Safety of Roxadustat in Chronic Kidney Disease Patients: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Sources and Search Strategies
2.2. Selection and Data Collection Process
2.3. Inclusion Criteria and Data Extraction
2.4. Data Items
2.5. Study Risk of Bias Assessment
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of Included Trials
3.2. Safety Results
3.2.1. Incidence of Adverse Events (AEs)
3.2.2. Incidence of Serious Adverse Events (SAEs)
3.3. Adverse Events
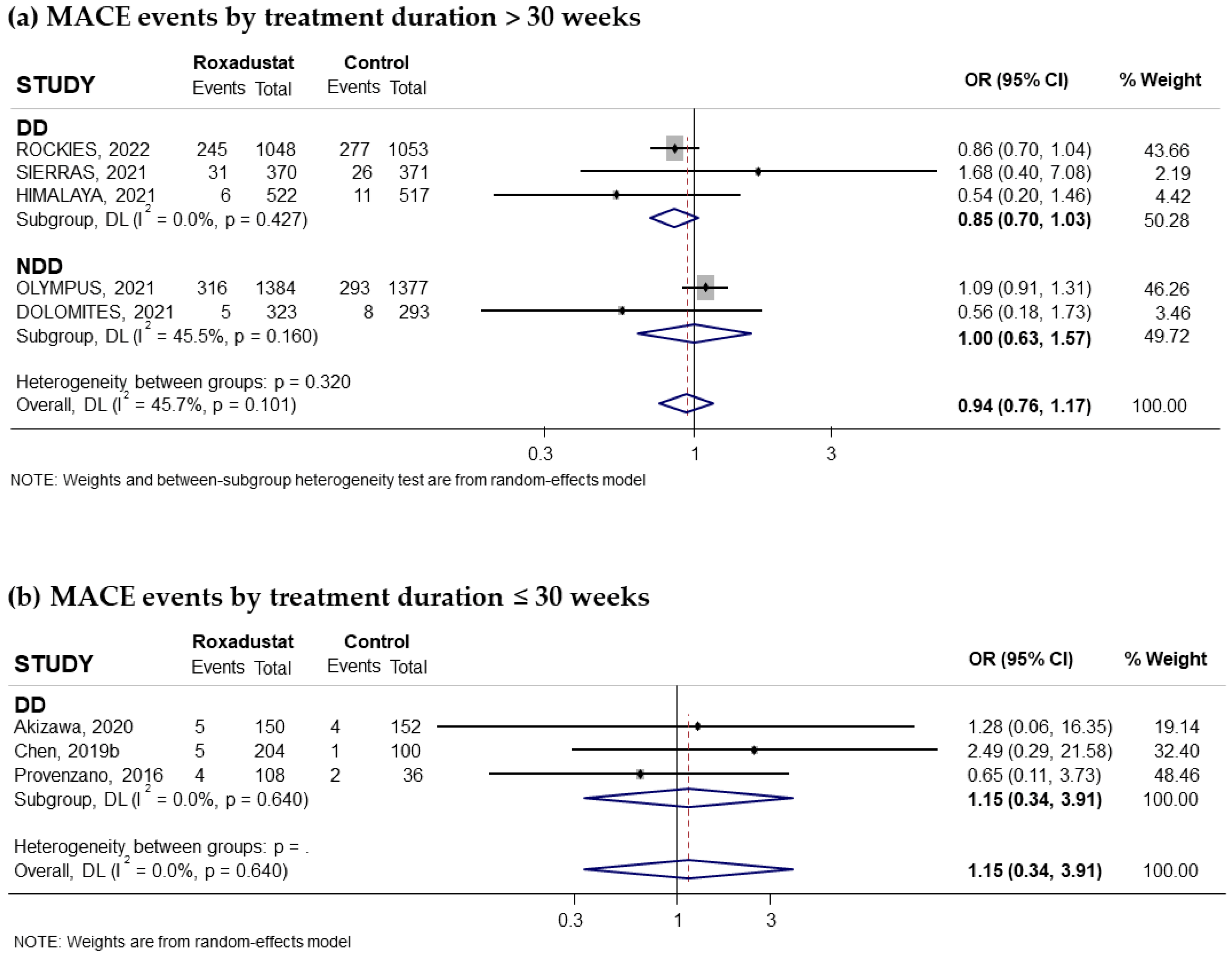
3.3.1. Effect of Roxadustat on MACEs
3.3.2. Effect of Roxadustat on Hypertension
3.3.3. Effect of Roxadustat on Diarrhea
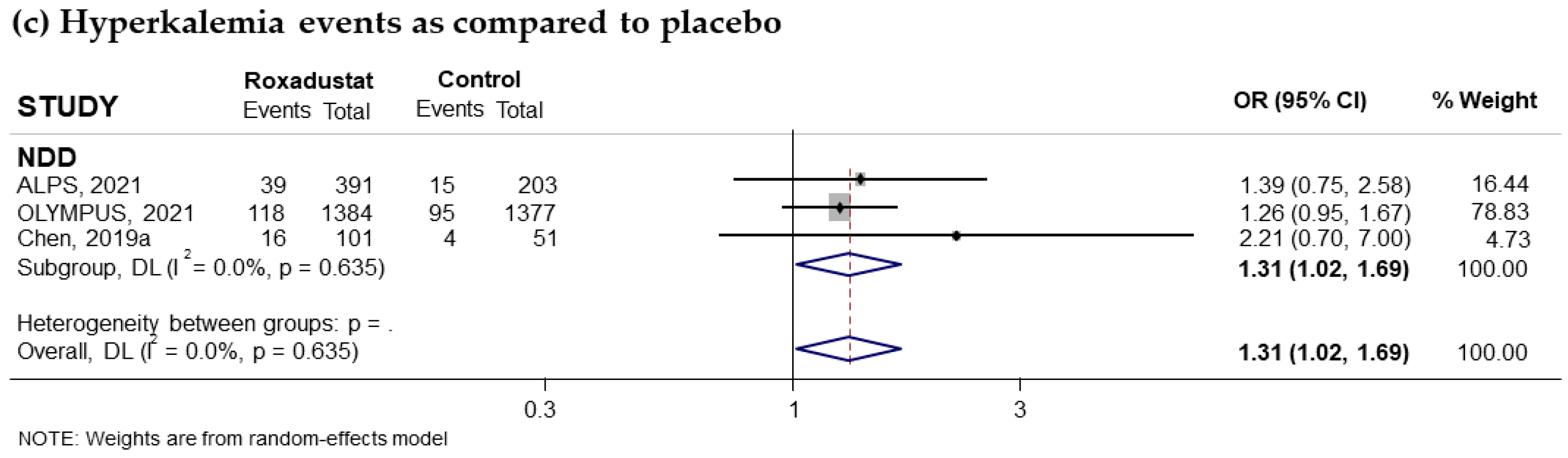
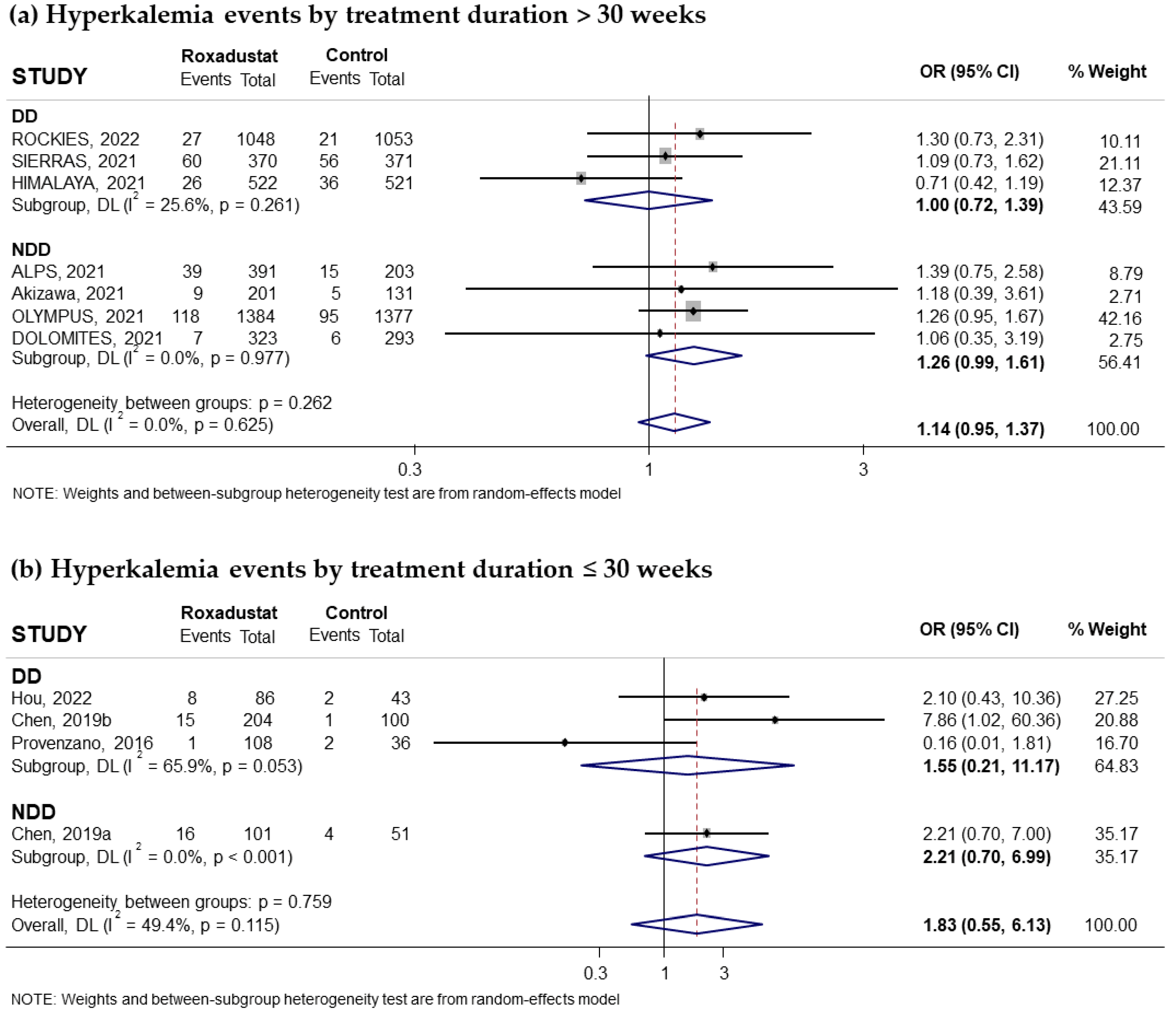
3.3.4. Effect of Roxadustat on Hyperkalemia
3.4. Analysis of the Impact of Risk of Bias on the Results
4. Discussion
Limitations and Strengths
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AEs | Adverse Events |
| CIs | Confidence Intervals |
| CKD | Chronic Kidney Disease |
| DD | Dialysis-dependent |
| EPO | Erythropoietin |
| ESAs | Erythropoietic-Stimulating Agents |
| Hb | Hemoglobin |
| HD | Hemodialysis |
| HIF | Hypoxia-Inducible Factor |
| MACEs | Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events |
| NDD | Non-dialysis-dependent |
| OR | Odds Ratio |
| PD | Peritoneal Dialysis |
| PHs | Prolyl hydroxylases |
| SAEs | Serious Adverse Events |
References
- Khwaja, A. KDIGO clinical practice guidelines for acute kidney injury. Nephron Clin. Pract. 2012, 120, c179–c184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakhoul, G.; Simon, J.F. Anemia of chronic kidney disease: Treat it, but not too aggressively. Clevel. Clin. J. Med. 2016, 83, 613–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorp, M.L.; Johnson, E.S.; Yang, X.; Petrik, A.F.; Platt, R.; Dmith, D.H. Effect of anaemia on mortality, cardiovascular hospitalizations and end-stage renal disease among patients with chronic kidney disease. Nephrology 2009, 14, 240–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amaral, S.; Hwang, W.; Fivush, B.; Neu, A.; Frankenfield, D.; Furth, S. Association of mortality and hospitalization with achievement of adult hemoglobin targets in adolescents maintained on hemodialysis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2006, 17, 2878–2885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kular, D.; Macdougall, I.C. HIF stabilizers in the management of renal anemia: From bench to bedside to pediatrics. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2019, 34, 365–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besarab, A.; Bolton, W.K.; Browne, J.K.; Egrie, J.C.; Nissenson, A.R.; Okamoto, D.M.; Schwab, S.J.; Goodkin, D.A. The effects of normal as compared with low hematocrit values in patients with cardiac disease who are receiving hemodialysis and epoetin. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998, 339, 584–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besarab, A.; Frinak, S.; Yee, J. What is so bad about a hemoglobin level of 12 to 13 g/dL for chronic kidney disease patients anyway? Adv. Chronic Kidney Dis. 2009, 16, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Thamer, M.; Stefanik, K.; Kaufman, J.; Cotter, D.J. Epoetin requirements predict mortality in hemodialysis patients. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2004, 44, 866–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koulouridis, I.; Alfayez, M.; Trikalinos, T.A.; Balk, E.M.; Jaber, B.L. Dose of erythropoiesis-stimulating agents and adverse outcomes in CKD: A metaregression analysis. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2013, 61, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crathorne, L.; Huxley, N.; Haasova, M.; Snowsill, T.; Jones-Hughes, T.; Hoyle, M.; Briscoe, S.; Coelho, H.; Long, L.; Medina-Lara, A.; et al. The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of erythropoiesis-stimulating agents (epoetin and darbepoetin) for treating cancer treatment-induced anaemia (including review of technology appraisal no. 142): A systematic review and economic model. Health Technol. Assess. 2016, 20, 1–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, H. Cost-effectiveness of continuous erythropoietin receptor activator in anemia. Clin. Outcomes Res. 2014, 6, 319–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostoker, G. When should iron supplementation in dialysis patients be avoided, minimized or withdrawn? Semin. Dial. 2019, 32, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nangaku, M.; Kojima, I.; Tanaka, T.; Oshe, T.; Kato, H.; Fujita, F. Novel drugs and the response to hypoxia: HIF stabilizers and prolyl hydroxylase. Recent Pat Cardiovasc. Drug Discov. 2006, 1, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besarab, A.; Provenzano, R.; Hertel, J.; Zabaneh, R.; Klaus, S.J.; Lee, T.; Leong, R.; Hemmerich, S.; Yu, K.-H.P.; Neff, T.B. Randomized placebo-controlled dose-ranging and pharmacodynamics study of roxadustat (FG-4592) to treat anemia in nondialysis-dependent chronic kidney disease (NDD-CKD) patients. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2015, 30, 1665–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Qian, J.; Chen, J.; Yu, X.; Mei, C.; Hao, C.; Jiang, G.; Lin, H.; Zhang, X.; Zuo, L.; et al. Phase 2 studies of oral hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor FG-4592 for treatment of anemia in China. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2017, 32, 1373–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, N.; Hao, C.; Peng, X.; Lin, H.; Yin, A.; Hao, L.; Tao, Y.; Yu, K.-H.P. Roxadustat for Anemia in Patients with Kidney Disease Not Receiving Dialysis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 1001–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, N.; Hao, C.; Liu, B.C.; Lin, H.; Wang, C.; Xing, C.; Liang, X.; Jiang, G.; Liu, Z.; Li, X.; et al. Roxadustat Treatment for Anemia in Patients Undergoing Long-Term Dialysis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 1011–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akizawa, T.; Iwasaki, M.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Majikawa, Y.; Reusch, M. Phase 3, Randomized, Double-Blind, Active-Comparator (Darbepoetin Alfa) Study of Oral Roxadustat in CKD Patients with Anemia on Hemodialysis in Japan. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2020, 31, 1628–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akizawa, T.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Otsuka, T.; Reusch, M. A Phase 3, Multicenter, Randomized, Two-Arm, Open-Label Study of Intermittent Oral Dosing of Roxadustat for the Treatment of Anemia in Japanese Erythropoiesis-Stimulating Agent-Naïve Chronic Kidney Disease Patients Not on Dialysis. Nephron 2020, 144, 372–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Moher, D. Updating guidance for reporting systematic reviews: Development of the PRISMA 2020 statement. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2021, 134, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begg, C.B.; Mazumdar, M. Operating characteristics of a rank correlation test for publication bias. Biometrics 1994, 50, 1088–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provenzano, R.; Besarab, A.; Wright, S.; Dua, S.; Zeig, S.; Nguyen, P.; Poole, L.; Saikali, K.G.; Saha, G.; Hemmerich, S.; et al. Roxadustat (FG-4592) Versus Epoetin Alfa for Anemia in Patients Receiving Maintenance Hemodialysis: A Phase 2, Randomized, 6 to 19-Week, Open-Label, Active-Comparator, Dose-Ranging, Safety and Exploratory Efficacy Study. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2016, 67, 912–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akizawa, T.; Iwasaki, M.; Otsuka, T.; Reusch, M.; Misumi, T. Roxadustat Treatment of Chronic Kidney Disease-Associated Anemia in Japanese Patients Not on Dialysis: A Phase 2, Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Adv. Ther. 2019, 36, 1438–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akizawa, T.; Iwasaki, M.; Otsuka, T.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Reusch, M. Phase 3 Study of Roxadustat to Treat Anemia in Non-Dialysis-Dependant CKD. Kidney Int. Rep. 2021, 6, 1810–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barratt, J.; Andric, B.; Tataradze, A.; Schömig, M.; Reusch, M.; Valluri, U.; Mariat, C. Roxadustat for the treatment of anaemia in chronic kidney disease patients not on dialysis: A Phase 3, randomized, open-label, active-controlled study (DOLOMITES). Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2021, 36, 1616–1628, Erratum in Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2022, 37, 805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shutov, E.; Sułowicz, W.; Esposito, C.; Tataradze, A.; Andric, B.; Reusch, M.; Valluri, U.; Dimkovic, N. Roxadustat for the treatment of anemia in chronic kidney disease patients not on dialysis: A Phase 3, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study (ALPS). Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2021, 36, 1629–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provenzano, R.; Shutov, E.; Eremeeva, L.; Korneyeva, S.; Poole, L.; Saha, G.; Bradley, C.; Eyassu, M.; Besarab, A.; Leong, R.; et al. Roxadustat for anemia in patients with end-stage renal disease incident to dialysis. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2021, 36, 1717–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fishbane, S.; El-Shahawy, M.A.; Pecoits-Filho, R.; Van, B.P.; Houser, M.T.; Frison, L.; Little, D.J.; Guzman, N.J.; Pergola, P.E. Roxadustat for Treating Anemia in Patients with CKD Not on Dialysis: Results from a Randomized Phase 3 Study. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2021, 32, 737–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Csiky, B.; Schömig, M.; Esposito, C.; Barratt, J.; Reusch, M.; Vallari, U.; Sulowicz, W. Roxadustat for the Maintenance Treatment of Anemia in Patients with End-Stage Kidney Disease on Stable Dialysis: A European Phase 3, Randomized, Open-Label, Active-Controlled Study (PYRENEES). Adv. Ther. 2021, 38, 5361–5380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charytan, C.; Manllo-Karim, R.; Martin, E.R.; Steer, D.; Bernardo, M.; Dua, S.L.; Moustafa, M.A.; Saha, G.; Bradley, C.; Eyassu, M.; et al. A Randomized Trial of Roxadustat in Anemia of Kidney Failure: SIERRAS Study. Kidney Int. Rep. 2021, 6, 1829–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fishbane, S.; Pollock, C.A.; El-Shahawy, M.; Escudero, E.T.; Rastogi, A.; Van, B.P.; Frison, L.; Houser, M.; Pola, M.; Little, D.J.; et al. Roxadustat Versus Epoetin Alfa for Treating Anemia in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease on Dialysis: Results from the Randomized Phase 3 ROCKIES Study. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2022, 33, 850–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.-P.; Mao, X.-Y.; Wang, C.; Xu, Z.-H.; Bu, Z.-H.; Xu, M.; Li, B. Roxadustat treatment for anemia in peritoneal dialysis patients: A randomized controlled trial. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2022, 121, 529–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, M.; Zhu, C.; Yan, T.; Zhou, Y.; Lv, Q.; Chuan, J. Safe and effective treatment for anemic patients with chronic kidney disease: An updated systematic Review and Meta-Analysis on Roxadustat. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 658079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, L.; Wang, M.; Liu, M.; Pang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zheng, B.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, W. Cardiovascular and renal safety outcomes of hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl-hydroxylase inhibitor roxadustat for anemia patients with chronic kidney disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ren. Fail. 2024, 46, 2313864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Wang, Y.; Yang, H.; Sun, L.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, X.; Guo, J.; Liu, Y.N.; Liu, W.J. Cardiac and Kidney Adverse Effects of HIF Prolyl-Hydroxylase Inhibitors for Anemia in Patients With CKD Not Receiving Dialysis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Meta-Analysis. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2023, 81, 434–445.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Cheng, Q.; Wang, J.; Zhao, X.; Zhu, S. Long-term efficacy and safety of hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl hydroxylase inhibitors in anaemia of chronic kidney disease: A meta-analysis including 13,146 patients. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 2021, 46, 999–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Niu, Y.; Liu, F.; Yang, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, P.; Chen, X. Safety of HIF prolyl hydroxylase inhibitors for anemia in dialysis patients: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1163908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, S.; Xie, Q.; Ma, T.; Xiang, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Cui, Y. Risk of infection in roxadustat treatment for anemia in patients with chronic kidney disease: A systematic review with meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 967532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Tian, J.; Liu, D.; Zhao, Y.; Fang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y. Efficacy and safety of roxadustat for anaemia in dialysis-dependent and non-dialysis-dependent chronic kidney disease patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2022, 88, 919–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, J.; Ren, S.; Feng, Y. Hypoxia-inducible factor-prolyl hydroxylase inhibitors for treatment of anemia in chronic kidney disease: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1406588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Li, P.; Zhang, H.