Development of a Lateral Flow Assay for the Detection of the Hepatitis C Virus Core Antigen
Abstract
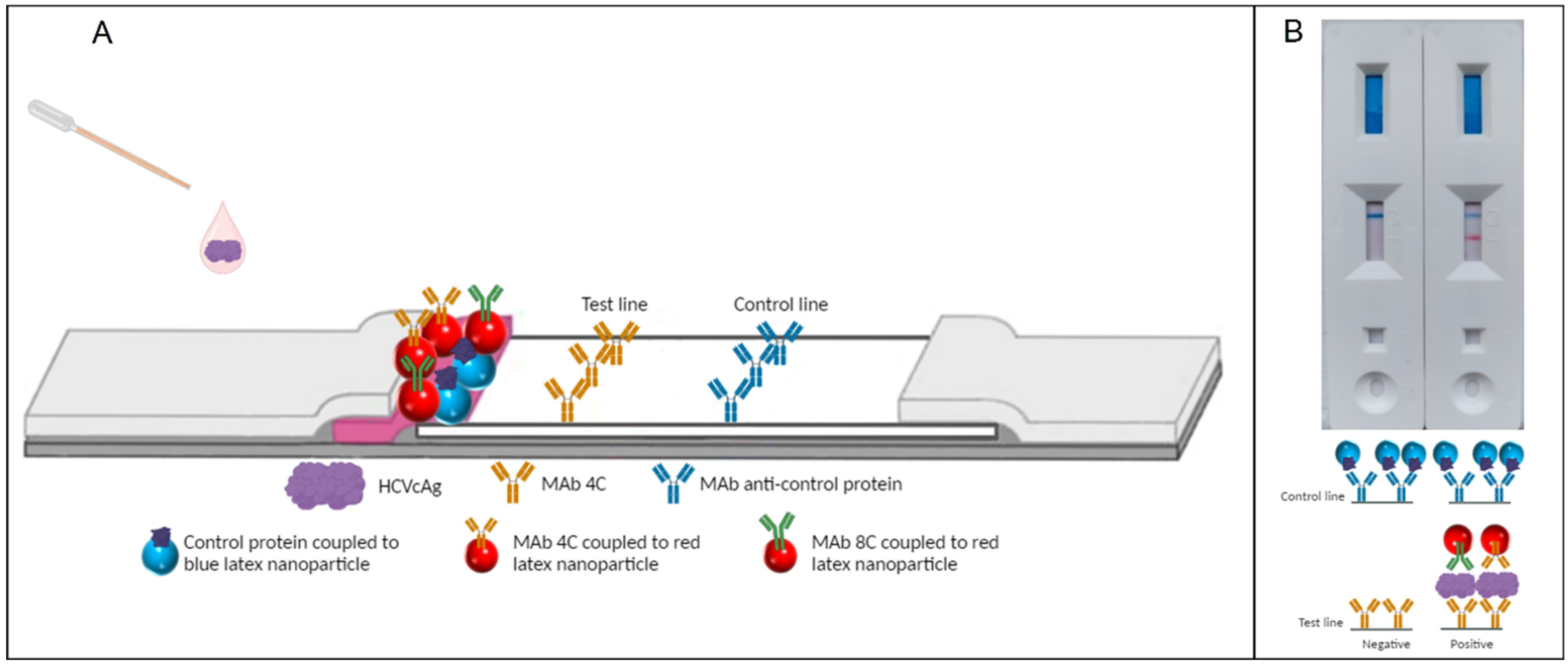
1. Introduction
2. Results
3. Discussion
Limitations and Future Directions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Capture Reagent
4.2. Detector Reagent
4.2.1. Latex Nanoparticles
4.2.2. Colloidal Gold
4.3. Preparation of Lateral Flow Strips
4.4. Evaluation of Antibody Pairs
4.5. Matrix Effect Evaluation of Spiked Samples
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
List of Abbreviations
| Aa | Amino acids |
| AU | Arbitrary units |
| CG | Colloidal gold |
| CHC | Chronic hepatitis C |
| DAAs | Direct-acting antivirals |
| DAS | Double antibody sandwich |
| EDC | 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl) carbodiimide hydrochloride |
| Gt | Genotype |
| IDUs | Injecting drug users |
| HBV | Hepatitis B virus |
| HCl | Hydrochloric acid |
| HCV | Hepatitis C virus |
| HCVcAg | Hepatitis C virus core antigen |
| LN | Latex nanoparticles |
| LoD | Limit of detection |
| Mab | Monoclonal antibodies |
| MSM | Men who have sex with men |
| NHS | N-hydroxysuccinimide |
| O.D. | Optical density |
| PCR | Polymerase chain reaction |
| RDAT | Rapid diagnostic antigen tests |
| RNA | Ribonucleic acid |
| Tris | Tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
References
- World Health Organization. Hepatitis C. 2024. Available online: https://www.who.int/es/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hepatitis-c (accessed on 9 April 2024).
