Assessment of Radiolabelled Derivatives of R954 for Detection of Bradykinin B1 Receptor in Cancer Cells: Studies on Glioblastoma Xenografts in Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
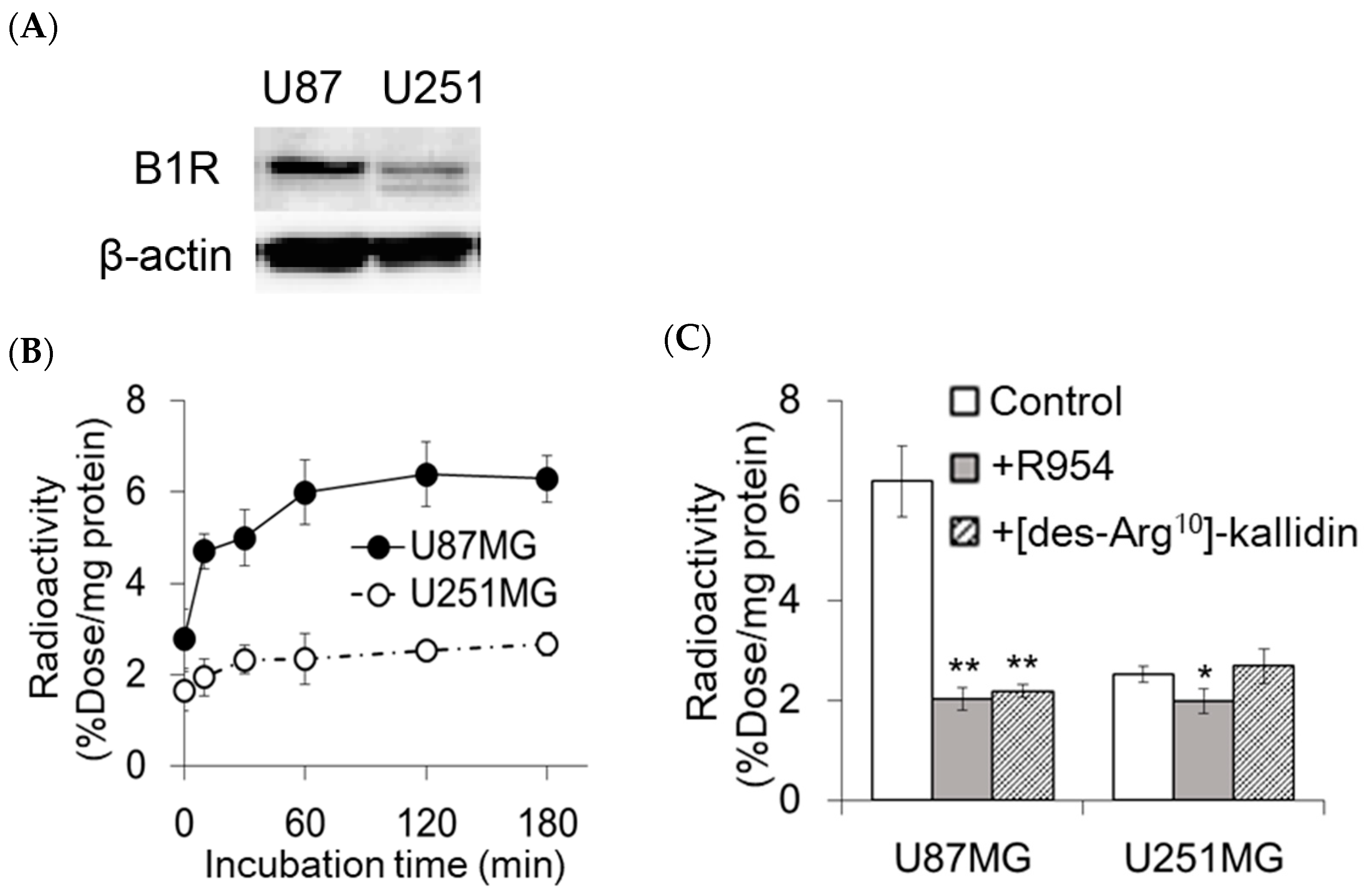
2.1. In Vitro Accumulation of [111In]In-DOTA-Ahx-R954 in U87MG and U251MG Cells
2.2. Biodistribution of [111In]In-DOTA-Ahx-R954 in U87MG-Bearing Mice
2.3. Ex Vivo Autoradiography of [111In]In-DOTA-Ahx-R954 and [14C]iodoantipyrine
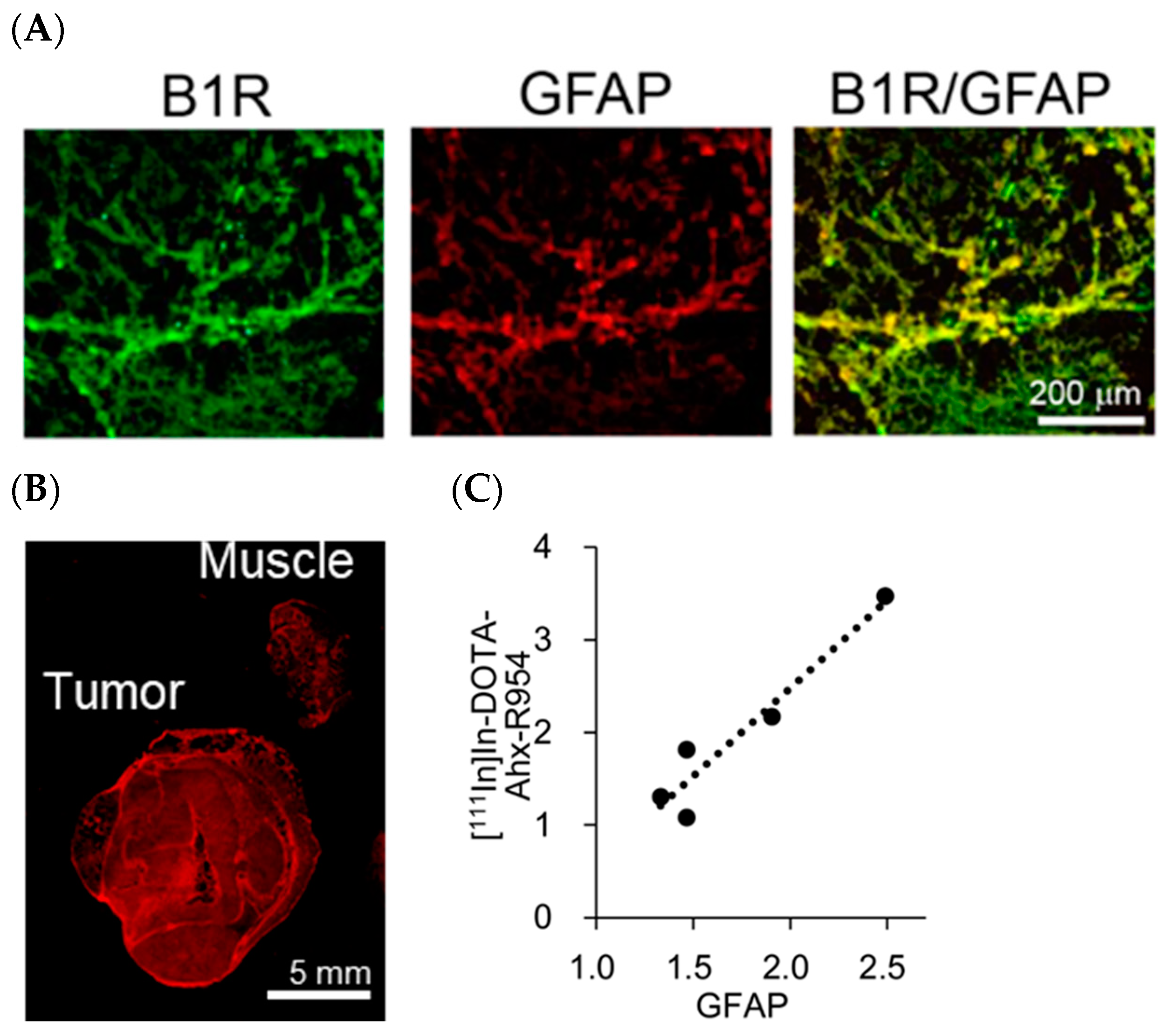
2.4. B1R Expression and Intratumoural Distribution of Glioblastoma Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Synthesis
4.2. Radiolabelling
4.3. In Vitro Assay Using Glioblastoma Cells
4.4. Western Blotting
4.5. Animal Model
4.6. Biodistribution in Glioblastoma-Bearing Mice
4.7. Ex Vivo Autoradiography
4.8. Immunohistochemistry
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Leeb-Lundberg, L.M.F.; Marceau, F.; Müller-Esterl, W.; Pettibone, D.J.; Zuraw, B.L. International union of pharmacology. XLV. Classification of the kinin receptor family: From molecular mechanisms to pathophysiological consequences. Pharmacol. Rev. 2005, 57, 27–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golias, C.; Charalabopoulos, A.; Stagikas, D.; Charalabopoulos, K.; Batistatou, A. The kinin system-bradykinin: Biological effects and clinical implications. Multiple role of the kinin system-bradykinin. Hippokratia 2007, 11, 124–128. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- da Costa, P.L.N.; Sirois, P.; Tannock, I.F.; Chammas, R. The role of kinin receptors in cancer and therapeutic opportunities. Cancer Lett. 2014, 345, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deepak, K.; Roy, P.K.; Kola, P.; Mukherjee, B.; Mandal, M. An overview of kinin mediated events in cancer progression and therapeutic applications. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Rev. Cancer 2022, 1877, 188807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dlamini, Z. Upregulation of tissue kallikrein, kinin B1 receptor, and kinin B2 receptor in mast and giant cells infiltrating oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J. Clin. Pathol. 