An Investigational Study on the Role of ADME Agents’ Genetic Variation on DD217 Pharmacokinetics and Safety Profile
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Genotyping Results
2.2. Association Between Pharmacogenetic Markers and Pharmacokinetic Parameters of DD217
2.3. Association Between Pharmacogenetic Markers and the Incidence of Adverse Events During DD217 Therapy
3. Discussion
Limitations
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Population
4.2. In Silico Assessment of Pharmacological Potential of DD217
4.3. Candidate Gene Selection
4.4. Genotyping
4.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ABCB1 | ATP Binding Cassette Subfamily B Member 1 (P-glycoprotein) |
| ABCG2 | ATP Binding Cassette Subfamily G Member 2 |
| ADME | Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, and Excretion |
| AUC | Area Under the Concentration-Time Curve |
| AUClast | Area Under the Concentration-Time Curve from time zero to last measurable concentration |
| Cmax | Maximum Plasma Concentration |
| DOAC | Direct Oral Anticoagulant |
| DVT | Deep Vein Thrombosis |
| EM | Extensive Metabolizer |
| HWE | Hardy–Weinberg Equilibrium |
| IM | Intermediate Metabolizer |
| NM | Normal Metabolizer |
| PCR | Polymerase Chain Reaction |
| PE | Pulmonary Embolism |
| PK | Pharmacokinetics |
| PM | Poor Metabolizer |
| RM | Rapid Metabolizer |
| SNP | Single Nucleotide Polymorphism |
| Tmax | Time to Maximum Plasma Concentration |
| UM | Ultrarapid Metabolizer |
| VTE | Venous Thromboembolism |
References
- Heit, J.A. Epidemiology of venous thromboembolism. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2015, 12, 464–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steffel, J.; Verhamme, P.; Potpara, T.S.; Albaladejo, P.; Antz, M.; Desteghe, L.; Haeusler, K.G.; Oldgren, J.; Reinecke, H.; Roldan-Schilling, V.; et al. The 2018 European Heart Rhythm Association Practical Guide on the use of non-vitamin K antagonist oral anticoagulants in patients with atrial fibrillation. Eur. Heart J. 2018, 39, 1330–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connolly, S.J.; Ezekowitz, M.D.; Yusuf, S.; Eikelboom, J.; Oldgren, J.; Parekh, A.; Pogue, J.; Reilly, P.A.; Themeles, E.; Varrone, J.; et al. Dabigatran versus warfarin in patients with atrial fibrillation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 1139–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connolly, S.J.; Wallentin, L.; Ezekowitz, M.D.; Eikelboom, J.; Oldgren, J.; Reilly, P.A.; Brueckmann, M.; Pogue, J.; Alings, M.; Amerena, J.V.; et al. The Long-Term Multicenter Observational Study of Dabigatran Treatment in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation (RELY-ABLE) Study. Circulation 2013, 128, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinberg, B.A.; Shrader, P.; Pieper, K.; Thomas, L.; Allen, L.A.; Ansell, J.; Chan, P.S.; Ezekowitz, M.D.; Fonarow, G.C.; Freeman, J.V.; et al. Frequency and outcomes of reduced dose non-vitamin K antagonist anticoagulants: Results from ORBIT-AF II. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2018, 7, e007633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chornenki, N.L.J.; Tritschler, T.; Stucki, F.; Odabashian, R.; Leentjens, J.; Khan, F.; Ly, V.; Siegal, D.M. All-cause mortality after major gastrointestinal bleeding among patients receiving direct oral anticoagulants: A protocol for a systematic review and meta-analysis. Syst. Rev. 2022, 11, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paré, G.; Eriksson, N.; Lehr, T.; Connolly, S.; Eikelboom, J.; Ezekowitz, M.D.; Axelsson, T.; Haertter, S.; Oldgren, J.; Reilly, P.; et al. Genetic determinants of dabigatran plasma levels and their relation to bleeding. Circulation 2013, 127, 1404–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attelind, S.; Hallberg, P.; Wadelius, M.; Hamberg, A.K.; Siegbahn, A.; Granger, C.B.; Lopes, R.D.; Alexander, J.H.; Wallentin, L.; Eriksson, N. Genetic determinants of apixaban plasma levels and their relationship to bleeding and thromboembolic events. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 982955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raymond, J.; Imbert, L.; Cousin, T.; Duflot, T.; Varin, R.; Wils, J.; Lamoureux, F. Pharmacogenetics of direct oral anticoagulants: A systematic review. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos-Staffico, A.M.; Dorsch, M.P.; Barnes, G.D.; Zhu, H.J.; Limdi, N.A.; Luzum, J.A. Eight pharmacokinetic genetic variants are not associated with the risk of bleeding from direct oral anticoagulants in non-valvular atrial fibrillation patients. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 1007113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lähteenmäki, J.; Vuorinen, A.L.; Pajula, J.; Harno, K.; Lehto, M.; Niemi, M.; van Gils, M. Pharmacogenetics of bleeding and thromboembolic events in direct oral anticoagulant users. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 110, 768–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueshima, S.; Hira, D.; Fujii, R.; Kimura, Y.; Tomitsuka, C.; Yamane, T.; Tabuchi, Y.; Ozawa, T.; Itoh, H.; Horie, M.; et al. Impact of ABCB1, ABCG2, and CYP3A5 polymorphisms on plasma trough concentrations of apixaban in Japanese patients with atrial fibrillation. Pharmacogenet. Genom. 2017, 27, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Song, T.J.; Yee, J.; Kim, D.H.; Park, J.; Gwak, H.S. ABCG2 gene polymorphisms may affect the bleeding risk in patients on apixaban and rivaroxaban. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2023, 17, 2513–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cross, B.; Turner, R.M.; Zhang, J.E.; Pirmohamed, M. Being precise with anticoagulation to reduce adverse drug reactions: Are we there yet? Pharmacogenom. J. 2024, 24, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PharmaDiall. Results of Work. Available online: https://www.pharmadiall.com/en/about/results-of-work.html (accessed on 24 August 2025).
