VDAC1 Intervention Alleviates Bisphenol AF-Induced Succinate Metabolism Dysregulation and Inflammatory Responses
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Cell Experiments
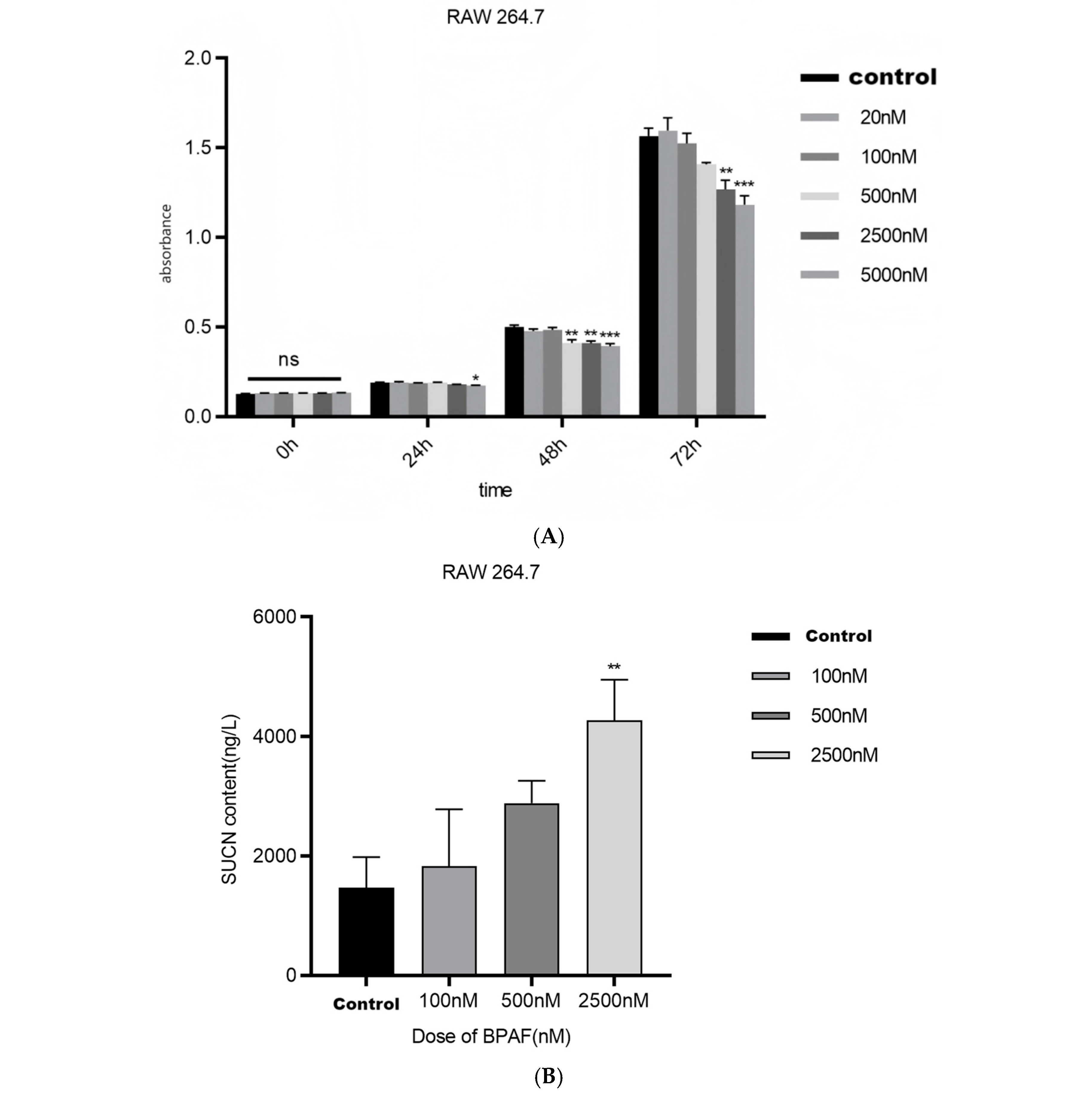
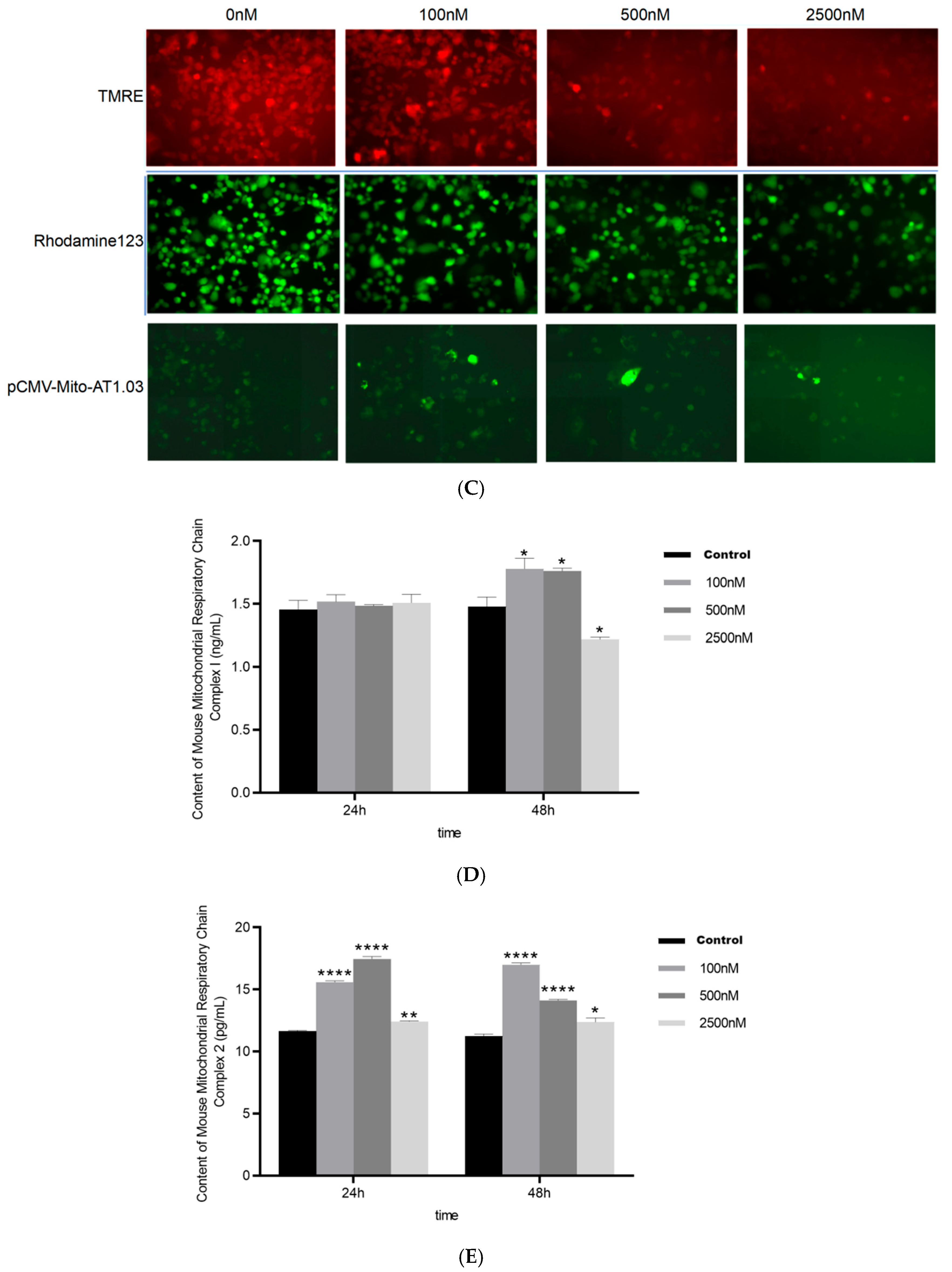
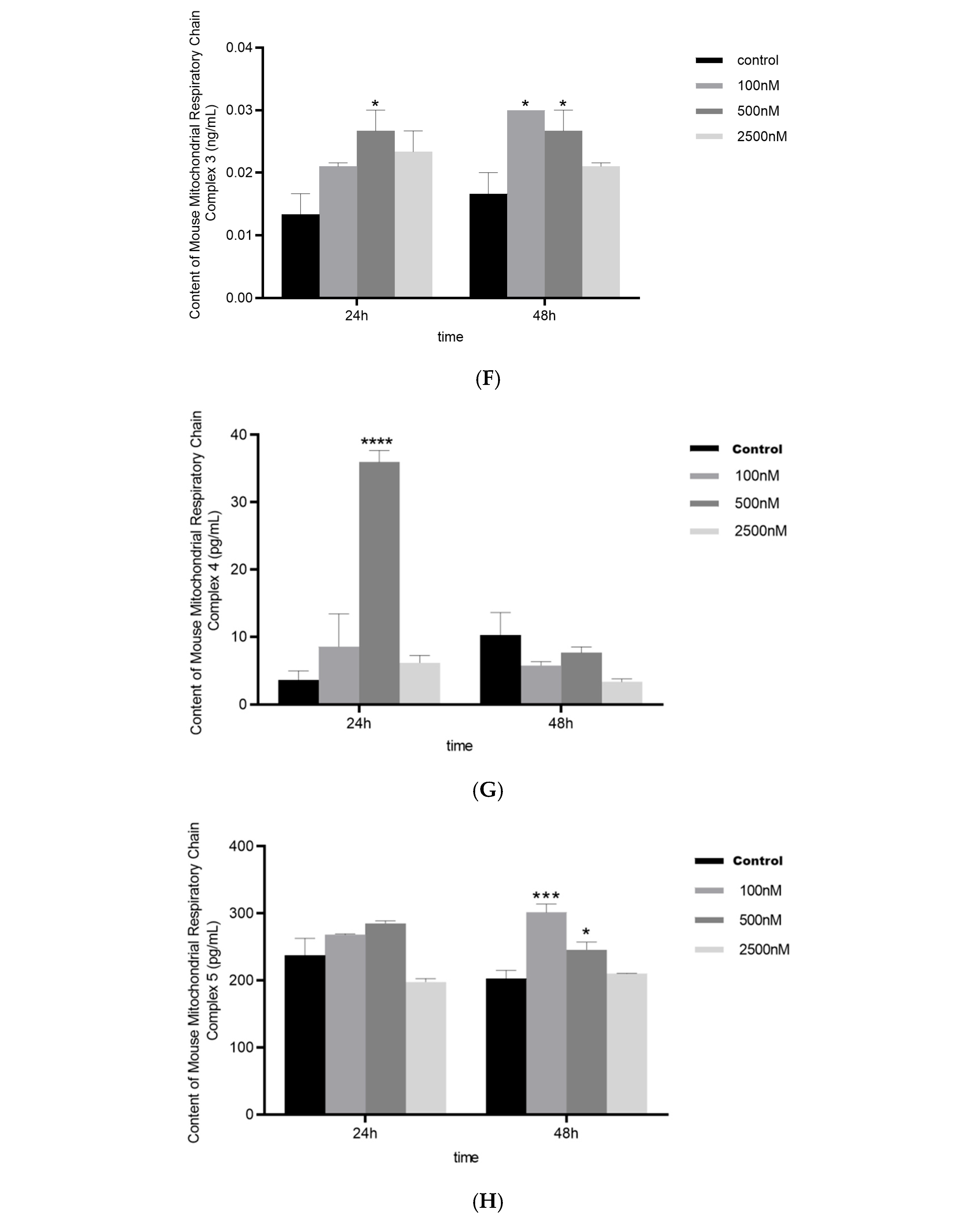
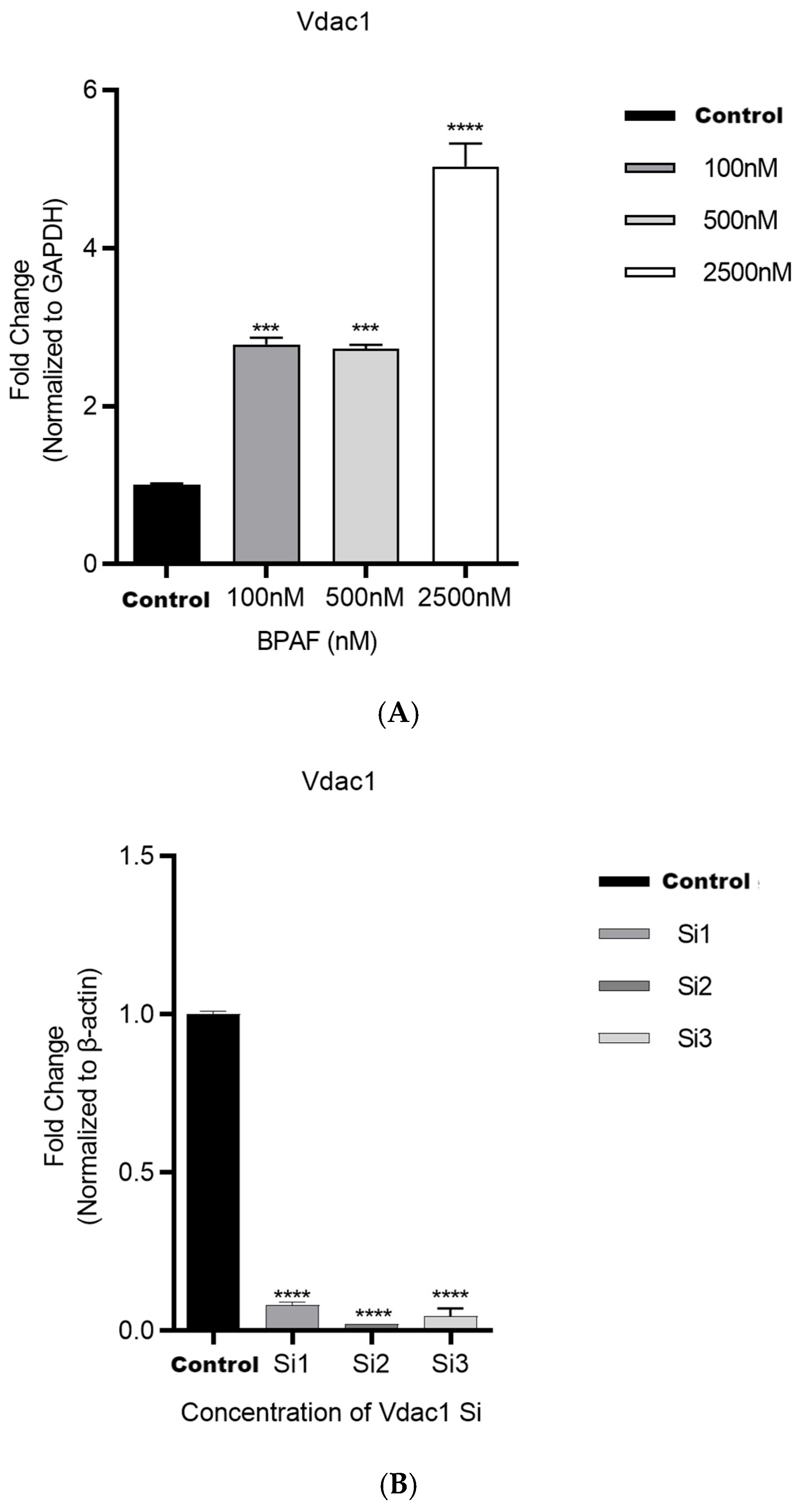
2.1.1. BPAF Induces Succinate Accumulation and Alters Mitochondrial Function
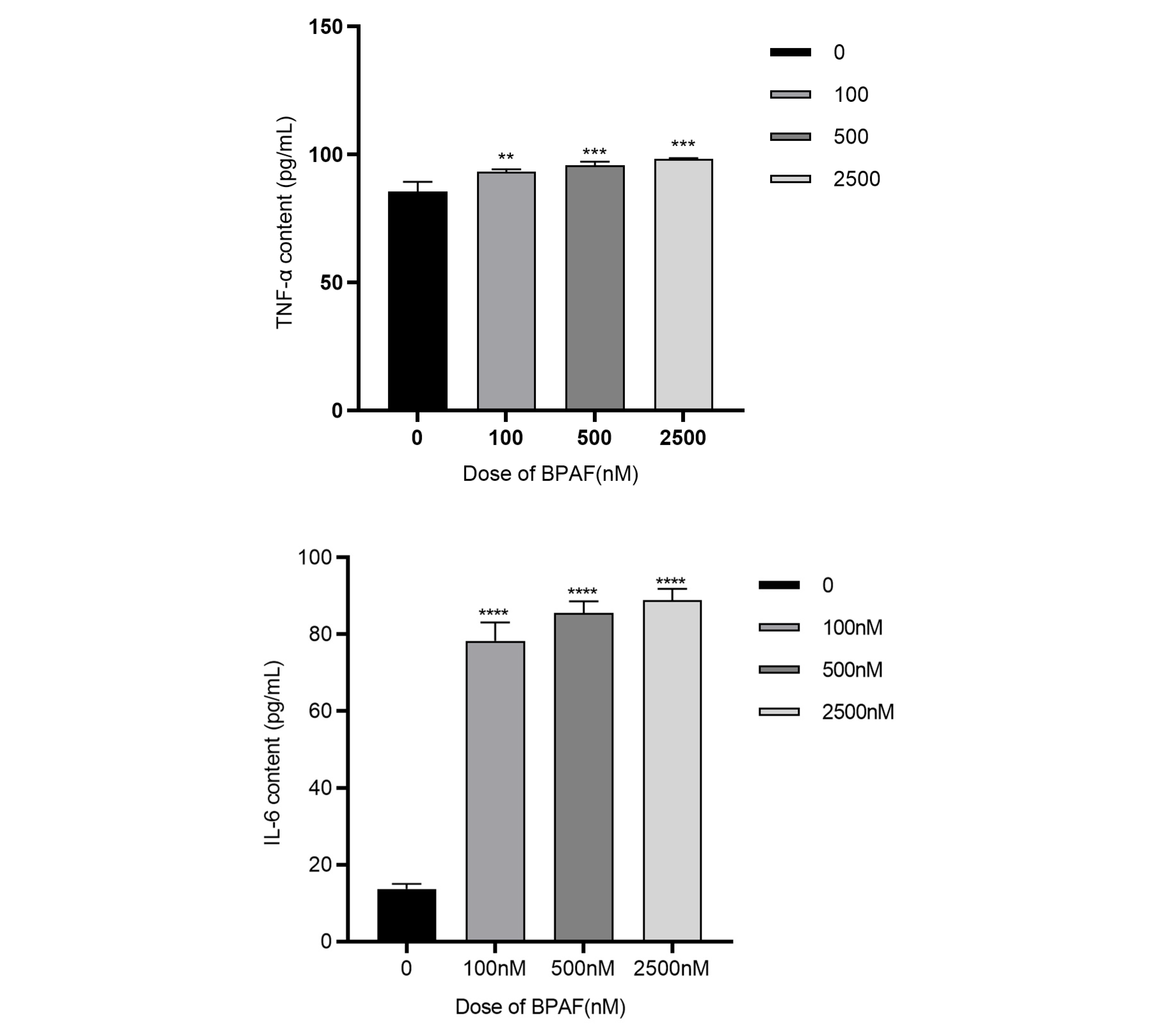
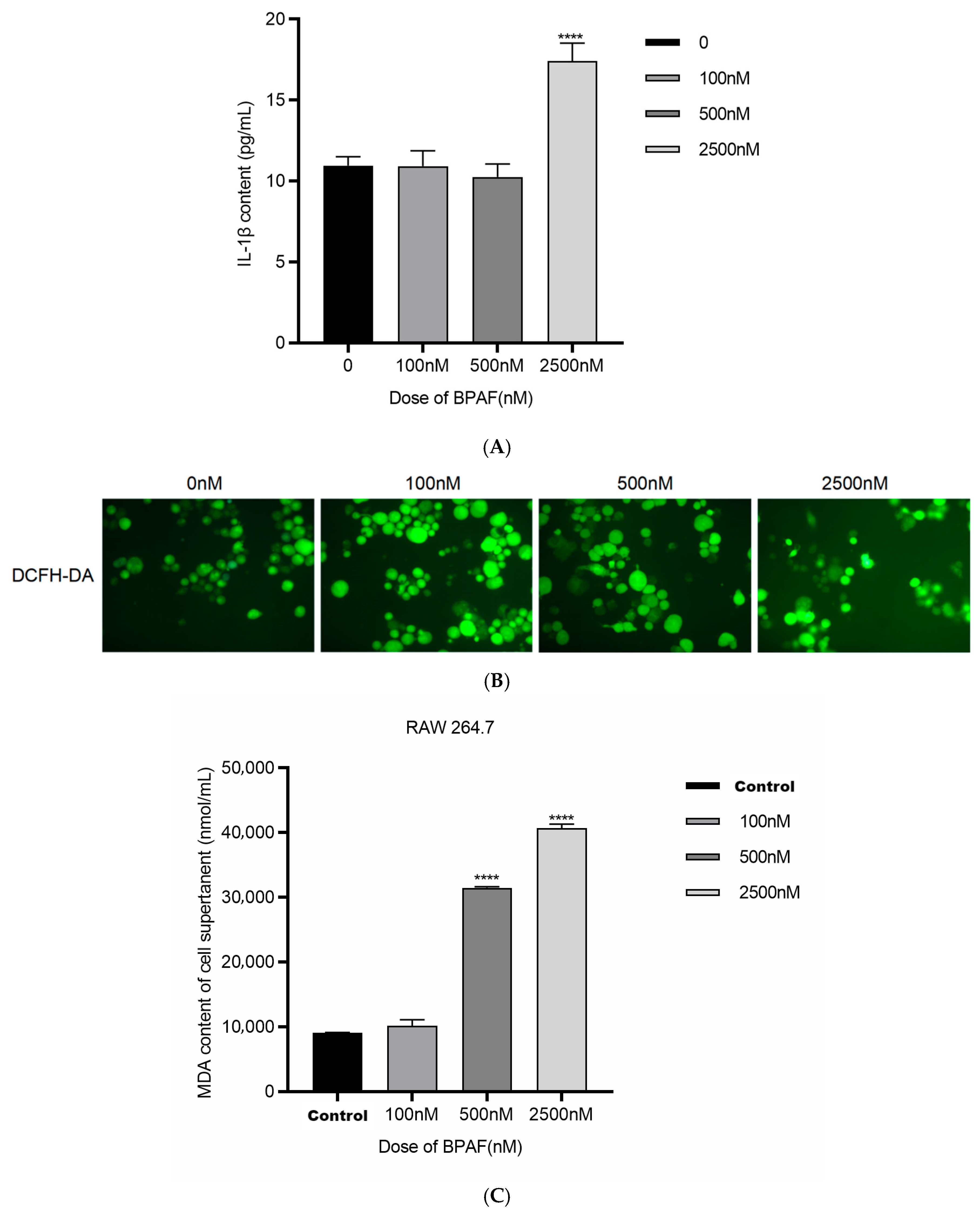
2.1.2. BPAF Induces Inflammatory Cytokine Production and Oxidative Stress
2.1.3. VDAC1 In Vitro siRNA Approach Modulates BPAF-Induced Effects
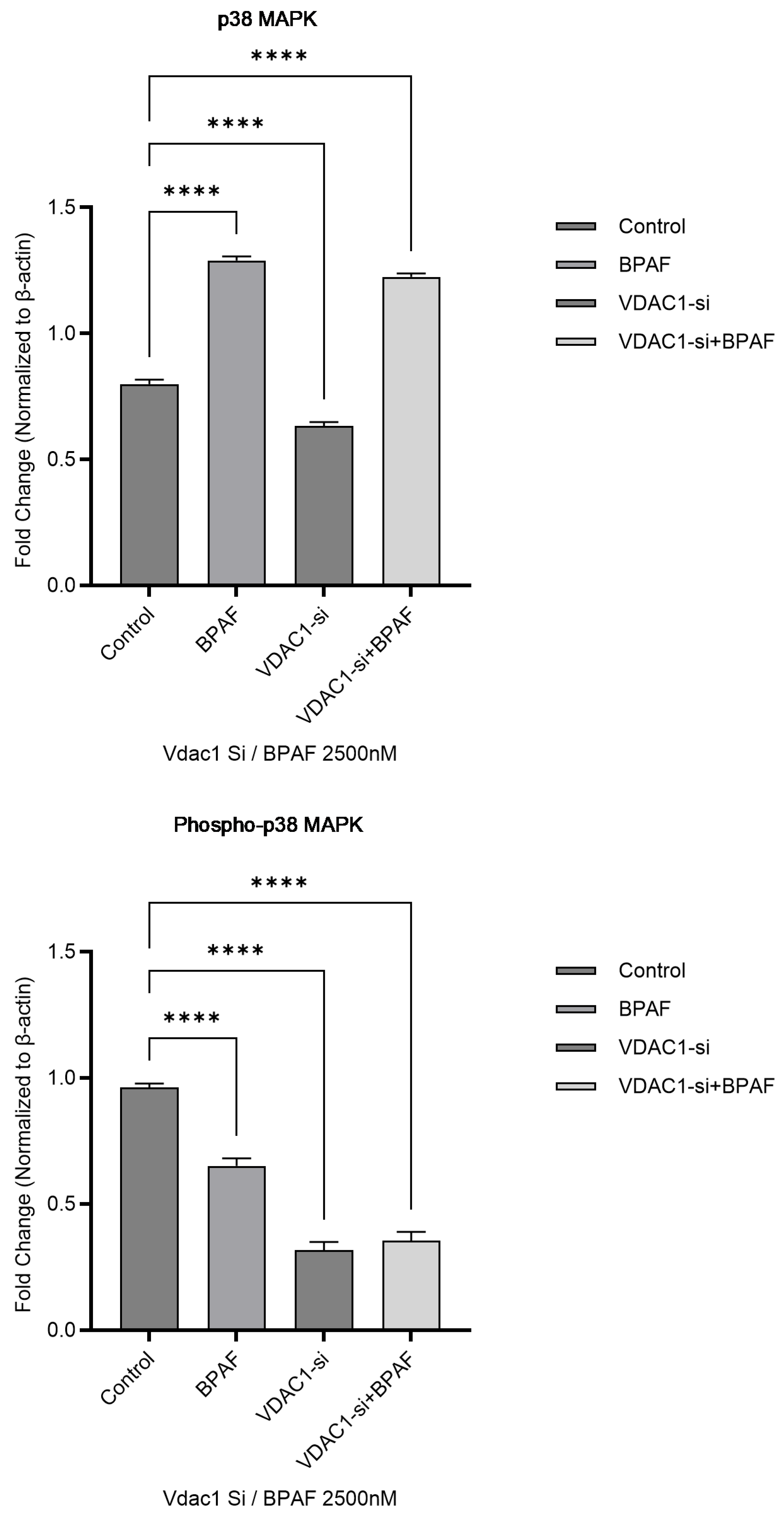
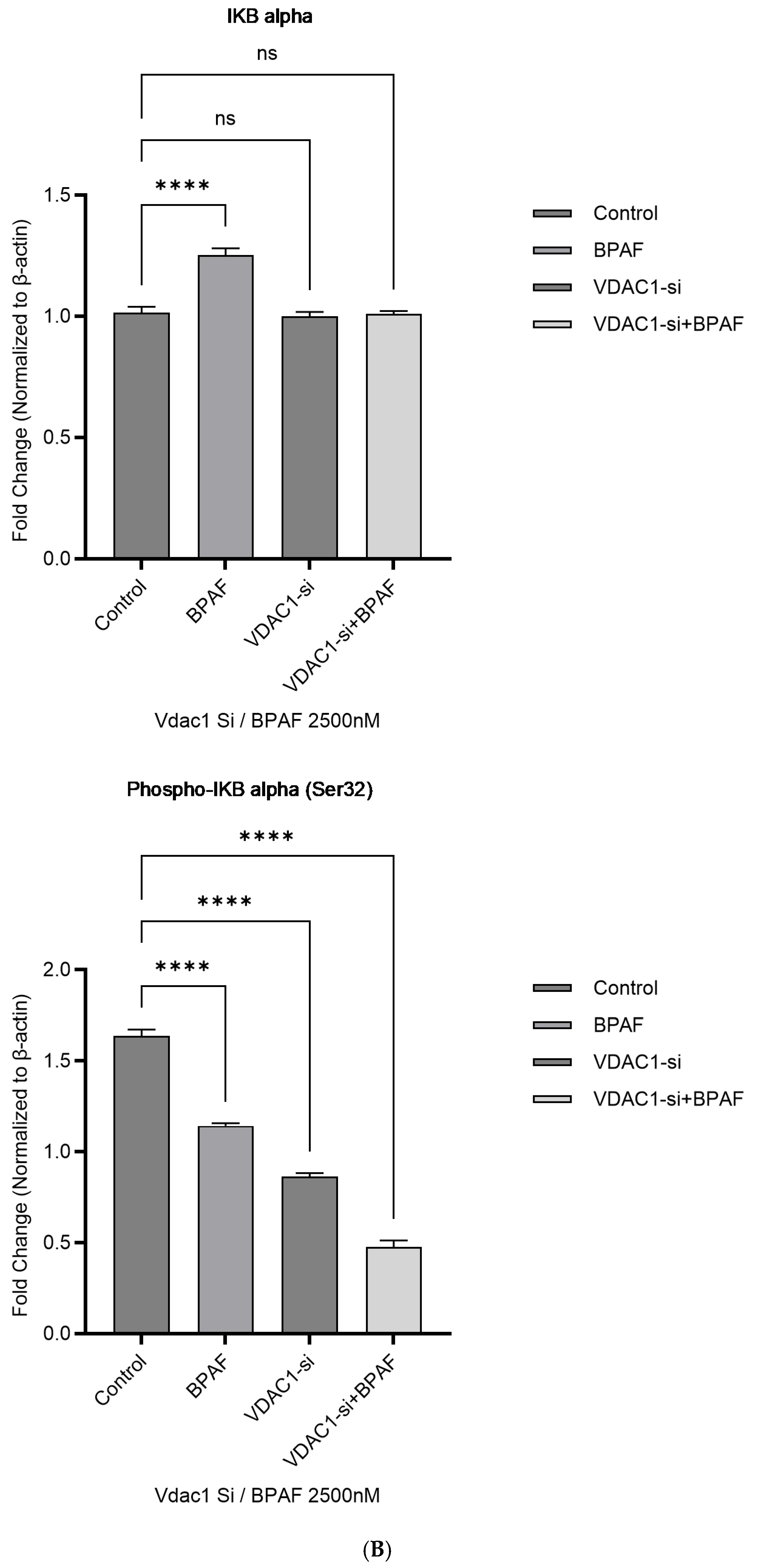
2.1.4. Western Blot Analysis of the p38 MAPK Pathway
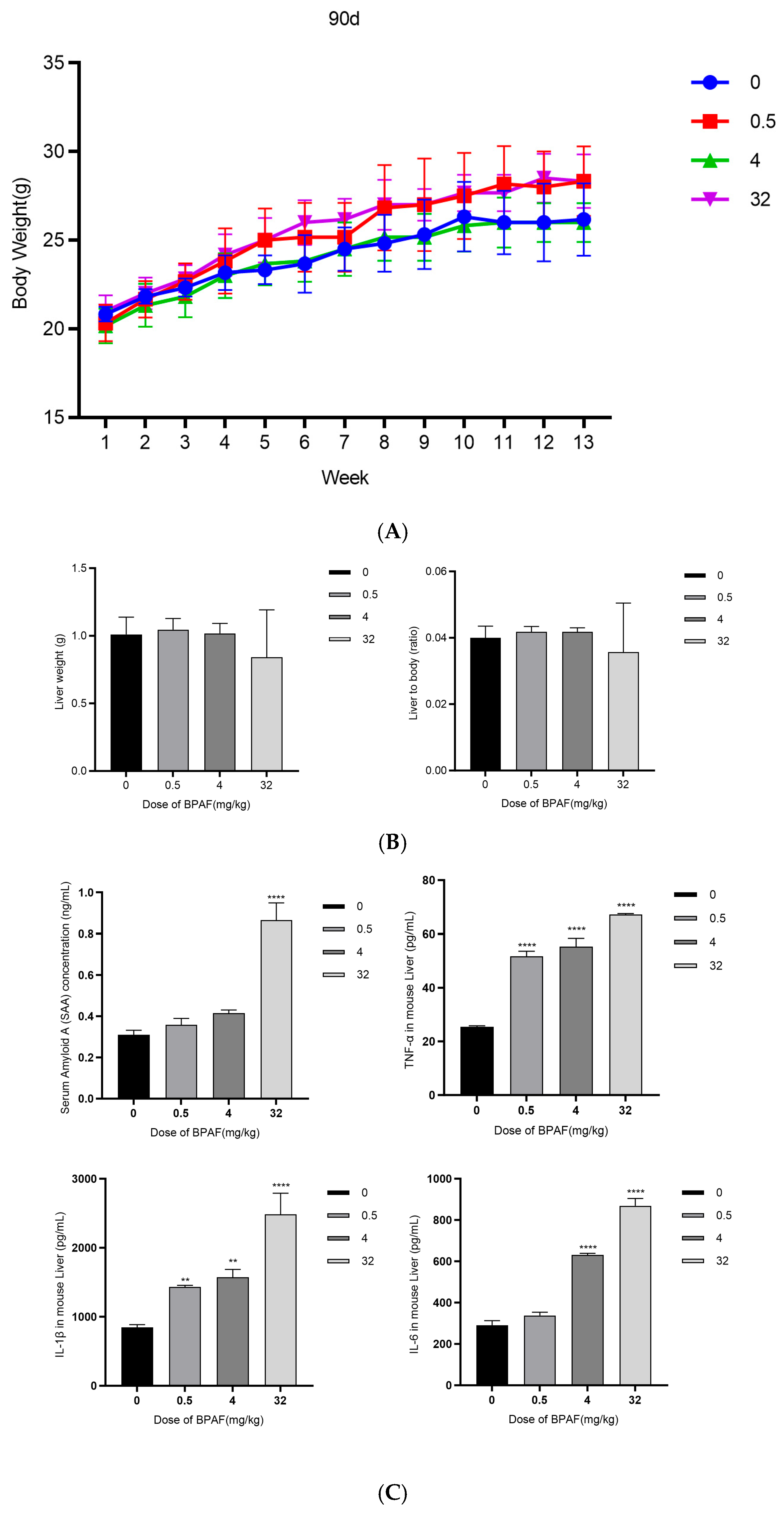
2.2. Animal Experiments
2.2.1. Body Weight Growth Curve
2.2.2. Liver Weight and Organ Index
2.2.3. Biochemical Analysis of Blood
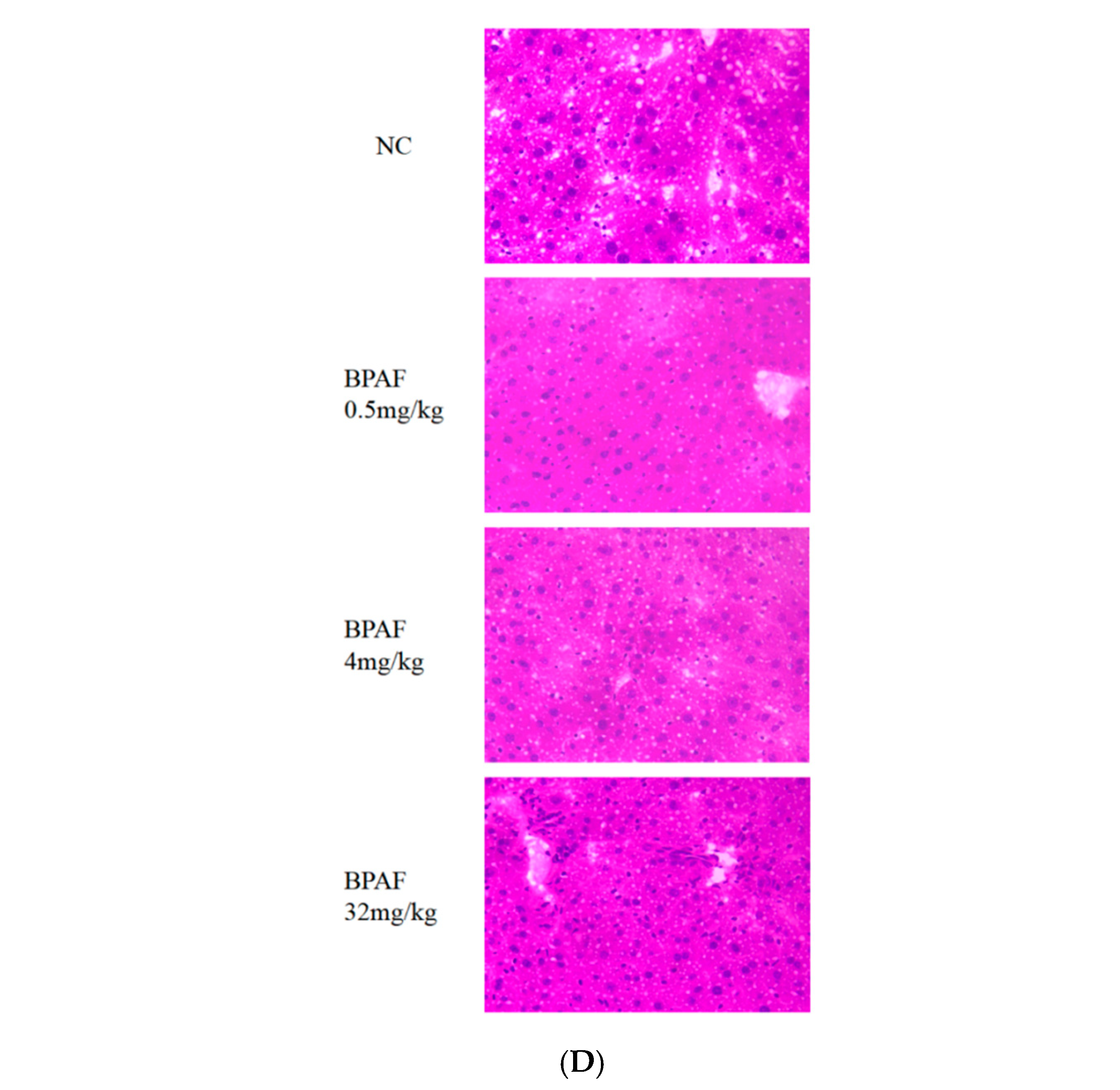
2.2.4. Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) Staining
2.2.5. Immunofluorescence Staining of Frozen Sections
2.2.6. Fluorescence Microplate Reader Analysis of Relative Fluorescence Units (RFU) of M1 and M2 Macrophage
2.2.7. Transmission Electron Microscopy
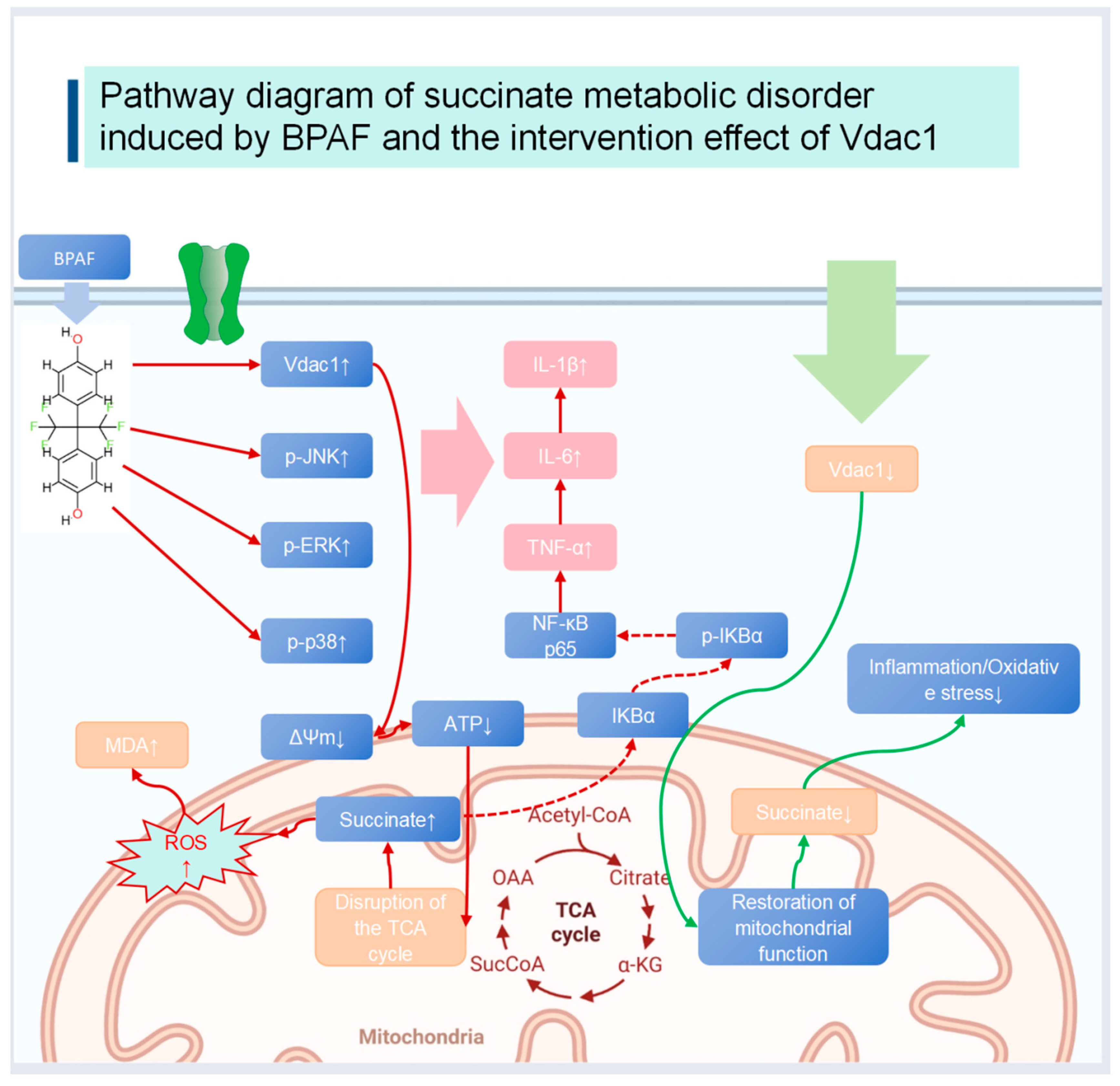
3. Discussion
Limitations and Future Directions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Experiments
4.1.1. Cell Culture and Treatment
4.1.2. Cell Viability Assay
4.1.3. Succinate Metabolism Detection
4.1.4. Vdac1 Expression Analysis
4.1.5. Mitochondrial Function Analysis
