3D-Printed Melatonin Tablets with Braille Motifs for the Visually Impaired
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
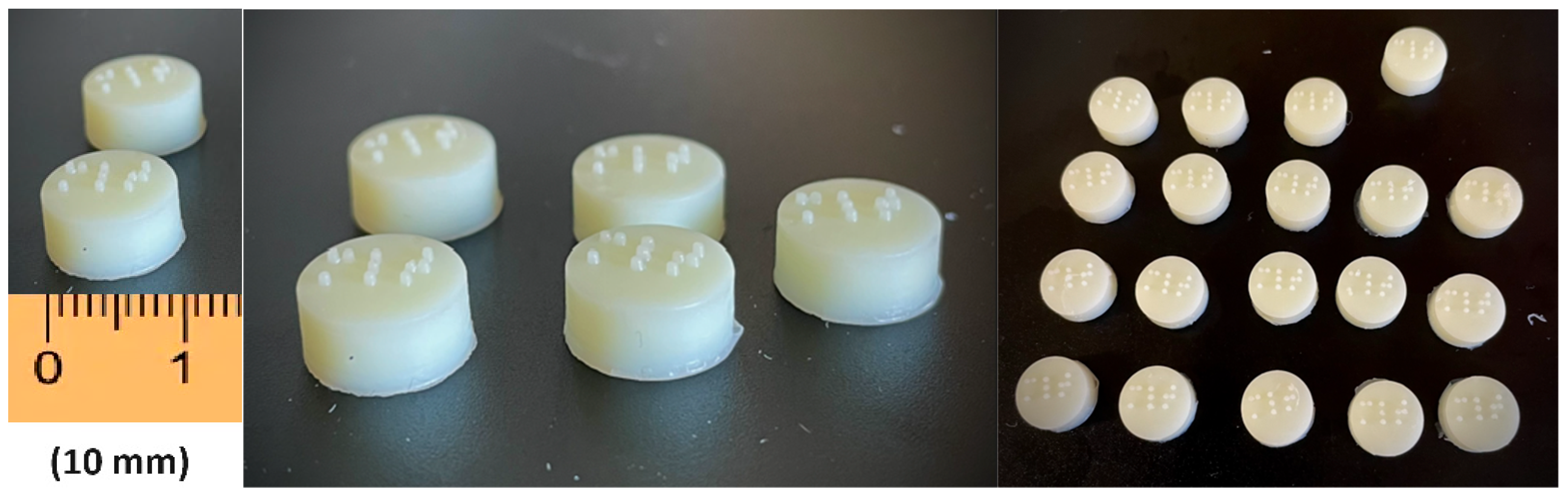
2.1. Printing Process
2.2. Characterization of 3D-Printed Tablets
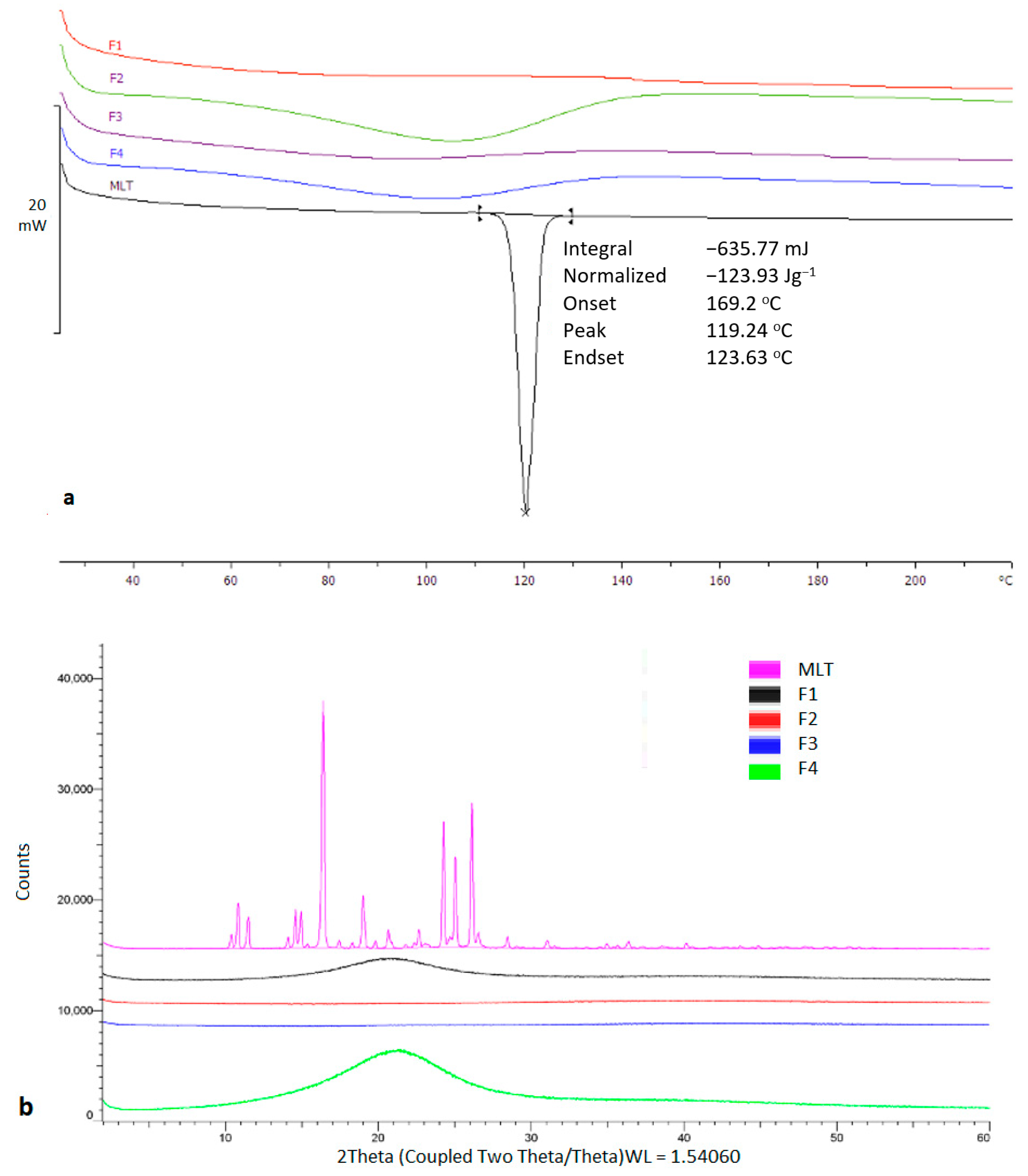
2.3. Physicochemical Characterization
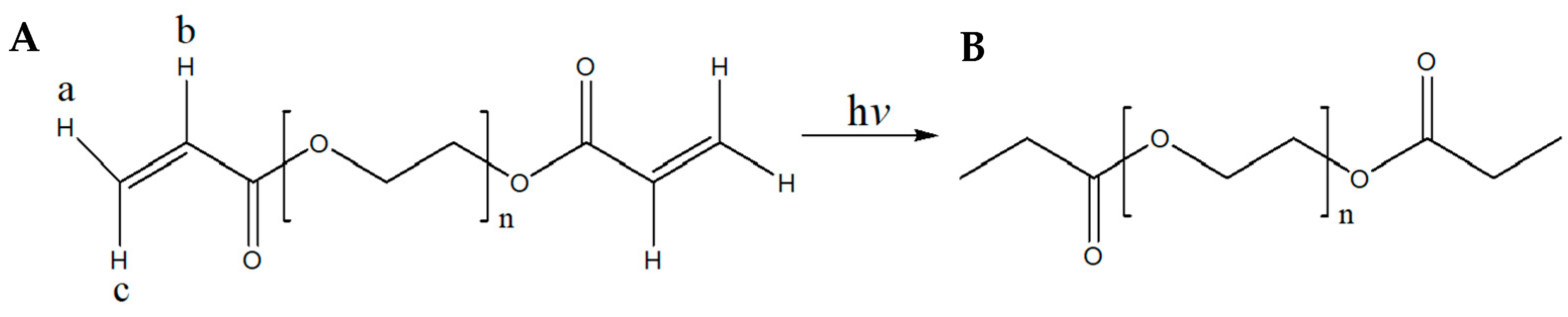
2.4. 1H-NMR Spectral Analysis
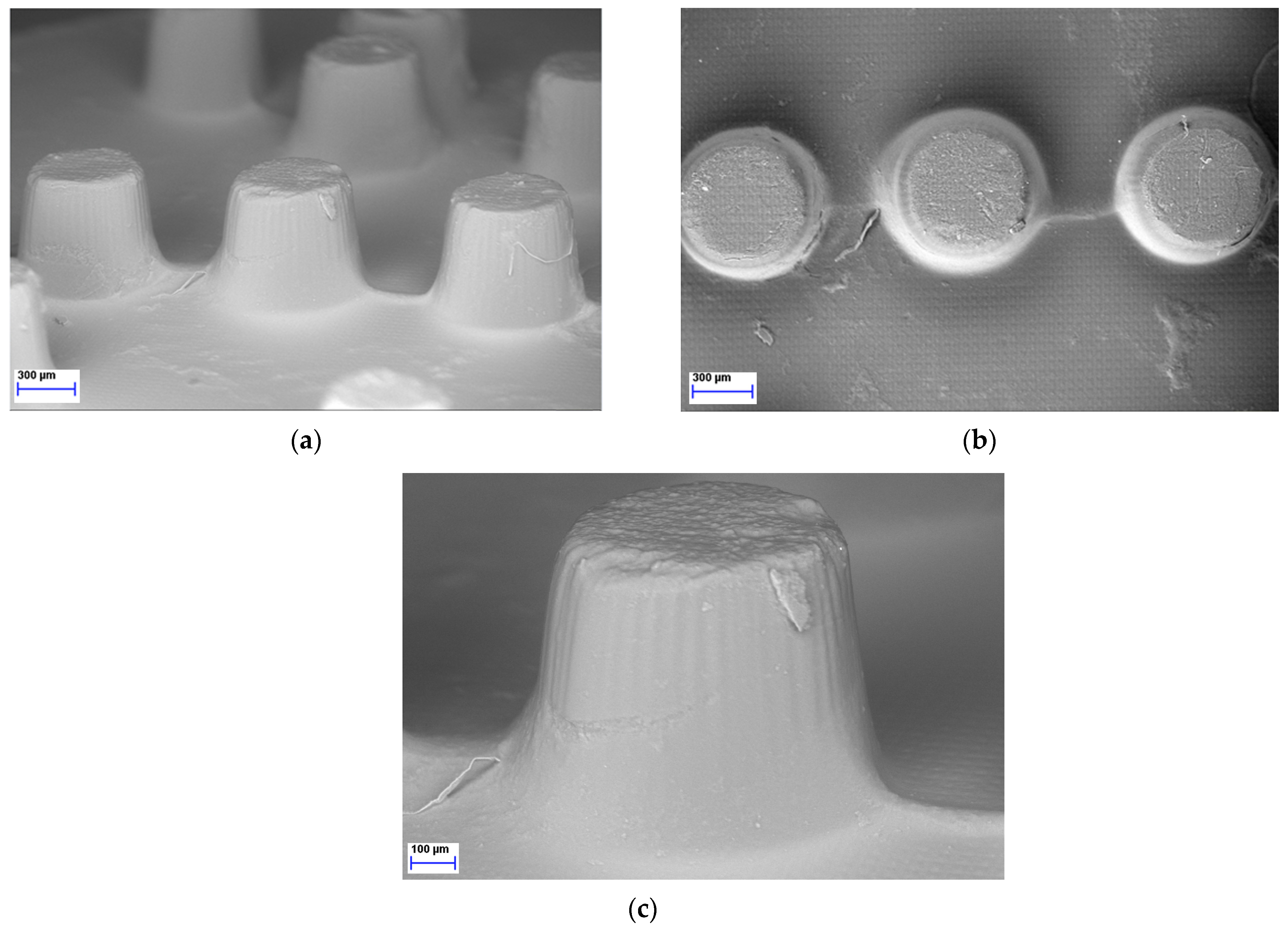
2.5. SEM Image Analysis
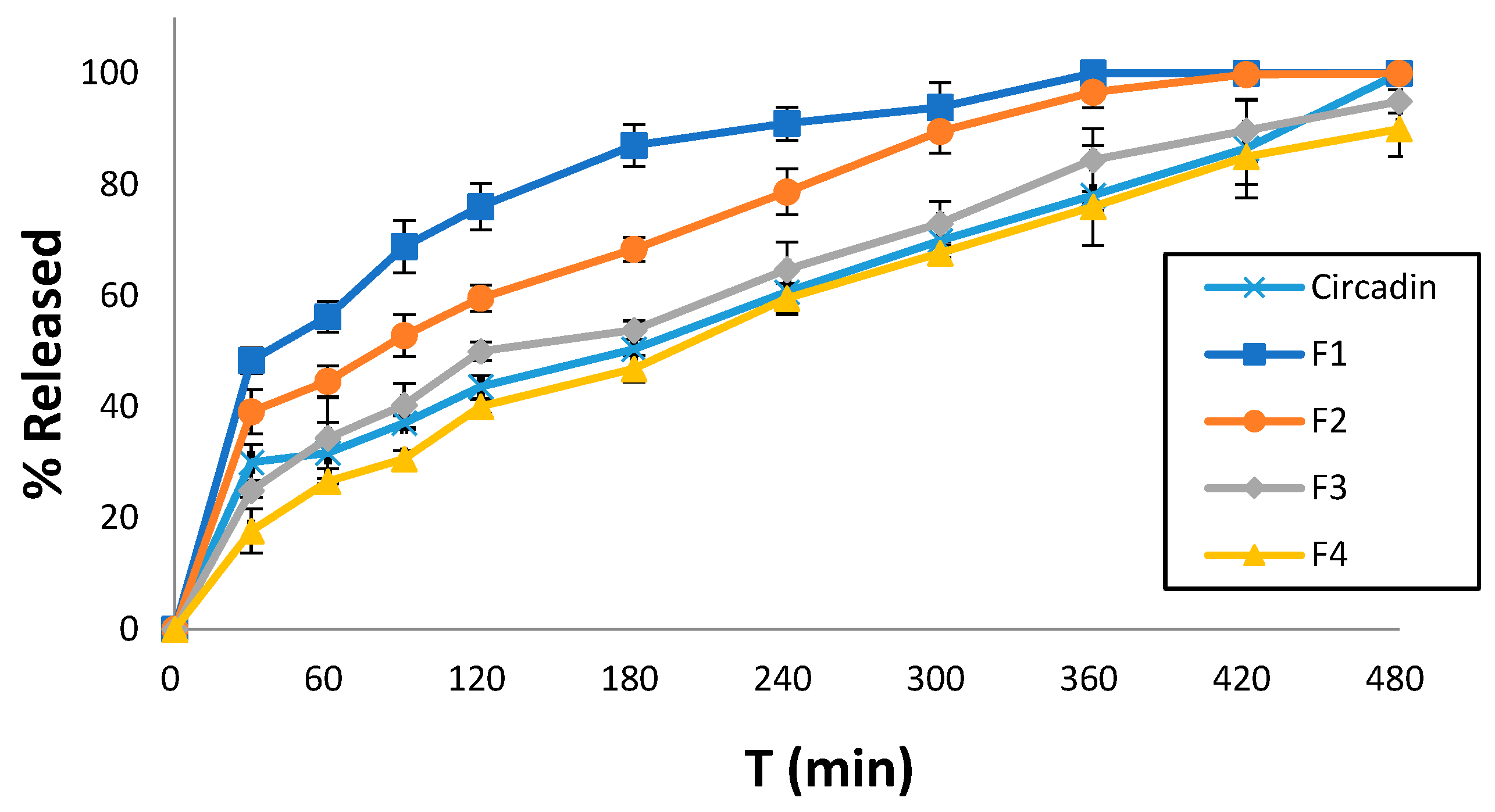
2.6. Dissolution Studies
2.7. Mathematical and Statistical Analysis
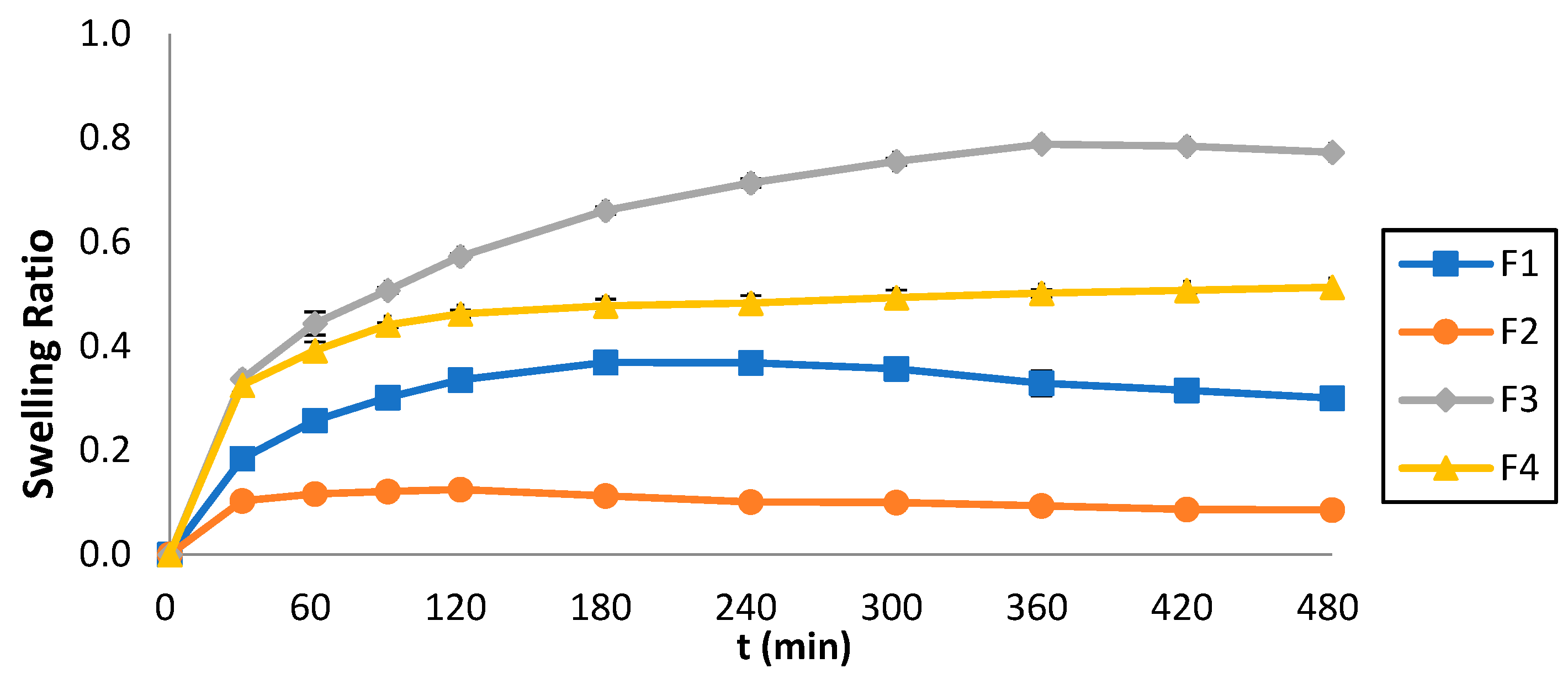
2.8. Determination of Swelling Ratio (Q)
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Three-Dimensional Printing
4.3. Physical Properties and Breaking Force of the 3D-printed Tablets
4.4. X-ray Diffraction (XRPD)
4.5. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
4.6. 1H-NMR Spectral Analysis
4.7. SEM Image Analysis
4.8. Determination of MLT Tablet Strength
4.9. Dissolution Studies
4.10. Mathematical and Statistical Analysis
4.11. Determination of Swelling Ratio (Q)
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pascolini, D.; Mariotti, S.P. Global estimates of visual impairment: 2010. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2012, 96, 614–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giles, S.J.; Panagioti, M.; Riste, L.; Cheraghi-Sohi, S.; Lewis, P.; Adeyemi, I.; Davies, K.; Morris, R.; Phipps, D.; Dickenson, C.; et al. Visual impairment and medication safety: A protocol for a scoping review. Syst. Rev. 2021, 10, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pezzullo, L.; Streatfeild, J.; Simkiss, P.; Shickle, D. The economic impact of sight loss and blindness in the UK adult population. BMC Health Serv. Res. 2018, 18, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cupples, M.E.; Hart, P.M.; Johnston, A.; Jackson, A.J. Improving healthcare access for people with visual impairment and blindness. BMJ (Clin. Res. Ed.) 2012, 344, e542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, Z.