Integrated Network Pharmacology and Molecular Dynamics Reveal Multi-Target Anticancer Mechanisms of Myrtus communis Essential Oils
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Chemical Composition and Phytochemical Profile of McEO
2.2. Antioxidant Activity
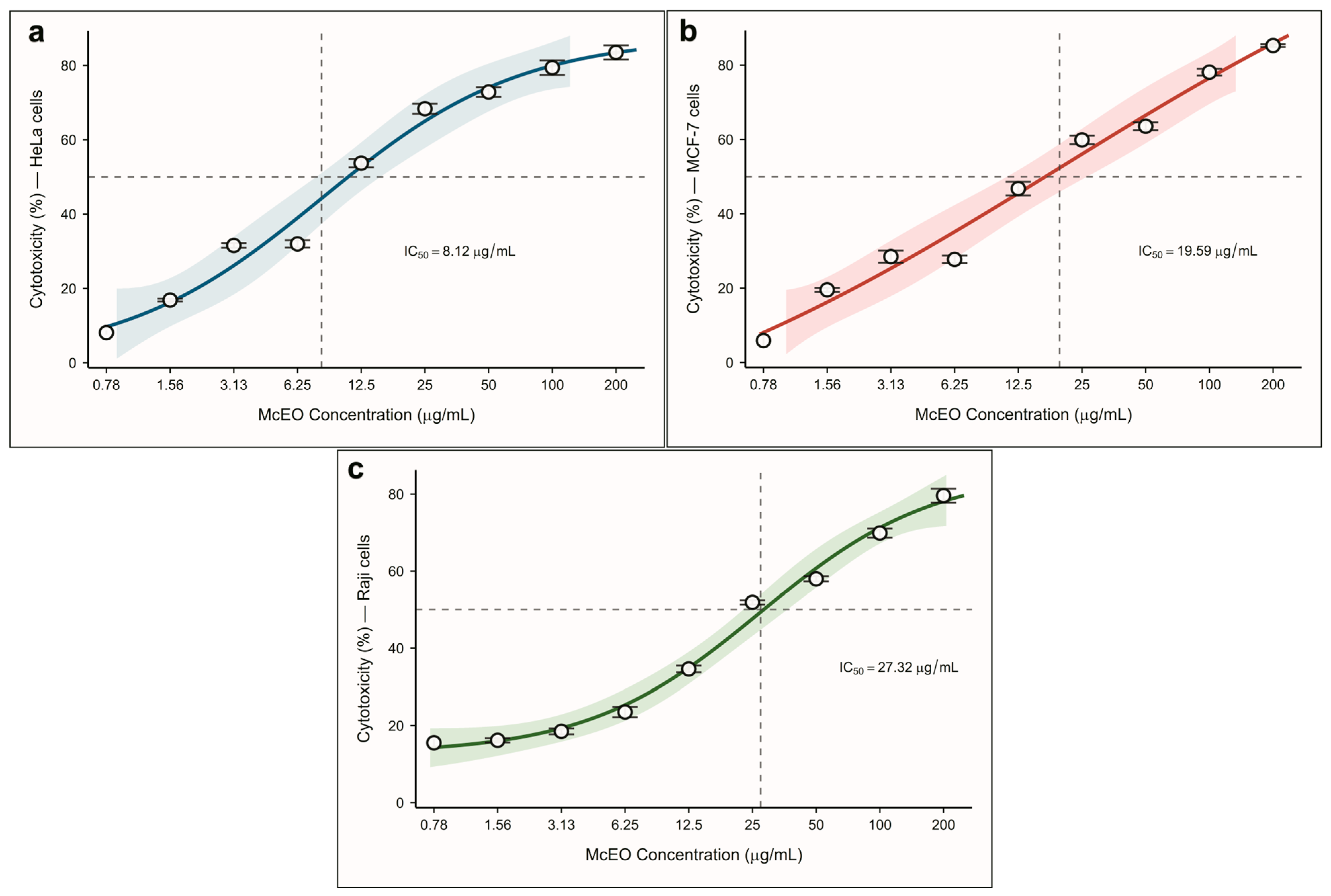
2.3. Antiproliferative Effects
| Cell Line | McEO (IC50, µg/mL) | Doxorubicin (IC50, µg/mL) |
|---|---|---|
| HeLa | 8.12 ± 0.54 | 1.11 ± 0.10 [38] |
| MCF-7 | 19.59 ± 1.02 | 1.16 ± 0.03 [39] |
| Raji | 27.32 ± 1.65 | 1.36 ± 0.04 [40] |
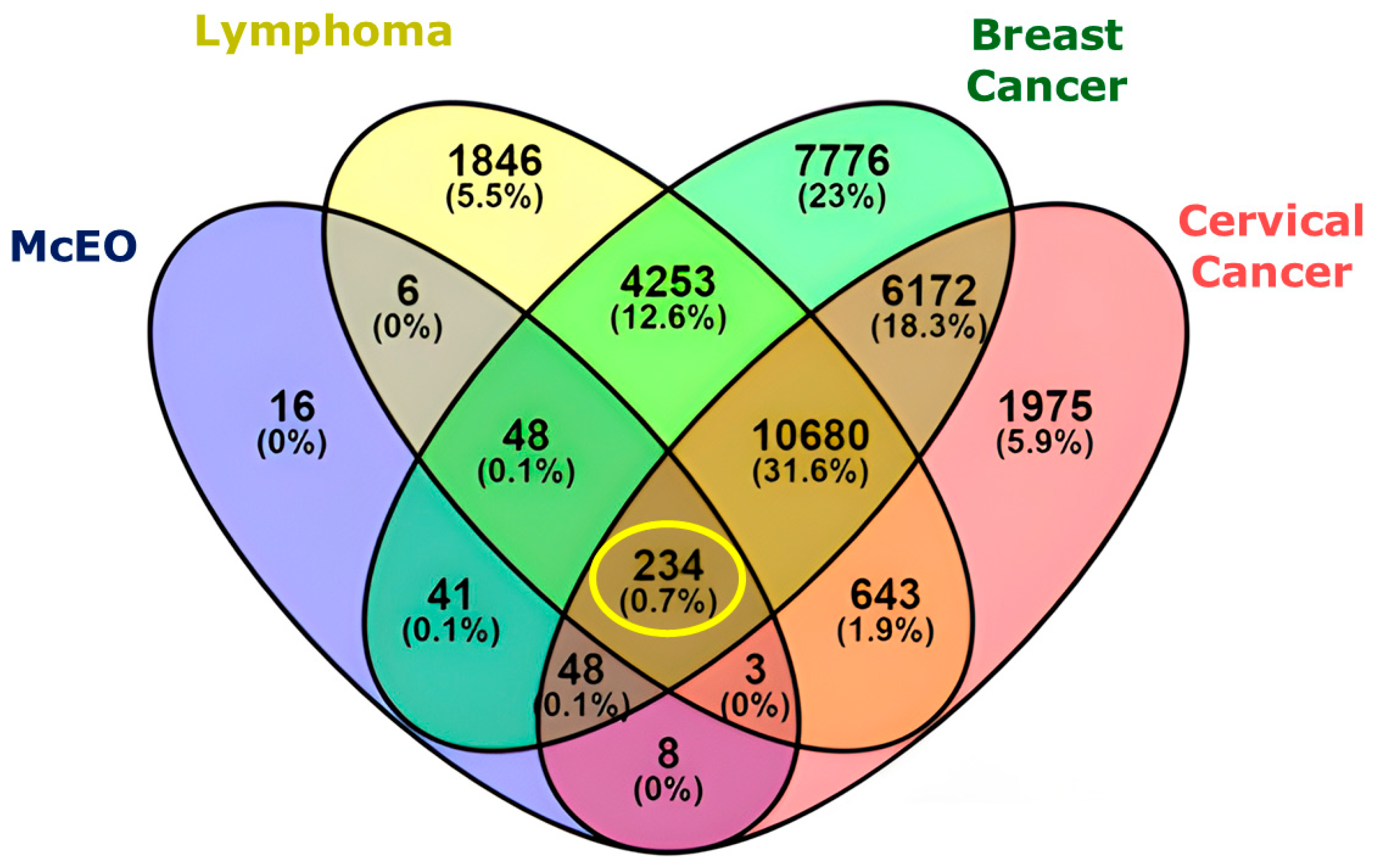
2.4. Network Pharmacology Analysis
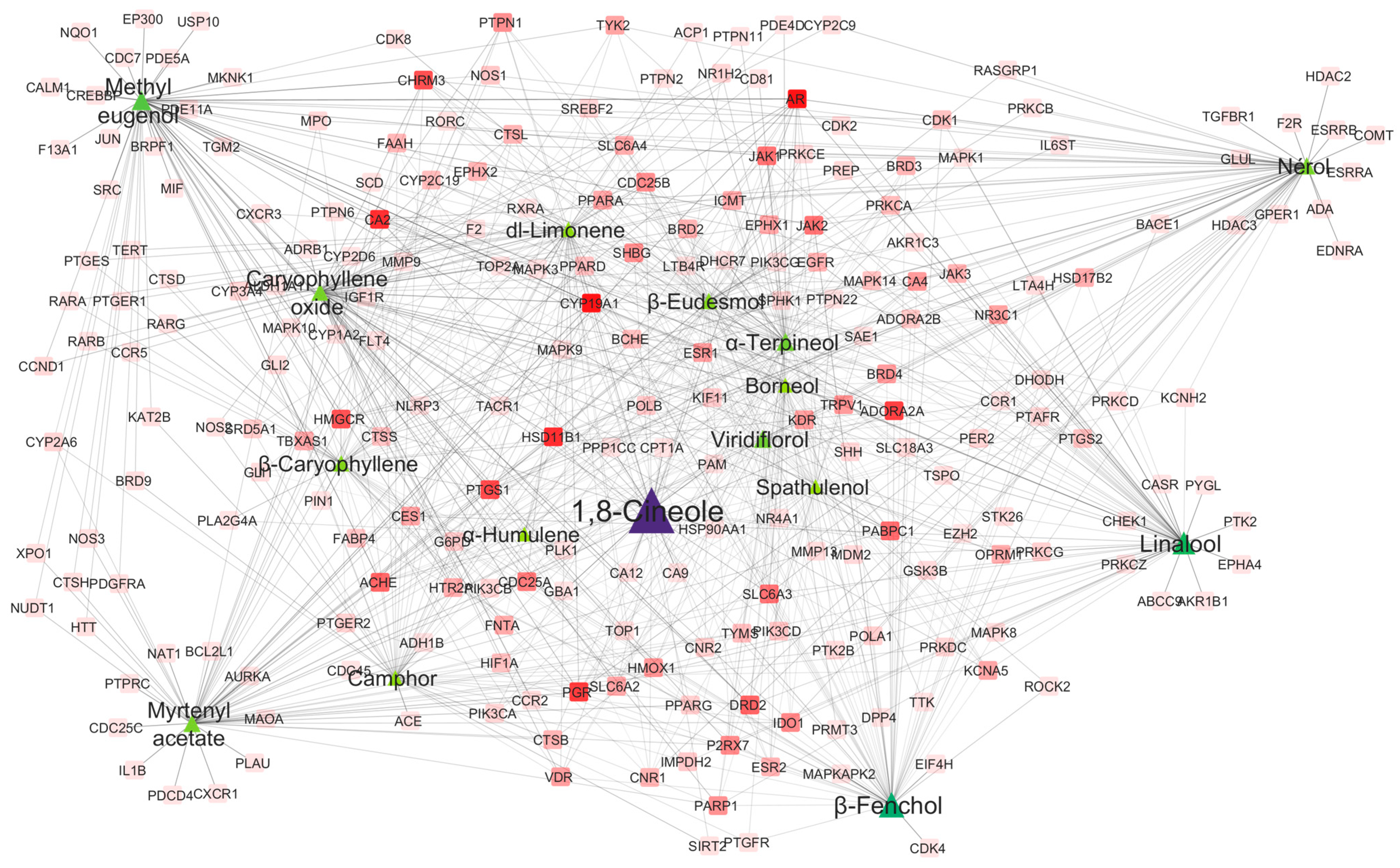
2.4.1. Hub Compounds and Network Connectivity
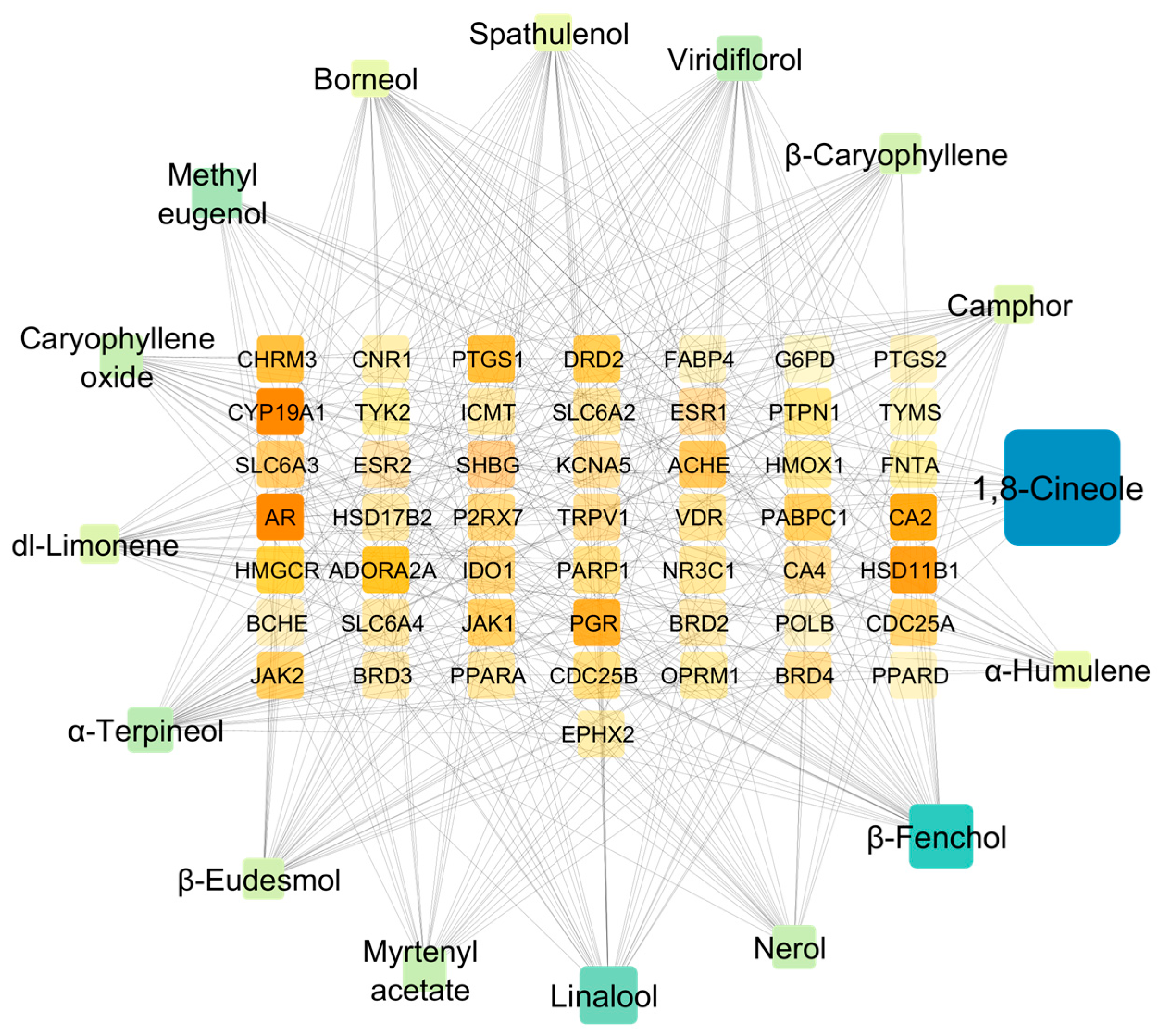
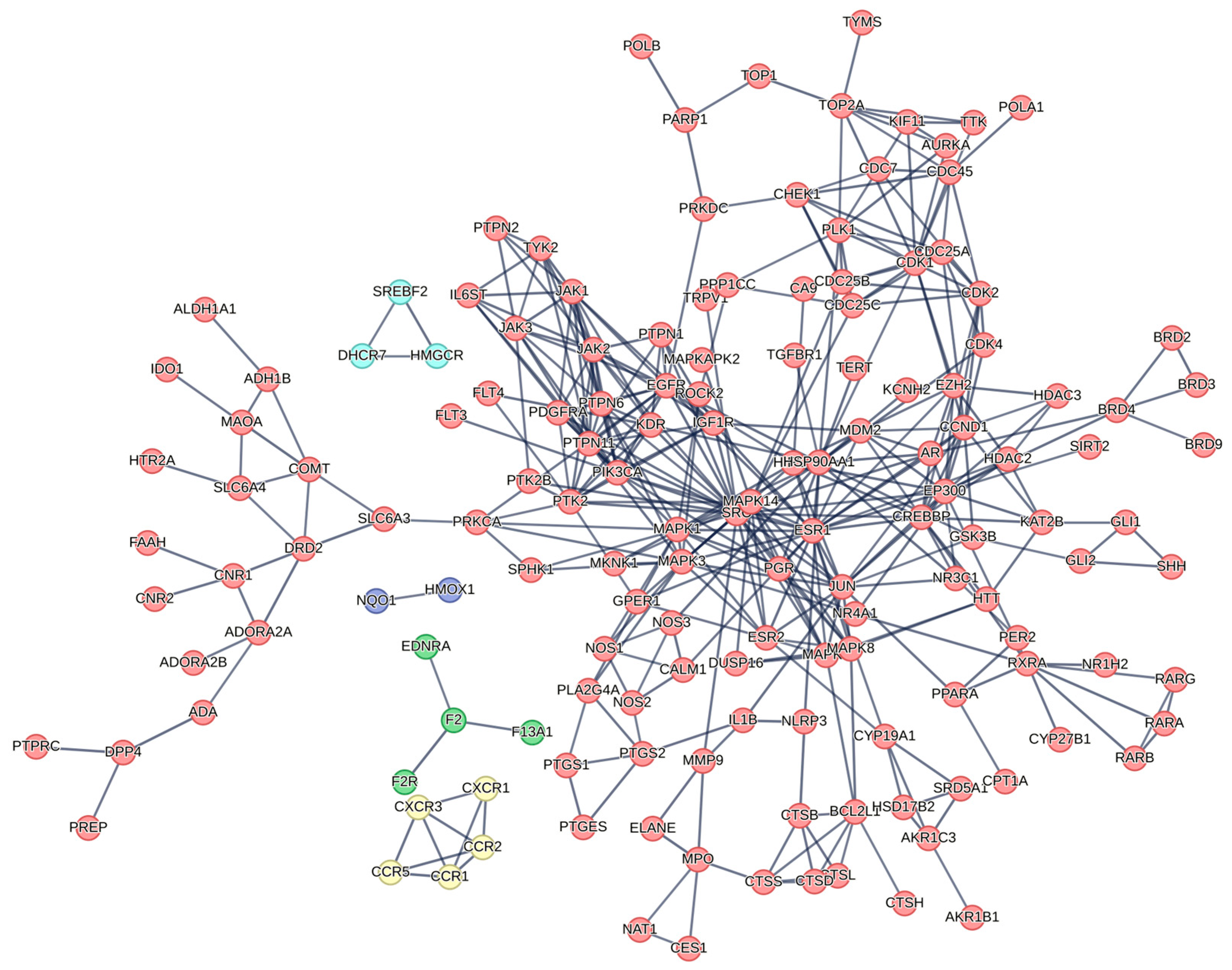
2.4.2. Protein Target Network Analysis
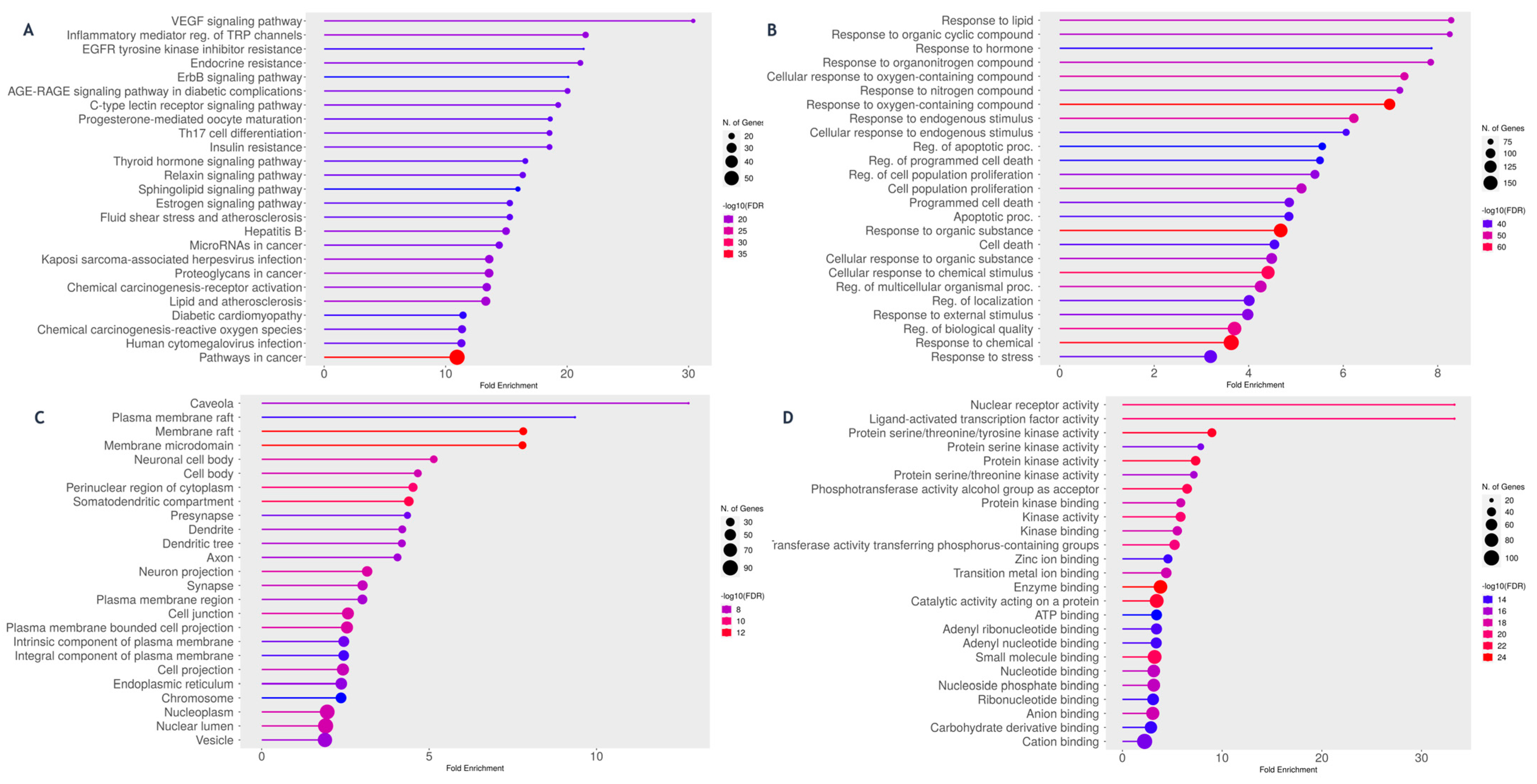
2.4.3. Protein–Protein Interaction (PPI) and Functional Enrichment Analysis
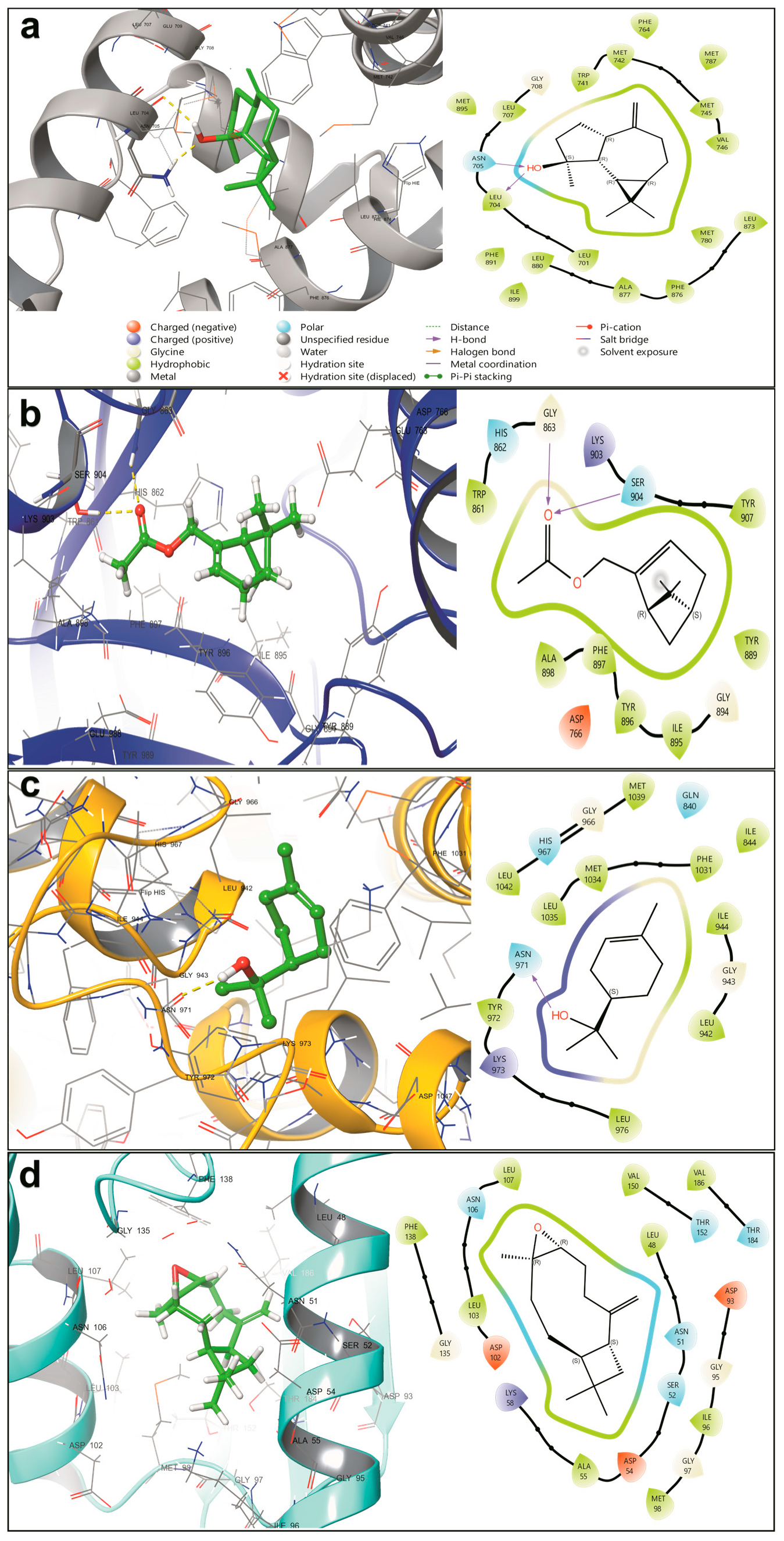
2.5. Molecular Docking
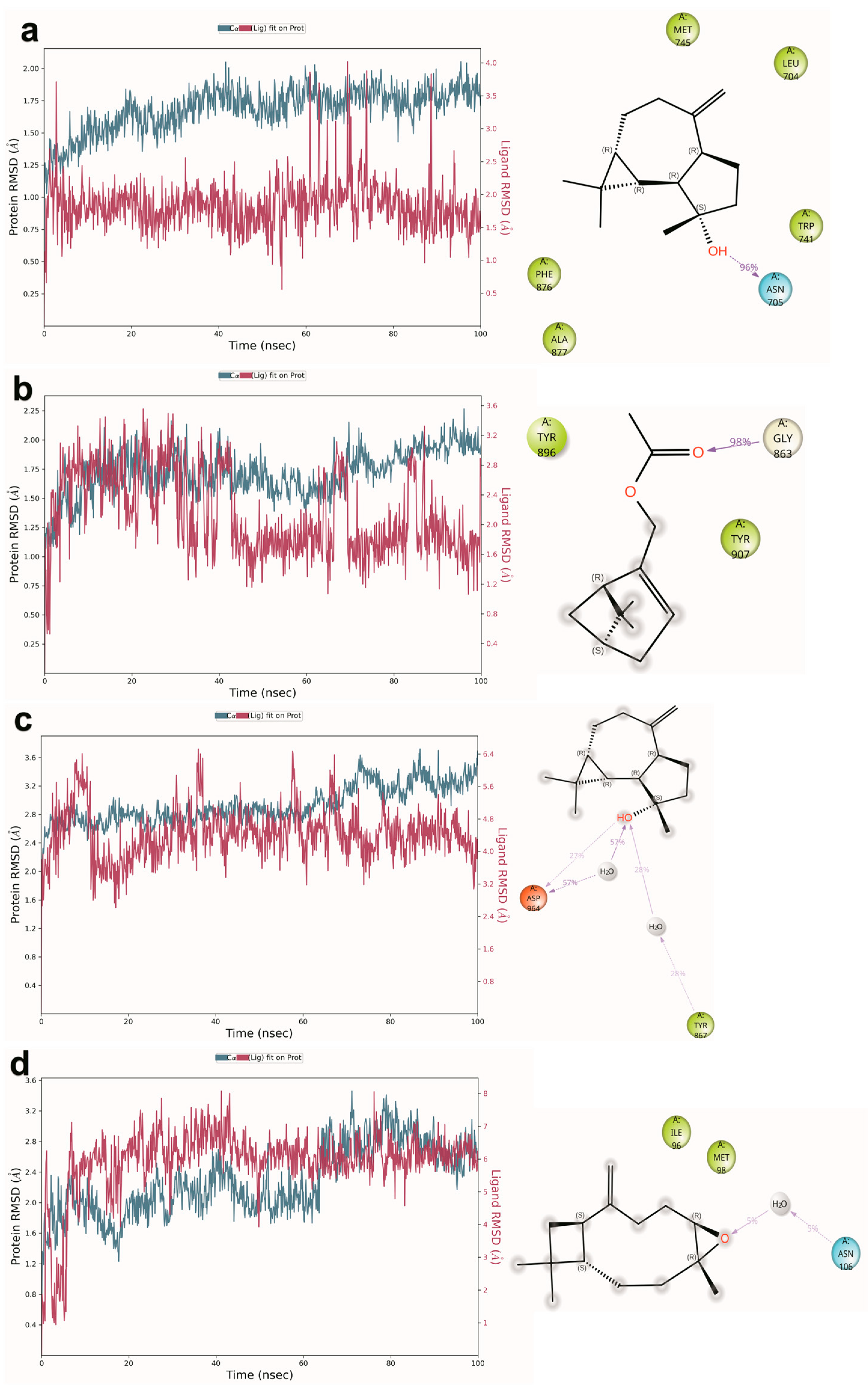
2.6. Molecular Dynamics Simulation
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Plant Material and Essential Oil Extraction
3.1.1. Plant Collection
3.1.2. Essential Oil Extraction
3.2. Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS)
3.3. Cell Lines and Culture Conditions
3.4. Antioxidant Activity
3.5. Computational Analysis: A Network Pharmacology Approach
3.5.1. Compound Identification and Target Prediction
3.5.2. Collection of Cancer-Associated Genes
3.5.3. Network Construction and Topological Analysis
3.5.4. Functional and Pathway Enrichment Analysis
3.6. Molecular Docking
3.7. Molecular Dynamics Simulations
3.8. Data Visualization and Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Sung, H. Global Cancer Statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowden, H.; Munro, J. Trends in Clinical Success Rates and Therapeutic Focus. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2019, 18, 495–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of Cancer: The Next Generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badria, F.A.; De Filippis, B.; El-Magd, M.A.; Elbadawi, M.M.; Hamdi, A.; Elgazar, A.A. Editorial: Multi-Target Drug Discovery and Design for Complex Health Disorders. Front. Pharmacol. 2025, 16, 1633600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarhouni, N.; Bayoudh, A.; Ben Slima, A.; Mekrazi, S.; El Aguel, A.; Khabir, A.; Kallel, I.; Soussi, A. Preventing Bifenthrin-Induced Testicular Toxicity in Rats with Citrus sinensis (‘Maltese Half-Blood’) Essential Oil: A Multidisciplinary Approach. J. Essent. Oil Bear. Plants 2024, 27, 849–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atanasov, A.G.; Zotchev, S.B.; Dirsch, V.M. Natural Products in Drug Discovery: Advances and Opportunities. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021, 20, 200–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chunarkar-Patil, P.; Kaleem, M.; Mishra, R.; Ray, S.; Ahmad, A.; Verma, D.; Bhayye, S.; Dubey, R.; Singh, H.N.; Kumar, S. Anticancer Drug Discovery Based on Natural Products: From Computational Approaches to Clinical Studies. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Shon, K.; Li, X.; Cui, G.; Wu, Y.; Wei, Z.; Wang, A.; Li, X.; Lu, Y. Recent Advances in Identifying Protein Targets of Bioactive Natural Products. Heliyon 2024, 10, e33917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, D.J.; Cragg, G.M. Natural Products as Sources of New Drugs over the Nearly Four Decades from 01/1981 to 09/2019. