New Assay Systems to Characterize the Broad-Spectrum Antiherpesviral and Non-Herpesviral Activity of Cyclin-Dependent Kinase (CDK) 8 Inhibitors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
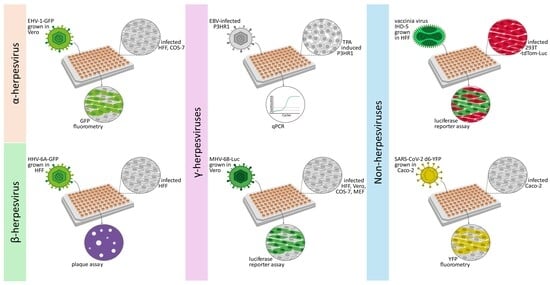
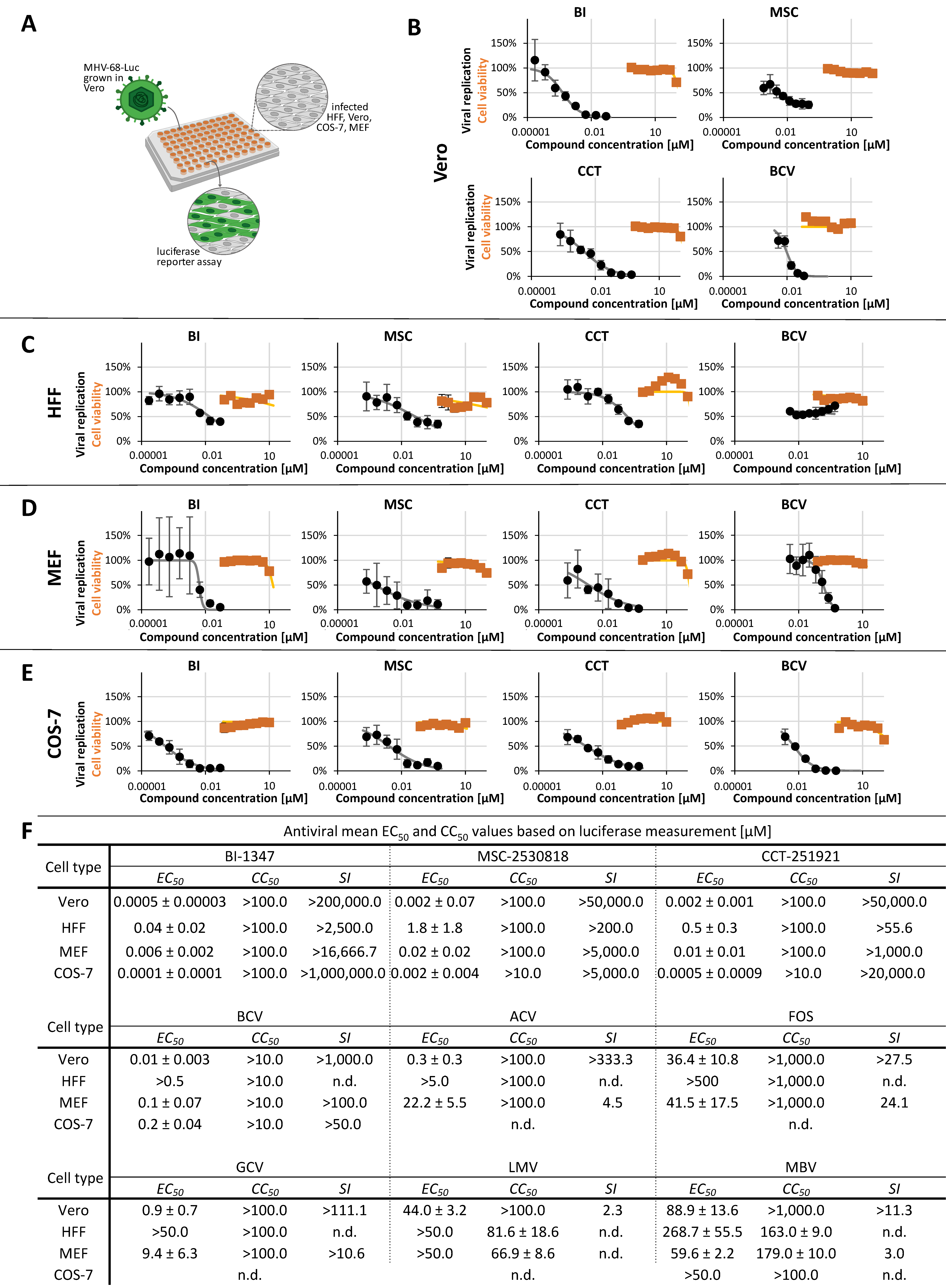
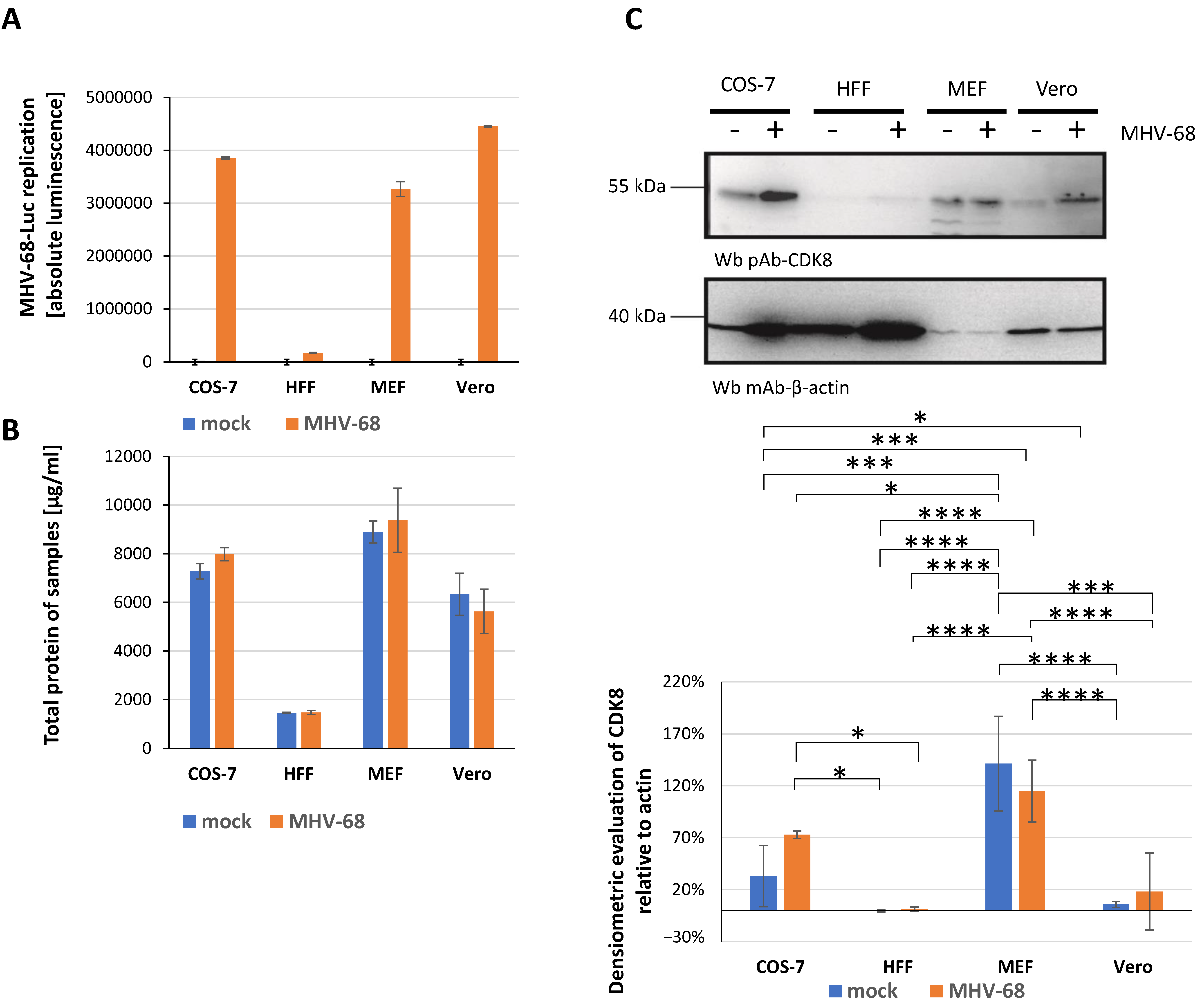
2.1. Establishment of New Antiviral Assay Systems for a Selection of Human and Animal Pathogenic Viruses
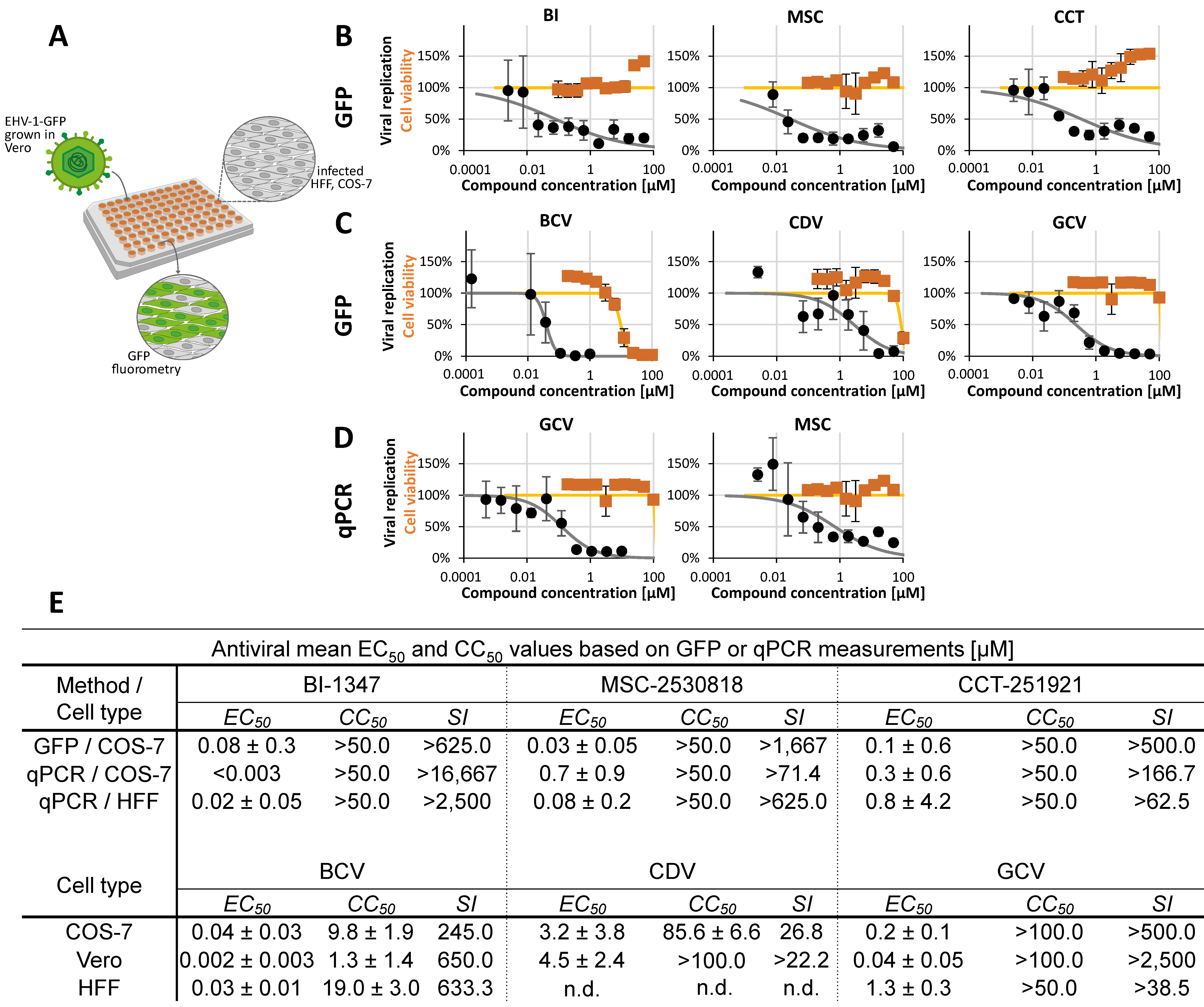
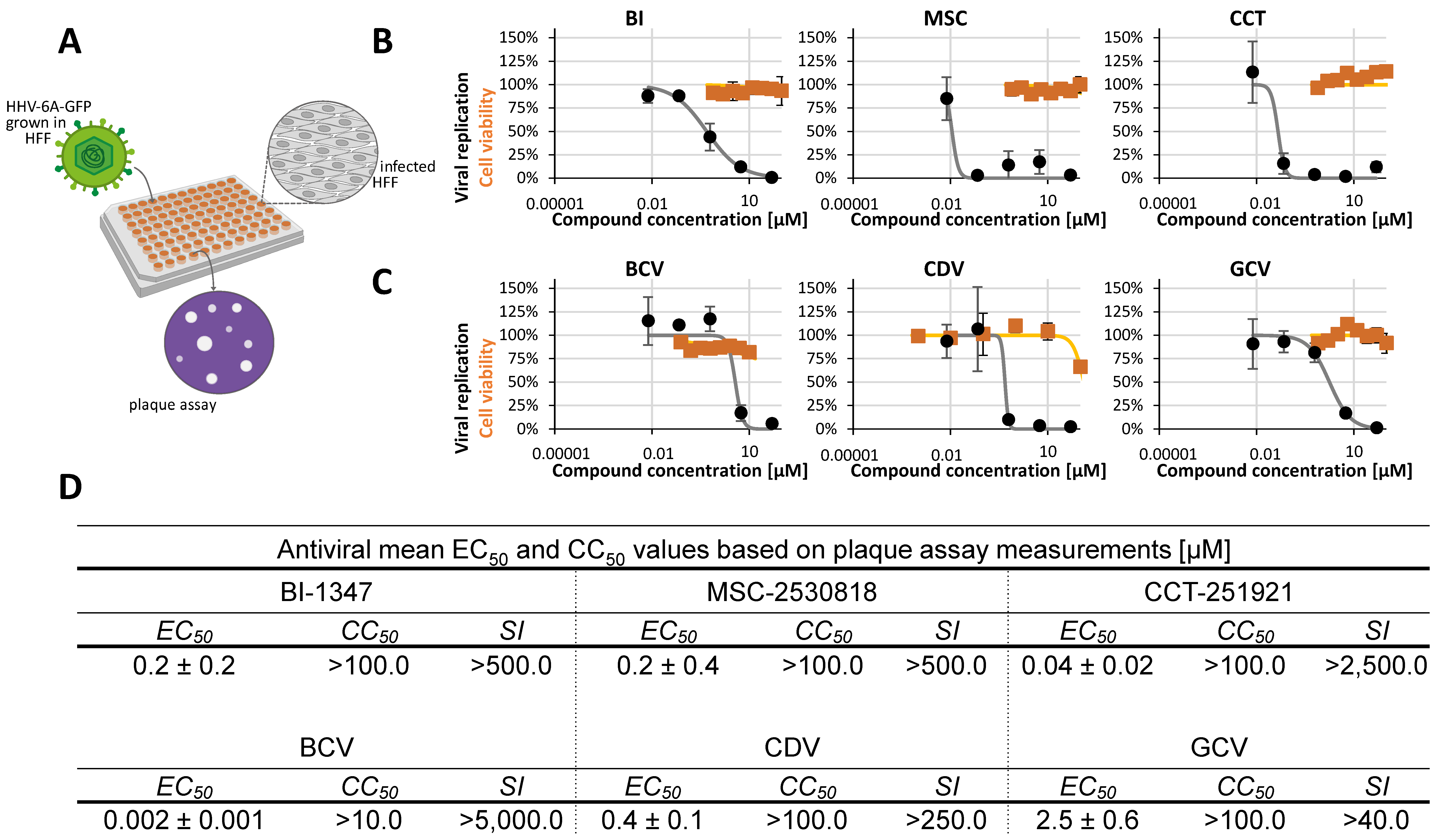
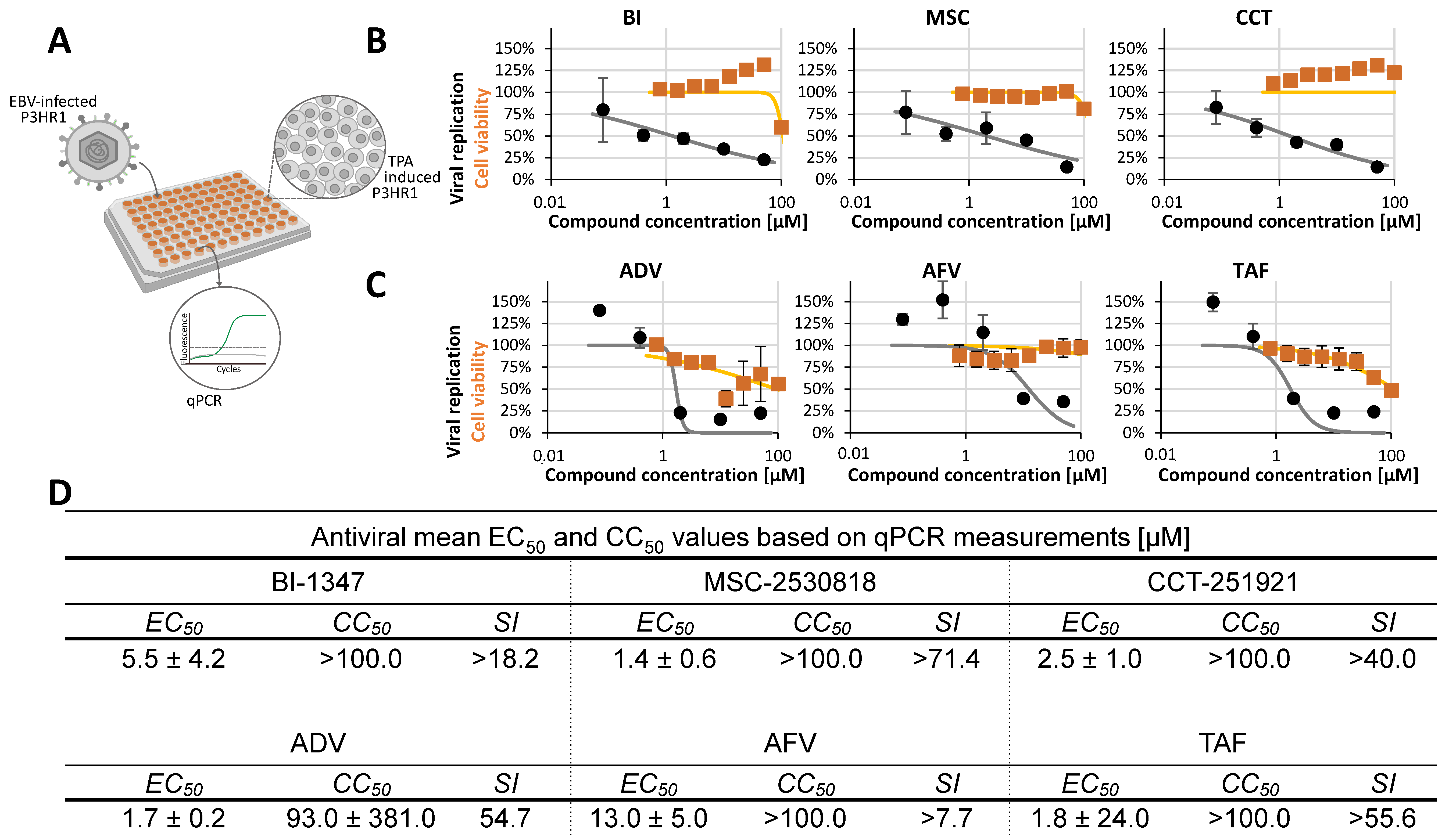
2.2. Assessment of Antiviral Activity of Three Selected CDK8 Inhibitors Against α-, β-, and γ-Herpesviruses
2.3. Antiviral Activity of CDK8 Inhibitors Across Herpesviral Subfamilies
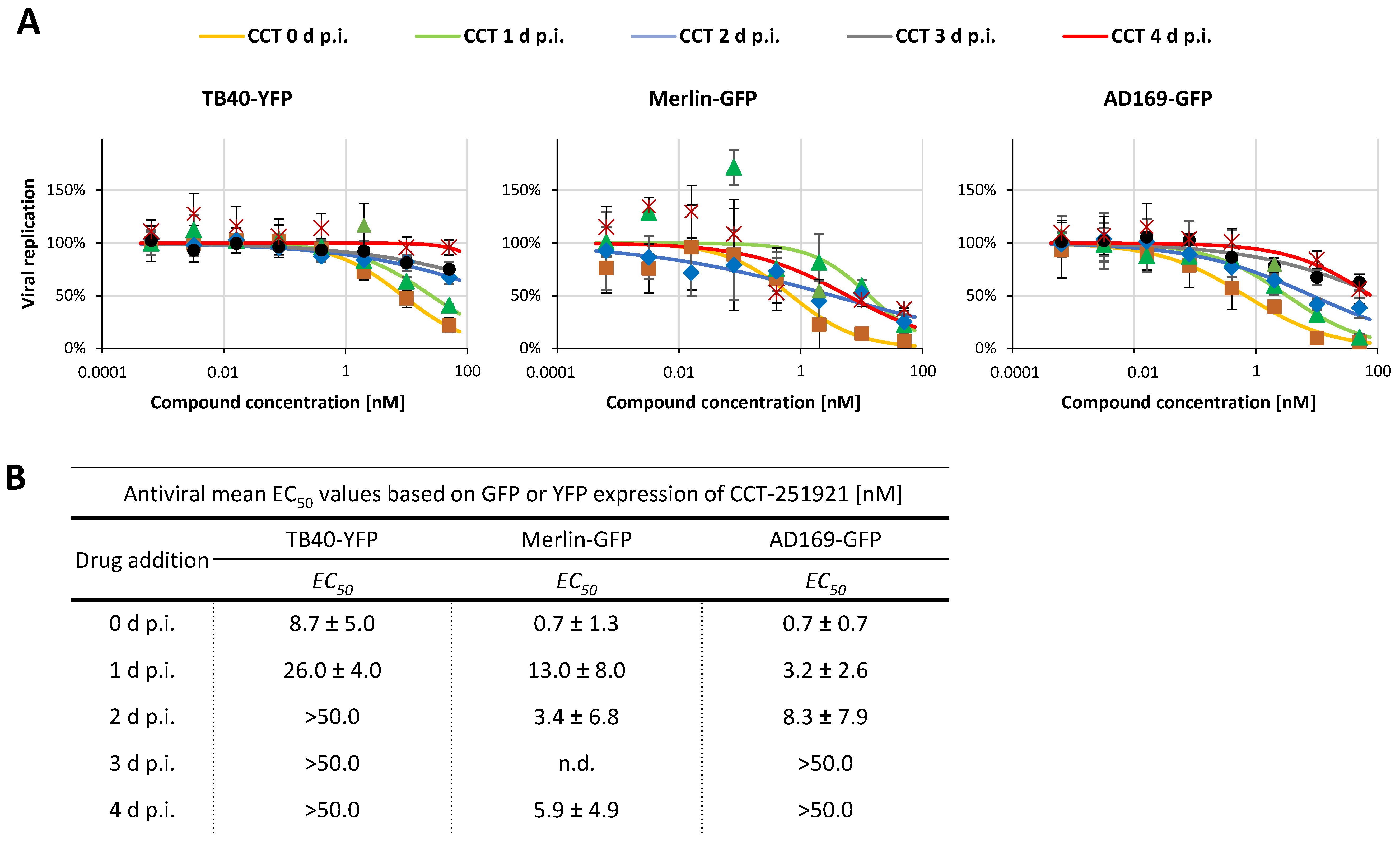
2.4. Addressing the Characteristics of Antiviral MoA Displayed by CDK8 Inhibitors Against Three Strains of HCMV: Time-of-Addition Experimentation
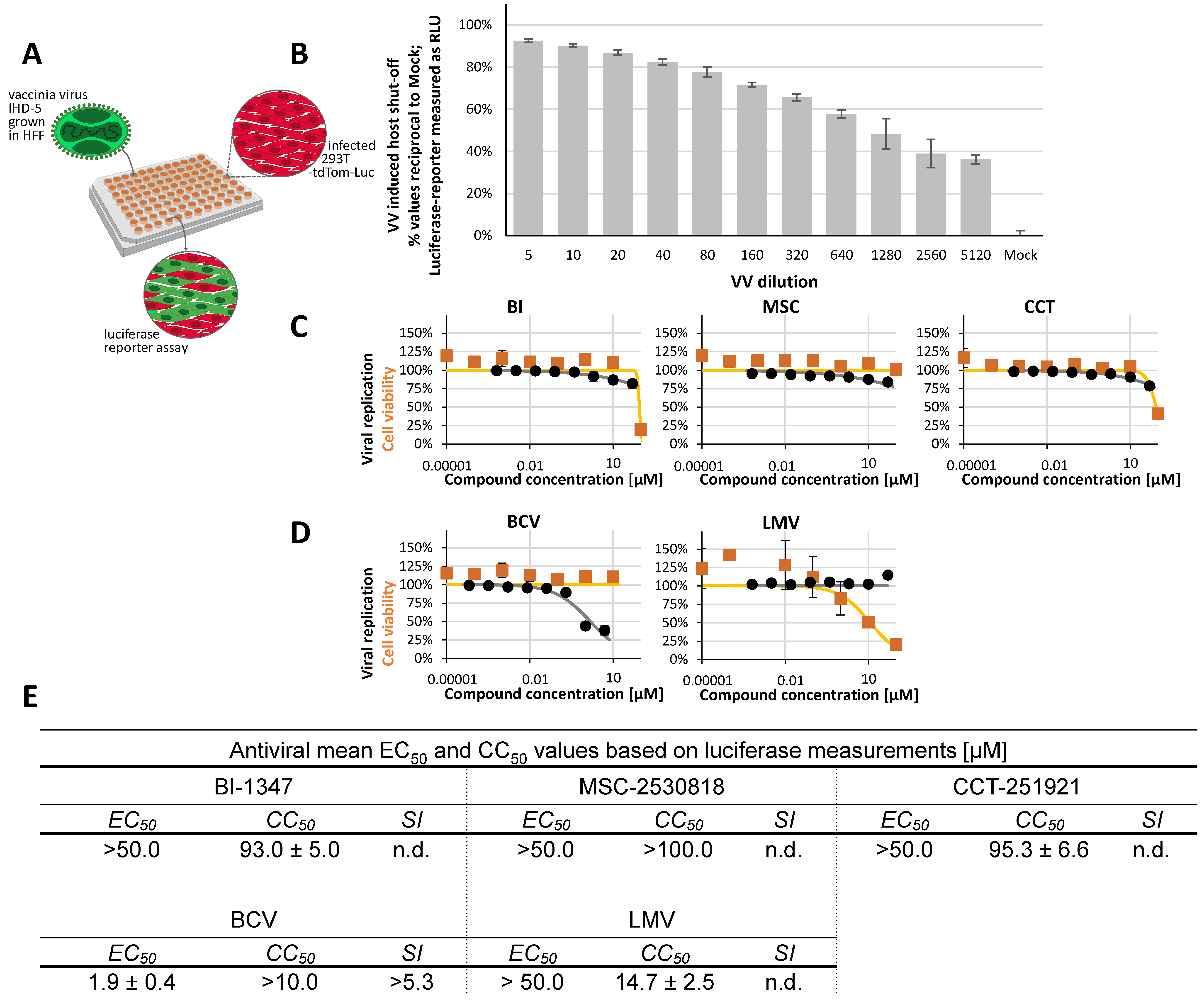
2.5. Non-Herpesviral Activities of CDK8 Inhibitors
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Cells and Viruses
3.2. Antiviral Compounds
3.3. Virus Infection of Cultured Cells and Quantitative Readouts of Viral Replication
3.4. Neutral Red (NR) Uptake and Alamar Blue (AB) Cell Viability Assays
3.5. Western Blot Analysis of MHV-68-Infected Cells
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Buxmann, H.; Hamprecht, K.; Meyer-Wittkopf, M.; Friese, K. Primary Human Cytomegalovirus (HCMV) Infection in Pregnancy. Dtsch. Arztebl. Int. 2017, 114, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.J.; Wang, S.C.; Chen, Y.C. Challenges, Recent Advances and Perspectives in the Treatment of Human Cytomegalovirus Infections. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2022, 7, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, S.; Ercolani, R.J.; Derakhchan, K. Antiviral activity of maribavir in combination with other drugs active against human cytomegalovirus. Antivir. Res. 2018, 157, 128–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, P.; Reeves, M. Pathogenesis of human cytomegalovirus in the immunocompromised host. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 759–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gugliesi, F.; Coscia, A.; Griffante, G.; Galitska, G.; Pasquero, S.; Albano, C.; Biolatti, M. Where do we Stand after Decades of Studying Human Cytomegalovirus? Microorganisms 2020, 8, 685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsutsui, Y. Effects of cytomegalovirus infection on embryogenesis and brain development. Congenit. Anom. 2009, 49, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fröhlich, T.; Hahn, F.; Belmudes, L.; Leidenberger, M.; Friedrich, O.; Kappes, B.; Couté, Y.; Marschall, M.; Tsogoeva, S.B. Synthesis of Artemisinin-Derived Dimers, Trimers and Dendrimers: Investigation of Their Antimalarial and Antiviral Activities Including Putative Mechanisms of Action. Chemistry 2018, 24, 