Effect of Crude Extract from the Sea Anemone Bunodeopsis globulifera on Voltage-Gated Ion Channels from Central and Peripheral Murine Nervous Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
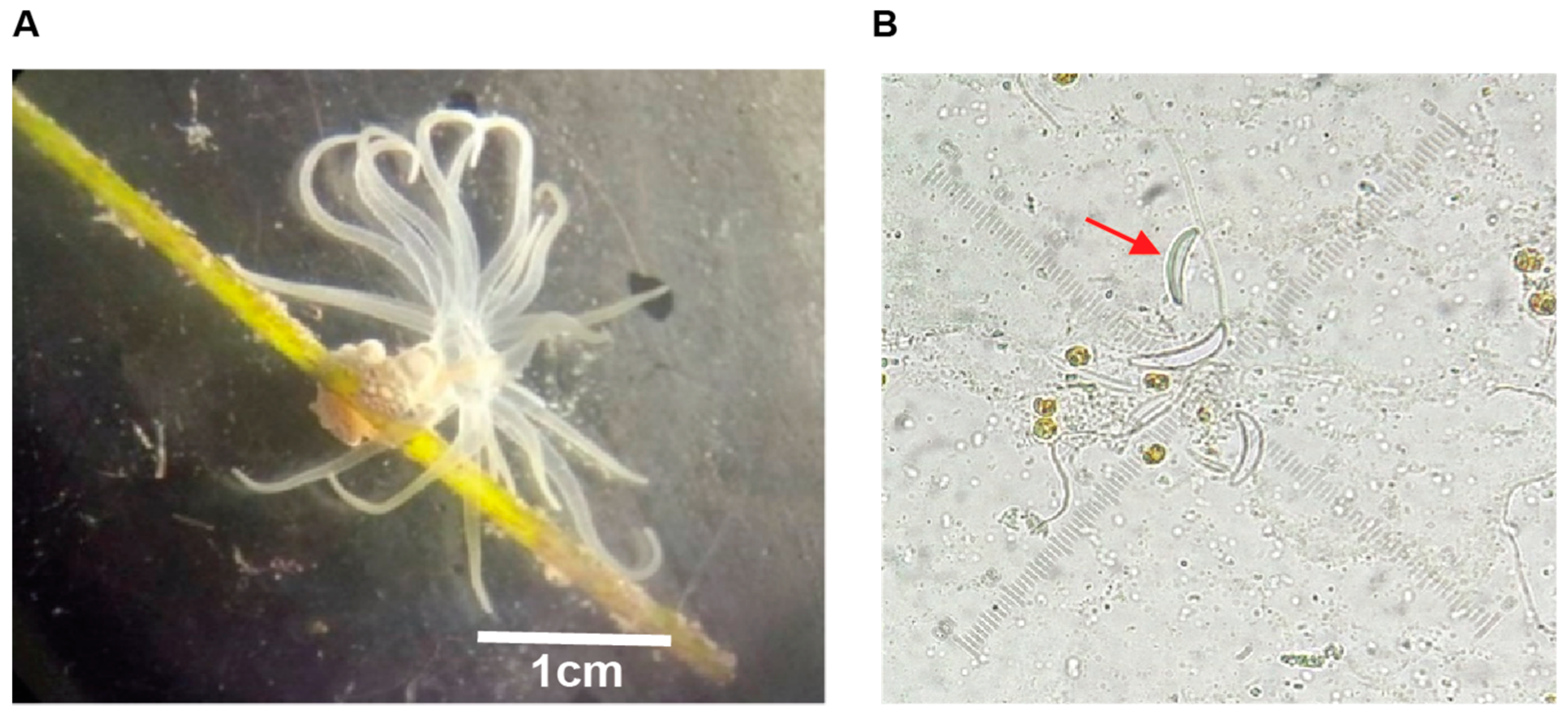
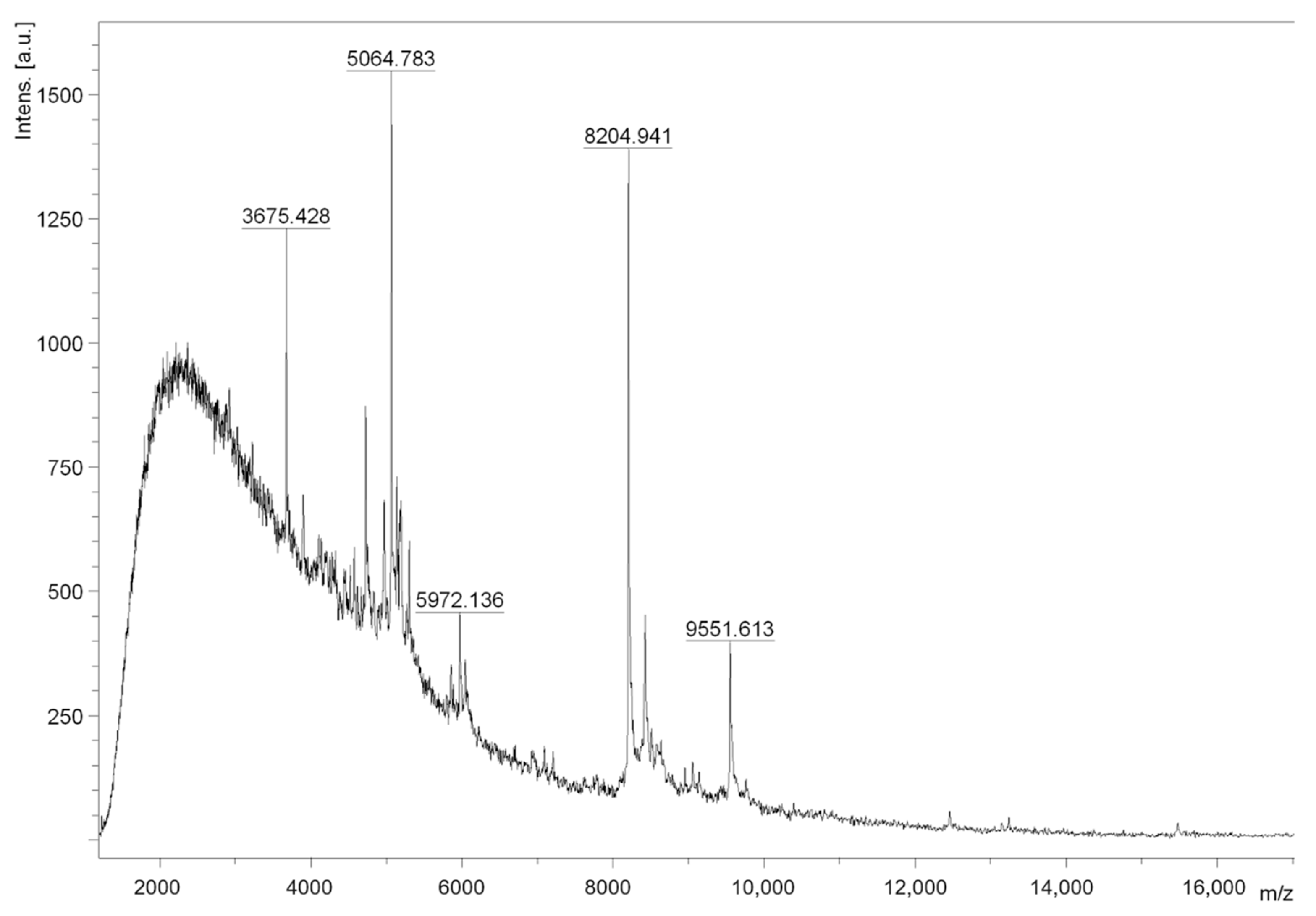
2.1. Crude Extract and F1 Bioactivity
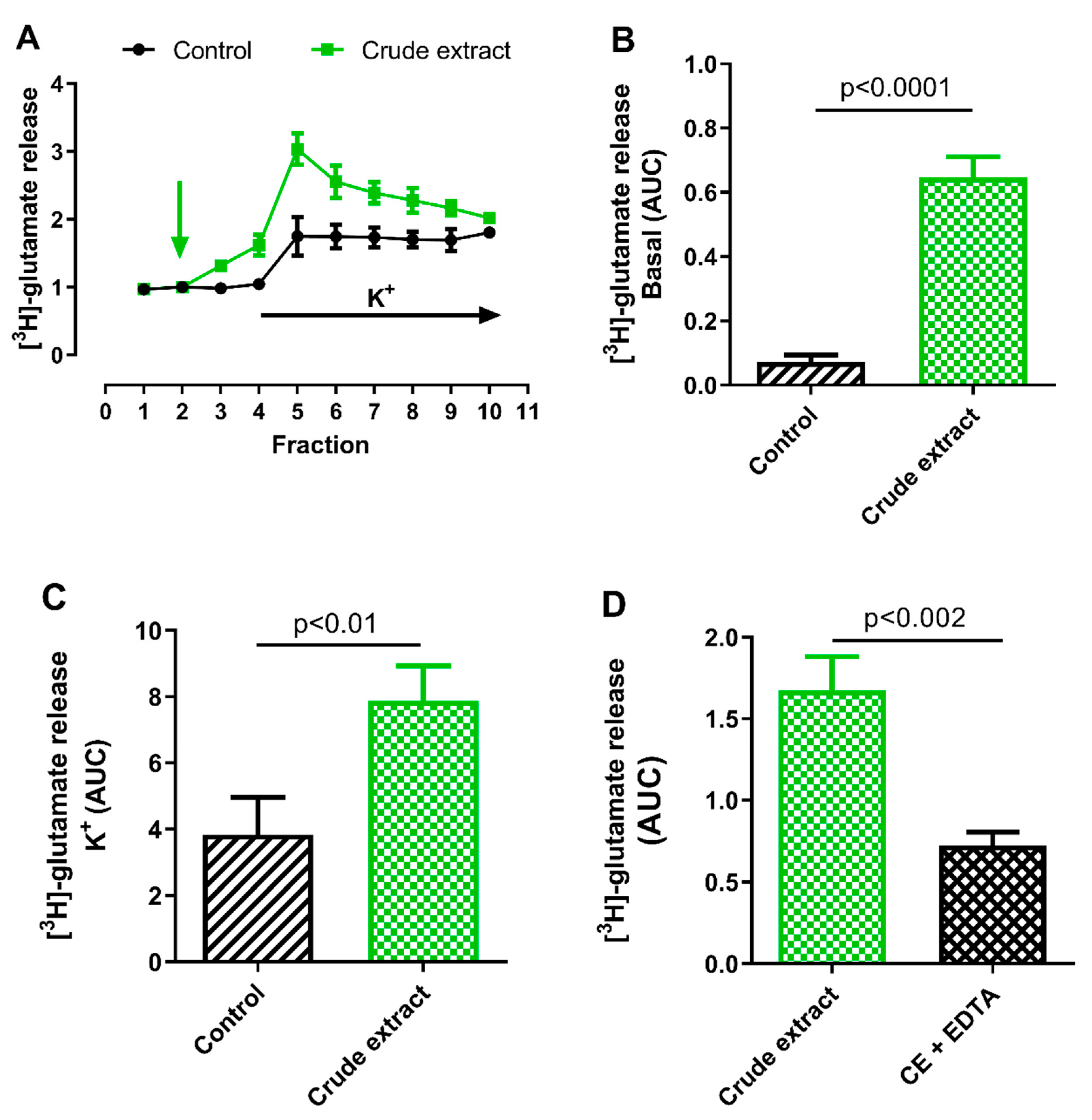
2.2. Neurotoxic Activity
2.2.1. Effect of B. globulifera CE on Cortical [3H]-Glutamate Release
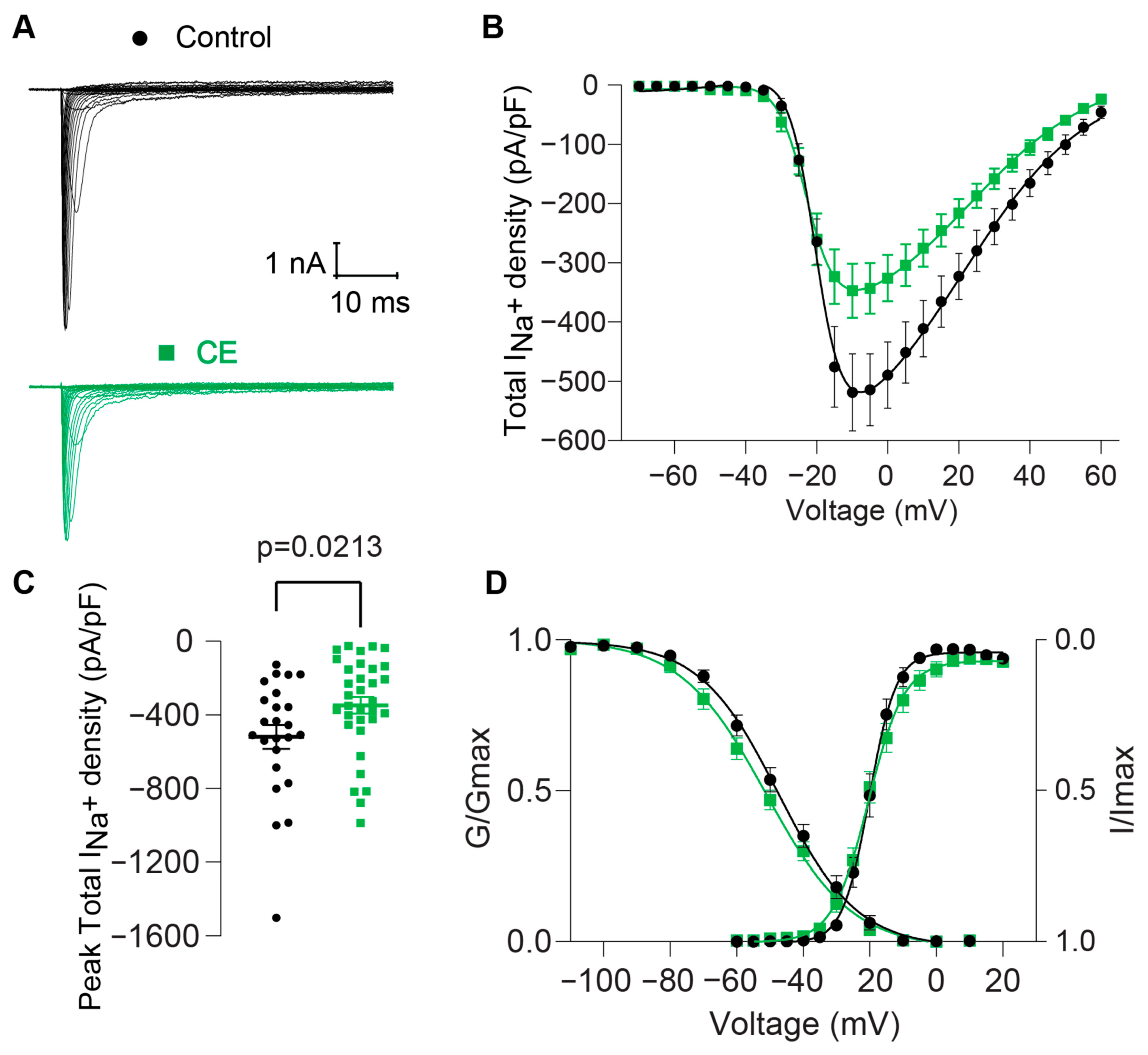
2.2.2. Effect of B. globulifera CE on Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels of Rat DRG Sensory Neurons
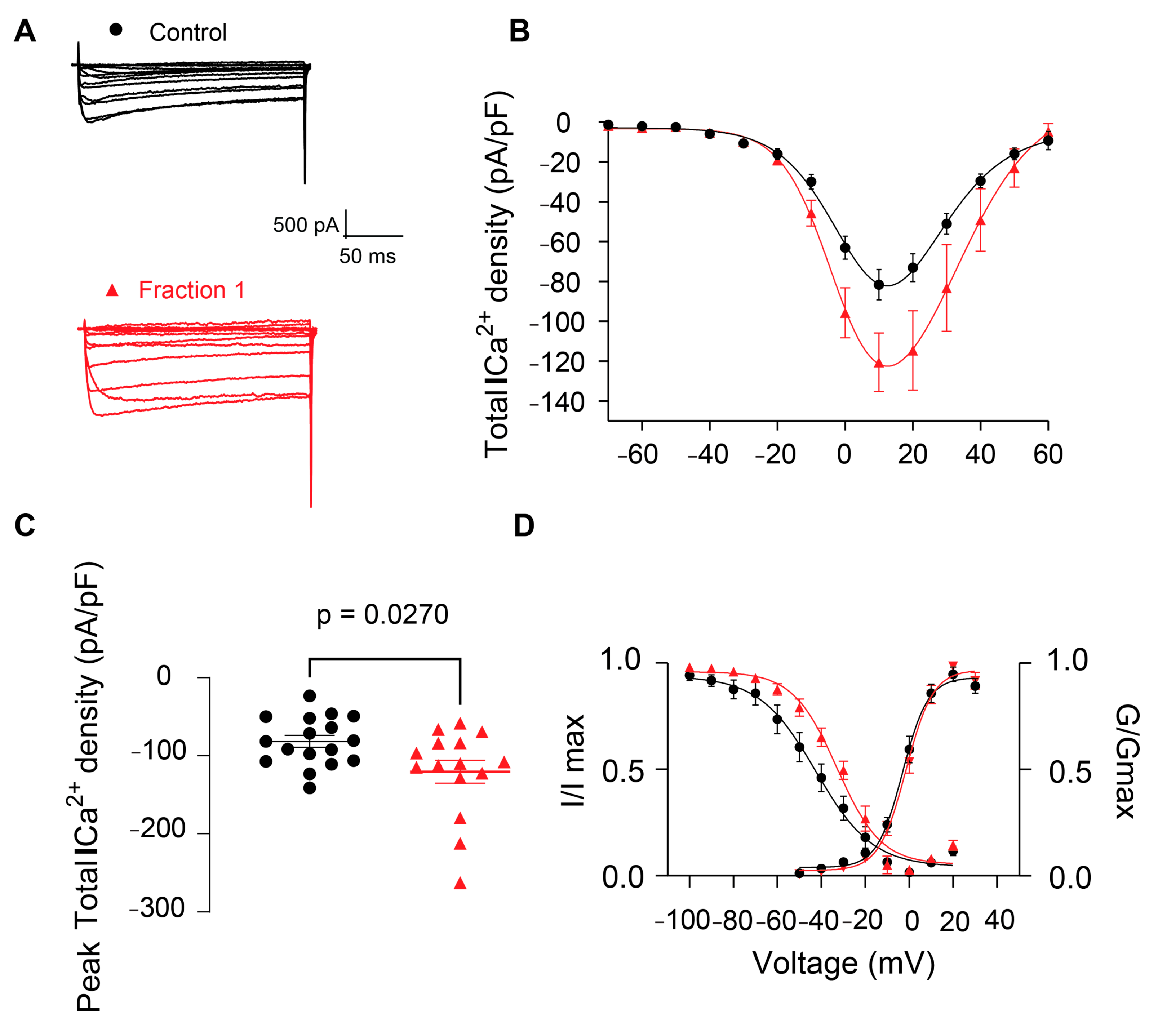
2.2.3. Effect of B. globulifera CE and F1 in Voltage-Gated Calcium Channels of Rat DRG Sensory Neurons
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Sea Anemone Collection
3.2. Crude Extract Obtention
3.3. Protein Quantification
3.4. Biological Activity Assay
3.5. Crude Extract Fractionation and Fraction F1 Mass Spectrometry Analysis
3.6. Neurotoxic Activity Assays
3.6.1. [3H]-Glutamate Release
Radioactive Labeling with [3H]-Glutamate
Experimental Protocol
Quantification of [3H]-Glutamate Release
Statistical Analysis
3.6.2. Electrophysiology
Animals
Isolation and Culture of Rat Dorsal Root Ganglion Neurons
Patch-Clamp Electrophysiology
Voltage-Clamp Recordings
Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Calvete, J.J. Venomics: Integrative venom proteomics and beyond. Biochem. J. 2017, 474, 611–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schendel, V.; Rash, L.D.; Jenner, R.A.; Undheim, A.B. The Diversity of Venom: The Importance of Behavior and Venom System Morphology in Understanding Its Ecology and Evolution. Toxins 2019, 11, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayathilake, J.M.N.J.; Gunathilake, K.V.K. Cnidarian toxins: Recent evidences for potential therapeutic uses. Eur. Zool. J. 2020, 87, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGivern, J.G. Targeting N-type and T-type calcium channels for the treatment of pain. Drug Discov. Today 2006, 11, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maatuf, Y.; Geron, M.; Priel, A. The Role of Toxins in the Pursuit for Novel Analgesics. Toxins 2019, 11, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goyffon, M. The venomous function. In Perspectives in Molecular Toxinology; Ménez, A., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2002; p. 423. [Google Scholar]
- Arai, M.N. A Functional Biology of Scyphozoa; Chapman & Hall: London, UK, 1997; p. 316. [Google Scholar]
- Frazão, B.; Vasconcelos, V.; Antunes, A. Sea Anemone (Cnidaria, Anthozoa, Actiniaria) Toxins: An Overview. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 1812–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stabili, L.; Schirosi, R.; Parisi, M.G.; Pirano, S.; Cammarata, M. The Mucus od Actinia equina (Anthozoa, Cnidaria): An Unexplored Resource for Potential Applicative Purposes. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 5276–5296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Q.; Feng, Y.; Yang, B.; Ming-Yuen, L.S. Cnidarian peptide neurotoxins: A new source of various ion channel modulators or blockers against central nervous systems disease. Drug Discov. Today 2019, 24, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menezes, C.; Thakur, N.L. Sea anemone venom: Ecological interactions and bioactive potential. Toxicon 2022, 208, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colom-Casasnovas, A.; Garay, E.; Cisneros-Mejorado, A.; Aguilar, M.B.; Lazcano-Pérez, F.; Arellano, R.O.; Sánchez-Rodríguez, J. Sea anemone Bartholomea annulata venom inhibits voltage-gated Na+ channels and activates GABAA receptors from mammals. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 5352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honma, T.; Shiomi, K. Peptide Toxins in Sea Anemones: Structural and Functional Aspects. Mar. Biotechnol. 2006, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keen, T.E.B.; Crone, H.D. The hemolytic properties of extracts of tentacles from the cnidarian Chironex fleckeri. Toxicon 1969, 7, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diochot, S.; Baron, A.; Rash, L.D.; Deval, E.; Escoubas, P.; Scarzello, S.; Salinas, M.; Lazdunski, M. A new sea anemone peptide, APETx2, inhibits ASIC3, a major acid-sensitive channel in sensory neurons. EMBO J. 2004, 23, 1516–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuypers, E.; Peigneur, S.; Debaveye, S.; Shiomi, K.; Tytgat, J. TRPV1 Channel as New Target for Marine Toxins: Example of Gigantoxin I, a Sea Anemone Toxin Acting