Berberine Targets PKM2 to Activate the t-PA-Induced Fibrinolytic System and Improves Thrombosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
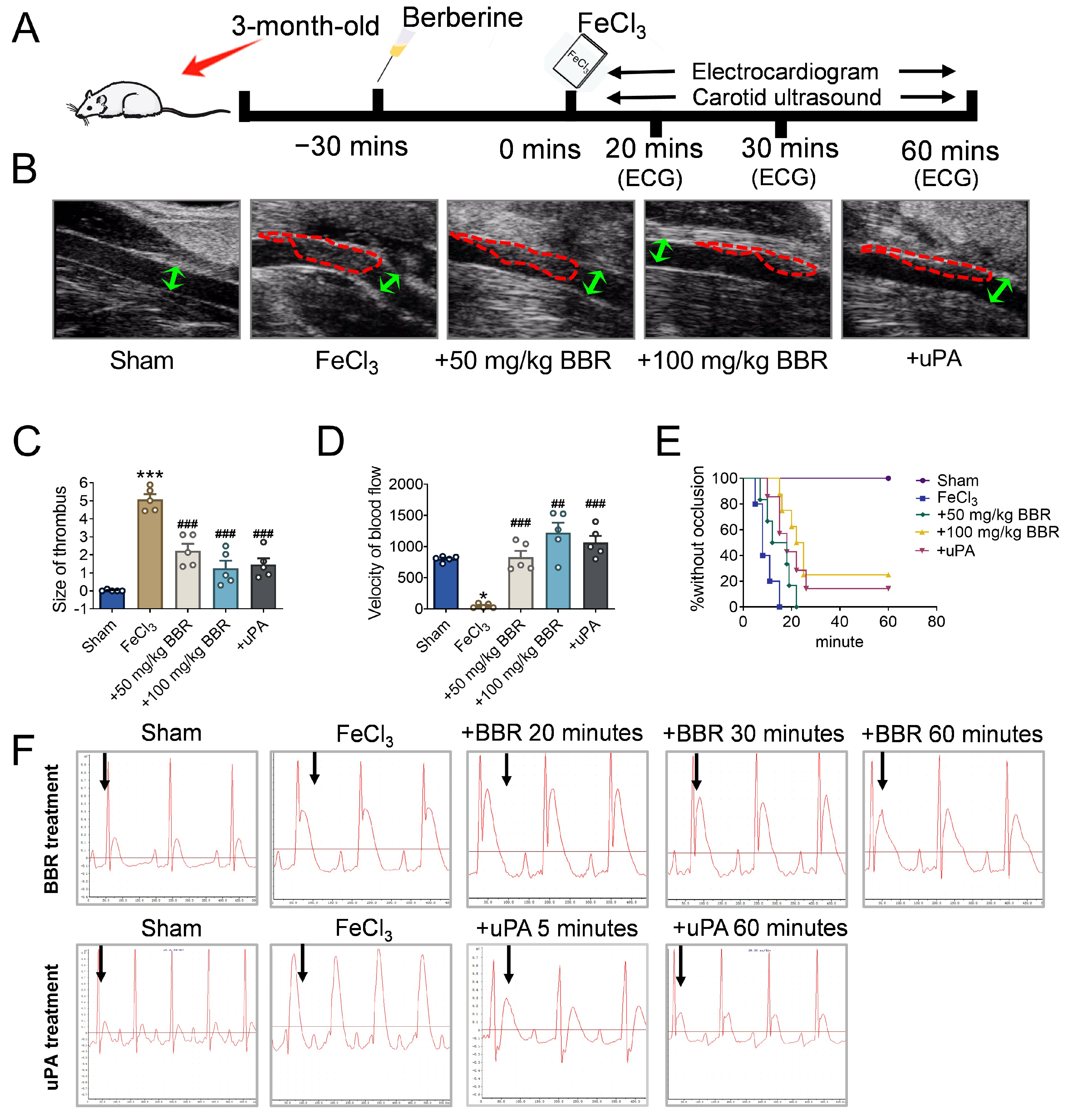
2.1. BBR Prevents Thrombosis in a Dosage-Dependent Manner
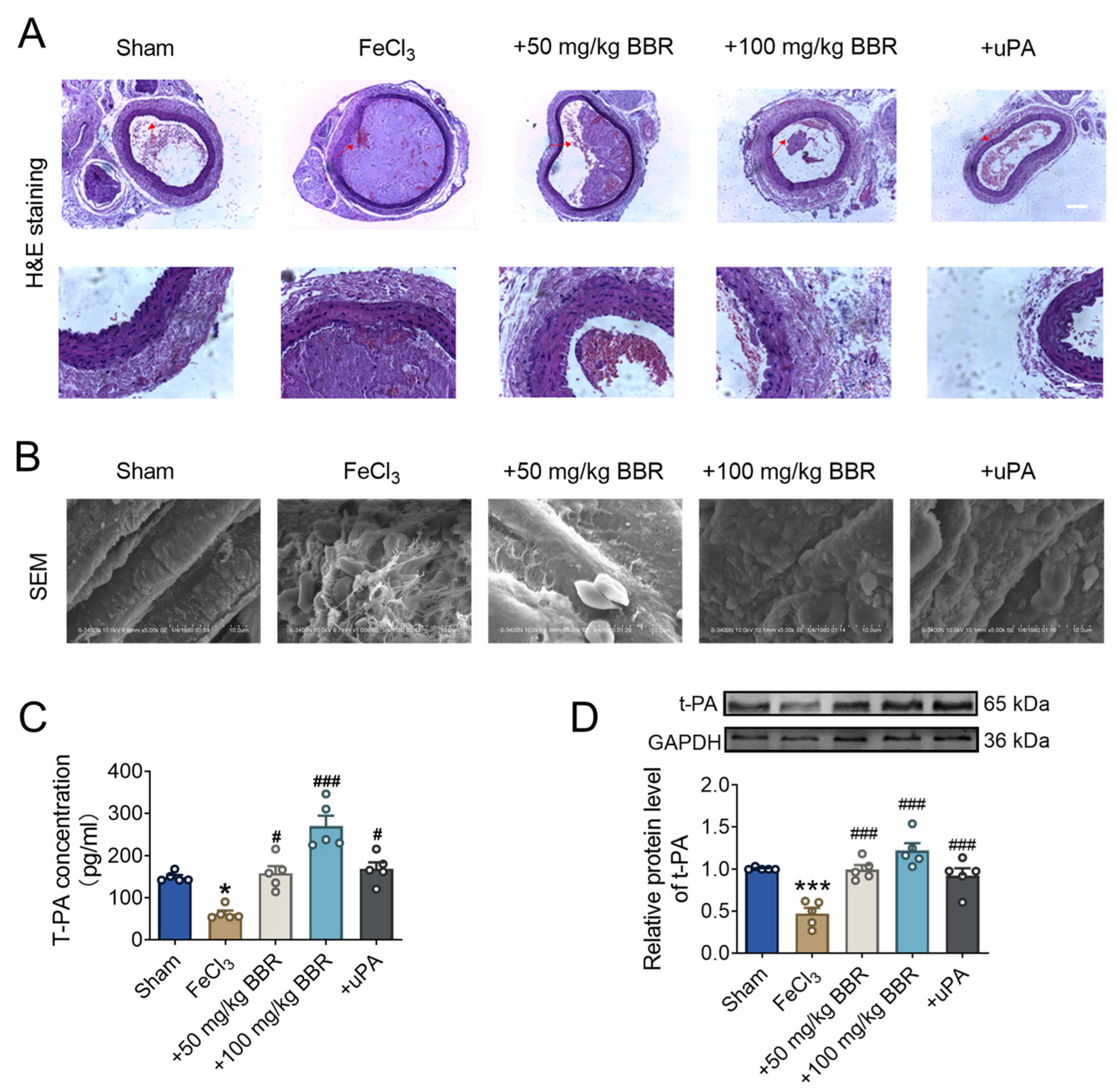
2.2. BBR Regulates Fibrinolytic System Balance in Rat Model of Common Carotid Artery Thrombosis
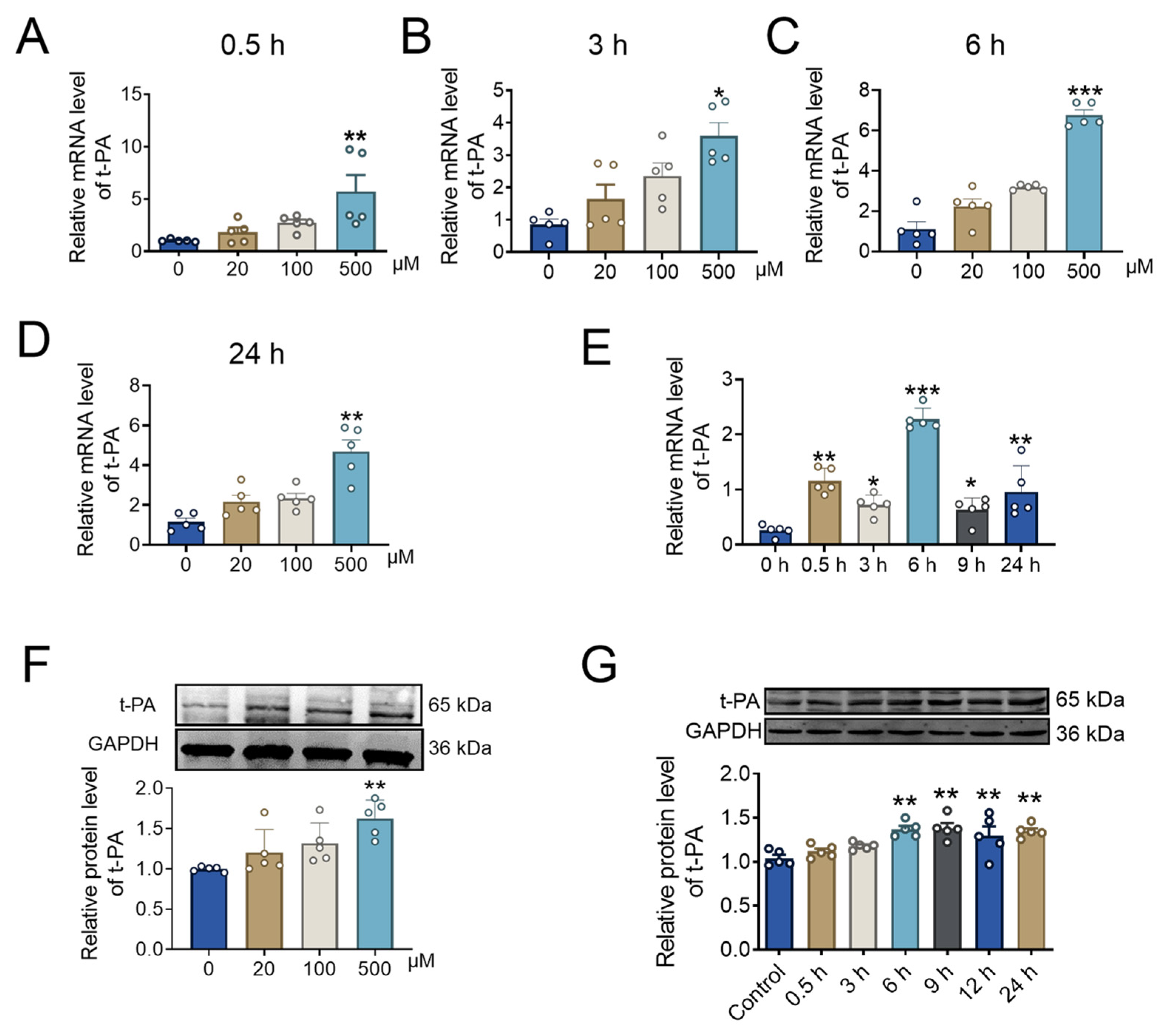
2.3. BBR Concentration and Incubation Time Affect t-PA Expression
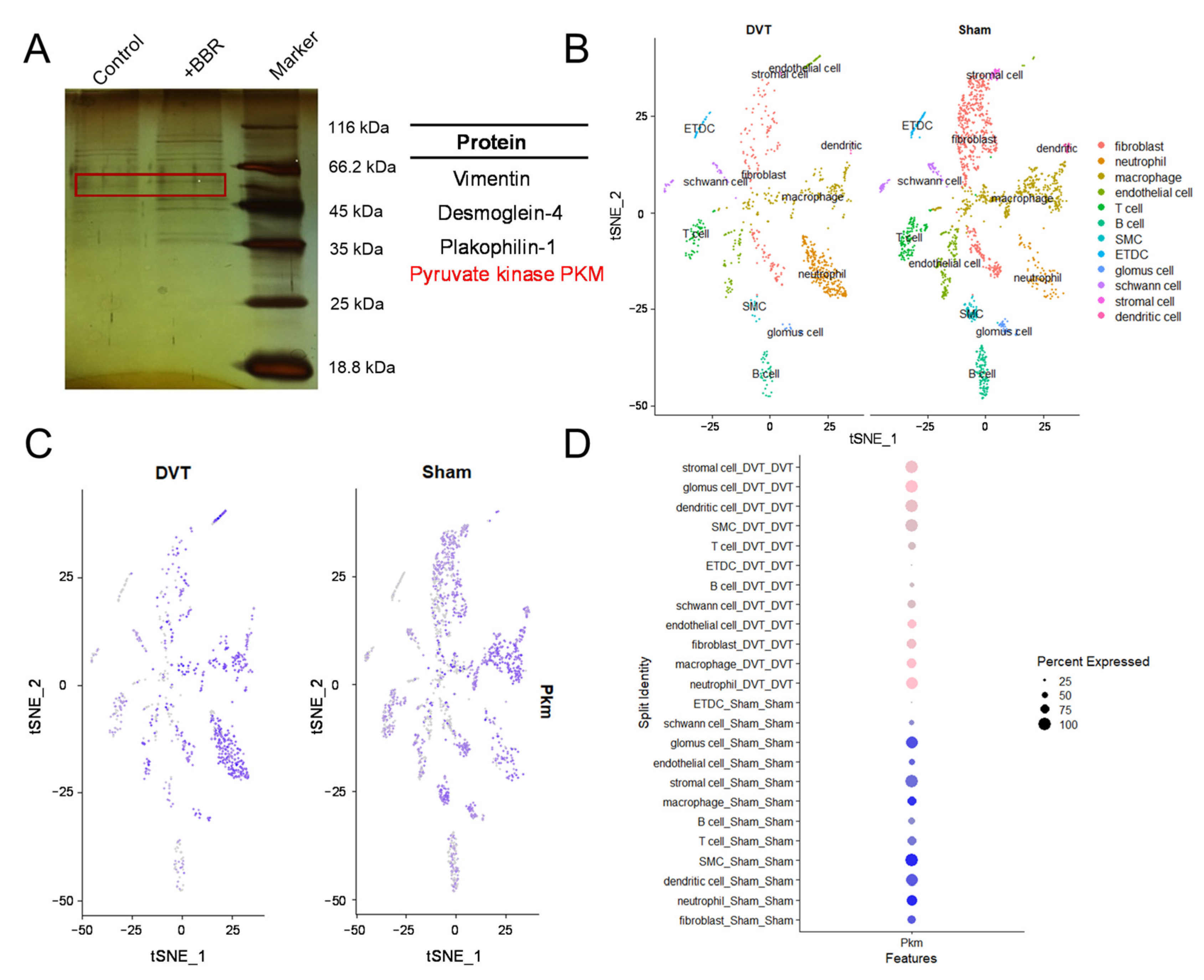
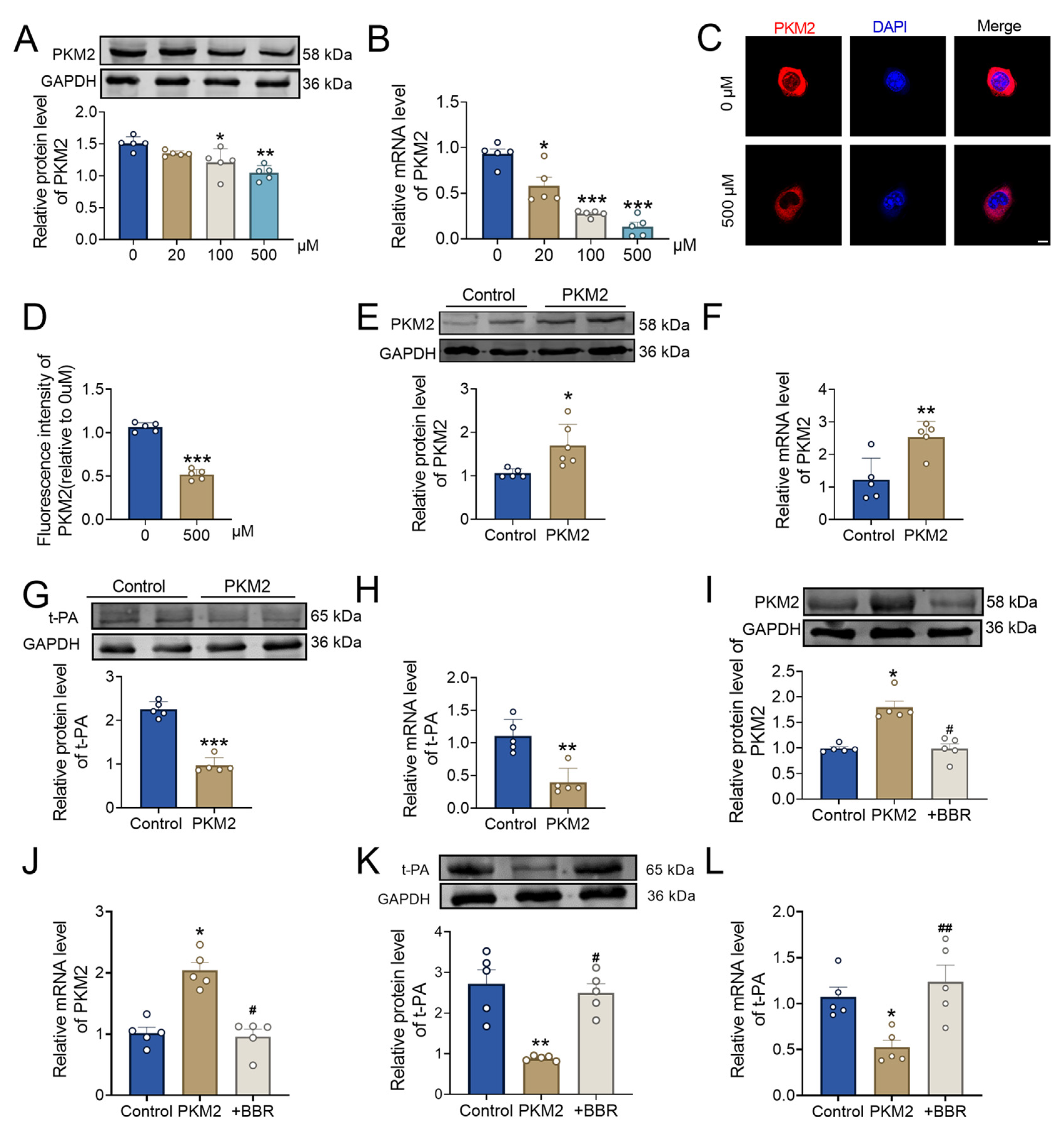
2.4. BBR Regulates PKM2 and Affects Thrombus Formation
2.5. BBR Plays a Thrombolytic Role by Regulating the PKM2 and Then Affect t-PA
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. FeCl3-Injury-Induced Carotid Thrombosis
4.3. Cell Viability
4.4. Acute Toxicity
4.5. Doppler Ultrasound Diagnostic Apparatus
4.6. Electrocardiogram (ECG)
4.7. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
4.8. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) Kit
4.9. Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) Staining
4.10. Pulldown and Mass Spectrometry
4.11. Cell Culture and Transfection
4.12. Immunofluorescence
4.13. Western Blot
4.14. Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR)
4.15. Single-Cell RNA Sequencing (Sc-RNA)
4.16. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, D.; Liu, J.; Wang, M.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, M. Epidemiology of cardiovascular disease in China: Current features and implications. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2019, 16, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okafor, O.N.; Gorog, D.A. Endogenous Fibrinolysis: An Important Mediator of Thrombus Formation and Cardiovascular Risk. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2015, 65, 1683–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Lu, A.D.; Zhang, L.P.; Zuo, Y.X.; Jia, Y.P. Study of clinical outcome and prognosis in pediatric core binding factor-acute myeloid leukemia. Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi 2019, 40, 52–57. [Google Scholar]
- Bartholomew, J.R. Update on the management of venous thromboembolism. Cleve Clin. J. Med. 2017, 84 (Suppl. S3), 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, C.; Osmolovskiy, A.; Singh, R. Microbial Fibrinolytic Enzymes as Anti-Thrombotics: Production, Characterisation and Prodigious Biopharmaceutical Applications. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, V.; Xiong, B.; Kumari, T.; Brown, G.; Wang, J.; Kim, K.; Lee, J.; Asquith, N.; Gallagher, J.; Asherman, L.; et al. A Critical Role for ERO1alpha in Arterial Thrombosis and Ischemic Stroke. Circ. Res. 2023, 132, e206–e222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemaître, A.; Picard, F.; Maurin, V.; Faure, M.; Dos Santos, P.; Girerd, N. Clinical profile and midterm prognosis of left ventricular thrombus in heart failure. ESC Heart Fail. 2021, 8, 1333–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nattel, S. Atrial Fibrosis, Endocardial Damage, and Thrombosis in Atrial Fibrillation: Association with Underlying Conditions or Causal? JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2023, 9 Pt 2, 1169–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NaveenKumar, S.K.; Hemshekhar, M.; Sharathbabu, B.N.; Kemparaju, K.; Mugesh, G.; Girish, K.S. Platelet activation and ferroptosis mediated NETosis drives heme induced pulmonary thrombosis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2023, 1869, 166688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wendelboe, A.M.; Raskob, G.E. Global Burden of Thrombosis: Epidemiologic Aspects. Circ. Res. 2016, 118, 1340–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou-Taleb, H.A.; Aldosari, B.N.; Zaki, R.M.; Afzal, O.; Tulbah, A.S.; Shahataa, M.G.; El-Ela, F.I.A.; Salem, H.F.; Fouad, A.G. Formulation and Therapeutic Evaluation of Isoxsuprine-Loaded Nanoparticles against Diabetes-Associated Stroke. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Meyer, S.F.; Stoll, G.; Wagner, D.D.; Kleinschnitz, C. von Willebrand factor: An emerging target in stroke therapy. Stroke 2012, 43, 599–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konieczynska, M.; Natorska, J.; Undas, A. Thrombosis and Aging: Fibrin Clot Properties and Oxidative Stress. Antioxid. Redox Signal 2024, 1, 233–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Bao, B.; Bao, C.; Wu, W. Fungi Fibrinolytic Compound 1 Plays a Core Role in Modulating Fibrinolysis, Altering Plasma Clot Structure, and Promoting Susceptibility to Lysis. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolberg, A.S.; Monroe, D.M.; Roberts, H.R.; Hoffman, M. Elevated prothrombin results in clots with an altered fiber structure: A possible mechanism of the increased thrombotic risk. Blood 2003, 101, 3008–3013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Boffa, M.B.; Bajzar, L.; Walker, J.B.; Nesheim, M.E. A study of the mechanism of inhibition of fibrinolysis by activated thrombin-activable fibrinolysis inhibitor. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 27176–27181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Undas, A.; Ariens, R.A. Fibrin clot structure and function: A role in the pathophysiology of arterial and venous thromboembolic diseases. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2011, 31, e88–e99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, J.-W.; Chiu, W.-C.; Chang, H.-T.; Hsu, P.-H.; Huang, C.-C. Fibrinolysis and thrombosis of fibrinogen-modified gold nanoparticles for detection of fibrinolytic-related proteins. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 774, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piras, A.M.; Zambito, Y.; Lugli, M.; Ferro, B.; Roncucci, P.; Mori, F.; Salvatore, A.; Ascione, E.; Bellini, M.; Crea, R. Repurposing of Plasminogen: An Orphan Medicinal Product Suitable for SARS-CoV-2 Inhalable Therapeutics. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longstaff, C.; Kolev, K. Basic mechanisms and regulation of fibrinolysis. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2015, 13 (Suppl. S1), S98–S105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, S.; Chen, H.; Lee, E.; Chen, T.; Lin, H.; Hung, Y.; Huang, S.; Chen, Y.; Lee, W.; Wu, T. Melatonin inhibits postischemic matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) activation via dual modulation of plasminogen/plasmin system and endogenous MMP inhibitor in mice subjected to transient focal cerebral ischemia. J. Pineal Res. 2010, 49, 332–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, E.G.; Marzec, U.; Anderson, J.; A Harker, L. Thrombin stimulates tissue plasminogen activator release from cultured human endothelial cells. J. Clin. Investig. 1984, 74, 1988–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Aziz, T.A.; Rezk, N.A. Relation of PAI-1 and TPA genes polymorphisms to acute myocardial infarction and its outcomes in Egyptian patients. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2015, 71, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, X.; Wang, Y.; Pan, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhao, X.; Wang, D.Z.; Wang, C.; Liu, L.; Wang, Y. Standard-dose intravenous tissue-type plasminogen activator for stroke is better than low doses. Stroke 2014, 45, 2354–2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmeliet, P.; Collen, D. Role of the plasminogen/plasmin system in thrombosis, hemostasis, restenosis and atherosclerosis evaluation in transgenic animals. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 1995, 5, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gue, Y.X.; Gorog, D.A. Importance of Endogenous Fibrinolysis in Platelet Thrombus Formation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, J.; Hao, J.; Dong, Z.; Wu, J.; Shen, G.; Ying, T.; Feng, L.; Cai, X.; Liu, Z.; et al. Guiding Drug Through Interrupted Bloodstream for Potentiated Thrombolysis by C-Shaped Magnetic Actuation System In Vivo. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, e2105351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, D.; Hao, J.; Fan, D. Biological properties and clinical applications of berberine. Front. Med. 2020, 14, 564–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, C.; Fernandes, M.H.; Lima, S.A.C. Elucidating Berberine’s Therapeutic and Photosensitizer Potential through Nanomedicine Tools. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Kang, N.; Xia, H.; Li, J.; Chen, L.; Qiu, F. Metabolites of protoberberine alkaloids in human urine following oral administration of Coptidis Rhizoma decoction. Planta Med. 2010, 76, 1859–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allijn, I.E.; Czarny, B.M.; Wang, X.; Chong, S.Y.; Weiler, M.; da Silva, A.E.; Metselaar, J.M.; Lam, C.S.P.; Pastorin, G.; de Kleijn, D.P.; et al. Liposome encapsulated berberine treatment attenuates cardiac dysfunction after myocardial infarction. J. Control. Release 2017, 247, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.M.; Yan, H.; Jin, J.M.; Yu, C.; Zhang, H. Beneficial effects of berberine on hemodynamics during acute ischemic left ventricular failure in dogs. Chin. Med. J. 1992, 105, 1014–1019. [Google Scholar]
- Abudureyimu, M.; Yang, M.; Wang, X.; Luo, X.; Ge, J.; Peng, H.; Zhang, Y.; Ren, J. Berberine alleviates myocardial diastolic dysfunction by modulating Drp1-mediated mitochondrial fission and Ca2+ homeostasis in a murine model of HFpEF. Front. Med. 2023, 17, 1219–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, Q.; Liu, Z.; Yang, Y.; Cui, X. Suppressive effects of berberine on atherosclerosis via downregulating visfatin expression and attenuating visfatin-induced endothelial dysfunction. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 41, 1939–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, P.; Wang, Y.; Yan, J.; Bin, W.; Qiu, F.; Kang, N. Berberine metabolites exhibit triglyceride-lowering effects via activation of AMP-activated protein kinase in Hep G2 cells. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2013, 149, 576–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, J.; Zhao, Y.; Dong, F.; Yan, Z.; Zheng, W.; Fan, J.; Sun, G. Meta-analysis of the effect and safety of berberine in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus, hyperlipemia and hypertension. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 161, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, C.-M.; Jiang, X.; Ouyang, X.-X.; Zhang, Y.-O.; Xie, W.-D. Berberine enhances antidiabetic effects and attenuates untoward effects of canagliflozin in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2016, 14, 518–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.J.; Fu, J.; Yu, H.; Xu, H.; Hu, J.C.; Lu, J.Y.; Bu, M.M.; Zhai, Z.; Wang, J.Y.; Ye, M.L.; et al. Berberine promotes the degradation of phenylacetic acid to prevent thrombosis by modulating gut microbiota. Phytomedicine 2024, 128, 155517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wei, Y.; Bai, X.; Li, M.; Li, H.; Wang, L.; Zhang, S.; Li, X.; Zhao, T.; Liu, Y.; et al. Berberine prevents primary peritoneal adhesion and adhesion reformation by directly inhibiting TIMP-1. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2020, 10, 812–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, C.; Xie, Y.; Wang, H.; Chen, W.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Deng, Q.; Cheng, T.; Li, M.; Ju, J.; et al. Berberine inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome activation by regulating mTOR/mtROS axis to alleviate diabetic cardiomyopathy. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2024, 964, 176253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Israelsen, W.J.; Dayton, T.L.; Davidson, S.M.; Fiske, B.P.; Hosios, A.M.; Bellinger, G.; Li, J.; Yu, Y.; Sasaki, M.; Horner, J.W.; et al. PKM2 isoform-specific deletion reveals a differential requirement for pyruvate kinase in tumor cells. Cell 2013, 155, 397–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taniguchi, K.; Uchiyama, K.; Akao, Y. PTBP1-targeting microRNAs regulate cancer-specific energy metabolism through the modulation of PKM1/M2 splicing. Cancer Sci. 2021, 112, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, C.H.; Mercier, F.E.; Liu, N.; Dong, W.; Stephanopoulos, G.; Jiang, L.; Jung, Y.; Lin, C.P.; Leung, A.Y.H.; Scadden, D.T. Proton export alkalinizes intracellular pH and reprograms carbon metabolism to drive normal and malignant cell growth. Blood 2022, 139, 502–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.; Hwang, Y.; Kim, H.; Kim, G.U.; Ryu, Y.C.; Yoon, M.; Choi, K.Y. Pyruvate Kinase M2 Accelerates Cutaneous Wound Healing via Glycolysis and Wnt/beta-Catenin Signaling. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dejure, F.R.; Eilers, M. MYC and tumor metabolism: Chicken and egg. EMBO J. 2017, 36, 3409–3420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Zheng, Y.; Xia, Y.; Ji, H.; Chen, X.; Guo, F.; Lyssiotis, C.A.; Aldape, K.; Cantley, L.C.; Lu, Z. ERK1/2-dependent phosphorylation and nuclear translocation of PKM2 promotes the Warburg effect. Nat. Cell Biol. 2012, 14, 1295–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, N.; Ojo, D.; Yan, J.; Tang, D. PKM2 contributes to cancer metabolism. Cancer Lett. 2015, 356 Pt A, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, M.K.; Ghatge, M.; Flora, G.D.; Dhanesha, N.; Jain, M.; Markan, K.R.; Potthoff, M.J.; Lentz, S.R.; Chauhan, A.K. The metabolic enzyme pyruvate kinase M2 regulates platelet function and arterial thrombosis. Blood 2021, 137, 1658–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhanesha, N.; Patel, R.B.; Doddapattar, P.; Ghatge, M.; Flora, G.D.; Jain, M.; Thedens, D.; Olalde, H.; Kumskova, M.; Leira, E.C.; et al. PKM2 promotes neutrophil activation and cerebral thromboinflammation: Therapeutic implications for ischemic stroke. Blood 2022, 139, 1234–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurz, K.D.; Main, B.W.; Sandusky, G.E. Rat model of arterial thrombosis induced by ferric chloride. Thromb. Res. 1990, 60, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Hinsbergh, V.W. Endothelium—Role in regulation of coagulation and inflammation. Semin. Immunopathol. 