Novel Multifunctional Cannabidiol-Based Analogues with In Silico, In Vitro, and In Vivo Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Effect
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
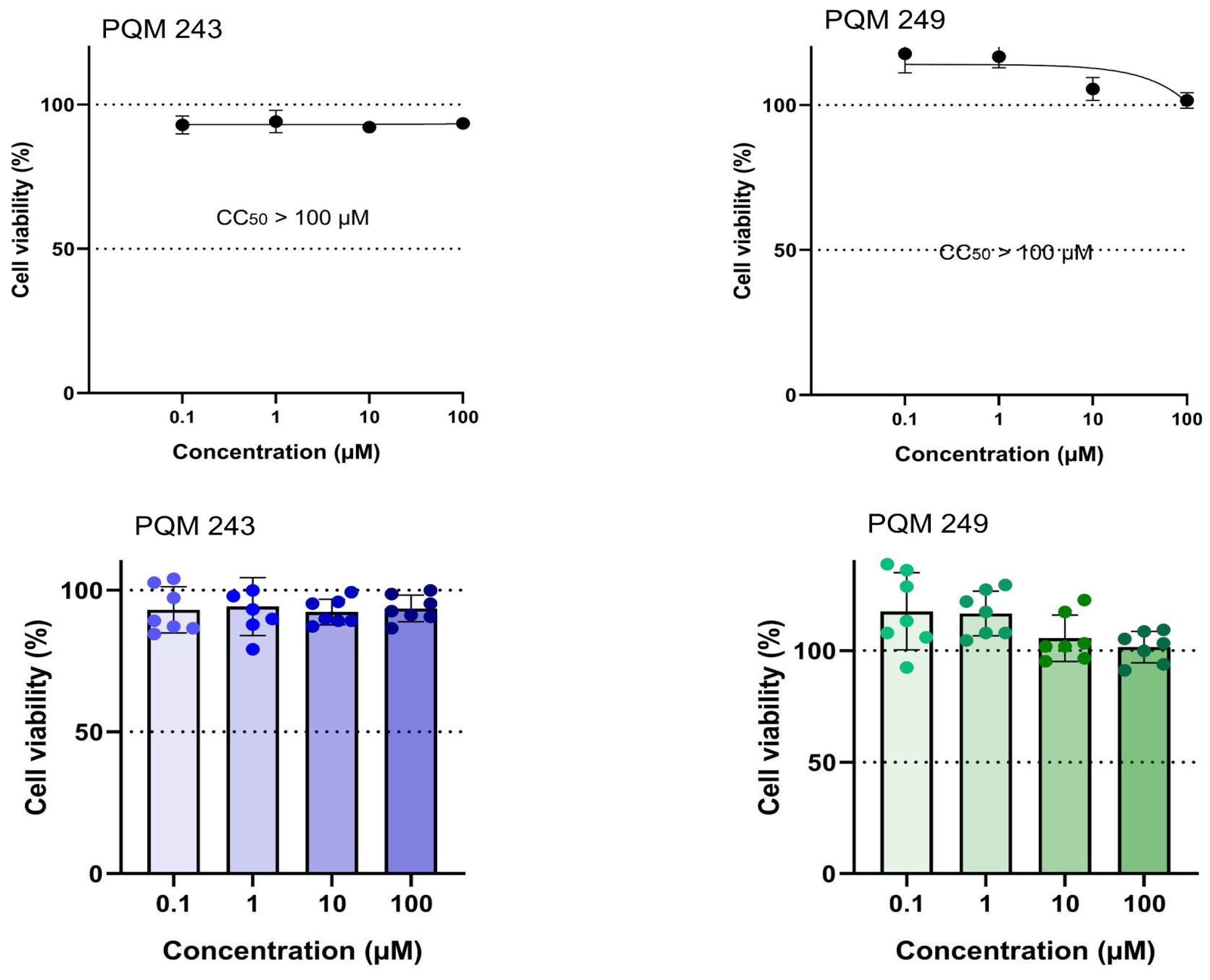
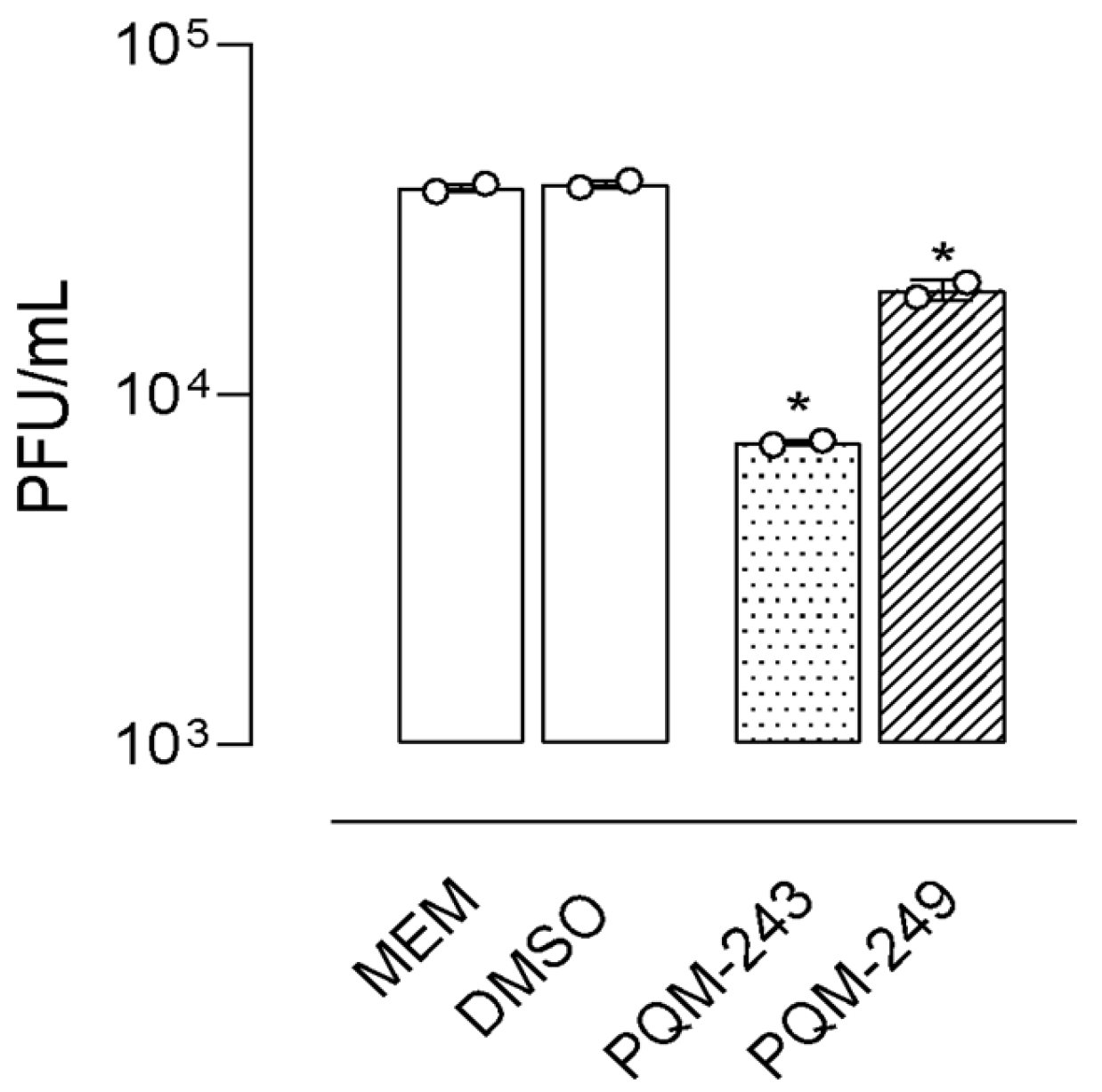
2.1. Antiviral Activity
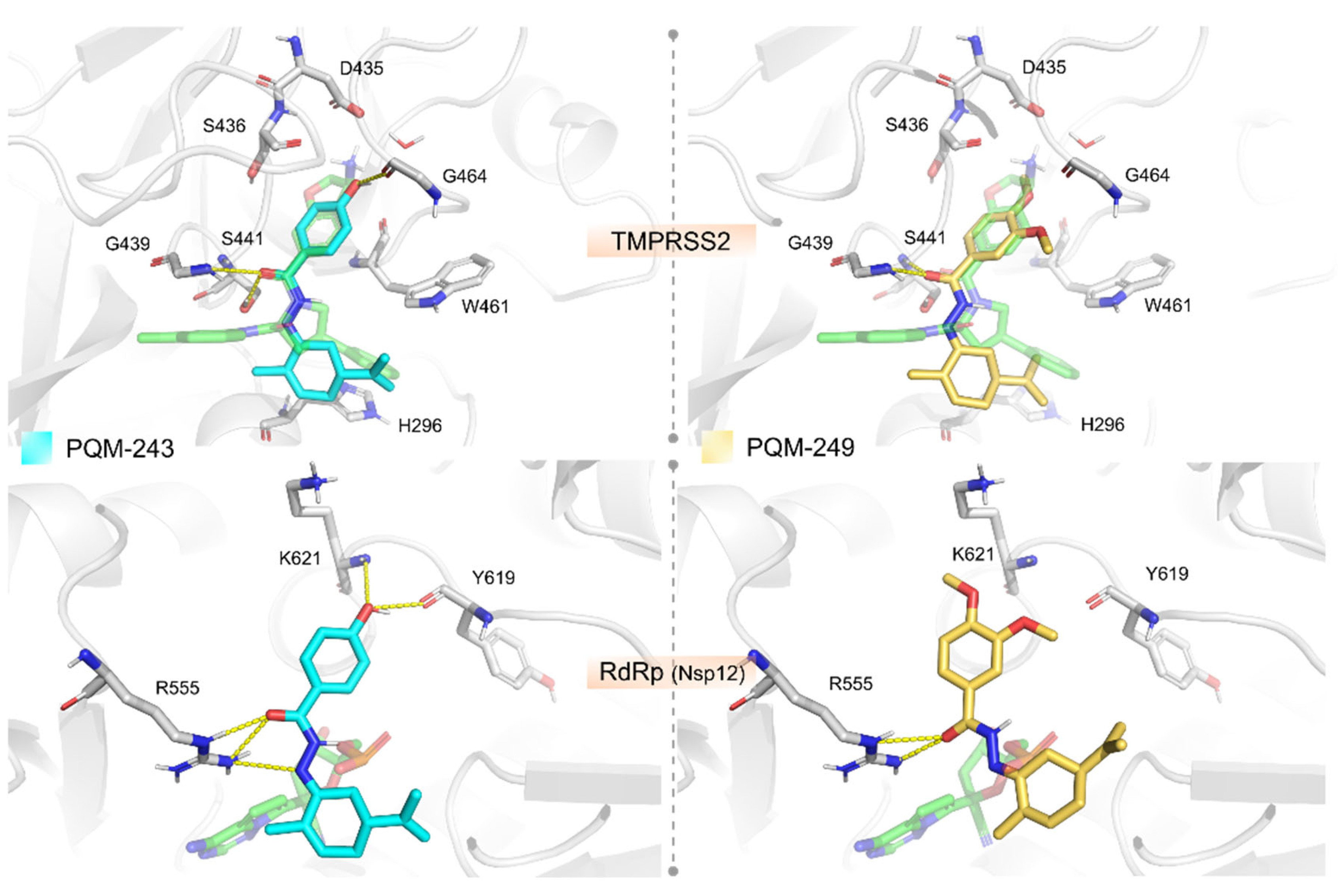
2.2. Molecular Modeling
2.3. Angiotensin Converting Enzyme-2 (ACE2) Inhibition Assays
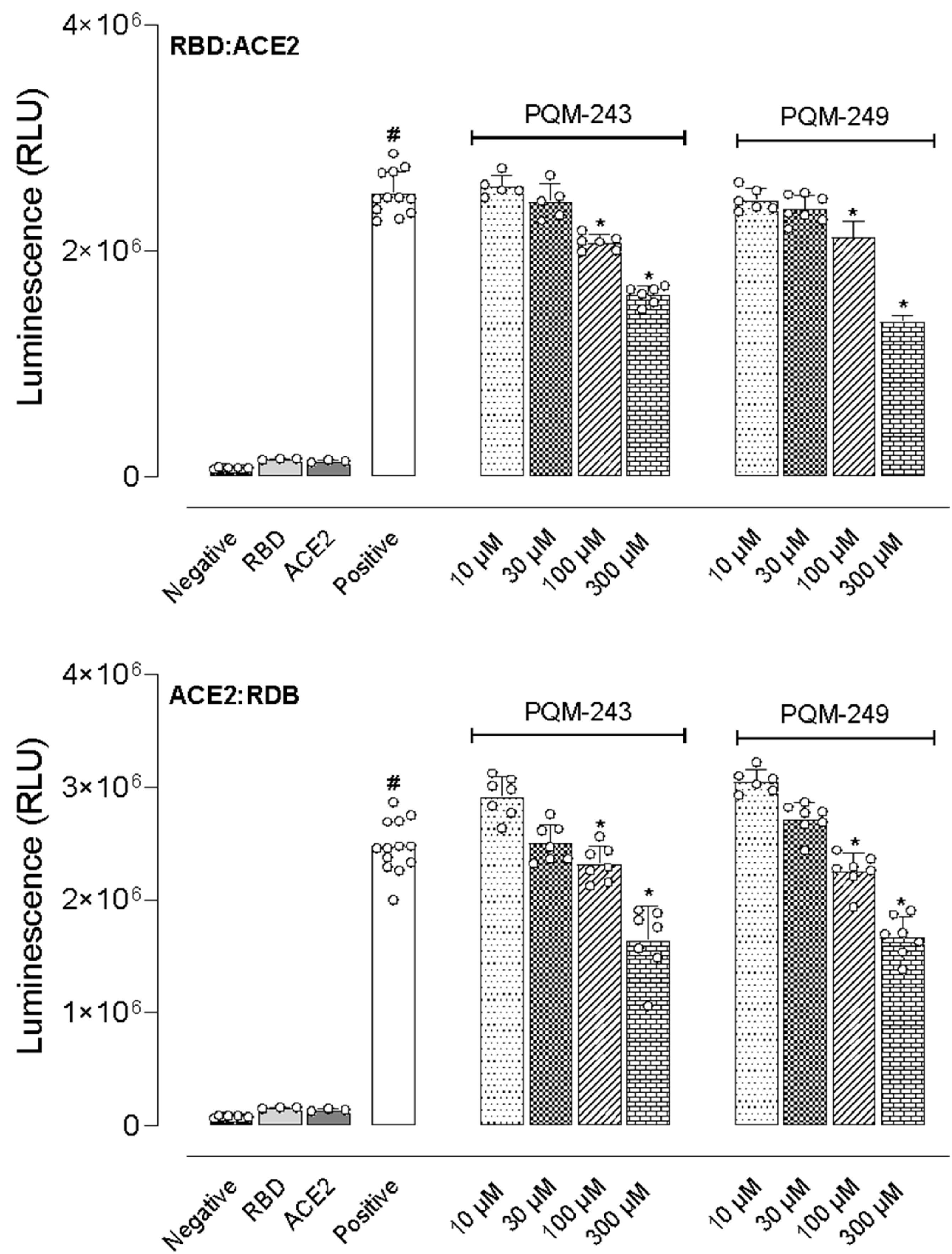
2.4. Inhibition of the Interaction Between the Receptor Binding Domain (RBD) and ACE2
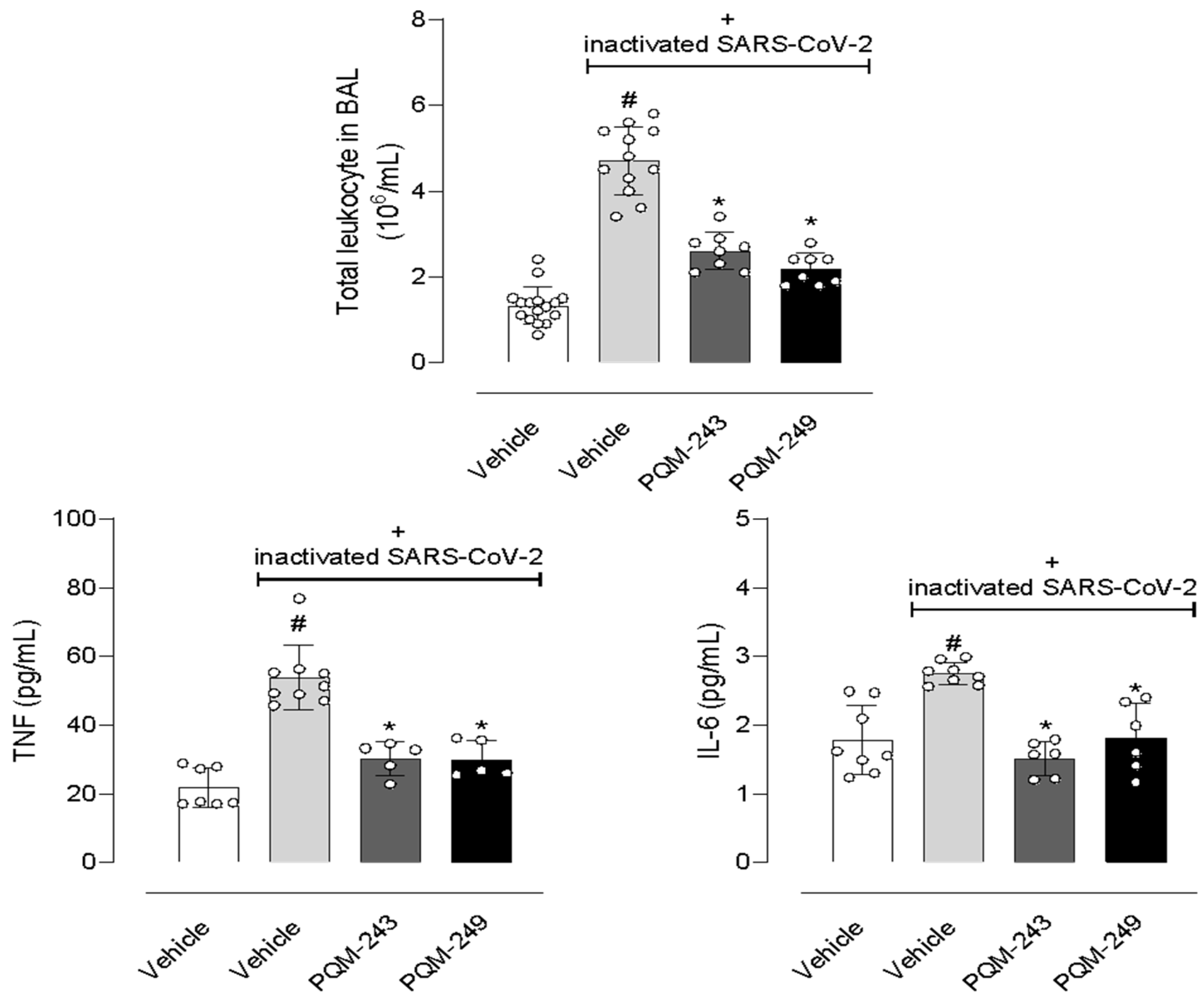
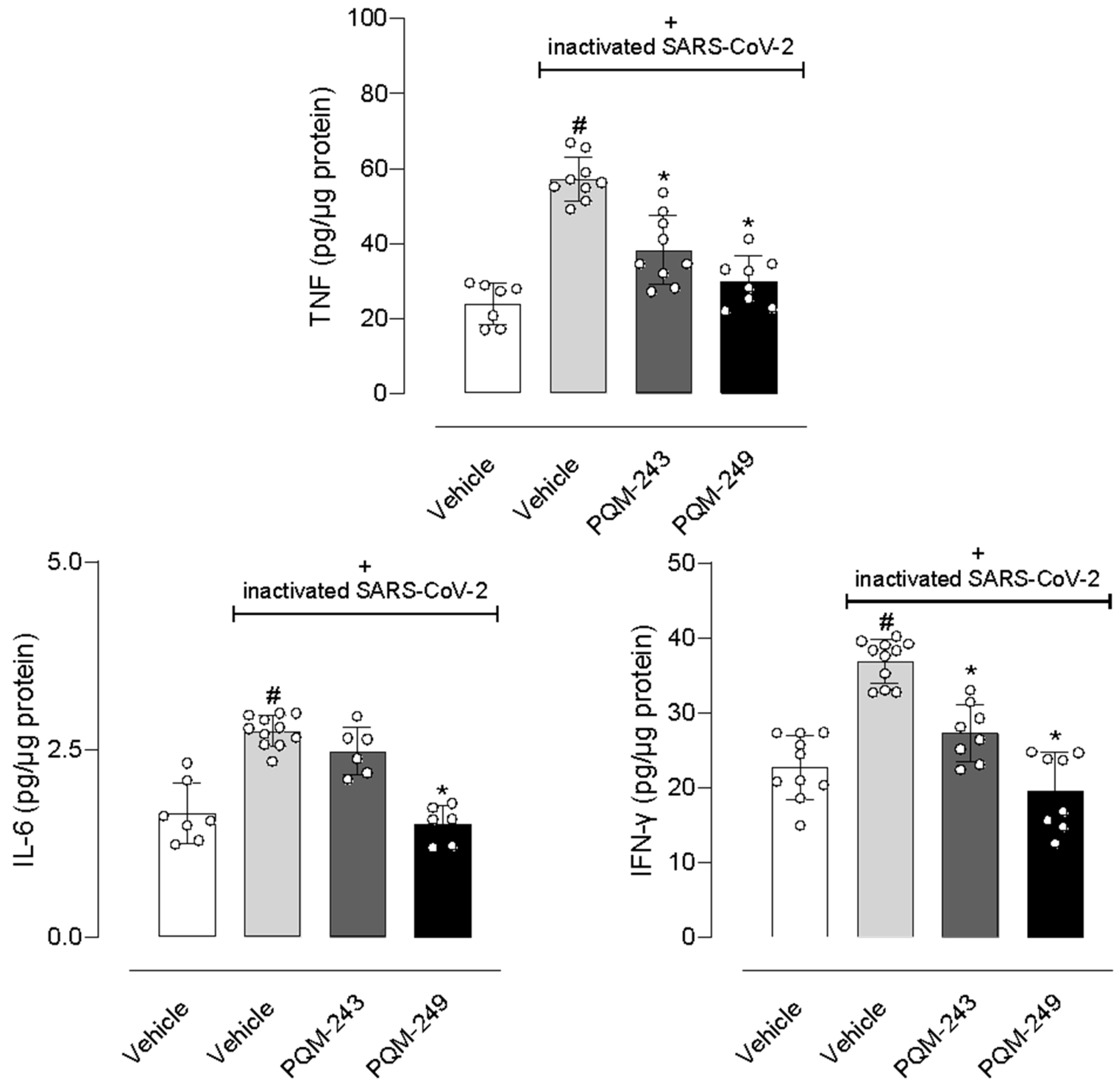
2.5. In Vivo Assays
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Synthesis of PQM-243 and PQM-249
4.2. Cell Lines and SARS-CoV-2 Cultures
4.3. Cytotoxicity Assay