- Tarasov, D.N.; Tovbin, D.G.; Malakhov, D.V.; Aybush, A.V.; Tserkovnikova, N.A.; Savelyeva, M.I.; Sychev, D.A.; Drozd, N.N.; Savchenko, A.Y. The development of new factor Xa inhibitors based on amide synthesis. Curr. Drug Discov. Technol. 2018, 15, 335–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shulga, D.A.; Tserkovnikova, N.A.; Tarasov, D.N.; Tovbin, D.G. Investigation of the tight binding mechanism of a new anticoagulant DD217 to factor Xa by means of molecular docking and molecular dynamics. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2023, 41, 4723–4734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dyer, S.C.; Austine-Orimoloye, O.; Azov, A.G.; Barba, M.; Barnes, I.; Barrera-Enriquez, V.P.; Becker, A.; Bennett, R.; Beracochea, M.; Berry, A.; et al. Ensembl 2025. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025, 53, D948–D957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tremaine, L.; Brian, W.; DelMonte, T.; Francke, S.; Groenen, P.; Johnson, K.; Li, L.; Pearson, K.; Marshall, J.C. The role of ADME pharmacogenomics in early clinical trials: Perspective of the Industry Pharmacogenomics Working Group (I-PWG). Pharmacogenomics 2015, 16, 2055–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Guidance for Industry: Clinical Pharmacogenomics—Premarket Evaluation in Early-Phase Clinical Studies and Recommendations for Labeling. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/regulatory-information/search-fda-guidance-documents/clinical-pharmacogenomics-premarket-evaluation-early-phase-clinical-studies-and-recommendations (accessed on 1 September 2025).
- European Medicines Agency (EMA). Good Pharmacogenomic Practice—Scientific Guideline. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/good-pharmacogenomic-practice-scientific-guideline (accessed on 1 September 2025).
- Relling, M.V.; Evans, W.E. Pharmacogenomics in the clinic. Nature 2015, 526, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehmann, F.; Caneva, L.; Prasad, K.; Paulmichl, M.; Maliepaard, M.; Llerena, A.; Ingelman-Sundberg, M.; Papaluca-Amati, M. Pharmacogenomic information in drug labels: European Medicines Agency perspective. Pharmacogenom. J. 2015, 15, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suchkov, I.A.; Mzhavanadze, N.D.; Shuldyakov, A.A.; Tatarintseva, Z.G.; Kirichenko, N.V.; Sychev, D.A.; Brizhan, L.K.; Balashov, O.E.; Chobanian, A.A.; Maksaev, D.A.; et al. Efficacy and safety of a new selective oral factor Xa inhibitor amidine hydrochloride for prevention of thromboembolic events in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: A multicenter prospective randomized controlled study. J. Venous Disord. 2024, 18, 154–162. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Drug–Drug Interaction Studies—Guidance for Industry. Available online: https://downloads.regulations.gov/FDA-2017-D-5961-0023/attachment_1.pdf (accessed on 4 September 2025).
- European Medicines Agency (EMA). Investigation of Drug Interactions—Scientific Guideline. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/investigation-drug-interactions-scientific-guideline (accessed on 4 September 2025).
- Klomp, S.D.; Manson, M.L.; Guchelaar, H.J.; Swen, J.J. Phenoconversion of cytochrome P450 metabolism: A systematic review. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Bevyxxa (Betrixaban) Prescribing Information. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2017/208383s000lbl.pdf (accessed on 7 September 2025).
- Nguyen, T.T.; Duong, V.A.; Maeng, H.J. Pharmaceutical formulations with P-glycoprotein inhibitory effect as promising approaches for enhancing oral drug absorption and bioavailability. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sennesael, A.L.; Panin, N.; Vancraeynest, C.; Pochet, L.; Spinewine, A.; Haufroid, V.; Elens, L. Effect of ABCB1 genetic polymorphisms on the transport of rivaroxaban in HEK293 recombinant cell lines. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Li, Z.; Huang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Zhao, L.; Wang, H.; Gao, H.; Chen, M.; Lin, Y.; Li, X.; et al. Effect of ABCB1 SNP polymorphisms on the plasma concentrations and clinical outcomes of rivaroxaban in Chinese NVAF patients: A population pharmacokinetic-based study. Front. Pharmacol. 2025, 16, 1574949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodges, L.M.; Markova, S.M.; Chinn, L.W.; Gow, J.M.; Kroetz, D.L.; Klein, T.E.; Altman, R.B. Very important pharmacogene summary: ABCB1 (MDR1, P-glycoprotein). Pharmacogenet. Genom. 2011, 21, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Q.; Xiang, Q.; Mu, G.; Ma, L.; Chen, S.; Zhou, S.; Hu, K.; Zhang, Z.; Cui, Y.; Jiang, J. Effect of ABCB1 genotypes on the pharmacokinetics and clinical outcomes of new oral anticoagulants: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2018, 24, 3558–3565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Wu, T.; Wu, S.; Chen, X.; Ye, Q.; Zhang, J. Effect of genotype on the pharmacokinetics and bleeding events of direct oral anticoagulants: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2023, 63, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballestri, S.; Romagnoli, E.; Arioli, D.; Coluccio, V.; Marrazzo, A.; Athanasiou, A.; Di Girolamo, M.; Cappi, C.; Marietta, M.; Capitelli, M. Risk and management of bleeding complications with direct oral anticoagulants in patients with atrial fibrillation and venous thromboembolism: A narrative review. Adv. Ther. 2023, 40, 41–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hindricks, G.; Potpara, T.; Dagres, N.; Arbelo, E.; Bax, J.J.; Blomström-Lundqvist, C.; Boriani, G.; Castella, M.; Dan, G.A.; Dilaveris, P.E.; et al. 2020 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS). Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 373–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimatteo, C.; D’Andrea, G.; Vecchione, G.; Paoletti, O.; Tiscia, G.L.; Santacroce, R.; Correale, M.; Brunetti, N.; Grandone, E.; Testa, S.; et al. ABCB1 SNP rs4148738 modulation of apixaban interindividual variability. Thromb. Res. 2016, 145, 24–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullell, N.; Carrera, C.; Muiño, E.; Torres, N.; Krupinski, J.; Fernandez-Cadenas, I. Pharmacogenetic studies with oral anticoagulants: Genome-wide association studies in vitamin K antagonist and direct oral anticoagulants. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 29238–29258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ClinicalTrials.gov. NCT05189002: DD217. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT05189002 (accessed on 28 August 2025).
- GOST R 52379-2005; Good Clinical Practice. National Standard of the Russian Federation: Moscow, Russia, 2006. Available online: https://docs.cntd.ru/document/1200041147 (accessed on 26 August 2025).