Cuypers, E.; Peigneur, S.; Debaveye, S.; Shiomi, via Modulation of the PLA2 Pathway. Acta Chim. Slov. 2011, 58, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Lazcano-Pérez, F.; Castro, H.; Arenas, I.; García, D.E.; González-Muñoz, R.; Arreguín-Espinosa, R. Activity of Palythoa caribeorum Venom on Voltage-Gated Ion Channels in Mammalian Superior Cervical Ganglion Neurons. Toxins 2016, 8, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milla, L.; Sánchez-Rodríguez, J.; Segura-Puertas, L. Dermatitis por contacto con Bunodeopsis globulifera (Cnidaria anthozoa). Dermatol. Rev. Mex. 2003, 47, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Monroy-Estrada, H.I.; Chirino, Y.I.; Soria-Mercado, I.E.; Sánchez-Rodríguez, J. Toxins from the Caribbean sea anemone Bunodeopsis globulifera increase cisplatin induced cytotoxicity of lung adenocarcinoma cells. J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop. Dis. 2013, 19, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazcano-Pérez, F.; Bermeo, K.; Castro, H.; Salazar, C.Z.; Arenas, I.; Zavala-Moreno, A.; Chávez-Villela, S.N.; Jiménez, I.; Arreguín-Espinosa, R.; Fierro, R.; et al. A Sea Anemone Lebrunia neglecta Venom Fraction Decreases Boar Sperm Cells Capacitation: Possible Involvement of HVA Calcium Channels. Toxins 2022, 14, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elnahriry, K.A.; Wai, D.C.C.; Ashwood, L.M.; Naseem, M.U.; Szanto, T.G.; Guo, S.; Panyi, G.; Prentis, P.J.; Norton, R.S. Structural and functional characterization of Tst2, a novel TRPV1 inhibitory peptide from the Australian sea anemone Telmactatis Stephensoni. BBA Proteins Proteom. 