2005, 58, 915–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zelawski, W.; Machnik, G.; Nowaczyk, G.; Plewka, D.; Lorenc, Z.; Sosada, K.; Stadnicki, A. Expression and localisation of kinin receptors in colorectal polyps. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2006, 6, 997–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dillenburg-Pilla, P.; Maria, A.G.; Reis, R.I.; Floriano, E.M.; Pereira, C.D.; De Lucca, F.L.; Ramos, S.G.; Pesquero, J.B.; Jasiulionis, M.G.; Costa-Neto, C.M. Activation of the kinin B1 receptor attenuates melanoma tumour growth and metastasis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e64453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molina, L.; Matus, C.E.; Astroza, A.; Pavicic, F.; Tapia, E.; Toledo, C.; Perez, J.A.; Nualart, F.; Gonzalez, C.B.; Burgos, R.A.; et al. Stimulation of the bradykinin B1 receptor induces the proliferation of estrogen-sensitive breast cancer cells and activates the ERK1/2 signaling pathway. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2009, 118, 499–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Costa, P.L.N.; Wynne, D.; Fifis, T.; Nguyen, L.; Perini, M.; Christophi, C. The kallikrein-kinin system modulates the progression of colorectal liver metastases in a mouse model. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naidu, N.; Botha, J.; Naidoo, S. B1 but not B2 bradykinin receptor agonists promote DU145 prostate cancer cell proliferation and migration. Afr. Health Sci. 2014, 14, 657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Nicoletti, N.F.; Sénécal, J.; da Silva, V.D.; Roxo, M.R.; Ferreira, N.P.; de Morais, R.L.T.; Pesquero, J.B.; Campos, M.M.; Couture, R.; Morrone, F.B. Primary role for kinin B1 and B2 receptors in glioma proliferation. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 54, 7869–7882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, M.N.; Breznik, B.; Pillat, M.M.; Pereira, R.L.; Ulrich, H.; Lah, T.T. Kinins in glioblastoma microenvironment. Cancer Microenviron. 2019, 12, 77–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, K.-S.; Pan, J.; Amouroux, G.; Turashvili, G.; Mesak, F.; Hundal-Jabal, N.; Pourghiasian, M.; Lau, J.; Jenni, S.; Aparicio, S.; et al. In vivo radioimaging of bradykinin receptor B1, a widely overexpressed molecule in human cancer. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amouroux, G.; Pan, J.; Jenni, S.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Z.; Hundal-Jabal, N.; Colpo, N.; Liu, Z.; Bénard, F.; Lin, K.-S. Imaging bradykinin B1 receptor with 68Ga-labelled [Des-Arg10] kallidin derivatives: Effect of the linker on biodistribution and tumour uptake. Mol. Pharm. 2015, 12, 2879–2888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, K.-S.; Amouroux, G.; Pan, J.; Zhang, Z.; Jenni, S.; Lau, J.; Liu, Z.; Hundal-Jabal, N.; Colpo, N.; Bénard, F. Comparative studies of three 68Ga-labelled [Des-Arg10] kallidin derivatives for imaging bradykinin B1 receptor expression with PET. J. Nucl. Med. 2015, 56, 622–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Amouroux, G.; Zhang, Z.; Pan, J.; Hundal-Jabal, N.; Colpo, N.; Lau, J.; Perrin, D.M.; Bénard, F.; Lin, K.-S. 18F-trifluoroborate derivatives of [Des-Arg10] bradykinin B1 receptor expression with positron emission tomography. Mol. Pharm. 2015, 12, 974–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, H.-T.; Pan, J.; Lau, J.; Zhang, C.; Zeisler, J.; Colpo, N.; Bénard, F.; Lin, K.-S. Radiolabelled R954 derivatives for imaging bradykinin B1 receptor expression with positron emission tomography. Mol. Pharm. 2017, 14, 821–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, J.; Rousseau, J.; Kwon, D.; Bénard, F.; Lin, K.-S. A Systematic review of molecular imaging agents targeting bradykinin B1 and B2 Receptors. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicoletti, N.F.; Erig, T.C.; Zanin, R.F.; Pereira, T.C.B.; Bogo, M.R.; Campos, M.M.; Morrone, F.B. Mechanisms involved in kinin-induced glioma cells proliferation: The role of ERK1/2 and PI3K/Akt pathways. J. Neurooncol. 2014, 120, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Lei, B.; Xiang, W.; Wang, H.; Feng, W.; Liu, Y.; Qi, S. Differences in protein expression between the U251 and U87 cell lines. Turk. Neurosurg. 