8103–8113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oiknine-Djian, E.; Bar-On, S.; Laskov, I.; Lantsberg, D.; Haynes, R.K.; Panet, A.; Wolf, D.G. Artemisone demonstrates synergistic antiviral activity in combination with approved and experimental drugs active against human cytomegalovirus. Antivir. Res. 2019, 172, 104639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wild, M.; Hahn, F.; Grau, B.; Herrmann, L.; Niesar, A.; Schütz, M.; Lorion, M.M.; Ackermann, L.; Tsogoeva, S.B.; Marschall, M. The Artemisinin-Derived Autofluorescent Compound BG95 Exerts Strong Anticytomegaloviral Activity Based on a Mitochondrial Targeting Mechanism. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wild, M.; Karner, D.; Eickhoff, J.; Wagner, S.; Kicuntod, J.; Chang, W.; Barry, P.; Jonjic, S.; Lenac Rovis, T.; Marschall, M. Combined Treatment with Host-Directed and Anticytomegaloviral Kinase Inhibitors: Mechanisms, Synergisms and Drug Resistance Barriers. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wild, M.; Kicuntod, J.; Seyler, L.; Wangen, C.; Bertzbach, L.D.; Conradie, A.M.; Kaufer, B.B.; Wagner, S.; Michel, D.; Eickhoff, J.; et al. Combinatorial Drug Treatments Reveal Promising Anticytomegaloviral Profiles for Clinically Relevant Pharmaceutical Kinase Inhibitors (PKIs). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachman, L.O.; Zwezdaryk, K.J. Targeting the Host Mitochondria as a Novel Human Cytomegalovirus Antiviral Strategy. Viruses 2023, 15, 1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogner, E.; Egorova, A.; Makarov, V. Small Molecules-Prospective Novel HCMV Inhibitors. Viruses 2021, 13, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna, B.A.; Wills, M.R.; Sinclair, J.H. Advances in the treatment of cytomegalovirus. Br. Med. Bull. 2019, 131, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yost, R.; Pasquale, T.R.; Sahloff, E.G. Maraviroc: A coreceptor CCR5 antagonist for management of HIV infection. Am. J. Health-Syst. Pharm. 2009, 66, 715–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Luca, A.; Pezzotti, P.; Boucher, C.; Döring, M.; Incardona, F.A.-O.; Kaiser, R.; Lengauer, T.; Pfeifer, N.; Schülter, E.; Vandamme, A.M.; et al. Clinical use, efficacy, and durability of maraviroc for antiretroviral therapy in routine care: A European survey. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0225381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abel, S.; Back, D.J.; Vourvahis, M. Maraviroc: Pharmacokinetics and drug interactions. Antivir. Ther. 2024, 14, 607–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loustaud-Ratti, V.; Debette-Gratien, M.; Jacques, J.; Alain, S.; Marquet, P.; Sautereau, D.; Rousseau, A.; Carrier, P. Ribavirin: Past, present and future. World J. Hepatol. 