-L.; Jia, L. An updated meta-analysis on the efficacy and safety of hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor treatment of anemia in nondialysis-dependent chronic kidney disease. Ren. Fail. 2023, 45, 2258986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Jiang, S.; Gu, X.; Liu, X.; Shang, S.; Zhang, J.; Pang, K.; Li, W. Assessment of the safety of Roxadustat for cardiovascular events in chronic kidney disease-related anemia using meta-analysis and bioinformatics. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1380326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartnicki, P. Hypoxia-Inducible Factor Prolyl Hydroxylase Inhibitors as a New Treatment Option for Anemia in Chronic Kidney Disease. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czock, D.; Keller, F. Clinical pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of roxadustat. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2022, 61, 347–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akizawa, T.; Yamada, T.; Nobori, K.; Matsuda, Y.; Hayashi, Y.; Hayasaki, T.; Yamamoto, H. Molidustat for Japanese Patients With Renal Anemia Receiving Dialysis. Kidney Int. Rep. 2021, 6, 2604–2616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nangaku, M.; Kondo, K.; Kokado, Y.; Ueta, K.; Kaneko, G.; Tandai, T.; Kawaguchi, Y.; Yasuhiro, K. Phase 3 Randomized Study Comparing Vadadustat with Darbepoetin Alfa for Anemia in Japanese Patients with Nondialysis-Dependent CKD. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2021, 32, 1779–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nangaku, M.; Kondo, K.; Ueta, K.; Kokado, Y.; Kanedo, G.; Matsuda, H.; Kawaguchi, Y.; Komatsu, Y. Efficacy and safety of vadadustat compared with darbepoetin alfa in Japanese anemic patients on hemodialysis: A Phase 3, multicenter, randomized, double-blind study. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2021, 36, 1731–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yap, D.Y.H.; McMahon, L.P.; Hao, C.M.; Hu, N.; Okada, H.; Suzuki, Y.; Kim, S.G.; Lim, S.K.; Vareesangthip, K.; Hung, C.C.; et al. HIF-PHI Recommendation Committee. Recommendations by the Asian Pacific society of nephrology (APSN) on the appropriate use of HIF-PH inhibitors. Nephrology 2021, 26, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.T.; Lo, Y.C.; Gao, Z.H.; Wu, S.-N. Evidence for the Capability of Roxadustat (FG-4592), an Oral HIF Prolyl-Hydroxylase Inhibitor, to Perturb Membrane Ionic Currents: An Unidentified yet Important Action. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, X.; Ruan, W.; Bobrow, B.; Carmeliet, P.; Eltzschig, H.K. Targeting hypoxia-inducible factors: Therapeutic opportunities and challenges. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2024, 23, 175–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.G. Hypertension Induced by Hypoxia-Inducible Factor Prolyl Hydroxylase Inhibitors in Treating Anemia in Patients With Chronic Kidney Disease: A Mini-Review. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2024, 26, 1375–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Szczech, L.; Tang, K.L.; Barnhart, H.; Sapp, S.; Wolfson, M.; Reddan, D. Correction of anemia with epoetin alfa in chronic kidney disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 355, 2085–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, N.; Wish, J.B. Hypoxia-Inducible Factor Prolyl Hydroxylase Inhibitors: A Potential New Treatment for Anemia in Patients With CKD. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2017, 69, 815–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semenza, G.L. Hypoxia-inducible factors in physiology and medicine. Cell 2012, 148, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naito, Y.; Yasumura, S.; Okuno, K.; Asakura, M.; Tsujino, T.; Masuyama, T.; Ishihara, M. Hypoxia-inducible factor-prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor Roxadustat (FG-4592) reduces renal fibrosis in Dahl salt-sensitive rats. J. Hypertens. 2024, 42, 497–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Wang, S.; Shi, W.; Zhou, W.; Niu, Y.; Huang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, A.; Jia, Z. Roxadustat prevents Ang II hypertension by targeting angiotensin receptors and eNOS. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 6, e133690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakagawa, K.; Oshiba, Y.; Sukita, R.; Hosomi, A.; Tawa, M.; Ohkita, M. Roxadustat has beneficial effects on the vascular tone of the rat thoracic aorta. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2025, 86, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fishbane, S.; Nissenson, A.R. Anemia management in chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2010, 78 (Suppl. S117), S3–S9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Zhou, T.; Yu, L.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, M.; Cui, J.; Yu, W.; Zhou, J.; Yu, Y. Comparison between the influence of roxadustat and recombinant human erythropoietin treatment on blood pressure and cardio-cerebrovascular complications in patients undergoing peritoneal dialysis. Front. Med. 2023, 10, 1166024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchida, L.; Tanaka, T.; Saito, H.; Sugahara, M.; Wakashima, T.; Fukui, K.; Nangaku, M. Effects of a prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor on kidney and cardiovascular complications in a rat model of chronic kidney disease. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2020, 318, F388–F401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coulet, F.; Nadaud, S.; Agrapart, M.; Soubrier, F. Identification of hypoxia-response element in the human endothelial nitric-oxide synthase gene promoter. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 46230–46240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasegawa, S.; Tanaka, T.; Nangaku, M. Hypoxia-inducible factor stabilizers for treating anemia of chronic kidney disease. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2018, 27, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semenza, G.L. HIF-1 and mechanisms of hypoxia sensing. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2001, 13, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Packer, M. Mutual Antagonism of Hypoxia-Inducible Factor Isoforms in Cardiac, Vascular, and Renal Disorders. JACC Basic Transl. Sci. 2020, 5, 961–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cioffi, C.L.; Liu, X.Q.; Kosinski, P.A.; Garay, M.; Bowen, B.R. Differential regulation of HIF-1 alpha prolyl-4-hydroxylase genes by hypoxia in human cardiovascular cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2003, 303, 947–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appelhoff, R.J.; Tian, Y.M.; Raval, R.R. Differential function of the prolyl hydroxylases PHD1, PHD2, and PHD3 in the regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 38458–38465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aprelikova, O.; Chandramouli, G.V.; Wood, M. Regulation of HIF prolyl hydroxylases by hypoxia-inducible factors. J. Cell Biochem. 2004, 92, 491–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miikkulainen, P.; Högel, H.; Seyednasrollah, F.; Rantanen, K.; Elo, L.L.; Jaakkola, P.M. Hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-prolyl hydroxylase 3 (PHD3) maintains high HIF2A mRNA levels in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 3760–3771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smythies, J.A.; Sun, M.; Masson, N. Inherent DNA-binding specificities of the HIF-1α and HIF-2α transcription factors in chromatin. EMBO Rep. 2019, 20, e46401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukui, K.; Shinozaki, Y.; Kobayashi, H. JTZ-951 (enarodustat), a hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor, stabilizes HIF-α protein and induces erythropoiesis without effects on the function of vascular endothelial growth factor. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 859, 172532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]













| Scheme | 1. | Phase of Study, Location | Number of Patients | Gender (%) | Age Range (Years) | Intervention: ROXADUSTAT (Dose) | Control | Duration of Study (Weeks) | Patient Disease | Baseline Hb 1 (g/dL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Besarab et al., 2015 [14] | NCT00761657 | II, USA | 116 | Male (42) Female (58) | 18−80 Mean: 65.8 | 0.7, 1, 1.5 or 2 mg/kg | Placebo | 4 | Anemia in patients with stages 3–4 CKD who were not receiving dialysis. | 10.3 ± 0.9 10.3 ± 0.9 |
| Chen et al., 2019 [16] | NCT02652819 | III, China | 152 | Male (37) Female (63) | 18–75 Mean: 54 | 70 or 100 mg | Placebo | 9 | Anemia in patients with stages 3–5 CKD who were not receiving dialysis. | 8.9 ± 0.8 8.9 ± 0.7 |
| Akizawa et al., 2019 [23] | NCT01964196 | II, Japan | 107 | Male (47) Female (53) | 20–74 Mean: 63.15 | 50, 70 or 100 mg | Placebo | 24 | Anemia and CKD who were not receiving dialysis. | 9.4 ± 0.6 9.3 ± 0.7 |
| Akizawa et al., 2021 [24] | NCT02988973 | III, Japan | 334 | Male (58) Female (42) | ≥20 Mean: 70 <65 años (26%) >65 años (74%) | Initial dose conversion to roxadustat, based on ESA use | Darbopoetin alfa | 52 | Anemia and CKD who were not receiving dialysis | 11.03 ± 0.56 10.96 ± 0.52 |
| Shutov et al., 2021 [26] | NCT01887600 ALPS | III, Russia | 594 | Male (45) Female (55) | ≥18 Mean: 62.5 | 70 or 100 mg | Placebo | 52 | Anemia in patients with stages 3–5 CKD, who were not receiving dialysis. | 9.1 ± 0.8 9.1 ± 0.7 |
| Fishbane et al., 2021 [28] | NCT02174627 OLYMPUS | III, USA | 2761 | Male (42) Female (58) | ≥18 Mean: 61.7 | 70 mg | Placebo | 52 weeks up to 4 years | Anemia in patients with stages 3–5 CKD who were not receiving dialysis. | 9.1 ± 0.7 9.1 ± 0.7 |
