Optimizing Lenvatinib Therapy for Prognostic Improvement in Advanced Thyroid Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Strategies to Maximize Therapeutic Benefit of First-Line LEN Therapy
2.1. Mechanism of Action of LEN
2.2. Clinical Evidence from SELECT, Real-World Data, and Comparisons
2.3. Timing of Treatment Initiation
2.4. Optimization of Dosing Strategies
2.5. Limitations in Specific Patient Subgroups
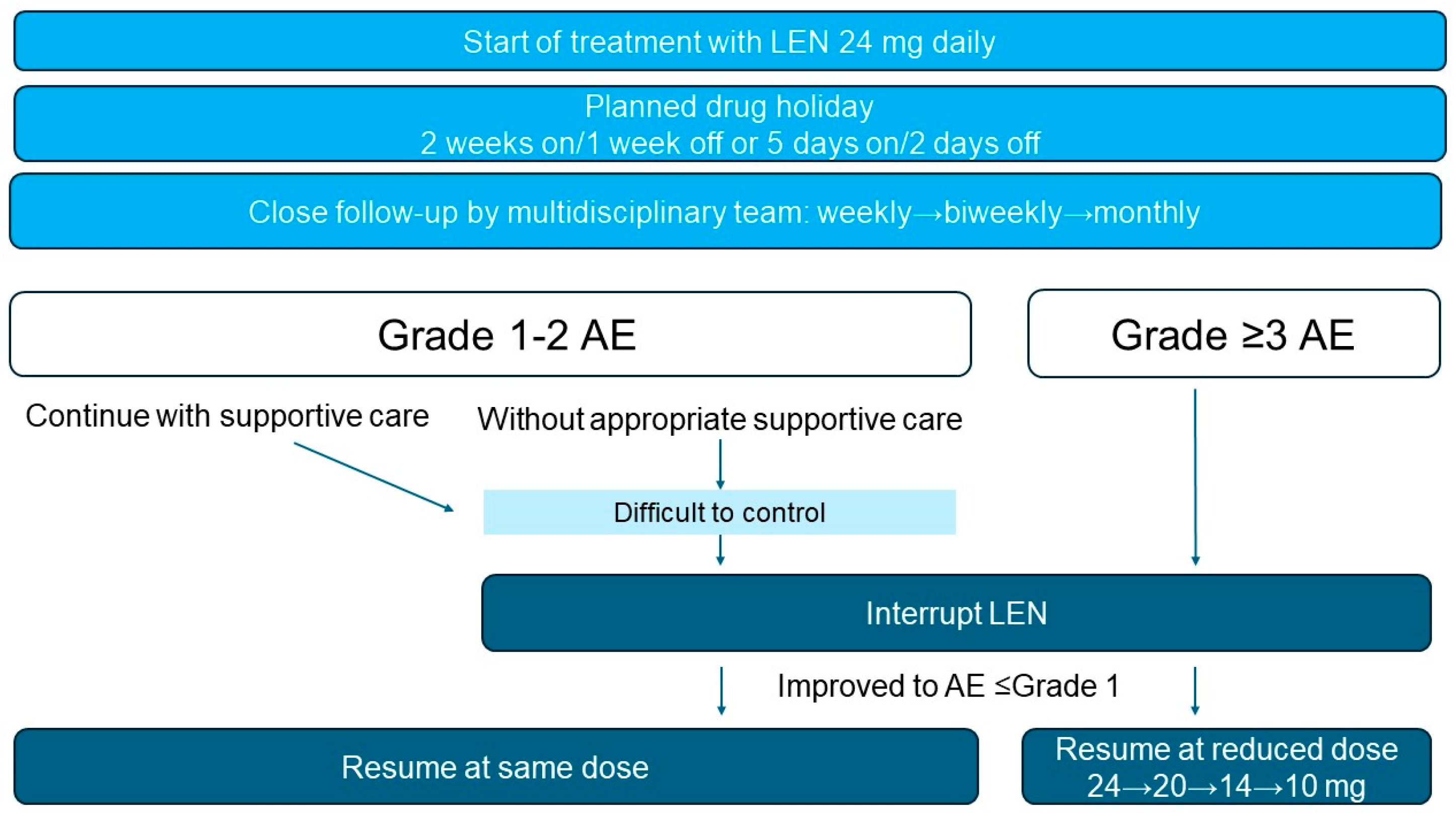
2.6. Adverse Event Management
2.7. Planned Drug Holidays
2.8. Dose Adjustment and Rechallenge
3. Expanding Clinical Utility and Future Perspectives
3.1. Emerging Biomarkers
3.2. Neoadjuvant Use
3.2.1. Clinical Experience and Real-World Applicability
3.2.2. Evidence from Prospective Trials and Other Malignancies
3.3. Combination with Immunotherapy
3.4. Remaining Challenges
4. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AE | Adverse event |
| CI | Confidence interval |
| eGFR | Estimated glomerular filtration rate |
| HR | Hazard ratio |
| ICI | Immune checkpoint inhibitor |
| LEN | Lenvatinib |
| MKI | Multi-target tyrosine kinase inhibitor |
| NCCN | National Comprehensive Cancer Network |
| NE | Not estimable |
| NLR | Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio |
| ORR | Objective response rate |
| OS | Overall survival |
| PBO | Placebo |
| PD | Progressive disease |
| PFS | Progression-free survival |
| PR | Partial response |
| PS | Performance status |
| RAI | Radioactive iodine |
| RAIR-DTC | Radioiodine-refractory differentiated thyroid cancer |
| RECIST v1.1 | Response evaluation criteria in solid tumors version 1.1 |
| TEAE | Treatment-emergent adverse event |
| TKI | Tyrosine kinase inhibitor |
| VEGF | Vascular endothelial growth factor |
| VEGFR | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor |
References
- Schlumberger, M.; Brose, M.; Elisei, R.; Leboulleux, S.; Luster, M.; Pitoia, F.; Pacini, F. Definition and management of radioactive iodine-refractory differentiated thyroid cancer. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2014, 2, 356–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brose, M.S.; Nutting, C.M.; Jarzab, B.; Elisei, R.; Siena, S.; Bastholt, L.; de la Fouchardiere, C.; Pacini, F.; Paschke, R.; Shong, Y.K.; et al. Sorafenib in radioactive iodine-refractory, locally advanced or metastatic differentiated thyroid cancer: A randomised, double-blind, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2014, 384, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlumberger, M.; Tahara, M.; Wirth, L.J.; Robinson, B.; Brose, M.S.; Elisei, R.; Habra, M.A.; Newbold, K.; Shah, M.H.; Hoff, A.O.; et al. Lenvatinib versus placebo in radioiodine-refractory thyroid cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 621–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, M. Molecular pathogenesis and mechanisms of thyroid cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2013, 13, 184–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, J.; Yamamoto, Y.; Funahashi, Y.; Tsuruoka, A.; Watanabe, T.; Wakabayashi, T.; Uenaka, T.; Asada, M. E7080, a novel inhibitor that targets multiple kinases, has potent antitumor activities against stem cell factor producing human small cell lung cancer H146, based on angiogenesis inhibition. Int. J. Cancer. 