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 770–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhifi, W.; Bellili, S.; Jazi, S.; Bahloul, N.; Mnif, W. Essential Oils’ Chemical Characterization and Investigation of Some Biological Activities: A Critical Review. Medicines 2016, 3, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, T.; Khan, M.U.; Sharma, V.; Gupta, K. Terpenoids in Essential Oils: Chemistry, Classification, and Potential Impact on Human Health and Industry. Phytomedicine Plus 2024, 4, 100549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallel, I.; Tarhouni, N.; Elaguel, A.; Mekrazi, S.; Khabir, A.; Hadrich, B.; Bayoudh, A. The Phytochemical and Pharmacological Properties of Citrus sinensis ‘Maltese Half-Blood’ Essential Oil Peels Extracted and Optimized by Response-Surface Methodology. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2023, 24, 1938–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunse, M.; Daniels, R.; Gründemann, C.; Heilmann, J.; Kammerer, D.R.; Keusgen, M.; Lindequist, U.; Melzig, M.F.; Morlock, G.E.; Schulz, H.; et al. Essential Oils as Multicomponent Mixtures and Their Potential for Human Health and Well-Being. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 956541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kallel, I.; Tarhouni, N.; Elaguel, A.; Gargouri, B.; Hadrich, B.; Allouche, N.; Bayoudh, A. Exploration of the Antiproliferative and Antioxidant Effects and the Molecular Docking Study EGFR and VEGFR2 of Essential Oil from Citrus aurantium Peels. J. Essent. Oil Bear. Plants 2023, 26, 1130–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsay, R.R.; Popovic-Nikolic, M.R.; Nikolic, K. A Perspective on Multi-Target Drug Discovery and Design for Complex Diseases. Clin. Transl. Med. 2018, 7, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alipour, G.; Dashti, S.; Hosseinzadeh, H. Review of Pharmacological Effects of Myrtus communis L. and its Active Constituents. Phytother. Res. 2014, 28, 1125–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabbaghi, M.M.; Fadaei, M.S.; Soleimani Roudi, H.; Baradaran Rahimi, V.; Askari, V.R. A Review of the Biological Effects of Myrtus communis. Physiol. Rep. 2023, 11, e15770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snoussi, A.; Essaidi, I.; Ben Haj Koubaier, H.; Chaabouni, M.M.; Bouzouita, N. Chemical Composition and Antioxidant Activity of Essential Oils and Ethanol Extracts of Myrtus communis L. Organs (Berries, Leaves, and Floral Buds). J. Soc. Chim. Tunisie 2012, 14, 69–76. [Google Scholar]
- Giuliani, C.; Moretti, R.M.; Bottoni, M.; Santagostini, L.; Fico, G.; Montagnani Marelli, M. The Leaf Essential Oil of Myrtus communis subsp. Tarentina (L.) Nyman: From Phytochemical Characterization to Cytotoxic and Antimigratory Activity in Human Prostate Cancer Cells. Plants 2023, 12, 1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, A.L. Network Pharmacology: The Next Paradigm in Drug Discovery. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2008, 4, 682–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Zhu, X.; Bai, H.; Ning, K. Network Pharmacology Databases for Traditional Chinese Medicine: Review and Assessment. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kibble, M.; Saarinen, N.; Tang, J.; Wennerberg, K.; Mäkelä, S.; Aittokallio, T. Network Pharmacology Applications to Map the Unexplored Target Space and Therapeutic Potential of Natural Products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2015, 32, 1249–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noor, F.; Qamar, M.T.U.; Ashfaq, U.A.; Albutti, A.; Alwashmi, A.S.S.; Aljasir, M.A. Network Pharmacology Approach for Medicinal Plants: Review and Assessment. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vithalkar, M.P.; Sandra, K.S.; Bharath, H.B.; Krishnaprasad, B.; Fayaz, S.M.; Sathyanarayana, B.; Nayak, Y. Network Pharmacology-Driven Therapeutic Interventions for Interstitial Lung Diseases Using Traditional Medicines: A Narrative Review. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2025, 147, 113979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhouibi, I.; Flamini, G.; Bouaziz, M. Comparative Study on the Essential Oils Extracted from Tunisian Rosemary and Myrtle: Chemical Profiles, Quality, and Antimicrobial Activities. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 6431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben Hsouna, A.; Hamdi, N.; Miladi, R.; Abdelkafi, S. Myrtus communis Essential Oil: Chemical Composition and Antimicrobial Activities against Food Spoilage Pathogens. Chem. Biodivers. 2014, 11, 571–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benddine, H.; Zaid, R.; Babaali, D.; Daoudi-Hacini, S. Biological Activity of Essential Oils of Myrtus communis (Myrtaceae, Family) and Foeniculum vulgare (Apiaceae, Family) on Open Fields Conditions against Corn Aphids Rhopalosiphum Maidis (Fitch, 1856) in Western Algeria. J. Saudi Soc. Agric. Sci. 2023, 22, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.N.; Bristi, N.J.; Rafiquzzaman, M. Review on in Vivo and in Vitro Methods Evaluation of Antioxidant Activity. Saudi Pharm. J. 2013, 21, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berka-Zougali, B.; Ferhat, M.A.; Hassani, A.; Chemat, F.; Allaf, K.S. Comparative Study of Essential Oils Extracted from Algerian Myrtus communis L. Leaves Using Microwaves and Hydrodistillation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 4673–4695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdessemed, M.; Bouacida, S.; Turki, M.; Ben Haj Koubaier, H.; Omrani, S.; Allouache, R.; Bouzouita, N.; Karoui, R.; Snoussi, A. Chemical Characterization and Biological Activities Evaluation of Myrtus communis L. Essential Oil Extraction By-Product towards Circular Economy and Sustainability. Foods 2024, 13, 2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yangui, I.; Younsi, F.; Ghali, W.; Boussaid, M.; Messaoud, C. Phytochemicals, Antioxidant and Anti-Proliferative Activities of Myrtus communis L. Genotypes from Tunisia. South. Afr. J. Bot. 2021, 137, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mir, M.A.; Memish, L.A.; Elbehairi, S.E.; Bashir, N.; Masoud, F.S.; Shati, A.A.; Alfaifi, M.Y.; Alamri, A.M.; Alkahtani, S.A.; Ahmad, I. Antimycobacterial and Anticancer Properties of Myrtus communis Leaf Extract. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mimica-Dukic, N.; Bugarin, D.; Grbovic, S.; Mitic-Culafic, D.; Vukovic-Gacic, B.; Orcic, D.; Jovin, E.; Couladis, M. Essential Oil of Myrtus communis L. as a Potential Antioxidant and Antimutagenic Agents. Molecules 2010, 15, 2759–2770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallel, I.; Hadrich, B.; Gargouri, B.; Chaabane, A.; Lassoued, S.; Gdoura, R.; Bayoudh, A.; Ben Messaoud, E. Optimization of Cinnamon (Cinnamomum zeylanicum Blume) Essential Oil Extraction: Evaluation of Antioxidant and Antiproliferative Effects. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2019, 2019, 6498347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elaguel, A.; Kallel, I.; Gargouri, B.; Ben Amor, I.; Hadrich, B.; Ben Messaoud, E.; Gdoura, R.; Lassoued, S.; Gargouri, A. Lawsonia inermis Essential Oil: Extraction Optimization by RSM, Antioxidant Activity, Lipid Peroxydation and Antiproliferative Effects. Lipids Health Dis. 2019, 18, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marković, T.; Popović, S.; Matić, S.; Mitrović, M.; Anđić, M.; Kočović, A.; Vukić, M.; Petrović, V.; Branković, J.; Vuković, N.; et al. Insights into Molecular Mechanisms of Anticancer Activity of Juniperus communis Essential Oil in HeLa and HCT 116 Cells. Plants 2024, 13, 2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Fátima Braga Magalhães, I.; Junqueira Moraga Tellis, C.; da Silva Calabrese, K.; Lucia