Synthesis of Novel Arylhydrazones Bearing 8-Trifluoromethyl Quinoline: Crystal Insights, Larvicidal Activity, ADMET Predictions, and Molecular Docking Studies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Chemistry
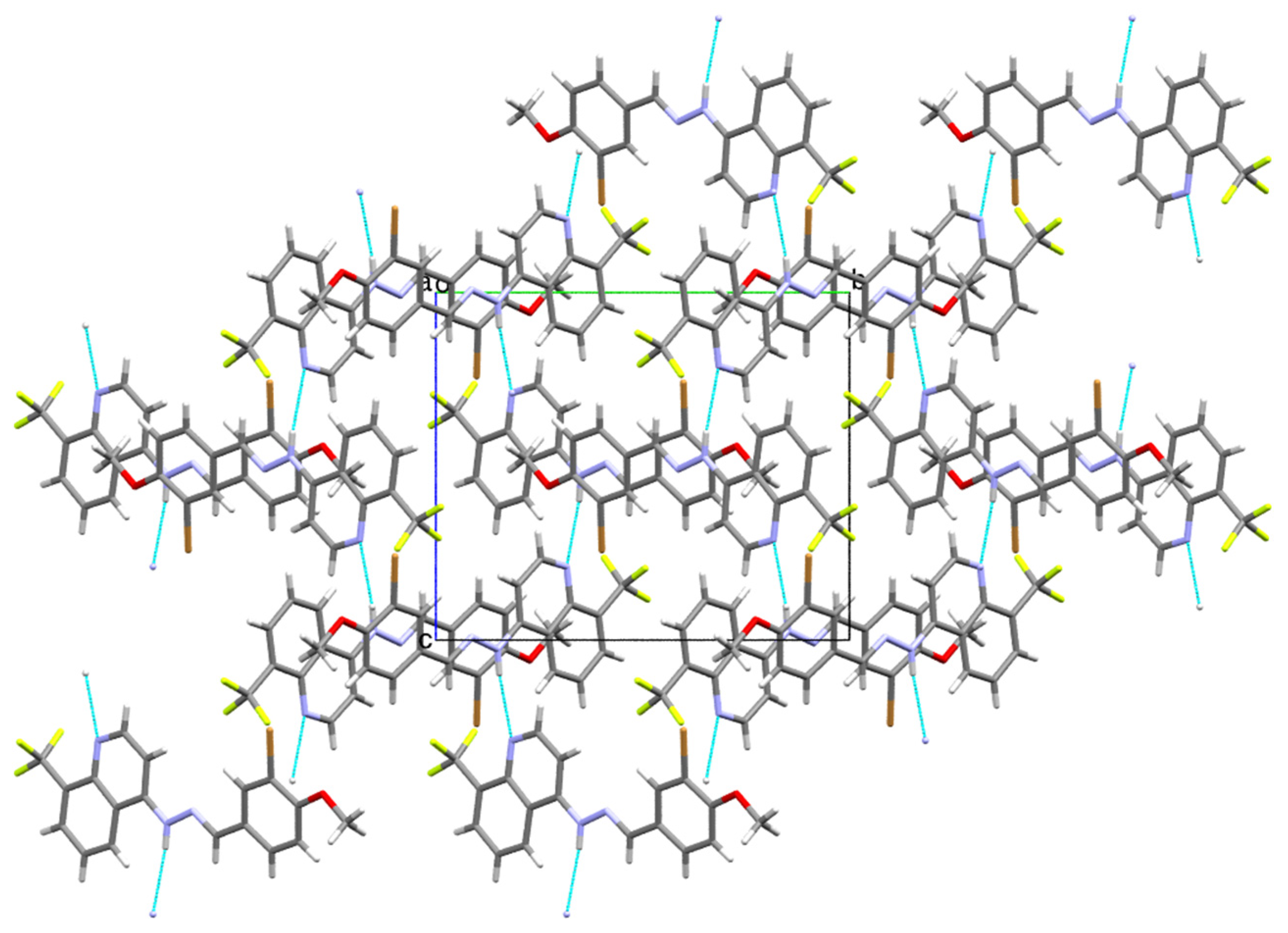
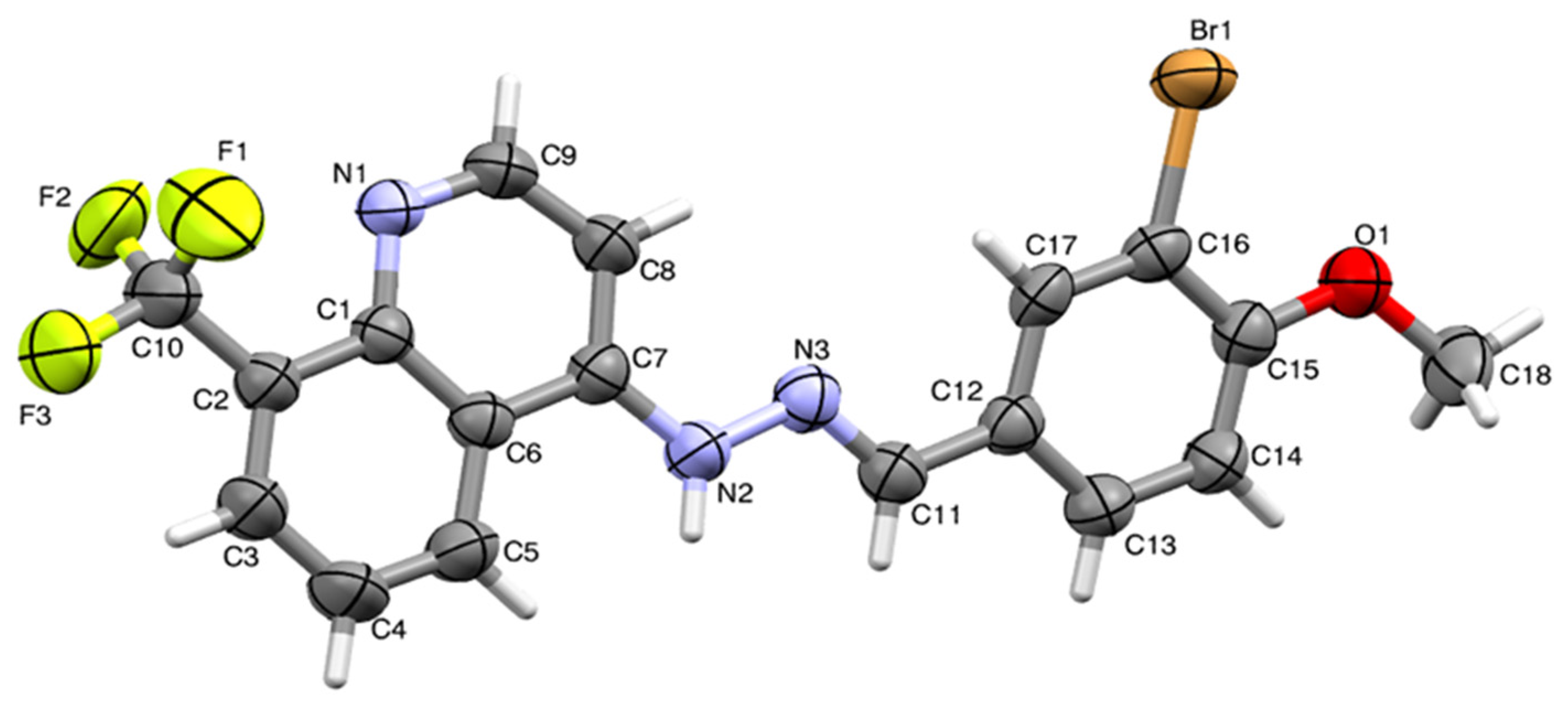
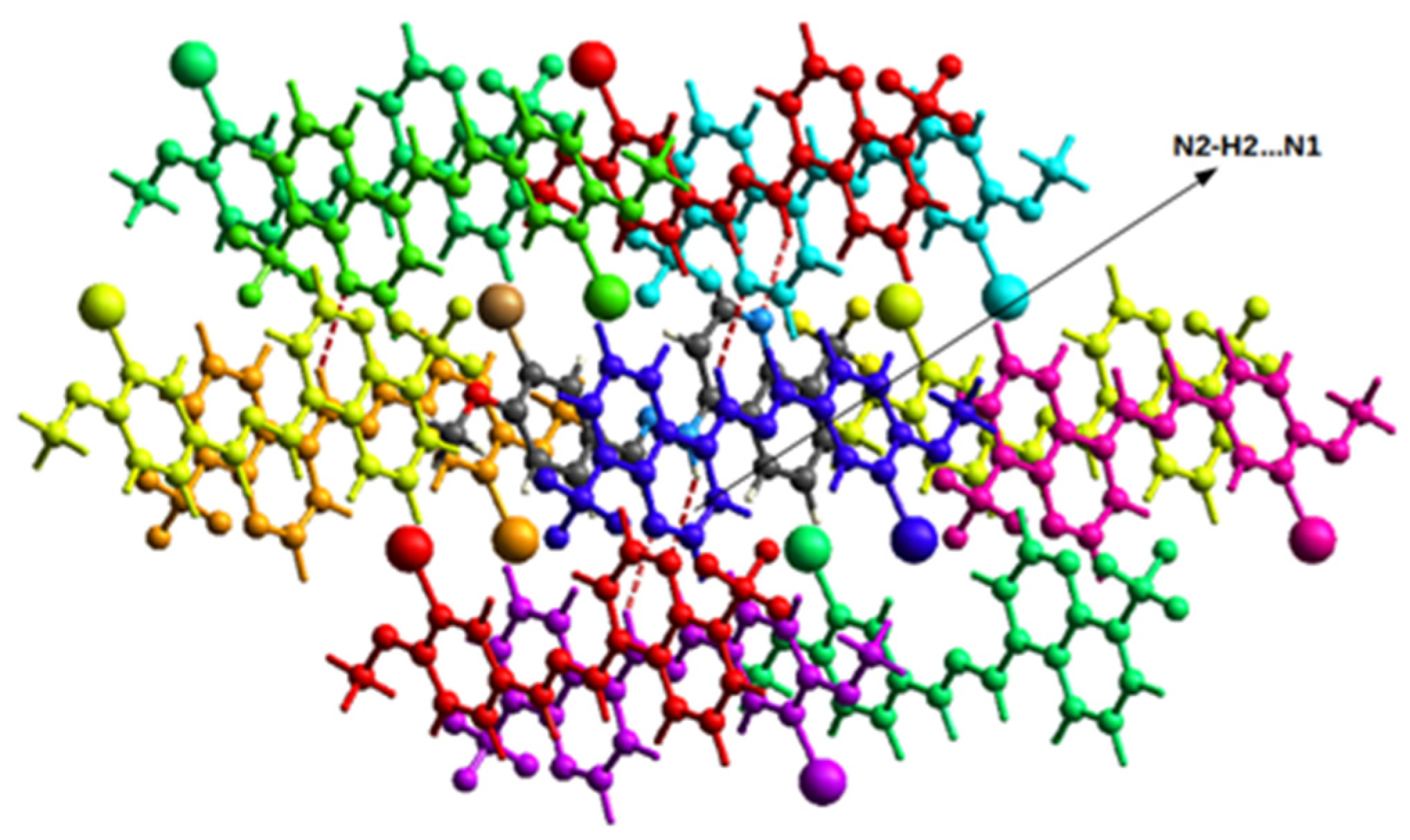
2.2. Single-Crystal Structural Analysis
2.3. Computation Analyses
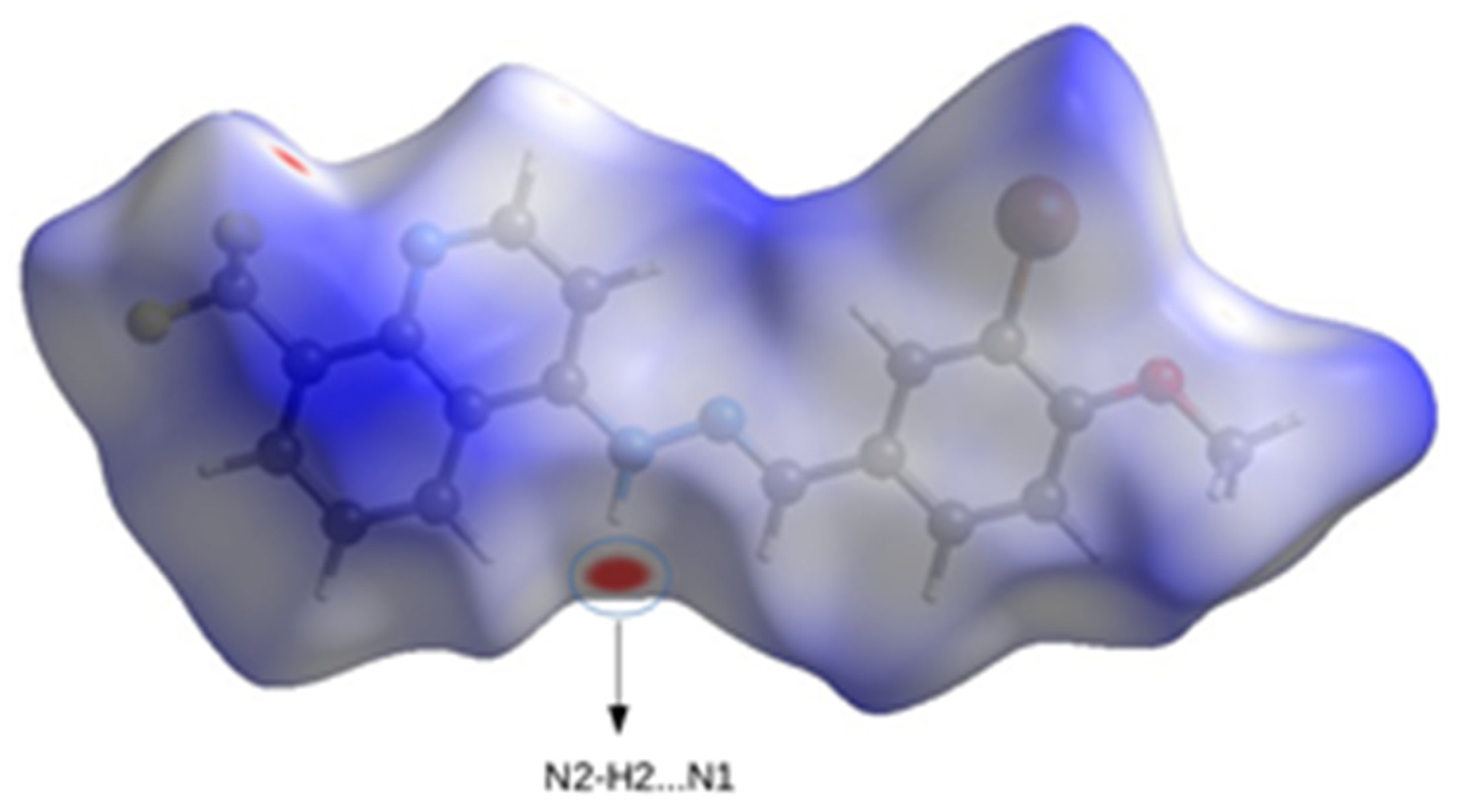
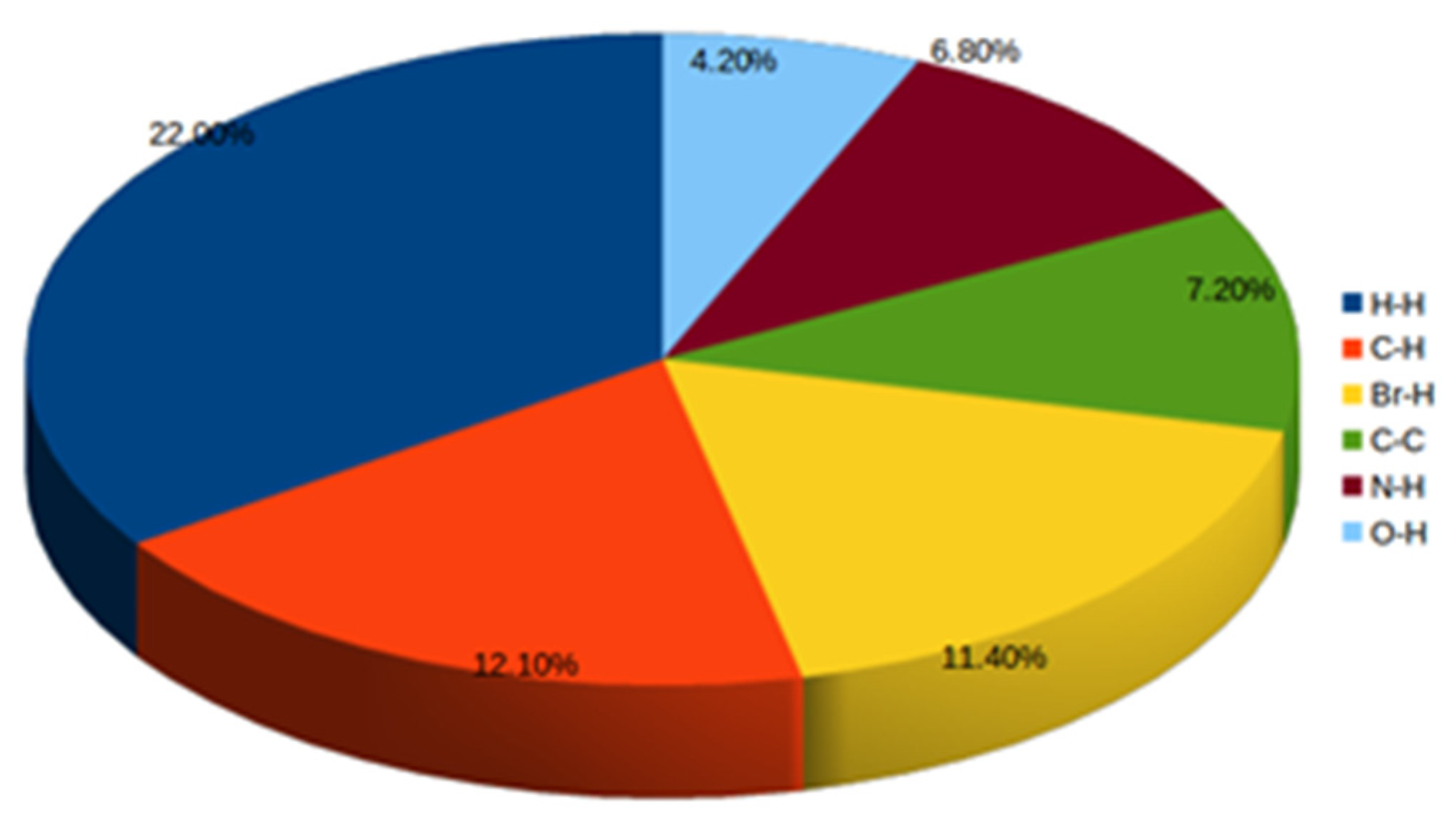
2.3.1. Hirshfeld Surface Calculations
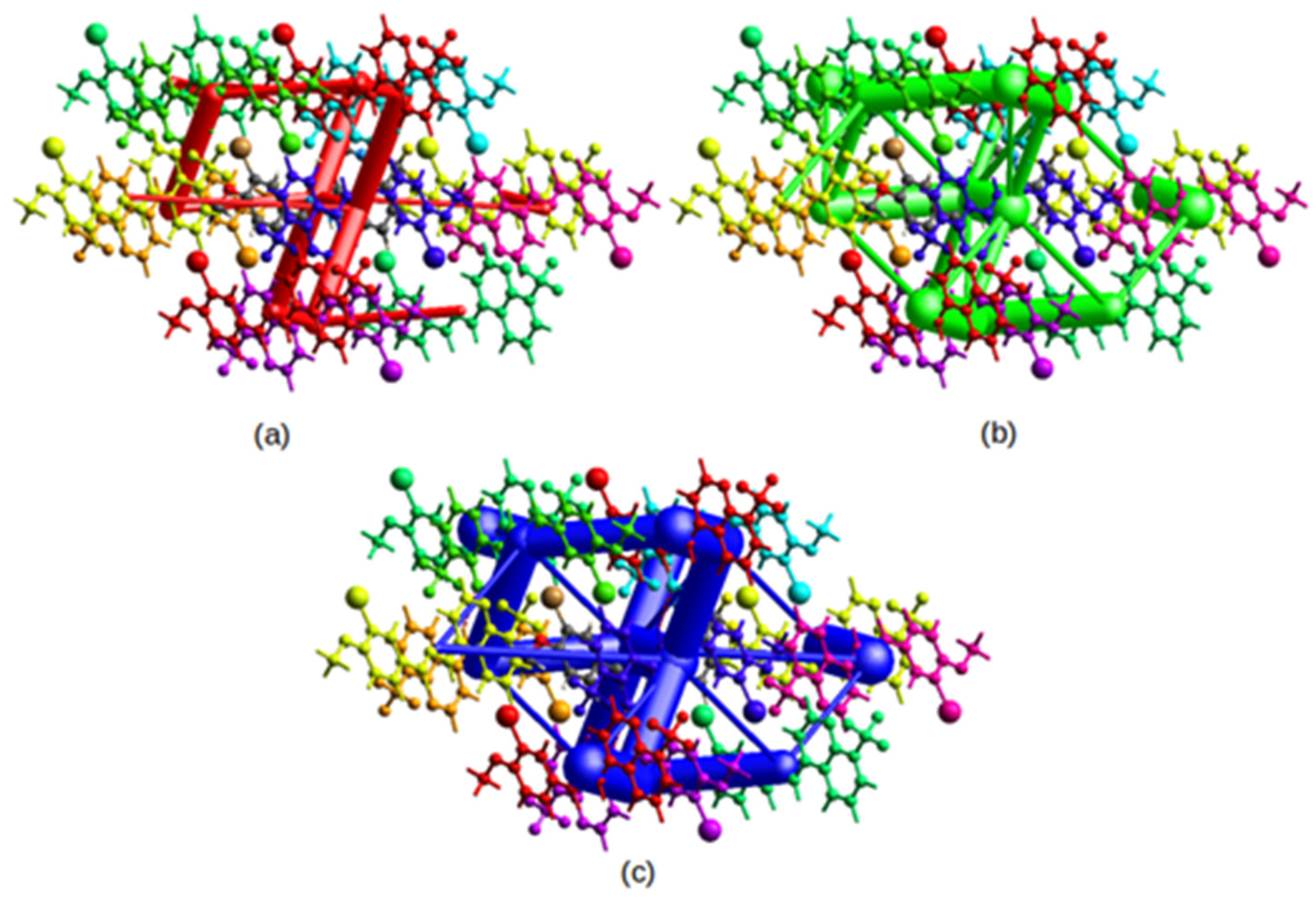
2.3.2. Three-Dimensional Interaction Energy Frameworks
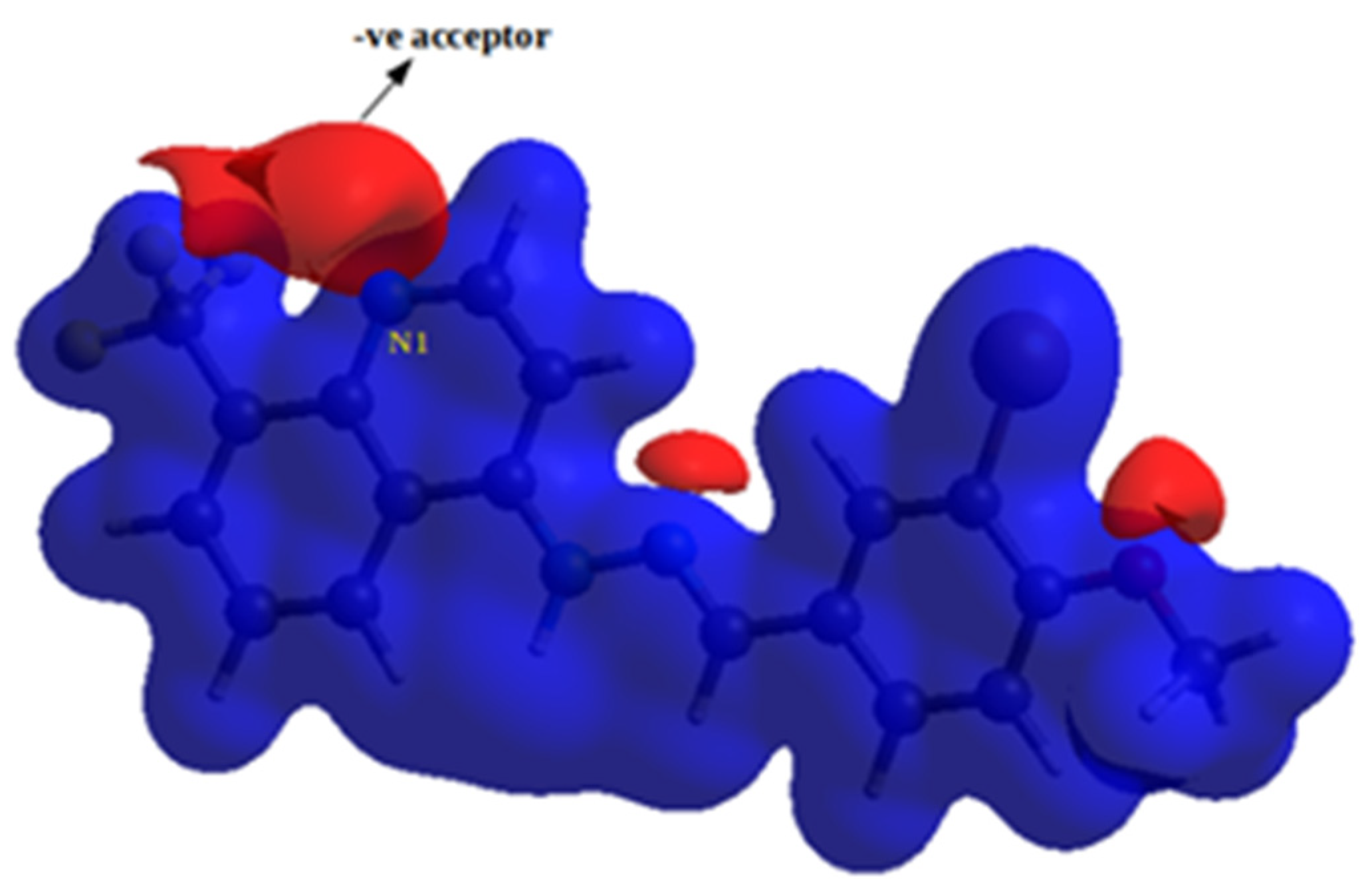
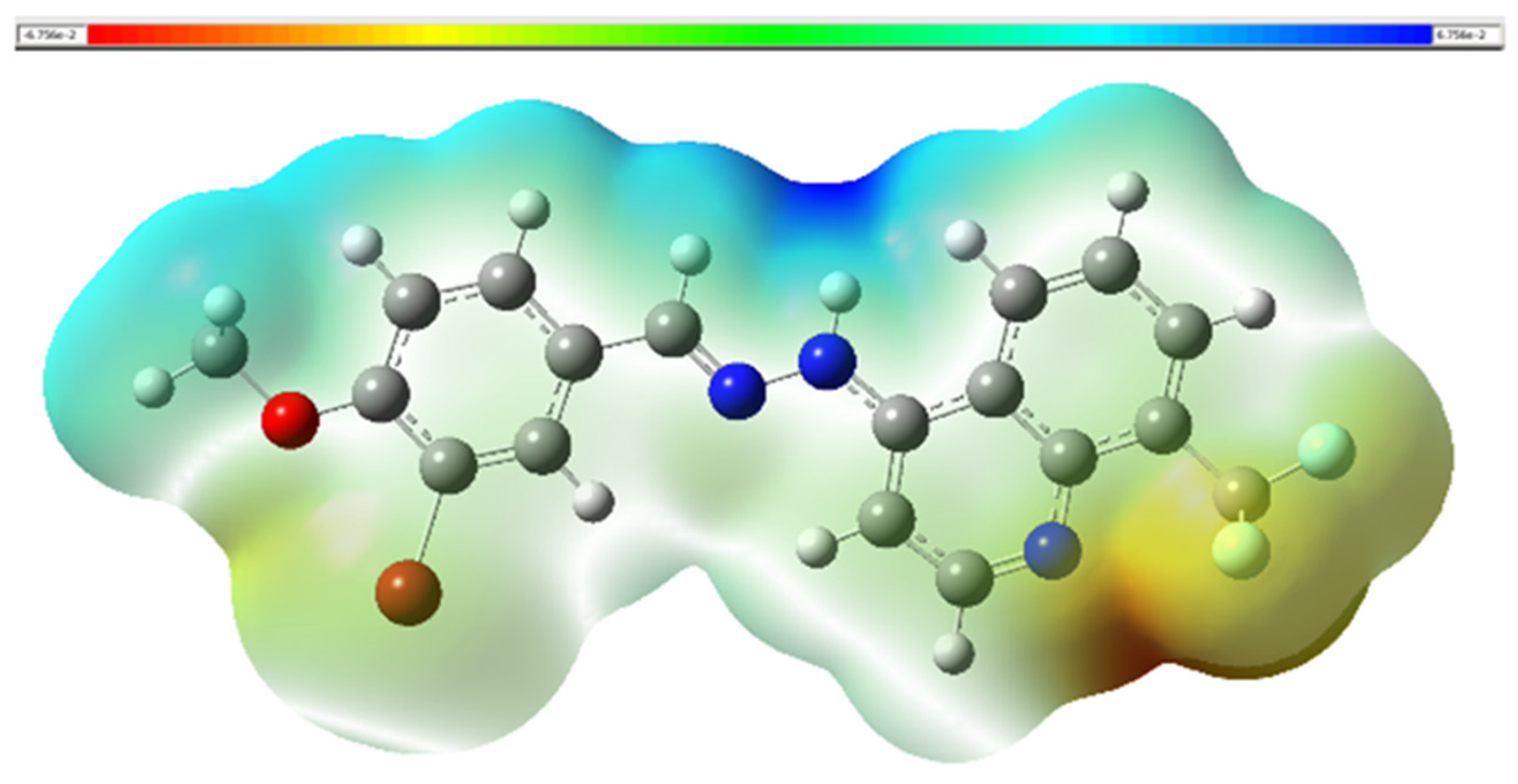
2.3.3. Molecular Electrostatic Potential (MEP)
2.3.4. Frontier Molecular Orbitals (HOMO–LUMO Energy)
2.4. Computational Studies
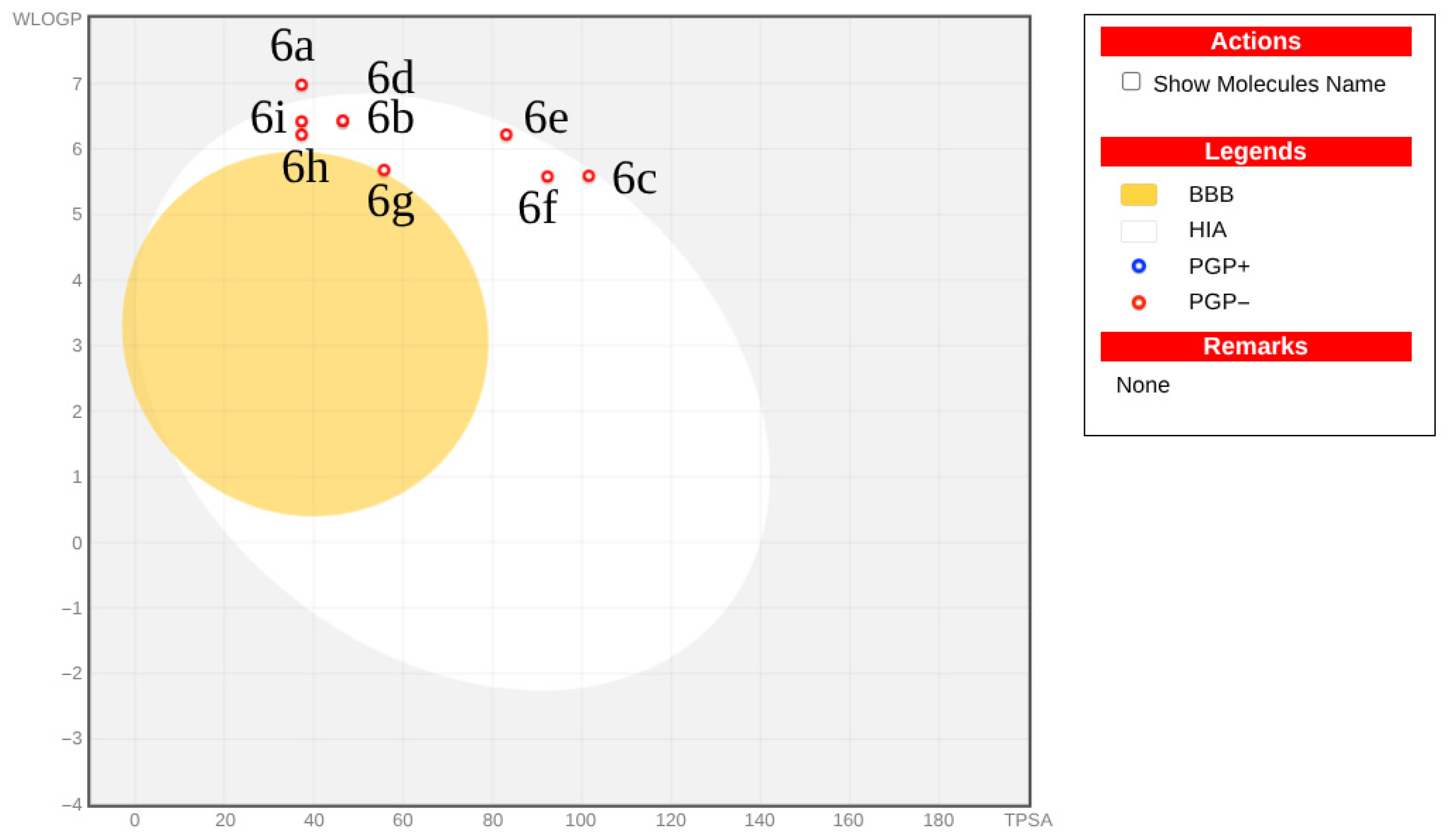
2.5. ADMET Properties
2.6. Toxicity Studies
2.7. Larvicidal Activity
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General
3.2. Synthetic Procedure of 4-Hydrazinyl-8-(trifluoromethyl)quinoline (5) [35]
3.3. General Method for the Synthesis of (E)-4-(2-Benzylidenehydrazinyl)-8-(trifluoromethyl)quinolone (6a–i) [35]
3.3.1. (E)-4-(2-(3-Bromo-4-fluorobenzylidene)hydrazinyl)-8-(trifluoromethyl)quinoline (6a)
3.3.2. (E)-4-(2-(5-Bromo-2-methoxybenzylidene)hydrazinyl)-8-(trifluoromethyl)quinoline (6b)
3.3.3. (E)-4-(2-(4,5-Dimethoxy-2-nitrobenzylidene)hydrazinyl)-8-(trifluoromethyl)quinoline (6c)
3.3.4. (E)-4-(2-(3-Bromo-4-methoxybenzylidene)hydrazinyl)-8-(trifluoromethyl)quinoline (6d)
3.3.5. (E)-4-(2-(2-Chloro-5-nitrobenzylidene)hydrazinyl)-8-(trifluoromethyl)quinoline (6e)
3.3.6. (E)-4-(2-(4-Methoxy-3-nitrobenzylidene)hydrazinyl)-8-(trifluoromethyl)quinoline (6f)
3.3.7. (E)-4-(2-(2,4-Dimethoxybenzylidene)hydrazinyl)-8-(trifluoromethyl)quinoline (6g)
3.3.8. (E)-4-(2-(4-Fluorobenzylidene)hydrazinyl)-8-(trifluoromethyl)quinoline (6h)
3.3.9. (E)-4-(2-(4-Bromobenzylidene)hydrazinyl)-8-(trifluoromethyl)quinoline (6i)
3.4. Single-Crystal X-Ray Studies
Computational Studies
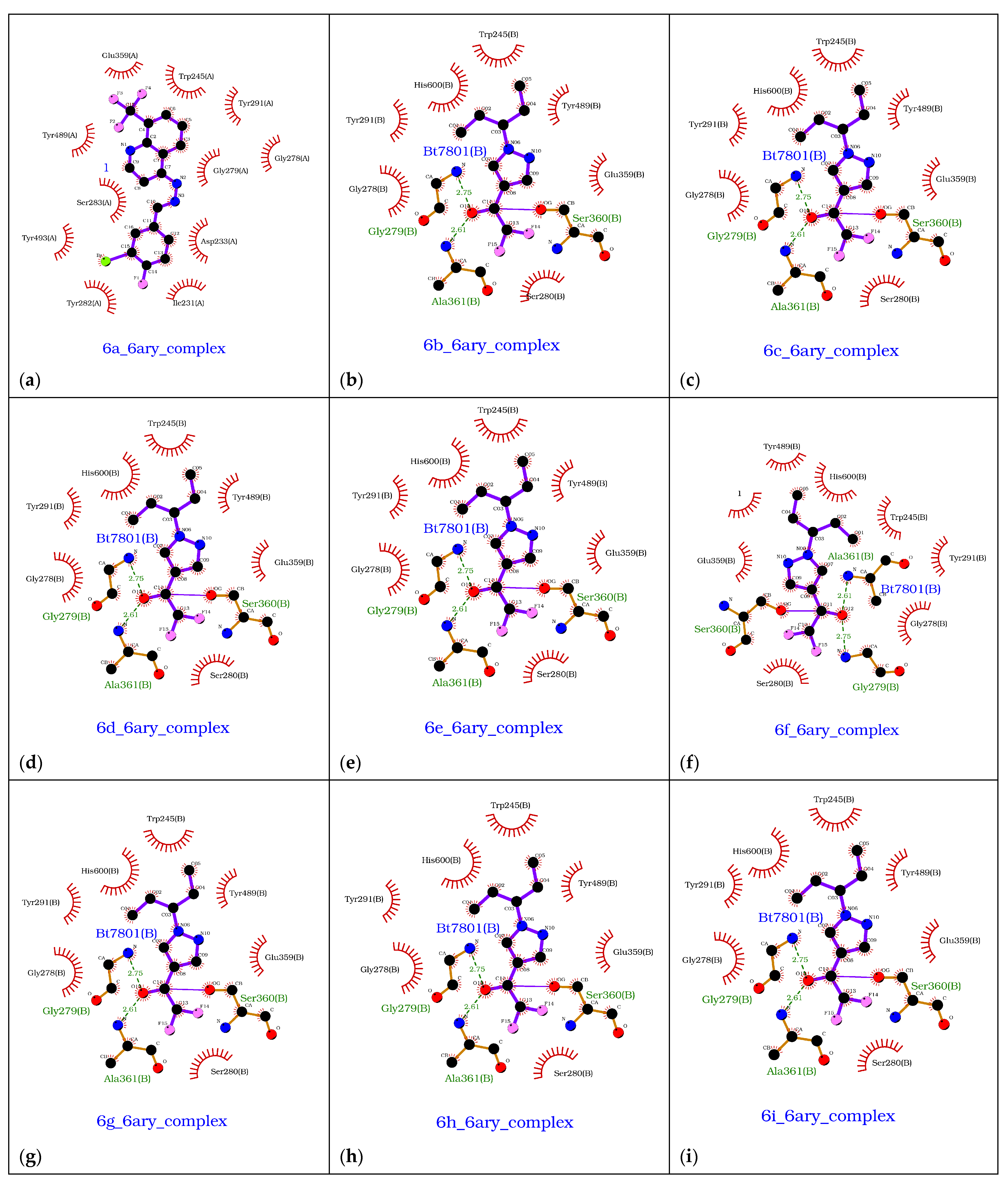
3.5. Computational Studies (Molecular Docking)
3.6. ADMET Prediction
3.7. Larvicidal Activity
3.8. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Patel, A.A.; Mehta, A.G. Synthesis of novel heterocyclic compounds and their biological evaluation. Pharma Chem. 2010, 2, 215–223. [Google Scholar]
- Ginsburg, H.; Krugliak, M. Quinoline-containing antimalarials—Mode of action, drug resistance and its reversal an update with unresolved puzzles. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1992, 43, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afzal, O.; Kumar, S.; Haider, M.R.; Ali, M.R.; Kumar, R.; Jaggi, M.; Bawa, S. A review on anticancer potential of bioactive heterocycle quinoline. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 97, 871–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorababu, A. Recent update on antibacterial and antifungal activity of quinoline scaffolds. Arch. Pharm. 2021, 354, 2000232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venugopala, K.N.; Deb, P.K.; Pillay, M.; Chandrashekharappa, S.; Morsy, M.A.; Aldhubiab, B.; Attimarad, M.; Nair, A.B.; Sreeharsha, N.; Tratrat, C. Ethyl 2-Substituted-1-(substitutedbenzoyl)-7-methylpyrrolo[1,2-a]quinoline-3-carboxylate Derivatives as Anti-Tubercular Agents. U.S. Patent 11938120B1, 19 December 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Uppar, V.; Chandrashekharappa, S.; Shivamallu, C.; Kollur, S.P.; Kollur, S.P.; Ortega-Castro, J.; Frau, J.; Flores-Holguín, N.; Basarikatti, A.I.; Chougala, M. Investigation of antifungal properties of synthetic dimethyl-4-bromo-1-(substituted benzoyl) pyrrolo[1,2-a] quinoline-2,3-dicarboxylates analogues: Molecular docking studies and conceptual DFT-based chemical reactivity descriptors and pharmacokinetics evaluation. Molecules 2021, 26, 2722. [Google Scholar]
