Fingerprint Profile Analysis of Eupolyphaga steleophaga Polypeptide Based on UHPLC-MS and Its Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Method Validation of Eupolyphaga steleophaga Polypeptide Fingerprint
2.1.1. Precision Investigation
2.1.2. Repeatability Investigation
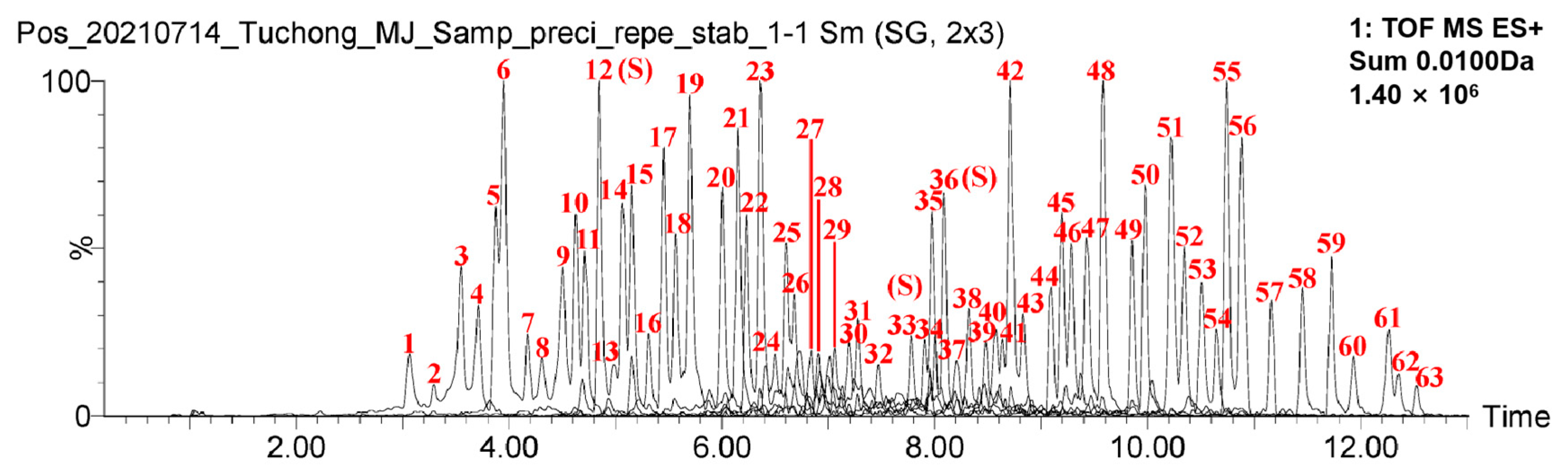
2.1.3. Stability Investigation
2.2. UHPLC-MS Detection of Eupolyphaga steleophaga Polypeptide Fingerprint
2.3. Application
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Methods
4.2.1. Preparation of Simulated Gastric Juice
4.2.2. Preparation of Eupolyphaga steleophaga Enzymolysis Polypeptide Test Solution
4.2.3. Chromatographic Conditions
4.2.4. MS Conditions
4.2.5. Screening and Identification of Eupolyphaga steleophaga Enzymolysis Polypeptides
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, Y.; Zhan, Y.; Zhang, D.; Dai, B.; Ma, W.; Qi, J.; Liu, R.; He, L. Eupolyphaga sinensis walker displays inhibition on hepatocellular carcinoma through regulating cell growth and metastasis signaling. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 5518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Huis, A. Edible insects: Challenges and prospects. Entomol. Res. 2022, 52, 161–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancini, S.; Riccioli, F.; Tzompa-Sosa, D.A.; Moruzzo, R.; Schouteten, J.J.; Liu, A.; Li, J.; Menozzi, D.; Sogari, G. Exploring the intention to consume whole vs processed edible insects: Insights from traditional and non-traditional entomophagy countries. J. Agric. Food Res. 2024, 18, 101532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission. Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China; The Medicine Science and Technology Press of China: Beijing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, H.J.; Xu, T.; Yan, Y.M.; Tu, Z.C.; Cheng, Y.X. Neolignans and Norlignans from Insect Medicine Polyphaga plancyi and Their Biological Activities. Nat. Prod. Bioprospect. 2021, 11, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, X.; Shao, B.H.; Wei, X.; Wang, H.H.; Chen, X.; Zhao, T.T.; Wang, C.M. Tubiechong: A review on ethnomedicinal uses, bioactive chemical constituents and pharmacological activities. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 298, 115642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, J.; Zhang, D.; Liu, C.; Wang, L. A periodic review of chemical and pharmacological profiles of Tubiechong as insect Chinese medicine. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 33952–33968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.N.; Ruan, L.J.; Jiang, X.; Song, Z.J.; Wei, K.H.; Qin, S.S.; Liang, Y.; Hou, X.L.; Wang, X.J.; Miao, J.H. Overview of research and development of polypeptide drugs and traditional Chinese medicine-peptides. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 2022, 47, 5978–5990. [Google Scholar]
- Dolton, G.; Bulek, A.; Wall, A.; Thomas, H.; Hopkins, J.R.; Rius, C.; Galloway, S.A.; Whalley, T.; Tan, L.R.; Morin, T.; et al. HLA A*24:02-restricted T cell receptors cross-recognize bacterial and preproinsulin peptides in type 1 diabetes. J. Clin. Investig. 2024, 134, e164535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allemann, A.; Staubli, S.M.; Nebiker, C.A. Trypsin and Trypsinogen Activation Peptide in the Prediction of Severity of Acute Pancreatitis. Life 2024, 14, 1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Zhao, Y.; Shi, Y.; Chen, R.; Fu, X.; Zhao, Y. Polypeptides extracted from Eupolyphaga sinensis walker via enzymic digestion alleviate UV radiation-induced skin photoaging. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 112, 108636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Wang, J.; Chen, J.; Peng, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Kaplan, D.L.; Wang, Q. Challenges and opportunities in delivering oral peptides and proteins. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2023, 20, 1349–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Z.; Zhu, X.; Zhou, Y.; Wu, J.; Cao, M.; Hu, C.; Yu, L.; Xu, R.; Chen, Z. Polypeptides from traditional Chinese medicine: Comprehensive review of perspective towards cancer management. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 260 Pt 1, 129423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.X.; Wu, N.; Wei, J.T.; Liu, J.; Zhao, J.; Ji, A.G.; Lin, X.K. A novel protein from Eupolyphaga sinensis inhibits adhesion, migration, and invasion of human lung cancer A549 cells. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2013, 91, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, X.M.; Guo, J.L.; Chen, L.; Ho, P.C.L. Application for proteomics analysis technology in studying animal-derived traditional Chinese medicine: A review. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2020, 191, 113609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, H.J. The Annotated Catalogue of Famous Physicians; People’s Medical Publishing House: Beijing, China, 1986; Volume 6. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.Z. The Compendium of Materia Medica; Heilongjiang Science and Technology Press: Harbin, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Su, J. Tang Materia Medica; Anhui Science and Technology Publishing House: Hefei, China, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y. Identification of Eupolyphaga steleophaga and their adulterants. Chin. J. Clin. Res. 2011, 24, 529–539. [Google Scholar]
- Albenzio, M.; Santillo, A.; Caroprese, M.; Della Malva, A.; Marino, R. Bioactive Peptides in Animal Food Products. Foods 2017, 6, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michelfelder, A.J. Soy: A complete source of protein. Am. Fam. Physician 2009, 79, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Toldrá, F.; Mora, L. Proteins and Bioactive Peptides in High Protein Content Foods. Foods 2021, 10, 1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marciniak, A.; Suwal, S.; Naderi, N.; Pouliot, Y.; Doyen, A. Enhancing enzymatic hydrolysis of food proteins and production of bioactive peptides using high hydrostatic pressure technology. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 80, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbarian, M.; Khani, A.; Eghbalpour, S.; Uversky, V.N. Bioactive Peptides: Synthesis, Sources, Applications, and Proposed Mechanisms of Action. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, A.C.; Harris, J.L.; Khanna, K.K.; Hong, J.H. A Comprehensive Review on Current Advances in Peptide Drug Development and Design. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, J.L.; Dunn, M.K. Therapeutic peptides: Historical perspectives, current development trends, and future directions. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2018, 26, 2700–2707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Z.; Mondor, M.; Goycoolea, V.F.; Hernández-Álvarez, A.J. Current state of insect proteins: Extraction technologies, bioactive peptides and allergenicity of edible insect proteins. Food Funct. 