Translational Pharmaco-Nutritional Approaches in the Management of Clinical Acute Pancreatitis—A Narrative Review
Abstract
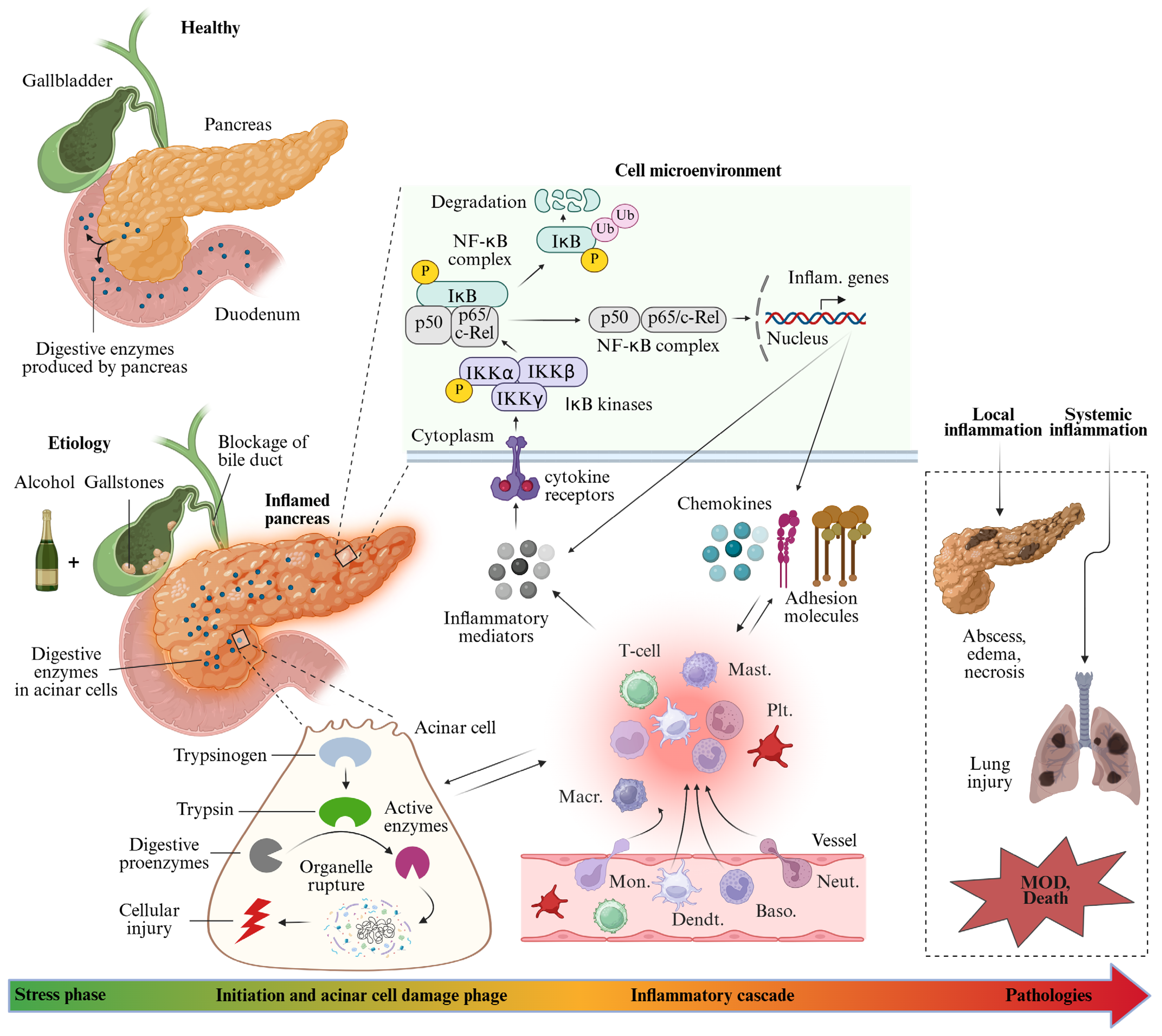
1. Introduction
2. Literature Search Methodology
3. Pharmaco-Nutritional Management of Clinical AP
4. Pharmacological Approaches
4.1. NSAID Therapy in Clinical AP
4.2. Antibiotics Therapy in Clinical AP
4.3. Cytokine and Immunomodulatory Therapy in Clinical AP
5. Nutritional Approaches
5.1. Nutrition Therapy in Clinical AP
5.2. Antioxidant Therapy in Clinical AP
5.3. Probiotic Therapy in Clinical AP
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AP | Acute pancreatitis |
| TOF | transient organ failure |
| POF | persistent organ failure |
| EPC | exacerbation of pre-exiting comorbidity |
| N/A | not applicable |
| SOFA | sepsis-related organ failure assessment |
| TNF-α | tumor necrosis-alpha |
| IL | interleukin |
| SIRS | systemic inflammatory response syndrome |
| MOD | multiple organ dysfunction |
| Iκ | I kappa |
| NF-κB | nuclear factor kappa B |
| PAF | platelet-activating factor |
| Neut. | neutrophils |
| Baso. | basophils |
| Dendt. | dendritic cell |
| Mon. | monocytes |
| Macr. | macrophages |
| Plt. | platelet |
| Mast. | mast cell |
| REL | proto-oncogne |
| P | phosphorylation |
| Ub | ubiquitination |
| NSAID | non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs |
| ERCP | endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) |
| PEP | post-ERCP pancreatitis |
| NBP | nothing by mouth |
| TEN | total enteral nutrition |
| TPN | total parenteral nutrition |
| EEN | early enteral nutrition |
| DEN | delayed enteral nutrition |
| EIN | eco immune nutrition |
| SD | solid diet |
| CLD | clear liquid diet |
| ODN | on demand nutrition |
| FA | Fatty acids |
| Abx | antibiotics |
| Ctl | control |
| vs. | comparison |
| RCT | randomized control trial |
| PCT | pilot/prospective clinical trial |
| HCS | hospital conducted study |
| PRT | prospective randomized trial |
| PNR | prospective non-randomized |
| RIT | randomized interventional trial |
| MOF | multiple organ failure |
| IAP | intra-abdominal pressure |
| IAH | intra-abdominal hypertension |
| CRP | C-reactive protein |
| APACHE II | Acute physiology and chronic health evaluation II |
| sTNFRI | soluble tumor necrosis factor receptor I. |
| NAC | n-acetylcysteine |
| ROS | reactive oxygen species |
References
- Lee, P.J.; Papachristou, G.I. New Insightss into Acute Pancreatitis. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 479–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iannuzzi, J.P.; King, J.A.; Leong, J.H.; Quan, J.; Windsor, J.W.; Tanyingoh, D.; Coward, S.; Forbes, N.; Heitman, S.J.; Shaheen, A.-A.; et al. Global Incidence of Acute Pancreatitis Is Increasing Over Time: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Gastroenterology 2022, 162, 122–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Qin, C.; Zhao, B.; Li, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Lin, C.; Wang, W. Global and Regional Burden of Pancreatitis: Epidemiological Trends, Risk Factors, and Projections to 2050 from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. BMC Gastroenterol. 2024, 24, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peery, A.F.; Murphy, C.C.; Anderson, C.; Jensen, E.T.; Deutsch-Link, S.; Egberg, M.D.; Lund, J.L.; Subramaniam, D.; Dellon, E.S.; Sperber, A.D.; et al. Burden and Cost of Gastrointestinal, Liver, and Pancreatic Diseases in the United States: Update 2024. Gastroenterology 2025, 168, 1000–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schepers, N.J.; Bakker, O.J.; Besselink, M.G.; Ahmed Ali, U.; Bollen, T.L.; Gooszen, H.G.; van Santvoort, H.C.; Bruno, M.J. Dutch Pancreatitis Study Group Impact of Characteristics of Organ Failure and Infected Necrosis on Mortality in Necrotising Pancreatitis. Gut 2019, 68, 1044–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, J.Y.; Wilcox, C.M.; Arnoletti, J.P.; Varadarajulu, S. Superiority of Endoscopic Interventions over Minimally Invasive Surgery for Infected Necrotizing Pancreatitis: Meta-analysis of Randomized Trials. Dig. Endosc. 2020, 32, 298–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.-L.; Li, J.; Shamoon, M.; Bhatia, M.; Sun, J. Recent Advances on Nutrition in Treatment of Acute Pancreatitis. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandrasegaran, K.; Heller, M.T.; Panda, A.; Shetty, A.; Menias, C.O. MRI in Acute Pancreatitis. Abdom. Radiol. 2020, 45, 1232–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trikudanathan, G.; Yazici, C.; Phillips, A.E.; Forsmark, C.E. Diagnosis and Management of Acute Pancreatitis. Gastroenterology 2024, 167, 673–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Wan, Y.; Tong, Y.; He, J.; Xu, S.; Hu, X.; Luo, C.; Xu, L.; Guo, F.; Shen, B.; et al. A Clinic-Radiomics Model for Predicting the Incidence of Persistent Organ Failure in Patients with Acute Necrotizing Pancreatitis. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2023, 2023, 2831024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, M.; Lin, S.; Xie, D.; Wang, H.; Gao, Q.; Zou, L.; Xiao, X.; Jia, Y. The Value of CT-Based Radiomics in Predicting the Prognosis of Acute Pancreatitis. Front. Med. 2023, 10, 1289295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, M.; Lu, C.; Dai, R.; Zhang, J.; Hu, H.; Shan, X. Prediction of Acute Pancreatitis Severity Based on Early CT Radiomics. BMC Med. Imaging. 2024, 24, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenner, S.; Vege, S.S.; Sheth, S.G.; Sauer, B.; Yang, A.; Conwell, D.L.; Yadlapati, R.H.; Gardner, T.B. American College of Gastroenterology Guidelines: Management of Acute Pancreatitis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2024, 119, 419–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, E.L. A Clinically Based Classification System for Acute Pancreatitis. Summary of the International Symposium on Acute Pancreatitis, Atlanta, Ga, September 11 through 13, 1992. Arch. Surg. 1993, 128, 586–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colvin, S.D.; Smith, E.N.; Morgan, D.E.; Porter, K.K. Acute Pancreatitis: An Update on the Revised Atlanta Classification. Abdom. Radiol. 2020, 45, 1222–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banks, P.A.; Bollen, T.L.; Dervenis, C.; Gooszen, H.G.; Johnson, C.D.; Sarr, M.G.; Tsiotos, G.G.; Vege, S.S.; Acute Pancreatitis Classification Working Group. Classification of Acute Pancreatitis—2012: Revision of the Atlanta Classification and Definitions by International Consensus. Gut 2013, 62, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dellinger, E.P.; Forsmark, C.E.; Layer, P.; Lévy, P.; Maraví-Poma, E.; Petrov, M.S.; Shimosegawa, T.; Siriwardena, A.K.; Uomo, G.; Whitcomb, D.C.; et al. Determinant-Based Classification of Acute Pancreatitis Severity: An International Multidisciplinary Consultation. Ann. Surg. 2012, 256, 875–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, F.U.; Laemmerhirt, F.; Lerch, M.M. Etiology and Risk Factors of Acute and Chronic Pancreatitis. Visc. Med. 2019, 35, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, W.; Liu, G.; Shi, N.; Tang, D.; Ferdek, P.E.; Jakubowska, M.A.; Liu, S.