2016, 8, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crotty, S.; Cameron, C.; Andino, R. Ribavirin’s antiviral mechanism of action: Lethal mutagenesis? J. Mol. Med. 2022, 80, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feld, J.J.; Jacobson, I.M.; Sulkowski, M.S.; Poordad, F.; Tatsch, F.; Pawlotsky, J.M. Ribavirin revisited in the era of direct-acting antiviral therapy for hepatitis C virus infection. Liver Int. 2017, 37, 5–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janowski, A.B.; Dudley, H.; Wang, D. Antiviral activity of ribavirin and favipiravir against human astroviruses. J. Clin. Virol. 2020, 123, 104247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixit, N.M.; Perelson, A.S. The metabolism, pharmacokinetics and mechanisms of antiviral activity of ribavirin against hepatitis C virus. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2006, 63, 832–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snell, N.J. Ribavirin--current status of a broad spectrum antiviral agent. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2001, 2, 1317–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Degasperi, E.; Anolli, M.P.; Lampertico, P.A.-O. Bulevirtide-based treatment strategies for chronic hepatitis delta: A review. J. Viral. Hepat. 2023, 30, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, C.; Syed, Y.Y. Bulevirtide: First Approval. Drugs 2020, 80, 1601–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wedemeyer, H.; Aleman, S.; Brunetto, M.R.; Blank, A.; Andreone, P.; Bogomolov, P.; Chulanov, V.; Mamonova, N.; Geyvandova, N.; Morozov, V.; et al. A Phase 3, Randomized Trial of Bulevirtide in Chronic Hepatitis D. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wedemeyer, H.; Schöneweis, K.; Bogomolov, P.; Blank, A.; Voronkova, N.; Stepanova, T.; Sagalova, O.; Chulanov, V.; Osipenko, M.; Morozov, V.; et al. Safety and efficacy of bulevirtide in combination with tenofovir disoproxil fumarate in patients with hepatitis B virus and hepatitis D virus coinfection (MYR202): A multicentre, randomised, parallel-group, open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2023, 23, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietz-Fricke, C.; Tacke, F.; Zollner, C.; Demir, M.; Schmidt, H.H.; Schramm, C.; Willuweit, K.; Lange, C.M.; Weber, S.; Denk, G.; et al. Treating hepatitis D with bulevirtide—Real-world experience from 114 patients. JHEP Rep. 2023, 5, 100686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brillanti, S. Management of Delta Hepatitis 45 Years after the Discovery of HDV. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marschall, M.; Feichtinger, S.; Milbradt, J. Regulatory roles of protein kinases in cytomegalovirus replication. Adv. Virus Res. 2011, 80, 69–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avery, R.K.; Alain, S.; Alexander, B.D.; Blumberg, E.A.; Chemaly, R.F.; Cordonnier, C.; Duarte, R.F.; Florescu, D.F.; Kamar, N.; Kumar, D.; et al. Maribavir for Refractory Cytomegalovirus Infections with or Without Resistance Post-Transplant: Results From a Phase 3 Randomized Clinical Trial. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2022, 75, 690–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maertens, J.; Cordonnier, C.; Jaksch, P.; Poire, X.; Uknis, M.; Wu, J.; Wijatyk, A.; Saliba, F.; Witzke, O.; Villano, S. Maribavir for Preemptive Treatment of Cytomegalovirus Reactivation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 1136–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marschall, M.; Schütz, M.; Wild, M.; Socher, E.; Wangen, C.; Dhotre, K.; Rawlinson, W.D.; Sticht, H. Understanding the Cytomegalovirus Cyclin-Dependent Kinase Ortholog pUL97 as a Multifaceted Regulator and an Antiviral Drug Target. Cells 2024, 13, 1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutterer, C.; Niemann, I.; Milbradt, J.; Fröhlich, T.; Reiter, C.; Kadioglu, O.; Bahsi, H.; Zeittrager, I.; Wagner, S.; Einsiedel, J.; et al. The broad-spectrum antiinfective drug artesunate interferes with the canonical nuclear factor kappa B (NF-kappaB) pathway by targeting RelA/p65. Antivir. Res. 2015, 124, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obergfäll, D.; Wild, M.; Sommerer, M.; Barillas Dahm, M.; Kicuntod, J.; Tillmanns, J.; Kögler, M.; Lösing, J.; Dhotre, K.; Müller, R.; et al. Cyclin-Dependent Kinase 8 Represents a Positive Regulator of Cytomegalovirus Replication and a Novel Host Target for Antiviral Strategies. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rechter, S.; Scott, G.M.; Eickhoff, J.; Zielke, K.; Auerochs, S.; Müller, R.; Stamminger, T.; Rawlinson, W.D.; Marschall, M. Cyclin-dependent Kinases Phosphorylate the Cytomegalovirus RNA Export Protein pUL69 and Modulate Its Nuclear Localization and Activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 8605–8613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schang, L.M. First demonstration of the effectiveness of inhibitors of cellular protein kinases in antiviral therapy. Expert Rev. Anti Infect. Ther. 2006, 4, 953–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wild, M.; Hahn, F.; Bruckner, N.; Schütz, M.; Wangen, C.; Wagner, S.; Sommerer, M.; Strobl, S.; Marschall, M. Cyclin-Dependent Kinases (CDKs) and the Human Cytomegalovirus-Encoded CDK Ortholog pUL97 Represent Highly Attractive Targets for Synergistic Drug Combinations. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hume, A.J.; Finkel, J.S.; Kamil, J.P.; Coen, D.M.; Culbertson, M.R.; Kalejta, R.F. Phosphorylation of Retinoblastoma Protein by Viral Protein with Cyclin-Dependent Kinase Function. Science 2008, 320, 797–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuny, C.V.; Chinchilla, K.; Culbertson, M.R.; Kalejta, R.F. Cyclin-dependent kinase-like function is shared by the beta- and gamma- subset of the conserved herpesvirus protein kinases. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1001092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feichtinger, S.; Stamminger, T.; Muller, R.; Graf, L.; Klebl, B.; Eickhoff, J.; Marschall, M. Recruitment of cyclin-dependent kinase 9 to nuclear compartments during cytomegalovirus late replication: Importance of an interaction between viral pUL69 and cyclin T1. J. Gen. Virol. 