Structural Basis for Monoclonal Antibody Therapy for Transthyretin Amyloidosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Mechanisms of Action of Silencers, Stabilizers, and Depleters
3. Antibodies to TTR and Their Binding Specificities
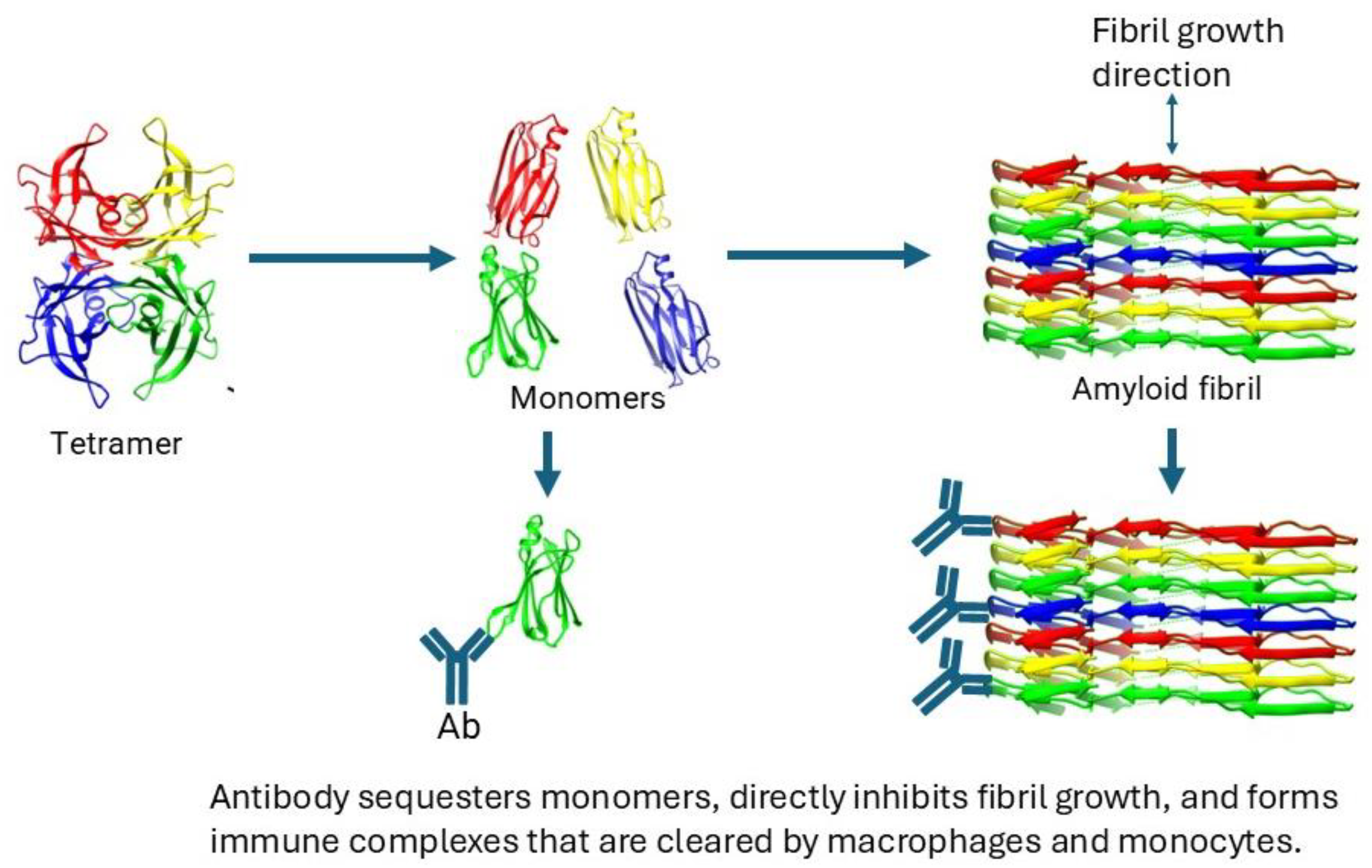
4. ATTR Depleter Antibodies in Clinical Trials
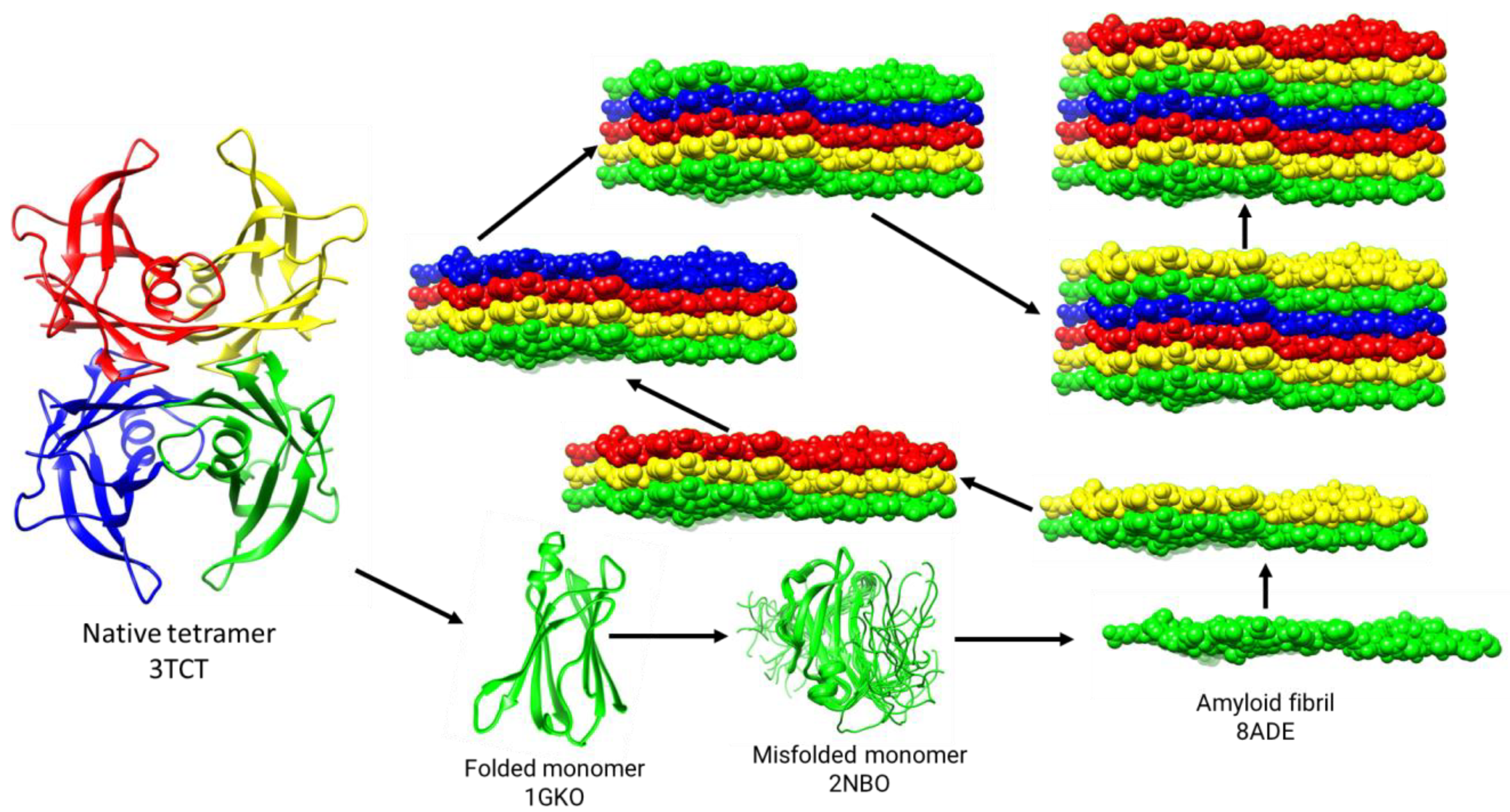
5. Cryo-EM Structure of the TTR Amyloid Fibril
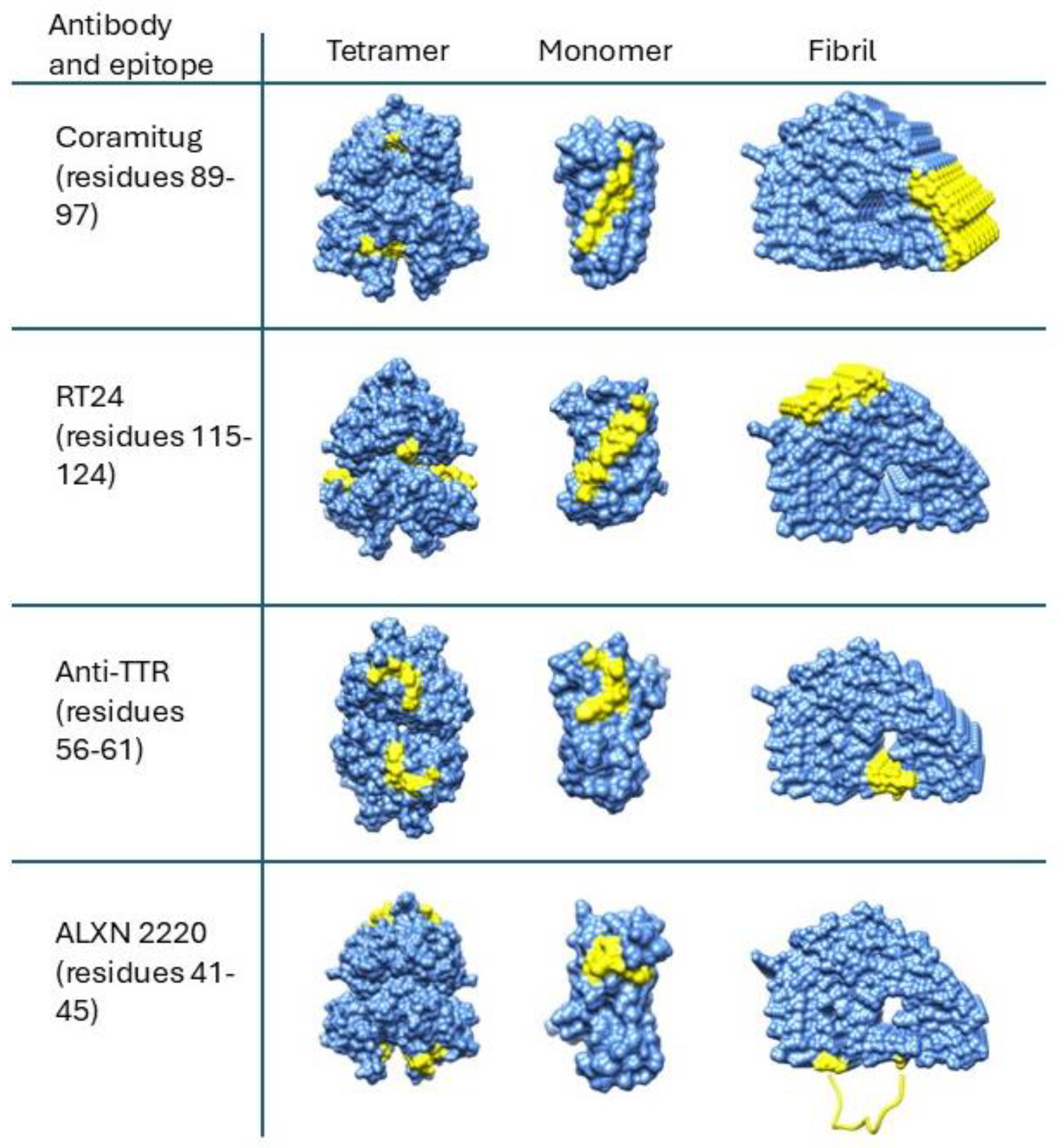
6. Structural Disposition of Depleter Antibody Epitopes on Cryo-EM Structures of TTR Amyloid Fibrils
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Said, G.; Grippon, S.; Kirkpatrick, P. Tafamidis. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2012, 11, 185–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brito, D.; Albrecht, F.C. World Heart Federation Consensus on Transthyretin Amyloidosis Cardiomyopathy (ATTR-CM). Glob. Heart. 2023, 18, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morfino, P.; Aimo, A. Transthyretin Stabilizers and Seeding Inhibitors as Therapies for Amyloid Transthyretin Cardiomyopathy. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ioannou, A.; Fontana, M. RNA Targeting and Gene Editing Strategies for Transthyretin Amyloidosis. BioDrugs 2023, 37, 127–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aimo, A.; Castiglione, V.; Rapezzi, C.; Franzini, M.; Panichella, G.; Vergaro, G.; Gillmore, J.; Fontana, M.; Passino, C.; Emdin, M. RNA-targeting and gene editing therapies for transthyretin amyloidosis. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2022, 19, 655–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US Food and Drug Administration. Onpattro (Patisiran) Labeling-Package Insert. FDA. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cder/daf/index.cfm?event=overview.process&ApplNo=210922 (accessed on 15 September 2024).