- Spearman, C.W.; Dusheiko, G.M.; Hellard, M.; Sonderup, M. Hepatitis C. Lancet 2019, 394, 1451–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koopsen, J.; Matthews, G.; Rockstroh, J.; Applegate, T.L.; Bhagani, S.; Rauch, A.; Grebely, J.; Sacks-Davis, R.; Ingiliz, P.; Boesecke, C.; et al. Hepatitis C virus transmission between eight high-income countries among men who have sex with men: A whole-genome analysis. Lancet Microbe 2023, 4, e622–e631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponziani, F.R.; Mangiola, F.; Binda, C.; Zocco, M.A.; Siciliano, M.; Grieco, A.; Rapaccini, G.L.; Pompili, M.; Gasbarrini, A. Future of liver disease in the era of direct acting antivirals for the treatment of hepatitis C. World J. Hepatol. 2017, 9, 352–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- World Health Organization. The Global Health Sector Strategies on, Respectively, HIV, Viral Hepatitis and Sexually Transmitted Infections 2022–2030; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Global Hepatitis Report 2024. Action for Access in Low- and Middle-Income Countries. 2024. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240091672 (accessed on 16 July 2024).
- World Health, Organization. Global Health Sector Strategies on Viral Hepatitis 2016–2021. 2016. Available online: http://apps.who.int/gb/ebwha/pdf_files/WHA69/A69_32-en.pdf?ua=1 (accessed on 16 July 2024).
- World Health Organization. Treatment of Adolescents and Children with Chronic HCV Infection, and HCV Simplified Service Delivery and Diagnostics. 2022. Available online: https://iris.who.int/bitstream/handle/10665/363590/9789240052734-eng.pdf?sequence=1 (accessed on 16 July 2024).