- Filimonov, D.A.; Lagunin, A.A.; Gloriozova, T.A.; Rudik, A.V.; Druzhilovskiy, D.S.; Pogodin, P.V.; Poroikov, V.V. Prediction of the biological activity spectra of organic compounds using the PASS Online web resource. Chem. Heterocycl. Compd. 2014, 50, 444–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filimonov, D.; Druzhilovskiy, D.; Lagunin, A.; Gloriozova, T.; Rudik, A.; Dmitriev, A.; Pogodin, P.; Poroikov, V. Computer-aided prediction of biological activity spectra for chemical compounds: Opportunities and limitations. Biomed. Chem. Res. Methods 2018, 1, e00004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul-Hammed, M.; Adedotun, I.O.; Olajide, M.; Irabor, C.O.; Afolabi, T.I.; Gbadebo, I.O.; Rhyman, L.; Ramasami, P. Virtual screening, ADMET profiling, PASS prediction, and bioactivity studies of potential inhibitory roles of alkaloids, phytosterols, and flavonoids against COVID-19 main protease (Mpro). Nat. Prod. Res. 2022, 36, 3110–3116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocharova, O.A.; Ionov, N.S.; Kazeev, I.V.; Shevchenko, V.E.; Bocharov, E.V.; Karpova, R.V.; Sheychenko, O.P.; Aksenov, A.A.; Chulkova, S.V.; Kucheryanu, V.G.; et al. Computer-Aided Evaluation of Polyvalent Medications’ Pharmacological Potential: Multiphytoadaptogen as a Case Study. Mol. Inform. 2023, 41, 2200176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangwal, A.; Lavecchia, A. Artificial Intelligence in Natural Product Drug Discovery: Current Applications and Future Perspectives. J. Med. Chem. 2025, 68, 3948–3969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medvedeva, S.M.; Petrou, A.; Fesatidou, M.; Gavalas, A.; Geronikaki, A.A.; Savosina, P.I.; Druzhilovskiy, D.S.; Poroikov, V.V.; Shikhaliev, K.S.; Kartsev, V.G. Anti-inflammatory action of new hybrid N-acyl-[1,2]dithiolo-[3,4-c]quinoline-1-thione. SAR QSAR Environ. Res. 2024, 35, 343–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muratov, E.N.; Bajorath, J.; Sheridan, R.P.; Tetko, I.; Filimonov, D.; Poroikov, V.; Oprea, T.; Baskin, I.I.; Varnek, A.; Roitberg, A.; et al. QSAR Without Borders. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 3525–3564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panina, S.B.; Pei, J.; Baran, N.; Tjahjono, E.; Patel, S.; Alatrash, G.; Konoplev, S.N.; Stolbov, L.A.; Poroikov, V.V.; Konopleva, M.; et al. Novel mitochondria-targeting compounds selectively kill human leukemia cells. Leukemia 2022, 36, 2009–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schimunek, J.; Seidl, P.; Elez, K.; Hempel, T.; Le, T.; Noé, F.; Olsson, S.; Raich, L.; Winter, R.; Gokcan, H.; et al. A community effort in SARS-CoV-2 drug discovery. Mol. Inform. 2024, 43, e202300262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sukhachev, V.S.; Dmitriev, A.V.; Ivanov, S.M.; Savosina, P.I.; Druzhilovskiy, D.S.; Filimonov, D.A.; Poroikov, V.V. Assessment of the Efficiency of Selecting Promising Compounds during Virtual Screening Based on Various Estimations of Drug-Likeness. Pharm. Chem. J. 2024, 58, 1388–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daina, A.; Michielin, O.; Zoete, V. SwissADME: A free web tool to evaluate pharmacokinetics, drug-likeness and medicinal chemistry friendliness of small molecules. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmer, M.; de Bruyn Kops, C.; Stork, C.; Kirchmair, J. CYPstrate: A set of machine learning models for the accurate classification of cytochrome P450 enzyme substrates and non-substrates. Molecules 2021, 26, 4678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudik, A.; Dmitriev, A.; Lagunin, A.; Filimonov, D.; Poroikov, V. Computational prediction of inhibitors and inducers of the major isoforms of cytochrome P450. Molecules 2022, 27, 5875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plonka, W.; Stork, C.; Šícho, M.; Kirchmair, J. CYPlebrity: Machine learning models for the prediction of inhibitors of cytochrome P450 enzymes. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2021, 46, 116388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, G.; Wu, Z.; Yi, J.; Fu, L.; Yang, Z.; Hsieh, C.; Yin, M.; Zeng, X.; Wu, C.; Lu, A.; et al. ADMETlab 2.0: An integrated online platform for accurate and comprehensive predictions of ADMET properties. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W5–W14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudik, A.; Pogodin, P.; Lagunin, A.; Filimonov, D.; Poroikov, V. MetaPASS 2024: Visualization of biological activity spectra of organic compounds taking into account their biotransformation. Biomed. Chem. Res. Methods 2025, 8, e00243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filimonov, D.A.; Zakharov, A.V.; Lagunin, A.A.; Poroikov, V.V. QNA-based “Star Track” QSAR approach. SAR QSAR Environ. Res. 2009, 20, 679–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, N.C.; Bhagirath, V.; Eikelboom, J.W. Profile of betrixaban and its potential in the prevention and treatment of venous thromboembolism. Vasc. Health Risk Manag. 2015, 11, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
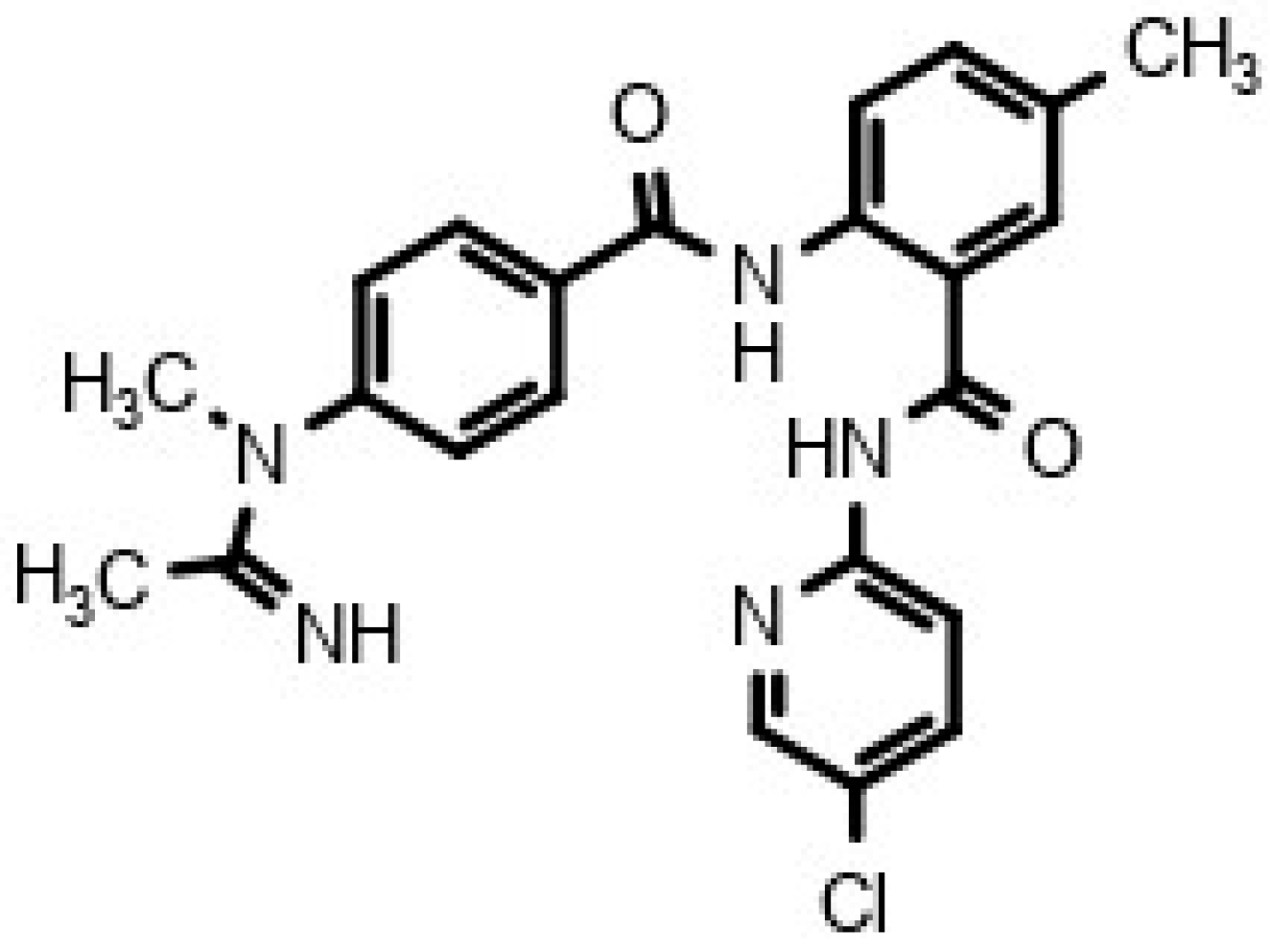
| Gene | SNP | Frequency | Minor Allele Frequency (%) | HWE Conformity | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genotype | Observed (n) | Expected (n) | χ2 | p-Value | |||
| CYP2C9 | rs1799853 | CC | 41 | 41.58 | 10.6 | 0.727 | 0.695 |
| CT | 11 | 9.84 | |||||
| TT | 0 | 0.58 | |||||
| rs1057910 | AA | 42 | 41.58 | 10.6 | 0.376 | 0.829 | |
| AC | 9 | 9.84 | |||||
| CC | 1 | 0.58 | |||||
| CYP2C19 | rs4244285 | GG | 44 | 43.39 | 8.7 | 1.147 | 0.563 |
| GA | 7 | 8.22 | |||||
| AA | 1 | 0.39 | |||||
| rs4986893 | GG | 51 | 51.00 | 1.0 | 0.005 | 0.998 | |
| GA | 1 | 0.99 | |||||
| AA | 0 | 0.00 | |||||
| 12248560 | CC | 29 | 29.25 | 25.0 | 0.034 | 0.983 | |
| CT | 20 | 19.50 | |||||
| TT | 3 | 3.25 | |||||
| CYP2C8 | rs10509681 | TT | 45 | 45.24 | 6.7 | 0.271 | 0.873 |
| TC | 7 | 6.53 | |||||
| CC | 0 | 0.24 | |||||
| rs11572080 | CC | 45 | 45.24 | 6.7 | 0.271 | 0.873 | |
| CT | 7 | 6.53 | |||||
| TT | 0 | 0.24 | |||||
| CYP3A4 | rs35599367 | CC | 50 | 50.02 | 1.9 | 0.020 | 0.990 |
| CT | 2 | 1.96 | |||||
| TT | 0 | 0.02 | |||||
| rs28371759 | AA | 52 | NA | 0 | - | - | |
| AG | 0 | NA | |||||
| GG | 0 | NA | |||||
| rs2740574 | AA | 48 | 48.08 | 3.8 | 0.083 | 0.959 | |
| AG | 4 | 3.85 | |||||
| GG | 0 | 0.08 | |||||
| CYP3A5 | rs776746 | GG | 45 | 45.24 | 6.7 | 0.271 | 0.873 |
| GA | 7 | 6.53 | |||||
| AA | 0 | 0.24 | |||||
| ABCB1 | rs1045642 | TT | 12 | 12.50 | 51.0 | 0.078 | 0.962 |
| TC | 27 | 25.99 | |||||
| CC | 13 | 13.50 | |||||
| rs2032582 | GG | 19 | 17.89 | 41.3 | 0.403 | 0.817 | |
| GT | 23 | 25.22 | |||||
| TT | 10 | 8.89 | |||||
| rs1128503 | TT | 19 | 19.08 | 39.4 | 0.002 | 0.999 | |
| TC | 25 | 24.84 | |||||
| CC | 8 | 8.08 | |||||
| rs4148738 | CC | 10 | 8.89 | 58.7 | 0.403 | 0.817 | |
| CT | 23 | 25.22 | |||||
| TT | 19 | 17.89 | |||||
| Cytochrome | Phenotype | 40 mg (n, %) | 60 mg (n, %) | Genotypes | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CYP2C9 | PM | 2 (12.5) | 2 (11.1) | *2/*3, *3/*3 | 0.884 |
| IM | 6 (37.5) | 5 (27.8) | *1/*3, *1/*2 | 0.765 | |
| NM | 8 (50) | 11 (61.1) | *1/*1 | 0.491 | |
| CYP2C19 | PM | - | 1 (5.6) | *2/*2 | NA |
| IM | 1 (6.25) | 3 (16.7) | *1/*2, *2/*17 | 0.722 | |
| NM | 6 (37.5) | 8 (44.4) | *1/*1 | 0.287 | |
| RM | 7 (43.75) | 6 (33.3) | *1/*17 | 1.000 | |
| UM | 2 (12.5) | - | *17/*17 | NA | |
| CYP3A | IM | 12 (75) | 16 (88.9) | *1/*1 + *3/*3 *1/*22 + *1/*3 | 0.132 |
| EM | 4 (25) | 2 (11.1) | *1/*1 + *1/*3 *1/*1 + *1/*1 | 0.378 |
| Cytochrome | DD217 Dose | Genotype | Phenotype | Tmax | AUClast | Cmax | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CYP2C9 | 40 mg | *1/*1 | NM (n = 8) | 8.00 ± 7.15 | 54.50 ± 49.37 | 7.28 ± 8.71 | >0.05 Tmax: p NM vs. IM+PM = 0.3894 AUC: p NM vs. IM+PM = 0.2786 Cmax: p NM vs. IM+PM = 0.2345 |
| *1/*2, *1/*3 | IM (n = 6) | 9.00 ± 8.17 | 33.86 ± 36.25 | 3.72 ± 5.61 | |||
| *2/*3, *3/*3 | PM (n = 2) | 24.0 | 18.65 ± 22.50 | 3.11 ± 3.75 | |||
| 60 mg | *1/*1 | NM (n = 11) | 12.91 ± 9.14 | 37.55 ± 42.41 | 3.66 ± 4.07 | 0.002 * Tmax: p = 0.005227 * AUC: p NM vs. IM+PM = 0.06926 Cmax: p NM vs. IM+PM = 0.1259 | |
