Discovery of Sphingosine Kinase Inhibition by Modified Quinoline-5,8-Diones
Abstract
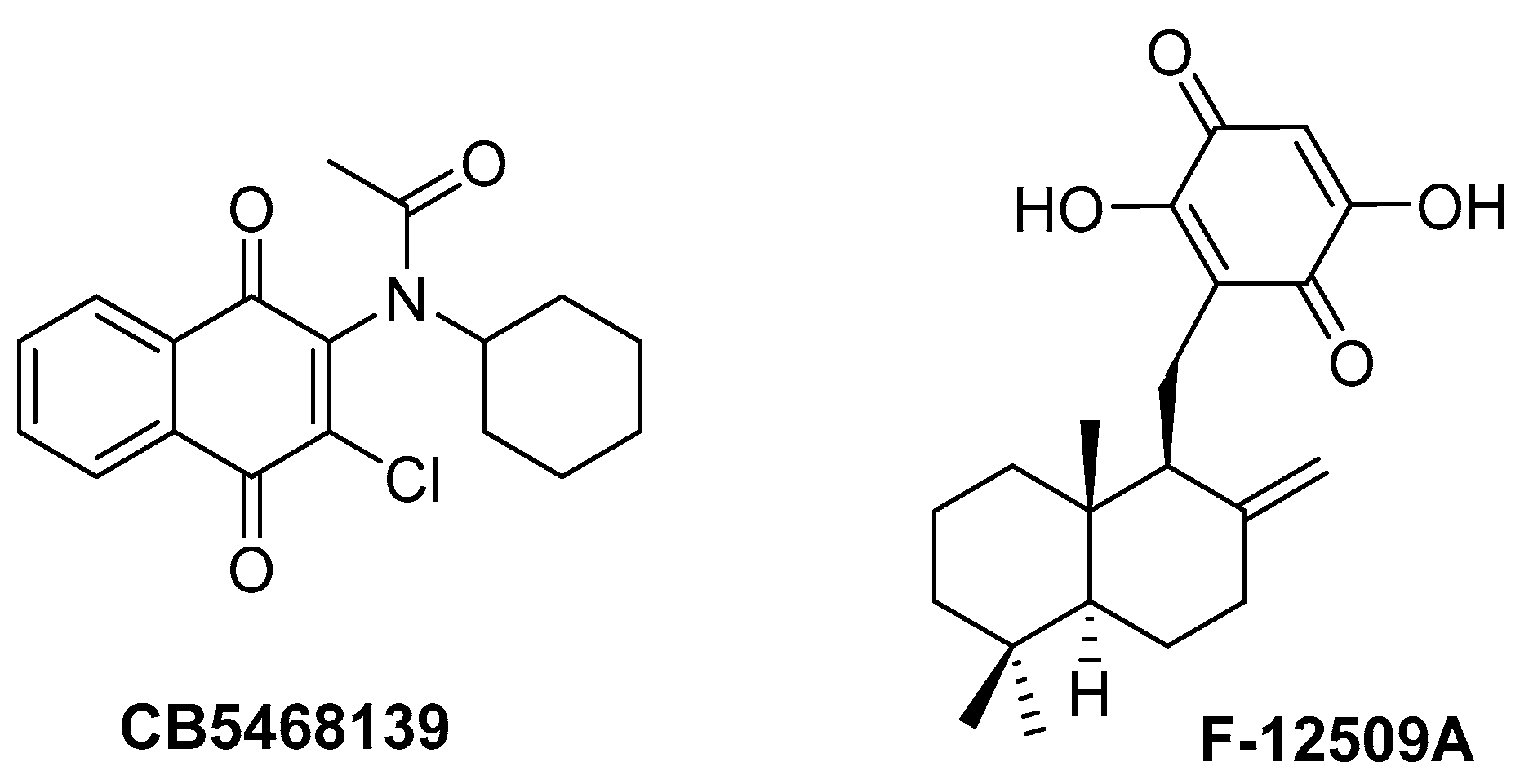
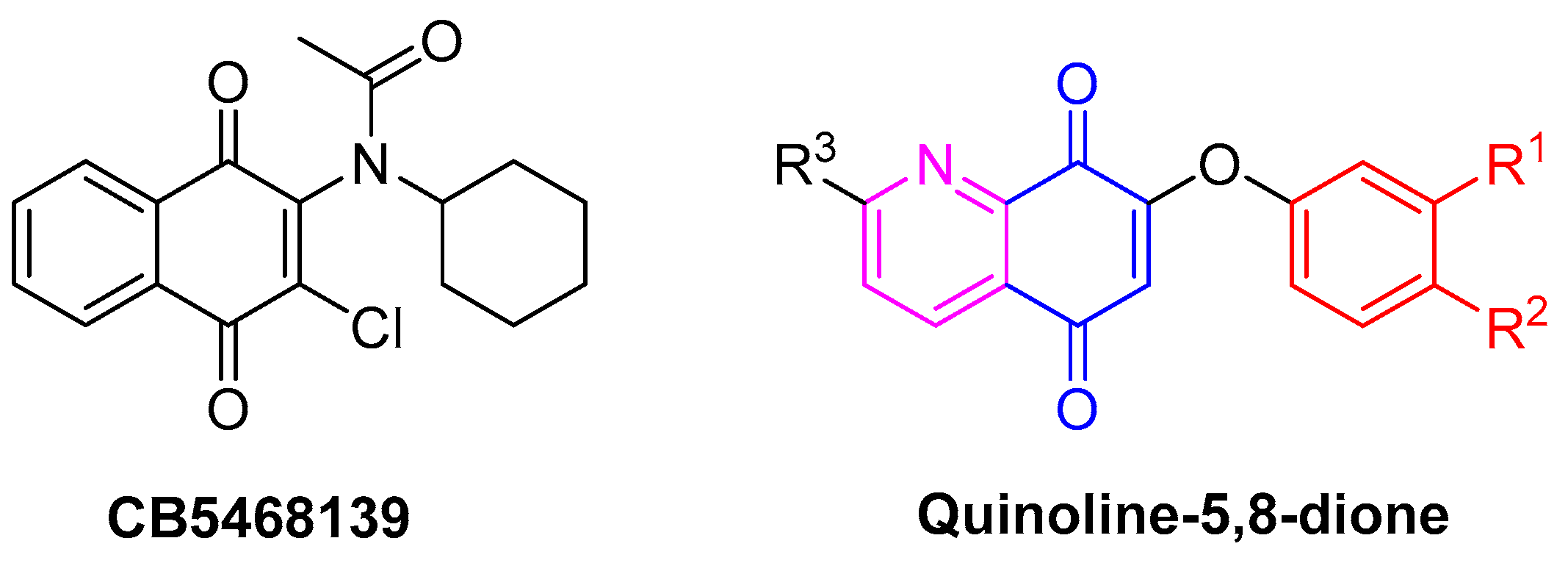
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
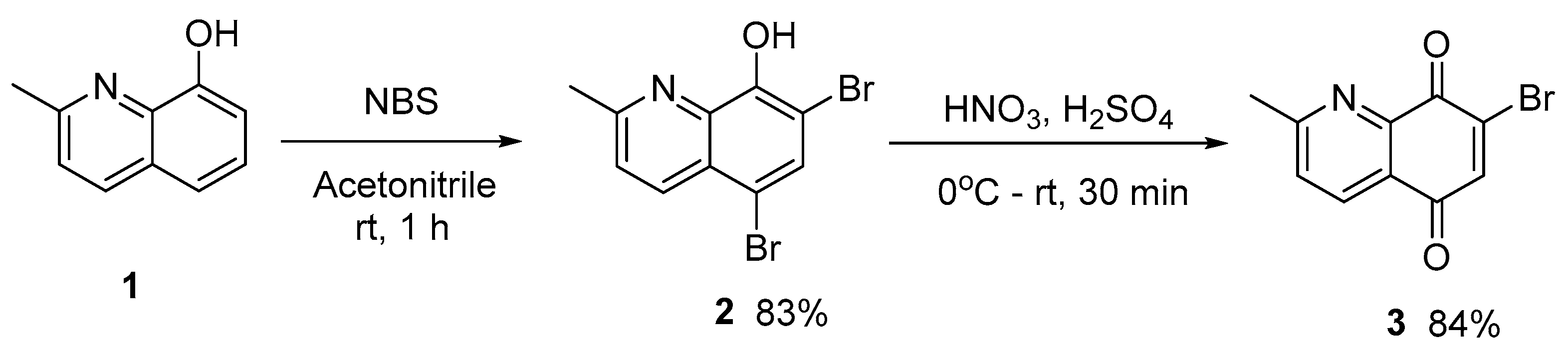
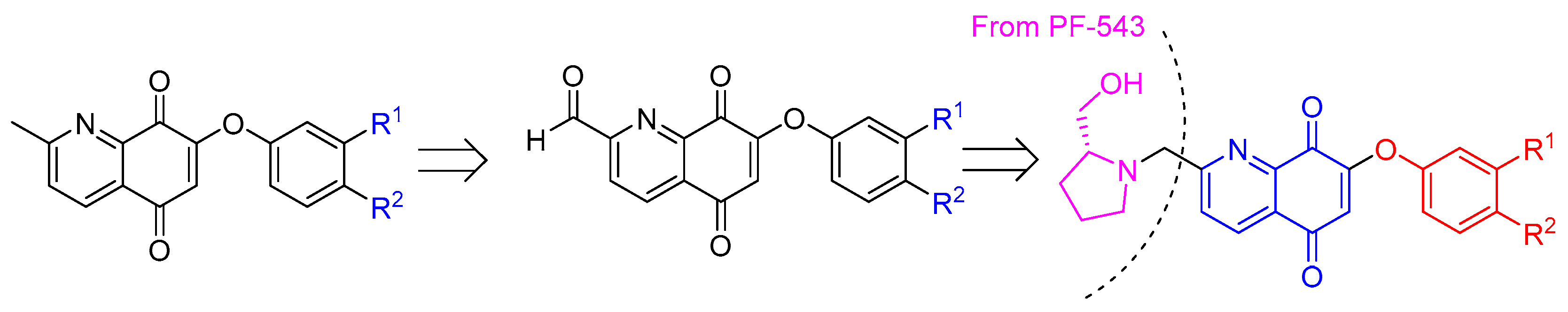
2.1. Development of the Quinoline-5,8-Dione Intermediate
2.2. Synthetic Route to 7-Phenoxy Quinoline-5,8-Diones
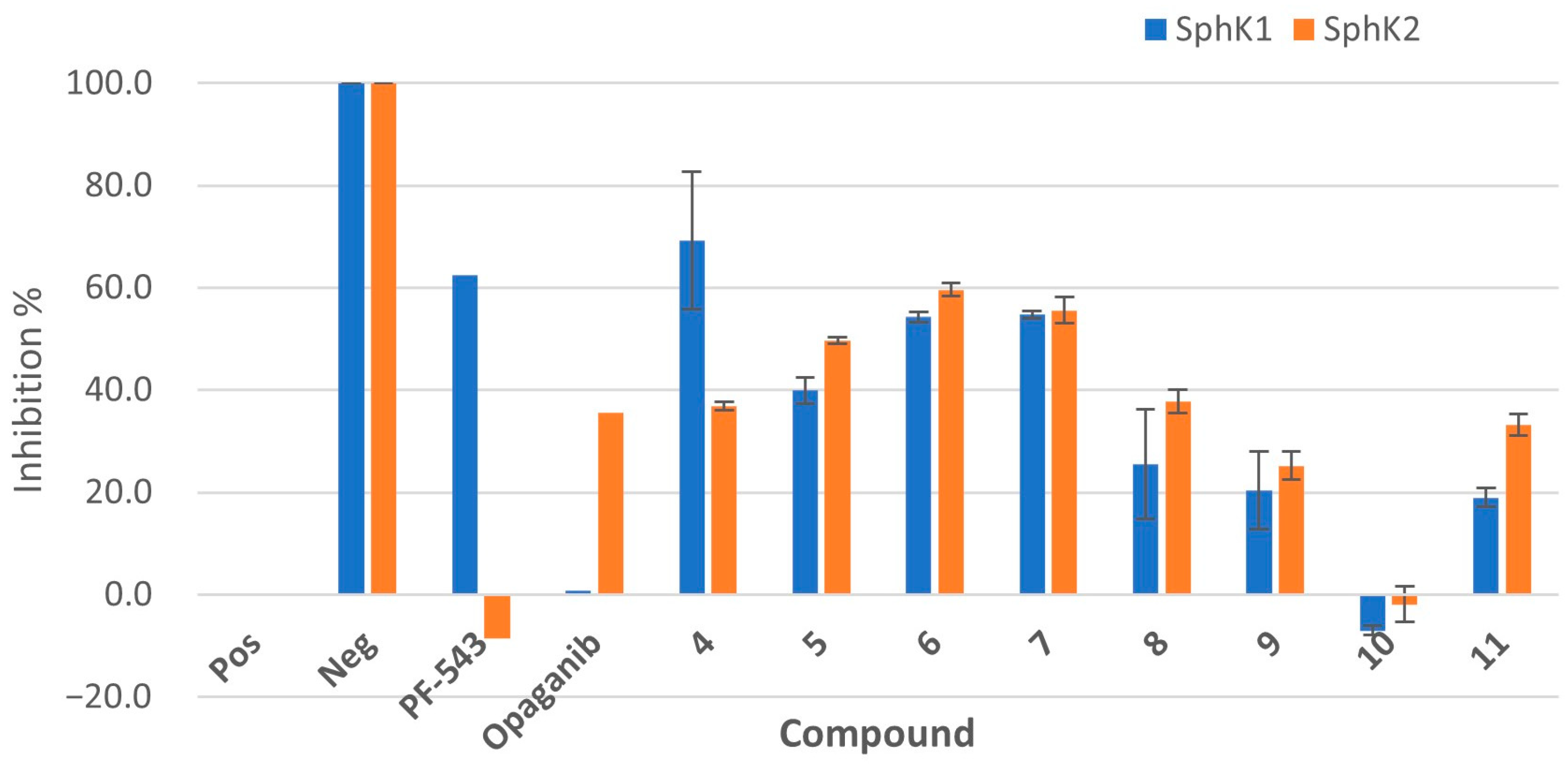
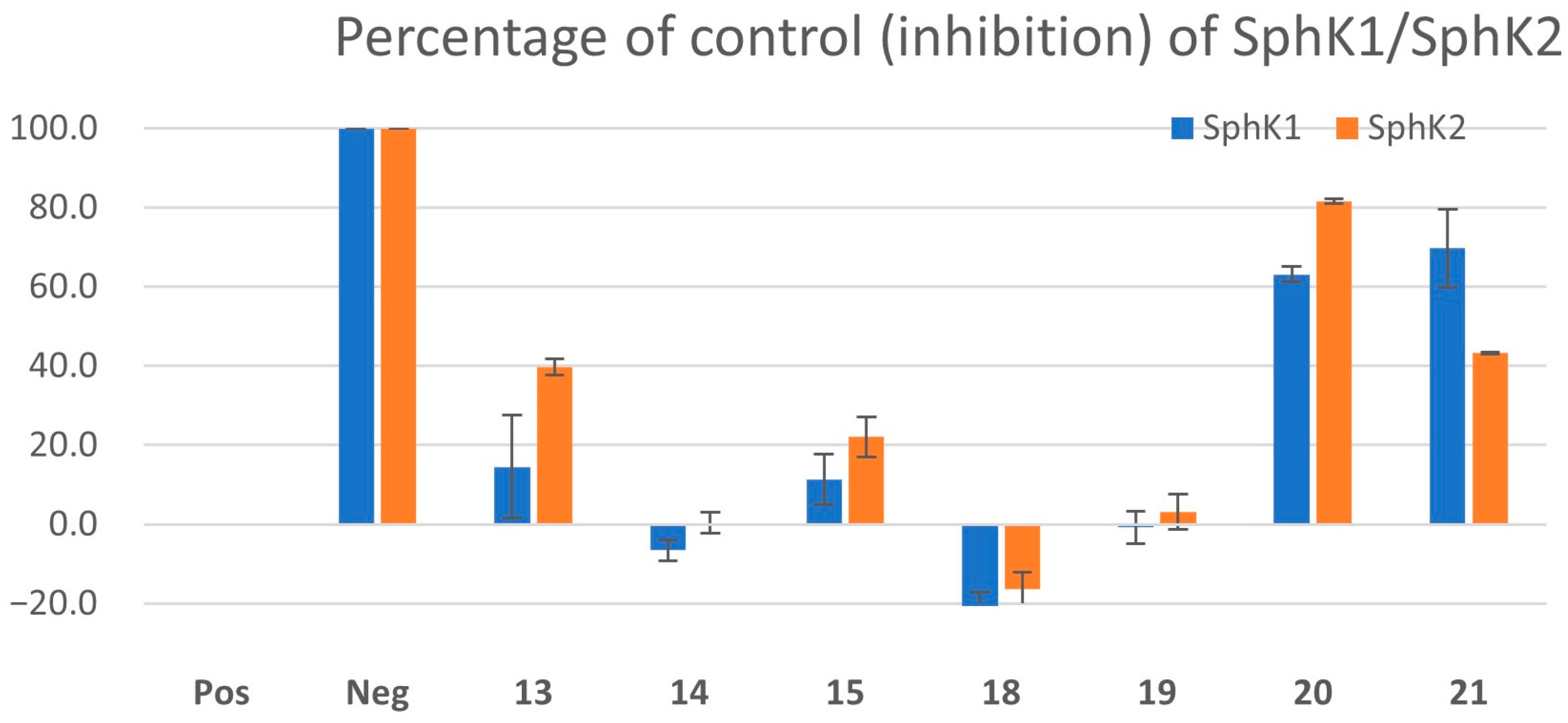
2.3. Screening of Quinoline-5,8-Diones for Sphingosine Kinase Inhibition
2.4. Extension of the Quinoline-5,8-Dione Framework to Target SphK1 Inhibition
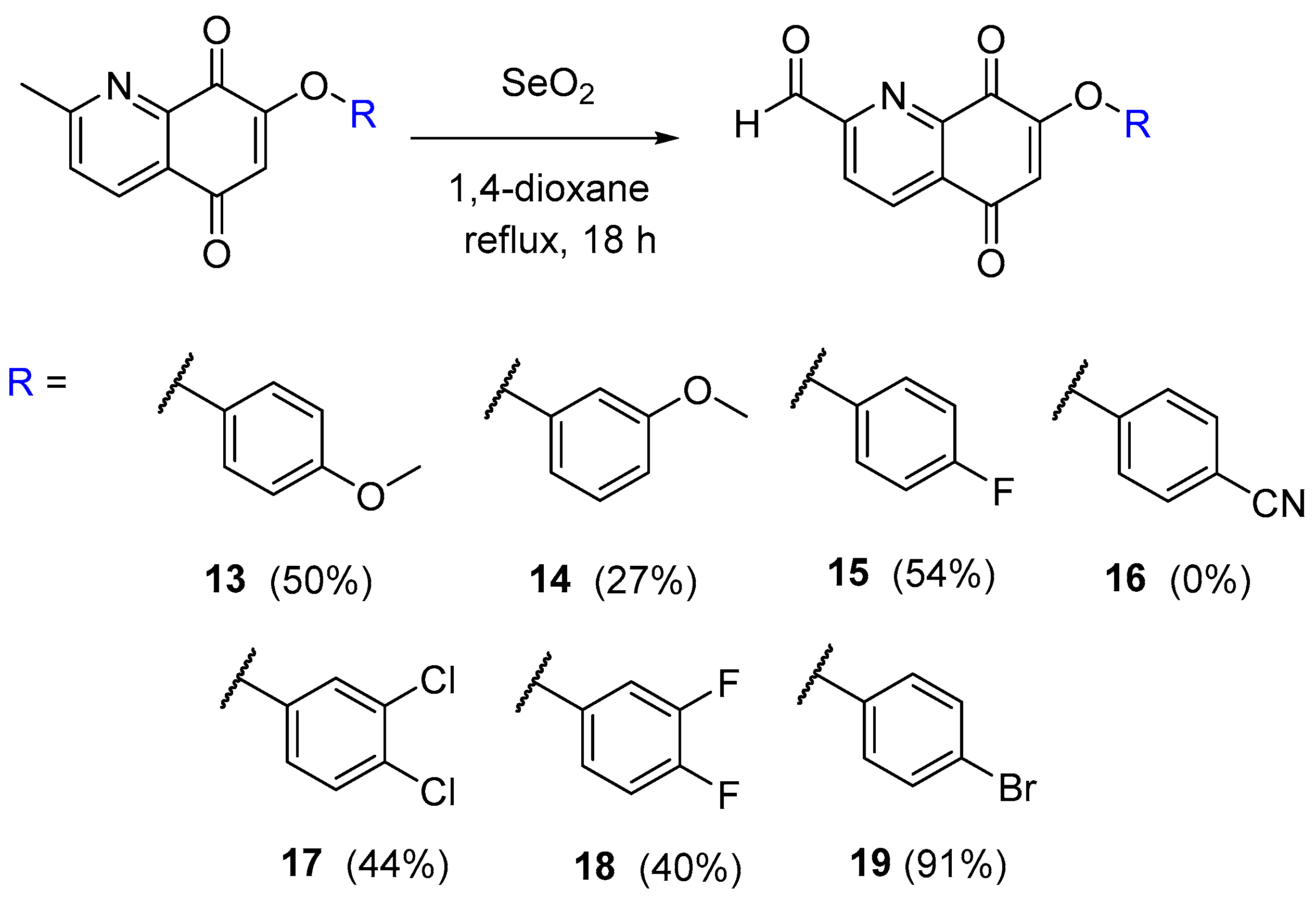
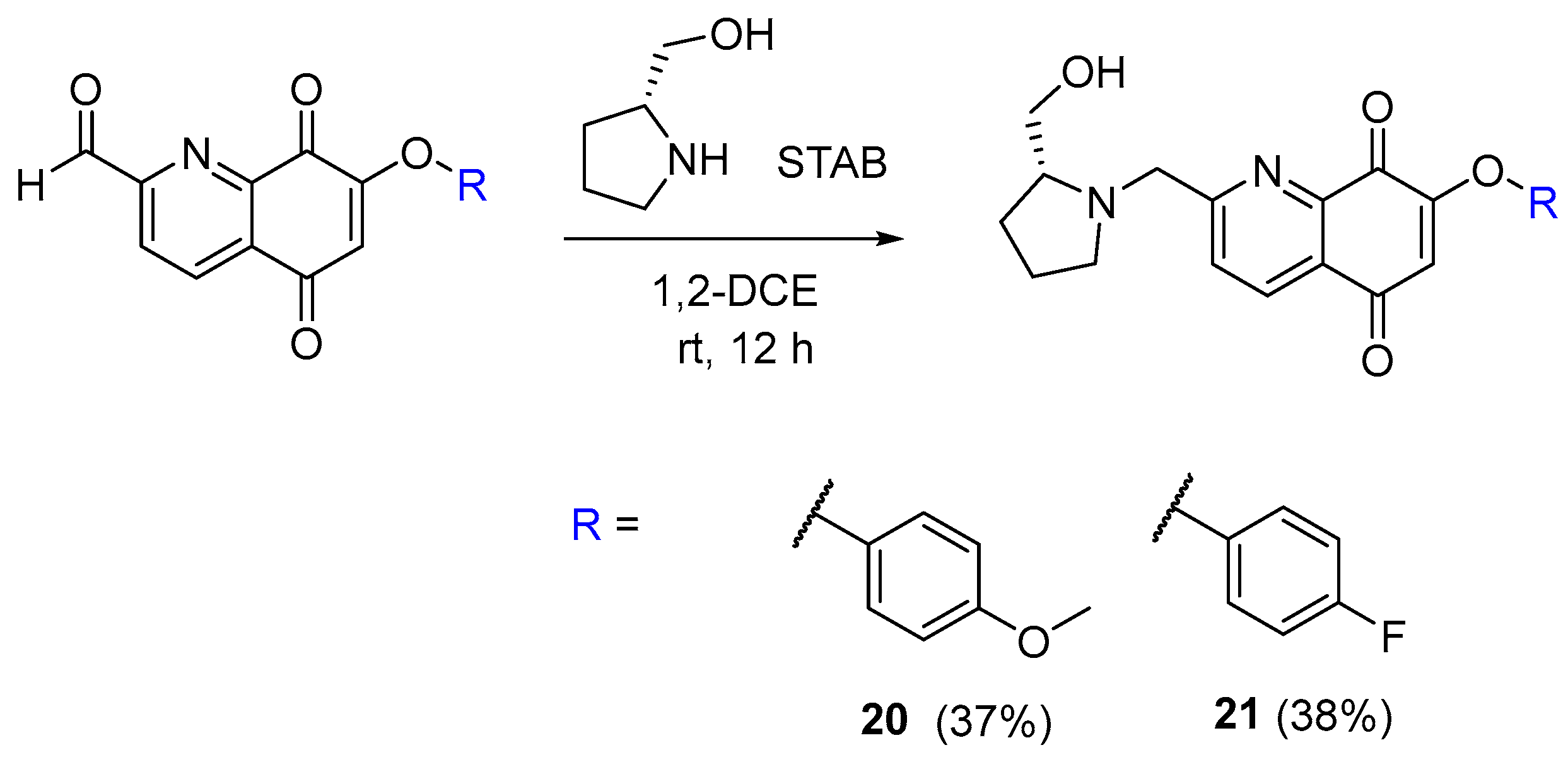
2.5. Synthesis of the Quinoline-5,8-Dione Framework to Target SphK1 Inhibition
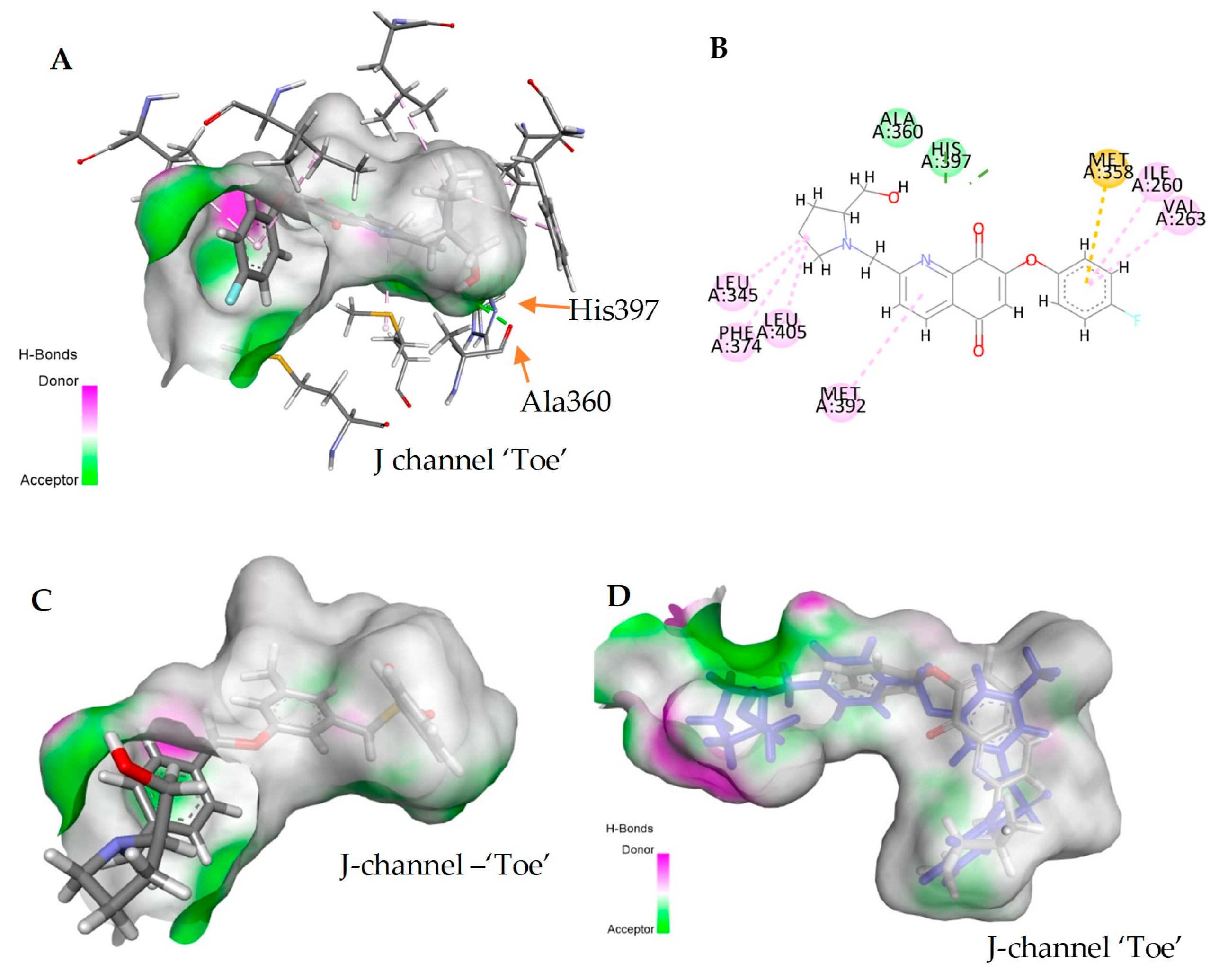
2.6. Molecular Model of the Quinoline-5,8-Dione Framework in SphK1
2.7. Anticancer Screening of Quinoline-5,8-Diones
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials, Reagents and General Experimental Procedures
3.2. Chemical Synthesis
3.2.1. 5,7-Dibromo-2-methylquinolin-8-ol (2)
3.2.2. 7-Bromo-2-methylquinoline-5,8-dione (3)
3.2.3. 7-(4-Methoxyphenoxy)-2-methyl-6,7-dihydroquinoline-5,8-dione (4)
3.2.4. 7-(3-Methoxyphenoxy)-2-methylquinoline-5,8-dione (5)
3.2.5. 7-(4-Fluorophenoxy)-2-methylquinoline-5,8-dione (6)
3.2.6. 2-Methyl-7-(4-(cyano)phenoxy)quinoline-5,8-dione (7)
3.2.7. 7-(3,4-Dichlorophenoxy)-2-methylquinoline-5,8-dione (8)
3.2.8. 7-(3,4-Difluorophenoxy)-2-methylquinoline-5,8-dione (9)
3.2.9. 7-(3-Chloro-4-fluorophenoxy)-2-methylquinoline-5,8-dione (10)
3.2.10. 7-(4-(2-Hydroxyethyl)phenoxy)-2-methylquinoline-5,8-dione (11)
3.2.11. 7-(4-Bromophenoxy)-2-methylquinoline-5,8-dione (12)
3.2.12. 7-(4-Methoxyphenoxy)-5,8-dioxo-5,8-dihydroquinoline-2-carbaldehyde (13)
3.2.13. 7-(3-Methoxyphenoxy)-5,8-dioxo-5,8-dihydroquinoline-2-carbaldehyde (14)
3.2.14. 7-(4-Fluorophenoxy)-5,8-dioxo-5,8-dihydroquinoline-2-carbaldehyde (15)
3.2.15. 7-(3,4-Dichlorophenoxy)-5,8-dioxo-5,8-dihydroquinoline-2-carbaldehyde (17)
3.2.16. 7-(3,4-Difluorophenoxy)-5,8-dioxo-5,8-dihydroquinoline-2-carbaldehyde (18)
3.2.17. 7-(4-Bromophenoxy)-5,8-dioxo-5,8-dihydroquinoline-2-carbaldehyde (19)
3.2.18. (R)-2-((2-(Hydroxymethyl)pyrrolidin-1-yl)methyl)-7-(4-methoxyphenoxy)quinoline-5,8-dione (20)
3.2.19. (R)-7-(4-Fluorophenoxy)-2-((2-(hydroxymethyl)pyrrolidin-1-yl)methyl)quinoline-5,8-dione (21)
3.3. Sphingosine Kinase Assays