- Uppar, V.; Mudnakudu-Nagaraju, K.K.; Basarikatti, A.I.; Chougala, M.; Chandrashekharappa, S.; Mohan, M.K.; Banuprakash, G.; Venugopala, K.N.; Ningegowda, R.; Padmashali, B. Microwave induced synthesis, and pharmacological properties of novel 1-benzoyl-4-bromopyrrolo[1,2-a]quinoline-3-carboxylate analogues. Chem. Data Collect. 2020, 25, 100316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiglani, D.; Salahuddin; Mazumder, A.; Kumar, R.; Yar, M.S.; Ahsan, M.J.; Shabana, K. Synthesis Anticonvulsant and Cytotoxic Evaluation of Benzimidazole-Quinoline Hybrids Schiff Base Analogs. Polycycl. Aromat. Compd. 2024, 44, 960–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.K.; Mishra, A. Synthesis, Characterization & Screening for Anti-Inflammatory & Analgesic Activity of Quinoline Derivatives Bearing Azetidinones Scaffolds. Anti-Inflamm. Antiallergy Agents Med. Chem. 2016, 15, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venugopala, K.N.; Deb, P.K.; Patil, P.; Alwassil, O.I.; Morsy, M.A.; Aldhubiab, B.; Uppar, V.; Kandeel, M.; Managutti, P.B.; Padmashali, B. Dimethyl 7-Bromo-1-(4-substituted benzoyl)pyrrolo[1,2-a]quinoline-2,3-dicarboxylates as Anti-Inflammatory Agents. U.S. Patent 11945819B1, 2 April 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Cairns, H.; Cox, D.; Gould, K.J.; Ingall, A.H.; Suschitzky, J.L. New antiallergic pyrano [3,2-g]quinoline-2,8-dicarboxylic acids with potential for the topical treatment of asthma. J. Med. Chem. 1985, 28, 1832–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayat, F.; Salahuddin, A.; Zargan, J.; Azam, A. Synthesis, characterization, antiamoebic activity and cytotoxicity of novel 2-(quinolin-8-yloxy) acetohydrazones and their cyclized products (1,2,3-thiadiazole and 1,2,3-selenadiazole derivatives). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 45, 6127–6134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- File, S.E.; Lister, R.G. Quinolines and anxiety: Anxiogenic effects of CGS 8216 and partial anxiolytic profile of PK 9084. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 1983, 18, 185–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uppar, V.; Chandrashekharappa, S.; Venugopala, K.N.; Deb, P.K.; Kar, S.; Alwassil, O.I.; Gleiser, R.M.; Garcia, D.; Odhav, B.; Mohan, M.K. Synthesis and characterization of pyrrolo[1,2-a]quinoline derivatives for their larvicidal activity against Anopheles arabiensis. Struct. Chem. 2020, 31, 1533–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venugopala, K.N.; Uppar, V.; Chandrashekharappa, S.; Abdallah, H.H.; Pillay, M.; Deb, P.K.; Morsy, M.A.; Aldhubiab, B.E.; Attimarad, M.; Nair, A.B. Cytotoxicity and antimycobacterial properties of pyrrolo[1,2-a]quinoline derivatives: Molecular target identification and molecular docking studies. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Zhang, G.; Zhao, J.; Cheng, N.; Wang, Y.; Fu, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhu, M.; Cen, S.; et al. Synthesis and antiviral activity of a series of novel quinoline derivatives as anti-RSV or anti-IAV agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 214, 113208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foley, M.; Tilley, L. Quinoline antimalarials: Mechanisms of action and resistance. Int. J. Parasitol. 1997, 27, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahal, S.M.; Baichwal, M.R.; Khorana, M.L. Studies on quinoline derivatives as Anti-infective agents I. J. Pharm. Sci. 1961, 50, 127–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venugopala, K.N.; Kandeel, M.; Pillay, M.; Deb, P.K.; Abdallah, H.H.; Mahomoodally, M.F.; Chopra, D. Anti-Tubercular Properties of 4-Amino-5-(4-fluoro-3-phenoxyphenyl)-4H-1,2,4-triazole-3-thiol and Its Schiff Bases: Computational Input and Molecular Dynamics. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillis, E.P.; Eastman, K.J.; Hill, M.D.; Donnelly, D.J.; Meanwell, N.A. Applications of Fluorine in Medicinal Chemistry. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 8315–8359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo, P.; Diliddo, D.; Resnati, G. An efficient entry to perfluoroalkyl substituted azoles starting from β-perfluoroalkyl-β-dicarbonyl compounds. Tetrahedron 1994, 50, 8827–8836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Hu, H.; Gong, S.; Xu, X.; Wang, B.; Zhou, H.; Xu, D. Synthesis and Herbicidal Activity of Trifluoromethyl-Substituted Phenyl Alkyl Ketoxime Esters of Bispyribac. ChemistrySelect 2020, 5, 4194–4199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdou, I.M.; Saleh, A.M.; Zohdi, H.F. Synthesis and antitumor activity of 5-trifluoromethyl-2,4-dihydropyrazol-3-one nucleosides. Molecules 2004, 9, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, C.; Fehr, M. Chapter 26—Discovery of the trifluoromethyloxadiazoles—A new class of fungicides with a novel mode-of-action. In Recent Highlights in the Discovery and Optimization of Crop Protection Products; Maienfisch, P., Mangelinckx, S., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021; pp. 401–423. [Google Scholar]