2011, 92 Pt 7, 1519–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, F.; Hamilton, S.T.; Wangen, C.; Wild, M.; Kicuntod, J.; Bruckner, N.; Follett, J.E.L.; Herrmann, L.; Kheimar, A.; Kaufer, B.B.; et al. Development of a PROTAC-Based Targeting Strategy Provides a Mechanistically Unique Mode of Anti-Cytomegalovirus Activity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutterer, C.; Eickhoff, J.; Milbradt, J.; Korn, K.; Zeittrager, I.; Bahsi, H.; Wagner, S.; Zischinsky, G.; Wolf, A.; Degenhart, C.; et al. A novel CDK7 inhibitor of the Pyrazolotriazine class exerts broad-spectrum antiviral activity at nanomolar concentrations. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 2062–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelso, T.W.; Baumgart, K.; Eickhoff, J.; Albert, T.; Antrecht, C.; Lemcke, S.; Klebl, B.; Meisterernst, M. Cyclin-dependent kinase 7 controls mRNA synthesis by affecting stability of preinitiation complexes, leading to altered gene expression, cell cycle progression, and survival of tumor cells. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2014, 34, 3675–3688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kicuntod, J.; Häge, S.; Hahn, F.; Sticht, H.; Marschall, M. The Oligomeric Assemblies of Cytomegalovirus Core Nuclear Egress Proteins Are Associated with Host Kinases and Show Sensitivity to Antiviral Kinase Inhibitors. Viruses 2022, 14, 1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovnak, J.; Quackenbush, S.L. Exploitation of the Mediator complex by viruses. PLoS Pathog. 2022, 18, e1010422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schang, L.M. Cellular proteins (cyclin dependent kinases) as potential targets for antiviral drugs. Antivir. Chem. Chemother. 2001, 12 (Suppl. S1), 157–178. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, D.; Wagner, S.; Schütz, M.; Jeon, Y.; Seo, M.; Kim, J.; Bruckner, N.; Kicuntod, J.; Tillmanns, J.; Wangen, C.; et al. An Antiherpesviral Host-Directed Strategy Based on CDK7 Covalently Binding Drugs: Target-Selective, Picomolar-Dose, Cross-Virus Reactivity. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akoulitchev, S.; Chuikov, S.; Reinberg, D. TFIIH is negatively regulated by cdk8-containing mediator complexes. Nature 2000, 407, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, S.; Kim, S.M.; Rodriguez, C.; Songock, W.; Raikhy, G.; Lopez, R.; Henderson, L.; Yusufji, A.; Bodily, J. Suppression of a Subset of Interferon-Induced Genes by Human Papillomavirus Type 16 E7 via a Cyclin Dependent Kinase 8-Dependent Mechanism. Viruses 2020, 12, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehringer Ingelheim. opnMe.com—Boehringer Ingelheim Open Innovation Portal. 2017. Available online: https://www.opnme.com/molecules/cdk8-bi-1347 (accessed on 16 September 2025).
