Modulators of the Human Voltage-Gated Proton Channel Hv1
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Voltage-Gated Proton Channels
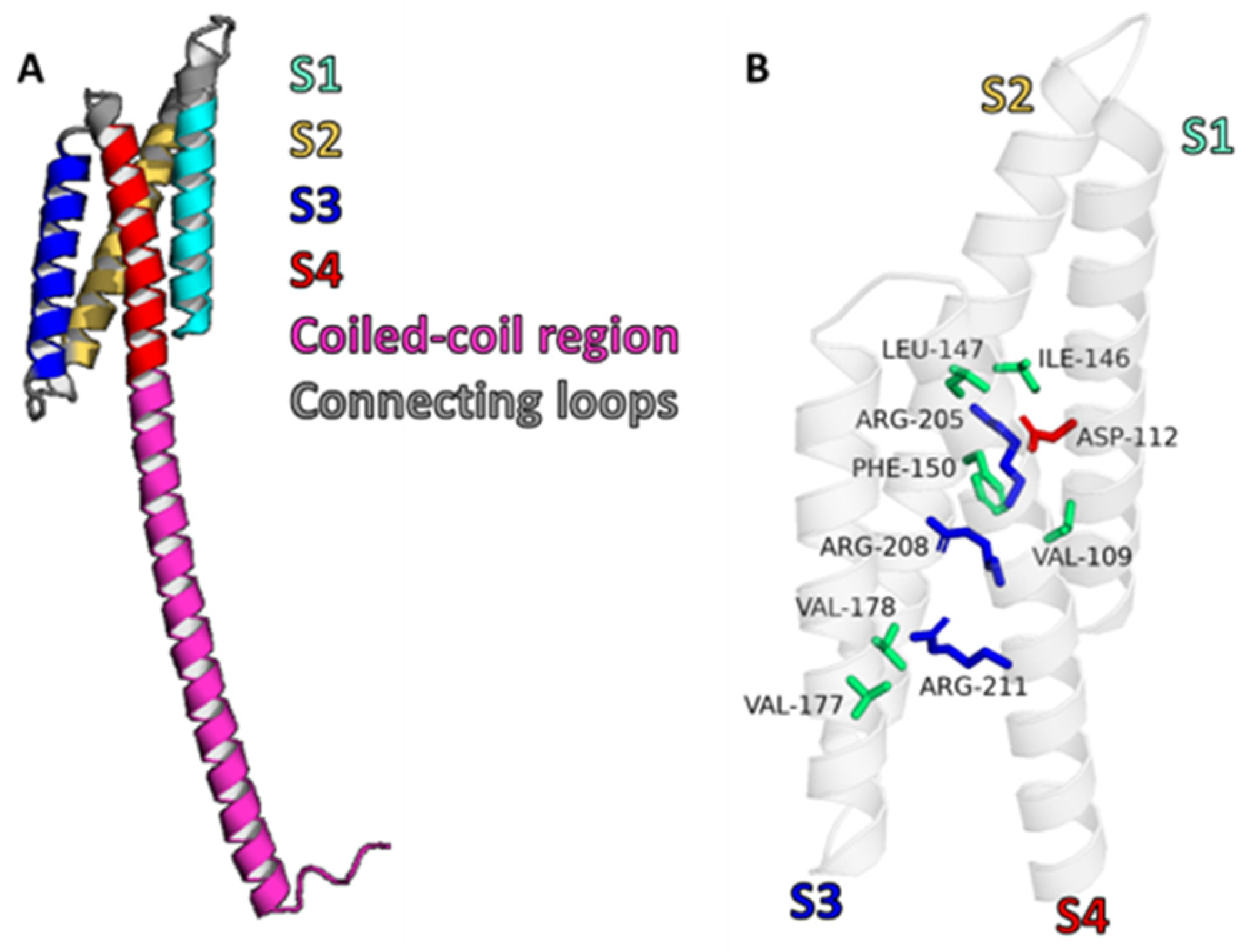
1.2. Structure of Hv1
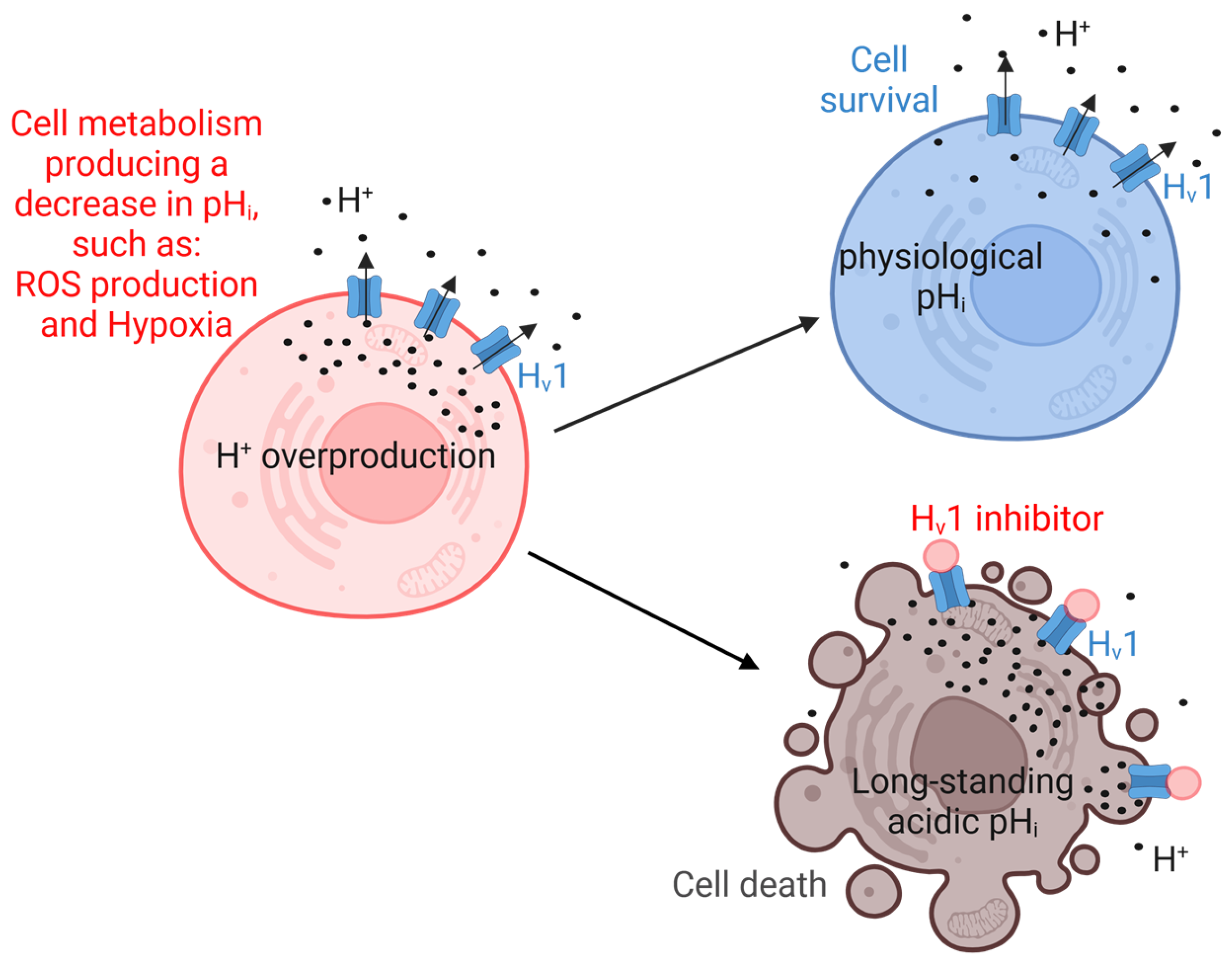
1.3. Functions of Hv1 and Its Role in Cancer
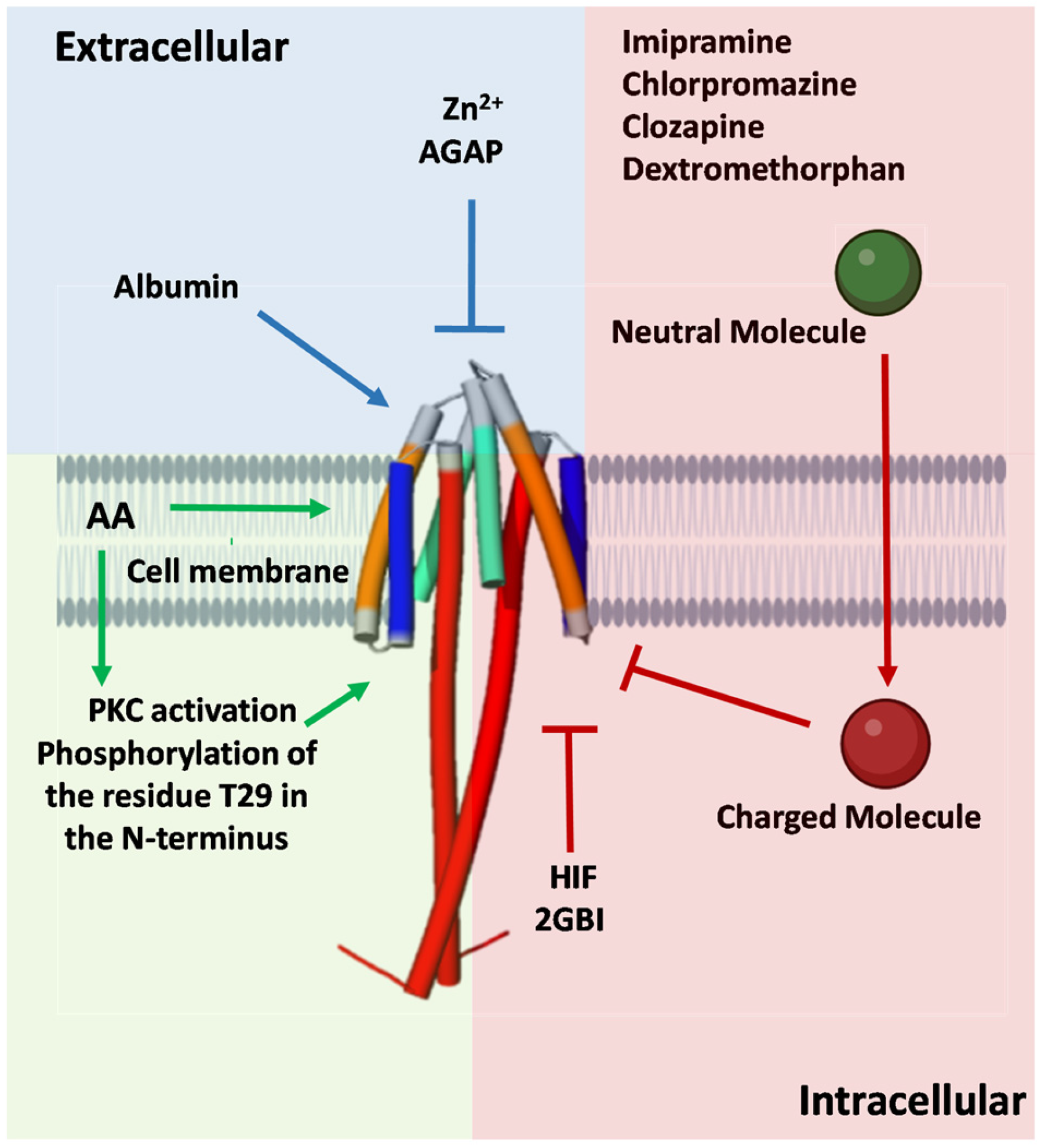
2. Hv1 Modulators
2.1. Hv1 Inhibitors
2.2. Hv1 Activators
3. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| VSD | Voltage-sensing domain |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| VGIC | Voltage-gated ion channel |
| ic | Intracellular |
| ec | Extracellular |
| memb | Membrane |
| NADPH | Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate |
| SW620 | A colorectal cell line |
| HT29 | A colorectal cell line |
| MDSC | Myeloid-derived suppressor cell |
| WBC | White blood cell |
| NLRP3 | NLR family pyrin domain-containing 3 |
| KO | Knockout |
| HVCN1 | The gene that encodes “Voltage-gated hydrogen channel 1” |
| NOX2 | NADPH oxidase 2 |
| HIF | 3-(2-amino-5-methyl-1H-imidazol-4-yl)-1-(3,5-difluorophenyl)propan-1-one |
| AGAP | Anti-tumor analgesic peptide, isolated from the scorpion Buthus martensii |
| BV2 | A mouse-derived microglial cell |
| EGCG | Epigallocatechin-3-gallate, the principal bioactive constituent of green tea |
| OPE | Onion peel extract |
| PKC | Protein kinase C |
| LPS | Lipopolysaccharide |
| AA | Arachidonic acid |
References
- Thomas, R.C.; Meech, R.W. Hydrogen ion currents and intracellular pH in depolarized voltage-clamped snail neurones. Nature 1982, 299, 826–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, M.; Takagi, M.; Okamura, Y. A voltage sensor-domain protein is a voltage-gated proton channel. Science 2006, 312, 589–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsey, I.S.; Moran, M.M.; Chong, J.A.; Clapham, D.E. A voltage-gated proton-selective channel lacking the pore domain. Nature 2006, 440, 1213–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeCoursey, T.E. The Voltage-Gated Proton Channel: A Riddle, Wrapped in a Mystery, inside an Enigma. Biochemistry 2015, 54, 3250–3268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaves, G.; Ayuyan, A.G.; Cherny, V.V.; Morgan, D.; Franzen, A.; Fieber, L.; Nausch, L.; Derst, C.; Mahorivska, I.; Jardin, C.; et al. Unexpected expansion of the voltage-gated proton channel family. FEBS J. 2023, 290, 1008–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaves, G.; Jardin, C.; Franzen, A.; Mahorivska, I.; Musset, B.; Derst, C. Proton channels in molluscs: A new bivalvian-specific minimal HV4 channel. FEBS J. 2023, 290, 3436–3447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okochi, Y.; Okamura, Y. Regulation of Neutrophil Functions by Hv1/VSOP Voltage-Gated Proton Channels. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petheo, G.L.; Orient, A.; Barath, M.; Kovacs, I.; Rethi, B.; Lanyi, A.; Rajki, A.; Rajnavolgyi, E.; Geiszt, M. Molecular and functional characterization of Hv1 proton channel in human granulocytes. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e14081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Chemaly, A.; Nunes, P.; Jimaja, W.; Castelbou, C.; Demaurex, N. Hv1 proton channels differentially regulate the pH of neutrophil and macrophage phagosomes by sustaining the production of phagosomal ROS that inhibit the delivery of vacuolar ATPases. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2014, 95, 827–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.J. Voltage-gated proton channel Hv1 in microglia. Neuroscientist 2014, 20, 599–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coe, D.; Poobalasingam, T.; Fu, H.; Bonacina, F.; Wang, G.; Morales, V.; Moregola, A.; Mitro, N.; Cheung, K.C.; Ward, E.J.; et al. Loss of voltage-gated hydrogen channel 1 expression reveals heterogeneous metabolic adaptation to intracellular acidification by T cells. JCI Insight 2022, 7, e147814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capasso, M.; Bhamrah, M.K.; Henley, T.; Boyd, R.S.; Langlais, C.; Cain, K.; Dinsdale, D.; Pulford, K.; Khan, M.; Musset, B.; et al. HVCN1 modulates BCR signal strength via regulation of BCR-dependent generation of reactive oxygen species. Nat. Immunol. 