| *1/*2, *1/*3 | IM (n = 5) | 3.20 ± 2.17 | 89.75 ± 89.27 | 9.24 ± 9.59 | |||
| *2/*3 | PM (n = 2) | 2.50 ± 2.12 | 177.19 ± 223.61 | 11.28 ± 13.60 | |||
| CYP2C19 | 40 mg | *1/*17, *17/*17 | RM + UM (n = 9) | 7.67 ± 6.71 | 47.70 ± 42.56 | 5.80 ± 6.73 | >0.05 Tmax: p RM+UM vs. NM vs. IM+PM = 0.2123 AUC: p RM+UM vs. NM vs. IM+PM = 0.3765 Cmax: p RM+UM vs. NM vs. IM+PM = 0.6185 |
| *1/*1 | NM (n = 6) | 15.50 ± 9.95 | 33.13 ± 48.12 | 5.25 ± 8.82 | |||
| *1/*2 | IM (n = 1) | 4.00 | 48.45 | 3.12 | |||
| 60 mg | *1/*17 | RM (n = 6) | 9.17 ± 7.33 | 50.5 ± 51.61 | 4.50 ± 4.61 | >0.05 Tmax: p RM vs. NM vs. IM+PM = 0.5459 AUC: p RM vs. NM vs. IM+PM = 0.8896 Cmax: p RM vs. NM vs. IM+PM = 0.806 | |
| *1/*1 | NM (n = 8) | 8.75 ± 10.07 | 98.0 ± 123.81 | 8.44 ± 9.71 | |||
| *1/*2, *2/*2, *2/*17 | IM + PM (n = 4) | 9.50 ± 9.98 | 32.28 ± 22.5 | 3.64 ± 3.51 | |||
| CYP3A | 40 mg | *1/*1 | EM (n = 12) | 11.75 ± 9.50 | 40.04 ± 42.11 | 5.02 ± 6.92 | >0.05 Tmax: p EM vs. IM = 0.5345 AUC: p EM vs. IM = 0.5989 Cmax: p EM vs. IM = 0.5209 |
| *1/*22, *1/*3 | IM (n = 4) | 6.25 ± 3.50 | 48.99 ± 48.74 | 6.63 ± 8.63 | |||
| 60 mg | *1/*1 | EM (n = 16) | 9.75 ± 8.93 | 52.71 ± 63.32 | 5.32 ± 6.58 | >0.05 Tmax: p EM vs. IM = 0.3201 AUC: p EM vs. IM = 0.2092 Cmax: p EM vs. IM = 0.3268 | |
| *1/*3 | IM (n = 2) | 3.50 ± 3.54 | 186.36 ± 210.65 | 11.94 ± 12.67 |
| Group | SNP | Genotype | n | Tmax (h, SD) | p-Value (Tmax) | AUClast (SD) | p-Value (AUClast) | Cmax (SD) | p-Value (Cmax) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 40 mg | rs10509681 | T/C | 3 | 16.67 (7.33) | 0.17 | 46.88 (28.46) | 0.84 | 7.06 (4.27) | 0.67 |
| T/T | 13 | 8.92 (2.04) | 41.22 (11.86) | 5.05 (2.02) | |||||
| rs11572080 | C/C | 13 | 8.92 (2.04) | 0.17 | 41.22 (11.86) | 0.84 | 5.05 (2.02) | 0.67 | |
| C/T | 3 | 16.67 (7.33) | 46.88 (28.46) | 7.06 (4.27) | |||||
| 60 mg | rs10509681 | T/C | 2 | 3 (1) | 0.31 | 62.47 (43.39) | 0.94 | 5.69 (4.02) | 0.94 |
| T/T | 16 | 9.81 (2.23) | 68.2 (23.49) | 6.11 (1.89) | |||||
| rs11572080 | C/C | 16 | 9.81 (2.23) | 0.31 | 68.2 (23.49) | 0.94 | 6.11 (1.89) | 0.94 | |
| C/T | 2 | 3 (1) | 62.47 (43.39) | 5.69 (4.02) |
| Group | rs10509681 | rs11572080 | Haplotype Frequency | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tmax | AUClast | Cmax | ||||
| 40 mg/day | T | C | 0.9062 | 0.17 | 0.84 | 0.67 |
| C | T | 0.0938 | ||||
| 60 mg/day | T | C | 0.9444 | 0.31 | 0.94 | 0.94 |
| C | T | 0.0556 | ||||
| SNP | Genotype | n | Tmax (SD) | p-Value (Tmax) | AUClast (SD) | p-Value (AUClast) | Cmax (SD) | p-Value (Cmax) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs1045642 T>C | T/T | 4 | 9.5 (4.99) | 0.074 | 35.53 (22.23) | 0.17 | 4.63 (3.47) | 0.42 |
| T/C | 7 | 6 (1.56) | 63.6 (18.31) | 8.03 (3.45) | ||||
| C/C | 5 | 17.2 (4.18 | 17.83 (5.08) | 2.42 (1) | ||||
| rs2032582 G>T | G/G | 8 | 12.88 (3.44) | 0.36 | 34.57 (14.34) | 0.73 | 4.84 (2.64) | 0.84 |
| G/T | 6 | 9.5 (3.12) | 46.36 (19.01) | 5.24 (2.94) | ||||
| T/T | 2 | 3 (1) | 60.88 (40.28) | 8.35 (6.66) | ||||
| rs1128503 T>C | C/C | 8 | 12.88 (3.44) | 0.36 | 34.57 (14.34) | 0.73 | 4.84 (2.64) | 0.84 |
| C/T | 6 | 9.5 (3.12) | 46.36 (19.01) | 5.24 (2.94) | ||||
| T/T | 2 | 3 (1) | 60.88 (40.28) | 8.35 (6.66) | ||||
| rs4148738 C>T | C/C | 2 | 3 (1) | 0.36 | 60.88 (40.28) | 0.73 | 8.35 (6.66) | 0.84 |
| T/C | 6 | 9.5 (3.12) | 46.36 (19.01) | 5.24 (2.94) | ||||
| T/T | 8 | 12.88 (3.44) | 34.57 (14.34) | 4.84 (2.64) |
| # | rs1045642 | rs2032582 | rs1128503 | rs4148738 | Frequency | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tmax | AUClast | Cmax | ||||||
| 1 | C | G | C | T | 0.5312 | 0.61 | 0.9 | 0.84 |
| 2 | T | T | T | C | 0.3125 | |||
| 3 | T | G | C | T | 0.1563 | |||
| 4 | C | T | T | C | 0 | |||
| SNP | Genotype | n | Tmax (SD) | p-Value (Tmax) | AUClast (SD) | p-Value (AUClast) | Cmax (SD) | p-Value (Cmax) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs1045642 | T/T | 7 | 13.57 (3.72) | 0.13 | 27.6 (5.59) | 0.0094 * | 2.42 (0.56) | 0.013 * |
| T/C | 8 | 7.75 (2.63) | 53.88 (18.59) | 5.54 (1.74) | ||||