3.4. Cancer Cell Growth Assays (NCI60 Screening)
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Pitman, M.R.; Costabile, M.; Pitson, S.M. Recent advances in the development of sphingosine kinase inhibitors. Cell Signal. 2016, 28, 1349–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, W.L.; Lynch, K.R. Drugging Sphingosine Kinases. ACS Chem. Biol. 2015, 10, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neubauer, H.A.; Pitson, S.M. Roles, regulation and inhibitors of sphingosine kinase 2. FEBS J. 2013, 280, 5317–5336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pyne, N.J.; Pyne, S. Recent advances in the role of sphingosine 1-phosphate in cancer. FEBS Lett. 2020, 594, 3583–3601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyne, N.J.; Pyne, S. Sphingosine 1-phosphate and cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2010, 10, 489–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wattenberg, B.W.; Pitson, S.M.; Raben, D.M. The sphingosine and diacylglycerol kinase superfamily of signaling kinases: Localization as a key to signaling function. J. Lipid Res. 2006, 47, 1128–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Echten-Deckert, G.; Hagen-Euteneuer, N.; Karaca, I.; Walter, J. Sphingosine-1-Phosphate: Boon and Bane for the Brain. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2014, 34, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyne, N.J.; Pyne, S. Sphingosine Kinase 1: A Potential Therapeutic Target in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension? Trends Mol. Med. 2017, 23, 786–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horga, A.; Montalban, X. FTY720 (fingolimod) for relapsing multiple sclerosis. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2008, 8, 699–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonica, J.; Mao, C.; Obeid, L.M.; Hannun, Y.A. Transcriptional Regulation of Sphingosine Kinase 1. Cells 2020, 9, 2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plano, D.; Amin, S.; Sharma, A.K. Importance of Sphingosine Kinase (SphK) as a Target in Developing Cancer Therapeutics and Recent Developments in the Synthesis of Novel SphK Inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 5509–5524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.; Tian, J.; Sun, J.; Han, N.; Feng, L.; Yu, B.; Wang, Y. Lentivirus-mediated siRNA knockdown of SPHK1 inhibits proliferation and tumorigenesis of neuroblastoma. OncoTargets Ther. 2018, 11, 7187–7196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orr Gandy, K.A.; Obeid, L.M. Targeting the sphingosine kinase/sphingosine 1-phosphate pathway in disease: Review of sphingosine kinase inhibitors. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. Spec. Sect. Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2013, 1831, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houck, J.D.; Dawson, T.K.; Kennedy, A.J.; Kharel, Y.; Naimon, N.D.; Field, S.D.; Lynch, K.R.; Macdonald, T.L. Structural Requirements and Docking Analysis of Amidine-Based Sphingosine Kinase 1 Inhibitors Containing Oxadiazoles. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 7, 487–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuvillier, O. Downregulating sphingosine kinase-1 for cancer therapy. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2008, 12, 1009–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, M.; Ji, C.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, W.; Ni, W.; Tong, X.; Wei, J.-F. Sphingosine kinase inhibitors: A patent review. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 41, 2450–2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, X.; Tang, X.; Li, T.; Chen, L.; He, H.; Wu, X.; Xiang, C.; Cao, M.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; et al. Therapeutic potential of the sphingosine kinase 1 inhibitor, PF-543. Biomed. Pharm. 2023, 163, 114401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, T.; Gao, D.; Fang, Z.-Y. Targeting colorectal cancer cells by a novel sphingosine kinase 1 inhibitor PF-543. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 2016, 470, 728–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamada, M.; Kameyama, H.; Iwai, S.; Yura, Y. Induction of autophagy by sphingosine kinase 1 inhibitor PF-543 in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cells. Cell Death Discov. 2017, 3, 17047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Gao, F.; Chen, K.; Tian, M.L.; Zhao, D.L. Sphingosine kinase 1 as an anticancer therapeutic target. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2015, 9, 3239–3245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Britten, C.D.; Garrett-Mayer, E.; Chin, S.H.; Shirai, K.; Ogretmen, B.; Bentz, T.A.; Brisendine, A.; Anderton, K.; Cusack, S.L.; Maines, L.W.; et al. A Phase I Study of ABC294640, a First-in-Class Sphingosine Kinase-2 Inhibitor, in Patients with Advanced Solid Tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 4642–4652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- French, K.J.; Zhuang, Y.; Maines, L.W.; Gao, P.; Wang, W.; Beljanski, V.; Upson, J.J.; Green, C.L.; Keller, S.N.; Smith, C.D. Pharmacology and Antitumor Activity of ABC294640, a Selective Inhibitor of Sphingosine Kinase-2. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2010, 333, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, C.S.; Voelkel-Johnson, C.; Smith, C.D. Targeting Sphingosine Kinases for the Treatment of Cancer. Adv. Cancer Res. 2018, 140, 295–325. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Maines, L.W.; Keller, S.N.; Smith, C.D. Opaganib (ABC294640) Induces Immunogenic Tumor Cell Death and Enhances Checkpoint Antibody Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 16901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynch, K.R.; Thorpe, S.B.; Santos, W.L. Sphingosine kinase inhibitors: A review of patent literature (2006–2015). Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2016, 26, 1409–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickson, M.A.; Carvajal, R.D.; Merrill, A.H.; Gonen, M.; Cane, L.M.; Schwartz, G.K. A Phase I Clinical Trial of Safingol in Combination with Cisplatin in Advanced Solid Tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 2484–2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noack, J.; Choi, J.; Richter, K.; Kopp-Schneider, A.; Régnier-Vigouroux, A. A sphingosine kinase inhibitor combined with temozolomide induces glioblastoma cell death through accumulation of dihydrosphingosine and dihydroceramide, endoplasmic reticulum stress and autophagy. Cell Death Dis. 2014, 5, e1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Peterson, Y.K.; Smith, R.A.; Smith, C.D. Characterization of isoenzyme-selective inhibitors of human sphingosine kinases. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, 44543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kono, K.; Tanaka, M.; Ogita, T.; Hosoya, T.; Kohama, T. F-12509A, a New Sphingosine Kinase Inhibitor, Produced by a Discomycete. J. Antibiot. 2000, 53, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadela-Tomanek, M.; Bębenek, E.; Chrobak, E.; Boryczka, S. 5,8-Quinolinedione Scaffold as a Promising Moiety of Bioactive Agents. Molecules 2019, 24, 4115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadela-Tomanek, M.; Jastrzebska, M.; Chrobak, E.; Bebenek, E.; Latocha, M. Hybrids of 1,4-Quinone with Quinoline Derivatives: Synthesis, Biological Activity, and Molecular Docking with DT-Diaphorase (NQO1). Molecules 2022, 27, 6206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, H.; Specht, S.; Sarite, S.R.; Hoerauf, A.; Krohn, K. New quinoline-5,8-dione and hydroxynaphthoquinone derivatives inhibit a chloroquine resistant Plasmodium falciparum strain. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 54, 936–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, K.-H.; Gambari, R.; Lee, K.K.-H.; Chen, Y.-X.; Kok, S.H.-L.; Wong, R.S.-M.; Lau, F.-Y.; Cheng, C.-H.; Wong, W.-Y.; Bian, Z.-X.; et al. Preparation of 8-hydroxyquinoline derivatives as potential antibiotics against Staphylococcus aureus. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 24, 367–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egu, S.A.; Okoro, U.C.; Onoabedje, E.A. New Aryl Derivatives of Quinolinedione and Related Heterocyclic Compounds. J. Het. Chem. 2017, 54, 1572–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.Y.; Chi, D.Y. Simple preparation of 7-alkylamino-2-methylquinoline-5,8-diones: Regiochemistry in nucleophilic substitution reactions of the 6- or 7-bromo-2-methylquinoline-5,8-dione with amines. Tetrahedron 2004, 60, 4945–4951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez, K.; Espinosa-Bustos, C.; Soto-Delgado, J.; Tapia, R.A.; Varela, J.; Birriel, E.; Segura, R.; Pizarro, J.; Cerecetto, H.; González, M.; et al. New aryloxy-quinone derivatives as potential anti-Chagasic agents: Synthesis, trypanosomicidal activity, electrochemical properties, pharmacophore elucidation and 3D-QSAR analysis. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 65153–65166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verniest, G.; Wang, X.; Kimpe, N.D.; Padwa, A. Heteroaryl Cross-Coupling as an Entry toward the Synthesis of Lavendamycin Analogues: A Model Study. J. Org. Chem. 2010, 75, 424–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priimagi, A.; Cavallo, G.; Metrangolo, P.; Resnati, G. The Halogen Bond in the Design of Functional Supramolecular Materials: Recent Advances. Acc. Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 2686–2695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentry, C.L.; Egleton, R.D.; Gillespie, T.; Abbruscato, T.J.; Bechowski, H.B.; Hruby, V.J.; Davis, T.P. The effect of halogenation on blood–brain barrier permeability of a novel peptide drug. Peptides 1999, 20, 1229–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, P.S. Halogen