- Oru, E.; Trickey, A.; Shirali, R.; Kanters, S.; Easterbrook, P. Decentralisation, integration, and task-shifting in hepatitis C virus infection testing and treatment: A global systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Glob. Health 2021, 9, e431–e445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bukh, J.; Purcell, R.H.; Miller, R.H. Sequence analysis of the core gene of 14 hepatitis C virus genotypes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 8239–8243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed Central]
- Hitomi, Y.; McDonnell, W.M.; Killeen, A.A.; Askari, F.K. Sequence analysis of the hepatitis C virus (HCV) core gene suggests the core protein as an appropriate target for HCV vaccine strategies. J. Viral Hepat. 1995, 2, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laperche, S.; Nübling, C.M.; Stramer, S.L.; Brojer, E.; Grabarczyk, P.; Yoshizawa, H.; Kalibatas, V.; El Elkyabi, M.; Moftah, F.; Girault, A.; et al. Sensitivity of hepatitis C virus core antigen and antibody combination assays in a global panel of window period samples. Transfusion 2015, 55, 2489–2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Moradpour, D.; Penin, F. Hepatitis C virus proteins: From structure to function. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2013, 369, 113–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galli, C.; Julicher, P.; Plebani, M. HCV core antigen comes of age: A new opportunity for the diagnosis of hepatitis C virus infection. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2018, 56, 880–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguilera, A.; Alados, J.C.; Alonso, R.; Eiros, J.M.; García, F. Current position of viral load versus hepatitis C core antigen testing. Enfermedades Infecc. Microbiol. Clin. (Engl. Ed.) 2020, 38 (Suppl. S1), 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gay, B. HCV Diagnostics Pipeline 2020. In 2020 Pipeline Report; TAG: New York, NY, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Koczula, K.M.; Gallotta, A. Lateral flow assays. Essays Biochem. 2016, 60, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Mirica, A.C.; Stan, D.; Chelcea, I.C.; Mihailescu, C.M.; Ofiteru, A.; Bocancia-Mateescu, L.A. Latest Trends in Lateral Flow Immunoassay (LFIA) Detection Labels and Conjugation Process. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 922772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Vidal-Alcántara, E.J.; Mas, V.; Yélamos, M.B.; Gómez, J.; Amigot-Sánchez, R.; Resino, S.; Martinez, I. Production and characterization of monoclonal antibodies for the detection of the hepatitis C core antigen. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2023, 10, 1225553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Clerc, O.; Greub, G. Routine use of point-of-care tests: Usefulness and application in clinical microbiology. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2010, 16, 1054–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozel, T.R.; Burnham-Marusich, A.R. Point-of-Care Testing for Infectious Diseases: Past, Present, and Future. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2017, 55, 2313–2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Nordgren, J.; Sharma, S.; Olsson, H.; Jamtberg, M.; Falkeborn, T.; Svensson, L.; Hagbom, M. SARS-CoV-2 rapid antigen test: High sensitivity to detect infectious virus. J. Clin. Virol. 2021, 140, 104846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zeuzem, S.; Franke, A.; Lee, J.H.; Herrmann, G.; Ruster, B.; Roth, W.K. Phylogenetic analysis of hepatitis C virus isolates and their correlation to viremia, liver function tests, and histology. Hepatology 1996, 24, 1003–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omidfar, K.; Riahi, F.; Kashanian, S. Lateral Flow Assay: A Summary of Recent Progress for Improving Assay Performance. Biosensors 2023, 13, 837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Aira, C.; Monedero, A.; Hernandez-Anton, S.; Martinez-Cano, J.; Camunas, A.; Casado, N.; Nieto, R.; Gallardo, C.; Garcia-Duran, M.; Rueda, P.; et al. Improving African Swine Fever Surveillance Using Fluorescent Rapid Tests. Pathogens 2023, 12, 811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bouvier-Alias, M.; Patel, K.; Dahari, H.; Beaucourt, S.; Larderie, P.; Blatt, L.; Hezode, C.; Picchio, G.; Dhumeaux, D.; Neumann, A.U.; et al. Clinical utility of total HCV core