| Barratt et al., 2021 [25] | NCT02021318 DOLOMITES | III, Europe | 616 | Male (44) Female (56) | ≥18 Mean: 66.3 | 70 or 100 mg | Darbopoetin alfa | 104 | Anemia in patients with stages 3–5 CKD who were not receiving dialysis. | 9.55 ± 0.75 9.55 ± 0.69 |
| Provenzano et al., 2016 [22] | NCT01147666 | II, USA | 144 | Male (66) Female (34) | 18–75 Mean: 57.3 | 1, 1.5, 1.8 or 2 mg/kg | Epoetin alfa | 6–19 | Anemia in patients with end-stage CKD on stable HD. | 11.2 ± 0.7 11.2 ± 1.0 |
| Chen et al., 2019 [17] | NCT02652806 | III, China | 304 | Male (61) Female (39) | 18–75 Mean: 49.3 | 100 or 120 mg | Epoetin alfa | 27 | Anemia in patients with stages 3–5 CKD on stable HD (89%) or PD (11%). | 10.4 ± 0.7 10.5 ± 0.7 |
| Akizawa et al., 2020 [18] | NCT02952092 | III, Japan | 303 | Male (67) Female (33) | ≥20 Mean: 64.75 | 70 or 100 mg | Darbopoetin alfa | 24 | Anemia and CKD on stable HD. | 11.0 ± 0.6 11.0 ± 0.6 |
| Provenzano et al., 2021 [27] | NCT02052310 HIMALAYAS | III, USA, Asia, South America, Europe | 1043 | Male (59) Female (41) | ≥18 Mean: 54 | 70 or 100 mg | Epoetin alfa | 89 | Anemia and CKD on stable HD (89%) or PD (11%). | 8.4 ± 1.0 8.5 ± 1.0 |
| Charytan et al., 2021 [30] | NCT02273726 SIERRAS | III, USA | 741 | Male (54) Female (46) | ≥18 Mean: 58 | 70, 100, 150 or 200 mg | Epoetin alfa | 28–52 | Anemia and CKD on stable HD (96%) and PD (4%) | 10.30 ± 0.66 10.31 ± 0.66 |
| Csiky et al., 2021 [29] | NCT02278341 EudraCT2013-001497-16 PYRENESS | III, Europe | 834 | Male (58) Female (42) | ≥18 Mean: 61.4 | 20, 50 or 100 mg | Epoetin alfa or Darbopoetin alfa | 52–104 | Anemia in patients with end-stage CKD on stable HD (94%) or PD (6%). | 10.75 ± 0.62 10.78 ± 0.62 |
| Hou et al., 2022 [32] | ChiCTR2000035054 | China | 129 | Male (56) Female (44) | 18–75 Mean: 48.2 | 100 or 120 mg | ESA | 24 | Anemia and CKD on stable PD. | 9.0 ± 1.4 9.0 ± 1.2 |
| Fishbane et al., 2022 [31] | NCT02174731 ROCKIES | III, USA, Asia, Latin America, Europe and Australia, | 2106 | Male (59) Female (41) | ≥18 Mean: 54 | 70, 100 or 200 mg | Epoetin alfa | Up to 4 years | Anemia in patients with end-stage CKD on stable HD (89%) or PD (11%). | 10.2 (9.3–10.9) 10.3 (9.2–11.0) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martínez-Miguel, P.; Fernández-Antón, E.; Rodríguez-Puyol, D.; de Abajo, F.J.; López Ongil, S. Safety of Roxadustat in Chronic Kidney Disease Patients: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 1566. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18101566
Martínez-Miguel P, Fernández-Antón E, Rodríguez-Puyol D, de Abajo FJ, López Ongil S. Safety of Roxadustat in Chronic Kidney Disease Patients: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(10):1566. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18101566
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartínez-Miguel, Patricia, Encarnación Fernández-Antón, Diego Rodríguez-Puyol, Francisco J. de Abajo, and Susana López Ongil. 2025. "Safety of Roxadustat in Chronic Kidney Disease Patients: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 10: 1566. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18101566
APA StyleMartínez-Miguel, P., Fernández-Antón, E., Rodríguez-Puyol, D., de Abajo, F. J., & López Ongil, S. (2025). Safety of Roxadustat in Chronic Kidney Disease Patients: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Pharmaceuticals, 18(10), 1566. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18101566