2024, 1872, 140952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Muñoz, R.; Simoes, N.; Sánchez-Rodríguez, J.; Rodríguez, E.; Segura-Puertas, L. First Inventory of Sea Anemones (Cnidaria: Actinaria) of the Mexican Caribbean. Zootaxa 2012, 3556, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Rodríguez, J.; Zugasti, A.; Santamaría, A.; Galván-Arzate, S.; Segura-Puertas, L. Isolation, Partial Purification and Characterization of Active Polypeptide from the Sea Anemone Bartholomea annulata. Basic. Clin. Pharmacol. Toxic. 2006, 99, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kem, W.R. Marine Venoms and Toxins. Encycl. Toxicol. 2014, 3, 160–163. [Google Scholar]
- Nestler, E.J.; Hyman, S.E.; Malenka, R.C. Molecular Neuropharmacology; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2001; p. 539. [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi, A.; Takeuchi, N. The effect on crayfish muscle of ionotophoretically applied glutamate. J. Physiol. 1964, 170, 296–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garateix, A.; Flores, A.; García-Andrade, J.M.; Palmero, A.; Aneiros, A.; Vega, R.; Soto, E. Antagonism of glutamate receptors by a chromatographic fraction from the exudate of the sea anemone Phyllactis flosculifera. Toxicon 1996, 34, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Migues, P.V.; Leal, R.B.; Mantovani, M.; Nicolau, M.; Gabilan, N.H. Synaptosomal glutamate reléase induced by the fraction Bc2 from the venom of