2012, 34, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D.; Jiang, Y.; Qu, C.; Yuan, H.; Hu, K.; He, L.; Chen, P.; Li, J.; Tu, M.; Lin, L.; et al. Pyruvate Kinase M2 Tetramerization Protects against Hepatic Stellate Cell Activation and Liver Fibrosis. Am. J. Pathol. 2020, 190, 2267–2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, X.; Sureda, A.; Jafari, S.; Memariani, Z.; Tewari, D.; Annunziata, G.; Barrea, L.; Hassan, S.T.; Šmejkal, K.; Malaník, M.; et al. Berberine in Cardiovascular and Metabolic Diseases: From Mechanisms to Therapeutics. Theranostics 2019, 9, 1923–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, N.; Yin, M.; Dong, J.; Zeng, Q.; Mao, G.; Song, D.; Liu, L.; Deng, H. Berberine diminishes cancer cell PD-L1 expression and facilitates antitumor immunity via inhibiting the deubiquitination activity of CSN5. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2020, 10, 2299–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Ren, H.; Zhong, H.; Zhao, X.; Li, C.; Ma, J.; Gu, X.; Xue, Y.; Huang, S.; Yang, J.; et al. Combined berberine and probiotic treatment as an effective regimen for improving postprandial hyperlipidemia in type 2 diabetes patients: A double blinded placebo controlled randomized study. Gut Microbes 2022, 14, 2003176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ma, J.; Zhang, W. Berberine for bone regeneration: Therapeutic potential and molecular mechanisms. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 277, 114249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Jin, H.; Zuo, Z.; Wang, A.; Huang, J.; Jiang, J.; Kong, W. Berberine and Its Main Metabolite Berberrubine Inhibit Platelet Activation Through Suppressing the Class I PI3Kbeta/Rasa3/Rap1 Pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 734603. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Ma, X.-J.; Guo, C.-Y.; Wang, M.-M.; Kou, N.; Qu, H.; Mao, H.-M.; Shi, D.-Z. Pretreatment with a combination of ligustrazine and berberine improves cardiac function in rats with coronary microembolization. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2016, 37, 463–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, W.; Che, S.; Li, J.; Luo, J.; Zhang, W.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Wei, H.; Xie, W. Synthesis of Berberine and Canagliflozin Chimera and Investigation into New Antibacterial Activity and Mechanisms. Molecules 2022, 27, 2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askri, H.; Scheftel, J.M. Effects of chlorpromazine, berberine and verapamil on Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin-induced intestinal hypersecretion in rabbit ileal loops. J. Med. Microbiol. 