4.4. SARS-CoV-2 Virucidal and Dose–Response Assays
4.5. Molecular Modelling
4.6. Animals
4.7. SARS-CoV-2-Induced Lung Inflammation
4.8. Angiotensin Converting Enzyme-2 (ACE2) Enzyme Assay
4.9. Interaction Between Spike Protein with Angiotensin Converting Enzyme-2 (ACE2)
4.10. Cytokine Measurements
4.11. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sanders, J.M.; Monogue, M.L.; Jodlowski, T.Z.; Cutrell, J.B. Pharmacologic Treatments for Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): A Review. JAMA—J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2020, 323, 1824–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. WHO COVID-19 Dashboard; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Dhama, K.; Sharun, K.; Tiwari, R.; Dadar, M.; Malik, Y.S.; Singh, K.P.; Chaicumpa, W. COVID-19, an Emerging Coronavirus Infection: Advances and Prospects in Designing and Developing Vaccines, Immunotherapeutics, and Therapeutics. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2020, 16, 1232–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, N.; Zhang, D.; Wang, W.; Li, X.; Yang, B.; Song, J.; Zhao, X.; Huang, B.; Shi, W.; Lu, R.; et al. A Novel Coronavirus from Patients with Pneumonia in China, 2019. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, M.; Kleine-Weber, H.; Schroeder, S.; Krüger, N.; Herrler, T.; Erichsen, S.; Schiergens, T.S.; Herrler, G.; Wu, N.H.; Nitsche, A.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Cell Entry Depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and Is Blocked by a Clinically Proven Protease Inhibitor. Cell 2020, 181, 271–280.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radzikowska, U.; Ding, M.; Tan, G.; Zhakparov, D.; Peng, Y.; Wawrzyniak, P.; Wang, M.; Li, S.; Morita, H.; Altunbulakli, C.; et al. Distribution of ACE2, CD147, CD26, and Other SARS-CoV-2 Associated Molecules in Tissues and Immune Cells in Health and in Asthma, COPD, Obesity, Hypertension, and COVID-19 Risk Factors. Allergy Eur. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020, 75, 2829–2845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, Q.; Guo, D. Emerging Coronaviruses: Genome Structure, Replication, and Pathogenesis. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 418–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- COVID-19 Deaths Reported (2024 Global). Available online: https://data.who.int/dashboards/covid19/ (accessed on 15 September 2024).