2016, 27, 894–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillat, M.M.; Oliveira, M.N.; Motaln, H.; Breznik, B.; Glaser, T.; Lah, T.T.; Ulrich, H. Glioblastoma-mesenchymal stem cell communication modulates expression patterns of kinin receptors: Possible involvement of bradykinin in information flow. Cytom. Part A 2016, 89, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, P.Y.; Kesari, S. Malignant gliomas in adults. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 492–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, M.N.; Pillat, M.M.; Baranova, J.; Andrejew, R.; dos Santos, B.L.; Costa, S.L.; Lah, T.T.; Ulrich, H. Glioblastoma cell invasiveness and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transitioning are modulated by kinin receptors. Adv. Cancer Biol.-Metastasis 2022, 4, 100045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, M.N.; Pillat, M.M.; Motaln, H.; Ulrich, H.; Lah, T.T. Kinin-B1 receptor stimulation promotes invasion and is involved in cell-cell interaction of co-cultured glioblastoma and mesenchymal stem cells. Sci Rep. 2018, 8, 1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gera, L.; Roy, C.; Bawolak, M.T.; Charest-Morin, X.; Marceau, F. N-terminal extended conjugates of the agonists and antagonists of both bradykinin receptor subtypes: Structure-activity relationship, cell imaging using ligands conjugated with fluorophores and prospect for functionally active cargoes. Peptides 2012, 34, 433–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamaya, K.; Doi, K.; Tanaka, T.; Nishimoto, A. The determination of glial fibrillary acidic protein for the diagnosis and histogenetic study of central nervous system tumours: A study of 152 cases. Acta Med. Okayama 1985, 39, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadipour, Y.; Gembruch, O.; Pierscianek, D.; Sure, U.; Jabbarli, R. Does the expression of glial fibrillary acid protein (GFAP) stain in glioblastoma tissue have a prognostic impact on survival? Neurochirurgie 2020, 66, 150–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulut, O.P.; Dipp, S.; El-Dahr, S. Ontogeny of bradykinin B1 receptors in the mouse kidney. Pediatr. Res. 2009, 66, 519–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gene Expression Database (GXD), Mouse Genome Informatics Web Site. [MGI:3625021]. Available online: http://www.informatics.jax.org (accessed on 22 December 2023).