- Czodrowski, P.; Mallinger, A.; Wienke, D.; Esdar, C.; Poschke, O.; Busch, M.; Rohdich, F.; Eccles, S.A.; Ortiz-Ruiz, M.J.; Schneider, R.; et al. Structure-Based Optimization of Potent, Selective, and Orally Bioavailable CDK8 Inhibitors Discovered by High-Throughput Screening. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 9337–9349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallinger, A.; Schiemann, K.; Rink, C.; Stieber, F.; Calderini, M.; Crumpler, S.; Stubbs, M.; Adeniji-Popoola, O.; Poeschke, O.; Busch, M.; et al. Discovery of Potent, Selective, and Orally Bioavailable Small-Molecule Modulators of the Mediator Complex-Associated Kinases CDK8 and CDK19. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 1078–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, F.; Häge, S.; Herrmann, A.; Wangen, C.; Kicuntod, J.; Jungnickl, D.; Tillmanns, J.; Müller, R.; Fraedrich, K.; Überla, K.; et al. Methodological Development of a Multi-Readout Assay for the Assessment of Antiviral Drugs against SARS-CoV-2. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tillmanns, J.; Battisti, V.; Kicuntod, J.; Hahn, F.; Obergfäll, D.; Geiger, P.; Wagner, S.; Buschmann, H.; Lesch, B.; Lischka, P.; et al. The conserved core nuclear egress complex (NEC) as an antiherpesviral drug target: Pharmacophore-based identification of NEC-specific inhibitors. Antivir. Res. 2025, 239, 106168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesquita, L.P.; Costa, R.C.; Zanatto, D.A.; Bruhn, F.R.P.; Mesquita, L.L.R.; Lara, M.; Villalobos, E.M.C.; Massoco, C.O.; Mori, C.M.C.; Mori, E.; et al. Equine herpesvirus 1 elicits a strong pro-inflammatory response in the brain of mice. J. Gen. Virol. 2021, 102, 001556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA Panel on Animal Health and Welfare (AHAW); Nielsen, S.S.; Alvarez, J.; Bicout, D.J.; Calistri, P.; Canali, E.; Drewe, J.A.; Garin-Bastuji, B.; Gonzales Rojas, J.L.; Gortázar, C.; et al. Assessment of listing and categorisation of animal diseases within the framework of the Animal Health Law (Regulation (EU) No 2016/429): Infection with Equine Herpesvirus-1. EFSA J. 2022, 20, e07036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillmanns, J.; Kicuntod, J.; Ehring, A.; Elbasani, E.; Borst, E.M.; Obergfäll, D.; Müller, R.; Hahn, F.; Marschall, M. Establishment of a Luciferase-Based Reporter System to Study Aspects of Human Cytomegalovirus Infection, Replication Characteristics, and Antiviral Drug Efficacy. Pathogens 2024, 13, 645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, M.; Kleine-Weber, H.; Schroeder, S.; Kruger, N.; Herrler, T.; Erichsen, S.; Schiergens, T.S.; Herrler, G.; Wu, N.H.; Nitsche, A.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Cell Entry Depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and Is Blocked by a Clinically Proven Protease Inhibitor. Cell 2020, 181, 271–280.