Abreu-Silva, A.; Almeida-Souza, F. Essential Oils’ Potential in Breast Cancer Treatment: An Overview. In Essential Oils—Bioactive Compounds, New Perspectives and Applications; IntechOpen: England, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Milliana, A.; Sari, R.A.; Al Miranda, S.; Mutiah, R. Evaluation of Anticancer Activity and Mechanism of Action of Myricetin on HeLa, T47D, and Vero Cells: Comparative Analysis with Cisplatin and Doxorubicin. Biomed. Pharmacol. J. 2025, 18, 835–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramazi, S.; Salimian, M.; Allahverdi, A.; Kianamiri, S.; Abdolmaleki, P. Synergistic Cytotoxic Effects of an Extremely Low-Frequency Electromagnetic Field with Doxorubicin on MCF-7 Cell Line. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 8844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hira, S.K.; Mishra, A.K.; Ray, B.; Manna, P.P. Targeted Delivery of Doxorubicin-Loaded Poly (ε-Caprolactone)-b-Poly (N-Vinylpyrrolidone) Micelles Enhances Antitumor Effect in Lymphoma. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e94309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Maharik, N.; Jaradat, N.; Al-Hajj, N.; Jaber, S. Myrtus communis L.: Essential Oil Chemical Composition, Total Phenols and Flavonoids Contents, Antimicrobial, Antioxidant, Anticancer, and α-Amylase Inhibitory Activity. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 2023, 10, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, C.B.; Kanunfre, C.C.; Farago, P.V.; Borsato, D.M.; Budel, J.M.; de Noronha Sales Maia, B.H.L.; Campesatto, E.A.; Sartoratto, A.; Miguel, M.D.; Miguel, O.G. Cytotoxic Mechanism of Baccharis milleflora (Less.) DC. Essential Oil. Toxicol. Vitr. 2017, 42, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghavam, M. In Vitro Biological Potential of the Essential Oil of Some Aromatic Species Used in Iranian Traditional Medicine. Inflammopharmacology 2022, 30, 855–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masyita, A.; Mustika Sari, R.; Dwi Astuti, A.; Yasir, B.; Rahma Rumata, N.; Bin Emran, T.; Nainu, F.; Simal-Gandara, J. Terpenes and Terpenoids as Main Bioactive Compounds of Essential Oils, Their Roles in Human Health and Potential Application as Natural Food Preservatives. Food Chem. X 2022, 13, 100217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alotaibi, N.M.; Alotaibi, M.O.; Alshammari, N.; Adnan, M.; Patel, M. Network Pharmacology Combined with Molecular Docking, Molecular Dynamics, and In Vitro Experimental Validation Reveals the Therapeutic Potential of Thymus vulgaris L. Essential Oil (Thyme Oil) against Human Breast Cancer. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 48344–48359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maitisha, G.; Zhou, J.; Zhao, Y.; Han, S.; Zhao, Y.; Abliz, A.; Liu, G. Network Pharmacology-Based Approach to Investigate the Molecular Targets of Essential Oil Obtained from Lavender for Treating Breast Cancer. Heliyon 2023, 9, e21759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harassi, Y.; Tilaoui, M.; Idir, A.; Frédéric, J.; Baudino, S.; Ajouaoi, S.; Mouse, H.A.; Zyad, A. Phytochemical Analysis, Cytotoxic and Antioxidant Activities of Myrtus communis Essential Oil from Morocco. J. Complement. Integr. Med. 2019, 16, 20180100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, A.J.; Elkahoui, S.; Alshammari, A.M.; Patel, M.; Ghoniem, A.E.M.; Abdalla, R.A.H.; Dwivedi-Agnihotri, H.; Badraoui, R.; Adnan, M. Mechanistic Insights into the Anticancer Potential of Asparagus Racemosus Willd. Against Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: A Network Pharmacology and Experimental Validation Study. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaala, L.A.; Youssef, D.T.A.; Ramadan, M.A.; Khalifa, A.A.; Ibrahim, R.S.; Valeriote, F.; Celik, I.; Dawood, H.M. Molecular Mechanisms of Phytoconstituents from Selected Egyptian Plants against Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Using Integrated in Vitro Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking Approach. Naunyn Schmiedeb. Arch. Pharmacol. 2025, 398, 9061–9082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, C.H.; Chen, S.H.; Wu, H.H.; Ho, C.W.; Ko, M.T.; Lin, C.Y. CytoHubba: Identifying Hub Objects and Sub-Networks from Complex Interactome. BMC Syst. Biol. 2014, 8 (Suppl. 4), S11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raut, J.S.; Karuppayil, S.M. A Status Review on the Medicinal Properties of Essential Oils. Ind. Crops Prod. 2014, 62, 250–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangral, Z.A.; Bhat, B.A.; Sheikh, S.; Islam, S.U.; Tariq, L.; Dar, R.; Varadharajan, V.; Hassan Dar, T.U. Exploring the Therapeutic Potential of Rhododendron anthopogon D.Don Essential Oil Constituents against Lung Cancer: A Network Pharmacology-Based Analysis with Molecular Docking and Experimental Studies. Comput. Biol. Med. 2025, 187, 109827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmi, S.G.; Kamaraj, M.; Nithya, T.G.; Chidambaranathan, N.; Pushpalatha, G.G.L.; Santhosh, P.; Balavaishnavi, B.; Mahajan, M. Network Pharmacology Integrated with Molecular Docking Reveals the Anticancer Mechanism of Jasminum sambac Linn. Essential Oil against Human Breast Cancer and Experimental Validation by in Vitro and in Vivo Studies. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2024, 196, 350–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fikry, E.; Orfali, R.; Perveen, S.; Ghaffar, S.; El-Shafae, A.M.; El-Domiaty, M.M.; Tawfeek, N. Chemical Composition and Anti-Lung Cancer Activities of Melaleuca quinquenervia Leaf Essential Oil: Integrating Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry (GC/MS) Profiling, Network Pharmacology, and Molecular Docking. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Zhao, G.; Zhang, D.; An, W.; Lai, H.; Li, X.; Cao, S.; Lin, X. Active Fraction of Clove Induces Apoptosis via PI3K/Akt/MTOR-Mediated Autophagy in Human Colorectal Cancer HCT-116 Cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2018, 53, 1363–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, J.L.; Shi, S.; Shen, Y.L.; Wang, L.; Chen, H.Y.; Zhu, J.; Ding, Y. Myricetin and Methyl Eugenol Combination Enhances the Anticancer Activity, Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis Induction of Cis-Platin against HeLa Cervical Cancer Cell Lines. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 1116. [Google Scholar]
- Karakuş, F.; Tanrıverdi, Z.; Kuzu, B. In Silico Network Toxicology, Molecular Docking, and Multi-Level Bioinformatics Reveal Methyl Eugenol-Induced Hepatocellular Carcinoma Mechanisms in Humans. Cancer Med. 2025, 14, e70768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronca, R.; Supuran, C.T. Carbonic Anhydrase IX: An Atypical Target for Innovative Therapies in Cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Rev. Cancer 2024, 1879, 189120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, X.; Jie, L.; Wu, P.; Mao, J.; Wang, P.; Liu, Z.; Yin, S. Comprehensive Network Pharmacological Analysis and In Vitro Verification Reveal the Potential Active Ingredients and Potential Mechanisms of Frankincense and Myrrh in Knee Osteoarthritis. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2022, 17, 1934578X221116984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, D.; Padhee, S.; Sahoo, C.; Jena, S.; Sahoo, A.; Chandra Panda, P.; Nayak, S.; Ray, A. Integrating Network Pharmacology and Experimental Verification to Decipher the Multitarget Pharmacological Mechanism of Cinnamomum zeylanicum Essential Oil in Treating Inflammation. Heliyon 2024, 10, e24120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Y.; Yu, J.; Douglas Kinghorn, A. Development of Anticancer Agents from Plant-Derived Sesquiterpene Lactones. Curr. Med. Chem. 2016, 23, 2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Oezguen, N.; Urvil, P.; Ferguson, C.; Dann, S.M.; Savidge, T.C. Regulation of Protein-Ligand Binding Affinity by Hydrogen Bond Pairing. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, e1501240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, H.; Qi, X.; Hu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Z.; Qin, Z. Targeting Sirtuins for Cancer Therapy: Epigenetics Modifications and Beyond. Theranostics 2024, 14, 6726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, S.; Chun, J.; Lee, J.; Kim, Y.S.; Noh, M.; Ko, H. Unraveling Stereochemical Structure-Activity Relationships of Sesquiterpene Lactones for Inhibitory Effects on STAT3 Activation. Biomol. Ther. 2024, 32, 627–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahleh, M.M.M.; Boeira, S.P.; Segat, H.J.; Guerra, G.P.; Prigol, M. A SARM a Day Keeps the Weakness Away: A Computational Approach for Selective Androgen Receptor Modulators (SARMs) and Their Interactions with Androgen Receptor and 5-Alpha Reductase Proteins. ACS Omega 2025, 10, 31649–31667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negreiros, H.A.; de Moura, K.G.; Barreto do Nascimento, M.L.L.; do Nascimento Rodrigues, D.C.; Ferreir, P.M.P.; Braz, D.C.; de Farias, M.G.; de Sousa Corrêia, L.; Pereira, A.R.S.; Santos, L.K.B.; et al. Alpha-Terpineol as Antitumor Candidate in Pre-Clinical Studies. Anticancer. Agents Med. Chem. 2021, 21, 2023–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Grewal, K.; Jandrotia, R.; Batish, D.R.; Singh, H.P.; Kohli, R.K. Essential Oils as Anticancer Agents: Potential Role in Malignancies, Drug Delivery Mechanisms, and Immune System Enhancement. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 146, 112514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kováts, E. Gas-chromatographische Charakterisierung Organischer Verbindungen. Teil 1: Retentionsindices Aliphatischer Halogenide, Alkohole, Aldehyde Und Ketone. Helv. Chim. Acta 1958, 41, 1915–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Amor, I.; Gargouri, B.; Attia, H.; Tlili, K.; Kallel, I.; Musarra-Pizzo, M.; Sciortino, M.T.; Pennisi, R. In Vitro Anti-Epstein Barr Virus Activity of Olea europaea L. Leaf Extracts. Plants 2021, 10, 2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben Mansour, R.; Gargouri, B.; Bouaziz, M.; Elloumi, N.; Belhadj Jilani, I.; Ghrabi, Z.; Lassoued, S. Antioxidant Activity of Ethanolic Extract of Inflorescence of Ormenis Africana in Vitro and in Cell Cultures. Lipids Health Dis. 2011, 10, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strober, W. Trypan Blue Exclusion Test of Cell Viability. Curr. Protoc. Immunol. 2015, 111, A3.B.1–A3.B.3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerlier, D.; Thomasset, N. Use of MTT Colorimetric Assay to Measure Cell Activation. J. Immunol. Methods 1986, 94, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, O.P.; Bhat, T.K. DPPH Antioxidant Assay Revisited. Food Chem. 2009, 113, 1202–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Re, R.; Pellegrini, N.; Proteggente, A.; Pannala, A.; Yang, M.; Rice-Evans, C. Antioxidant Activity Applying an Improved ABTS Radical Cation Decolorization Assay. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1999, 26, 1231–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olszowy, M.; Dawidowicz, A.L. Essential Oils as Antioxidants: Their Evaluation by DPPH, ABTS, FRAP, CUPRAC, and β-Carotene Bleaching Methods. Monatsh Chem. 2016, 147, 2083–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcocci, L.; Packer, L.; Droy-Lefaix, M.T.; Sekaki, A.; Gardès-Albert, M. [46] Antioxidant Action of Ginkgo biloba Extract EGb 761. Methods Enzymol. 