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, J.; Yao, L.; et al. A microRNA Checkpoint for Ca2+ Signaling and Overload in Acute Pancreatitis. Mol. Ther. 2022, 30, 1754–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modenbach, J.M.; Möller, C.; Asgarbeik, S.; Geist, N.; Rimkus, N.; Dörr, M.; Wolfgramm, H.; Steil, L.; Susemihl, A.; Graf, L.; et al. Biochemical Analyses of Cystatin-C Dimers and Cathepsin-B Reveals a Trypsin-Driven Feedback Mechanism in Acute Pancreatitis. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sendler, M.; Weiss, F.-U.; Golchert, J.; Homuth, G.; Van Den Brandt, C.; Mahajan, U.M.; Partecke, L.-I.; Döring, P.; Gukovsky, I.; Gukovskaya, A.S.; et al. Cathepsin B-Mediated Activation of Trypsinogen in Endocytosing Macrophages Increases Severity of Pancreatitis in Mice. Gastroenterology 2018, 154, 704–718.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.; Ma, Y.; Li, H.; Cui, J.; Guo, X.; Wang, G.; Ji, L. Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Promotes Caspase-1-Dependent Acinar Cell Pyroptosis through the PERK Pathway to Aggravate Acute Pancreatitis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2023, 120, 110293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Ren, Y.; Wang, T.; Wang, M.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Bi, J.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, R. Blocking CIRP Protects against Acute Pancreatitis by Improving Mitochondrial Function and Suppressing Pyroptosis in Acinar Cells. Cell Death Discov. 2024, 10, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, L.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Tang, D.; Yan, C.; Ma, J.; Fang, K.; Gao, L.; Ren, N.; et al. ATG7-Enhanced Impaired Autophagy Exacerbates Acute Pancreatitis by Promoting Regulated Necrosis via the miR-30b-5p/CAMKII Pathway. Cell Death Discov. 2022, 13, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Chen, X.; Yan, D.; Zhang, N.; Fu, W.; Wu, M.; Ge, F.; Wang, J.; Li, X.; Geng, M.; et al. GV-971 Prevents Severe Acute Pancreatitis by Remodeling the Microbiota-Metabolic-Immune Axis. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 8278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Yan, Q.; Li, S.; Jiao, J.; Hao, Y.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, Q.; Luo, F.; Zhang, Y.; Lv, Q.; et al. Integrative Metagenomic and Metabolomic Analyses Reveal the Potential of Gut Microbiota to Exacerbate Acute Pancreatitis. npj Biofilms Microbiomes 2024, 10, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Shi, C.; He, M.; Xiong, S.; Xia, X. Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress: Molecular Mechanism and Therapeutic Targets. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shamoon, M.; Deng, Y.; Chen, Y.Q.; Bhatia, M.; Sun, J. Therapeutic Implications of Innate Immune System in Acute Pancreatitis. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2016, 20, 73–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, T.; Kudo, M.; Strober, W. Immunopathogenesis of Pancreatitis. Mucosal Immunol. 2017, 10, 283–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakkampudi, A.; Jangala, R.; Reddy, B.R.; Mitnala, S.; Reddy, D.N.; Talukdar, R. NF-κB in Acute Pancreatitis: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Potential. Pancreatology 2016, 16, 477–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, B.M.; Al-Mokaddem, A.K.; Selim, H.M.R.M.; Alherz, F.A.; Saleh, A.; Hamdan, A.M.E.; Ousman, M.S.; El-Emam, S.Z. Pinocembrin’s Protective Effect against Acute Pancreatitis in a Rat Model: The Correlation between TLR4/NF-κB/NLRP3 and miR-34a-5p/SIRT1/Nrf2/HO-1 Pathways. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 176, 116854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuhöfer, P.; Liang, S.; Einwächter, H.; Schwerdtfeger, C.; Wartmann, T.; Treiber, M.; Zhang, H.; Schulz, H.; Dlubatz, K.; Lesina, M.; et al. Deletion of IκBα Activates RelA to Reduce Acute Pancreatitis in Mice Through Up-Regulation of Spi2A. Gastroenterology 2013, 144, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Wu, H.; Peng, Y.; He, P.; Qian, S.; Lin, H.; Chen, H.; Qian, R.; Wang, D.; Chu, M.; et al. Gastrodin Ameliorates Acute Pancreatitis by Modulating Macrophage Inflammation Cascade via Inhibition the P38/NF-κB Pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 129, 111593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahapatra, S.J.; Garg, P.K. Organ Failure and Prediction of Severity in Acute Pancreatitis. Gastroenterol. Clin. N. Am. 2025, 54, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mofidi, R.; Duff, M.D.; Wigmore, S.J.; Madhavan, K.K.; Garden, O.J.; Parks, R.W. Association between Early Systemic Inflammatory Response, Severity of Multiorgan Dysfunction and Death in Acute Pancreatitis. Br. J. Surg. 2006, 93, 738–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Zhu, S.; Shi, L.; Zhang, H.; Xu, X.; Xiang, B.; Wang, M. Automated Machine Learning for Early Prediction of Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome in Acute Pancreatitis. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2025, 25, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatia, M. Acute Pancreatitis as a Model of SIRS. Front. Biosci. 2009, 14, 2042–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machicado, J.D.; Gougol, A.; Tan, X.; Gao, X.; Paragomi, P.; Pothoulakis, I.; Talukdar, R.; Kochhar, R.; Goenka, M.K.; Gulla, A.; et al. Mortality in Acute Pancreatitis with Persistent Organ Failure Is Determined by the Number, Type, and Sequence of Organ Systems Affected. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2021, 9, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, L.; Jian, L.; Xu, J.; He, Q.; Wang, Y.; Sun, C.; Wang, W.; Sun, X. Pharmacological Interventions for Acute Pancreatitis in Adults: An Overview of Systematic Reviews. J. Evid. Based Med. 2025, 18, e70007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marik, P.E. What Is the Best Way to Feed Patients with Pancreatitis? Curr. Opin. Crit. Care 2009, 15, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carnevale, S.; Vitale, A.; Razzi, M.; Onori, C.; Cornacchia, G.; Grispo, O.; Corsinovi, E.; Rossl, L.; Spinetti, E.; Tosi, M.; et al. Non-Evidence-Based Dietary Restrictions in Hospital Nutrition and Their Impact on Malnutrition: A Narrative Review of International and National Guidelines. Dietetics 2024, 3, 568–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, S.; Wang, J.; Guo, X.; Song, Y.; Fu, K.; Gao, Z.; Liu, D.; He, W.; Yang, L.-L. Energy Metabolism in Health and Diseases. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2025, 10, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-Y.; He, C.; Zhu, Y.; Lu, N.