-H.; Yow, H.-Y.; Mohd, M.-B. Medication-handling challenges among visually impaired population. Arch. Pharm. Pract. 2017, 8, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheraghi-Sohi, S.; Jeffries, M.; Stevenson, F.; Ashcroft, D.M.; Carr, M.; Oliver, K.; Rogers, A. The influence of personal communities on the self-management of medication taking: A wider exploration of medicine work. Chronic Illn. 2015, 11, 77–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobnath, D.; Rehman, I.U.; Nasralla, M.M. Smart Cities to Improve Mobility and Quality of Life of the Visually Impaired. In Technological Trends in Improved Mobility of the Visually Impaired; Paiva, S., Ed.; EAI/Springer Innovations in Communication and Computing; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weeraratne, C.L.; Opatha, S.T.; Rosa, C.T. Challenges faced by visually disabled people in use of medicines, self-adopted coping strategies and medicine-related mishaps. WHO South-East Asia J. Public Health 2012, 1, 256–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller Smedema, S.; McKenzie, A.R. The relationship among frequency and type of internet use, perceived social support, and sense of well-being in individuals with visual impairments. Disabil. Rehabil. 2010, 32, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, L.; Fuzesi, P.; Jacob, S.A.; Kamalakannan, S.; Lennon, M.; Macaden, L.; Smith, A.; Welsh, T.; Broadfoot, K.; Watson, M.C. Assistive technologies and strategies to support the medication management of individuals with hearing and/or visual impairment: A scoping review. Disabil. Health J. 2023, 16, 101500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, A.; Yao, A.; Trenfield, S.J.; Goyanes, A.; Gaisford, S.; Basit, A.W. 3D Printed Tablets (Printlets) with Braille and