1994, 234, 462–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruch, R.J.; Cheng, S.J.; Klaunig, J.E. Prevention of Cytotoxicity and Inhibition of Intercellular Communication by Antioxidant Catechins Isolated from Chinese Green Tea. Carcinogenesis 1989, 10, 1003–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagi, A.; Kabash, A.; Okamura, N.; Haraguchi, H.; Moustafa, S.M.; Khalifa, T.I. Antioxidant, Free Radical Scavenging and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Aloesin Derivatives in Aloe vera. Planta Med. 2002, 68, 957–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Chen, J.; Cheng, T.; Gindulyte, A.; He, J.; He, S.; Li, Q.; Shoemaker, B.A.; Thiessen, P.A.; Yu, B.; et al. PubChem 2023 Update. Nucleic Acids Res 2023, 51, D1373–D1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daina, A.; Michielin, O.; Zoete, V. SwissTargetPrediction: Updated Data and New Features for Efficient Prediction of Protein Targets of Small Molecules. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W357–W364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Santos, A.; Von Mering, C.; Jensen, L.J.; Bork, P.; Kuhn, M. STITCH 5: Augmenting Protein–Chemical Interaction Networks with Tissue and Affinity Data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D380–D384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Guo, X.; Yun, Y.; Lu, L.; Huang, X.; Jia, S. DisGeNet: A Disease-Centric Interaction Database among Diseases and Various Associated Genes. Database 2025, 2025, baae122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Nastou, K.; Koutrouli, M.; Kirsch, R.; Mehryary, F.; Hachilif, R.; Hu, D.; Peluso, M.E.; Huang, Q.; Fang, T.; et al. The STRING Database in 2025: Protein Networks with Directionality of Regulation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025, 53, D730–D737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, S.X.; Jung, D.; Jung, D.; Yao, R. ShinyGO: A Graphical Gene-Set Enrichment Tool for Animals and Plants. Bioinformatics 2020, 36, 2628–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berman, H.M.; Westbrook, J.; Feng, Z.; Gilliland, G.; Bhat, T.N.; Weissig, H.; Shindyalov, I.N.; Bourne, P.E. The Protein Data Bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, C.; Wu, C.; Ghoreishi, D.; Chen, W.; Wang, L.; Damm, W.; Ross, G.A.; Dahlgren, M.K.; Russell, E.; Von Bargen, C.D.; et al. OPLS4: Improving Force Field Accuracy on Challenging Regimes of Chemical Space. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2021, 17, 4291–4300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friesner, R.A.; Murphy, R.B.; Repasky, M.P.; Frye, L.L.; Greenwood, J.R.; Halgren, T.A.; Sanschagrin, P.C.; Mainz, D.T. Extra Precision Glide: Docking and Scoring Incorporating a Model of Hydrophobic Enclosure for Protein-Ligand Complexes. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 6177–6196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayoudh, A.; Tarhouni, N.; Ben Hassena, A.; Khannous, L.; Balti, M.A.; Kriaa, K.; Ahmed, Z.; Kallel, I.; Hadrich, B. Exploring the Dual Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Potential of Cymbopogon flexuosus Essential Oil: Insights from Molecular Docking and Dynamics Simulations. Chem. Methodol. 2025, 9, 809–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, E.; Rendleman, C.A.; Bowers, K.J.; Dror, R.O.; Hughes, D.H.; Gullingsrud, J.; Sacerdoti, F.D.; Shaw, D.E. Desmond Performance on a Cluster of Multicore Processors. D. E. Shaw Research Technical Report DESRES/TR–2008-01. 2008. Available online: https://www.deshawresearch.com/publications/Desmond_Performance_Cluster.pdf (accessed on 29 September 2025).