- Pruitt, J.R.; Pinto, D.J.; Galemmo, R.A.; Alexander, R.S.; Rossi, K.A.; Wells, B.L.; Drummond, S.; Bostrom, L.L.; Burdick, D.; Bruckner, R. Discovery of 1-(2-Aminomethylphenyl)-3-trifluoromethyl-N-[3-fluoro-2′-(aminosulfonyl)[1,1′-biphenyl)]-4-yl]-1H-pyrazole-5-carboxyamide (DPC602), a Potent, Selective, and Orally Bioavailable Factor Xa Inhibitor. J. Med. Chem. 2003, 46, 5298–5315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nefisath, P.; Dasappa, J.P.; Haripriya, B.; Chopra, D.; Venugopala, K.N.; Deb, P.K.; Gleiser, R.M.; Mohanlall, V.; Maharaj, R.; Shashiprabha; et al. Synthesis, structural elucidation and larvicidal activity of novel arylhydrazones. J. Mol. Struct. 2021, 1236, 130305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Wahab, B.F.; Awad, G.E.; Badria, F.A. Synthesis, antimicrobial, antioxidant, anti-hemolytic and cytotoxic evaluation of new imidazole-based heterocycles. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 46, 1505–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamat, V.; Venuprasad, K.; Shadakshari, A.; Bhat, R.S.; D’souza, A.; Chapi, S.; Kumar, A.; Kuthe, P.V.; Sankaranarayanan, M.; Venugopala, K.N. Synthesis, anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, and antioxidant evaluation of novel pyrazole-linked hydrazone derivatives. J. Mol. Struct. 2024, 1312, 138634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajitha, G.; Saideepa, N.; Praneetha, P. Synthesis and evaluation of N-(α-benzamido cinnamoyl) aryl hydrazone derivatives for anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activities. Indian J. Chem. Sect. B Org. Med. Chem. 2011, 50, 729–733. [Google Scholar]
- van den Berg, H.; da Silva Bezerra, H.S.; Al-Eryani, S.; Chanda, E.; Nagpal, B.N.; Knox, T.B.; Velayudhan, R.; Yadav, R.S. Recent trends in global insecticide use for disease vector control and potential implications for resistance management. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 23867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, P.F.; Elanga-Ndille, E.; Tchouakui, M.; Sandeu, M.M.; Tagne, D.; Wondji, C.; Ndo, C. Impact of insecticide resistance on malaria vector competence: A literature review. Malar. J. 2023, 22, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, A.L.; Courtenay, O.; Kelly-Hope, L.A.; Scott, T.W.; Takken, W.; Torr, S.J.; Lindsay, S.W. The importance of vector control for the control and elimination of vector-borne diseases. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2020, 14, e0007831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, M.; Jin, J.-I.; Lee, C.; Kim, N.; Park, K. Synthesis and Characterization of Nonlinear Optical Polymers Having Quinoline-based Chromophores. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2002, 23, 964–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farag, A.A.M.; Roushdy, N.; Halim, S.A.; El-Gohary, N.M.; Ibrahim, M.A.; Said, S. Synthesis, molecular, electronic structure, linear and non-linear optical and phototransient properties of 8-methyl-1,2-dihydro-4H-chromeno [2,3-b]quinoline-4,6(3H)-dione (MDCQD): Experimental and DFT investigations. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2018, 191, 478–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bispo, M.; Cataldi de Alcantara, C.; Moraes, M.; Pessoa, C.; Rodrigues, F.; Kaiser, C.; Wardell, S.; Wardell, J.; Nora de Souza, M. A new and potent class of quinoline derivatives against cancer. Monatshefte Chem. Chem. Mon. 2015, 146, 2041–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yathirajan, H.; Sreevidya, T.; Prathap, M.; Narayana, B.; Bolte, M. 4-Chloro-8-(trifluoromethyl)quinoline. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. E 2007, 63, o763–o765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreenatha, N.R.; Jeevan Chakravarthy, A.S.; Lakshminarayana, B.N.; Hariprasad, S. Structural characterization, computational, charge density studies of 2-chloro-3-(2’-methoxy)-5,5-dimethyl-2-cyclohexenone. J. Mol. Struct. 2021, 1225, 129116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faizi, M.S.H.; Cinar, E.B.; Aydin, A.S.; Agar, E.; Dege, N.; Mashrai, A. Crystal structure, Hirshfeld surface analysis and DFT studies of (E)-2-{[(3-chloro-4-methyl-phen-yl)imino]-meth-yl}-4-methyl-phenol. Acta Crystallogr. E Crystallogr. Commun. 2020, 76, 1320–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangubhai, G.S.; Deb, P.K.; Rakshit, G.; Tiwari, P.; Mohanlall, V.; Gleiser, R.M.; Morsy, M.A.; Venugopala, K.N.; Chandrashekharappa, S. Synthesis, biological evaluation, and molecular modelling studies of novel Ethyl 3-benzoyl-6,8-dichloroindolizine-1-carboxylates against malaria vector Anopheles arabiensis. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2025, 4, 40613554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- pkCSM. 2025. Available online: https://biosig.lab.uq.edu.au/pkcsm/prediction# (accessed on 6 November 2025).