2008, 122, 664–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stjepanovic, N.; Capdevila, J. Multikinase inhibitors in the treatment of thyroid cancer: Specific role of lenvatinib. Biol. Targets Ther. 2014, 8, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Worden, F.; Rajkovic-Hooley, O.; Reynolds, N.; Milligan, G.; Zhang, J. Real-world treatment patterns and clinical outcomes in patients with radioiodine-refractory differentiated thyroid cancer (RAI-R DTC) treated with first line lenvatinib monotherapy in the United States. Endocrine 2024, 84, 663–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NCCN. Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines®). Thyroid Carcinoma. Version 2.2024; National Comprehensive Cancer Network: Fort Washington, PA, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Brose, M.S.; Robinson, B.; Sherman, S.I.; Jarzab, B.; Lin, C.-C.; Vaisman, F.; Hoff, A.O.; Hitre, E.; Bowles, D.W.; Sen, S.; et al. Cabozantinib for Previously Treated Radioiodine-Refractory Differentiated Thyroid Cancer: Updated Results from the Phase 3 COSMIC-311 Trial. Cancer 2022, 128, 4203–4212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brose, M.S.; Panaseykin, Y.; Konda, B.; de la Fouchardiere, C.; Hughes, B.G.M.; Gianoukakis, A.G.; Joo Park, Y.; Romanov, I.; Krzyzanowska, M.K.; Leboulleux, S.; et al. A randomized study of lenvatinib 18 mg vs 24 mg in patients with radioiodine-refractory differentiated thyroid cancer. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 107, 776–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tremblay, G.; Livings, C.; Crowe, L.; Kapetanakis, V.; Briggs, A. Determination of the most appropriate method for extrapolating overall survival data from a placebo-controlled clinical trial of lenvatinib for progressive, radioiodine-refractory differentiated thyroid cancer. Clin. Outcomes Res. 2016, 8, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahara, M.; Kiyota, N.; Hoff, A.O.; Badiu, C.; Owonikoko, T.K.; Dutcus, C.E.; Suzuki, T.; Ren, M.; Wirth, L.J. Impact of lung metastases on overall survival in the phase 3 SELECT study of lenvatinib in patients with radioiodine-refractory differentiated thyroid cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 2021, 147, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brose, M.S.; Worden, F.P.; Newbold, K.L.; Guo, M.; Hurria, A. Effect of age on the efficacy and safety of lenvatinib in radioiodine-refractory differentiated thyroid cancer in the phase III SELECT trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 2692–2699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, R.I.; Schlumberger, M.; Wirth, L.J.; Sherman, E.J.; Shah, M.H.; Robinson, B.; Dutcus, C.E.; Teng, A.; Gianoukakis, A.G.; Sherman, S.I. Incidence and timing of common adverse events in Lenvatinib-treated patients from the SELECT trial and their association with survival outcomes. Endocrine 2017, 56, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiyota, N.; Tahara, M.; Robinson, B.; Schlumberger, M.; Sherman, S.I.; Leboulleux, S.; Lee, E.K.; Suzuki, T.; Ren, M.; Fushimi, K.; et al. Impact of baseline tumor burden on overall survival in patients with