antigen quantification: A new indirect marker of HCV replication. Hepatology 2002, 36, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Courouce, A.M.; Le Marrec, N.; Bouchardeau, F.; Razer, A.; Maniez, M.; Laperche, S.; Simon, N. Efficacy of HCV core antigen detection during the preseroconversion period. Transfusion 2000, 40, 1198–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterson, J.; Green, G.; Iida, K.; Caldwell, B.; Kerrison, P.; Bernich, S.; Aoyagi, K.; Lee, S.R. Detection of hepatitis C core antigen in the antibody negative ‘window’ phase of hepatitis C infection. Vox Sang. 2000, 78, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Icardi, G.; Ansaldi, F.; Bruzzone, B.M.; Durando, P.; Lee, S.; de Luigi, C.; Crovari, P. Novel approach to reduce the hepatitis C virus (HCV) window period: Clinical evaluation of a new enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for HCV core antigen. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2001, 39, 3110–3114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ruta, S.; Cernescu, C. Injecting drug use: A vector for the introduction of new hepatitis C virus genotypes. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 10811–10823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Mikawa, A.Y.; Santos, S.A.; Kenfe, F.R.; da Silva, F.H.; da Costa, P.I. Development of a rapid one-step immunochromatographic assay for HCV core antigen detection. J. Virol. Methods 2009, 158, 160–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, J.; Sharma, P. Design of a novel rapid immunoassay for simultaneous detection of hepatitis C virus core antigen and antibodies. Arch. Virol. 2020, 165, 627–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, L.; Shen, X. Development of a nucleic acid lateral flow strip for detection of hepatitis C virus (HCV) core antigen. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids 2013, 32, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palacio, I.; Moreno, M.; Nanez, A.; Purwidyantri, A.; Domingues, T.; Cabral, P.D.; Borme, J.; Marciello, M.; Mendieta-Moreno, J.I.; Torres-Vazquez, B.; et al. Attomolar detection of hepatitis C virus core protein powered by molecular antenna-like effect in a graphene field-effect aptasensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2023, 222, 115006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Combination | Detector Antibody | Capture Antibody | Gt1a-125 ng/strip | Gt1a ng/strip | Gt1b ng/strip | Gt2a ng/strip | Gt3a ng/strip | Gt4a ng/strip |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LN1 | 4C | 2C | 12 | 24 | >96 | 48-96 | 12 | 12 |
| LN2 | 8C | 2C | 6 | 24 | 48–96 | 48-96 | 12 | 12 |
| LN3 | 4C | 4C | 6 | 12 | 24 | 24 | 6 | 24 |
| LN4 | 8C | 4C | 6 | 6 | 48 | 96 | 6 | 12 |
| LN5 | 1C | 8C | 6 | 12 | 24 | 96 | 6 | 6 |
| LN6 | 2C | 8C | 6 | 24 | 48 | >96 | 12 | 6 |
| CG1 | 8C | 2C | 12 | 12 | 24 | >96 | 12 | 24 |
| CG2 | 8C | 4C | 12 | 12 | 24 | 96 | 12 | 12 |
| CG3 | 4C | 8C | 12 | 24 | 24 | 96 | 6 | 12 |
| LN17 | 8C-4C | 4C | 6 | 6 | 6 | 12 | 24 | 12 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vidal-Alcántara, E.J.; Antón, S.H.; Rueda, P.; Yélamos, M.B.; Gómez, J.; Resino, S.; Fresco-Taboada, A.; Martínez, I. Development of a Lateral Flow Assay for the Detection of the Hepatitis C Virus Core Antigen. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 1022. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17081022
Vidal-Alcántara EJ, Antón SH, Rueda P, Yélamos MB, Gómez J, Resino S, Fresco-Taboada A, Martínez I. Development of a Lateral Flow Assay for the Detection of the Hepatitis C Virus Core Antigen. Pharmaceuticals. 2024; 17(8):1022. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17081022
Chicago/Turabian StyleVidal-Alcántara, Erick Joan, Sonia Hernández Antón, Paloma Rueda, María Belén Yélamos, Julián Gómez, Salvador Resino, Alba Fresco-Taboada, and Isidoro Martínez. 2024. "Development of a Lateral Flow Assay for the Detection of the Hepatitis C Virus Core Antigen" Pharmaceuticals 17, no. 8: 1022. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17081022
APA StyleVidal-Alcántara, E. J., Antón, S. H., Rueda, P., Yélamos, M. B., Gómez, J., Resino, S., Fresco-Taboada, A., & Martínez, I. (2024). Development of a Lateral Flow Assay for the Detection of the Hepatitis C Virus Core Antigen. Pharmaceuticals, 17(8), 1022. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17081022