- Available online: http://www.swissadme.ch/ (accessed on 5 November 2025).
- Hasija, A.; Prakash, V.; Prakash, M.; Vasu; Krishnasamy, G.; Chopra, D. Apex2, version 2; User Manual, M86-E01078; Bruker Analytical X-Ray Systems: Madison, WI, USA, 2006.
- Sheldrick, G. A short history of SHELX. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. A 2008, 64, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Cryst. C 2015, 71, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spek, A.L. Structure validation in chemical crystallography. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2009, 65, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macrae, C.F.; Bruno, I.J.; Chisholm, J.A.; Edgington, P.R.; McCabe, P.; Pidcock, E.; Rodriguez-Monge, L.; Taylor, R.; van de Streek, J.; Wood, P.A. Mercury CSD 2.0—New features for the visualization and investigation of crystal structures. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2008, 41, 466–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisch, M.; Trucks, G.; Schlegel, H.; Scuseria, G.; Robb, M.; Cheeseman, J.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Mennucci, B.; Petersson, G.; et al. Gaussian 09; Revision A 1; Gaussian, Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Dennington, R.; Keith, T.A.; Millam, J.M. GaussView, Version 6.1; Semichem Inc.: Shawnee Mission, KS, USA, 2016.
- Turner, M.; McKinnon, J.; Wolff, S.; Grimwood, D.; Spackman, P.; Jayatilaka, D.; Spackman, M. CrystalExplorer17; University of Western Australia: Perth, Australia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Nagdeve, R.D.; Thakur, J.S.; Chandrashekharappa, S.; Bairagi, K.M.; Deb, P.K.; Katharigatta, N.V.; Mondal, P.K.; Polentarutti, M.; Alwassil, O.I.; Mohanlall, V. Crystal structure, hydrogen bonding interactions, Hirshfeld surfaces, energy frameworks, and DFT calculation of Diethyl 3-(4-substitutedbenzoyl) indolizine-1,2-dicarboxylates. J. Mol. Struct. 2024, 1308, 138080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKinnon, J.J.; Spackman, M.A.; Mitchell, A.S. Novel tools for visualizing and exploring intermolecular interactions in molecular crystals. Acta Crystallogr. B 2004, 60, 627–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackenzie, C.F.; Spackman, P.R.; Jayatilaka, D.; Spackman, M.A. CrystalExplorer model energies and energy frameworks: Extension to metal coordination compounds, organic salts, solvates and open-shell systems. IUCrJ 2017, 4, 575–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huey, R.; Morris, G. Using AutoDock with AutoDockTools: A Tutorial; The Scripps Research Institute: La Jolla, CA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, S.; Chan, H.C.S.; Hu, Z. Using PyMOL as a platform for computational drug design. WIREs Comput. Mol. Sci. 2017, 7, e1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laskowski, R.A.; Swindells, M.B. LigPlot+: Multiple Ligand–Protein Interaction Diagrams for Drug Discovery. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2011, 51, 2778–2786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daina, A.; Michielin, O.; Zoete, V. SwissADME: A free web tool to evaluate pharmacokinetics, drug-likeness and medicinal chemistry friendliness of small molecules. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daina, A.; Zoete, V. A BOILED-Egg To Predict Gastrointestinal Absorption and Brain Penetration of Small Molecules. ChemMedChem 2016, 11, 1117–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Manual on Practical Entomology; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- DiRienzo, J.A.; Casanoves, F.; Balzarini, M.G.; Gonzalez, L.; Tabalada, M.; Robledo, C.W. InfoStat Version 2014, Group InfoStat, FCA, Universidad Nacional de Cordoba, Argentina. Available online: http://www.infostat.com.ar/ (accessed on 12 February 2022).