radioiodine-refractory differentiated thyroid cancer treated with lenvatinib in the SELECT global phase 3 trial. Cancer 2022, 128, 2281–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, M.H.; Takahashi, S.; Capdevila, J.; Tahara, M.; Leboulleux, S.; Kiyota, N.; Dutcus, C.E.; Xie, R.; Robinson, B.; Sherman, S.; et al. Correlation of performance status and neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio with efficacy in radioiodine-refractory differentiated thyroid cancer treated with lenvatinib. Thyroid 2021, 31, 1226–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, B.; Schlumberger, M.; Wirth, L.J.; Dutcus, C.E.; Song, J.; Taylor, M.H.; Kim, S.B.; Krzyzanowska, M.K.; Capdevila, J.; Sherman, S.I.; et al. Characterization of tumor size changes over time from the phase 3 study of lenvatinib in thyroid cancer. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 101, 4103–4109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suyama, K.; Murakami, D.; Fujiwara, S.; Takeshita, T.; Sueta, A.; Inao, T.; Yamamoto-Ibusuki, M.; Yamamoto, Y.; Shiraishi, S.; Iwase, H. Massive arterial bleeding after lenvatinib therapy for thyroid cancer. Int. J. Cancer Clin. Res. 2016, 3, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blevins, D.P.; Dadu, R.; Hu, M.; Baik, C.; Balachandran, D.; Ross, W.; Gunn, B.; Cabanillas, M.E. Aerodigestive fistula formation as a rare side effect of antiangiogenic tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy for thyroid cancer. Thyroid 2014, 24, 918–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wirth, L.J.; Tahara, M.; Robinson, B.; Francis, S.; Brose, M.S.; Habra, M.A.; Newbold, K.; Kiyota, N.; Dutcus, C.E.; Mathias, E.; et al. Treatment-emergent hypertension and efficacy in the phase 3 Study of (E7080) lenvatinib in differentiated cancer of the thyroid (SELECT). Cancer 2018, 124, 2365–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibutani, Y.; Suzuki, S.; Sagara, A.; Enokida, T.; Okano, S.; Fuzisawa, T.; Sato, F.; Yumoto, T.; Sano, M.; Kawasaki, T.; et al. Impact of lenvatinib-induced proteinuria and renal dysfunction in patients with thyroid cancer. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1154771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, S.; Kiyota, N.; Tahara, M. Optimal Use of Lenvatinib in the Treatment of Advanced Thyroid Cancer. Cancers Head Neck 2017, 2, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tahara, M. Management of recurrent or metastatic thyroid cancer. ESMO Open 2018, 3, e000359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, S.; Horinouchi, A.; Uozumi, S.; Matsuyama, C.; Kamata, H.; Kaneko, A.; Yamaguchi, M.; Okudera, H.; Tahara, M.; Kawasaki, T. Impact of outpatient pharmacy interventions on management of thyroid patients receiving lenvatinib. SAGE Open Med. 2020, 8, 2050312120930906. [Google Scholar]