2010, 11, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iovannisci, D.; Illek, B.; Fischer, H. Function of the HVCN1 proton channel in airway epithelia and a naturally occurring mutation, M91T. J. Gen. Physiol. 2010, 136, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Chemaly, A.; Guinamard, R.; Demion, M.; Fares, N.; Jebara, V.; Faivre, J.F.; Bois, P. A voltage-activated proton current in human cardiac fibroblasts. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 340, 512–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meszaros, B.; Papp, F.; Mocsar, G.; Kokai, E.; Kovacs, K.; Tajti, G.; Panyi, G. The voltage-gated proton channel hHv1 is functionally expressed in human chorion-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.; Che, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhang, S.; Gao, Y.T.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Xi, W.; Zuo, W.; Li, S.J. The voltage-gated proton channel Hv1 is expressed in pancreatic islet beta-cells and regulates insulin secretion. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 468, 746–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lishko, P.V.; Botchkina, I.L.; Fedorenko, A.; Kirichok, Y. Acid extrusion from human spermatozoa is mediated by flagellar voltage-gated proton channel. Cell 2010, 140, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.Y.; Morgan, D.; Sharma, L.; Cherny, V.V.; Tidswell, N.; Molo, M.W.; DeCoursey, T.E. Voltage-gated proton channels exist in the plasma membrane of human oocytes. Hum. Reprod. 2019, 34, 1974–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hondares, E.; Brown, M.A.; Musset, B.; Morgan, D.; Cherny, V.V.; Taubert, C.; Bhamrah, M.K.; Coe, D.; Marelli-Berg, F.; Gribben, J.G.; et al. Enhanced activation of an amino-terminally truncated isoform of the voltage-gated proton channel HVCN1 enriched in malignant B cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 18078–18083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro-Silva, L.; Queiroz, F.O.; da Silva, A.M.; Hirata, A.E.; Arcisio-Miranda, M. Voltage-Gated Proton Channel in Human Glioblastoma Multiforme Cells. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2016, 7, 864–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asuaje, A.; Smaldini, P.; Martin, P.; Enrique, N.; Orlowski, A.; Aiello, E.A.; Gonzalez Leon, C.; Docena, G.; Milesi, V. The inhibition of voltage-gated H+ channel (HVCN1) induces acidification of leukemic Jurkat T cells promoting cell death by apoptosis. Pflug. Arch. 2017, 469, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventura, C.; Leon, I.E.; Asuaje, A.; Martin, P.; Enrique, N.; Nunez, M.; Cocca, C.; Milesi, V. Differential expression of the long and truncated Hv1 isoforms in breast-cancer cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 2020, 235, 8757–8767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Li, S.J.; Pan, J.; Che, Y.; Yin, J.; Zhao, Q. Specific expression of the human voltage-gated proton channel Hv1 in highly metastatic breast cancer cells, promotes tumor progression and metastasis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 412, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, X.; Li, Q.; Zhang, S.; Li, S.J. Human voltage-gated proton channel Hv1: A new potential biomarker for diagnosis and prognosis of colorectal cancer. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e70550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koch, H.P.; Kurokawa, T.; Okochi, Y.; Sasaki, M.; Okamura, Y.; Larsson, H.P. Multimeric nature of voltage-gated proton channels. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 9111–9116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Letts, J.A.; Mackinnon, R. Dimeric subunit stoichiometry of the human voltage-dependent proton channel Hv1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 7692–7695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakata, S.; Kurokawa, T.; Norholm, M.H.; Takagi, M.; Okochi, Y.; von Heijne, G.; Okamura, Y. Functionality of the voltage-gated proton channel truncated in S4. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 2313–2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, C.; Koch, H.P.; Drum, B.M.; Larsson, H.P. Strong cooperativity between subunits in voltage-gated proton channels. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2010, 17, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tombola, F.; Ulbrich, M.H.; Kohout, S.C.; Isacoff, E.Y. The opening of the two pores of the Hv1 voltage-gated proton channel is tuned by cooperativity. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2010, 17, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musset, B.; Smith, S.M.; Rajan, S.; Cherny, V.V.; Morgan, D.; DeCoursey, T.E. Oligomerization of the voltage-gated proton channel. Channels 2010, 4, 260–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsey, I.S.; Mokrab, Y.; Carvacho, I.; Sands, Z.A.; Sansom, M.S.P.; Clapham, D.E. An aqueous H+ permeation pathway in the voltage-gated proton channel Hv1. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2010, 17, 869–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeCoursey, T.E.; Cherny, V.V. Deuterium isotope effects on permeation and gating of proton channels in rat alveolar epithelium. J. Gen. Physiol. 1997, 109, 415–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Keulen, S.C.; Gianti, E.; Carnevale, V.; Klein, M.L.; Rothlisberger, U.; Delemotte, L. Does Proton Conduction in the Voltage-Gated H+ Channel hHv1 Involve Grotthuss-Like Hopping via Acidic Residues? J. Phys. Chem. B 2017, 121, 3340–3351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boytsov, D.; Brescia, S.; Chaves, G.; Koefler, S.; Hannesschlaeger, C.; Siligan, C.; Goessweiner-Mohr, N.; Musset, B.; Pohl, P. Trapped Pore Waters in the Open Proton Channel HV1. Small 2023, 19, e2205968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeshita, K.; Sakata, S.; Yamashita, E.; Fujiwara, Y.; Kawanabe, A.; Kurokawa, T.; Okochi, Y.; Matsuda, M.; Narita, H.; Okamura, Y.; et al. X-ray crystal structure of voltage-gated proton channel. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2014, 21, 352–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tombola, F.; Ulbrich, M.H.; Isacoff, E.Y. The voltage-gated proton channel Hv1 has two pores, each controlled by one voltage sensor. Neuron 2008, 58, 546–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudev, T.; Musset, B.; Morgan, D.; Cherny, V.V.; Smith, S.M.; Mazmanian, K.; DeCoursey, T.E.; Lim, C. Selectivity Mechanism of the Voltage-gated Proton Channel, HV1. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamberlin, A.; Qiu, F.; Wang, Y.; Noskov, S.Y.; Larsson, H.P. Mapping the gating and permeation pathways in the voltage-gated proton channel Hv1. J. Mol. Biol. 2015, 427, 131–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, T.K.; Isacoff, E.Y. The pore of the voltage-gated proton channel. Neuron 2011, 72, 991–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaves, G.; Derst, C.; Franzen, A.; Mashimo, Y.; Machida, R.; Musset, B. Identification of an HV 1 voltage-gated proton channel in insects. FEBS J. 2016, 283, 1453–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- DeCoursey, T.E.; Morgan, D.; Musset, B.; Cherny, V.V. Insights into the structure and function of HV1 from a meta-analysis of mutation studies. J. Gen. Physiol. 