| C/C | 3 | 2 (1) | 197.3 (93.48) | 15.95 (7.25) | ||||
| rs2032582 | G/G | 4 | 2 (0.71) | 0.12 | 163.65 (74.17) | 0.03 * | 14.13 (5.44) | 0.018 * |
| T/G | 9 | 9.56 (2.82) | 51.62 (16.19) | 4.87 (1.49) | ||||
| T/T | 5 | 13.8 (4.39) | 19.38 (5.28) | 1.74 (0.51) | ||||
| rs1128503 | T/T | 4 | 16.25 (4.7) | 0.057 | 14 (4.32) | 0.029 * | 1.49 (0.41) | 0.019 * |
| T/C | 10 | 9 (2.59) | 50.55 (14.43) | 4.66 (1.36) | ||||
| C/C | 4 | 2 (0.71) | 163.65 (74.17) | 14.13 (5.44) | ||||
| rs4148738 | C/C | 5 | 10.6 (3.63) | 0.18 | 18.86 (5.38) | 0.03 * | 1.78 (0.5) | 0.019 * |
| C/T | 9 | 11.33 (3.23) | 51.92 (16.11) | 4.85 (1.5) | ||||
| T/T | 4 | 2 (0.71) | 163.65 (74.17) | 14.13 (5.44) |
| # | rs1045642 | rs2032582 | rs1128503 | rs4148738 | Frequency | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tmax | AUClast | Cmax | ||||||
| 1 | T | T | T | C | 0.4416 | 0.17 | 0.99 | 0.94 |
| 2 | C | G | C | T | 0.3021 | |||
| 3 | T | G | C | T | 0.1139 | |||
| 4 | C | T | T | C | 0.0306 | |||
| 5 | C | G | T | T | 0.0284 | |||
| 6 | T | T | C | C | 0.0284 | |||
| 7 | C | G | C | C | 0.0278 | |||
| 8 | T | T | C | T | 0.0278 | |||
| Adverse Event | Patient ID | DD217 Dose | Phenotype | CYP2C8*3 | ABCB1 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CYP2C9 | CYP2C19 | CYP3A | rs10509681 | rs11572080 | rs1045642 | rs2032582 | rs1128503 | rs4148738 | |||
| DVT/PE | 112001 | 40 mg | NM | RM | EM | T | C | C | G | C | T |
| 113030 | 40 mg | NM | RM | EM | T | C | C | G | C | T | |
| 113032 | 40 mg | PM | NM | EM | C | T | C | G | C | T | |
| 113035 | 40 mg | NM | RM | IM | T | C | T | T | T | C | |
| 113036 | 60 mg | NM | RM | EM | T | C | T | T | T | C | |
| Bleeding | 112008 | 60 mg | IM | NM | EM | T | C | C | G | C | T |
| Cytochrome | DD217 Dose | Genotype | Phenotype | DVT/PE (n) | p-Value | Bleeding (n) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CYP2C9 | 40 mg | *1/*1 | NM (n = 8) | 3 | p NM vs. IM+PM = 0.5692 | 0 | NA |
| *1/*2, *1/*3 | IM (n = 6) | 0 | 0 | ||||
| *2/*3, *3/*3 | PM (n = 2) | 1 | 0 | ||||
| 60 mg | *1/*1 | NM (n = 11) | 1 | p NM vs. IM+PM = 1.0000 | 0 | p NM vs. IM+PM = 0.3889 | |
| *1/*2, *1/*3 | IM (n = 5) | 0 | 1 | ||||
| *2/*3 | PM (n = 2) | 0 | 0 | ||||
| CYP2C19 | 40 mg | *1/*17, *17/*17 | RM + UM (n = 9) | 3 | p RM+UM vs. NM vs. IM+PM = 0.5846 | 0 | NA |
| *1/*1 | NM (n = 6) | 1 | 0 | ||||
| *1/*2 | IM (n = 1) | 0 | 0 | ||||
| 60 mg | *1/*17 | RM (n = 6) | 1 | p RM vs. NM vs. IM+PM = 0.3333 | 0 | p RM vs. NM+IM+PM = 0.3333 | |
| *1/*1 | NM (n = 8) | 0 | 1 | ||||
| *1/*2, *2/*2, *2/*17 | IM + PM (n = 4) | 0 | 0 | ||||
| CYP3A | 40 mg | *1/*1 | EM (n = 12) | 3 | p EM vs. IM = 1.0000 | 0 | NA |
| *1/*22, *1/*3 | IM (n = 4) | 1 | 0 | ||||
| 60 mg | *1/*1 | EM (n = 16) | 1 | p EM vs. IM = 1.0000 | 1 | p EM vs. IM = 1.0000 | |
| *1/*3 | IM (n = 2) | 0 | 0 |
| # | rs1045642 | rs2032582 | rs1128503 | rs4148738 | Frequency | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | C | G | C | T | 0.5312 | 0.038 * |
| 2 | T | T | T | C | 0.3125 | |
| 3 | T | G | C | T | 0.1563 | |
| 4 | C | T | T | C | 0 |
| SNP | Genotype | n | Without DVT/PE | With DVT/PE | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs1045642 | T/T | 4 | 4 | 0 | 0.063 |
| T/C | 7 | 6 | 1 | ||
| C/C | 5 | 2 | 3 | ||
| rs2032582 | G/G | 8 | 5 | 3 | 0.37 |
| G/T | 6 | 5 | 1 | ||
| T/T | 2 | 2 | 0 | ||
| rs1128503 | C/C | 8 | 5 | 3 | 0.37 |
| C/T | 6 | 5 | 1 | ||
| T/T | 2 | 2 | 0 | ||
| rs4148738 | C/C | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0.37 |
| T/C | 6 | 5 | 1 | ||
| T/T | 8 | 5 | 3 |
| SNP | Genotype | n | DVT/PE (n) | p-Value (DVT/PE) | Bleeding (n) | p-Value (Bleeding) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs1045642 | T/T | 7 | 0 | 0.43 | 0 | 0.14 |
| T/C | 8 | 1 | 0 | |||
| C/C | 3 | 0 | 1 | |||
| rs2032582 | G/G | 4 | 0 | 0.49 | 1 | 0.2 |
| G/T | 9 | 1 | 0 | |||
| T/T | 5 | 0 | 0 | |||
| rs1128503 | C/C | 4 | 0 | 0.54 | 1 | 0.2 |
| C/T | 10 | 1 | 0 | |||
| T/T | 4 | 0 | 0 | |||
| rs4148738 | C/C | 5 | 0 | 0.49 | 0 | 0.2 |
| T/C | 9 | 1 | 0 | |||
| T/T | 4 | 0 | 1 |