- Tahara, M.; Brose, M.S.; Wirth, L.J.; Suzuki, T.; Miyagishi, H.; Fujino, K.; Dutcus, C.E.; Gianoukakis, A. Impact of dose interruption on the efficacy of lenvatinib in a phase 3 study in patients with radioiodine-refractory differentiated thyroid cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 2019, 106, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuyama, C.; Enokida, T.; Ueda, Y.; Suzuki, S.; Fujisawa, T.; Ito, K.; Okano, S.; Tahara, M. Planned drug holidays during treatment with lenvatinib for radioiodine-refractory differentiated thyroid cancer: A retrospective study. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1139659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahara, M.; Takami, H.; Ito, Y.; Okamoto, T.; Sugitani, I.; Sugino, K.; Takahashi, S.; Takeyama, H.; Tsutsui, H.; Hara, H.; et al. A prospective cohort study exploring the effect of lenvatinib planned drug holidays in treatment of differentiated thyroid cancer. Thyroid 2024, 34, 566–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuda, N.; Toda, K.; Wang, X.; Ohmoto, A.; Hayashi, N.; Urasaki, T.; Sato, Y.; Nakano, K.; Ono, M.; Tomomatsu, J.; et al. Prognostic significance of 8 weeks’ relative dose intensity of lenvatinib in treatment of radioiodine-refractory differentiated thyroid cancer patients. Endocr. J. 2021, 68, 639–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onaga, R.; Enokida, T.; Okano, S.; Fujisawa, T.; Tanaka, N.; Hoshi, Y.; Kishida, T.; Tanaka, H.; Sato, M.; Takeshita, N.; et al. Clinical impact of a dose-escalation strategy for lenvatinib in differentiated thyroid cancer. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 29, 1435–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kish, J.K.; Chatterjee, D.; Wan, Y.; Yu, H.T.; Liassou, D.; Feinberg, B.A. Lenvatinib and subsequent therapy for radioactive iodine-refractory differentiated thyroid cancer: A real-world study of clinical effectiveness in the United States. Adv. Ther. 2020, 37, 2841–2852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokota, T.; Hamauchi, S.; Kawakami, T.; Fushiki, K. Lenvatinib rechallenge after failure of lenvatinib and sorafenib in metastatic thyroid cancer. Investig. New Drugs 2024, 42, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohno, K.; Shibata, T.; Ito, K.I. Epidermal growth factor receptor activation confers resistance to lenvatinib in thyroid cancer cells. Cancer Sci. 2022, 113, 3193–3210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, W.; Chen, Y. Lenvatinib resistance mechanism and potential ways to conquer. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1153991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talpacci, E.; Morelli, S.; Leone, V.; Moretti, S.; Paci, M.; Bini, V.; Puxeddu, E. Predictors of Response to Lenvatinib in Advanced Differentiated Thyroid Cancer: Focus on the CONUT Score. Endocrine 2025, 89, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeuchi, S.; Hirata, K.; Magota, K.; Watanabe, S.; Moku, R.; Shiiya, A.; Taguchi, J.; Ariga, S.; Goda, T.; Ohhara, Y.; et al. Early Prediction of Treatment Outcome for Lenvatinib Using 18F-FDG PET/CT in Patients with Unresectable or Advanced Thyroid Carcinoma Refractory to Radioiodine Treatment: A Prospective, Multicentre, Non-Randomised Study. EJNMMI Res. 2023, 13, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, S.; Bychkov, A.; Jung, C.