-H. Role of Gut Microbiota on Intestinal Barrier Function in Acute Pancreatitis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 26, 2187–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, P.; Luo, Y.; Okoye, C.S.; Chen, H.; Liu, J.; Zhang, G.; Xu, C.; Chen, H. Intestinal Barrier Damage, Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome, and Acute Lung Injury: A Troublesome Trio for Acute Pancreatitis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 132, 110770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Wu, D.H.; Wang, T.; Wang, M.; Xu, Y.; Ren, Y.; Lyu, Y.; Wu, R. CIRP Contributes to Multiple Organ Damage in Acute Pancreatitis by Increasing Endothelial Permeability. Commun. Biol. 2025, 8, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazici, C.; Priyadarshini, M.; Boulay, B.; Dai, Y.; Layden, B.T. Alterations in Microbiome Associated with Acute Pancreatitis. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 2024, 40, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, W. Shaping the Gut Microbiome from the Pancreas. Sci. Signal. 2017, 10, eaan3016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.; Mei, Q.; Yin, N.; Huang, Z.; Li, B.; Luo, S.; Xu, B.; Fan, J.; Huang, C.; Zeng, Y. Paneth Cells Protect against Acute Pancreatitis via Modulating Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis. mSystems 2022, 7, e0150721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, B.; Yan, R.; Hu, X.; Lou, J.; Zhu, Y.; Shao, Y.; Jiang, H.; Hao, Y.; Lv, L. Role of Bifidobacterium Animalis Subsp. Lactis BB-12 in Mice with Acute Pancreatitis. AMB Express 2025, 15, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werawatganon, D.; Vivatvakin, S.; Somanawat, K.; Tumwasorn, S.; Klaikeaw, N.; Siriviriyakul, P.; Chayanupatkul, M. Effects of Probiotics on Pancreatic Inflammation and Intestinal Integrity in Mice with Acute Pancreatitis. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2023, 23, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.-D.; Zhu, R.-X.; Bian, Z.-Z.; Sun, T.-W. Effect of Probiotics on Length of Hospitalization in Mild Acute Pancreatitis: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. World J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 27, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakker, O.J.; Van Brunschot, S.; Van Santvoort, H.C.; Besselink, M.G.; Bollen, T.L.; Boermeester, M.A.; Dejong, C.H.; Van Goor, H.; Bosscha, K.; Ali, U.A.; et al. Early versus On-Demand Nasoenteric Tube Feeding in Acute Pancreatitis. N. Engl. J. Med 2014, 371, 1983–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Li, W.; Ke, L.; Tong, Z.; Ni, H.; Li, G.; Zhang, L.; Nie, Y.; Wang, X.; Ye, X.; et al. Early Enteral Nutrition Prevents Intra-abdominal Hypertension and Reduces the Severity of Severe Acute Pancreatitis Compared with Delayed Enteral Nutrition: A Prospective Pilot Study. World J. Surg. 2013, 37, 2053–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajkumar, N.; Karthikeyan, V.S.; Ali, S.M.; Sistla, S.C.; Kate, V. Clear Liquid Diet vs Soft Diet as the Initial Meal in Patients With Mild Acute Pancreatitis: A Randomized Interventional Trial. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2013, 28, 365–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wereszczynska-Siemiatkowska, U.; Swidnicka-Siergiejko, A.; Siemiatkowski, A.; Dabrowski, A. Early Enteral Nutrition Is Superior to Delayed Enteral Nutrition for the Prevention of Infected Necrosis and Mortality in Acute Pancreatitis. Pancreas 2013, 42, 640–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.-M.; Ji, K.-Q.; Wang, H.-Y.; Li, G.-F.; Zang, B.; Chen, W.-M. Total Enteral Nutrition in Prevention of Pancreatic Necrotic Infection in Severe Acute Pancreatitis. Pancreas 2010, 39, 248–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doley, R.P.; Yadav, T.D.; Wig, J.D.; Kochhar, R.; Singh, G.; Bharathy, K.G.S.; Kudari, A.; Gupta, R.; Gupta, V.; Poornachandra, K.S.; et al. Enteral Nutrition in Severe Acute Pancreatitis. JOP J. Pancreas 2009, 10, 157–162. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, H.-L.; Zheng, J.-J.; Tong, D.-N.; Chen, W.-X.; Fan, X.-B.; Hang, X.-M.; Jiang, Y.-Q. Effect of Lactobacillus Plantarum Enteral Feeding on the Gut Permeability and Septic Complications in the Patients with Acute Pancreatitis. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 62, 923–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casas, M.; Mora, J.; Fort, E.; Aracil, C.; Busquets, D.; Galter, S.; Jáuregui, C.E.; Ayala, E.; Cardona, D.; Gich, I.; et al. Total enteral nutrition vs. total parenteral nutrition in patients with severe acute pancreatitis. Rev. Esp. Enferm. Dig. 2007, 99, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrov, M.S.; Kukosh, M.V.; Emelyanov, N.V. A Randomized Controlled Trial of Enteral versus Parenteral Feeding in Patients with Predicted Severe Acute Pancreatitis Shows a Significant Reduction in Mortality and in Infected Pancreatic Complications with Total Enteral Nutrition. Dig. Surg. 2006, 23, 336–344; Discussion 344–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Targarona Modena, J.; Barreda Cevasco, L.; Arroyo Basto, C.; Orellana Vicuna, A.; Portanova Ramirez, M. Total Enteral Nutrition as Prophylactic Therapy for Pancreatic Necrosis Infection in Severe Acute Pancreatitis. Pancreatology 2006, 6, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louie, B.E.; Noseworthy, T.; Hailey, D.; Gramlich, L.M.; Jacobs, P.; Warnock, G.L. 2004 MacLean-Mueller Prize Enteral or Parenteral Nutrition for Severe Pancreatitis: A Randomized Controlled Trial and Health Technology Assessment. Can. J. Surg. 2005, 48, 298–306. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhao, G.; Wang, C.-Y.; Wang, F.; Xiong, J.-X. Clinical Study on Nutrition Support in Patients with Severe Acute Pancreatitis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2003, 9, 2105–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, R.; Patel, K.; Calder, P.C.; Yaqoob, P.; Primrose, J.N.; Johnson, C.D. A Randomised Clinical Trial to Assess the Effect of Total Enteral and Total Parenteral Nutritional Support on Metabolic, Inflammatory and Oxidative Markers in Patients with Predicted Severe Acute Pancreatitis (APACHE II > or =6). Pancreatology 2003, 3, 406–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abou-Assi, S.; Craig, K.; O’Keefe, S.J.D. Hypocaloric Jejunal Feeding Is Better than Total Parenteral Nutrition in Acute Pancreatitis: Results of a Randomized Comparative Study. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2002, 97, 2255–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oláh, A.; Pardavi, G.; Belágyi, T.; Nagy, A.; Issekutz, A.; Mohamed, G.E. Early Nasojejunal Feeding in Acute Pancreatitis Is Associated with a Lower Complication Rate. Nutrition 2002, 18, 259–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohail, R.; Mathew, M.; Patel, K.K.; Reddy, S.A.; Haider, Z.; Naria, M.; Habib, A.; Abdin, Z.U.; Razzaq Chaudhry, W.; Akbar, A. Effects of Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs) and Gastroprotective NSAIDs on the Gastrointestinal Tract: A Narrative Review. Cureus 2023, 15, e37080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Ma, X.; Jia, X.; Wang, R.; Liu, L.; Zhang, M.; Wan, X.; Tang, C.; Huang, L. Prevention of Severe Acute Pancreatitis with Cyclooxygenase-2 Inhibitors: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 115, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montaño Loza, A.; García Correa, J.; González Ojeda, A.; Fuentes Orozco, C.; Dávalos Cobián, C.; Rodríguez Lomelí, X. Prevention of hyperamilasemia and pancreatitis after endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography with rectal administration of indomethacin. Rev. Gastroenterol. Mex. 2006, 71, 262–268. [Google Scholar]