| # | rs1045642 | rs2032582 | rs1128503 | rs4148738 | Frequency | p-Value (DVT/PE) | p-Value (Bleeding) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | T | T | T | C | 0.441 | 0.98 | 0.79 |
| 2 | C | G | C | T | 0.3021 | ||
| 3 | T | G | C | T | 0.1139 | ||
| 4 | C | T | T | C | 0.0306 | ||
| 5 | C | G | T | T | 0.0284 | ||
| 6 | T | T | C | C | 0.0284 | ||
| 7 | C | G | C | C | 0.0278 | ||
| 8 | T | T | C | T | 0.0278 |
| Parameter (Me ± SD/M/n) | In Total Cohort | DD217 | Dalteparin Sodium | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 40 mg/day | 60 mg/day | ||||
| Sample size | 52 | 16 | 18 | 18 | |
| Sex | Male | 7 | 3 | 2 | 2 |
| Female | 45 | 13 | 16 | 16 | |
| Age, years | 63 ± 6.11 | 62.5 ± 6.02 | 62 ± 4.9 | 63 ± 7.48 | |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 34 ± 4.69 | 34 ± 3.41 | 34.3 ± 4.7 | 34.2 ± 5.78 | |
| Complete blood count and biochemical blood test | |||||
| Sodium, mmol/L | 141 | 141 | 141.5 | 142 | |
| Potassium, mmol/L | 4.21 ± 0.47 | 4.28 ± 0.33 | 4.32 ± 0.56 | 4.03 ± 0.45 | |
| Glucose, mmol/L | 6.1 | 6.11 | 6.1 | 6.14 | |
| Total protein, g/L | 72.44 ± 3.68 | 72.44 ± 3.29 | 73.06 ± 3.69 | 71.83 ± 4.09 | |
| Albumin, g/L | 41.69 ± 2.37 | 41.68 ± 2.88 | 41.81 ± 2.33 | 41.59 ± 2.02 | |
| C-reactive protein, mg/L | 2.65 | 2.05 | 3.1 | 3.25 | |
| Total cholesterol, mmol/L | 6.05 ± 1.21 | 6.24 ± 1.46 | 5.82 ± 1.04 | 6.1 ± 1.16 | |
| Total bilirubin, µmol/L | 11.1 | 11.25 | 11.5 | 10.8 | |
| Direct bilirubin, µmol/L | 2.13 ± 0.68 | 2.08 ± 0.57 | 2.23 ± 0.69 | 2.08 ± 0.78 | |
| Indirect bilirubin, µmol/L | 9.15 | 9 | 9.35 | 8.9 | |
| ALT, U/L | 17 | 18 | 17.5 | 16.5 | |
| AST, U/L | 20.5 | 20.5 | 20.5 | 20 | |
| GGT, U/L | 23 | 21.5 | 23 | 20 | |
| Alkaline phosphatase, U/L | 78.65 ± 22.57 | 72.81 ± 19.23 | 79.33 ± 24.91 | 83.17 ± 22.95 | |
| Lipase, U/L | 24 ± 15.03 | 28 ± 17.81 | 24 ± 13.2 | 23 ± 14.35 | |
| Amylase, U/L | 20.35 ± 8.94 | 20.9 ± 11.18 | 19.75 ± 8.78 | 21.1 ± 6.69 | |
| Creatinine, µmol/L | 76.3 ± 12.05 | 79.85 ± 8.85 | 77.15 ± 16.45 | 72.35 ± 8.94 | |
| eGFR, mL/min/1.73 m2 | 74.47 ± 10.86 | 73.21 ± 10.92 | 73.42 ± 10.69 | 76.64 ± 11.26 | |
| Hematology | |||||
| RBC, ×1012/L | 4.67 ± 0.41 | 4.6 ± 0.49 | 4.74 ± 0.43 | 4.65 ± 0.29 | |
| MCV, fL | 90.35 | 90.85 | 90.8 | 89.95 | |
| MCH, pg | 30.05 | 30.05 | 30 | 30.4 | |
| MCHC, g/dL | 33.28 ± 0.67 | 33.35 ± 0.8 | 33.13 ± 0.58 | 33.37 ± 0.65 | |
| ESR, mm/h | 16.71 ± 8.24 | 15.81 ± 6.73 | 17.22 ± 7.02 | 17 ± 10.66 | |
| Hematocrit, % | 41.79 ± 3.31 | 41.73 ± 4.32 | 42.23 ± 2.98 | 41.42 ± 2.68 | |
| Hemoglobin, g/dL | 13.91 ± 1.13 | 13.91 ± 1.52 | 13.97 ± 0.85 | 13.84 ± 1.05 | |
| Platelets, ×109/L | 248 | 240 | 259 | 250.5 | |
| WBC, ×109/L | 6.05 | 5.6 | 5.9 | 6.15 | |
| Neutrophils, % | 57.75 ± 8.22 | 55.66 ± 8.99 | 60.23 ± 8.82 | 57.13 ± 6.53 | |
| Eosinophils, % | 1.75 | 2.05 | 1.5 | 1.85 | |
| Basophils, % | 1 | 1.2 | 1 | 0.9 | |
| Monocytes, % | 5.95 | 5.6 | 5.65 | 6.2 | |
| Lymphocytes, % | 29 ± 6.93 | 30.61 ± 7.47 | 26.36 ± 7.17 | 30.22 ± 5.66 | |
| Coagulation tests | |||||
| aPTT, sec | 34.48 ± 3.48 | 35.29 ± 3.68 | 34.45 ± 3.83 | 33.8 ± 2.91 | |
| INR | 0.97 ± 0.05 | 0.98 ± 0.06 | 0.96 ± 0.05 | 0.98 ± 0.05 | |
| D-dimer, ng/mL | 455 | 462.5 | 359 | 508.5 | |
| Safety outcomes | |||||
| PE/DVT, n | 7 | 4 | 1 | 2 | |
| Bleeding, n | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | |
| Subject ID | Dose, mg/day | Age | Sex | BMI | Tmax, h | AUClast | Cmax |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 112001 | 40 | 57 | Woman | 36.30 | 24 | 21.211 | 3.535 |
| 112013 | 40 | 54 | Woman | 34.00 | 24 | 2.735 | 0.456 |
| 112018 | 40 | 63 | Woman | 35.30 | 8 | 84.631 | 5.034 |
| 112020 | 40 | 65 | Woman | 30.50 | 12 | 10.412 | 0.72 |
| 112027 | 40 | 70 | Man | 28.70 | 24 | 4.928 | 0.405 |
| 112031 | 40 | 72 | Woman | 29.70 | 4 | 48.451 | 3.119 |
| 112034 | 40 | 63 | Woman | 38.90 | 8 | 17.602 | 1.379 |
| 112040 | 40 | 56 | Man | 37.90 | 8 | 39.7 | 3.95 |
| 113004 | 40 | 62 | Woman | 39.10 | 1 | 128.526 | 22.764 |
| 113014 | 40 | 58 | Man | 34.00 | 4 | 20.601 | 1.686 |