the sea anemone Bunodosoma caissarum. NeuroReport 1999, 10, 67–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gondran, M.; Eckeli, A.L.; Migues, P.V.; Gabilan, N.H.; Rodrigues, A.L.S. The crude extract from the sea anemone, Bunodosoma caissarum elicits convulsions in mice: Possible involvement of the glutamatergic system. Toxicon 2002, 40, 1667–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazcano-Pérez, F.; Hernández-Guzmán, U.; Sánchez-Rodríguez, J.; Arreguín-Espinosa, R. Cnidarian Neurotoxic Peptides Affecting Central Nervous System Targets. Cent. Nerv. Syst. Agents Med. Chem. 2016, 16, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catterall, W.A. From Ionic Currents to Molecular Mechanisms: The Structure and Function of Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels. Neuron 2000, 26, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, J.J.; Blumenthal, K.M. Site-3 sea anemone toxins: Molecular probes of gating mechanisms in voltage-dependent sodium channels. Toxicon 2007, 49, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazcano-Pérez, F.; Vivas, O.; Román-González, S.A.; Rodríguez-Bustamante, E.; Castro, H.; Arenas, I.; García, D.E.; Sánchez-Puig, N.; Arreguín-Espinosa, R. A purified Palythoa venom fraction delays sodium current inactivation in sympathetic neurons. Toxicon 2014, 82, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qar, J.; Schweitz, H.; Schmid, A.; Lazdunski, M. A polypeptide toxin from the coral Goniopora: Purification and action on Ca2+ channels. FEBS Lett. 1986, 202, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domínguez-Pérez, D.; Diaz-Garcia, C.M.; García-Delgado, N.; Sierra-Gómez, Y.; Castañeda, O.; Antunes, A. Insights into the toxicological properties of a low molecular weight fraction from Zoanthus sociatus (Cnidaria). Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kochegarov, A.A. Therapeutical application of voltage-gated calcium channel modulators. Expert Opin. Ther. Patents 2002, 12, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Béress, L.; Béress, R. Reinigung zweier krabbenlahmender Toxine aus der Sea anemone Anemonia sulcata. Kiel. Meeresforsch. 1971, 27, 117–127. [Google Scholar]
- Briones-Lizardi, L.J.; Cortés, H.; Avalos-Fuentes, J.A.; Paz-Bermudez, F.; Aceves, J.; Erlij, D.; Florán, B. Presynantic control of [3H]-glutamate release by dopamine receptor subtypes in the rat substantia nigra. Central role of D1 and D3 receptors. Neuroscience 2019, 406, 563–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paxinos, G.; Watson, C. The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Loya-Lopez, S.I.; Allen, H.N.; Duran, P.; Calderon-Rivera, A.; Gomez, K.; Kumar, U.; Shields, R.; Zeng, R.; Dwivedi, A.; Saurabh, S.; et al. Intranasal CRMP2-Ubc9 inhibitor regulates Nav1.7 to alleviate trigeminal neurophatic Pain. Pain 2023, 165, 573–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Flores-Pérez, A.J.; Loya-López, S.; Ávalos-Fuentes, A.; Calderon-Rivera, A.; Damo, E.; Lazcano-Pérez, F.; Khanna, R.; Florán-Garduño, B.; Sánchez-Rodríguez, J. Effect of Crude Extract from the Sea Anemone Bunodeopsis globulifera on Voltage-Gated Ion Channels from Central and Peripheral Murine Nervous Systems. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 1006. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17081006
Flores-Pérez AJ, Loya-López S, Ávalos-Fuentes A, Calderon-Rivera A, Damo E, Lazcano-Pérez F, Khanna R, Florán-Garduño B, Sánchez-Rodríguez J. Effect of Crude Extract from the Sea Anemone Bunodeopsis globulifera on Voltage-Gated Ion Channels from Central and Peripheral Murine Nervous Systems. Pharmaceuticals. 2024; 17(8):1006. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17081006
Chicago/Turabian StyleFlores-Pérez, Aleida Jeannette, Santiago Loya-López, Arturo Ávalos-Fuentes, Aida Calderon-Rivera, Elisa Damo, Fernando Lazcano-Pérez, Rajesh Khanna, Benjamin Florán-Garduño, and Judith Sánchez-Rodríguez. 2024. "Effect of Crude Extract from the Sea Anemone Bunodeopsis globulifera on Voltage-Gated Ion Channels from Central and Peripheral Murine Nervous Systems" Pharmaceuticals 17, no. 8: 1006. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17081006
APA StyleFlores-Pérez, A. J., Loya-López, S., Ávalos-Fuentes, A., Calderon-Rivera, A., Damo, E., Lazcano-Pérez, F., Khanna, R., Florán-Garduño, B., & Sánchez-Rodríguez, J. (2024). Effect of Crude Extract from the Sea Anemone Bunodeopsis globulifera on Voltage-Gated Ion Channels from Central and Peripheral Murine Nervous Systems. Pharmaceuticals, 17(8), 1006. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17081006