- Sotoudehmanesh, R.; Khatibian, M.; Kolahdoozan, S.; Ainechi, S.; Malboosbaf, R.; Nouraie, M. Indomethacin May Reduce the Incidence and Severity of Acute Pancreatitis after ERCP. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 102, 978–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmunzer, B.J.; Scheiman, J.M.; Lehman, G.A.; Chak, A.; Mosler, P.; Higgins, P.D.R.; Hayward, R.A.; Romagnuolo, J.; Elta, G.H.; Sherman, S.; et al. A Randomized Trial of Rectal Indomethacin to Prevent Post-ERCP Pancreatitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 1414–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, B.; Carter, R.; Imrie, C.; Evans, S.; O’Suilleabhain, C. Diclofenac Reduces the Incidence of Acute Pancreatitis after Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography. Gastroenterology 2003, 124, 1786–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsuka, T.; Kawazoe, S.; Nakashita, S.; Kamachi, S.; Oeda, S.; Sumida, C.; Akiyama, T.; Ario, K.; Fujimoto, M.; Tabuchi, M.; et al. Low-Dose Rectal Diclofenac for Prevention of Post-Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography Pancreatitis: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 47, 912–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Bao, J.; Hu, C.; Ding, H.; Liu, X.; Mei, Q.; Xu, J. Effect of Diclofenac on the Levels of Lipoxin A4 and Resolvin D1 and E1 in the Post-ERCP Pancreatitis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2014, 59, 2992–2996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomoda, T.; Kato, H.; Miyamoto, K.; Matsumi, A.; Ueta, E.; Fujii, Y.; Saragai, Y.; Yamazaki, T.; Uchida, D.; Matsumoto, K.; et al. Efficacy of Low Dose Rectal Diclofenac for Preventing Post-Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography Pancreatitis: Propensity Score-Matched Analysis. Dig. Endosc. 2021, 33, 656–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werge, M.; Novovic, S.; Schmidt, P.N.; Gluud, L.L. Infection Increases Mortality in Necrotizing Pancreatitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Pancreatology 2016, 16, 698–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Campos, T.; Assef, J.C.; Rasslan, S. Questions about the Use of Antibiotics in Acute Pancreatitis. World J. Emerg. Surg. 2006, 1, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sun, E.; Tharakan, M.; Kapoor, S.; Chakravarty, R.; Salhab, A.; Buscaglia, J.M.; Nagula, S. Poor Compliance with ACG Guidelines for Nutrition and Antibiotics in the Management of Acute Pancreatitis: A North American Survey of Gastrointestinal Specialists and Primary Care Physicians. JOP J. Pancreas 2013, 14, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isenmann, R.; Rünzi, M.; Kron, M.; Kahl, S.; Kraus, D.; Jung, N.; Maier, L.; Malfertheiner, P.; Goebell, H.; Beger, H.G.; et al. Prophylactic Antibiotic Treatment in Patients with Predicted Severe Acute Pancreatitis: A Placebo-Controlled, Double-Blind Trial. Gastroenterology 2004, 126, 997–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Xu, L.; Zhang, D.; Sun, W.; Che, Z.; Zhao, B.; Chen, Y.; Yang, Z.; Chen, E.; Ni, T.; et al. Effect of Early Antibiotic Treatment Strategy on Prognosis of Acute Pancreatitis. BMC Gastroenterol. 2023, 23, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.; Dai, W.; Shen, J.; Zhang, M.; Shi, Y.; Jiang, K.; Guo, L. Assessment of Prophylactic Carbapenem Antibiotics Administration for Severe Acute Pancreatitis: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Digestion 2022, 103, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassi, C.; Falconi, C.; Casetti, L.; Valerio, A.; Caldiron, E.; Butturini, G.; Pederzoli, P. Antibiotics in Severe Pancreatitis: The Current Status. HPB 1999, 1, 57–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Røkke, O.; Bache Harbitz, T.; Liljedal, J.; Pettersen, T.; Fetvedt, T.; Øystein Heen, L.; Skreden, K.; Viste, A. Early Treatment of Severe Pancreatitis with Imipenem: A Prospective Randomized Clinical Trial. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 42, 771–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villatoro, E.; Bassi, C.; Larvin, M. Antibiotic Therapy for Prophylaxis against Infection of Pancreatic Necrosis in Acute Pancreatitis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2006, 4, CD002941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villatoro, E.; Mulla, M.; Larvin, M. Antibiotic Therapy for Prophylaxis against Infection of Pancreatic Necrosis in Acute Pancreatitis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2010, 2010, CD002941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordback, I.; Sand, J.; Saaristo, R.; Paajanen, H. Early Treatment with Antibiotics Reduces the Need for Surgery in Acute Necrotizing Pancreatitis--a Single-Center Randomized Study. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2001, 5, 113–118; Discussion 118–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Räty, S.; Sand, J.; Pulkkinen, M.; Matikainen, M.; Nordback, I. Post-ERCP Pancreatitis: Reduction by Routine Antibiotics. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2001, 5, 339–345; Discussion 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saraiva, M.; O’Garra, A. The Regulation of IL-10 Production by Immune Cells. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 10, 170–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berney, T.; Gasche, Y.; Robert, J.; Jenny, A.; Mensi, N.; Grau, G.; Vermeulen, B.; Morel, P. Serum Profiles of Interleukin-6, Interleukin-8, and Interleukin-10 in Patients with Severe and Mild Acute Pancreatitis. Pancreas 1999, 18, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pezzilli, R.; Billi, P.; Miniero, R.; Barakat, B. Serum Interleukin-10 in Human Acute Pancreatitis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 1997, 42, 1469–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devière, J.; Le Moine, O.; Van Laethem, J.L.; Eisendrath, P.; Ghilain, A.; Severs, N.; Cohard, M. Interleukin 10 Reduces the Incidence of Pancreatitis after Therapeutic Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography. Gastroenterology 2001, 120, 498–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oruc, N.; Ozutemiz, A.O.; Yukselen, V.; Nart, D.; Celik, H.A.; Yuce, G.; Batur, Y. Infliximab: A New Therapeutic Agent in Acute Pancreatitis? Pancreas 2004, 28, e1–e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tekin, S.O.; Teksoz, S.; Terzioglu, D.; Arikan, A.E.; Ozcevik, H.; Uslu, E. Use of Infliximab in Treatment of Acute Pancreatitis. Bratisl. Lek. J. 2015, 116, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malleo, G.; Mazzon, E.; Genovese, T.; Di Paola, R.; Muià, C.; Centorrino, T.; Siriwardena, A.K.; Cuzzocrea, S. Etanercept Attenuates the Development of Cerulein-Induced Acute Pancreatitis in Mice: A Comparison with TNF-Alpha Genetic Deletion. Shock 2007, 27, 542–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohwada, S.; Ishigami, K.; Yokoyama, Y.; Kazama, T.; Masaki, Y.; Takahashi, M.; Yoshii, S.; Yamano, H.; Chiba, H.; Nakase, H. Immune-Related Colitis and Pancreatitis Treated with Infliximab. Clin. J. Gastroenterol. 