Distinct Swimming Behavioral Phenotypes Following Serotonin and Dopamine Transporter Modulation in the Adult Zebrafish Novel Tank Diving Test (NTT)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
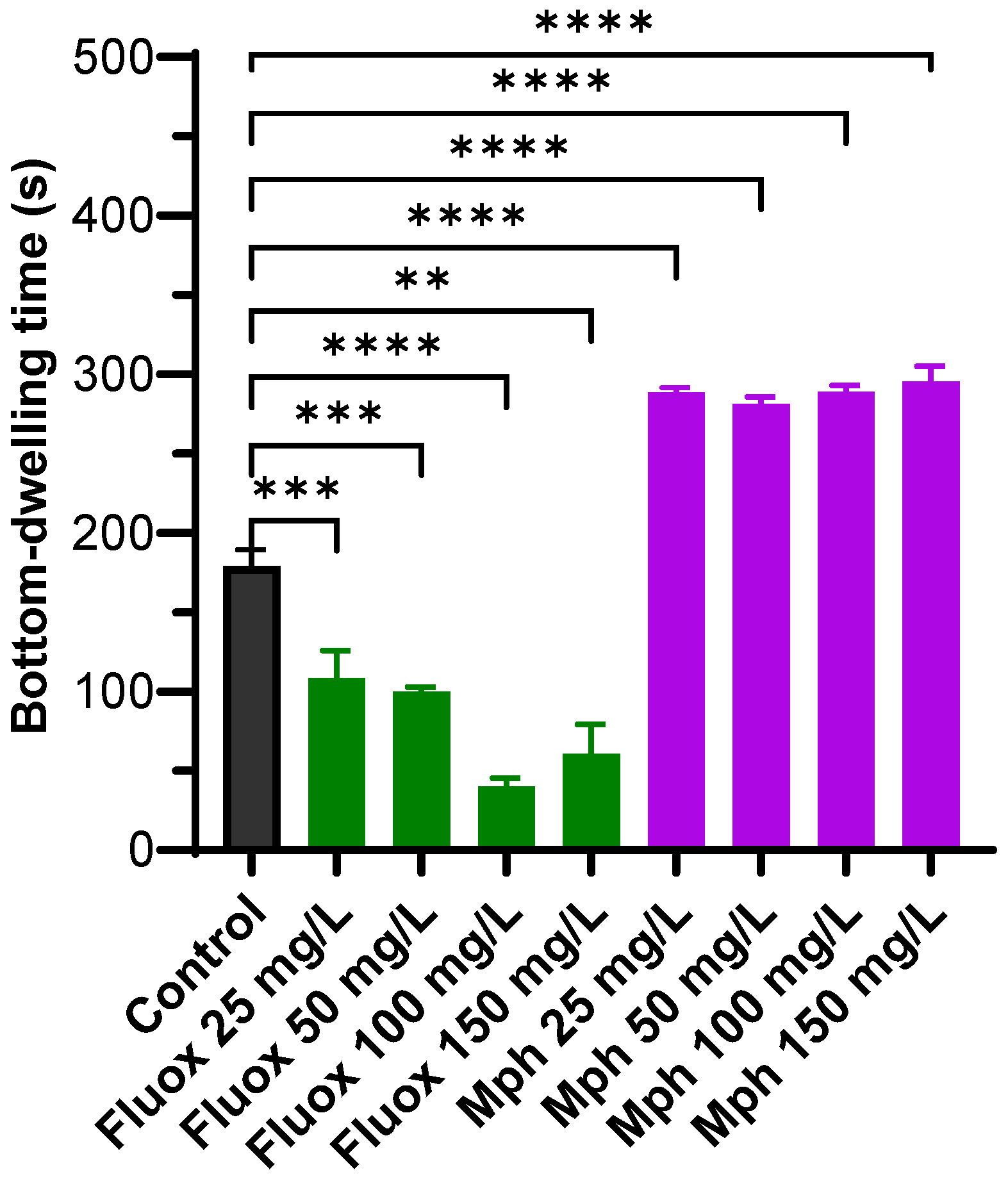
2.1. Bottom-Dwelling Time
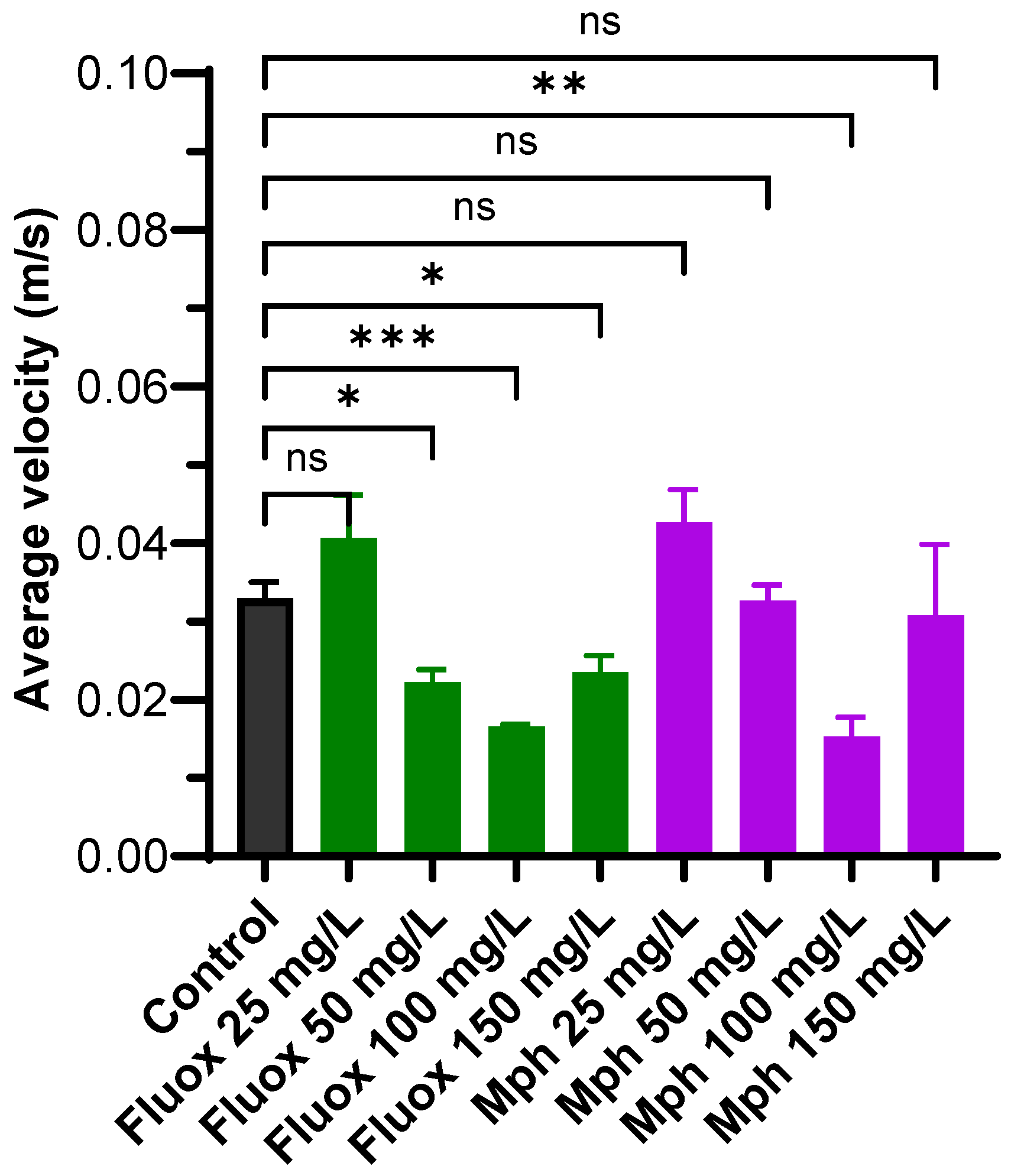
2.2. Average Velocity
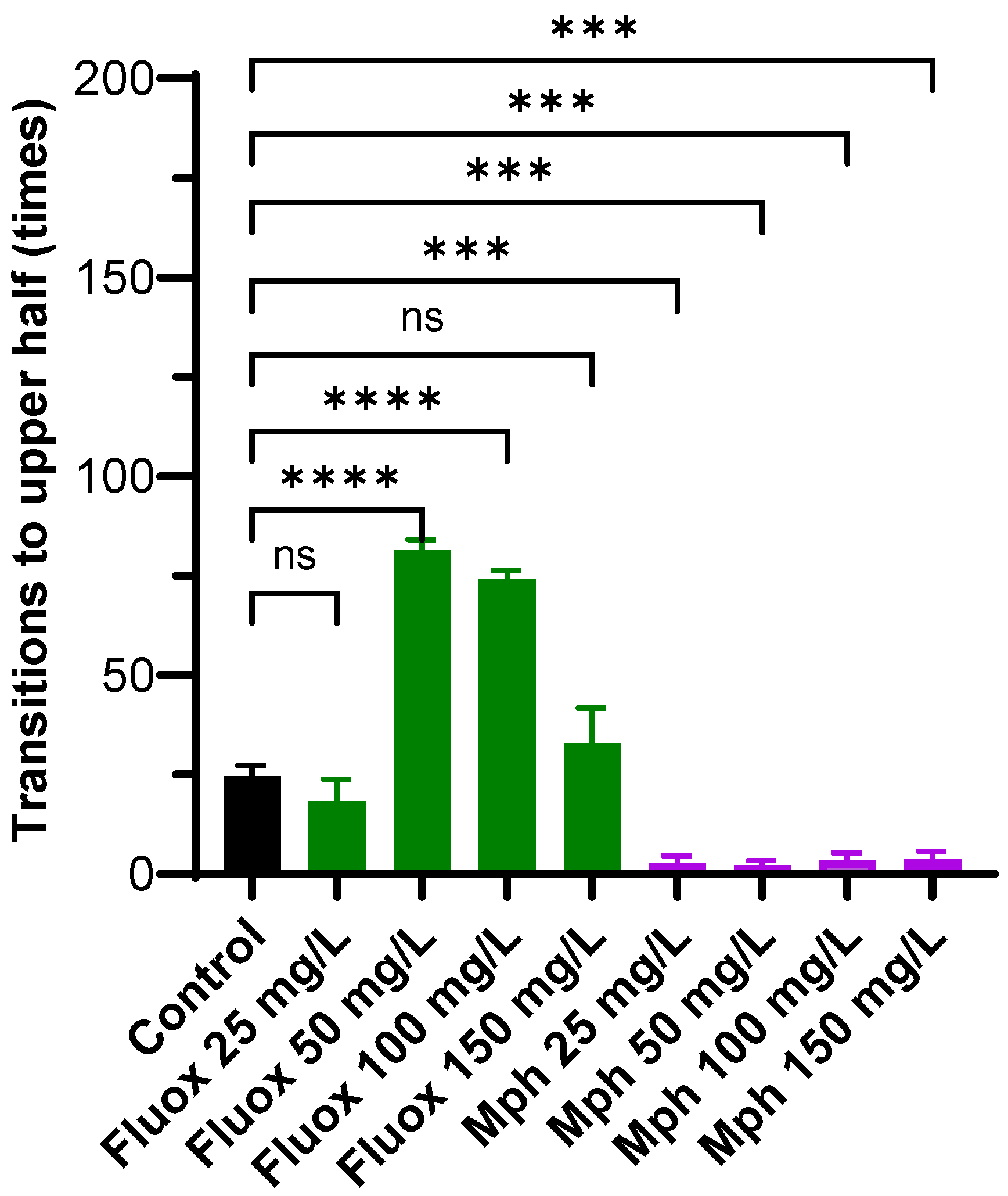
2.3. Transitions to the Upper Half
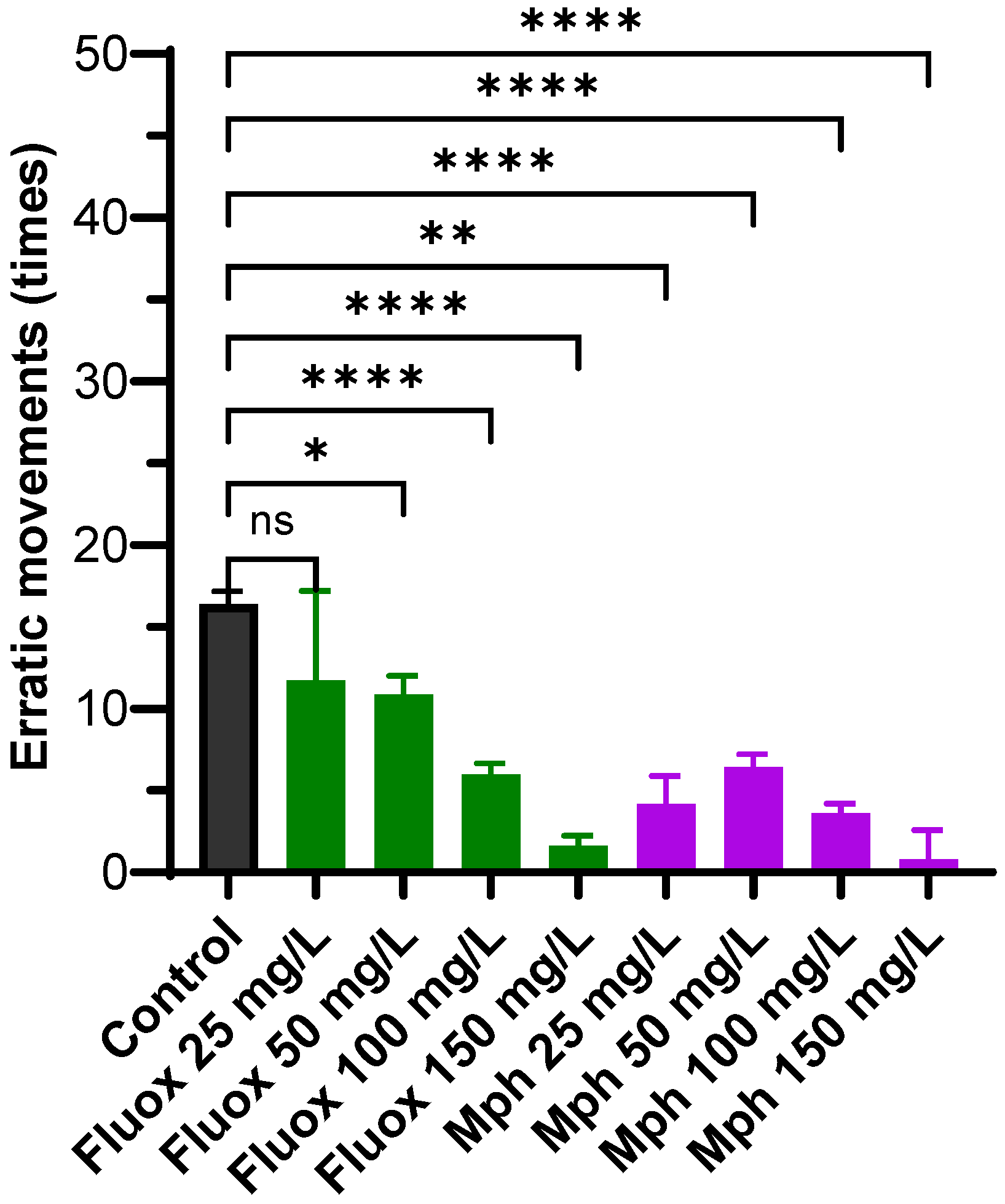
2.4. Erratic Movements
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Drugs and Treatment
4.3. Novel Tank Diving Test
4.4. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kandel, E.R.; Koester, J.D.; Mack, S.H.; Siegelbaum, S.A. Principles of Neural Science, 6th ed.; Kandel, E.R., Koester, J.D., Mack, S.H., Siegelbaum, S.A., Eds.; McGraw Hill: Columbus, OH, USA, 2021; ISBN 978-1-25-964224-1. [Google Scholar]
- Squire, L.R.; Berg, D.; Bloom, F.E.; du Lac, S.; Ghosh, A.; Spitzer, N.C. Fundamental Neuroscience, 4th ed.; Squire, L.R., Ed.; Academic Press: Oakland, CA, USA, 2014; ISBN 9780123858702. [Google Scholar]
- Speranza, L.; di Porzio, U.; Viggiano, D.; de Donato, A.; Volpicelli, F. Dopamine: The Neuromodulator of Long-Term Synaptic Plasticity, Reward and Movement Control. Cells 2021, 10, 735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slavova, D.; Ortiz, V.; Blaise, M.; Bairachnaya, M.; Giros, B.; Isingrini, E. Role of the Locus Coeruleus-Noradrenergic System in Stress-Related Psychopathology and Resilience: Clinical and Pre-Clinical Evidences. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2024, 167, 105925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes, B.A.S. The Locus Coeruleus: Anatomy, Physiology, and Stress-Related Neuropsychiatric Disorders. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2025, 61, e70111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fröhlich, F. Network Neuroscience, 1st ed.; Press, A., Ed.; Elsevier: San Diego, CA, USA, 2016; ISBN 9780128015605. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, J.; Liu, W.; Guan, J.; Cui, J.; Shi, R.; Wang, L.; Chen, D.; Liu, Y. Latest Updates on the Serotonergic System in Depression and Anxiety. Front. Synaptic Neurosci. 2023, 15, 1124112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teleanu, R.I.; Niculescu, A.G.; Roza, E.; Vladâcenco, O.; Grumezescu, A.M.; Teleanu, D.M. Neurotransmitters—Key Factors in Neurological and Neurodegenerative Disorders of the Central Nervous System. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristensen, A.S.; Andersen, J.; Jørgensen, T.N.; Sørensen, L.; Eriksen, J.; Loland, C.J.; Strømgaard, K.; Gether, U. SLC6 Neurotransmitter Transporters: Structure, Function, and Regulation. Pharmacol. Rev. 2011, 63, 585–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pramod, A.B.; Foster, J.; Carvelli, L.; Henry, L.K. SLC6 Transporters: Structure, Function, Regulation, Disease Association and Therapeutics. Mol. Asp. Med. 2013, 34, 197–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Zou, D.; Li, Y.; Gu, S.; Dong, J.; Ma, X.; Xu, S.; Wang, F.; Huang, J.H. Monoamine Neurotransmitters Control Basic Emotions and Affect Major Depressive Disorders. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, D.T.; Horng, J.S.; Bymaster, F.P.; Hauser, K.L.; Molloy, B.B. A Selective Inhibitor of Serotonin Uptake: Lilly 110140, 3-(p-Trifluoromethylphenoxy)-n-Methyl-3-Phenylpropylamine. Life Sci. 1974, 15, 471–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuller, R.W.; Perry, K.W.; Molloy, B.B. Effect of an Uptake Inhibitor on Serotonin Metabolism in Rat Brain: Studies with 3-(p-Trifluoromethylphenoxy)-n-Methyl-3-Phenylpropylamine (Lilly 110140). Life Sci. 1974, 15, 1161–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, D.T.; Perry, K.W.; Bymaster, F.P. The Discovery of Fluoxetine Hydrochloride (Prozac). Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2005, 4, 764–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birmaher, B.; Axelson, D.A.; Monk, K.; Kalas, C.; Clark, D.B.; Ehmann, M.; Bridge, J.; Heo, J.; Brent, D.A. Fluoxetine for the Treatment of Childhood Anxiety Disorders. J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2003, 42, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birmaher, B.; Waterman, G.S.; Ryan, N.; Cully, M.; Balach, L.; Ingram, J.; Brodsky, M. Fluoxetine for Childhood Anxiety Disorders. J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 1994, 33, 993–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slee, A.; Nazareth, I.; Bondaronek, P.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, Z.; Freemantle, N. Pharmacological Treatments for Generalised Anxiety Disorder: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. Lancet 2019, 393, 768–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kryst, J.; Majcher-Maślanka, I.; Chocyk, A. Effects of Chronic Fluoxetine Treatment on Anxiety- and Depressive-like Behaviors in Adolescent Rodents—Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Pharmacol. Rep. 2022, 74, 920–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tollefson, G.D.; Holman, S.L.; Sayler, M.E.; Potvin, J.H. Fluoxetine, Placebo, and Tricyclic Antidepressants in Major Depression with and without Anxious Features. J. Clin. Psychiatry 1994, 55, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Panizzon, L. La Preparazione Di Piridil- e Piperidil-arilacetonitrili e Di Alcuni Prodotti Di Trasformazione (Parte I A). Helv. Chim. Acta 1944, 27, 1748–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morton, W.A.; Stock, G.G. Methylphenidate Abuse and Psychiatric Side Effects. Prim. Care Companion, J. Clin. Psychiatry 2000, 2, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silczuk, A.; Lewandowska, A.; Filip, M.; Atroszko, P.A.; Podolec, J.; Gałecka, M.; Madejek, R.; Czyżewski, Ł. Current Insights into the Safety and Adverse Effects of Methylphenidate in Children, Adolescents, and Adults—Narrative Review. Pharmacol. Rep. 2025, 77, 1247–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storebø, O.J.; Storm, M.R.O.; Pereira Ribeiro, J.; Skoog, M.; Groth, C.; Callesen, H.E.; Schaug, J.P.; Darling Rasmussen, P.; Huus, C.-M.L.; Zwi, M.; et al. Methylphenidate for Children and Adolescents with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD). Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2023, 2023, CD009885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorpy, M.J.; Bogan, R.K. Update on the Pharmacologic Management of Narcolepsy: Mechanisms of Action and Clinical Implications. Sleep Med. 2020, 68, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, K.R.; Kahlon, C.H.; Brown, J.N.; Britt, R.B. Methylphenidate Use in Geriatric Depression: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2021, 36, 1304–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theleritis, C.; Siarkos, K.; Katirtzoglou, E.; Politis, A. Pharmacological and Nonpharmacological Treatment for Apathy in Alzheimer Disease: A systematic review across modalities. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry Neurol. 2017, 30, 26–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilieva, I.P.; Hook, C.J.; Farah, M.J. Prescription Stimulants’ Effects on Healthy Inhibitory Control, Working Memory, and Episodic Memory: A Meta-Analysis. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2015, 27, 1069–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trenque, T.; Herlem, E.; Taam, M.A.; Drame, M. Methylphenidate Off-Label Use and Safety. SpringerPlus 2014, 3, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Docherty, J.R.; Alsufyani, H.A. Pharmacology of Drugs Used as Stimulants. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2021, 61, S53–S69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shellenberg, T.P.; Stoops, W.W.; Lile, J.A.; Rush, C.R. An Update on the Clinical Pharmacology of Methylphenidate: Therapeutic Efficacy, Abuse Potential and Future Considerations. Expert Rev. Clin. Pharmacol. 2020, 13, 825–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gatley, S.J.; Pan, D.; Chen, R.; Chaturvedi, G.; Ding, Y.-S. Affinities of Methylphenidate derivatives for dopamine, norepinephrine and serotonin transporters. Life Sci. 1996, 58, PL231–PL239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozzi, M.; Carnovale, C.; Peeters, G.G.; Gentili, M.; Antoniazzi, S.; Radice, S.; Clementi, E.; Nobile, M. Adverse Drug Events Related to Mood and Emotion in Paediatric Patients Treated for ADHD: A Meta-Analysis. J. Affect. Disord. 2018, 238, 161–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Froehlich, T.E.; Brinkman, W.B.; Peugh, J.L.; Piedra, A.N.; Vitucci, D.J.; Epstein, J.N. Pre-Existing Comorbid Emotional Symptoms Moderate Short-Term Methylphenidate Adverse Effects in a Randomized Trial of Children with Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder. J. Child Adolesc. Psychopharmacol. 2020, 30, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloch, Y.; Aviram, S.; Segev, A.; Nitzan, U.; Levkovitz, Y.; Braw, Y.; Bloch, A.M. Methylphenidate Reduces State Anxiety During a Continuous Performance Test That Distinguishes Adult ADHD Patients from Controls. J. Atten. Disord. 2017, 21, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kritchman, M.; Koubi, M.; Bloch, A.M.; Bloch, Y. Effect of Methylphenidate on State Anxiety in Children With ADHD-A Single Dose, Placebo Controlled, Crossover Study. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolder, P.C.; Müller, F.; Schmid, Y.; Borgwardt, S.J.; Liechti, M.E. Direct Comparison of the Acute Subjective, Emotional, Autonomic, and Endocrine Effects of MDMA, Methylphenidate, and Modafinil in Healthy Subjects. Psychopharmacology 2018, 235, 467–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaillard, C.; Lago, T.R.; Gorka, A.X.; Balderston, N.L.; Fuchs, B.A.; Reynolds, R.C.; Grillon, C.; Ernst, M. Methylphenidate Modulates Interactions of Anxiety with Cognition. Transl. Psychiatry 2021, 11, 544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, A.M.S.; Avilés, Á.G.; Gascó, H.A.; Arias, J.S.; Bordonau, F.E.O. Efectos Del Metilfenidato Sobre La Ansiedad. Rev. De Neurol. 2012, 55, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jager, A.; Kanters, D.; Geers, F.; Buitelaar, J.K.; Kozicz, T.; Glennon, J.C. Methylphenidate Dose-Dependently Affects Aggression and Improves Fear Extinction and Anxiety in BALB/CJ Mice. Front. Psychiatry 2019, 10, 768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howe, K.; Clark, M.D.; Torroja, C.F.; Torrance, J.; Berthelot, C.; Muffato, M.; Collins, J.E.; Humphray, S.; McLaren, K.; Matthews, L.; et al. The Zebrafish Reference Genome Sequence and Its Relationship to the Human Genome. Nature 2013, 496, 498–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, Y.M.; Toro, S.; Ramachandran, S.; Ruzicka, L.; Howe, D.G.; Eagle, A.; Kalita, P.; Martin, R.; Moxon, S.A.T.; Schaper, K.; et al. Zebrafish Models of Human Disease: Gaining Insight into Human Disease at ZFIN. ILAR J. 2017, 58, 4–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalueff, A.V.; Stewart, A.M.; Gerlai, R. Zebrafish as an Emerging Model for Studying Complex Brain Disorders. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2014, 35, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalueff, A.V.; Gebhardt, M.; Stewart, A.M.; Cachat, J.M.; Brimmer, M.; Chawla, J.S.; Craddock, C.; Kyzar, E.J.; Roth, A.; Landsman, S.; et al. Towards a Comprehensive Catalog of Zebrafish Behavior 1.0 and beyond. Zebrafish 2013, 10, 70–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, J.; Oliveri, A.; Levin, E.D. Zebrafish model systems for developmental neurobehavioral toxicology. Birth Defects Res. Part C Embryo Today Rev. 2013, 99, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, R.G.; Oliveri, A.N.; Sinnott-Armstrong, W.; Levin, E.D. Effects of sub-chronic Methylphenidate on risk-taking and sociability in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2020, 393, 1373–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ninkovic, J.; Folchert, A.; Makhankov, Y.V.; Neuhauss, S.C.; Sillaber, I.; Straehle, U.; Bally-Cuif, L. Genetic Identification of AChE as a Positive Modulator of Addiction to the Psychostimulant D-Amphetamine in Zebrafish. J. Neurobiol. 2006, 66, 463–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, E.D.; Bencan, Z.; Cerutti, D.T. Anxiolytic Effects of Nicotine in Zebrafish. Physiol. Behav. 