- Martyna, G.J.; Klein, M.L.; Tuckerman, M. Nosé–Hoover Chains: The Canonical Ensemble via Continuous Dynamics. J. Chem. Phys. 1992, 97, 2635–2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Compound | RT (min) | Percentage (%) | KI (Exp) | KI (Lit) | Chemical Class |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| dl-Limonene | 8.397 | 1.37 | 1024 | 1028 | Monoterpene |
| 1,8-Cineole | 8.454 | 38.94 | 1026 | 1031 | Oxygenated monoterpene |
| Linalool | 10.079 | 10.65 | 1095 | 1098 | |
| Camphor | 11.189 | 1.76 | 1141 | 1146 | |
| β-Fenchol | 12.294 | 13.36 | 1121 | 1125 | |
| Borneol | 13.795 | 0.62 | 1165 | 1169 | |
| α-Terpineol | 16.243 | 4.68 | 1186 | 1189 | |
| Nerol | 16.608 | 3.12 | 1227 | 1230 | |
| Methyl eugenol | 17.083 | 6.76 | 1401 | 1405 | Phenylpropanoid |
| Myrtenyl acetate | 18.272 | 3.52 | 1324 | 1326 | Oxygenated sesquiterpene |
| Caryophyllene oxide | 19.515 | 3.58 | 1581 | 1583 | |
| Viridiflorol | 20.843 | 4.72 | 1590 | 1593 | |
| β-Eudesmol | 21.016 | 2.15 | 1649 | 1652 | |
| α-Humulene | 23.249 | 0.21 | 1452 | 1455 | Sesquiterpene |
| β-Caryophyllene | 28.994 | 2.30 | 1417 | 1419 | |
| Spathulenol | 29.061 | 0.29 | 1577 | 1580 | Oxygenated sesquiterpene |
| Total identified | 98.03 |
| Assay | McEO IC50 (mg/mL) | Reference Control | Control IC50 |
|---|---|---|---|
| FRAP | 0.008 ± 0.001 | Vitamin C | <0.019 mg/mL |
| DPPH | 0.138 ± 0.112 | BHT | 0.041 ± 0.005 mg/mL |
| ABTS | 0.505 ± 0.050 | Trolox | <0.1 mg/mL |
| H2O2 | 0.555 ± 0.055 | Vitamin C | <0.1 mg/mL |
| NO | 0.582 ± 0.058 | Vitamin C | <0.1 mg/mL |
| O2− | 1.482 ± 0.148 | Vitamin C | <0.1 mg/mL |
| Target Protein | Compound | XP GScore (kcal/mol) |
|---|---|---|
| PARP1 (PDB: 4UND) | Ref [Talazoparib—fluorinated pyrido-phthalazinone] | −12.187 |
| β-Eudesmol | −5.702 | |
| Myrtenyl acetate | −5.634 | |
| Spathulenol | −5.297 | |
| Mcl-1 (PDB: 5FC4) | Ref [6-chloro-N-methylsulfonyl indole carboxamide] | −11.651 |
| Methyleugenol | −6.519 | |
| Limonene | −6.511 | |
| α-Terpineol | −6.126 | |
| CDK6 (PDB: 5L2I) | Ref [Palbociclib—pyrido-pyrimidine kinase inhibitor] | −11.303 |
| Spathulenol | −7.388 | |
| β-Eudesmol | −6.356 | |
| Myrtenyl acetate | −6.251 | |
| PI3Kγ (PDB: 5OQ4) | Ref [PQR309—dimorpholinyl-triazine derivative] | −9.218 |
| α-Terpineol | −6.970 | |
| Spathulenol | −5.941 | |
| Myrtenyl acetate | −5.645 | |
| Sirt2 (PDB: 5YQO) | Ref [L5C—pyrazole carboxamide derivative] | −12.818 |
| Viridiflorol | −9.207 | |
| β-Eudesmol | −8.936 | |
| Spathulenol | −8.649 | |
| Erα (PDB: 6CHZ) | Ref [H3B-9224—indazole-phenylbutene derivative] | −14.240 |
| Spathulenol | −8.650 | |
| Viridiflorol | −8.547 | |
| β-Eudesmol | −8.207 | |
| HSP90 (PDB: 8AGI) | Ref [JMC31—triazole carboxamide derivative] | −11.854 |
| Spathulenol | −6.391 | |
| Viridiflorol | −6.355 | |
| β-Caryophyllene | −6.108 | |
| Androgen Receptor (PDB: 8E1A) | Ref [Thiazole-morpholine derivative] | −9.721 |
| Spathulenol | −9.650 | |
| β-Eudesmol | −8.989 | |
| Viridiflorol | −8.564 | |
| β-Caryophyllene oxide | −7.967 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bayoudh, A.; Tarhouni, N.; Ben Mansour, R.; Mekrazi, S.; Sadraoui, R.; Kriaa, K.; Ahmed, Z.; Soussi, A.; Kallel, I.; Hadrich, B. Integrated Network Pharmacology and Molecular Dynamics Reveal Multi-Target Anticancer Mechanisms of Myrtus communis Essential Oils. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 1542. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18101542
Bayoudh A, Tarhouni N, Ben Mansour R, Mekrazi S, Sadraoui R, Kriaa K, Ahmed Z, Soussi A, Kallel I, Hadrich B. Integrated Network Pharmacology and Molecular Dynamics Reveal Multi-Target Anticancer Mechanisms of Myrtus communis Essential Oils. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(10):1542. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18101542
Chicago/Turabian StyleBayoudh, Ahmed, Nidhal Tarhouni, Riadh Ben Mansour, Saoussen Mekrazi, Raoudha Sadraoui, Karim Kriaa, Zakarya Ahmed, Ahlem Soussi, Imen Kallel, and Bilel Hadrich. 2025. "Integrated Network Pharmacology and Molecular Dynamics Reveal Multi-Target Anticancer Mechanisms of Myrtus communis Essential Oils" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 10: 1542. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18101542
APA StyleBayoudh, A., Tarhouni, N., Ben Mansour, R., Mekrazi, S., Sadraoui, R., Kriaa, K., Ahmed, Z., Soussi, A., Kallel, I., & Hadrich, B. (2025). Integrated Network Pharmacology and Molecular Dynamics Reveal Multi-Target Anticancer Mechanisms of Myrtus communis Essential Oils. Pharmaceuticals, 18(10), 1542. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18101542