- European Medicines Agency. Onpattro. EMA. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/onpattro (accessed on 15 September 2024).
- Liz, M.A.; Coelho, T.; Bellotti, V.; Fernandez-Arias, M.I.; Mallaina, P.; Obici, L. A Narrative Review of the Role of Transthyretin in Health and Disease. Neurol. Ther. 2020, 9, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magalhães, J.; Eira, J.; Liz, M.A. The role of transthyretin in cell biology: Impact on human pathophysiology. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2021, 78, 6105–6117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalon, A.; Combaluzier, B.; Varela, E.; Hagenbuch, A.; Suhr, O.; Saraiva, M.; Grimm, J. Characterization of conformation-specific, human-derived monoclonal antibodies against TTR aggregates with potential for diagnostic and therapeutic use. Orphanet. J. Rare Dis. 2015, 10, P39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalon, A.; Hagenbuch, A.; Huy, C.; Varela, E.; Combaluzier, B.; Damy, T.; Suhr, O.B.; Saraiva, M.J.; Hock, C.; Nitsch, R.M.; et al. A human antibody selective for transthyretin amyloid removes cardiac amyloid through phagocytic immune cells. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Pavia, P.; Aus dem Siepen, F.; Donal, E.; Lairez, O.; van der Meer, P.; Kristen, A.V.; Mercuri, M.F.; Michalon, A.; Frost, R.J.A.; Grimm, J.; et al. Phase 1 Trial of Antibody NI006 for Depletion of Cardiac Transthyretin Amyloid. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galant, N.J.; Bugyei-Twum, A.; Rakhit, R.; Walsh, P.; Sharpe, S.; Arslan, P.E.; Westermark, P.; Higaki, J.N.; Torres, R.; Tapia, J.; et al. Substoichiometric inhibition of transthyretin misfolding by immune-targeting sparsely populated misfolding intermediates: A potential diagnostic and therapeutic for TTR amyloidoses. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higaki, J.N.; Chakrabartty, A.; Galant, N.J.; Hadley, K.C.; Hammerson, B.; Nijjar, T.; Torres, R.; Tapia, J.R.; Salmans, J.; Barbour, R.; et al. Novel conformation-specific monoclonal antibodies against amyloidogenic forms of transthyretin. Amyloid 2016, 23, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontana, M.; Buchholtz, K.; Engelmann, M.D.M.; Grogan, M.; Hovingh, G.K.; Kristen, A.V.; Poulsen, P.; Shah, S.J.; Maurer, M.S. NNC6019–0001, a humanized monoclonal antibody, in patients with transthyretin amyloid cardiomyopathy (ATTR-CM): Rationale and study design of a phase 2, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Eur. Heart J. 2022, 43 (Suppl. S2), ehac544.1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosoi, A.; Su, Y.; Torikai, M.; Jono, H.; Ishikawa, D.; Soejima, K.; Higuchi, H.; Guo, J.; Ueda, M.; Suenaga, G.; et al. Novel Antibody for the Treatment of Transthyretin Amyloidosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 25096–25105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldsteins, G.; Persson, H.; Andersson, K.; Olofsson, A.; Dacklin, I.; Edvinsson, A.; Saraiva, M.J.; Lundgren, E. Exposure of cryptic epitopes on transthyretin only in amyloid and in amyloidogenic mutants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 3108–3113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palha, J.A.; Moreira, P.; Olofsson, A.; Lundgren, E.; Saraiva, M.J. Antibody recognition of amyloidogenic transthyretin variants in serum of patients with familial amyloidotic polyneuropathy. J. Mol. Med. 2001, 78, 703–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eneqvist, T.; Olofsson, A.; Ando, Y.; Miyakawa, T.; Katsuragi, S.; Jass, J.; Lundgren, E.; Sauer-Eriksson, A.E. Disulfide-bond formation in the transthyretin mutant Y114C prevents amyloid fibril formation in vivo and in vitro. Biochemistry 2002, 41, 13143–13151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, A.; Olofsson, A.; Eneqvist, T.; Sauer-Eriksson, A.E. Cys114-linked dimers of transthyretin are compatible with amyloid formation. Biochemistry 2005, 44, 13063–13070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phay, M.; Blinder, V.; Macy, S.; Greene, M.J.; Wooliver, D.C.; Liu, W.; Planas, A.; Walsh, D.M.; Connors, L.H.; Primmer, S.R.; et