2016, 148, 97–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmona, E.M.; Larsson, H.P.; Neely, A.; Alvarez, O.; Latorre, R.; Gonzalez, C. Gating charge displacement in a monomeric voltage-gated proton (Hv1) channel. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 9240–9245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, M.; Alvear-Arias, J.J.; Carmona, E.M.; Carrillo, C.; Pena-Pichicoi, A.; Hernandez-Ochoa, E.O.; Neely, A.; Alvarez, O.; Latorre, R.; Garate, J.A.; et al. Trapping Charge Mechanism in Hv1 Channels (CiHv1). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 25, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musset, B.; Decoursey, T. Biophysical properties of the voltage gated proton channel HV1. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Membr. Transp. Signal. 2012, 1, 605–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, F.; Rebolledo, S.; Gonzalez, C.; Larsson, H.P. Subunit interactions during cooperative opening of voltage-gated proton channels. Neuron 2013, 77, 288–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papp, F.; Toombes, G.E.S.; Petho, Z.; Bagosi, A.; Feher, A.; Almassy, J.; Borrego, J.; Kuki, A.; Keki, S.; Panyi, G.; et al. Multiple mechanisms contribute to fluorometry signals from the voltage-gated proton channel. Commun. Biol. 2022, 5, 1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherny, V.V.; Markin, V.S.; DeCoursey, T.E. The voltage-activated hydrogen ion conductance in rat alveolar epithelial cells is determined by the pH gradient. J. Gen. Physiol. 1995, 105, 861–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangel-Yescas, G.; Cervantes, C.; Cervantes-Rocha, M.A.; Suarez-Delgado, E.; Banaszak, A.T.; Maldonado, E.; Ramsey, I.S.; Rosenbaum, T.; Islas, L.D. Discovery and characterization of Hv1-type proton channels in reef-building corals. eLife 2021, 10, e69248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaves, G.; Bungert-Plumke, S.; Franzen, A.; Mahorivska, I.; Musset, B. Zinc modulation of proton currents in a new voltage-gated proton channel suggests a mechanism of inhibition. FEBS J. 2020, 287, 4996–5018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villalba-Galea, C.A. Hv1 proton channel opening is preceded by a voltage-independent transition. Biophys. J. 2014, 107, 1564–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- DeCoursey, T.E. Voltage and pH sensing by the voltage-gated proton channel, HV1. J. R. Soc. Interface 2018, 15, 20180108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Droste, A.; Chaves, G.; Stein, S.; Trzmiel, A.; Schweizer, M.; Karl, H.; Musset, B. Zinc accelerates respiratory burst termination in human PMN. Redox Biol. 2021, 47, 102133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzio, E.A.; Smith, B.; Soliman, K.F. Evaluation of endogenous acidic metabolic products associated with carbohydrate metabolism in tumor cells. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 2010, 26, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeCoursey, T.E.; Morgan, D.; Cherny, V.V. The voltage dependence of NADPH oxidase reveals why phagocytes need proton channels. Nature 2003, 422, 531–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, D.; Capasso, M.; Musset, B.; Cherny, V.V.; Rios, E.; Dyer, M.J.; DeCoursey, T.E. Voltage-gated proton channels maintain pH in human neutrophils during phagocytosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 18022–18027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Chemaly, A.; Okochi, Y.; Sasaki, M.; Arnaudeau, S.; Okamura, Y.; Demaurex, N. VSOP/Hv1 proton channels sustain calcium entry, neutrophil migration, and superoxide production by limiting cell depolarization and acidification. J. Exp. Med. 2010, 207, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, A.; Pupo, A.; Mena-Ulecia, K.; Gonzalez, C. Pharmacological Modulation of Proton Channel Hv1 in Cancer Therapy: Future Perspectives. Mol. Pharmacol. 