2023, 16, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triantafillidis, J.K.; Cheracakis, P.; Hereti, I.A.; Argyros, N.; Karra, E. Acute Idiopathic Pancreatitis Complicating Active Crohn’s Disease: Favorable Response to Infliximab Treatment. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2000, 95, 3334–3336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randomised Treatment of Acute Pancreatitis with Infliximab: Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Multi-Centre Trial (RAPID-I). Available online: https://www.centerwatch.com (accessed on 18 May 2025).
- Ashraf, M.A.; Nookala, V. Biochemistry of Platelet Activating Factor. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Xia, S.-H.; Chen, H.; Li, X.-H. Therapy for Acute Pancreatitis with Platelet-Activating Factor Receptor Antagonists. World J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 14, 4735–4738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konturek, S.J.; Dembinski, A.; Konturek, P.J.; Warzecha, Z.; Jaworek, J.; Gustaw, P.; Tomaszewska, R.; Stachura, J. Role of Platelet Activating Factor in Pathogenesis of Acute Pancreatitis in Rats. Gut 1992, 33, 1268–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emanuelli, G.; Montrucchio, G.; Dughera, L.; Gaia, E.; Lupia, E.; Battaglia, E.; De Martino, A.; De Giuli, P.; Gubetta, L.; Camussi, G. Role of Platelet Activating Factor in Acute Pancreatitis Induced by Lipopolysaccharides in Rabbits. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1994, 261, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lane, J.S.; Todd, K.E.; Gloor, B.; Chandler, C.F.; Kau, A.W.; Ashley, S.W.; Reber, H.A.; McFadden, D.W. Platelet Activating Factor Antagonism Reduces the Systemic Inflammatory Response in a Murine Model of Acute Pancreatitis. J. Surg. Res. 2001, 99, 365–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, C.D. Platelet-Activating Factor and Platelet-Activating Factor Antagonists in Acute Pancreatitis. Dig. Surg. 1999, 16, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingsnorth, A.N.; Galloway, S.W.; Formela, L.J. Randomized, Double-Blind Phase II Trial of Lexipafant, a Platelet-Activating Factor Antagonist, in Human Acute Pancreatitis. J. Br. Surg. 1995, 82, 1414–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKay, C.J.; Curran, F.; Sharples, C.; Baxter, J.N.; Imrie, C.W. Prospective Placebo-Controlled Randomized Trial of Lexipafant in Predicted Severe Acute Pancreatitis. Br. J. Surg. 1997, 84, 1239–1243. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, C.D. Double Blind, Randomised, Placebo Controlled Study of a Platelet Activating Factor Antagonist, Lexipafant, in the Treatment and Prevention of Organ Failure in Predicted Severe Acute. Gut 2001, 48, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raggio, M.J.; Morris, P.E. Drotrecogin Alfa. Drugs Today 2004, 40, 517–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindstrom, O.; Kylanpaa, L.; Mentula, P.; Puolakkainen, P.; Kemppainen, E.; Haapiainen, R.; Fernandez, J.A.; Griffin, J.H.; Repo, H.; Petaja, J. Upregulated but Insufficient Generation of Activated Protein C Is Associated with Development of Multiorgan Failure in Severe Acute Pancreatitis. Crit. Care 2006, 10, R16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamdar, S.; Babu, B.I.; Nirmalan, M.; Jeziorska, M.; McMahon, R.F.; Siriwardena, K. Activated Protein c in L-Arginine-Induced Experimental Acute Pancreatitis. Pancreas 2008, 37, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsfasser, G. Decreased Inflammation and Improved Survival with Recombinant Human Activated Protein C Treatment in Experimental Acute Pancreatitis. Arch. Surg. 2006, 141, 670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanel, L.; Mas, M.R.; Comert, B.; Isik, A.T.; Aydin, S.; Mas, N.; Deveci, S.; Ozyurt, M.; Tasci, I.; Unal, T. The Effect of Activated Protein C on Experimental Acute Necrotizing Pancreatitis. Crit. Care 2005, 9, R184-190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machała, W.; Wachowicz, N.; Komorowska, A.; Gaszyński, W. The Use of Drotrecogin Alfa (Activated) in Severe Sepsis during Acute Pancreatitis—Two Case Studies. Med. Sci. Monit. 2004, 10, CS31-6. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lanzillotta, M.; Vujasinovic, M.; Löhr, J.-M.; Della Torre, E. Update on Autoimmune Pancreatitis and IgG4-Related Disease. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2025, 13, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, C.J.; Mason, J.M.; Babu, B.I.; Sheen, A.J.; Eddleston, J.M.; Parker, M.J.; Pemberton, P.; Siriwardena, A.K. Twenty-Four Hour Infusion of Human Recombinant Activated Protein C (Xigris) Early in Severe Acute Pancreatitis: The XIG-AP 1 Trial. Pancreatology 2015, 15, 635–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernard, G.R.; Vincent, J.-L.; Laterre, P.-F.; LaRosa, S.P.; Dhainaut, J.-F.; Lopez-Rodriguez, A.; Steingrub, J.S.; Garber, G.E.; Helterbrand, J.D.; Ely, E.W.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Recombinant Human Activated Protein C for Severe Sepsis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 344, 699–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuraishi, Y.; Uehara, T.; Watanabe, T.; Ashihara, N.; Ozawa, M.; Kanai, K.; Kawa, S. Corticosteroids Prevent the Progression of Autoimmune Pancreatitis to Chronic Pancreatitis. Pancreatology 2020, 20, 1062–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, P.A.; Topazian, M.D.; Witzig, T.E.; Clain, J.E.; Gleeson, F.C.; Klebig, R.R.; Levy, M.J.; Pearson, R.K.; Petersen, B.T.; Smyrk, T.C.; et al. Treatment of Relapsing Autoimmune Pancreatitis with Immunomodulators and Rituximab: The Mayo Clinic Experience. Gut 2013, 62, 1607–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masaki, Y.; Nakase, H.; Tsuji, Y.; Nojima, M.; Shimizu, K.; Mizuno, N.; Ikeura, T.; Uchida, K.; Ido, A.; Kodama, Y.; et al. The Clinical Efficacy of Azathioprine as Maintenance Treatment for Autoimmune Pancreatitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 56, 869–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinberg, W.; Tenner, S. Acute Pancreatitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 1994, 330, 1198–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leppäniemi, A.; Tolonen, M.; Tarasconi, A.; Segovia-Lohse, H.; Gamberini, E.; Kirkpatrick, A.W.; Ball, C.G.; Parry, N.; Sartelli, M.; Wolbrink, D.; et al. 2019 WSES Guidelines for the Management of Severe Acute Pancreatitis. World J. Emerg. Surg. 2019, 14, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crockett, S.D.; Wani, S.; Gardner, T.B.; Falck-Ytter, Y.; Barkun, A.N.; Crockett, S.; Falck-Ytter, Y.; Feuerstein, J.; Flamm, S.; Gellad, Z.; et al. American Gastroenterological Association Institute Guideline on Initial Management of Acute Pancreatitis. Gastroenterology 2018, 154, 1096–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de-Madaria, E.; Herrera-Marante, I.; González-Camacho, V.; Bonjoch, L.; Quesada-Vázquez, N.; Almenta-Saavedra, I.; Miralles-Maciá, C.; Acevedo-Piedra, N.G.; Roger-Ibáñez, M.; Sánchez-Marin, C.; et al. Fluid Resuscitation with Lactated Ringer’s Solution vs Normal Saline in Acute Pancreatitis: A Triple-Blind, Randomized, Controlled Trial. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2018, 6, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Wang, R.; Song, P.; Peng, Q.; Jin, X.; Li, B.; Ni, J.; Shen, J.; Bao, J.; Wu, Z.; et al. Lactate Facilitates Pancreatic Repair Following Acute Pancreatitis by Promoting Reparative Macrophage Polarization. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2025, 19, 101535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoque, R.; Farooq, A.; Ghani, A.; Gorelick, F.; Mehal, W.Z. Lactate Reduces Liver and Pancreatic Injury in Toll-Like Receptor– and Inflammasome-Mediated Inflammation via GPR81-Mediated Suppression of Innate Immunity. Gastroenterology 2014, 146, 1763–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, S.; Goswami, P.; Poudel, S.; Gunjan, D.; Singh, N.; Yadav, R.; Kumar, U.; Pandey, G.; Saraya, A. Acute Pancreatitis Is Characterized by Generalized Intestinal Barrier Dysfunction in Early Stage. Pancreatology 2023, 23, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhao, H.-X.; Bai, C.; Zhou, X.-Y. Blockade of High-Mobility Group Box 1 Attenuates Intestinal Mucosal Barrier Dysfunction in Experimental Acute Pancreatitis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 6799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, Q.; Hu, J.; Huang, Z.; Fan, J.; Huang, C.; Lu, Y.; Wang, X.; Zeng, Y. Pretreatment with Chitosan Oligosaccharides Attenuate Experimental Severe Acute Pancreatitis via Inhibiting Oxidative Stress and Modulating Intestinal Homeostasis. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2021, 42, 942–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakananurak, N.; Gramlich, L. Nutrition Management in Acute Pancreatitis: Clinical Practice Consideration. World J. Clin. Cases 2020, 8, 1561–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dancu, G.; Tarta, C.; Socaciu, C.; Bende, F.; Danila, M.; Sirli, R.; Sporea, I.; Miutescu, B.; Popescu, A. Unraveling the Metabolic Changes in Acute Pancreatitis: A Metabolomics-Based Approach for Etiological Differentiation and Acute Biomarker Discovery. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahajan, U.M.; Weiss, F.U.; Lerch, M.M.; Mayerle, J. Molecular, Biochemical, and Metabolic Abnormalities of Acute Pancreatitis. In The Pancreas; Beger, H.G., Büchler, M.W., Hruban, R.H., Mayerle, J., Neoptolemos, J.P., Shimosegawa, T., Warshaw, A.L., Whitcomb, D.C., Zhao, Y., Groß, C., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 155–163. ISBN 978-1-119-87597-0. [Google Scholar]
- Wasyluk, W.; Zwolak, A. Metabolic Alterations in Sepsis. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gianotti, L.; Meier, R.; Lobo, D.N.; Bassi, C.; Dejong, C.H.C.; Ockenga, J.; Irtun, O.; MacFie, J. ESPEN Guidelines on Parenteral Nutrition: Pancreas. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 28, 428–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyers, C.; Rigassio Radler, D.; Zelig, R.S. Impact of Solid Food Provision within 24 Hours of Hospital Admission on Clinical Outcomes for Adult Patients with Acute Pancreatitis: A Literature Review. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2023, 38, 976–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arvanitakis, M.; Ockenga, J.; Bezmarevic, M.; Gianotti, L.; Krznarić, Ž.; Lobo, D.N.; Löser, C.; Madl, C.; Meier, R.; Phillips, M.; et al. ESPEN Guideline on Clinical Nutrition in Acute and Chronic Pancreatitis. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 39, 612–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Windsor, A.C.; Kanwar, S.; Li, A.G.; Barnes, E.; Guthrie, J.A.; Spark, J.I.; Welsh, F.; Guillou, P.J.; Reynolds, J.V. Compared with Parenteral Nutrition, Enteral Feeding Attenuates the Acute Phase Response and Improves Disease Severity in Acute Pancreatitis. Gut 1998, 42, 431–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, P.; He, C.; Liao, G.; Chen, Y. Early Enteral Nutrition versus Delayed Enteral Nutrition in Acute Pancreatitis: A PRISMA-Compliant Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Medicine 2017, 96, e8648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanathan, M.; Aadam, A.A. Nutrition Management in Acute Pancreatitis. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2019, 34, S7–S12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gezer, A.; Üstündağ, H.; Özkaraca, M.; Sari, E.K.; Gür, C. Therapeutic Effects of Resveratrol and β-Carotene on L-Arginine-Induced Acute Pancreatitis through Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory Pathways in Rats. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 32068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-U.; Kweon, B.; Oh, J.-Y.; Noh, G.-R.; Lim, Y.; Yu, J.; Kim, M.-J.; Kim, D.-G.; Park, S.-J.; Bae, G.-S. Curcumin Ameliorates Cerulein-induced Chronic Pancreatitis through Nrf-2/HO-1 Signaling. Mol. Med. Rep. 2025, 31, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yang, G.; Chen, Y.; Mu, Z.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, L. Resveratrol Pre-Treatment Alleviated Caerulein-Induced Acute Pancreatitis in High-Fat Diet-Feeding Mice via Suppressing the NF-κB Proinflammatory Signaling and Improving the Gut Microbiota. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2022, 22, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Bu, C.; Wu, K.; Wang, R.; Wang, J. Curcumin Protects the Pancreas from Acute Pancreatitis via the Mitogen-activated Protein Kinase Signaling Pathway. Mol. Med. Rep. 2019, 20, 3027–3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chegini, M.; Sadeghi, A.; Zaeri, F.; Zamani, M.; Hekmatdoost, A. Nano-curcumin Supplementation in Patients with Mild and Moderate Acute Pancreatitis: A Randomized, Placebo-controlled Trial. Phytother. Res. 2023, 37, 5279–5288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Liu, J.; Xu, Z.; Song, Q.; Tao, J.; Zhu, H.; Li, Q.; Li, L. Quercetin Alleviates Acute Pancreatitis by Modulating Glycolysis and Mitochondrial Function via PFKFB3 Inhibition. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2025, 82, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Lhamo, G.; Ma, M.; Ye, X.; Chen, J.; He, Y.; Xu, J.; Huang, L. Quercetin as a Therapeutic Agent for Acute Pancreatitis: A Comprehensive Review of Antioxidant, Anti-Inflammatory, and Immunomodulatory Mechanisms. Front. Pharmacol. 