- Saleem, A.; Price, P.M. Early tumor drug pharmacokinetics is influenced by tumor perfusion but not plasma drug exposure. Clin Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 8184–8190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.P.; Codd, E.E. Characterization of bradykinin receptors in human lung fibroblasts using the binding of 3[H][Des-Arg10,Leu9]kallidin and [3H]NPC17731. Life Sci. 1998, 62, 2303–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurusamy, M.; Nasseri, S.; Lee, H.; Jung, B.; Lee, D.; Khang, G.; Abraham, W.M.; Doods, H.; Wu, D. Kinin B1 receptor antagonist BI113823 reduces allergen-induced airway inflammation and mucus secretion in mice. Pharmacol. Res. 2016, 104, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues-Junior, V.S.; Pail, P.B.; Villela, A.D.; Falcão, V.C.A.; Dadda, A.S.; Abbadi, B.L.; Pesquero, J.B.; Santos, D.S.; Basso, L.A.; Campos, M.M. Effect of the bradykinin 1 receptor antagonist SSR240612 after oral administration in mycobacterium tuberculosis-infected mice. Tuberculosis 2018, 109, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasaeifar, B.; Lupala, C.S.; Gomez-Gutierrez, P.; Perez, J.J. Molecular features characterizing non-peptide selectivity to the human B1 and B2 bradykinin receptors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2019, 29, 11–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Xue, Y.; Liu, Y.; Fu, W.; Jiang, N.; An, P.; Wang, P.; Yang, Z. Study of correlation between expression of bradykinin B2 receptor and pathological grade in human gliomas. Br. J. Neurosurg. 2005, 19, 322–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arano, Y.; Akizawa, H.; Uezono, T.; Akaji, K.; Ono, M.; Funakoshi, S.; Koizumi, M.; Yokoyama, A.; Kiso, Y.; Saji, H. Conventional and high-yield synthesis of DTPA-conjugated peptides: Application of a monoreactive DTPA to DTPA-D-Phe1-Octreotide Synthesis. Bioconjug. Chem. 1997, 8, 442–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobeil, F.; Sirois, P.; Regoli, D. Preclinical pharmacology, metabolic stability, pharmacokinetics and toxicology of the peptidic kinin B1 receptor antagonist R-954. Peptides 2014, 52, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regoli, D.; Nsa Allogho, S.; Rizzi, A.; Gobeil, F.J. Bradykinin receptors and their antagonists. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1998, 348, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugyo, A.; Tsuji, A.B.; Sudo, H.; Takano, K.; Kusakabe, M.; Higashi, T. Proof of concept study for increasing tenascin-C-targeted drug delivery to tumors previously subjected to therapy: X-irradiation increases tumor uptake. Cancers 2020, 12, 3652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, O.; Shukuri, M.; Hosoi, R.; Amitani, M.; Matsuura, N.; Hatazawa, J.; Takai, N. Distinct different intra-tumour distribution of FDG between early phase and late phase in mouse fibrosarcoma. Ann. Nucl. Med. 2005, 19, 655–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| 1 h | 4 h | 24 h | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Radioactivity (% Dose/g) | |||
| Plasma | 2.75 ± 0.26 | 0.06 ± 0.03 | 0.04 ± 0.01 |
| Heart | 0.83 ± 0.16 | 0.29 ± 0.05 | 0.21 ± 0.03 |
| Lung | 2.37 ± 0. 97 | 0.42 ± 0.07 | 0.26 ± 0.08 |
| Liver | 1.57 ± 1.36 | 2.36 ± 0.31 | 1.18 ± 0.27 |
| Kidney | 120.1± 19.9 | 159.3 ± 8.76 | 109.2 ± 22.9 |
| Stomach | 0.79 ± 0.09 | 0.31 ± 0.09 | 0.18 ± 0.04 |