1988, 27, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kheir, M.M.; Wang, Y.; Hua, L.; Hu, J.; Li, L.; Lei, F.; Du, L. Acute toxicity of berberine and its correlation with the blood concentration in mice. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2010, 48, 1105–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, J.-H.; Zhao, Y.-H.; Gao, J.; Gao, Z.-Y.; Shi, D.-Z. Berberine Decreases Thrombosis Potential Induced by a High-choline Diet by Inhibiting CutC Enzyme. Curr. Med. Chem. 2023, 31, 3844–3856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Yuan, Z.; Xie, J.; Lei, Y.; Li, Y.; Huang, J.; Kong, W.; Jiang, J. Integrated metabolomics and molecular docking reveal berberrubine inhibits thrombosis by regulating the vitamin K catalytic cycle in mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2023, 938, 175436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medcalf, R.L. Fibrinolysis: From blood to the brain. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2017, 15, 2089–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Qin, Q.; Zhang, C.; Sun, X.; Kazama, K.; Yi, B.; Cheng, F.; Guo, Z.-F.; Sun, J. NDRG1 Signaling Is Essential for Endothelial Inflammation and Vascular Remodeling. Circ. Res. 2023, 132, 306–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sacharidou, A.; Chambliss, K.L.; Ulrich, V.; Salmon, J.E.; Shen, Y.-M.; Herz, J.; Hui, D.Y.; Terada, L.S.; Shaul, P.W.; Mineo, C. Antiphospholipid antibodies induce thrombosis by PP2A activation via apoER2-Dab2-SHC1 complex formation in endothelium. Blood 2018, 131, 2097–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Feng, J.; Dou, Z.; Sun, X.; Hu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Liu, L.; Xu, H.; Du, M.; Tang, P.; et al. Berberine as a novel ACSL4 inhibitor to suppress endothelial ferroptosis and atherosclerosis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 177, 117081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koskinas, K.C.; Chatzizisis, Y.S.; Antoniadis, A.P.; Giannoglou, G.D. Role of endothelial shear stress in stent restenosis and thrombosis: Pathophysiologic mechanisms and implications for clinical translation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2012, 59, 1337–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwaan, H.C.; Samama, M.M. The significance of endothelial heterogeneity in thrombosis and hemostasis. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2010, 36, 286–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kejiou, N.S.; Ilan, L.; Aigner, S.; Luo, E.; Tonn, T.; Ozadam, H.; Lee, M.; Cole, G.B.; Rabano, I.; Rajakulendran, N.; et al. Pyruvate Kinase M (PKM) binds ribosomes in a poly-ADP ribosylation dependent manner to induce translational stalling. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, 6461–6478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Feng, M.; Su, Y.; Ma, T.; Zhang, H.; Wu, H.; Wang, X.; Shi, S.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Y.; et al. Jmjd4 Facilitates Pkm2 Degradation in Cardiomyocytes and Is Protective Against Dilated Cardiomyopathy. Circulation 2023, 147, 1684–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doddapattar, P.; Dev, R.; Ghatge, M.; Patel, R.B.; Jain, M.; Dhanesha, N.; Lentz, S.R.; Chauhan, A.K. Myeloid Cell PKM2 Deletion Enhances Efferocytosis and Reduces Atherosclerosis. Circ. Res. 2022, 130, 1289–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Chen, H.; Le, Y.; Guo, J.; Liu, Z.; Dou, X.; Lu, D. Salvianolic acid A regulates pyroptosis of endothelial cells via directly targeting PKM2 and ameliorates diabetic atherosclerosis. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 1009229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Escudero, J.; Clemente, C.; García-Weber, D.; Acín-Pérez, R.; Millán, J.; Enríquez, J.A.; Bentley, K.; Carmeliet, P.; Arroyo, A.G. PKM2 regulates endothelial cell junction dynamics and angiogenesis via ATP production. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 15022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanov, I.; Ranchev, S.; Stoychev, S. Experimental Ultrasound Approach for Studying Knee Intra-Articular Femur-Tibia Movements under Different Loads. J. Funct. Morphol. Kinesiol. 2023, 9, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, Z.; Zhao, T.; Bai, X.; Li, H.; Gao, J.; Hao, Y.; Li, Y.; Xie, Y.; Hu, A.; Huang, Q.; et al. Berberine Targets PKM2 to Activate the t-PA-Induced Fibrinolytic System and Improves Thrombosis. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 1219. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17091219
Sun Z, Zhao T, Bai X, Li H, Gao J, Hao Y, Li Y, Xie Y, Hu A, Huang Q, et al. Berberine Targets PKM2 to Activate the t-PA-Induced Fibrinolytic System and Improves Thrombosis. Pharmaceuticals. 2024; 17(9):1219. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17091219
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Zeqi, Tong Zhao, Xue Bai, Huimin Li, Jin Gao, Yutong Hao, Yiyang Li, Yanli Xie, Ange Hu, Qiang Huang, and et al. 2024. "Berberine Targets PKM2 to Activate the t-PA-Induced Fibrinolytic System and Improves Thrombosis" Pharmaceuticals 17, no. 9: 1219. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17091219
APA StyleSun, Z., Zhao, T., Bai, X., Li, H., Gao, J., Hao, Y., Li, Y., Xie, Y., Hu, A., Huang, Q., Liu, X., & Zhang, Y. (2024). Berberine Targets PKM2 to Activate the t-PA-Induced Fibrinolytic System and Improves Thrombosis. Pharmaceuticals, 17(9), 1219. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17091219