4.1.6. Inflammation and Oxidative Stress Detection
4.1.7. Western Blot Analysis
4.2. Animal Experiments
4.2.1. Animal Husbandry and Administration
4.2.2. Humane Endpoints and Animal Sacrifice
4.2.3. Body Weight Measurement
4.2.4. Liver Weight and Organ Index Measurement
4.2.5. Biochemical Analysis of Blood
4.2.6. Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) Staining
4.2.7. Immunofluorescence Staining of Frozen Sections
4.2.8. Fluorescence Microplate Reader Analysis of M1 and M2 Macrophage Ratios
4.2.9. Transmission Electron Microscopy
4.3. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Matsushima, A.; Liu, X.; Okada, H.; Shimohigashi, M.; Shimohigashi, Y. Bisphenol AF is a full agonist for the estrogen receptor ERα but a highly specific antagonist for ERβ. Environ. Health Perspect. 2010, 118, 1267–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.; Wang, K.; Huang, D.; Su, X.; Yang, R.; Shao, C.; Jiang, J.; Wu, J. Bisphenol AF induces prostatic dorsal lobe hyperplasia in rats through activation of the NF-κB signaling pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 16221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajkumar, A.; Luu, T.; Beal, M.A.; Barton-Maclaren, T.S.; Robaire, B.; Hales, B.F. Elucidation of the effects of bisphenol A and structural analogs on germ and steroidogenic cells using single-cell high-content imaging. Toxicol. Sci. 2021, 180, 224–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, W.; He, H.; Du, B.; Li, T.; Tang, H.; Liu, Y.; Li, L.; et al. Transcriptome changes and potential immunotoxicity analysis in RAW264.7 macrophages caused by bisphenol F. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 846562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.; Guo, L.; Overholser, J.; Wang, X. Mitochondrial VDAC1: A Potential Therapeutic Target of Inflammation-Related Diseases and Clinical Opportunities. Cells 2022, 11, 3174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Chen, M.; Peng, D.; Liang, Y.; Song, M.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, G. Exposure to bisphenol AF disrupts sex hormone levels and vitellogenin expression in zebrafish. Environ. Toxicol. 2016, 31, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Yang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Yin, J.; Zhang, J.; Feng, Y.; Shao, B. Biotransformation of bisphenol AF to its major glucuronide metabolite reduces estrogenic activity. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e83170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Guo, J.; Gao, W.; Yu, J.; Han, X.; Zhang, J.; Shao, B. Bisphenol AF-induced endogenous transcription is mediated by ERα and ERK1/2 activation in human breast cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e94725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Seira, N.; Yanagisawa, N.; Suganami, A.; Honda, T.; Wasai, M.; Regan, J.W.; Fukushima, K.; Yamaguchi, N.; Tamura, Y.; Arai, T.; et al. Anti-cancer Effects of MW-03, a Novel Indole Compound, by Inducing 15-Hydroxyprostaglandin Dehydrogenase and Cellular Growth Inhibition in the LS174T Human Colon Cancer Cell Line. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2017, 40, 1806–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodila, A.; Franko, N.; Sollner Dolenc, M. A review on immunomodulatory effects of bisphenol A analogues. Arch. Toxicol. 2023, 97, 1831–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skledar, D.G.; Trontelj, J.; Troberg, J.; Tomašič, T.; Zega, A.; Finel, M.; Mašič, L.P. Data on biosynthesis of BPAF glucuronide, enzyme kinetics of BPAF glucuronidation, and molecular modeling. Data Brief 2018, 22, 977–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, I.C.; Cohenour, E.R.; Harnett, K.G.; Schuh, S.M. BPA, BPAF and TMBPF alter adipogenesis and fat accumulation in human mesenchymal stem cells, with implications for obesity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escrivá, L.; Zilliacus, J.; Hessel, E.; Beronius, A. Assessment of the endocrine-disrupting properties of bisphenol AF: A case study applying the European regulatory criteria and guidance. Environ. Health 2021, 20, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikushima, A.; Ishimura, T.; Mori, K.P.; Yamada, H.; Sugioka, S.; Ishii, A.; Toda, N.; Ohno, S.; Kato, Y.; Handa, T.; et al. Deletion of p38 MAPK in macrophages ameliorates peritoneal fibrosis and inflammation in peritoneal dialysis. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 21220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dallio, M.; Ventriglia, L.; Romeo, M.; Scognamiglio, F.; Diano, N.; Moggio, M.; Cipullo, M.; Coppola, A.; Ziogas, A.; Netea, M.G.; et al. Environmental bisphenol A exposure triggers trained immunity-related pathways in monocytes. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1270391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyimah, E.; Xu, H.; Fosu, S.; Mensah, J.K.; Dong, X.; Akoto, O.; Issaka, E.; Zhang, Z. Gene expression patterns and DNA methylation of neuron and pancreatic β-cell developments in zebrafish embryos treated with bisphenol F and AF. Heliyon 2024, 10, e33805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnöder, L.; Hao, W.; Qin, Y.; Liu, S.; Tomic, I.; Liu, X.; Fassbender, K.; Liu, Y. Deficiency of neuronal p38α MAPK attenuates amyloid pathology in Alzheimer disease mouse and cell models through facilitating lysosomal degradation of BACE1. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 2067–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munoz, L.; Ranaivo, H.R.; Roy, S.M.; Hu, W.; Craft, J.M.; McNamara, L.K.; Chico, L.W.; Van Eldik, L.J.; Watterson, D.M. A novel p38δ MAPK inhibitor suppresses brain pro-inflammatory cytokine up-regulation and attenuates synaptic dysfunction and behavioral deficits in an Alzheimer’s disease mouse model. J. Neuroinflamm. 2007, 4, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Xu, R.; Feng, L.; Guo, W.; Cao, N.; Qian, C.; Teng, P.; Wang, L.; Wu, X.; Sun, Y.; et al. A novel chromone derivative with anti-inflammatory property via inhibition of ROS-dependent activation of TRAF6-ASK1-p38 pathway. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e37168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsuka, M.; Kang, Y.J.; Ren, J.; Jiang, H.; Wang, Y.; Omata, M.; Han, J. Distinct effects of p38α deletion in myeloid lineage and gut epithelia in mouse models of inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology 2010, 138, 1255–1265.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pålsson-McDermott, E.M.; O’Neill, L.A.J. Targeting immunometabolism as an anti-inflammatory strategy. Cell Res. 2020, 30, 300–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, R.N.; Jana, M.; Pahan, K. MAPK p38 regulates transcriptional activity of NF-kappaB in primary human astrocytes via acetylation of p65. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 7101–7109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- İpek, S.; Yurtcu, E.; Yavasoglu, A.; Duydu, Y. Evaluation of the cytotoxic effect of bisphenol A and its analogs in MCF-7 and HSeC cell lines in vitro. Fabad J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 1, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abu-Hamad, S.; Zaid, H.; Israelson, A.; Nahon, E.; Shoshan-Barmatz, V. Hexokinase-I protection against apoptotic cell death is mediated via interaction with the voltage-dependent anion channel-1: Mapping the site of binding. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 13482–13490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vollmer, T.R.; Stockhausen, A.; Zhang, Z.J. Anti-inflammatory effects of mapracorat, a novel selective glucocorticoid receptor agonist, is partially mediated by MAP kinase phosphatase-1 (MKP-1). J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 