2007, 90, 54–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frizzo, I.B.; Koakoski, G.; Freddo, N.; Maffi, V.C.; Bertol, C.D.; Barcellos, L.J.G.; Rossato-Grando, L.G. Chronic Exposure to Methylphenidate—Contaminated Water Elicits Social Impairment to Zebrafish. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2020, 80, 103473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farías-Cea, A.; Leal, C.; Hödar-Salazar, M.; Esparza, E.; Martínez-Duran, L.; Fuentes, I.; Iturriaga-Vásquez, P. Behavioral Study of 3- and 5-Halocytisine Derivatives in Zebrafish Using the Novel Tank Diving Test (NTT). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalueff, A.V.; Kaluyeva, A.; Maillet, E.L. Anxiolytic-like Effects of Noribogaine in Zebrafish. Behav. Brain Res. 2017, 330, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volgin, A.D.; Yakovlev, O.A.; Demin, K.A.; Alekseeva, P.A.; Kalueff, A.V. Acute Behavioral Effects of Deliriant Hallucinogens Atropine and Scopolamine in Adult Zebrafish. Behav. Brain Res. 2019, 359, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mocelin, R.; Marcon, M.; Araujo, A.S.D.R.; Herrmann, A.P.; Piato, A. Withdrawal Effects Following Repeated Ethanol Exposure Are Prevented by N-Acetylcysteine in Zebrafish. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2019, 93, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCammon, J.M.; Sive, H. Challenges in understanding psychiatric disorders and developing therapeutics: A role for zebrafish. Dis. Model. Mech. 2015, 8, 647–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.R.; Strupp, B.J. Animal Models of Childhood Exposure to Lead or Manganese: Evidence for Impaired Attention, Impulse Control, and Affect Regulation and Assessment of Potential Therapies. Neurotherapeutics 2023, 20, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norton, W.H.; Folchert, A.; Bally-Cuif, L. Comparative Analysis of Serotonin Receptor (HTR1A/HTR1B Families) and Transporter (Slc6a4a/b) Gene Expression in the Zebrafish Brain. J. Comp. Neurol. 2008, 511, 521–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, M.O.; Brock, A.J.; Walton, R.T.; Brennan, C.H. The Role of Zebrafish (Danio rerio) in Dissecting the Genetics and Neural Circuits of Executive Function. Front. Neural Circuits 2013, 7, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, K.M.; Collier, A.D.; Meshalkina, D.A.; Kysil, E.V.; Khatsko, S.L.; Kolesnikova, T.; Morzherin, Y.Y.; Warnick, J.E.; Kalueff, A.V.; Echevarria, D.J. Zebrafish Models in Neuropsychopharmacology and CNS Drug Discovery. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 174, 1925–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillman, C.; Fontana, B.D.; Amstislavskaya, T.G.; Gorbunova, M.A.; Altenhofen, S.; Barthelson, K.; Bastos, L.M.; Borba, J.V.; Bonan, C.D.; Brennan, C.H.; et al. Housing and Husbandry Factors Affecting Zebrafish Novel Tank Test Responses: A Global Multi-Laboratory Study. Lab Anim. 2025, 54, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cachat, J.; Stewart, A.; Grossman, L.; Gaikwad, S.; Kadri, F.; Chung, K.M.; Wu, N.; Wong, K.; Roy, S.; Suciu, C.; et al. Measuring Behavioral and Endocrine Responses to Novelty Stress in Adult Zebrafish. Nat. Protoc. 