| Compound Code | R | Molecular Formula | Molecular Weight [M+1] | M.P. (°C) | Yield % | cLogP a |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6a | 3-Br-4-F | C17H10BrF4N3 | 412.0067 | 179–180 | 82.7 | 6.2485 |
| 6b | 2-OCH3-5-Br | C18H13BrF3N3O | 424.0267 | 157–158 | 77 | 5.9320 |
| 6c | 2-NO2-4,5-(OCH3)2 | C19H15F3N4O4 | 421.1118 | 240–241 | 92 | 4.6361 |
| 6d | 3-Br-4-OCH3 | C18H13BrF3N3O | 424.0266 | 200–201 | 72 | 6.1320 |
| 6e | 2-Cl-5-NO2 | C17H10ClF3N4O2 | 395.0517 | 225–226 | 86.6 | 5.1141 |
| 6f | 3-NO2-4-OCH3 | C18H13F3N4O3 | 391.1011 | 219–220 | 86 | 5.0227 |
| 6g | 2,4-(OCH3)2 | C19H16F3N3O2 | 376.1267 | 217–218 | 95 | 5.0848 |
| 6h | 4-F | C17H11F4N3 | 334.0951 | 197–198 | 94 | 5.3807 |
| 6i | 4-Br | C17H11BrF3N3 | 393.0161 | 200–201 | 90 | 6.1007 |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Empirical formula | C18H13BrF3N3O |
| Formula weight | 424.21 |
| Temperature | 293 K |
| Radiation source | Monochromated Graphite |
| Radiation type | MoKα |
| Wavelength | 0.71073 Å |
| Crystal system, space group | monoclinic, P21/c |
| Unit cell dimensions | a = 10.0716(7) Å α = 90° b = 14.5234(8) Å β = 110.745(7)° c = 13.0461(7) Å γ = 90° |
| Volume | 1784.6(2) Å3 |
| Z | 4 |
| Density (calculated) | 1.579 g/m3 |
| Crystal shape | Needle |
| Crystal color | Colorless |
| Absorption coefficient | 2.345 mm−1 |
| F000 | 848 |
| Crystal size | 0.21 × 0.24 × 0.29 mm |
| θ range for data collection | 2.2 to 25.0° |
| Index ranges | −11 ≤ h ≤ 11, −17 ≤ k ≤ 17, −15 ≤ l ≤ 15 |
| Reflections collected/unique | 14,589/3142 [R(int) = 0.053] |
| Nref, Npar | 3142, 237 |
| Refinement method | Full-matrix least-squares on F2 |
| Observed Data [I > 2.0 sigma(I)] | 2404 |
| Goodness-of-fit | 1.06 |
| R, wR2, S | 0.0493, 0.1439, 1.06 |
| Largest diff. peak and hole | 0.78 and −0.63 e.Å−3 |
| CCDC | 2189866 |
| Type of Interaction | D–H···A | D–H | H···A | D···A | D–H···A | Symmetry Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intermolecular | N2–H2…N1 | 0.86 | 2.50 | 3.270(5) | 149 | x, 1/2 − y, 1/2 + z |
| Intramolecular | C3–H3…F3 | 0.93 | 2.32 | 2.671(6) | 102 |
| CgI…CgJ | Cg…Cg | α | β | γ | CgIperp | CgJperp |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cg1…Cg2 | 5.906(2) | 85.8(2) | 46.0 | 67.6 | −2.2528(17) | 4.1019(19) |
| Cg1…Cg3 | 4.215(2) | 12.7(2) | 28.9 | 40.7 | 3.1955(17) | 3.6898(17) |
| Cg2…Cg3 | 3.887(3) | 11.4(2) | 19.4 | 26.1 | 3.4895(19) | 3.6669(18) |
| Cg3…Cg1 | 4.215(2) | 12.7(2) | 40.7 | 28.9 | 3.6897(18) | 3.1955(17) |
| Cg3…Cg2 | 3.887(3) | 11.4(2) | 26.1 | 19.4 | 3.6669(18) | 3.4894(19) |
| Cg3…Cg3 | 3.772(3) | 0.0(2) | 22.9 | 22.9 | −3.4743(17) | −3.4742(17) |
| Atoms | Length | Atoms | Length | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| XRD | DFT | XRD | DFT | ||
| Br1-C16 | 1.884(4) | 1.886 | C8-C9 | 1.385(6) | 1.4026 |
| F1-C10 | 1.323(7) | 1.3197 | C11-C12 | 1.458(6) | 1.4608 |
| F2-C10 | 1.342(7) | 1.3445 | F3-C10 | 1.329(6) | 1.3312 |
