 |
| #stars | 0–5 | 0 | #in56 | N/A | 16 |
| SAfluorine | 0.0–100.0 | 0 | QPlogPoct | 8.0–35.0 | 21.294 |
| SAamideO | 0.0–35.0 | 0 | #nonHatm | N/A | 26 |
| RuleOfThree | maximum is 3 | 0 | QPPCaco | <25 poor, >500 great | 26.39 |
| RuleOfFive | maximum is 4 | 0 | QPPMDCK | <25 poor, >500 great | 30.436 |
| #in34 | N/A | 0 | FOSA | 0.0–750.0 | 35.632 |
| #noncon | N/A | 0 | QPpolrz | 13.0–70.0 | 39.832 |
| Jm | N/A | 0.000183 | WPSA | 0.0–175.0 | 71.346 |
| ACxDN^.5/SA | 0.0–0.05 | 0.0139316 | PercentHumanOralAbsorption | >80% is high, <25% is poor | 72.416 |
| dip^2/V | 0.0–0.13 | 0.057289 | PSA | 7.0–200.0 | 123.474 |
| QPlogKhsa | −1.5–1.5 | 0.082 | FISA | 7.0–330.0 | 208.59 |
| glob | 0.75–0.95 | 0.786111 | PISA | 0.0–450.0 | 357.365 |
| #acid | 0–1 | 1 | mol MW | 130.0–725.0 | 370.791 |
| EA(eV) | −0.9–1.7 | 1.037 | SASA | 300.0–1000.0 | 672.933 |
| #metab | 1–8 | 2 | volume | 500.0–2000.0 | 1144.025 |
| HumanOralAbsorption | N/A | 2 | Compound | N/A | Small |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hakeem, I.J.; Alahdal, H.; Baeissa, H.M.; Bakhsh, T.; Rafeeq, M.; Habib, A.H.; Karami, M.M.; AL-Ghamdi, M.A.; Abdullah, G.; Al Tuwaijri, A. Unveiling the Polypharmacological Potency of FDA-Approved Rebamipide for Alzheimer’s Disease. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 772. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18060772
Hakeem IJ, Alahdal H, Baeissa HM, Bakhsh T, Rafeeq M, Habib AH, Karami MM, AL-Ghamdi MA, Abdullah G, Al Tuwaijri A. Unveiling the Polypharmacological Potency of FDA-Approved Rebamipide for Alzheimer’s Disease. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(6):772. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18060772
Chicago/Turabian StyleHakeem, Israa J., Hadil Alahdal, Hanadi M. Baeissa, Tahani Bakhsh, Misbahuddin Rafeeq, Alaa Hamed Habib, Mohammed Matoog Karami, Maryam A. AL-Ghamdi, Ghadeer Abdullah, and Abeer Al Tuwaijri. 2025. "Unveiling the Polypharmacological Potency of FDA-Approved Rebamipide for Alzheimer’s Disease" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 6: 772. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18060772
APA StyleHakeem, I. J., Alahdal, H., Baeissa, H. M., Bakhsh, T., Rafeeq, M., Habib, A. H., Karami, M. M., AL-Ghamdi, M. A., Abdullah, G., & Al Tuwaijri, A. (2025). Unveiling the Polypharmacological Potency of FDA-Approved Rebamipide for Alzheimer’s Disease. Pharmaceuticals, 18(6), 772. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18060772