2010, 5, 1786–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haghani, S.; Karia, M.; Cheng, R.-K.; Mathuru, A.S. An Automated Assay System to Study Novel Tank Induced Anxiety. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontana, B.D.; Alnassar, N.; Parker, M.O. The Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Anxiety Test Battery: Comparison of Behavioral Responses in the Novel Tank Diving and Light–Dark Tasks Following Exposure to Anxiogenic and Anxiolytic Compounds. Psychopharmacology 2022, 239, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viscarra, F.; González-Gutierrez, J.; Esparza, E.; Figueroa, C.; Paillali, P.; Hödar-Salazar, M.; Cespedes, C.; Quiroz, G.; Sotomayor-Zárate, R.; Reyes-Parada, M.; et al. Nicotinic Antagonist UFR2709 Inhibits Nicotine Reward and Decreases Anxiety in Zebrafish. Molecules 2020, 25, 2998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egan, R.J.; Bergner, C.L.; Hart, P.C.; Cachat, J.M.; Canavello, P.R.; Elegante, M.F.; Elkhayat, S.I.; Bartels, B.K.; Tien, A.K.; Tien, D.H.; et al. Understanding Behavioral and Physiological Phenotypes of Stress and Anxiety in Zebrafish. Behav. Brain Res. 2009, 205, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, A.; Wu, N.; Cachat, J.; Hart, P.; Gaikwad, S.; Wong, K.; Utterback, E.; Gilder, T.; Kyzar, E.; Newman, A.; et al. Pharmacological Modulation of Anxiety-like Phenotypes in Adult Zebrafish Behavioral Models. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2011, 35, 1421–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minz, R.; Sharma, P.K. Blunted Cortisol and Altered Antioxidant Defense as Biomarkers of Systemic Stress in Hyperglycemic Zebrafish. Acta Diabetol. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudock, J.; Kenney, J.W. Aging in Zebrafish Is Associated with Reduced Locomotor Activity and Strain Dependent Changes in Bottom Dwelling and Thigmotaxis. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0300227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontana, B.D.; Parker, M.O. The Larval Diving Response (LDR): Validation of an Automated, High-Throughput, Ecologically Relevant Measure of Anxiety-Related Behavior in Larval Zebrafish (Danio rerio). J. Neurosci. Methods 2022, 381, 109706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evsiukova, V.S.; Bazovkina, D.; Bazhenova, E.; Kulikova, E.A.; Kulikov, A.V. Tryptophan Hydroxylase 2 Deficiency Modifies the Effects of Fluoxetine and Pargyline on the Behavior, 5-HT- and BDNF-Systems in the Brain of Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valcarce, D.G.; Martínez-Vázquez, J.M.; Riesco, M.F.; Robles, V. Probiotics Reduce Anxiety-Related Behavior in Zebrafish. Heliyon 2020, 6, e03973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacomini, A.C.V.; Abreu, M.S.; Giacomini, L.V.; Siebel, A.M.; Zimerman, F.F.; Rambo, C.L.; Mocelin, R.; Bonan, C.D.; Piato, A.L.; Barcellos, L.J. Fluoxetine and Diazepam Acutely Modulate Stress Induced-Behavior. Behav. Brain Res. 2016, 296, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Airhart, M.J.; Lee, D.H.; Wilson, T.D.; Miller, B.E.; Miller, M.N.; Skalko, R.G. Movement Disorders and Neurochemical Changes in Zebrafish Larvae after Bath Exposure to Fluoxetine (PROZAC). Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2007, 29, 652–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faria, M.; Prats, E.; Bellot, M.; Gomez-Canela, C.; Raldúa, D. Pharmacological Modulation of Serotonin Levels in Zebrafish Larvae: Lessons for Identifying Environmental Neurotoxicants Targeting the Serotonergic System. Toxics 2021, 9, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parolini, M.; Ghilardi, A.; De Felice, B.; Del Giacco, L. Environmental Concentration of Fluoxetine Disturbs Larvae Behavior and Increases the Defense Response at Molecular Level in Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 34943–34952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atzei, A.; Jense, I.; Zwart, E.; Legradi, J.; Venhuis, B.J.; van der Ven, L.T.M.; Heusinkveld, H.J.; Hessel, E.V.S. Developmental Neurotoxicity of Environmentally Relevant Pharmaceuticals and Mixtures Thereof in a Zebrafish Embryo Behavioural Test. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 6717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singer, M.L.; Oreschak, K.; Rhinehart, Z.; Robison, B.D. Anxiolytic Effects of Fluoxetine and Nicotine Exposure on Exploratory Behavior in Zebrafish. PeerJ 2016, 4, e2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkatachalam, A.B.; Levesque, B.; Achenbach, J.C.; Pappas, J.J.; Ellis, L.D. Long and Short Duration Exposures to the Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs) Fluoxetine, Paroxetine and Sertraline at Environmentally Relevant Concentrations Lead to Adverse Effects on Zebrafish Behaviour and Reproduction. Toxics 2023, 11, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vera-Chang, M.N.; St-Jacques, A.D.; Lu, C.; Moon, T.W.; Trudeau, V.L. Fluoxetine Exposure During Sexual Development Disrupts the Stress Axis and Results in Sex- and Time- Dependent Effects on the Exploratory Behavior in Adult Zebrafish Danio rerio. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Shuraiqi, A.; Barry, M.J. Urban stressors: Interactive effects of noise, light regime and Fluoxetine on zebrafish behavior. Sci. Total. Environ. 2025, 972, 179101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebauer, D.L.; Pagnussat, N.; Piato, Â.L.; Schaefer, I.C.; Bonan, C.D.; Lara, D.R. Effects of anxiolytics in zebrafish: Similarities and differences between benzodiazepines, buspirone and ethanol. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2011, 99, 480–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maximino, C.; da Silva, A.W.B.; Araújo, J.; Lima, M.G.; Miranda, V.; Puty, B.; Benzecry, R.; Picanço-Diniz, D.L.W.; Gouveia, A.; Oliveira, K.R.M.; et al. Fingerprinting of Psychoactive Drugs in Zebrafish Anxiety-Like Behaviors. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e103943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guedes, J.M.; Ferreira, M.K.A.; Oliveira, L.S.; da Silva, A.W.; de Menezes, J.E.S.A.; Bandeira, P.N.; Teixeira, A.M.R.; Marinho, E.M.; Marinho, M.M.; Marinho, E.S.; et al. Anxiolytic-like Effect in Adult Zebrafish (Danio rerio) through GABAergic System and Molecular Docking Study of Chalcone (E)-1-(2-hydroxy-3,4,6-trimethoxyphenyl)-3-(4-methoxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2022, 13, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, T.R.; Freire, P.d.T.C.; da Silva, A.W.; Ferreira, M.K.A.; Rebouças, E.d.L.; Mendes, F.R.S.; Marinho, E.M.; Marinho, M.M.; Teixeira, A.M.R.; Marinho, E.S.; et al. Anxiolytic and anticonvulsant effect of Ibuprofen derivative through GABAergic neuromodulation in adult Zebrafish. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2023, 41, 12055–12062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacomini, A.C.; Scolari, N.; Marcon, L.; Bueno, B.W.; dos Santos, B.E.; Demin, K.A.; Kalueff, A.V.; de Abreu, M.S. Putative anxiolytic-like behavioral effects of acute paracetamol in adult zebrafish. Behav. Brain Res. 2021, 409, 113293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkey, A.B.; Hoeng, J.; Peitsch, M.C.; Levin, E.D.; Koshibu, K. Subchronic Effects of Plant Alkaloids on Anxiety-like Behavior in Zebrafish. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2021, 207, 173223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Farías-Cea, A.; Pérez, L.; Leal, C.; Segura, K.; Hernández, V.; Atiés-Pérez, C.; Martínez, L.M.; Hödar-Salazar, M.; Reyes-Parada, M.; Sotomayor-Zárate, R.; et al. Distinct Swimming Behavioral Phenotypes Following Serotonin and Dopamine Transporter Modulation in the Adult Zebrafish Novel Tank Diving Test (NTT). Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 1807. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18121807
Farías-Cea A, Pérez L, Leal C, Segura K, Hernández V, Atiés-Pérez C, Martínez LM, Hödar-Salazar M, Reyes-Parada M, Sotomayor-Zárate R, et al. Distinct Swimming Behavioral Phenotypes Following Serotonin and Dopamine Transporter Modulation in the Adult Zebrafish Novel Tank Diving Test (NTT). Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(12):1807. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18121807
Chicago/Turabian StyleFarías-Cea, Amaury, Lisandra Pérez, Cristóbal Leal, Kerim Segura, Valentina Hernández, Caridad Atiés-Pérez, Luis Miguel Martínez, Martin Hödar-Salazar, Miguel Reyes-Parada, Ramón Sotomayor-Zárate, and et al. 2025. "Distinct Swimming Behavioral Phenotypes Following Serotonin and Dopamine Transporter Modulation in the Adult Zebrafish Novel Tank Diving Test (NTT)" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 12: 1807. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18121807
APA StyleFarías-Cea, A., Pérez, L., Leal, C., Segura, K., Hernández, V., Atiés-Pérez, C., Martínez, L. M., Hödar-Salazar, M., Reyes-Parada, M., Sotomayor-Zárate, R., Rojas-Hidalgo, F., Julio-Pieper, M., Bravo, J. A., Borroto-Escuela, D. O., & Iturriaga-Vásquez, P. (2025). Distinct Swimming Behavioral Phenotypes Following Serotonin and Dopamine Transporter Modulation in the Adult Zebrafish Novel Tank Diving Test (NTT). Pharmaceuticals, 18(12), 1807. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18121807