| O1-C15 | 1.357(5) | 1.355 | O1-C18 | 1.424(6) | 1.4461 |
| N1-C1 | 1.364(5) | 1.3722 | N1-C9 | 1.317(5) | 1.3206 |
| N2-N3 | 1.373(5) | 1.3796 | N2-C7 | 1.363(5) | 1.378 |
| N3-C11 | 1.273(5) | 1.2789 | C6-C7 | 1.442(6) | 1.3757 |
| Atoms | Angles | Atoms | Angles | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| XRD | DFT | XRD | DFT | ||
| C15-O1-C18 | 117.4(3) | 117.15 | N1-C9-C8 | 126.5(4) | 125.60 |
| C1-N1-C9 | 115.5(3) | 115.9269 | F1-C10-F2 | 106.4(4) | 107.55 |
| N3-N2-C7 | 117.6(3) | 116.5987 | N3-C11-C12 | 120.3(4) | 119.37 |
| N2-N3-C11 | 117.2(4) | 116.3818 | N1-C1-C2 | 118.7(3) | 118.45 |
| N1-C1-C6 | 123.6(4) | 123.79 | O1-C15-C16 | 117.0(3) | 117.13 |
| O1-C15-C14 | 124.6(4) | 123.86 | Br1-C16-C15 | 119.4(3) | 119.26 |
| N3-N2-H2 | 121.00 | 121.70 | F2-C10-F3 | 105.1(5) | 104.73 |
| N2-C7-C8 | 121.9(4) | 124.88 | |||
| Atoms | Angles | Atoms | Angles | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| XRD | DFT | XRD | DFT | ||
| C18-O1-C15-C14 | −9.7(6) | −10.119 | O1-C15-C16-C17 | −178.9(4) | −178.65 |
| C9-N1-C1-C2 | 178.8(4) | 178.61 | N1-C1-C2-C3 | 178.0(4) | 178.1 |
| C7-N2-N3-C11 | −174.4(4) | −174.19 | C6-C1-C2-C3 | −0.7(6) | −0.78 |
| N2-N3-C11-C12 | −179.7(4) | −179.52 | N1-C1-C6-C7 | 2.0(6) | 2.28 |
| N1-C1-C2-C10 | −2.5(6) | −1.82 | C1-C2-C10-F2 | −62.6(6) | −63.74 |
| N1-C1-C6-C5 | −177.3(4) | −177.68 | C1-C6-C7-N2 | −179.7(4) | −179.94 |
| C1-C2-C10-F1 | 58.1(6) | 58.18 | N2-C7-C8-C9 | 178.1(4) | 178.14 |
| C1-C2-C10-F3 | 179.0(4) | 178.86 | N3-C11-C12-C13 | −174.9(4) | −175.45 |
| N3-C11-C12-C17 | 6.7(6) | 6.74 | C13-C14-C15-O1 | 178.9(4) | 178.62 |
| C18-O1-C15-C16 | 169.6(4) | 169.027 | |||
| Color Code | N | Symop | R | Electron Density | E_ele | E_pol | E_dis | E_rep | E_tot |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | x, −y + 1/2, z + 1/2 | 12.57 | HF/3-21G | −4.4 | −1.1 | −8.4 | 6.1 | −7.8 | |
| 1 | −x, −y, −z | 8.56 | HF/3-21G | −19.3 | −4.6 | −67.1 | 29.0 | −59.5 | |
| 2 | x, y, z | 17.67 | HF/3-21G | 3.5 | −0.9 | −5.6 | 0.8 | −1.4 | |
| 2 | −x, y + 1/2, −z + 1/2 | 9.74 | HF/3-21G | −2.2 | −2.2 | −16.0 | 8.3 | −11.4 | |
| 2 | x, −y + 1/2, z + 1/2 | 10.57 | HF/3-21G | 0.2 | −0.5 | −8.1 | 2.3 | −5.7 | |
| 2 | −x, y + 1/2, -z + 1/2 | 9.58 | HF/3-21G | 2.2 | −2.7 | −17.4 | 4.6 | −11.4 | |
| 2 | x, −y + 1/2, z + 1/2 | 7.54 | HF/3-21G | −42.9 | −13.3 | −29.9 | 17.6 | −65.1 | |
| 1 | −x, −y, −z | 4.86 | HF/3-21G | −25.5 | −7.5 | −87.3 | 29.8 | −85.3 | |
| 2 | −x, y + 1/2, −z + 1/2 | 11.04 | HF/3-21G | 2.0 | −2.0 | −12.4 | 6.4 | −5.3 | |
| 1 | −x, −y, −z | 16.92 | HF/3-21G | −11.3 | −1.6 | −9.9 | 4.2 | −18.1 |
| Parameters | B3LYP/6–311++G(d,p) |
|---|---|
| EHOMO | −3.858 eV |
| ELUMO | −1.0748 eV |
| Energy gap | 2.7832 eV |
| Ionization energy (I) | −EHOMO = 3.858 eV |
| Electron affinity (A) | −ELUMO = 1.0748 eV |
| Electronegativity (χ) | [I + A]/2 = 2.4664 eV |
| Chemical potential (μ) | −[I + A]/2 = −2.4664 eV |