- Tasneem, A.; Sultan, A.; Singh, P.; Bairagya, H.R.; Almasoudi, H.H.; Alhazmi, A.Y.M.; Binshaya, A.S.; Hakami, M.A.; Alotaibi, B.S.; Abdulaziz Eisa, A.; et al. Identification of Potential Therapeutic Targets for COVID-19 through a Structural-Based Similarity Approach between SARS-CoV-2 and Its Human Host Proteins. Front. Genet. 2024, 15, 638334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanimozhi, G.; Pradhapsingh, B.; Pawar, C.S.; Khan, H.A.; Alrokayan, S.H.; Prasad, N.R. SARS-CoV-2: Pathogenesis, Molecular Targets and Experimental Models. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 638334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.; Misra, A. Contentious Issues and Evolving Concepts in the Clinical Presentation and Management of Patients with COVID-19 Infection with Reference to Use of Therapeutic and Other Drugs Used in Co-Morbid Diseases (Hypertension, Diabetes Etc). Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Clin. Res. Rev. 2020, 14, 251–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, M.; Tan, X. Current Strategies of Antiviral Drug Discovery for COVID-19. Front. Mol. Biosc. 2021, 8, 671263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salian, V.S.; Wright, J.A.; Vedell, P.T.; Nair, S.; Li, C.; Kandimalla, M.; Tang, X.; Porquera, E.M.C.; Kalari, K.R.; Kandimalla, K.K. COVID-19 Transmission, Current Treatment, and Future Therapeutic Strategies. Mol. Pharm. 2021, 18, 754–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gil, C.; Ginex, T.; Maestro, I.; Nozal, V.; Barrado-Gil, L.; Cuesta-Geijo, M.Á.; Urquiza, J.; Ramírez, D.; Alonso, C.; Campillo, N.E.; et al. COVID-19: Drug Targets and Potential Treatments. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 12359–12386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S. COVID-19 Drug Development. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 32, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, Y. Potential Interventions for Novel Coronavirus in China: A Systematic Review. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 479–490. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Lin, D.; Sun, X.; Curth, U.; Drosten, C.; Sauerhering, L.; Becker, S.; Rox, K.; Hilgenfeld, R. Crystal Structure of SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease Provides a Basis for Design of Improved a-Ketoamide Inhibitors. Science 2020, 368, 409–412. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, W.; Zhang, B.; Jiang, X.M.; Su, H.; Li, J.; Zhao, Y.; Xie, X.; Jin, Z.; Peng, J.; Liu, F.; et al. Structure-Based Design of Antiviral Drug Candidates Targeting the SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease. Science 2020, 368, 1331–1335. [Google Scholar]
- Senger, M.R.; Evangelista, T.C.S.; Dantas, R.F.; Santana, M.V.S.; Gonçalves, L.C.S.; Neto, L.R.S.; Ferreira, S.B.; Silva-Junior, F.P. COVID-19: Molecular Targets, Drug Repurposing and New Avenues for Drug Discovery. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2020, 115, e200254. [Google Scholar]
- Stasi, C.; Fallani, S.; Voller, F.; Silvestri, C. Treatment for COVID-19: An Overview. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 889, 173644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, P.; McAuley, D.F.; Brown, M.; Sanchez, E.; Tattersall, R.S.; Manson, J.J. COVID-19: Consider Cytokine Storm Syndromes and Immunosuppression. Lancet 2020, 395, 1033–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokic, G.; Hillen, H.S.; Tegunov, D.; Dienemann, C.; Seitz, F.; Schmitzova, J.; Farnung, L.; Siewert, A.; Höbartner, C.; Cramer, P. Mechanism of SARS-CoV-2 Polymerase Stalling by Remdesivir. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Mahase, E. COVID-19: Remdesivir Probably Reduces Recovery Time, but Evidence Is Uncertain, Panel Finds. BMJ 2020, 370, m3049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheahan, T.P.; Sims, A.C.; Leist, S.R.; Schäfer, A.; Won, J.; Brown, A.J.; Montgomery, S.A.; Hogg, A.; Babusis, D.; Clarke, M.O.; et al. Comparative Therapeutic Efficacy of Remdesivir and Combination Lopinavir, Ritonavir, and Interferon Beta against MERS-CoV. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, W.; Mao, C.; Luan, X.; Shen, D.-D.; Shen, Q.; Su, H.; Wang, X.; Zhou, F.; Zhao, W.; Gao, M.; et al. Structural Basis for the Inhibition of the RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase from SARS-CoV-2 by Remdesivir. Science 2020, 368, 1499–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rochwerg, B.; Agarwal, A.; Zeng, L.; Leo, Y.S.; Appiah, J.A.; Agoritsas, T.; Bartoszko, J.; Brignardello-Petersen, R.; Ergan, B.; Ge, L.; et al. Remdesivir for Severe COVID-19: A Clinical Practice Guideline. BMJ 2020, 370, m2924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Perlman, S. COVID-19: Inflammatory Profile. Annu. Rev. Med. 2022, 73, 65–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Chen, W.; Zhang, Z.; Deng, Y.; Lian, J.Q.; Du, P.; Wei, D.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, X.X.; Gong, L.; et al. CD147-Spike Protein Is a Novel Route for SARS-CoV-2 Infection to Host Cells. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tay, M.Z.; Poh, C.M.; Rénia, L.; MacAry, P.A.; Ng, L.F.P. The Trinity of COVID-19: Immunity, Inflammation and Intervention. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2020, 20, 363–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Li, Q.; Han, Y.; Liang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Ren, T. Prevention of Lps-Induced Acute Lung Injury in Mice by Progranulin. Mediat. Inflamm. 2012, 2012, 540794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, S.H.J.; McCarter, S.D.; Deng, Y.; Parker, C.H.; Liles, W.C.; Stewart, D.J. Prevention of LPS-Induced Acute Lung Injury in Mice by Mesenchymal Stem Cells Overexpressing Angiopoietin. PLoS Med. 2007, 4, 1525–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, L.D.; Milberg, J.A.; Anardi, D.; Maunder, R.J. Clinical Risks for Development of the Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1995, 151, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepe, P.E.; Ralph Potkin, W.T.; Reus, W.D.H.; Hudson, W.D.L.; Carrico, W.C.J. Clinical Predictors of the Adult Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Am. J. Surg. 1982, 1, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aeffner, F.; Bolon, B.; Davis, I.C. Mouse Models of Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Toxicol. Pathol. 2015, 43, 1074–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matute-Bello, G.; Downey, G.; Moore, B.B.; Groshong, S.D.; Matthay, M.A.; Slutsky, A.S.; Kuebler, W.M. An Official American Thoracic Society Workshop Report: Features and Measurements of Experimental Acute Lung Injury in Animals. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2011, 44, 725–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, H.S.; Lee, J.S.; Bastarache, J.A.; Kuebler, W.M.; Downey, G.P.; Albaiceta, G.M.; Altemeier, W.A.; Artigas, A.; Bates, J.T.; Calfee, C.S.; et al. Update on the Features and Measurements of Experimental Acute Lung Injury in Animals An Official American Thoracic Society Workshop Report. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2022, 66, E1–E14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F. Clinical Course and Risk Factors For Mortality Of Adult In Patients with COVID-19 In Wuhan, China: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Lancet 2020, 395, 1054–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heimfarth, L.; Serafini, M.R.; Martins-Filho, P.R.; Quintans, J.S.S.; Quintans-Júnior, L.J. Drug Repurposing and Cytokine Management in Response to COVID-19: A Review. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 88, 106947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrestha, R.; Johnson, P.M.; Ghimire, R.; Whitley, C.J.; Channappanavar, R. Differential TLR-ERK1/2 Activity Promotes Viral SsRNA and DsRNA Mimic-Induced Dysregulated Immunity in Macrophages. Pathogens 2024, 13, 1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, M.J.A.; Ribeiro, L.R.; Gouveia, M.I.M.; Marcelino, B.d.R.; dos Santos, C.S.; Lima, K.V.B.; Lima, L.N.G.C. Hyperinflammatory Response in COVID-19: A Systematic Review. Viruses 2023, 15, 553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fekete, R.; Simats, A.; Bíró, E.; Pósfai, B.; Cserép, C.; Schwarcz, A.D.; Szabadits, E.; Környei, Z.; Tóth, K.; Fichó, E.; et al. Microglia Dysfunction, Neurovascular Inflammation and Focal Neuropathologies Are Linked to IL-1- and IL-6-Related Systemic Inflammation in COVID-19. Nat. Neurosci. 2025, 28, 558–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caohuy, H.; Eidelman, O.; Chen, T.; Mungunsukh, O.; Yang, Q.; Walton, N.I.; Pollard, B.S.; Khanal, S.; Hentschel, S.; Florez, C.; et al. Inflammation in the COVID-19 Airway Is Due to Inhibition of CFTR Signaling by the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 16895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manjili, R.H.; Zarei, M.; Habibi, M.; Manjili, M.H. COVID-19 as an Acute Inflammatory Disease. J. Immunol. 2020, 205, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza, M.L.; Paiva, J.P.B.; Franco, G.R.R.; Gontijo, V.S.; Alves, M.A.; Souza, H.M.R.; Lontra, A.C.P.; Oliveira, E.A.; Giorno, T.B.S.; Guedes, I.A.; et al. Design, Synthesis, and Evaluation of Antinociceptive Properties of Novel CBD-Based Terpene-Cinnamoyl-Acyl-Hydrazone Analogues. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Freitas Silva, M.; Ortiz, C.J.C.; Coelho, L.F.; Pruccoli, L.; Pagliarani, B.; Pisani, L.; Catto, M.; Poli, G.; Tuccinardi, T.; Vilela, F.C.; et al. Synthesis and pharmacological evaluation of novel N-aryl-cinnamoyl-hydrazone hybrids designed as neuroprotective agents for the treatment of Parkinson’s disease. Bioorg. Chem. 2024, 150, 107587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baptistella, M.M.; Assunção, R.R.S.; Oliveira, C.S.; Siqueira, A.P.; dos Santos, E.G.; Silva, M.F.; Faleiros, E.T.; Caixeta, E.S.; Novaes, R.D.; Ferreira, E.B.; et al. A synthetic resveratrol-curcumin hybrid derivative exhibits chemopreventive effects on colon pre-neoplastic lesions by targeting Wnt/β-catenin signaling, anti-inflammatory and antioxidant pathways. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2023, 76, 479–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz, C.J.C.; Silva, M.F.; Pruccoli, L.; Nadur, N.F.; De Azevedo, L.L.; Kümmerle, A.E.; Guedes, I.A.; Dardenne, L.E.; Coelho, L.F.L.; Guimarães, M.J.; et al. Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of new thalidomide-donepezil hybrids as neuroprotective agents targeting cholinesterases and neuroinflammation. RSC Med. Chem. 2022, 13, 568–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz, C.J.C.; Damasio, C.M.; Pruccoli, L.; Nadur, N.F.; Azevedo, L.L.; Guedes, I.A.; Dardenne, L.E.; Kümmerle, A.E.; Tarozzi, A.; Viegas, C., Jr. Cinnamoyl-N-Acylhydrazone-Donepezil Hybrids: Synthesis and Evaluation of Novel Multifunctional Ligands Against Neurodegenerative Diseases. Neurochem. Res. 2020, 45, 3003–3020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, M.F.; Lima, E.T.; Pruccoli, L.; Castro, N.G.; Guimarães, M.J.R.; Silva, F.M.R.; Nadur, N.F.; Azevedo, L.L.; Kümmerle, A.E.; Guedes, I.A.; et al. Design, Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Novel Triazole N-acylhydrazone Hybrids for Alzheimer’s Disease. Molecules 2020, 25, 3165–3183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, A.; Nguyen, L.C.; Oumeslakht, L.; Bensussan, A.; Ben Mkaddem, S. Cannabinoids as Immune System Modulators: Cannabidiol Potential Therapeutic Approaches and Limitations. Cannabis Cannabinoid Res. 2023, 8, 254–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.C.; Yang, D.; Nicolaescu, V.; Best, T.J.; Gula, H.; Saxena, D.; Gabbard, J.D.; Chen, S.N.; Ohtsuki, T.; Friesen, J.B.; et al. Cannabidiol Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 Replication through Induction of the Host ER Stress and Innate Immune Responses. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabi6110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogoyavlenskiy, A.; Zaitseva, I.; Alexyuk, P.; Alexyuk, M.; Omirtaeva, E.; Manakbayeva, A.; Moldakhanov, Y.; Anarkulova, E.; Imangazy, A.; Berezin, V.; et al. Naturally Occurring Isorhamnetin Glycosides as Potential Agents Against Influenza Viruses: Antiviral and Molecular Docking Studies. ACS Omega 2023, 50, 48499–48514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguiar, A.C.C.; Murce, E.; Cortopassi, W.A.; Pimentel, A.S.; Almeida, M.M.F.S.; Barros, D.C.S.; Guedes, J.S.; Meneghetti, M.R.; Krettli, A.U. Chloroquine Analogs as Antimalarial Candidates with Potent in Vitro and in Vivo Activity. Int. J. Parasitol. Drugs Drug Resist. 2018, 8, 459–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- León, P.; Cañas-Arranz, R.; Bustos, M.J.; Sáiz, M.; Sobrino, F. Inhibition of Human Coronaviruses by Combinations of Host-Targeted and Direct-Acting Antivirals. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2023, 67, e0170322. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, T.L.; Colzani, M.T.; Macrae, R.G.C.; Robinson, E.L.; Bloor, S.; Greenwood, E.J.D.; Zhan, J.R.; Strachan, G.; Kuc, R.E.; Nyimanu, D.; et al. Human Embryonic Stem Cell-Derived Cardiomyocyte Platform Screens Inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merad, M.; Martin, J.C. Pathological Inflammation in Patients with COVID-19: A Key Role for Monocytes and Macrophages. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2020, 20, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catanzaro, M.; Fagiani, F.; Racchi, M.; Corsini, E.; Govoni, S.; Lanni, C. Immune Response in COVID-19: Addressing a Pharmacological Challenge by Targeting Pathways Triggered by SARS-CoV-2. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacchi, A.; Giannessi, F.; Sabatini, A.; Percario, Z.A.; Affabris, E. SARS-CoV-2 Evasion of the Interferon System: Can We Restore Its Effectiveness? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, G.M.; Clarindo, F.A.; Ribeiro, Á.L.; Gomes-de-Pontes, L.; Carvalho, L.D.; Martins-Filho, O.A.; Fonseca, F.G.; Teixeira, M.M.; Sabino, A.P.; Eapen, M.S.; et al. Taming the SARS-CoV-2-Mediated Proinflammatory Response with BromAc®. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1308477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, G.R.R.; Fernandes, I.M.; Souza, M.L.; Gontijo, V.S.; Alves, M.A.; Souza, H.M.R.; Invencio, C.G.G.; Lontra, A.C.P.; Paiva, J.P.B.; Santos, L.N.; et al. New cannabidiol structure-related terpene N-acyl-hydrazones with potent antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory activity. Future Med. Chem. 2025, 17, 1229–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, J.G.A.C.; Reis, E.V.S.; Moraes, T.F.S.; Clarindo, F.A.; Moraes, T.F.S.; Guedes, I.A.; Dardenne, L.E.; França, P.R.C.; Fernandes, P.D.; Viegas, C., Jr.; et al. Uso de hidrazonas análogas ao canabidiol em medicamentos antivirais. BR 10 2024 010067 0, 21 May 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Coelho dos Reis, J.G.A.; Ferreira, G.M.; Lourenço, A.A.; Ribeiro, Á.L.; Mata, C.P.S.M.; Oliveira, P.M.; Marques, D.P.A.; Ferreira, L.L.; Clarindo, F.A.; Silva, M.F.; et al. Ex-Vivo Mucolytic and Anti-Inflammatory Activity of BromAc in Tracheal Aspirates from COVID-19. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 148, 112753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimarães Santana, B.C.; Marques, D.P.A.; Freitas, A.S.; Ferreira, M.M.; Lopes, D.S.; Bagno, F.F.; Fonseca, F.G.; Reis, J.G.A.C.; Mendes, T.A.O.; Santos, J.L.; et al. Protease Inhibitors from Theobroma cacao Impair SARS-CoV-2 Replication in Vitro. Heliyon 2023, 9, e15860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verzola, M.M.S.A.; Marques, D.P.A.; Silva, E.B.; Serafim, M.S.M.; Ferreira, R.S.; Fajtová, P.; Kohlhoff, M.; O’Donoghue, A.J.; Maltarollo, V.G.; Coelho-dos-Reis, J.G.A.; et al. Synthesis of Indole-Based Ferulic Acid Derivatives and in Vitro Evaluation of Antiviral Activity against SARS-CoV-2. Med. Chem. Res. 2023, 32, 2256–2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, G.V.L.; Marques, D.P.A.; Clarindo, F.A.; Avendaño-Villarreal, J.A.; Guerra, F.S.; Fernandes, P.D.; Santos, E.N.; Gusevskaya, E.V.; Kohlhoff, M.; Moreira, F.A.; et al. Synthesis of Cannabidiol-Based Compounds as ACE2 Inhibitors with Potential Application in the Treatment of COVID-19. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 260, 115760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guedes, I.A.; Barreto, A.M.S.; Marinho, D.; Krempser, E.; Kuenemann, M.A.; Sperandio, O.; Dardenne, L.E.; Miteva, M.A. New Machine Learning and Physics-Based Scoring Functions for Drug Discovery. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 3198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guedes, I.A.; Silva, M.M.P.; Galheigo, M.; Krempser, E.; Magalhães, C.S.; Barbosa, H.J.C.; Dardenne, L.E. DockThor-VS: A Free Platform for Receptor-Ligand Virtual Screening. J. Mol. Biol. 2024, 436, 168548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, K.B.; Guedes, I.A.; Karl, A.L.M.; Dardenne, L.E. Highly Flexible Ligand Docking: Benchmarking of the DockThor Program on the LEADS-PEP Protein-peptide Dataset. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2020, 60, 667–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guedes, I.A.; Costa, L.S.C.; Santos, K.B.; Karl, A.L.M.; Rocha, G.K.; Teixeira, I.M.; Galheigo, M.M.; Medeiros, V.; Krempser, E.; Custódio, F.L.; et al. Drug Design and Repurposing with DockThor-VS Web Server Focusing on SARS-CoV-2 Therapeutic Targets and Their Non-Synonym Variants. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 5543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsson, M.H.M.; SØndergaard, C.R.; Rostkowski, M.; Jensen, J.H. PROPKA3: Consistent Treatment of Internal and Surface Residues in Empirical p K a Predictions. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2011, 7, 525–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelley, J.C.; Cholleti, A.; Frye, L.L.; Greenwood, J.R.; Timlin, M.R.; Uchimaya, M. Epik: A Software Program for PK a Prediction and Protonation State Generation for Drug-like Molecules. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 2007, 21, 681–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, R.C.; Yao, K.; Kaplan, Z.; Chelliah, M.; Leswing, K.; Seekins, S.; Watts, S.; Calkins, D.; Chief Elk, J.; Jerome, S.V.; et al. Epik: PKa and Protonation State Prediction through Machine Learning. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2023, 19, 2380–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magalhães, C.S.; Almeida, D.M.; Barbosa, H.J.C.; Dardenne, L.E. A dynamic niching genetic algorithm strategy for docking highly flexible ligands. Inf. Sci. 2014, 289, 206–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, M.; Vidal, L.; Guedes, I.; Magalhães, C.; Custódio, F.; Dardenne, L. Data-centric training enables meaningful interaction learning in protein–ligand binding affinity prediction. ChemRxiv 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

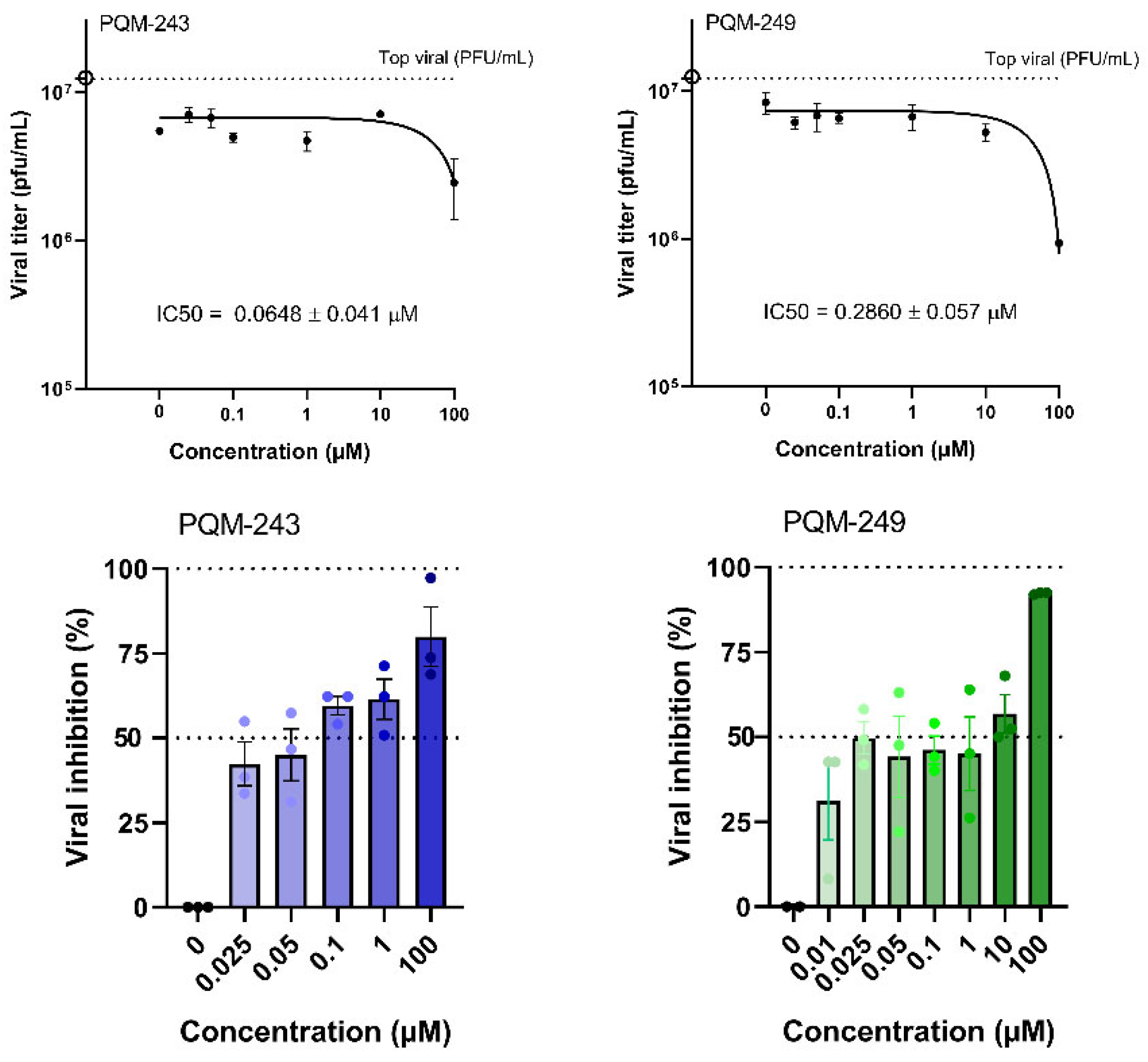
| Compounds | CC50 a (µM) | IC50 b (µM) | Selectivity Index (SI) c |
|---|---|---|---|
| PQM-243 | >100 | 0.0648 ± 0.041 | >1543.21 |
| PQM-249 | >100 | 0.2860 ± 0.057 | >349.65 |
| nirmatrelvir | >100 | 0.179 | >558.66 |
| Compound | IC50 (nM) |
|---|---|
| PQM-243 | 12.1 |
| PQM-249 | 13.3 |
| DX600 | 8300 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Franco, G.d.R.R.; Gontijo, V.S.; Viegas, F.P.D.; Silva, M.d.F.; Ortiz, C.J.C.; Damásio, C.M.; Silva, I.M.F.; Campos, T.G.; Reis, E.V.d.S.; Clarindo, F.A.; et al. Novel Multifunctional Cannabidiol-Based Analogues with In Silico, In Vitro, and In Vivo Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Effect. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 1565. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18101565
Franco GdRR, Gontijo VS, Viegas FPD, Silva MdF, Ortiz CJC, Damásio CM, Silva IMF, Campos TG, Reis EVdS, Clarindo FA, et al. Novel Multifunctional Cannabidiol-Based Analogues with In Silico, In Vitro, and In Vivo Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Effect. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(10):1565. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18101565
Chicago/Turabian StyleFranco, Graziella dos Reis Rosa, Vanessa Silva Gontijo, Flávia Pereira Dias Viegas, Matheus de Freitas Silva, Cindy Juliet Cristancho Ortiz, Caio Miranda Damásio, Isabella Marie Fernandes Silva, Thâmara Gaspar Campos, Erik Vinicius de Sousa Reis, Felipe Alves Clarindo, and et al. 2025. "Novel Multifunctional Cannabidiol-Based Analogues with In Silico, In Vitro, and In Vivo Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Effect" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 10: 1565. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18101565
APA StyleFranco, G. d. R. R., Gontijo, V. S., Viegas, F. P. D., Silva, M. d. F., Ortiz, C. J. C., Damásio, C. M., Silva, I. M. F., Campos, T. G., Reis, E. V. d. S., Clarindo, F. A., Moraes, T. d. F. S., Silva, M. M. P. d., França, P. R. d. C., Guedes, I. A., Dardenne, L. E., Reis, J. G. A. C. d., Fernandes, P. D., & Viegas, C., Jr. (2025). Novel Multifunctional Cannabidiol-Based Analogues with In Silico, In Vitro, and In Vivo Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Effect. Pharmaceuticals, 18(10), 1565. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18101565