| 113016 | 40 | 61 | Woman | 37.20 | 8 | 13.049 | 1.136 |
| 113021 | 40 | 64 | Woman | 30.40 | 8 | 18.213 | 1.739 |
| 113030 | 40 | 71 | Woman | 31.50 | 6 | 10.234 | 0.656 |
| 113032 | 40 | 72 | Woman | 36.70 | 24 | 34.56 | 5.76 |
| 113033 | 40 | 55 | Woman | 31.60 | 2 | 101.166 | 15.011 |
| 113035 | 40 | 61 | Woman | 32.90 | 1 | 120.462 | 19.462 |
| 112003 | 60 | 64 | Woman | 35.90 | 4 | 19.08 | 1.663 |
| 112008 | 60 | 60 | Woman | 33.80 | 1 | 237.522 | 25.28 |
| 112010 | 60 | 56 | Woman | 34.70 | 4 | 35.852 | 3.324 |
| 112012 | 60 | 58 | Man | 34.70 | 24 | 16.597 | 1.155 |
| 112021 | 60 | 60 | Woman | 34.90 | 6 | 21.462 | 1.59 |
| 112022 | 60 | 71 | Woman | 25.70 | 2 | 105.854 | 9.707 |
| 112028 | 60 | 60 | Woman | 36.40 | 2 | 58.513 | 7.329 |
| 112037 | 60 | 57 | Woman | 39.00 | 12 | 4.589 | 0.325 |
| 112039 | 60 | 65 | Woman | 42.10 | 5 | 25.375 | 2.291 |
| 113006 | 60 | 51 | Woman | 30.10 | 8 | 51.929 | 4.963 |
| 113015 | 60 | 61 | Woman | 37.90 | 6 | 37.407 | 2.974 |
| 113020 | 60 | 60 | Woman | 34.60 | 24 | 14.483 | 1.614 |
| 113025 | 60 | 66 | Woman | 30.00 | 8 | 13.976 | 1.37 |
| 113029 | 60 | 68 | Woman | 34.00 | 2 | 62.698 | 8.694 |
| 113031 | 60 | 63 | Woman | 30.20 | 24 | 11.57 | 1.712 |
| 113036 | 60 | 63 | Woman | 33.10 | 6 | 152.359 | 13.569 |
| 113038 | 60 | 65 | Man | 22.00 | 24 | 11.552 | 0.613 |
| 113039 | 60 | 68 | Woman | 31.60 | 1 | 335.306 | 20.897 |
| Pa | Pi | Activity |
|---|---|---|
| 0.894 | 0.004 | Anticoagulant |
| 0.609 | 0.002 | Factor Xa inhibitor |
| Pa | Pi | Activity |
|---|---|---|
| 0.229 | 0.109 | CYP2C29 substrate |
| 0.267 | 0.149 | CYP2C8 inhibitor |
| 0.185 | 0.144 | CYP2C3 substrate |
| Web-Resource | 1A2 | 2A6 | 2D6 | 2C8 | 2C19 | 2C9 | 3A4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CYPstrate (model “best performance”) | No prediction | Non-substrate | No prediction | Substrate | No prediction | Substrate | Substrate |
| CYPstrate (model “full coverage”) | Non-substrate | Non-substrate | Substrate | Substrate | Substrate | Substrate | Substrate |
| ADMETlab 2.0 | 0.917 | No prediction | 0.762 | No prediction | 0.079 | 0.213 | 0.600 |
| Web-Resource | 1A2 | 2D6 | 2C19 | 2C9 | 3A4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SwissADME | - | - | + | + | + |
| P450 Analyzer | 0.115 | −0.525 | 0.287 | 0.242 | −0.628 |
| CYPlebrity | 0.58 | 0.28 | 0.56 | 0.45 | 0.42 |
| ADMETlab 2.0 | 0.256 | 0.692 | 0.453 | 0.78 | 0.453 |
| Web-Resource | Substrate | Inhibitor |
|---|---|---|
| SwissADME | - | |
| ADMETlab 2.0 | 0.996 | 0.851 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sychev, D.A.; Abdullaev, S.P.; Rudik, A.V.; Dmitriev, A.V.; Tuchkova, S.N.; Denisenko, N.P.; Makarov, D.S.; Mirzaev, K.B. An Investigational Study on the Role of ADME Agents’ Genetic Variation on DD217 Pharmacokinetics and Safety Profile. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 1617. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18111617
Sychev DA, Abdullaev SP, Rudik AV, Dmitriev AV, Tuchkova SN, Denisenko NP, Makarov DS, Mirzaev KB. An Investigational Study on the Role of ADME Agents’ Genetic Variation on DD217 Pharmacokinetics and Safety Profile. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(11):1617. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18111617
Chicago/Turabian StyleSychev, Dmitry A., Sherzod P. Abdullaev, Anastasia V. Rudik, Alexander V. Dmitriev, Svetlana N. Tuchkova, Natalia P. Denisenko, Denis S. Makarov, and Karin B. Mirzaev. 2025. "An Investigational Study on the Role of ADME Agents’ Genetic Variation on DD217 Pharmacokinetics and Safety Profile" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 11: 1617. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18111617
APA StyleSychev, D. A., Abdullaev, S. P., Rudik, A. V., Dmitriev, A. V., Tuchkova, S. N., Denisenko, N. P., Makarov, D. S., & Mirzaev, K. B. (2025). An Investigational Study on the Role of ADME Agents’ Genetic Variation on DD217 Pharmacokinetics and Safety Profile. Pharmaceuticals, 18(11), 1617. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18111617