al. Transthyretin aggregate-specific antibodies recognize cryptic epitopes on patient-derived amyloid fibrils. Rejuvenation Res. 2014, 17, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, S.M.; Connelly, S. The transthyretin amyloidoses: From delineating the molecular mechanism of aggregation linked to pathology to a regulatory-agency-approved drug. J. Mol. Biol. 2012, 421, 185–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colon, W.; Kelly, J.W. Partial denaturation of transthyretin is sufficient for amyloid fibril formation in vitro. Biochemistry 1992, 31, 8654–8660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, Z.; Colón, W.; Kelly, J.W. The acid-mediated denaturation pathway of transthyretin yields a conformational intermediate that can self-assemble into amyloid. Biochemistry 1996, 35, 6470–6482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCutchen, S.L.; Colon, W.; Kelly, J.W. Transthyretin mutation Leu-55-Pro significantly alters tetramer stability and increases amyloidogenicity. Biochemistry 1993, 32, 12119–12127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colon, W.; Lai, Z.; McCutchen, S.L.; Miroy, G.J.; Strang, C.; Kelly, J.W. FAP mutations destabilize transthyretin facilitating conformational changes required for amyloid formation. Ciba Found. Symp. 1996, 199, 228–238, discussion 239–242. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Smith, C.S.; Petrassi, H.M.; Hammarström, P.; White, J.T.; Sacchettini, J.C.; Kelly, J.W. An engineered transthyretin monomer that is nonamyloidogenic, unless it is partially denatured. Biochemistry 2001, 40, 11442–11452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.; Cho, H.S.; Lashuel, H.A.; Kelly, J.W.; Wemmer, D.E. A glimpse of a possible amyloidogenic intermediate of transthyretin. Nat. Struct. Biol. 2000, 7, 754–757. [Google Scholar]
- Oroz, J.; Kim, J.H.; Chang, B.J.; Zweckstetter, M. Mechanistic basis for the recognition of a misfolded protein by the molecular chaperone Hsp90. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2017, 24, 407–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillmore, J.D.; Gane, E.; Taubel, J.; Kao, J.; Fontana, M.; Maitland, M.L.; Seitzer, J.; O’Connell, D.; Walsh, K.R.; Wood, K.; et al. CRISPR-Cas9 in vivo gene editing for transthyretin amyloidosis. New Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 493–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, D.; Gonzalez-Duarte, A.; O’Riordan, W.D.; Yang, C.-C.; Ueda, M.; Kristen, A.V.; Tournev, I.; Schmidt, H.H.; Coelho, T.; Berk, J.L.; et al. Patisiran, an RNAi Therapeutic, for Hereditary Transthyretin Amyloidosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, M.D.; Waddington-Cruz, M.; Berk, J.L.; Polydefkis, M.; Dyck, P.J.; Wang, A.K.; Planté-Bordeneuve, V.; Barroso, F.A.; Merlini, G.; Obici, L.; et al. Inotersen treatment for patients with hereditary transthyretin amyloidosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontana, M.; Martinez-Naharro, A.; Chacko, L.; Rowczenio, D.; Gilbertson, J.A.; Whelan, C.J.; Strehina, S.; Lane, T.; Moon, J.; Hutt, D.F.; et al. Reduction in CMR Derived Extracellular Volume with Patisiran Indicates Cardiac Amyloid Regression. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2021, 14, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miroy, G.J.; Lai, Z.; Lashuel, H.A.; Peterson, S.A.; Strang, C.; Kelly, J.W. Inhibiting transthyretin amyloid fibril formation via protein stabilization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 15051–15056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterson, S.A.; Klabunde, T.; Lashuel, H.A.; Purkey, H.; Sacchettini, J.C.; Kelly, J.W. Inhibiting transthyretin conformational changes that lead to amyloid fibril formation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 12956–12960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baures, P.W.; Peterson, S.A.; Kelly, J.W. Discovering transthyretin amyloid fibril inhibitors by limited screening. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 1998, 6, 1389–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulawa, C.E.; Connelly, S.; Devit, M.; Wang, L.; Weigel, C.; Fleming, J.A.; Packman, J.; Powers, E.T.; Wiseman, R.L.; Foss, T.R.; et al. Tafamidis, a potent and selective transthyretin kinetic stabilizer that inhibits the amyloid cascade. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 9629–9634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurer, M.S.; Schwartz, J.H.; Gundapaneni, B.; Elliott, P.M.; Merlini, G.; Waddington-Cruz, M.; Kristen, A.V.; Grogan, M.; Witteles, R.; Damy, T.; et al. ATTR-ACT Study Investigators. Tafamidis Treatment for Patients with Transthyretin Amyloid Cardiomyopathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 1007–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, T.J.; Davis, F.B.; Deziel, M.R.; Davis, P.J.; Ramsden, D.B.; Schoenl, M. Retinoic acid inhibition of thyroxine binding to human transthyretin. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1994, 1199, 76–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baures, P.W.; Oza, V.B.; Peterson, S.A.; Kelly, J.W. Synthesis and evaluation of inhibitors of transthyretin amyloid formation based on the non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug, flufenamic acid. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 1999, 7, 1339–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tess, D.A.; Maurer, T.S.; Li, Z.; Bulawa, C.; Fleming, J.; Moody, A.T. Relationship of binding-site occupancy, transthyretin stabilization and disease modification in patients with tafamidis-treated transthyretin amyloid cardiomyopathy. Amyloid 2022, 30, 208–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robbins, J.; Rall, J.E.; Petermann, M.L. Thyroxine-binding by serum and urine proteins in nephrosis; qualitative aspects. J. Clin. Investig. 1957, 36, 1333–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingbar, S.H. Pre-albumin: A thyroxine binding protein of human plasma. Endocrinology 1958, 63, 256–259. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Alvsaker, J.O.; Haugli, F.B.; Laland, S.G. The presence of vitamin A in human tryptophan-rich prealbumin. Biochem. J. 1967, 102, 326–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woeber, K.A.; Ingbar, S.H. The contribution of thyroxine-binding prealbumin to the binding of thyroxine in human serum, as assessed by immunoadsorption. J. Clin. Investig. 1968, 47, 1710–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, P.P.; Figueira, A.S.; Bravo, F.R. Amyloid fibril protein related to prealbumin in familial amyloidotic polyneuropathy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1978, 75, 4499–4503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornwell, G.G., 3rd; Westermark, P.; Natvig, J.B.; Murdoch, W. Senile cardiac amyloid: Evidence that fibrils contain a protein immunologically related to prealbumin. Immunology 1981, 44, 447–452. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gustavsson, A.; Engström, U.; Westermark, P. Mechanisms of transthyretin amyloidogenesis. Antigenic mapping of transthyretin purified from plasma and amyloid fibrils and within in situ tissue localizations. Am. J. Pathol. 1994, 144, 1301–1311. [Google Scholar]
- Planque, S.A.; Nishiyama, Y.; Hara, M.; Sonoda, S.; Murphy, S.K.; Watanabe, K.; Mitsuda, Y.; Brown, E.L.; Massey, R.J.; Primmer, S.R.; et al. Physiological IgM class catalytic antibodies selective for transthyretin amyloid. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 13243–13258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontana, M.; Gilbertson, J.; Verona, G.; Riefolo, M.; Slamova, I.; Leone, O.; Rowczenio, D.; Botcher, N.; Ioannou, A.; Patel, R.K.; et al. Antibody-Associated Reversal of ATTR Amyloidosis-Related Cardiomyopathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 2199–2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenberg, D.S.; Sawaya, M.R. Structural Studies of Amyloid Proteins at the Molecular Level. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2017, 86, 69–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tycko, R. Molecular structure of amyloid fibrils: Insights from solid-state NMR. Q Rev. Biophys. 