35212–35221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Huang, D.; Zhou, P.; Su, X.; Yang, R.; Shao, C.; Ma, A.; Wu, J. Individual and combined effect of bisphenol A and bisphenol AF on prostate cell proliferation through NF-κB signaling pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Xu, H.S.; Guo, T.L. Modulation of cytokine/chemokine production in human macrophages by bisphenol A: A comparison to analogues and interactions with genistein. J. Immunotoxicol. 2018, 15, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, Y.; Wang, T.; Fu, Y.; Yu, T.; Ding, Y.; Nie, H. Ferulic acid: A review of pharmacology, toxicology, and therapeutic effects on pulmonary diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, S.; Rajab, H.; Christ, I.; Schirdewahn, C.; Höfler, D.; Fischer, M.J.M.; Bruno, A.; Fenske, S.; Gruner, C.; Kramer, F.; et al. Protein kinase A regulates inflammatory pain sensitization by modulating HCN2 channel activity in nociceptive sensory neurons. Pain 2017, 158, 2012–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, E.L.; Kelly, B.; Logan, A.; Costa, A.S.H.; Varma, M.; Bryant, C.E.; Tourlomousis, P.; Däbritz, J.H.M.; Gottlieb, E.; Latorre, I.; et al. Succinate Dehydrogenase Supports Metabolic Repurposing of Mitochondria to Drive Inflammatory Macrophages. Cell 2016, 167, 457–470.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paes, D.; Schepers, M.; Rombaut, B.; van den Hove, D.; Vanmierlo, T.; Prickaerts, J. The Molecular Biology of Phosphodiesterase 4 Enzymes as Pharmacological Targets: An Interplay of Isoforms, Conformational States, and Inhibitors. Pharmacol. Rev. 2021, 73, 1016–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Gene Name | Forward Primer | Reverse Primer |