2016, 90, 385–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvear-Arias, J.J.; Pena-Pichicoi, A.; Carrillo, C.; Fernandez, M.; Gonzalez, T.; Garate, J.A.; Gonzalez, C. Role of voltage-gated proton channel (Hv1) in cancer biology. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1175702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, F.; Casares, N.; Martin-Otal, C.; Lasarte-Cia, A.; Gorraiz, M.; Sarrion, P.; Llopiz, D.; Reparaz, D.; Varo, N.; Rodriguez-Madoz, J.R.; et al. Overcoming T cell dysfunction in acidic pH to enhance adoptive T cell transfer immunotherapy. Oncoimmunology 2022, 11, 2070337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Luo, Y.; Liao, P.; Zuo, Y.; Jiang, R. Role of the Voltage-Gated Proton Channel Hv1 in Nervous Systems. Neurosci. Bull. 2023, 39, 1157–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Li, S.J. Zn2+ induces apoptosis in human highly metastatic SHG-44 glioma cells, through inhibiting activity of the voltage-gated proton channel Hv1. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 438, 312–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cozzolino, M.; Gyongyosi, A.; Korpos, E.; Gogolak, P.; Naseem, M.U.; Kallai, J.; Lanyi, A.; Panyi, G. The Voltage-Gated Hv1 H+ Channel Is Expressed in Tumor-Infiltrating Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, R.; Kennedy, K.; De Blas, G.A.; Orta, G.; Pavarotti, M.A.; Arias, R.J.; de la Vega-Beltran, J.L.; Li, Q.; Dai, H.; Perozo, E.; et al. Role of human Hv1 channels in sperm capacitation and white blood cell respiratory burst established by a designed peptide inhibitor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E11847–E11856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Ren, Y.; Mo, Y.; Guo, P.; Liao, P.; Luo, Y.; Mu, J.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; et al. Inhibiting Hv1 channel in peripheral sensory neurons attenuates chronic inflammatory pain and opioid side effects. Cell Res. 2022, 32, 461–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawanabe, A.; Okamura, Y. Effects of unsaturated fatty acids on the kinetics of voltage-gated proton channels heterologously expressed in cultured cells. J. Physiol. 2016, 594, 595–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szanto, T.G.; Feher, A.; Korpos, E.; Gyöngyösi, A.; Kállai, J.; Mészáros, B.; Ovari, K.; Lányi, Á.; Panyi, G.; Varga, Z. 5-Chloro-2-Guanidinobenzimidazole (ClGBI) Is a Non-Selective Inhibitor of the Human HV1 Channel. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; He, H.; Qi, M.; Jiang, Z.; Lin, B.; Wang, X.; Wang, D.; Ma, M.; Jiang, W.; Zhou, R. A small molecule directly targets NLRP3 to promote inflammasome activation and antitumor immunity. Cell Death Dis. 2025, 16, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bare, D.J.; Cherny, V.V.; DeCoursey, T.E.; Abukhdeir, A.M.; Morgan, D. Expression and function of voltage gated proton channels (Hv1) in MDA-MB-231 cells. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0227522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, S.J.; Wu, X.; Che, Y.; Li, Q. Clinicopathological and biological significance of human voltage-gated proton channel Hv1 protein overexpression in breast cancer. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 13877–13888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jardin, C.; Derst, C.; Franzen, A.; Mahorivska, I.; DeCoursey, T.E.; Musset, B.; Chaves, G. Biophysical Properties of Somatic Cancer Mutations in the S4 Transmembrane Segment of the Human Voltage-Gated Proton Channel hHV1. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Shen, R.; Dai, H.; Perozo, E.; Goldstein, S.A.N. Molecular determinants of inhibition of the human proton channel hHv1 by the designer peptide C6 and a bivalent derivative. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2120750119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petho, Z.; Pajtas, D.; Piga, M.; Magyar, Z.; Zakany, F.; Kovacs, T.; Zidar, N.; Panyi, G.; Varga, Z.; Papp, F. A synthetic flavonoid derivate in the plasma membrane transforms the voltage-clamp fluorometry signal of CiHv1. FEBS J. 2024, 291, 2354–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alabi, A.A.; Bahamonde, M.I.; Jung, H.J.; Kim, J.I.; Swartz, K.J. Portability of paddle motif function and pharmacology in voltage sensors. Nature 2007, 450, 370–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.H.; Marszalec, W.; Kai, L.; Yeh, J.Z.; Narahashi, T. Antidepressants inhibit proton currents and tumor necrosis factor-alpha production in BV2 microglial cells. Brain Res. 2012, 1435, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, H.; Song, J.H. Antipsychotics, chlorpromazine and haloperidol inhibit voltage-gated proton currents in BV2 microglial cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 738, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, D.; Yang, Y.; Xiao, Z.; Xu, J.; Yang, Q.; Dai, H.; Liang, S.; Tang, C.; Dong, H.; Liu, Z. Scorpion toxin inhibits the voltage-gated proton channel using a Zn2+-like long-range conformational coupling mechanism. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 177, 2351–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahpeymaei, A.; Mehrabi, S.; Csoti, A.; Borrego, J.; Husain, S.; Teshome, R.T.; Cardoso-Arenas, S.; Clement, H.; Arenas, I.; Panyi, G.; et al. Two peptides from tarantula venom inhibit the human voltage-gated proton channel by a unique mechanism. Authorea 2025. [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Park, M.; Song, J.H. (−)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate inhibits voltage-gated proton currents in BV2 microglial cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 698, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, S.P.H.; Mathie, A.A.; Peters, J.A.; Veale, E.L.; Striessnig, J.; Kelly, E.; Armstrong, J.F.; Faccenda, E.; Harding, S.D.; Davies, J.A.; et al. The Concise Guide to PHARMACOLOGY 2023/24: Ion channels. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2023, 180 (Suppl. S2), S145–S222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piga, M.; Varga, Z.; Feher, A.; Papp, F.; Korpos, E.; Bangera, K.C.; Frlan, R.; Ilas, J.; Dernovsek, J.; Tomasic, T.; et al. Identification of a Novel Structural Class of HV1 Inhibitors by Structure-Based Virtual Screening. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2024, 64, 4850–4862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.; Kim, J.; Song, J.H. Clozapine and olanzapine inhibit proton currents in BV2 microglial cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 755, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Hong, L.; Galpin, J.D.; Riahi, S.; Lim, V.T.; Webster, P.D.; Tobias, D.J.; Ahern, C.A.; Tombola, F. HIFs: New arginine mimic inhibitors of the Hv1 channel with improved VSD-ligand interactions. J. Gen. Physiol. 2021, 153, e202012832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, L.; Kim, I.H.; Tombola, F. Molecular determinants of Hv1 proton channel inhibition by guanidine derivatives. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 9971–9976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, L.; Pathak, M.M.; Kim, I.H.; Ta, D.; Tombola, F. Voltage-sensing domain of voltage-gated proton channel Hv1 shares mechanism of block with pore domains. Neuron 2013, 77, 274–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kornilov, P.; Peretz, A.; Lee, Y.; Son, K.; Lee, J.H.; Refaeli, B.; Roz, N.; Rehavi, M.; Choi, S.; Attali, B. Promiscuous gating modifiers target the voltage sensor of Kv7.2, TRPV1, and Hv1 cation channels. FASEB J. 2014, 28, 2591–2602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Chemaly, A.; Jaquet, V.; Cambet, Y.; Caillon, A.; Cherpin, O.; Balafa, A.; Krause, K.H.; Demaurex, N. Discovery and validation of new Hv1 proton channel inhibitors with onco-therapeutic potential. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2023, 1870, 119415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.H.; Yeh, J.Z. Dextromethorphan inhibition of voltage-gated proton currents in BV2 microglial cells. Neurosci. Lett. 2012, 516, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Chu, X.P.; Goodson, R.; Gamel, P.; Peng, S.; Vance, J.; Wang, S. Cholesterol inhibits human voltage-gated proton channel hHv1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2205420119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Dai, H.; Arias, R.J.; De Blas, G.A.; Orta, G.; Pavarotti, M.A.; Shen, R.; Perozo, E.; Mayorga, L.S.; Darszon, A.; et al. Direct activation of the proton channel by albumin leads to human sperm capacitation and sustained release of inflammatory mediators by neutrophils. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chae, M.R.; Kang, S.J.; Lee, K.P.; Choi, B.R.; Kim, H.K.; Park, J.K.; Kim, C.Y.; Lee, S.W. Onion (Allium cepa L.) peel extract (OPE) regulates human sperm motility via protein kinase C-mediated activation of the human voltage-gated proton channel. Andrology 2017, 5, 979–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherny, V.V.; DeCoursey, T.E. pH-dependent inhibition of voltage-gated H+ currents in rat alveolar epithelial cells by Zn2+ and other divalent cations. J. Gen. Physiol. 1999, 114, 819–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, F.; Chamberlin, A.; Watkins, B.M.; Ionescu, A.; Perez, M.E.; Barro-Soria, R.; González, C.; Noskov, S.Y.; Larsson, H.P. Molecular mechanism of Zn2+ inhibition of a voltage-gated proton channel. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E5962–E5971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jardin, C.; Chaves, G.; Musset, B. Assessing Structural Determinants of Zn2+ Binding to Human HV1 via Multiple MD Simulations. Biophys. J. 2020, 118, 1221–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musset, B.; Smith, S.M.; Rajan, S.; Cherny, V.V.; Sujai, S.; Morgan, D.; DeCoursey, T.E. Zinc inhibition of monomeric and dimeric proton channels suggests cooperative gating. J. Physiol. 2010, 588 Pt 9, 1435–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.; Applewhite, S.; DeCata, J.; Jones, S.; Cummings, J.; Wang, S. Arachidonic acid reverses cholesterol and zinc inhibition of human voltage-gated proton channels. J. Biol. Chem. 2023, 299, 104918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayuyan, A.G.; Cherny, V.V.; Chaves, G.; Musset, B.; Cohen, F.S.; DeCoursey, T.E. Interaction with stomatin directs human proton channels into cholesterol-dependent membrane domains. Biophys. J. 2024, 123, 4180–4190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, V.T.; Geragotelis, A.D.; Lim, N.M.; Freites, J.A.; Tombola, F.; Mobley, D.L.; Tobias, D.J. Insights on small molecule binding to the Hv1 proton channel from free energy calculations with molecular dynamics simulations. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 13587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pupo, A.; Gonzalez León, C. In pursuit of an inhibitory drug for the proton channel. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 9673–9674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuura, T.; Mori, T.; Hasaka, M.; Kuno, M.; Kawawaki, J.; Nishikawa, K.; Narahashi, T.; Sawada, M.; Asada, A. Inhibition of voltage-gated proton channels by local anaesthetics in GMI-R1 rat microglia. J. Physiol. 