Moon Patterns for Visually Impaired Patients. Pharmaceutics 2020, 19, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowley, S.J.; Eastman, C.I. Free-running circadian period in adolescents and adults. J. Sleep Res. 2018, 27, e12678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewy, A.J.; Emens, J.S.; Lefler, B.J.; Yuhas, K.; Jackman, A.R. Melatonin Entrains Free-running Blind People According to a Physiological Dose-response Curve. Chronobiol. Int. 2005, 22, 1093–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubocovich, M.L. Melatonin receptors: Role on sleep and circadian rhythm regulation. Sleep Med. 2007, 8, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakellaropoulou, A.; Siamidi, A.; Vlachou, M. Melatonin/Cyclodextrin Inclusion Complexes: A Review. Molecules 2022, 10, 445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, P.J.; Barrett, P.; Howell, H.E.; Helliwell, R. Melatonin receptors: Localization, molecular pharmacology and physiological significance. Neurochem. Int. 1994, 24, 101–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, A.; Januskaite, P.; Alkahtani, M.; Orlu, M.; Basit, A.W. 3D Printing: Advancements in the Development of Personalised Pharmaceuticals for Older Adults. In Pharmaceutical Formulations for Older Patients; Orlu, M., Liu, F., Eds.; AAPS Advances in the Pharmaceutical Sciences Series; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; Volume 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douroumis, D. 3D Printing of Pharmaceutical and Medical Applications: A New Era. Pharm. Res. 2019, 36, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trenfield, S.J.; Madla, C.M.; Basit, A.W.; Gaisford, S. Chapter 1: The Shape of Things to Come: Emerging Applications of 3D Printing in Healthcare. In 3D Printing of Pharmaceuticals; Basit, A.W., Gaisford, S., Eds.; AAPS Advances in the Pharmaceutical Sciences