-K. Emerging Biomarkers in Thyroid Practice and Research. Cancers 2022, 14, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.Y.; Nixon, I.J.; Patel, S.G.; Palmer, F.L.; Tuttle, R.M.; Shaha, A.; Shah, J.P.; Ganly, I. Operative management of locally advanced, differentiated thyroid cancer. Surgery 2016, 160, 738–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenhauer, E.A.; Therasse, P.; Bogaerts, J.; Schwartz, L.H.; Sargent, D.; Ford, R.; Dancey, J.; Arbuck, S.; Gwyther, S.; Mooney, M.; et al. New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours: Revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur. J. Cancer 2009, 45, 228–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, B.; Bryant, J.; Wolmark, N.; Mamounas, E.; Brown, A.; Fisher, E.R.; Wickerham, D.L.; Begovic, M.; DeCillis, A.; Robidoux, A.; et al. Effect of preoperative chemotherapy on the outcome of women with operable breast cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 1998, 16, 16–2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortazar, P.; Zhang, L.; Untch, M.; Mehta, K.; Costantino, J.P.; Wolmark, N.; Bonnefoi, H.; Cameron, D.; Gianni, L.; Valagussa, P.; et al. Pathological complete response and long-term clinical benefit in breast cancer: The CTNeoBC pooled analysis. Lancet 2014, 384, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Hagen, P.; Hulshof, M.C.; van Lanschot, J.J.; Steyerberg, E.W.; van Berge Henegouwen, M.I.; Wijnhoven, B.P.; Richel, D.J.; Nieuwenhuijzen, G.A.; Hospers, G.A.; Bonenkamp, J.J.; et al. Preoperative chemoradiotherapy for esophageal or junctional cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 2074–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Advanced Bladder Cancer Meta-analysis Collaboration. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy in invasive bladder cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet 2003, 361, 1927–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grossman, H.B.; Natale, R.B.; Tangen, C.M.; Speights, V.O.; Vogelzang, N.J.; Trump, D.L.; deVere White, R.W.; Sarosdy, M.F.; Wood, D.P., Jr.; Raghavan, D.; et al. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy plus cystectomy compared with cystectomy alone for locally advanced bladder cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 349, 859–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.A.; Zhou, N.K.; Wang, W.; Chu, X.Y.; Liang, C.Y.; Tian, X.D.; Guo, J.T.; Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Dai, W.M. Survival benefit of neoadjuvant chemotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer: An updated meta-analysis of 13 randomized control trials. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2010, 5, 510–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasaki, H.; Toda, S.; Ito, H.; Nemoto, D.; Murayama, D.; Okubo, Y.; Hayashi, H.; Yokose, T. A case of unresectable papillary thyroid carcinoma treated with lenvatinib as neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Case Rep. Endocrinol. 2020, 2020, 6438352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasaki, H.; Toda, S.; Murayama, D.; Matsui, A.; Kadoya, M. Preoperative neoadjuvant targeted therapy with lenvatinib for inoperable thyroid cancer. Med. Case Rep. Study Protoc. 2022, 3, e0240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gay, S.; Monti, E.; Antonelli, C.T.; Mora, M.; Spina, B.; Ansaldo, G.; Teliti, M.; Comina, M.; Conte, L.; Minuto, M.; et al. Case report: Lenvatinib in neoadjuvant setting in a patient affected by invasive poorly differentiated thyroid carcinoma. Future Oncol. 