2025, 16, 1587314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiyono, T.; Nisa, K.; Handayani, S.; Windarsih, A.; Hayati, S.N.; Wulanjati, M.P.; Sholikhah, E.N.; Pratiwi, W.R. Ameliorative Effect of Quercetin on Pancreatic Damage in Rodent: A Meta-Analysis. Egypt. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2023, 10, 433–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Leswas, D.; Eltweri, A.M.; Chung, W.-Y.; Arshad, A.; Stephenson, J.A.; Al-Taan, O.; Pollard, C.; Fisk, H.L.; Calder, P.C.; Garcea, G.; et al. Intravenous Omega-3 Fatty Acids Are Associated with Better Clinical Outcome and Less Inflammation in Patients with Predicted Severe Acute Pancreatitis: A Randomised Double Blind Controlled Trial. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 39, 2711–2719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunbar, R.L.; Gaudet, D.; Davidson, M.; Rensfeldt, M.; Yang, H.; Nilsson, C.; Kvarnström, M.; Oscarsson, J. Omega-3 Fatty Acid Exposure with a Low-Fat Diet in Patients with Past Hypertriglyceridemia-Induced Acute Pancreatitis; an Exploratory, Randomized, Open-Label Crossover Study. Lipids Health Dis. 2020, 19, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robles, L.; Vaziri, N.D.; Ichii, H. Role of Oxidative Stress in the Pathogenesis of Pancreatitis: Effect of Antioxidant Therapy. Pancreat. Disord. Ther. 2013, 3, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, C.-C.; Chen, H.-T.; Deng, H.; Huang, Y.-T.; Xu, G.-Q. Reactive Oxygen Species and Oxidative Stress in Acute Pancreatitis: Pathogenesis and New Therapeutic Interventions. World J. Gastroenterol. 2024, 30, 4771–4780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curran, F.J.; Sattar, N.; Talwar, D.; Baxter, J.N.; Imrie, C.W. Relationship of Carotenoid and Vitamins A and E with the Acute Inflammatory Response in Acute Pancreatitis. Br. J. Surg. 2000, 87, 301–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris-Stiff, G.J.; Bowrey, D.J.; Oleesky, D.; Davies, M.; Clark, G.W.B.; Puntis, M.C.A. The Antioxidant Profiles of Patients with Recurrent Acute and Chronic Pancreatitis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 1999, 94, 2135–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Firdous, S.M.; Pal, S.; Mandal, S.; Sindhu, R.K. Antioxidants in Inflammatory Diseases. In Antioxidants; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2025; pp. 83–126. ISBN 978-1-394-27057-6. [Google Scholar]
- Bhol, N.K.; Bhanjadeo, M.M.; Singh, A.K.; Dash, U.C.; Ojha, R.R.; Majhi, S.; Duttaroy, A.K.; Jena, A.B. The Interplay between Cytokines, Inflammation, and Antioxidants: Mechanistic Insights and Therapeutic Potentials of Various Antioxidants and Anti-Cytokine Compounds. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 178, 117177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blagov, A.V.; Summerhill, V.I.; Sukhorukov, V.N.; Zhigmitova, E.B.; Postnov, A.Y.; Orekhov, A.N. Potential Use of Antioxidants for the Treatment of Chronic Inflammatory Diseases. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1378335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sateesh, J.; Bhardwaj, P.; Singh, N.; Saraya, A. Effect of Antioxidant Therapy on Hospital Stay and Complications in Patients with Early Acute Pancreatitis: A Randomised Controlled Trial. Trop. Gastroenterol. 2009, 30, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bansal, D.; Bhalla, A.; Bhasin, D.; Pandhi, P.; Sharma, N.; Rana, S.; Malhotra, S. Safety and Efficacy of Vitamin-Based Antioxidant Therapy in Patients with Severe Acute Pancreatitis: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Saudi J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 17, 174–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antunes, D.; Gonçalves, S.M.; Matzaraki, V.; Rodrigues, C.S.; Gonçales, R.A.; Rocha, J.; Sáiz, J.; Marques, A.; Torrado, E.; Silvestre, R.; et al. Glutamine Metabolism Supports the Functional Activity of Immune Cells against Aspergillus Fumigatus. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e0225622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; You, Z.; Shi, H.; Sun, Y.; Du, X.; Palacios, G.; Guy, C.; Yuan, S.; Chapman, N.M.; Lim, S.A.; et al. SLC38A2 and Glutamine Signalling in cDC1s Dictate Anti-Tumour Immunity. Nature 2023, 620, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stehle, P.; Kuhn, K.S. Glutamine: An Obligatory Parenteral Nutrition Substrate in Critical Care Therapy. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asrani, V.; Chang, W.K.; Dong, Z.; Hardy, G.; Windsor, J.A.; Petrov, M.S. Glutamine Supplementation in Acute Pancreatitis: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Pancreatology 2013, 13, 468–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeurnink, S.M.; Nijs, M.M.; Prins, H.a.B.; Greving, J.P.; Siersema, P.D. Antioxidants as a Treatment for Acute Pancreatitis: A Meta-Analysis. Pancreatology 2015, 15, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, P.; Deng, L.-H.; Xia, Q.; Zhang, Z.-D.; Hu, W.-M.; Yang, X.-N.; Song, B.; Huang, Z.-W. Impact of Alanyl-Glutamine Dipeptide on Severe Acute Pancreatitis in Early Stage. World J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 14, 474–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Huang, L.; Luo, M.; Xia, X. Bacterial Translocation in Acute Pancreatitis. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 45, 539–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaubitz, J.; Wilden, A.; Frost, F.; Ameling, S.; Homuth, G.; Mazloum, H.; Rühlemann, M.C.; Bang, C.; Aghdassi, A.A.; Budde, C.; et al. Activated Regulatory T-Cells Promote Duodenal Bacterial Translocation into Necrotic Areas in Severe Acute Pancreatitis. Gut 2023, 72, 1355–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Chen, S.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Yu, W.; Wang, Y.; Si, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, T. Exploring the Mechanism of Intestinal Bacterial Translocation after Severe Acute Pancreatitis: The Role of Toll-like Receptor 5. Gut Microbes 2025, 17, 2489768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanders, M.E.; Merenstein, D.J.; Reid, G.; Gibson, G.R.; Rastall, R.A. Probiotics and Prebiotics in Intestinal Health and Disease: From Biology to the Clinic. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 605–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suez, J.; Zmora, N.; Segal, E.; Elinav, E. The Pros, Cons, and Many Unknowns of Probiotics. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 716–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, W.; Wang, G.; Xia, Y.; Song, X.; Xiong, Z.; Huang, C.; Gong, C.; Zeng, Y.; Ai, L. The Role of Probiotic Foods in Acute Pancreatitis: Current Status and Future Directions. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2024, 60, 101231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, R.; Wang, S.; Yang, C.; Wang, Y.; Fan, H.; Yang, M. Observation on the Therapeutic Effect of Probiotics on Early Oral Feeding in the Treatment of Severe Acute Pancreatitis. Front. Med. 2024, 11, 1492108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oláh, A.; Belágyi, T.; Issekutz, A.; Gamal, M.E.; Bengmark, S. Randomized Clinical Trial of Specific Lactobacillus and Fibre Supplement to Early Enteral Nutrition in Patients with Acute Pancreatitis. Br. J. Surg. 2002, 89, 1103–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oláh, A.; Belágyi, T.; Pótó, L.; Romics, L.; Bengmark, S. Synbiotic Control of Inflammation and Infection in Severe Acute Pancreatitis: A Prospective, Randomized, Double Blind Study. Hepatogastroenterology 2007, 54, 590–594. [Google Scholar]