Series; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, T.; Liu, D.; Li, Q.; Wei, M.; Sun, Y.; Xie, H.; Du, L.; Yuan, B.; Deng, P.; Guo, Y.; et al. 3D printing of melatonin-loaded esophageal stents for treatment of corrosive esophagitis. Appl. Mater. Today 2024, 37, 102161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabriz, A.G.; Mithu, S.; Antonijevic, M.D.; Vilain, L.; Derrar, Y.; Grau, C.; Morales, A.; Katsamenis, O.L.; Douroumis, D. 3D printing of LEGO® like designs with tailored release profiles for treatment of sleep disorder. Int. J. Pharm. 2023, 632, 122574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhao, W.; Li, Q.; Zhao, D.; Qu, J.; Yuan, Z.; Cheng, Z.; Zhu, X.; Zhuang, X.; Zhang, Z. 3D-printing magnesium–polycaprolactone loaded with melatonin inhibits the development of osteosarcoma by regulating cell-in-cell structures. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 19, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.; Hu, P.; Wu, Z.; Liu, W.; Lv, Q.; Nie, Z.; He, Z. Comparison of accuracy and precision of various types of photo-curing printing technology. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2020, 1549, 032151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidleithner, C.; Kalaskar, D.M. Stereolithography. In 3D Printing; Cvetkovi’c, D., Ed.; InTech: Vienna, Austria, 2018; ISBN 978-1-78923-965-2. [Google Scholar]
- Madžarević, M.; Ibrić, S. Evaluation of exposure time and visible light irradiation in LCD 3D printing of ibuprofen extended release tablets. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 158, 105688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlachou, M.; Papamichael, M.; Siamidi, A.; Fragouli, I.; Afroudakis, P.A.; Kompogennitaki, R.; Dotsikas, Y. Comparative in vitro controlled release studies on the chronobiotic hormone melatonin from cyclodextrins-containing matrices and cyclodextrin:melatonin complexes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlachou, M.; Siamidi, A.; Goula, E.; Georgas, P.; Pippa, N.; Sentoukas, T.; Pispas, S. Probing the release of the chronobiotic hormone melatonin from hybrid calcium alginate hydrogel beads. Acta Pharm. 