2019, 15, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, K.E.; Strachan, M.W.J.; Srinivasan, D.; MacNeill, M.; Wall, L.; Nixon, I.J. Tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy in locally advanced differentiated thyroid cancer: A case report. Eur. Thyroid. J. 2019, 8, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuboi, M.; Takizawa, H.; Aoyama, M.; Tangoku, A. Surgical treatment of locally advanced papillary thyroid carcinoma after response to lenvatinib: A case report. Int. J. Surg. Case Rep. 2017, 41, 89–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alshehri, K.; Alqurashi, Y.; Merdad, M.; Samargandy, S.; Daghistani, R.; Marzouki, H. Neoadjuvant lenvatinib for inoperable thyroid cancer: A case report and literature review. Cancer Rep. 2022, 5, e1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, H.; Kajita, S.; Yokota, M.; Sengoku, N.; Sangai, T. Neoadjuvant use of lenvatinib in locally advanced papillary thyroid carcinoma involving critical vessels. Int. J. Endocr. Oncol. 2020, 7, IJE33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichida, A.; Arita, J.; Hatano, E.; Eguchi, S.; Saiura, A.; Nagano, H.; Shindoh, J.; Hashimoto, M.; Takemura, N.; Taura, K.; et al. A multicenter phase 2 trial evaluating the efficacy and safety of preoperative lenvatinib therapy for patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (LENS-HCC Trial). Liver Cancer 2023, 13, 322–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Wu, Y. 2227P The efficacy and safety of lenvatinib in neoadjuvant therapy in patients with locally advanced thyroid cancer: A single-arm phase II clinical trial. Ann. Oncol. 2023, 34 (Suppl. 2), S1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, N.S.; Wei, W.J.; Xiang, J.; Chen, J.Y.; Guan, Q.; Lu, Z.W.; Ma, B.; Sun, G.H.; Wang, Y.L.; Ji, Q.H.; et al. The efficacy and safety of anlotinib in neoadjuvant treatment of locally advanced thyroid cancer: A single-arm phase II clinical trial. Thyroid 2021, 31, 1808–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.Y.; Huang, N.S.; Wei, W.J.; Hu, J.Q.; Cao, Y.M.; Shen, Q.; Lu, Z.W.; Wang, Y.L.; Wang, Y.; Ji, Q.H. The efficacy and safety of surufatinib combined with anti PD-1 antibody toripalimab in neoadjuvant treatment of locally advanced differentiated thyroid cancer: A phase II study. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2023, 30, 7172–7180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, T.; Kato, Y.; Ozawa, Y.; Kodama, K.; Ito, J.; Ichikawa, K.; Yamada, K.; Hori, Y.; Tabata, K.; Takase, K.; et al. Immunomodulatory activity of lenvatinib contributes to antitumor activity in the Hepa1-6 hepatocellular carcinoma model. Cancer Sci. 2018, 109, 3993–4002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Jin, J.; Du, Q.; Hu, M.; Wei, Y.; Wang, M.; Li, H.; Li, Q. Multi-omics analysis of the anti-tumor synergistic mechanism and potential application of immune checkpoint blockade combined with lenvatinib. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 730240. [Google Scholar]