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahn, F.; Niesar, A.; Wangen, C.; Wild, M.; Grau, B.; Herrmann, L.; Capci, A.; Adrait, A.; Coute, Y.; Tsogoeva, S.B.; et al. Target verification of artesunate-related antiviral drugs: Assessing the role of mitochondrial and regulatory proteins by click chemistry and fluorescence labeling. Antivir. Res. 2020, 180, 104861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazuhiro, O. Addgene Plasmid # 72486; Baylor College of Medicine: Houston, TX, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Kern, E.R.; Hartline, C.; Harden, E.; Keith, K.; Rodriguez, N.; Beadle, J.R.; Hostetler, K.Y. Enhanced inhibition of orthopoxvirus replication in vitro by alkoxyalkyl esters of cidofovir and cyclic cidofovir. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2002, 46, 991–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neubauer, A.; Rudolph, J.; Brandmuller, C.; Just, F.T.; Osterrieder, N. The equine herpesvirus 1 UL34 gene product is involved in an early step in virus egress and can be efficiently replaced by a UL34-GFP fusion protein. Virology 2002, 300, 189–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gravel, A.; Dubuc, I.; Wallaschek, N.; Gilbert-Girard, S.; Collin, V.; Hall-Sedlak, R.; Jerome, K.R.; Mori, Y.; Carbonneau, J.; Boivin, G.; et al. Cell Culture Systems to Study Human Herpesvirus 6A/B Chromosomal Integration. J. Virol. 2017, 91, e00473-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marschall, M.; Freitag, M.; Weiler, S.; Sorg, G.; Stamminger, T. Recombinant green fluorescent protein-expressing human cytomegalovirus as a tool for screening antiviral agents. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2000, 44, 1588–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auerochs, S.; Korn, K.; Marschall, M. A reporter system for Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) lytic replication: Anti-EBV activity of the broad anti-herpesviral drug artesunate. J. Virol. Methods 2011, 173, 334–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Häge, S.; Horsch, D.; Stilp, A.C.; Kicuntod, J.; Müller, R.; Hamilton, S.T.; Egilmezer, E.; Rawlinson, W.D.; Stamminger, T.; Sonntag, E.; et al. A quantitative nuclear egress assay to investigate the nucleocytoplasmic capsid release of human cytomegalovirus. J. Virol. Methods 2020, 283, 113909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lösing, J.; Häge, S.; Schütz, M.; Wagner, S.; Wardin, J.; Sticht, H.; Marschall, M. ‘Shared-Hook’ and ‘Changed-Hook’ Binding Activities of Herpesviral Core Nuclear Egress Complexes Identified by Random Mutagenesis. Cells 2022, 11, 4030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graf, L.; Feichtinger, S.; Naing, Z.; Hutterer, C.; Milbradt, J.; Webel, R.; Wagner, S.; Scott, G.M.; Hamilton, S.T.; Rawlinson, W.D.; et al. New insight into the phosphorylation-regulated intranuclear localization of human cytomegalovirus pUL69 mediated by cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) and viral CDK orthologue pUL97. J. Gen. Virol. 