2020, 70, 527–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlachou, M.; Siamidi, A.; Anagnostopoulou, D.; Protopapa, C.; Christodoulou, E.; Bikiaris, N.D.; Malletzidou, L.; Delli, E.; Siamidis, I. Tuning the release of the pineal hormone melatonin via poly(ε-caprolactone)-based copolymers matrix tablets. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2023, 79, 104051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzoccoli, J.P.; Feke, D.L.; Baskaran, H.; Pintauro, P.N. Mechanical and Cell Viability Properties of Crosslinked Low and High MW PEGDA blends. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2010, 93, 558–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruise, G.M.; Scharp, D.S.; Hubbell, J.A. Characterization of permeability and network structure of interfacially photopolymerized poly(ethylene glycol) diacrylate hydrogels. Biomaterials 1998, 19, 1287–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, M.S.; Miller, J.S.; West, J.L. Three-dimensional biochemical and biomechanical patterning of hydrogels for guiding cell behavior. Adv. Mater. 2006, 18, 2679–2684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamov, I.; Stanojević, G.; Medarević, D.; Ivković, B.; Kočović, D.; Mirković, D.; Ibrić, S. Formulation and characterization of immediate-release oral dosage forms with zolpidem tartrate fabricated by digital light processing (DLP) 3D printing technique. Int. J. Pharm. 2022, 624, 122046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.Y.; Zeng, J.J.; Lin, G.T. Fabrication of 5-fluorouracil-loaded tablets with hyperbranched polyester by digital light processing 3D printing technology. Eur. Polym. J. 2022, 171, 111190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadry, H.; Wadnap, S.; Xu, C.; Ahsan, F. Digital light processing (DLP)3D-printing technology and photoreactive polymers in fabrication of modified-release tablets. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 135, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krkobabić, M.; Medarević, D.; Cvijić, S.; Grujić, B.; Ibrić, S. Hydrophilic excipients in digital light processing (DLP) printing of sustained release tablets: Impact on internal structure and drug dissolution rate. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 572, 118790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pariskar, A.; Sharma, P.K.; Murty, U.S.; Banerjee, S. Effect of Tartrazine as Photoabsorber for Improved Printing Resolution of 3D Printed “Ghost Tablets”: Non-Erodible Inert Matrices. J. Pharm. Sci. 2023, 112, 1020–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robles-Martinez, P.; Xu, X.; Trenfield, S.J.; Awad, A.; Goyanes, A.; Telford, R.; Basit, A.W.; Gaisford, S. 3D printing of a multi-layered polypill containing six drugs using a novel stereolithographic method. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Goyanes, A.; Gaisford, S.; Basit, A.W. Stereolithographic (SLA) 3D printing of oral modified-release dosage forms. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 503, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, P.; Sousa Lobo, J.M. Modeling and comparison of dissolution profiles. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2001, 13, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Pang, J.; Hong, S.; Chen, X.; Shao, S.; Wang, H.; Lao, H.; Xiong, L.; Wu, H.; Yang, W.; et al. A novel technology for preparing the placebos of vortioxetine hydrobromide tablets using LCD 3D printing. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2022, 178, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imani, M.; Sharifi, S.; Mirzadeh, H.; Ziaee, F. Monitoring of Polyethylene Glycol-diacrylate-based Hydrogel Formation by Real Time NMR Spectroscopy. Iran. Polym. J. 2007, 16, 13–20. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Z.C.L.; Betts, D.E.; Pandya, A.; Hillmyer, M.A.; DeSimone, J.M. Optically transparent, amphiphilic networks based on blends of perfluoropolyethers and poly(ehtylene glycol). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 14244–14252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlachou, M.; Siamidi, A. Chapter Eight—Biopolymers, liposomes, and nanofibers as modified peroral drug release formulants. In Nanomaterials for Clinical Applications: Case Studies in Nanomedicines; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 249–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Guo, X.; Temenoff, J.S.; Tabata, Y.; Caplan, A.I.; Kasper, F.K.; Mikos, A.G. Effect of swelling ratio of injectable hydrogel composites on chondrogenic differentiation of encapsulated rabbit marrow mesenchymal stem cells in vitro. Biomacromolecules 2009, 10, 541–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Formulation | F1 (%w/w) | F2 (%w/w) | F3 (%w/w) | F4 (%w/w) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MLT | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| PEGDA400 | 28.21 | 28.21 | ||
| PEGDA700 | 28.21 | 28.21 | ||
| Tween80 | 56.59 | 56.59 | ||
| PEG200 | 56.59 | 56.59 | ||
| H2O | 13.7 | 13.7 | 13.7 | 13.7 |
| TPO | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Layer thickness | 0.050 mm |
| Initial exposure | 40 s |
| Exposure time | 3 s |
| Rising high | 8 mm |
| Motor speed | 5 mm/s |
| Turn off delay | 4 s |
| Bottom exposure layer | 2 |
| Formulations | Width (mm) | Height (mm) | Weight (mg) | Hardness (N) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | 10 ± 0.32 | 5.2 ± 0.23 | 398.34 ± 2.37 | 5.07 ± 0.48 |
| F2 | 10 ± 0.44 | 5.2 ± 0.30 | 408.33 ± 1.16 | 4.88 ± 0.81 |