| Global hardness (η) | I-A/2 = 1.3916 eV |
| Global softness (s) = 1/η | 0.7185/eV |
| Electrophilicity index (ω) = μ2/2η | 2.185 eV |
| Compounds | Docking Score (kcal/mol) | Docking Conformations | Binding Interactions | Amino Acids | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6a | −10.4 |  | 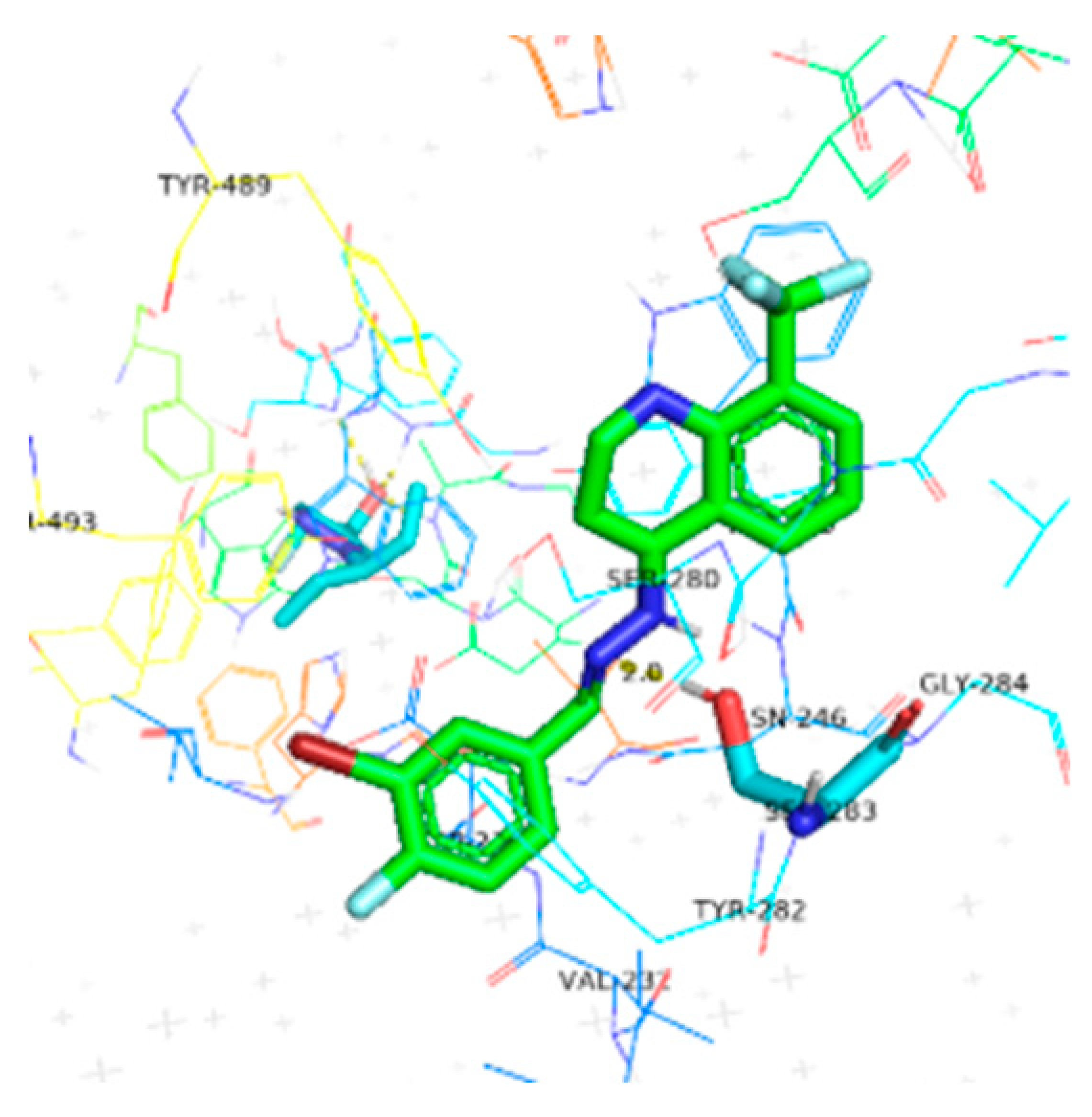 | Conventional hydrogen bond, Pi-Pi stacked, Pi-Pi T-stacked and Pi-alkyl | SER280, SN246, SE283, GLY284, TYR282, VAL232, TYR489, TYR493, ILE231 |
| 6b | −9.7 |  | 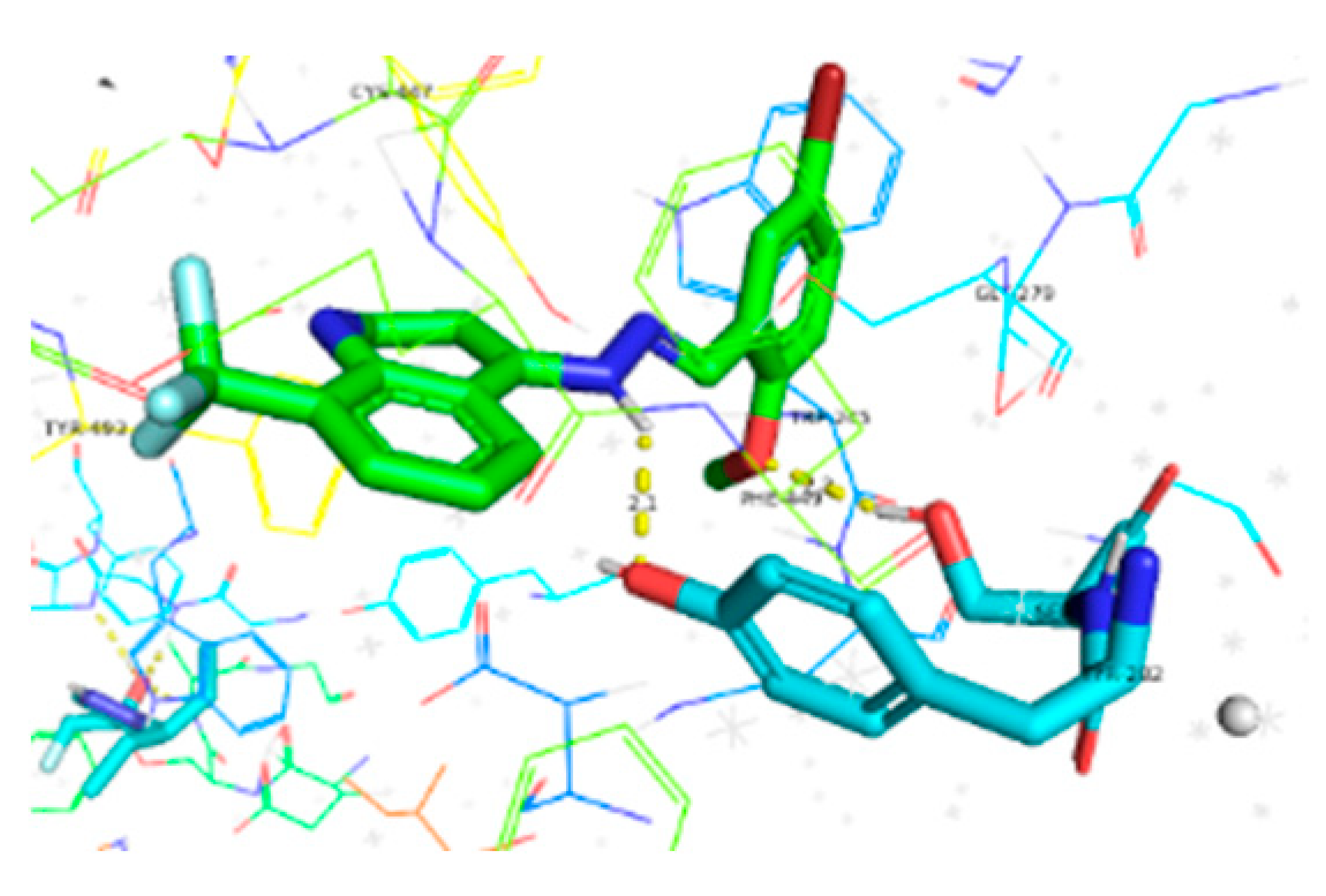 | Conventional hydrogen bond, Pi-Pi stacked, Pi-Pi T-stacked, Pi-sigma, Alkyl and Pi-alkyl | PHE449, TRP245, SER282, TYR282, TYR493, GL279 |
| 6c | −10.1 |  | 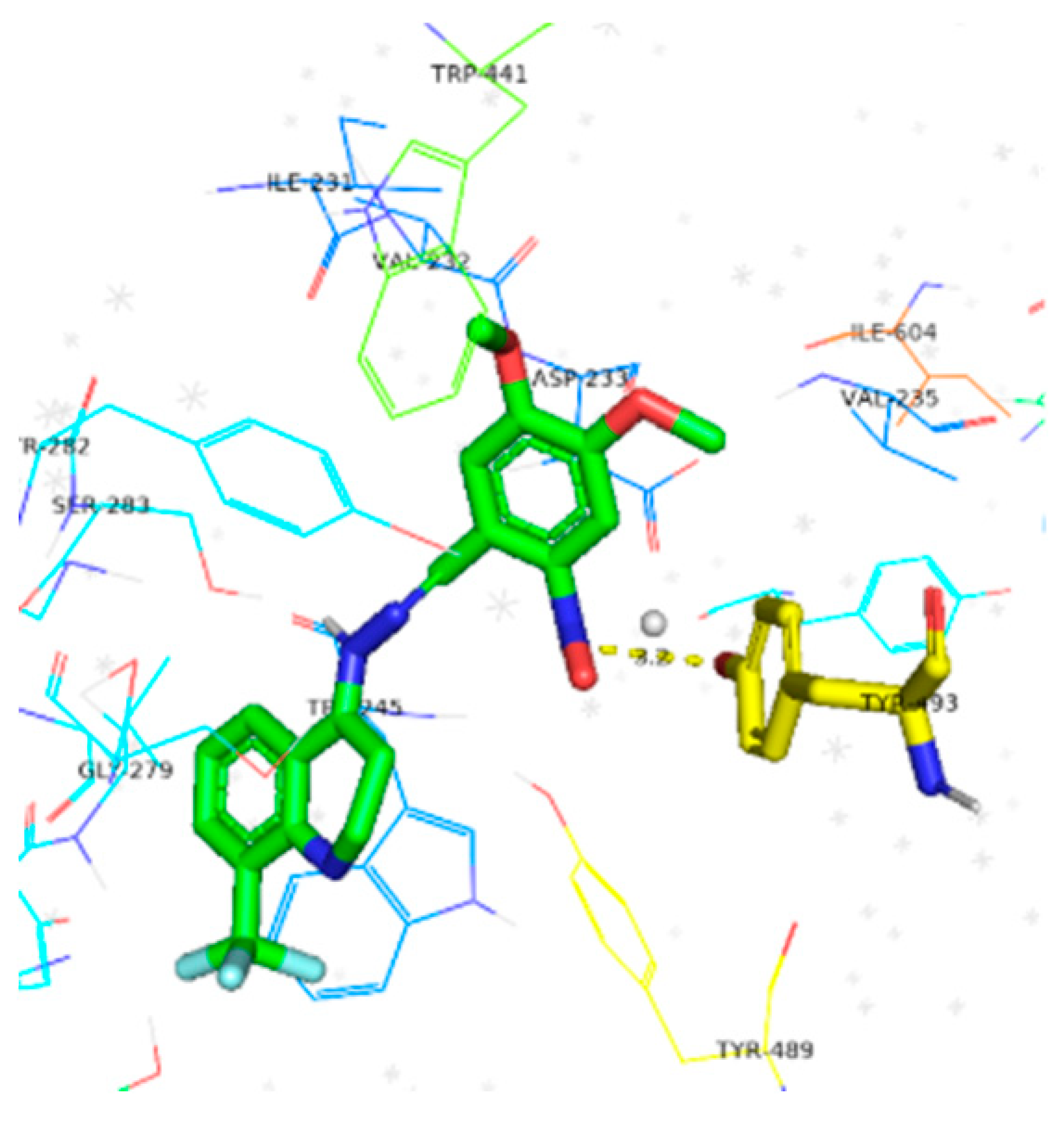 | Conventional hydrogen bond, Pi-Anion, Pi-sigma, Alkyl and Pi-alkyl | TYR493, TB245, GLY279, ASP233, TYR489, SER283 |
| 6d | −10.1 |  | 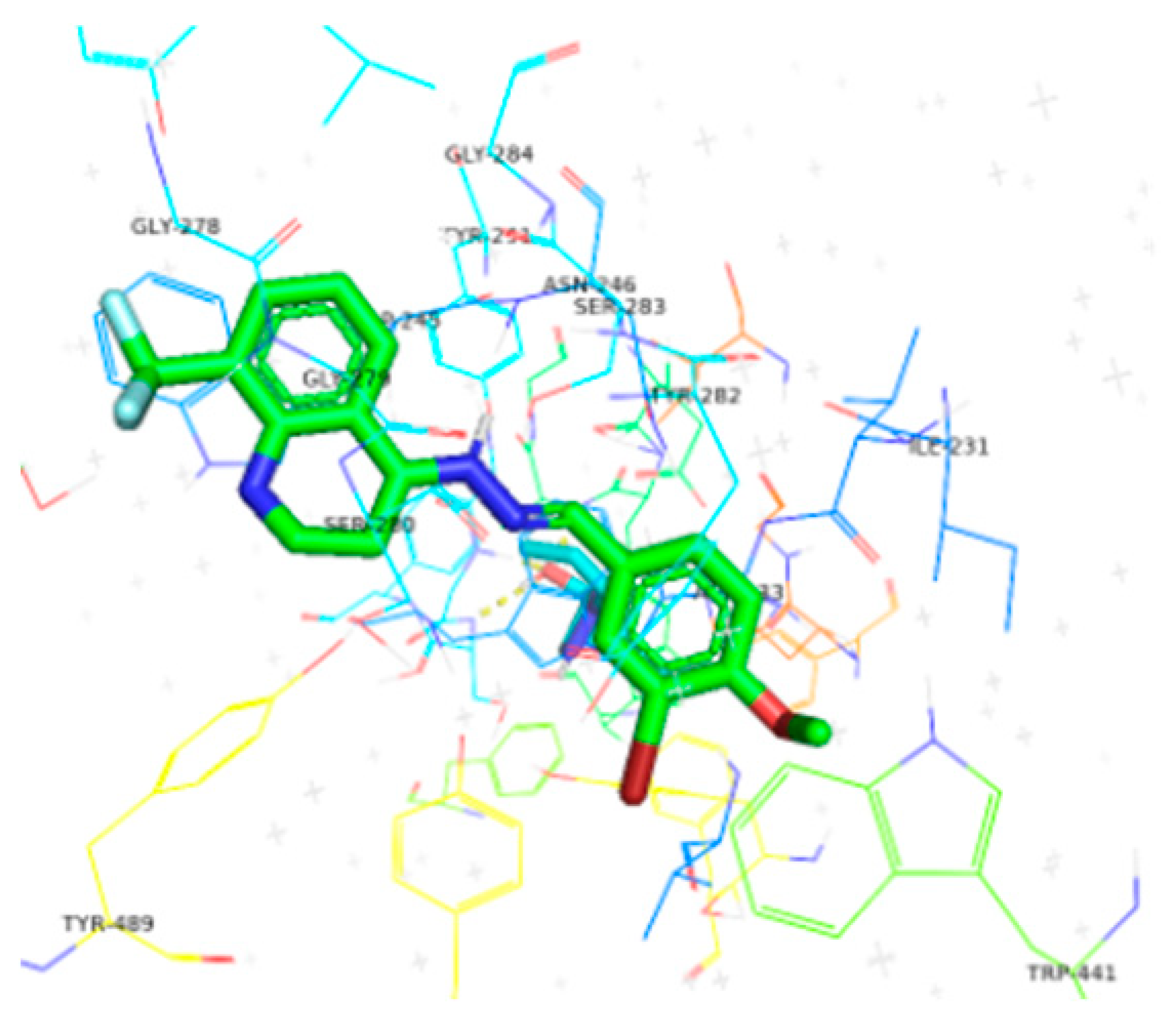 | Conventional hydrogen bond, Pi-Pi stacked, Amide-Pi-stacked, R-sigma, Alkyl and Pi-alkyl | SER280, GLY279, TYr282, GLY278, TYR489, TYR294 |
| 6e | −10.2 |  |  | Conventional hydrogen bond, Pi-Pi stacked, Pi-cation, Amide-Pi-Pi-stacked, Alkyl and Pi-alkyl | TYR489, ASP233, TYR493, SER283, PHE281, ASN248 |
| 6f | −9.8 |  | 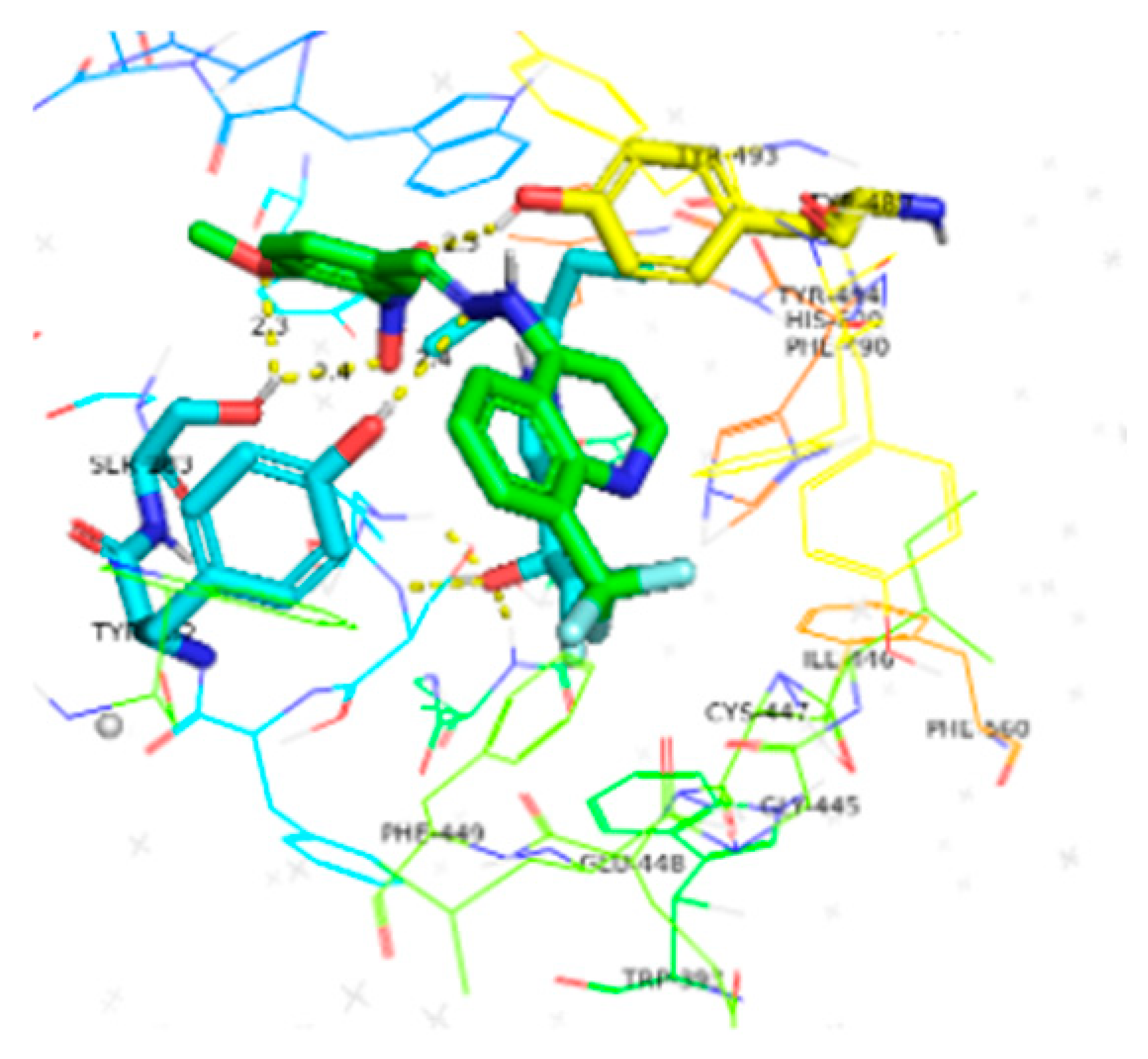 | Conventional hydrogen bond, Pi-Pi stacked, Pi-Anion and Pi-Pi-T-shaped | TYR493, TYR489, SER383, TYR494, HIS600, PHE490, PHE449 |
| 6g | −9.8 | 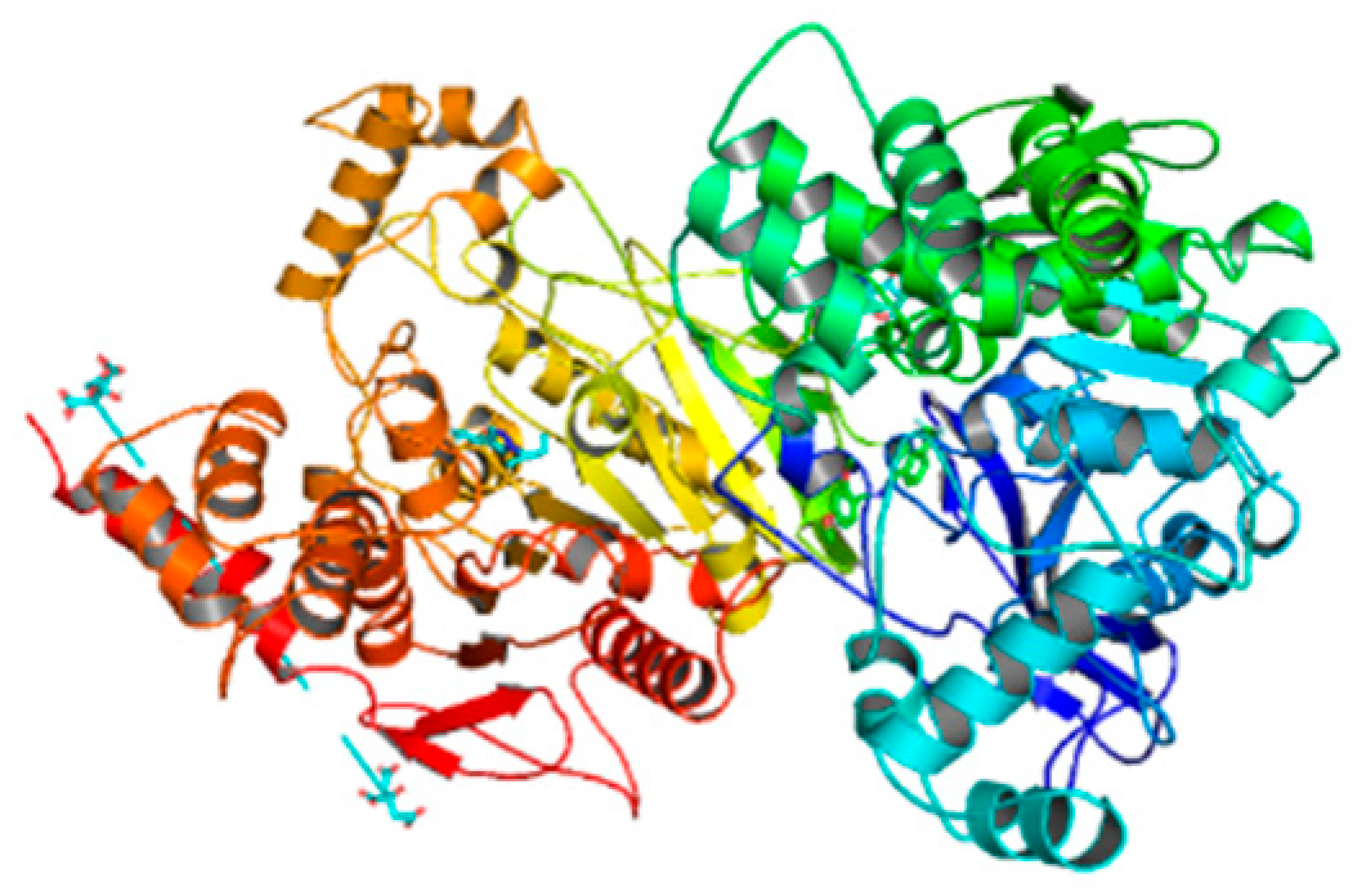 | 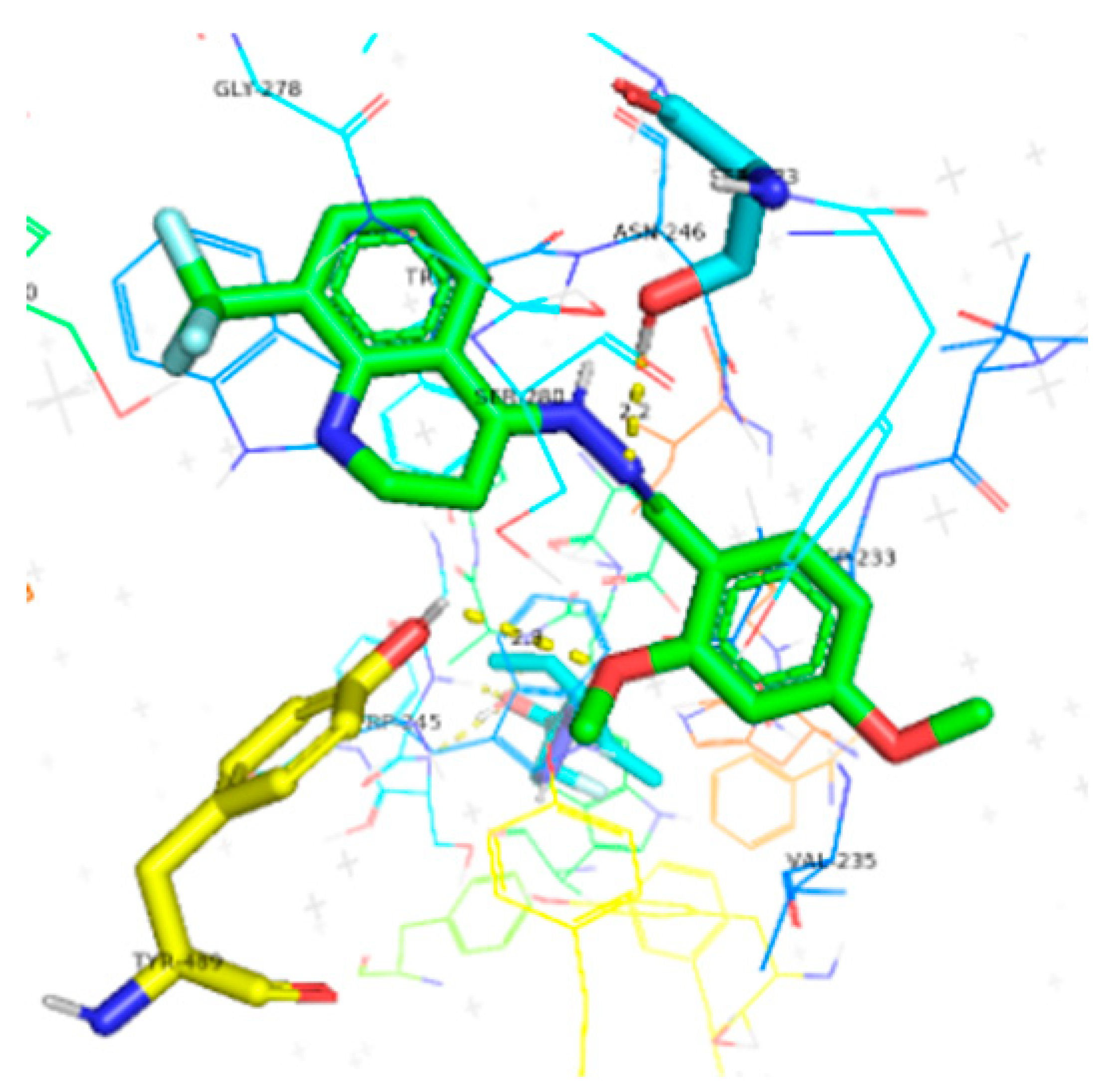 | Conventional hydrogen bond, Pi-Pi-T-stacked, Amide-Pi-stacked, Pi-sigma, Alkyl, Pi-Anion and P-alkyl | RP245, SER280, ASN246, SER283, TYR489, TRP245, GLY278, SER360, VAL235 |
| 6h | −10.1 | 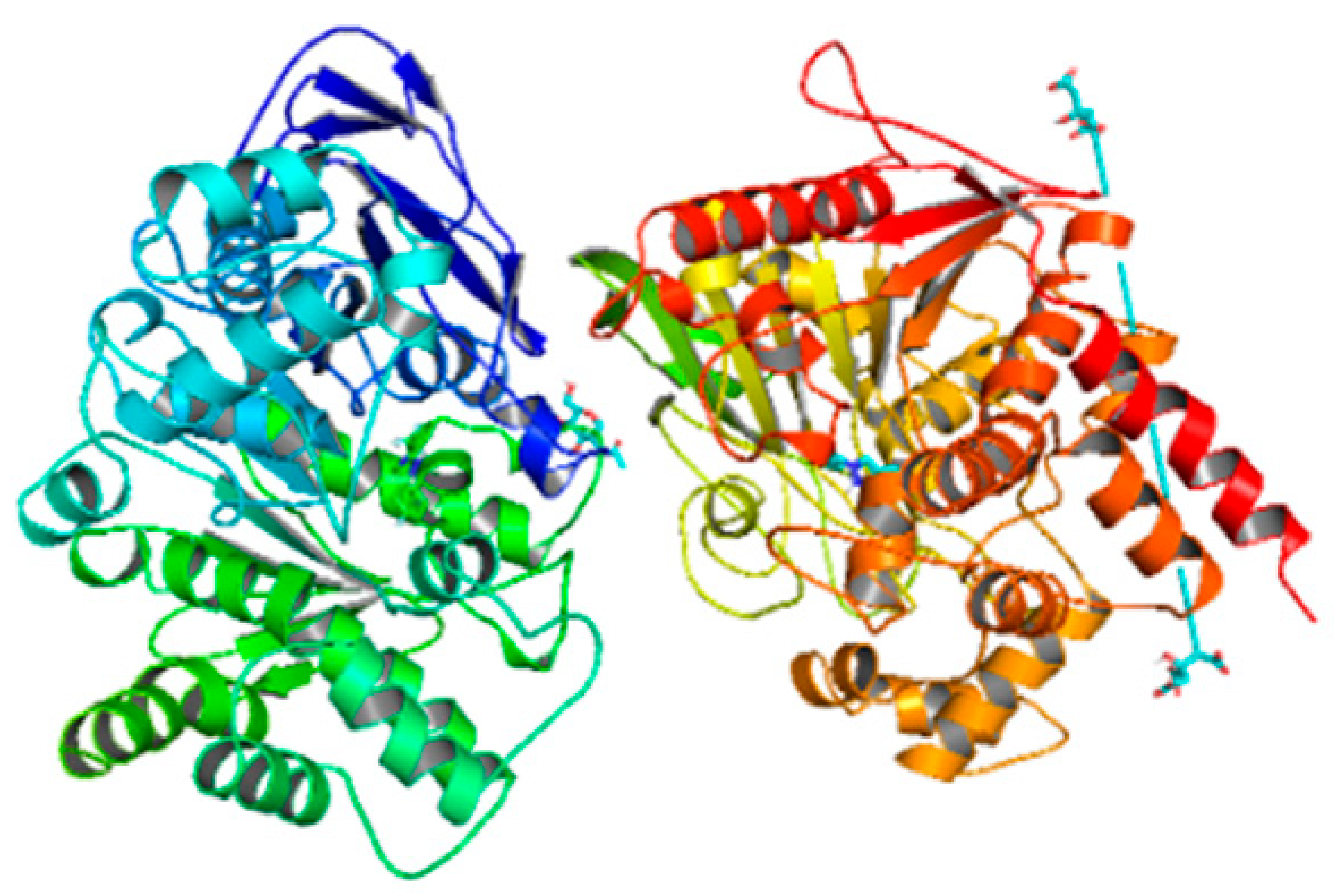 | 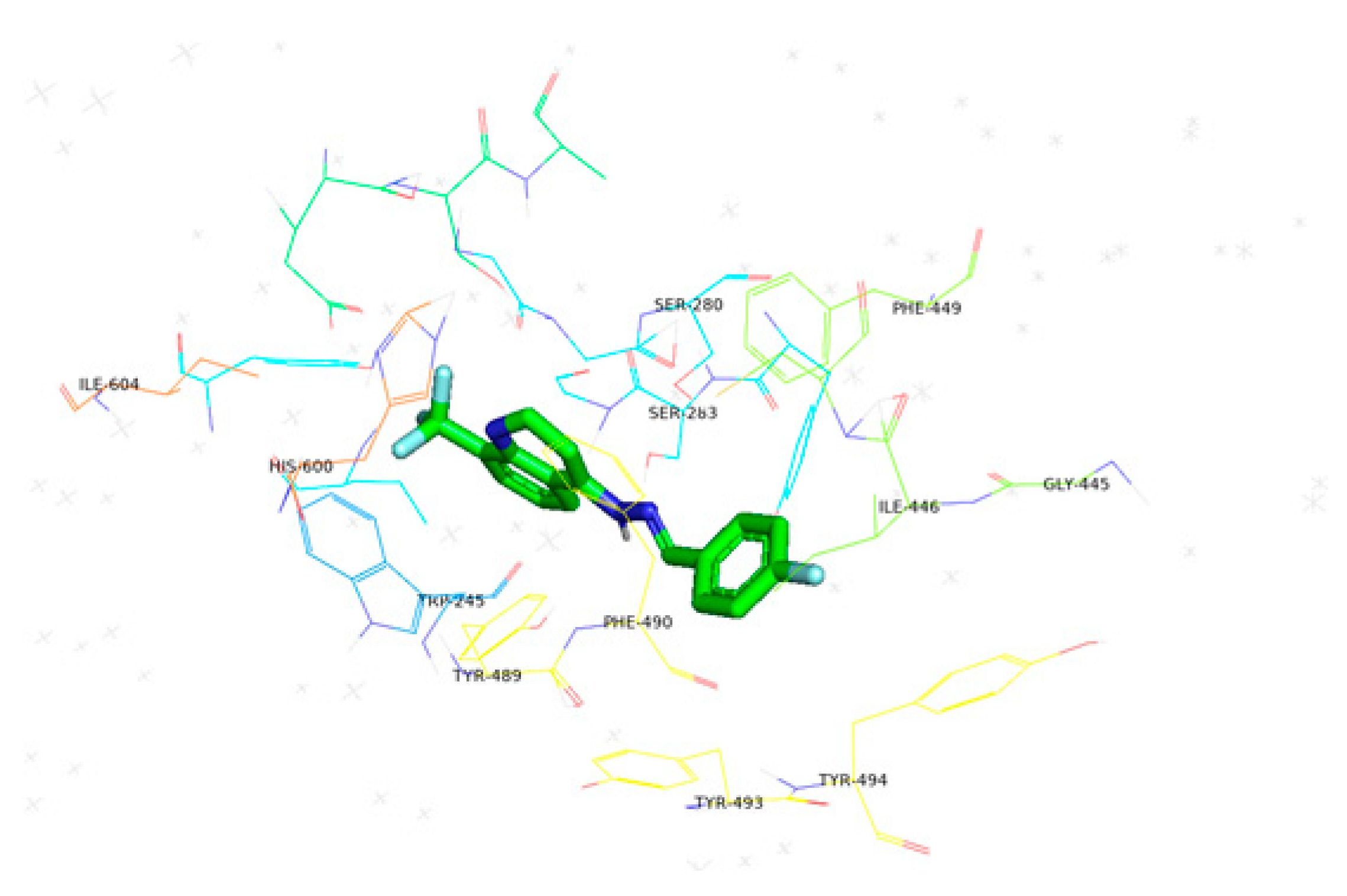 | Conventional hydrogen bond, Pi-Pi-T-shaped, Amide-Pi-stacked, and P-alkyl | SER280, PHE449, PHE490, CYS447, SER360, TYR489, ALA361 |
| 6i | −10.4 | 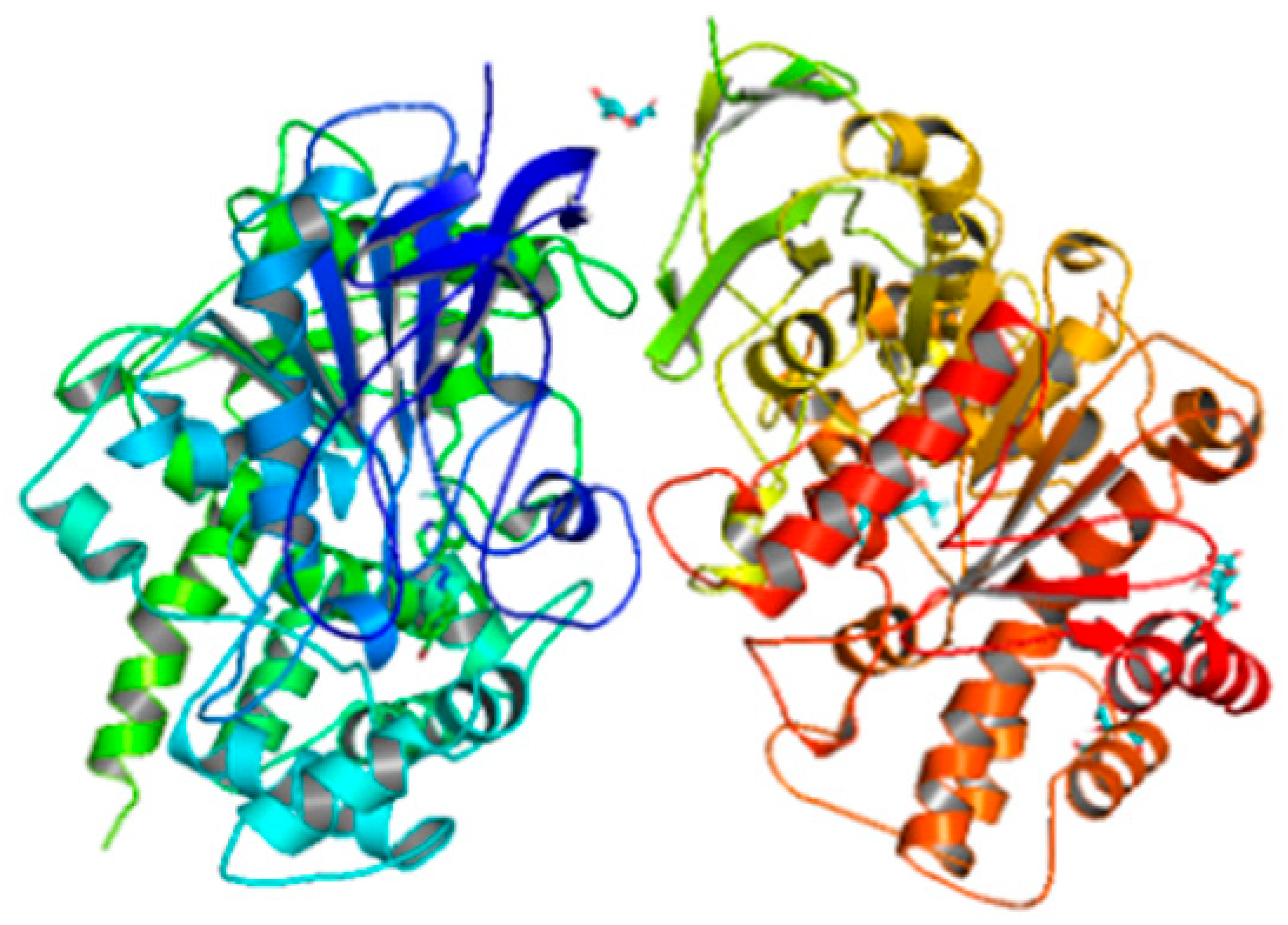 | 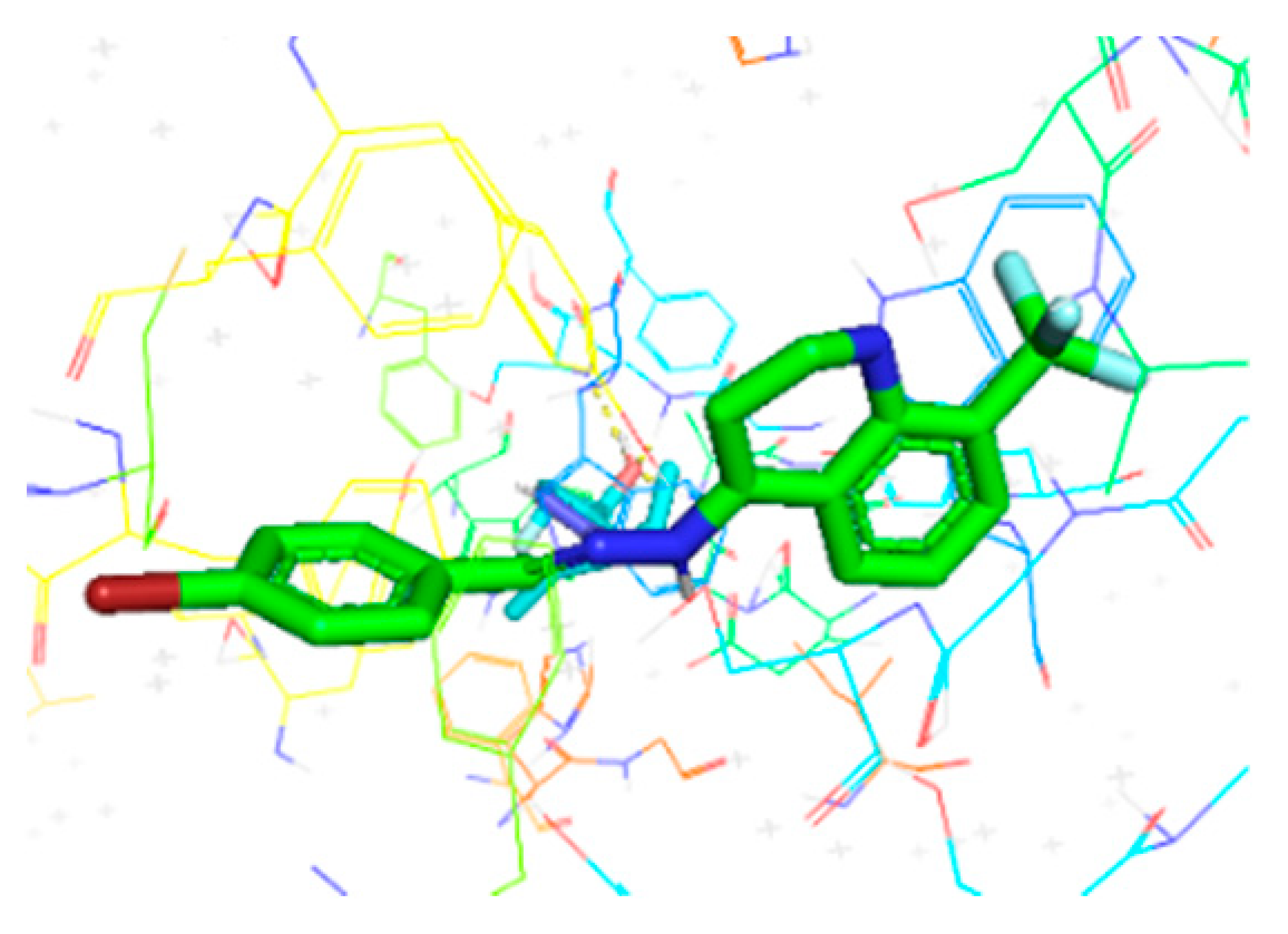 | Conventional hydrogen bond, Pi-Pi-T-shaped, Amide-Pi-stacked, Alkyl and P-alkyl | PHE444, TYR462, ALA364 |
| Model Name | Units | Compounds Code | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6a | 6b | 6c | 6d | 6e | 6f | 6g | 6h | 6i | ||
| AMES toxicity | Yes/No | Yes | No | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes |
| Max. tolerated dose (human) | Log mg/kg/day | 0.218 | 0.18 | −0.064 | 0.18 | −0.015 | −0.206 | 0.033 | 0.181 | 0.211 |
| hERG I inhibitor | Yes/No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No |
| hERG II inhibitor | Yes/No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Oral Rat Acute Toxicity (LD50) | Mol/kg | 2.839 | 2.855 | 3.437 | 2.779 | 2.823 | 3.347 | 2.878 | 2.657 | 2.705 |
| Oral Rat Chronic Toxicity (LOAEL) | Log mg/kg·bw/day | 0.663 | 1.151 | 1.318 | 0.805 | 1.084 | 1.613 | 1.095 | 1.082 | 0.903 |