- French, J.D.; Haugen, B.R.; Worden, F.P.; Bowles, D.W.; Gianoukakis, A.G.; Konda, B.; Dadu, R.; Sherman, E.J.; McCue, S.; Foster, N.R.; et al. Combination targeted therapy with pembrolizumab and lenvatinib in progressive, radioiodine-refractory differentiated thyroid cancers. Clin. Cancer Res. 2024, 30, 3757–3767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehnert, J.M.; Varga, A.; Brose, M.S.; Aggarwal, R.R.; Lin, C.-C.; Prawira, A.; de Braud, F.; Tamura, K.; Doi, T.; Piha-Paul, S.A.; et al. Safety and antitumor activity of the anti–PD-1 antibody pembrolizumab in patients with advanced, PD-L1–positive papillary or follicular thyroid cancer: Results from the phase Ib KEYNOTE-028 trial. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamidi, S.; Hamidi, S.; Hofmann, M.C.; Iyer, P.C.; Cabanillas, M.E.; Hu, M.I.; Busaidy, N.L.; Dadu, R.; Hofmann, M.C. Review article: New treatments for advanced differentiated thyroid cancers and potential mechanisms of drug resistance. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1176731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Trial (ClinicalTrials.gov No.) | Phase/Design | Enrolled Patients | Population | Intervention vs./Control | Primary Endpoint | Key Efficacy Outcomes | Key Grade ≥ 3 AEs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SELECT (NCT0132554) | Phase III, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter | 392 (LEN 261, PBO 131) | RAIR-DTC with radiographic progression ≤13 months; ECOG PS 0–2 | Lenvatinib 24 mg QD vs. placebo | PFS (RECIST v1.1) | Median PFS: 18.3 vs. 3.6 months; HR 0.21 (95% CI 0.14–0.31, p < 0.001). ORR: 64.8% vs. 1.5% | Hypertension (44%), proteinuria (31%), diarrhea (8%), weight loss (10%), decreased appetite (5%) |
| DECISION (NCT00984282) | Phase III, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter | 417 (SOR 207, PBO 210) | Progressive RAIR-DTC; no prior TKI | Sorafenib 400 mg BID vs. placebo | PFS | Median PFS: 10.8 vs. 5.8 months; HR 0.59 (95% CI 0.45–0.76, p < 0.0001). ORR: 12.2% vs. 0.5% | Hand–foot skin reaction (20%), hypertension (9%), diarrhea (6%), hypocalcemia (4%) |
| COSMIC-311 (NCT03690388) | Phase III, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter | 258 (Cabo 170, PBO 88) | RAIR-DTC previously treated with VEGFR-targeted TKI (lenvatinib or sorafenib) | Cabozantinib 60 mg QD vs. placebo | PFS and ORR (blinded independent review) | Median PFS: 11.0 vs. 1.9 months; HR 0.22 (95% CI 0.15–0.32, p < 0.0001). ORR: 11.0% vs. 0%, p = 0.0003 | Palmar–plantar erythrodysesthesia (10%), hypertension (9%), diarrhea (7%), fatigue (6%), hypocalcemia (3%) |
| Brose 2022 [10] (NCT02702388) | Phase II, randomized, open-label | 152 (LEN 18 mg 76, LEN 24 mg 76) | RAIR-DTC, TKI-naïve | LEN 18 mg vs. 24 mg | ORR at 24 weeks and frequency of grade ≥3 TEAEs at 24 weeks | ORR 40.3%(18 mg) vs. 57.3%(24 mg); odds ratio (18/24) 0.50 (95% CI 0.26–0.96); Grade ≥ 3 TEAEs at 24 weeks: 57.1% vs. 61.3%; | Hypertension 15%(18 mg) vs. 19%(24 mg), proteinuria 4%(18 mg) vs. 5%(24 mg), and Asthenia 4%(18 mg) vs. 2%(24 mg) |
| Worden 2024 [7] | Real-world, retrospective, multicenter (U.S.) | 308 | RAIR-DTC, first-line Lenvatinib monotherapy | Lenvatinib (initial dose 24 mg QD in 62% of patients) | Real-world outcomes | rwBOR 72.4% (CR + PR); median rwPFS 49.0 months; OS rates: 78.4% at 24 months, 57.0% at 72 months; median OS not reached | Not reported |
