Comparative Efficacy and Safety of Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists in Children and Adolescents with Obesity or Overweight: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
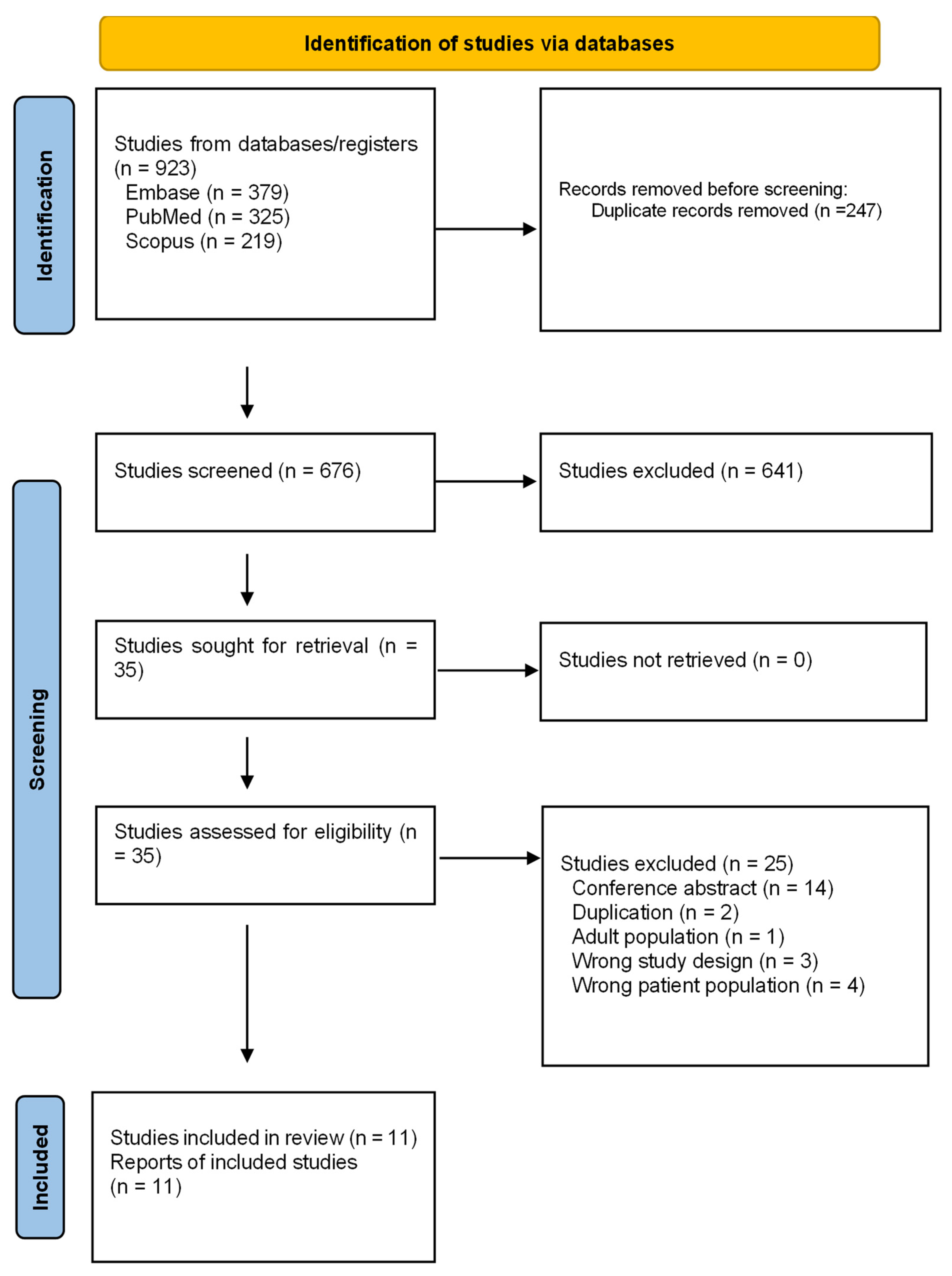
2.1. Search Results and Characteristics of Studies
2.2. Primary Efficacy Outcomes
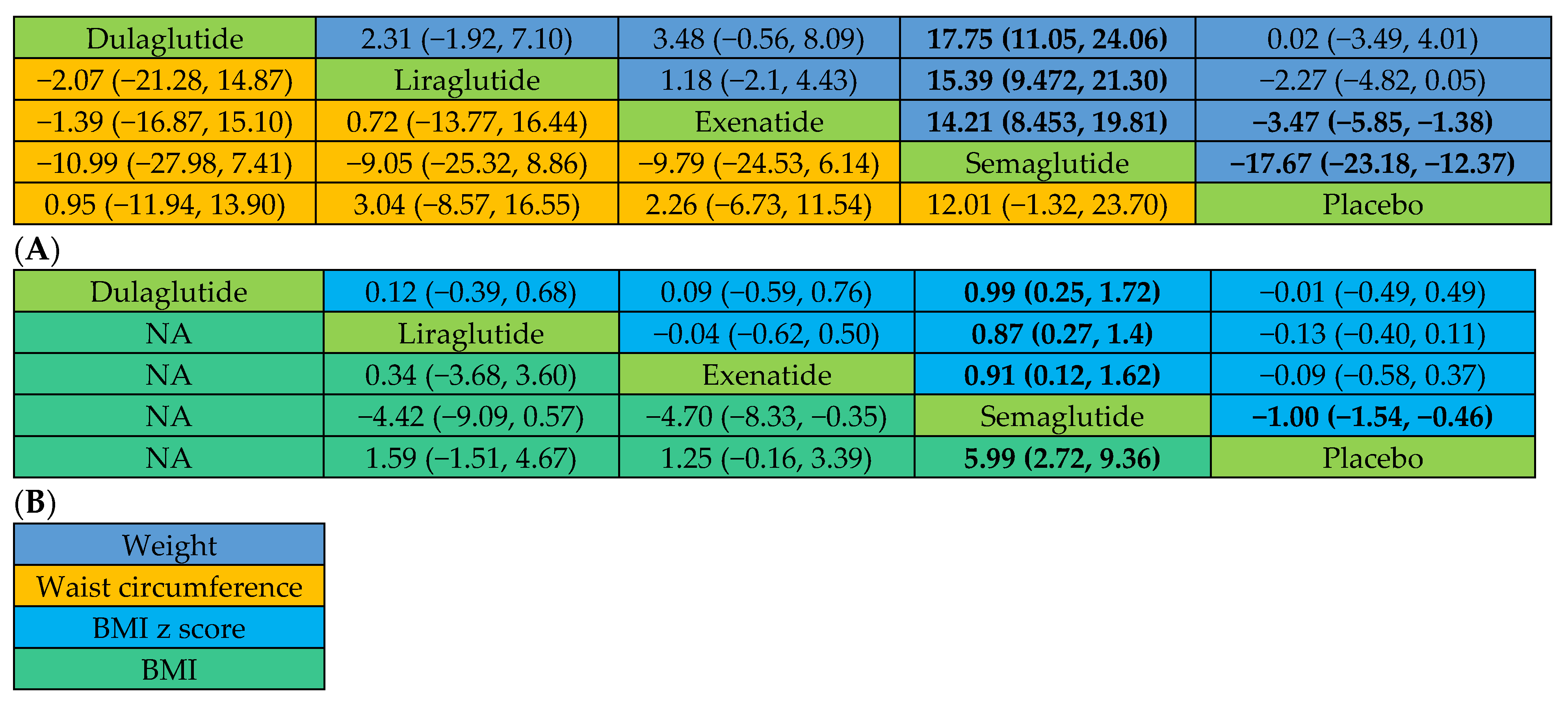
2.2.1. Actual Weight Changes
2.2.2. Changes in BMI and BMI z Score
2.2.3. Changes in Waist Circumference and Total Tissue Fat
2.3. Secondary Efficacy Outcomes
2.3.1. Changes in HbA1c, Insulin, and Fasting Plasma Glucose (FPG)
HbA1c
Insulin
FPG
2.3.2. Changes in Systolic and Diastolic Blood Pressure (SBP and DBP)
2.3.3. Changes in Low-Density Lipoproteins (LDLs), Triglycerides (TGs), and Total Cholesterol
2.3.4. Quality of Life (QoL)
2.4. Subgroup Analyses
2.4.1. All Participants with Therapy Duration ≥ 26 Weeks
2.4.2. Participants with Obesity and All Durations of Therapy
2.4.3. Participants with Obesity and Therapy Duration ≥ 26 Weeks
2.4.4. Participants with Overweight and Diabetes
2.5. Safety Outcomes
3. Discussion
Strengths and Limitations
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Search Strategy
4.2. Study Selection
4.3. Outcome Measures
4.4. Data Extraction and Risk of Bias Assessment
4.5. Data Analyses
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Skinner, A.C.; Ravanbakht, S.N.; Skelton, J.A.; Perrin, E.M.; Armstrong, S.C. Prevalence of Obesity and Severe Obesity in US Children, 1999–2016. Pediatrics 2018, 141, e20173459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simmonds, M.; Llewellyn, A.; Owen, C.G.; Woolacott, N. Predicting