| F3 | 10 ± 0.51 | 5.2 ± 0.13 | 378 ± 3.56 | 2.37 ± 0.42 |
| F4 | 10 ± 0.27 | 5.2 ± 0.15 | 415.67 ± 3.23 | 1.93 ± 0.30 |
| Formulation | Zero Order | First Order | Higuchi | Korsmeyer–Peppas | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | Y0 | K0 | R2 | Y1 | R2 | KH | R2 | KKP | n | |
| F1 | 0.90 | 52.05 | 0.15 | 0.85 | 56.38 | 0.62 | 6.01 | 0.90 | 14.35 | 0.35 |
| F2 | 0.96 | 40.00 | 0.14 | 0.90 | 46.70 | 0.93 | 5.03 | 0.95 | 10.55 | 0.36 |
| F3 | 0.98 | 26.27 | 0.15 | 0.93 | 34.33 | 0.99 | 4.32 | 0.95 | 4.47 | 0.49 |
| F4 | 0.99 | 17.43 | 0.16 | 0.93 | 27.31 | 0.97 | 3.91 | 0.99 | 1.99 | 0.62 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Protopapa, C.; Siamidi, A.; Sakellaropoulou, A.; Kolipaka, S.; Junqueira, L.A.; Tabriz, A.G.; Douroumis, D.; Vlachou, M. 3D-Printed Melatonin Tablets with Braille Motifs for the Visually Impaired. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 1017. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17081017
Protopapa C, Siamidi A, Sakellaropoulou A, Kolipaka S, Junqueira LA, Tabriz AG, Douroumis D, Vlachou M. 3D-Printed Melatonin Tablets with Braille Motifs for the Visually Impaired. Pharmaceuticals. 2024; 17(8):1017. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17081017
Chicago/Turabian StyleProtopapa, Chrystalla, Angeliki Siamidi, Aikaterini Sakellaropoulou, Siva Kolipaka, Laura Andrade Junqueira, Atabak Ghanizadeh Tabriz, Dennis Douroumis, and Marilena Vlachou. 2024. "3D-Printed Melatonin Tablets with Braille Motifs for the Visually Impaired" Pharmaceuticals 17, no. 8: 1017. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17081017
APA StyleProtopapa, C., Siamidi, A., Sakellaropoulou, A., Kolipaka, S., Junqueira, L. A., Tabriz, A. G., Douroumis, D., & Vlachou, M. (2024). 3D-Printed Melatonin Tablets with Braille Motifs for the Visually Impaired. Pharmaceuticals, 17(8), 1017. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17081017