2006, 39, 1–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinebrei, M.; Gottwald, J.; Baur, J.; Röcken, C.; Hegenbart, U.; Schönland, S.; Schmidt, M. Cryo-EM structure of an ATTRwt amyloid fibril from systemic non-hereditary transthyretin amyloidosis. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 6398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubnovitsky, A.; Sandberg, A.; Rahman, M.M.; Benilova, I.; Lendel, C.; Härd, T. Amyloid-β protofibrils: Size, morphology and synaptotoxicity of an engineered mimic. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e66101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, B.A.; Singh, V.; Afrin, S.; Yakubovska, A.; Wang, L.; Ahmed, Y.; Pedretti, R.; Fernandez-Ramirez, M.D.C.; Singh, P.; Pękała, M.; et al. Structural polymorphism of amyloid fibrils in ATTR amyloidosis revealed by cryo-electron microscopy. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suhr, O.B.; Lundgren, E.; Westermark, P. One mutation, two distinct disease variants: Unravelling the impact of transthyretin amyloid fibril composition. J. Intern. Med. 2017, 281, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schonhoft, J.D.; Monteiro, C.; Plate, L.; Eisele, Y.S.; Kelly, J.M.; Boland, D.; Parker, C.G.; Cravatt, B.F.; Teruya, S.; Helmke, S.; et al. Peptide probes detect misfolded transthyretin oligomers in plasma of hereditary amyloidosis patients. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9, eaam7621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stabilini, R.; Vergani, C.; Agostoni, A.; Agostoni, R.P. Influence of age and sex on prealbumin levels. Clin. Chim. Acta. 1968, 20, 358–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muchtar, E.; Dispenzieri, A.; Magen, H.; Grogan, M.; Mauermann, M.; McPhail, E.D.; Kurtin, P.J.; Leung, N.; Buadi, F.K.; Dingli, D.; et al. Systemic amyloidosis from A (AA) to T (ATTR): A review. J. Intern. Med. 2021, 289, 268–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Antibody Name | Other Names | Epitope | Clinical Trial Numbers | Current Stage of Trial | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALXN-2220 | NI006, NI301A, anti-TTR (41–45) | Residues 41–45 | NCT06183931—Phase 3 NCT04622046—Phase 3—Japan | Phase 3 | [10,11,12] |
| Coramitug | NNC6019-0001, PRX004, anti-TTR (89–97) | Residues 89–97 | NCT03336580—Phase 1, terminated NCT05442047—Phase 2 NCT06260709—Phase 2—long term | Phase 2 | [13,14,15] |
| RT24 | anti-TTR (115–124) | Residues 115–124 | - | - | [16] |
| anti-TTR (39–44) | - | Residues 39–44 | - | - | [17,18,19,20,21] |
| anti-TTR (56–61) | - | Residues 56–61 | - | - | [17] |
| Affinities (Kd) and Reference | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Drug | Tetramer | Monomer | Fibril |
| Thyroxine | Site 1: 3.2 nM; [39] Site 2: 8.1 µM; [39] | Not applicable | Not applicable |
| Flufenamic acid | Site 1: 30 nM; [40] Site 2: 255 nM; [40] | Not applicable | Not applicable |
| Tafamidis | Site 1: 5.1 nM; [41] Site 2: 203 nM; [41] | Not applicable | Not applicable |
| ALXN 2220 | No binding detected | 1.2 nM *; [11] | 0.35 nM **; [11] |
| Coramitug | No binding detected | 18.6 nM; [14] | 0.62 µM **; [13] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chakrabartty, A. Structural Basis for Monoclonal Antibody Therapy for Transthyretin Amyloidosis. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 1225. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17091225
Chakrabartty A. Structural Basis for Monoclonal Antibody Therapy for Transthyretin Amyloidosis. Pharmaceuticals. 2024; 17(9):1225. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17091225
Chicago/Turabian StyleChakrabartty, Avi. 2024. "Structural Basis for Monoclonal Antibody Therapy for Transthyretin Amyloidosis" Pharmaceuticals 17, no. 9: 1225. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17091225
APA StyleChakrabartty, A. (2024). Structural Basis for Monoclonal Antibody Therapy for Transthyretin Amyloidosis. Pharmaceuticals, 17(9), 1225. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17091225