|---|---|---|
| Vdac1 | AGTGACCCAGAGCAACTTCGCA | CAGGCGAGATTGACAGCAGTCT |
| β-actin | CATTGCTGACAGGATGCAGAAGG | TGCTGGAAGGTGGACAGTGAGG |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hong, X.; Wang, N.; Leng, J.; Xu, J.; Qian, K.; Zheng, Z.; Tao, G.; Xiao, P. VDAC1 Intervention Alleviates Bisphenol AF-Induced Succinate Metabolism Dysregulation and Inflammatory Responses. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 1600. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18111600
Hong X, Wang N, Leng J, Xu J, Qian K, Zheng Z, Tao G, Xiao P. VDAC1 Intervention Alleviates Bisphenol AF-Induced Succinate Metabolism Dysregulation and Inflammatory Responses. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(11):1600. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18111600
Chicago/Turabian StyleHong, Xinyu, Ning Wang, Jing Leng, Jing Xu, Kelei Qian, Zhiqing Zheng, Gonghua Tao, and Ping Xiao. 2025. "VDAC1 Intervention Alleviates Bisphenol AF-Induced Succinate Metabolism Dysregulation and Inflammatory Responses" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 11: 1600. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18111600
APA StyleHong, X., Wang, N., Leng, J., Xu, J., Qian, K., Zheng, Z., Tao, G., & Xiao, P. (2025). VDAC1 Intervention Alleviates Bisphenol AF-Induced Succinate Metabolism Dysregulation and Inflammatory Responses. Pharmaceuticals, 18(11), 1600. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18111600