2016, 97, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- König, P.; Buscher, N.; Steingruber, M.; Socher, E.; Sticht, H.; Tenzer, S.; Plachter, B.; Marschall, M. Dynamic regulatory interaction between cytomegalovirus major tegument protein pp65 and protein kinase pUL97 in intracellular compartments, dense bodies and virions. J. Gen. Virol. 2017, 98, 2850–2863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steingruber, M.; Marschall, M. The Cytomegalovirus Protein Kinase pUL97:Host Interactions, Regulatory Mechanisms and Antiviral Drug Targeting. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Virus Classification | Herpesviridae | Poxviridae | Coronaviridae | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| α (Animal) | β (Human) | γ (Human) | γ (Animal) | (DNA Genome, Human) | (RNA Genome, Human) | |
| Virus strain/reporter | equine herpesvirus EHV-1-GFP | human herpesvirus 6 HHV-6A-GFP | Epstein–Barr virus P3HR-1 | murine herpesvirus 68 MHV-68-Luc | vaccinia virus VV IHD-5 | SARS-CoV-2 d6-YFP |
| Host cells | Vero, COS-7 | HFF, J-Jhan | P3HR-1 | Vero, COS-7, MEF, HFF | 293T | Caco-2 |
| Incubation times | 3–5 d | 10–14 d | 10 d | 4–7 d | 2 d | 30 h |
| Readouts | GFP fluorometry | plaque reduction assay, GFP fluorometry | qPCR | luciferase reporter assay | luciferase reporter assay | YFP fluorometry |
| Reference drugs * | GCV, CDV, BCV | BCV, CDV | TFA, TDP, AFV | BCV, GCV, FOS, ACV, LMV, MBV | BCV, CDV | MPV (EIDD-1931) |
| CDK8 inhib. sensitivity § | strong | strong | intermediate | strong/variable | low | low |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Obergfäll, D.; Hahn, F.; Kicuntod, J.; Wangen, C.; Kögler, M.; Wagner, S.; Kaufer, B.; Marschall, M. New Assay Systems to Characterize the Broad-Spectrum Antiherpesviral and Non-Herpesviral Activity of Cyclin-Dependent Kinase (CDK) 8 Inhibitors. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 1560. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18101560
Obergfäll D, Hahn F, Kicuntod J, Wangen C, Kögler M, Wagner S, Kaufer B, Marschall M. New Assay Systems to Characterize the Broad-Spectrum Antiherpesviral and Non-Herpesviral Activity of Cyclin-Dependent Kinase (CDK) 8 Inhibitors. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(10):1560. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18101560
Chicago/Turabian StyleObergfäll, Debora, Friedrich Hahn, Jintawee Kicuntod, Christina Wangen, Melanie Kögler, Sabrina Wagner, Benedikt Kaufer, and Manfred Marschall. 2025. "New Assay Systems to Characterize the Broad-Spectrum Antiherpesviral and Non-Herpesviral Activity of Cyclin-Dependent Kinase (CDK) 8 Inhibitors" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 10: 1560. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18101560
APA StyleObergfäll, D., Hahn, F., Kicuntod, J., Wangen, C., Kögler, M., Wagner, S., Kaufer, B., & Marschall, M. (2025). New Assay Systems to Characterize the Broad-Spectrum Antiherpesviral and Non-Herpesviral Activity of Cyclin-Dependent Kinase (CDK) 8 Inhibitors. Pharmaceuticals, 18(10), 1560. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18101560