2012, 590, 827–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szteyn, K.; Yang, W.; Schmid, E.; Lang, F.; Shumilina, E. Lipopolysaccharide-sensitive H+ current in dendritic cells. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2012, 303, C204–C212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, D.; Cherny, V.V.; Finnegan, A.; Bollinger, J.; Gelb, M.H.; DeCoursey, T.E. Sustained activation of proton channels and NADPH oxidase in human eosinophils and murine granulocytes requires PKC but not cPLA2 alpha activity. J. Physiol. 2007, 579 Pt 2, 327–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Compound | Type | IC50 | Effect on the Channel | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Peptide C6 | Peptide | 31 nM | Inhibitor (ec) | [71] |
| Oxopench | Small molecule | 819 nM | Inhibitor | [72] |
| Zn2+ | Cation | 1.9 µM | Inhibitor (ec) | [3] |
| Hanatoxin | Peptide | 2 µM | Inhibitor (memb) | [73] |
| Fluoxetine | Small molecule | 2.1 µM | Inhibitor (ic) | [74] |
| Chlorpromazine | Small molecule | 2.2 µM | Inhibitor (ic) | [75] |
| AGAP/W38F | Peptide | 2.5 µM | Inhibitor (ec) | [76] |
| Gr1b/GsAF-l | Peptide | 3.2 µM | Inhibitor (ec) | [77] |
| Gr2c/GsAF-ll | Peptide | 3.6 µM | Inhibitor (ec) | [77] |
| Epigallocatechin | Small molecule | 3.7 µM | Inhibitor (ic) | [78] |
| Cd2+ | Cation | 5 µM | Inhibitor (ec) | [79] |
| Imipramine | Small molecule | 5.7 µM | Inhibitor (ic) | [74] |
| Mitriptyline | Small molecule | 5.8 µM | Inhibitor (ic) | [74] |
| Haloperidol | Small molecule | 8.4 µM | Inhibitor (ic) | [75] |
| 13 | Small molecule | 8.5 µM | Inhibitor (ic) | [80] |
| Clozapine | Small molecule | 9.8 µM | Inhibitor (ic) | [81] |
| Desipramine | Small molecule | <10 µM | Inhibitor (ic) | [74] |
| HIF | Small molecule | 26 µM | Inhibitor (ic) | [82] |
| ClGBI | Small molecule | 26.3 µM | Inhibitor (ic) | [83] |
| 2GBI | Small molecule | 38 µM | Inhibitor (ic) | [84] |
| NH17 | Small molecule | >50 µM | Inhibitor (ic) | [85] |
| PNX52429 | Small molecule | >50 µM | Inhibitor | [86] |
| PNX61442 | Small molecule | 50 µM | Inhibitor | [86] |
| Dextromethorphan | Small molecule | 51.7 µM | Inhibitor (ic) | [87] |
| Olanzapine | Small molecule | 84 µM | Inhibitor (ic) | [81] |
| Cholesterol | Lipid | ~10% (wt/wt, to total membrane lipids) | Inhibitor (memb) | [88] |
| Albumin | Protein | 158 µM | Activator (ec) | [89] |
| Arachidonic acid | Lipid | 10-100 µM | Activator (memb) | [65] |
| NH29 | Small molecule | 50 µM | Activator | [85] |
| OPE (onion peel extract) | Organic extract | 30 µg/ml | Activator (ec) | [90] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Borrego, J.; Mészáros, B.; Szanto, T.G.; Teshome, R.T.; Korpos, É.; Varga, Z.; Papp, F. Modulators of the Human Voltage-Gated Proton Channel Hv1. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 1480. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18101480
Borrego J, Mészáros B, Szanto TG, Teshome RT, Korpos É, Varga Z, Papp F. Modulators of the Human Voltage-Gated Proton Channel Hv1. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(10):1480. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18101480
Chicago/Turabian StyleBorrego, Jesús, Beáta Mészáros, Tibor G. Szanto, Russo Teklu Teshome, Éva Korpos, Zoltan Varga, and Ferenc Papp. 2025. "Modulators of the Human Voltage-Gated Proton Channel Hv1" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 10: 1480. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18101480
APA StyleBorrego, J., Mészáros, B., Szanto, T. G., Teshome, R. T., Korpos, É., Varga, Z., & Papp, F. (2025). Modulators of the Human Voltage-Gated Proton Channel Hv1. Pharmaceuticals, 18(10), 1480. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18101480