- Timmerman, H.M.; Niers, L.E.M.; Ridwan, B.U.; Koning, C.J.M.; Mulder, L.; Akkermans, L.M.A.; Rombouts, F.M.; Rijkers, G.T. Design of a Multispecies Probiotic Mixture to Prevent Infectious Complications in Critically Ill Patients. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 26, 450–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaudis, H.; Pupelis, G.; Zeiza, K.; Boka, V. Early Low Volume Oral Synbiotic/Prebiotic Supplemented Enteral Stimulation of the Gut in Patients with Severe Acute Pancreatitis: A Prospective Feasibility Study. Acta Chir. Belg. 2012, 112, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| AP Classification | Degree of Severity | Complications | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Local | Systemic | ||||
| TOF | POF | EPC | |||
| Atlanta 1992 [14] | Mild | × | × | × | N/A |
| Severe | √ | √ | √ | N/A | |
| * Revised Atlanta 2012 [15,16] | Mild | × | × | × | × |
| Moderate | √ | √ | × | √ | |
| Severe | √ | × | √ | √ or × | |
| # Determinant-based [17] | Mild | × | × | × | N/A |
| Moderate | Sterile | √ | × | N/A | |
| Severe | Infected | √ | √ | N/A | |
| Critical | Infected | × | √ | N/A | |
| Therapy | Examples | Evidence/Clinical Implications |
|---|---|---|
| NSAIDs | Indomethacin, Diclofenac | Effective prophylaxis in high-risk patients, standard of care in post- endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) settings |
| Antibiotics | Carbapenems, Quinolones | Guidelines discourage routine prophylaxis |
| Cytokines | Anti-TNF-α, infliximab | Experimental/under clinical investigation, not in routine practice, inconclusive survival benefits |
| Immunomodulatory | Platelet activated factor, Lexipafant | Limited therapeutic role |
| Nutrition | Study Design | N | Protective Role(s) in Clinical AP | Conclusion |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EEN vs. ODN [52] | RCT | 208 | ■ infection (25% vs. 26%), ↓ death (11% vs. 7%) | EEN showed no significant advantage over ODN in ↓ infection and mortality rates |
| EEN vs. DEN [53] | PCT, RCT | 60 | ■ IAP, ↓ IAH, beneficial for patients with an IAP < 15 mmHg, ■ mortality | EEN prevents IAH and ↓ the severity of severe AP compared with DEN |
| SD vs. CLD [54] | RIT | 60 | (*) ↓ hospitalization stay, (*) ↓ post-refeeding length of hospitalization | A SD as the initial meal in patients with mild AP is well tolerated and ↓ length of hospitalization |
| EEN vs. DEN [55] | HCS | 197 | ↓ pancreatic necrosis (4 vs. 18), ↓ respiratory failure and transfer to intensive care unit occurred (5 vs. 15), ↓ (9 vs. 16), ↓ surgery (7 vs. 11), (*) ↓ mortality (0 vs. 9) | EEN started within 48 h of admission improves clinical outcomes via reducing complications |
| TEN vs. TPN [56] | RCT | 107 | (*) ↓ MOF (21% vs. 80%), (*) ↓ surgery (22% vs. 80%), (*) ↓ pancreatic septic necrosis (23% vs. 72%), (*) ↓ mortality (11% vs. 43%). | TEN is better than TPN in preventing pancreatic necrotic infection |
| EN vs. TPN [57] | PCT, RCT | 50 | (*) ↓ serum CRP, (*) ↑ serum albumin, (*) ↑transferrin value, ■ surgery (56% vs. 60%), ■ infective complications (64% vs. 60%), ■ hospital stay, ■ mortality (20% vs. 16%) | EN is comparable to PNT in terms of hospital stay, need for surgical intervention, infections and mortality |
| EIN vs. TPN [58] | HCS | 76 | ↓ severity, ↑ intestinal permeability, ↑ clinical outcomes | Improved clinical outcomes with EIN compared to TPN |
| TEN vs. TPN [59] | PRT | 22 | ■ APACHE II score, CRP, TNF-a, IL-6, pre-albumin and albumin levels, ↓ severe complications, ■ surgery, ■ hospital stay | TEN tends to be associated with a better outcome compared to TPN |
| TEN vs. TPN [60] | RCT | 466 | (*) ↓pancreatic infectious complications (7 vs. 16), ↓ MOF (7 vs. 17), (*) ↓overall mortality 2 vs. 12) | Early TEN could be used as prophylactic therapy for infected pancreatic necrosis |
| TEN + Abx vs. TPN + Abx [61] | PNR | 87 | ↓ MOF (31% vs. 79%), ↓ surgery (25% vs. 88%), ↓ pancreatic necrosis infection (20% vs. 74%), (*) ↓ death rate (5% vs. 35%) | TEN could be used as a prophylactic therapy for infected pancreatic necrosis |
| EN vs. PN [62] | RCT | 728 | ↓ CRP, ■ cholecystokinin levels, ↓ mortality, ↓ infected pancreatic necrosis, ↓ cost | EN tends to be associated with fewer septic complications, quicker inflammation reduction, and greater cost-effectiveness compared to PN |
| EN + PN vs. TPN [63] | RCT | 96 | ↑ body weight and pre-albumin, ↓ APACHE II, ↓TNF-a, ↓ IL-6, ↓ serum CRP, ■ albumin, ■ pancreatic lesions, ■ endotoxin and lactulose/manicol of urine, (*) ↑ CD4:CD8 T-cells and IgG | Combined therapy of EN and PN may be better than TPN as it improves nutrition status, moderates inflammation, and protects the gut integrity and immunity more effectively |
| TEN vs. TPN [64] | RCT | 17 | ↓ fatigue, ■ oxidative stress, ■ plasma glutamine, ↓ respiratory failure, ↓ hospital stay, ↓ cost | TEN is as safe and as efficacious as TPN |
| TEN vs. TPN [65] | RCT | 156 | ↓ feeding duration, ↓nutrition costs, (*) ↓ nutritional requirements, (*) ↓ metabolic and septic complications | TEN seems to be safer and less expensive than TPN |
| TEN vs. TPN [66] | RCT | 89 | (*) ↓ septic complications, ↓ MOF, ↓ mortality | EEN in combination with abx prophylaxis may prevent MOF |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shamoon, M.; Alzaanin, S.; Naz, S.; Smith, P.N.; Li, R.W. Translational Pharmaco-Nutritional Approaches in the Management of Clinical Acute Pancreatitis—A Narrative Review. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 1621. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18111621
Shamoon M, Alzaanin S, Naz S, Smith PN, Li RW. Translational Pharmaco-Nutritional Approaches in the Management of Clinical Acute Pancreatitis—A Narrative Review. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(11):1621. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18111621
Chicago/Turabian StyleShamoon, Muhammad, Sara Alzaanin, Safia Naz, Paul N. Smith, and Rachel W. Li. 2025. "Translational Pharmaco-Nutritional Approaches in the Management of Clinical Acute Pancreatitis—A Narrative Review" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 11: 1621. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18111621
APA StyleShamoon, M., Alzaanin, S., Naz, S., Smith, P. N., & Li, R. W. (2025). Translational Pharmaco-Nutritional Approaches in the Management of Clinical Acute Pancreatitis—A Narrative Review. Pharmaceuticals, 18(11), 1621. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18111621