2023, 14, 8129–8156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasicka, V. Analysis of amino acids and peptides by separation and mass spectrometric methods. J. Sep. Sci. 2010, 33, 2383–2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Lv, X.; Li, B.; Liu, L.; Yu, C.; Cheng, H.; Zhou, J.; Zhu, Y.; Ma, H. Identification of peptides of cinobufacini by gel filter chromatography and peptidomics. J. Sep. Sci. 2022, 45, 2845–2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ren, Y.; Wang, L.; Huang, Z. Analysis of A1-type and A2-type β-casein in Maiwa Yak and Pien-niu milk by HPLC-high-resolution MS and tandem MS. J. Sep. Sci. 2021, 44, 1913–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, W.; Matsui, T. Current knowledge of intestinal absorption of bioactive peptides. Food Funct. 2017, 8, 4306–4314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Dong, P.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Li, H.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Dai, L.; Wang, S. Active Peptide AR-9 From Eupolyphaga sinensis Reduces Blood Lipid and Hepatic Lipid Accumulation by Restoring Gut Flora and Its Metabolites in a High Fat Diet-Induced Hyperlipidemia Rat. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 918505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, J.; Dong, P.; Li, H.; Xu, J.; Li, H.; Yu, Y.; Dai, L.; Gao, P.; Wang, S.; Zhang, J. Study on lipid-lowering mechanism of active peptide DP17 from Eupolyphaga steleophaga in hyperlipidemia rats. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 2020, 45, 5265–5272. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dong, P.; Wang, H.; Li, Y.; Yu, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Dai, L.; Wang, S. Active peptides from Eupolyphaga sinensis walker attenuates experimental hyperlipidemia by regulating the gut microbiota and biomarkers in rats with dyslipidemia. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 170, 116064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, G.F.; Yu, C.H.; Yu, B.; Shen, Z.H.; Zhang, D.L.; Wu, Q.F. Antitumor effects and chemical compositions of Eupolyphaga sinensis Walker ethanol extract. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2012, 141, 178–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.S.; Jin, S.; Park, J.Y.; Kim, S.Y. Scoping review of the medicinal effects of Eupolyphaga sinensis Walker and the underlying mechanisms. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 296, 115454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Sun, H.; Fang, H.; Yang, L.; Zhao, Q.; Sun, Y.; Yan, G.; Han, Y.; Wang, X. Fingerprint profile analysis of hirudo polypeptide based on UHPLC–MS and its application. Sep. Sci. Plus 2024, 7, e202300218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lai, X.; Song, H.; Yan, G.; Ren, J.; Wang, X. Fingerprint Profile Analysis of Eupolyphaga steleophaga Polypeptide Based on UHPLC-MS and Its Application. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 166. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18020166
Lai X, Song H, Yan G, Ren J, Wang X. Fingerprint Profile Analysis of Eupolyphaga steleophaga Polypeptide Based on UHPLC-MS and Its Application. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(2):166. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18020166
Chicago/Turabian StyleLai, Xin, Hongwei Song, Guangli Yan, Junling Ren, and Xijun Wang. 2025. "Fingerprint Profile Analysis of Eupolyphaga steleophaga Polypeptide Based on UHPLC-MS and Its Application" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 2: 166. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18020166
APA StyleLai, X., Song, H., Yan, G., Ren, J., & Wang, X. (2025). Fingerprint Profile Analysis of Eupolyphaga steleophaga Polypeptide Based on UHPLC-MS and Its Application. Pharmaceuticals, 18(2), 166. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18020166