| Progression-Free | Overall Survival | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| RAIR-DTC | HR, 0.20 (0.14–0.31) p < 0.001 | ≥65 years | HR, 0.53 (0.31–0.91) p = 0.020 |
| Lung metastasis ≥10 mm | HR, 0.20 (0.15–0.27) p < 0.0001 | Follicular thyroid cancer | HR, 0.36 (0.19–0.68) p = 0.002 |
| Lung metastasis ≥10 mm | HR, 0.63 (0.47–0.85) p = 0.025 | ||
| Baseline tumor burden ≥40 mm | HR, 0.42 (0.28–0.63) p = NE | ||
| Progression-Free Survival | Overall Survival | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance status 0 vs. 1 | HR, 0.52 (0.35–0.77) p = 0.001 | Performance status 0 vs. 1 | HR, 0.42 (0.26–0.69) p = 0.0004 |
| NLR ≤ 3 vs. >3 | HR, 0.43 (0.29–0.65) p < 0.0001 | NLR ≤ 3 vs. >3 | HR, 0.48 (0.29–0.78) p = 0.0 |
| Baseline tumor burden ≤40 mm vs. >40 mm | HR, 0.42 (0.28–0.63) p = NE | ||
| First Author | Age | Sex | Histology | TNM | Pretreatment Before LEN | Initial LEN Dose (mg) | Outcome | Treatment Duration | Off-Treatment Period | Surgery | Adjuvant Therapy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Iwasaki H | 72 | F | PTC | T4bN1bM1 | None | 20 | 30.8% reduction | 4.7 mo | 7 days | Yes | No |
| Iwasaki H | 72 | F | PTC | T4aN1bM0 | None | 14 | 20.0% reduction | 3.1 mo | 5 days | Yes | RAI |
| Iwasaki H | 68 | M | FTC | T4aN1bM1 | None | 24 | 33.3% reduction | 2.9 mo | 5 days | Yes | RAI |
| Iwasaki H | 61 | F | ATC | T4aN1bM1 | None | 24 | 42.0% reduction | 2.0 mo | 4 days | Yes | EBRT |
| Iwasaki H | 66 | F | PTC/ATC | T4aN1bM0 | None | 24 | 32.6% reduction | 1.7 mo | 10 days | Yes | No |
| Gay S | 81 | F | PDTC | T4aNXM0 | EBRT 20Gy | 10 | Reduction, improvement in vocal function | 8 w | 2 w | Yes | No |
| Stewart KE | 73 | F | PTC | T4aN0M1 | Sorafenib 800 mg × 4 w | 24 | 31 × 59 × 32 mm → 17 × 28 × 22 mm | 14 w | 2 w | Yes | No |
| Tsuboi M | 73 | M | PTC | T4aN1bM0 | None | 14 | Primary tumor 84% reduction, LN 45% reduction | 22 w | 17 days | Yes | RAI |
| Alshehri K | 56 | F | Not stated | — | EBRT 40Gy → Paclitaxel+Carboplatin → Doxorubicin → Sorafenib | 10 | 90 × 90 × 44 mm → 72 × 66 × 37 mm | 2.0 mo | 4 w | Yes | No |
| Katoh H | 65 | F | PTC | T4bNXM0 | None | 24 | 40% reduction | 2 w | 10 mo | Yes | No |
| Golingan H | 66 | F | MTC | — | None | 20 | 70% reduction | 4 mo | 3 days | Yes | No |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wakasugi, T. Optimizing Lenvatinib Therapy for Prognostic Improvement in Advanced Thyroid Cancer. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 1432. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18101432
Wakasugi T. Optimizing Lenvatinib Therapy for Prognostic Improvement in Advanced Thyroid Cancer. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(10):1432. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18101432
Chicago/Turabian StyleWakasugi, Tetsuro. 2025. "Optimizing Lenvatinib Therapy for Prognostic Improvement in Advanced Thyroid Cancer" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 10: 1432. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18101432
APA StyleWakasugi, T. (2025). Optimizing Lenvatinib Therapy for Prognostic Improvement in Advanced Thyroid Cancer. Pharmaceuticals, 18(10), 1432. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18101432