| Hepatotoxicity | Yes/No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Skin Sensitization | Yes/No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No |
| T. pyriformis toxicity | Log ug/L | 0.784 | 0.883 | 0.56 | 1.056 | 0.675 | 0.665 | 0.74 | 1.162 | 1.171 |
| Minnow toxicity | Log mM | −1.64 | −0.903 | −0.46 | −0.942 | −2.189 | 0.072 | −0.689 | −0.282 | −0.762 |
| Treatment | 24 h Mortality | 48 h Mortality |
|---|---|---|
| Temephos | 98.0 ± 1.0 AB | 100.0 ± 0.0 A |
| 6a | 88.9 ± 2.2 BC | 93.3 ± 1.8 B |
| 6d | 83.3 ± 2.6 C | 87.8 ± 2.3 BC |
| 6h | 77.8 ± 2.9 CD | 82.2 ± 2.7 CD |
| 6i | 68.9 ± 3.3 DE | 73.3 ± 3.1 D |
| 6e | 55.6 ± 3.5 E | 57.8 ± 3.5 E |
| 6b | 37.8 ± 3.4 F | 41.1 ± 3.5 F |
| 6c | 26.7 ± 3.1 FG | 28.9 ± 3.2 FG |
| 6f | 16.7 ± 2.6 G | 21.1 ± 2.9 G |
| 6g | 3.3 ± 1.3 H | 4.4 ± 1.5 H |
| Acetone | 1.1 ± 0.7 H | 2.2 ± 1.0 H |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kotyan, S.; Chandana, S.N.; Ganesha, D.P.; Lakshminarayana, B.N.; Pandikatte, N.; Deb, P.K.; Ghosh, M.; Gleiser, R.M.; Mahomoodally, M.F.; Alherz, S.A.; et al. Synthesis of Novel Arylhydrazones Bearing 8-Trifluoromethyl Quinoline: Crystal Insights, Larvicidal Activity, ADMET Predictions, and Molecular Docking Studies. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 1804. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18121804
Kotyan S, Chandana SN, Ganesha DP, Lakshminarayana BN, Pandikatte N, Deb PK, Ghosh M, Gleiser RM, Mahomoodally MF, Alherz SA, et al. Synthesis of Novel Arylhydrazones Bearing 8-Trifluoromethyl Quinoline: Crystal Insights, Larvicidal Activity, ADMET Predictions, and Molecular Docking Studies. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(12):1804. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18121804
Chicago/Turabian StyleKotyan, Sukumar, Shankaranahalli N. Chandana, Doddabasavanahalli P. Ganesha, Banavase N. Lakshminarayana, Nefisath Pandikatte, Pran Kishore Deb, Manik Ghosh, Raquel M. Gleiser, Mohamad Fawzi Mahomoodally, Sukainh Aiaysh Alherz, and et al. 2025. "Synthesis of Novel Arylhydrazones Bearing 8-Trifluoromethyl Quinoline: Crystal Insights, Larvicidal Activity, ADMET Predictions, and Molecular Docking Studies" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 12: 1804. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18121804
APA StyleKotyan, S., Chandana, S. N., Ganesha, D. P., Lakshminarayana, B. N., Pandikatte, N., Deb, P. K., Ghosh, M., Gleiser, R. M., Mahomoodally, M. F., Alherz, S. A., Morsy, M. A., Khalil, H. E., Attimarad, M., Nagaraja, S., Almuqbil, R. M., Balgoname, A. A., Al-Dhubiab, B. E., Asif, A. H., Venugopala, K. N., & Dasappa, J. P. (2025). Synthesis of Novel Arylhydrazones Bearing 8-Trifluoromethyl Quinoline: Crystal Insights, Larvicidal Activity, ADMET Predictions, and Molecular Docking Studies. Pharmaceuticals, 18(12), 1804. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18121804