bonding in medicinal chemistry: From observation to prediction. Future Med. Chem. 2017, 9, 637–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, S.; Milstien, S.; Spiegel, S. A real-time high-throughput fluorescence assay for sphingosine kinases. J. Lipid Res. 2014, 55, 1525–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.B.; Lee, T.; Moon, H.S.; Ki, S.H.; Oh, Y.S.; Lee, J.-Y.; Kim, S.-B.; Park, J.-E.; Kwon, Y.; Kim, S.; et al. Verification of the Necessity of the Tolyl Group of PF-543 for Sphingosine Kinase 1 Inhibitory Activity. Molecules 2020, 25, 2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vettorazzi, M.; Angelina, E.; Lima, S.; Gonec, T.; Otevrel, J.; Marvanova, P.; Padrtova, T.; Mokry, P.; Bobal, P.; Acosta, L.M.; et al. An integrative study to identify novel scaffolds for sphingosine kinase 1 inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 139, 461–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corvino, A.; Rosa, R.; Incisivo, G.M.; Fiorino, F.; Frecentese, F.; Magli, E.; Perissutti, E.; Saccone, E.; Santagada, V.; Cirino, G.; et al. Development of 1,2,3-Triazole-Based Sphingosine Kinase Inhibitors and Their Evaluation as Antiproliferative Agent. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, J.; Kim, S.W.; Kim, S.-B.; Oh, Y.S.; Ki, S.H.; Lee, T.; Kim, S.-B.; Park, T.; Baek, D.J.; Park, E.-Y. Determining the Anticancer Activity of Sphingosine Kinase Inhibitors Containing Heteroatoms in Their Tail Structure. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Sibley, C.D.; Kharel, Y.; Huang, T.; Brown, A.M.; Wonilowicz, L.G.; Bevan, D.R.; Lynch, K.R.; Santos, W.L. Lipophilic tail modifications of 2-(hydroxymethyl)pyrrolidine scaffold reveal dual sphingosine kinase 1 and 2 inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2021, 30, 115941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.B.; Oh, Y.S.; Kim, K.J.; Cho, S.W.; Park, S.K.; Baek, D.J.; Park, E.-Y. Synthesis of PP2A-Activating PF-543 Derivatives and Investigation of Their Inhibitory Effects on Pancreatic Cancer Cells. Molecules 2022, 27, 3346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Knapp, S.; Pyne, N.J.; Pyne, S.; Elkins, J.M. Crystal Structure of Sphingosine Kinase 1 with PF-543. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 5, 1329–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, D.R.; Pyne, S.; Pyne, N.J. Sphingosine Kinases: Emerging Structure-Function Insights. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2016, 41, 395–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, D.R.; Tawati, S.; Berretta, G.; Rivas, P.L.; Baiget, J.; Jiang, Z.; Alsfouk, A.; Mackay, S.P.; Pyne, N.J.; Pyne, S. Topographical Mapping of Isoform-Selectivity Determinants for J-Channel-Binding Inhibitors of Sphingosine Kinases 1 and 2. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 3658–3676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seradj, H.; Cai, W.; Erasga, N.O.; Chenault, D.V.; Knuckles, K.A.; Ragains, J.R.; Behforouz, M. Total Synthesis of Novel 6-Substituted Lavendamycin Antitumor Agents. Org. Lett. 2004, 6, 473–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassani, M.; Cai, W.; Holley, D.C.; Lineswala, J.P.; Maharjan, B.R.; Ebrahimian, G.R.; Seradj, H.; Stocksdale, M.G.; Mohammadi, F.; Marvin, C.C.; et al. Novel Lavendamycin Analogues as Antitumor Agents: Synthesis, in Vitro Cytotoxicity, Structure−Metabolism, and Computational Molecular Modeling Studies with NAD(P)H:Quinone Oxidoreductase 1. J. Med. Chem. 2005, 48, 7733–7749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, W.; Hassani, M.; Karki, R.; Walter, E.D.; Koelsch, K.H.; Seradj, H.; Lineswala, J.P.; Mirzaei, H.; York, J.S.; Olang, F.; et al. Synthesis, metabolism and in vitro cytotoxicity studies on novel lavendamycin antitumor agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 1899–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnute, M.E.; Mcreynolds, M.D.; Carroll, J.; Chrencik, J.; Highkin, M.K.; Iyanar, K.; Jerome, G.; Rains, J.W.; Saabye, M.; Scholten, J.A.; et al. Discovery of a Potent and Selective Sphingosine Kinase 1 Inhibitor through the Molecular Combination of Chemotype-Distinct Screening Hits. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 2562–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korb, O.; Stützle, T.; Exner, T.E. Empirical scoring functions for advanced protein-ligand docking with PLANTS. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2009, 49, 84–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daina, A.; Michielin, O.; Zoete, V. SwissADME: A free web tool to evaluate pharmacokinetics, drug-likeness and medicinal chemistry friendliness of small molecules. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42717–42730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkafaas, S.S.; Elsalahaty, M.I.; Ismail, D.F.; Radwan, M.A.; Elkafas, S.S.; Loutfy, S.A.; Elshazli, R.M.; Baazaoui, N.; Ahmed, A.E.; Hafez, W.; et al. The emerging roles of sphingosine 1-phosphate and SphK1 in cancer resistance: A promising therapeutic target. Cancer Cell Int. 2024, 24, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fer, N.D.; Shoemaker, R.H.; Monks, A. Adaphostin toxicity in a sensitive non-small cell lung cancer model is mediated through Nrf2 signaling and heme oxygenase 1. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 29, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrow, V.; Sturgeon, B. Some Quinoline-5,8-diones. J. Chem. Soc. 1954, 570–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Cancer Institute Developmental Therapeutics Program. NCI-60 Human Tumour Cell Lines Screen. Available online: https://dtp.cancer.gov/discovery_development/nci-60/default.htm (accessed on 11 November 2024).
- Shoemaker, R.H. The NCI60 human tumour cell line anticancer drug screen. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2006, 6, 813–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


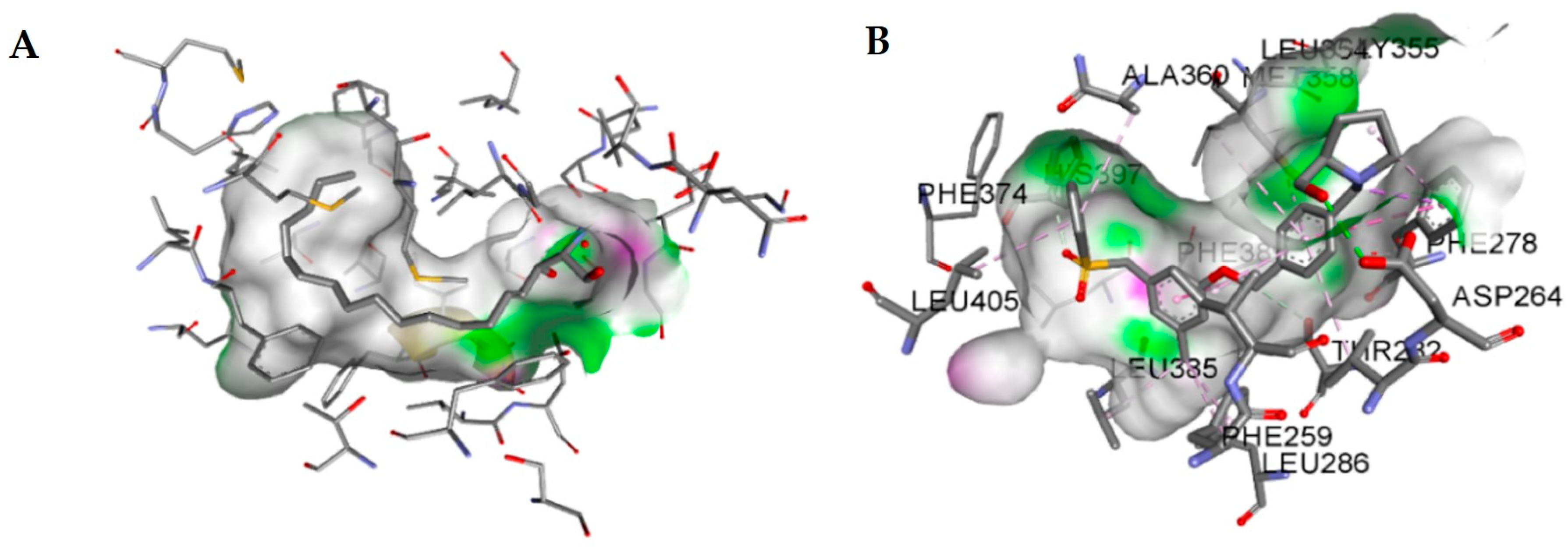

| Entry | Score | CLogP |
|---|---|---|
| PF-543 | −109.2 | 4.75 |
| 6 | −56.5 | 3.29 |
| 21 | −82.7 | 2.41 |
| Compound | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 12 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean Growth (%) 1 | 84.4 | 88.5 | 88.2 | 97.3 | 90.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kruschel, R.D.; Malone, K.; Walsh, A.N.; Waeber, C.; McCarthy, F.O. Discovery of Sphingosine Kinase Inhibition by Modified Quinoline-5,8-Diones. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 268. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18020268
Kruschel RD, Malone K, Walsh AN, Waeber C, McCarthy FO. Discovery of Sphingosine Kinase Inhibition by Modified Quinoline-5,8-Diones. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(2):268. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18020268
Chicago/Turabian StyleKruschel, Ryan D., Kyle Malone, Alison N. Walsh, Christian Waeber, and Florence O. McCarthy. 2025. "Discovery of Sphingosine Kinase Inhibition by Modified Quinoline-5,8-Diones" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 2: 268. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18020268
APA StyleKruschel, R. D., Malone, K., Walsh, A. N., Waeber, C., & McCarthy, F. O. (2025). Discovery of Sphingosine Kinase Inhibition by Modified Quinoline-5,8-Diones. Pharmaceuticals, 18(2), 268. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18020268