| Small Intestine | 0.68 ± 0.02 | 0.36 ± 0.04 | 0.22 ± 0.03 |
| Large Intestine | 0.34 ± 0.04 | 0.69 ± 0.29 | 0.46 ± 0.13 |
| Pancreas | 0.55 ± 0.06 | 0.28 ± 0.07 | 0.22 ± 0.06 |
| Spleen | 0.55 ± 0.10 | 0.35 ± 0.07 | 0.36 ± 0.08 |
| Bone | 0.60 ± 0.32 | 0.50 ± 0.27 | 0.42 ± 0.20 |
| Brain | 0.04 ± 0.003 | 0.02 ± 0.013 | 0.01 ± 0.004 |
| Muscle | 0.61 ± 0.10 | 0.41 ± 0.04 | 0.32 ± 0.07 |
| Tumour | 1.37 ± 0.06 * | 0.71 ± 0.09 * | 0.68 ± 0.12 * |
| Tumour/tissue ratios of radioactivity | |||
| Tumour/Plasma | 0.50 ± 0.03 | 13.12 ± 4.98 | 19.00 ± 3.53 |
| Tumour/Muscle | 2.31 ± 0.42 | 1.72 ± 0.16 | 2.15 ± 0.35 |
| 1 h | 4 h | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vehicle | R954 | Vehicle | R954 | |
| Radioactivity (% Dose/g) | ||||
| Plasma | 2.00 ± 0.58 | 7.49 ± 1.68 *** | 0.15 ± 0.09 | 0.50 ± 0.13 ** |
| Heart | 0.55 ± 0.20 | 1.45 ± 0.36 ** | 0.32 ± 0.06 | 0.36 ± 0.07 |
| Lung | 1.16 ± 0.30 | 3.49 ± 1.12 ** | 0.46 ± 0.16 | 0.53 ± 0.17 |
| Liver | 1.65 ± 0.33 | 2.82 ± 0.55 ** | 2.25 ± 0.68 | 2.99 ± 0.77 |
| Kidney | 67.2 ± 14.1 | 26.8 ± 13.7 ** | 111.0 ± 13.45 | 92.2± 9.86 * |
| Stomach | 0.54 ± 0.09 | 1.70 ± 0.54 ** | 0.55 ± 0.12 | 0.52 ± 0.26 |
| Small Intestine | 0.58 ± 0.18 | 1.22 ± 0.54 * | 0.54 ± 0.18 | 0.72 ± 0.32 |
| Large Intestine | 0.27 ± 0.08 | 0.65 ± 0.21 ** | 1.06 ± 0.60 | 1.50 ± 0.65 |
| Pancreas | 0.37 ± 0.09 | 0.85 ± 0.19 *** | 0.29 ± 0.05 | 0.28 ± 0.10 |
| Spleen | 0.36 ± 0.08 | 0.96 ± 0.24 *** | 0.42 ± 0.12 | 0.51 ± 0.21 |
| Bone | 0.44 ± 0.16 | 1.30 ± 0.26 *** | 0.49 ± 0.28 | 0.58 ± 0.19 |
| Brain | 0.03 ± 0.01 | 0.09 ± 0.03 ** | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 0.03 ± 0.01 |
| Muscle | 0.37 ± 0.08 | 1.21 ± 0.17 *** | 0.42 ± 0.06 | 0.31 ± 0.10 |
| Tumour | 0.82 ± 0.25 | 2.13 ± 0.48 *** | 0.66 ± 0.11 | 0.72 ± 0.10 |
| Tumour/tissue ratios of radioactivity | ||||
| Tumour/Plasma | 0.41 ± 0.03 | 0.29 ± 0.03 *** | 4.89 ± 1.27 | 1.51 ± 0.33 *** |
| Tumour/Muscle | 2.18 ± 0.24 | 1.76 ± 0.30 * | 1.57 ± 0.24 | 2.56 ± 1.05 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shukuri, M.; Onoe, S.; Karube, T.; Mokudai, R.; Wakui, H.; Asano, H.; Murai, S.; Akizawa, H. Assessment of Radiolabelled Derivatives of R954 for Detection of Bradykinin B1 Receptor in Cancer Cells: Studies on Glioblastoma Xenografts in Mice. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 902. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17070902
Shukuri M, Onoe S, Karube T, Mokudai R, Wakui H, Asano H, Murai S, Akizawa H. Assessment of Radiolabelled Derivatives of R954 for Detection of Bradykinin B1 Receptor in Cancer Cells: Studies on Glioblastoma Xenografts in Mice. Pharmaceuticals. 2024; 17(7):902. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17070902
Chicago/Turabian StyleShukuri, Miho, Satoru Onoe, Tsubasa Karube, Risa Mokudai, Hayate Wakui, Haruka Asano, Shin Murai, and Hiromichi Akizawa. 2024. "Assessment of Radiolabelled Derivatives of R954 for Detection of Bradykinin B1 Receptor in Cancer Cells: Studies on Glioblastoma Xenografts in Mice" Pharmaceuticals 17, no. 7: 902. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17070902
APA StyleShukuri, M., Onoe, S., Karube, T., Mokudai, R., Wakui, H., Asano, H., Murai, S., & Akizawa, H. (2024). Assessment of Radiolabelled Derivatives of R954 for Detection of Bradykinin B1 Receptor in Cancer Cells: Studies on Glioblastoma Xenografts in Mice. Pharmaceuticals, 17(7), 902. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17070902