adult obesity from childhood obesity: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes. Rev. 2016, 17, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahmouni, K.; Correia, M.L.; Haynes, W.G.; Mark, A.L. Obesity-associated hypertension: New insights into mechanisms. Hypertension 2005, 45, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaban Mohamed, M.A.; AbouKhatwa, M.M.; Saifullah, A.A.; Hareez Syahmi, M.; Mosaad, M.; Elrggal, M.E.; Dehele, I.S.; Elnaem, M.H. Risk Factors, Clinical Consequences, Prevention, and Treatment of Childhood Obesity. Children 2022, 9, 1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lister, N.B.; Baur, L.A.; Felix, J.F.; Hill, A.J.; Marcus, C.; Reinehr, T.; Summerbell, C.; Wabitsch, M. Child and adolescent obesity. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2023, 9, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Obesity in Children and Young People: Prevention and Lifestyle Weight Management Programmes; Quality Standard 94; National Institute for Health and Care Excellence: London, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Grossman, D.C.; Bibbins-Domingo, K.; Curry, S.J.; Barry, M.J.; Davidson, K.W.; Doubeni, C.A.; Epling, J.W.; Kemper, A.R.; Krist, A.H.; Kurth, A.E.; et al. Screening for Obesity in Children and Adolescents: US Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation Statement. JAMA 2017, 317, 2417–2426. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Skinner, A.C.; Staiano, A.E.; Armstrong, S.C.; Barkin, S.L.; Hassink, S.G.; Moore, J.E.; Savage, J.S.; Vilme, H.; Weedn, A.E.; Liebhart, J.; et al. Appraisal of Clinical Care Practices for Child Obesity Treatment. Part I: Interventions. Pediatrics 2023, 151, e2022060642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Drug Administration. FDA Approves Weight Management Drug for Patients Aged 12 and Older. 2020. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/drugs/news-events-human-drugs/fda-approves-weight-management-drug-patients-aged-12-and-older (accessed on 19 June 2024).
- Woodard, K.; Louque, L.; Hsia, D.S. Medications for the treatment of obesity in adolescents. Ther. Adv. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 11, 2042018820918789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- US Food and Drug Administration. QSYMIA (Phentermine and Topiramate Extended-Release Capsules) Prescribing Information. Available online: https://www-accessdata-fda-gov.proxy.lib.ohio-state.edu/drugsatfda_docs/label/2022/022580s021lbl.pdf (accessed on 23 June 2023).
- Wegovy® (Semaglutide) Injection 2.4 mg Prescribing Information; Novo Nordisk Inc.: Plainsboro, NJ, USA, 2022; Available online: https://www.novo-pi.com/wegovy.pdf (accessed on 23 June 2023).
- Gourgari, E.; Huerta-Saenz, L.; Tonyushkina, K.N.; Rosolowsky, E.T.; Guttmann-Bauman, I. Use of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists for pediatric patients with obesity and diabetes: The providers’ perspectives. Pediatr. Diabetes 2021, 22, 872–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drucker, D.J. Mechanisms of Action and Therapeutic Application of Glucagon-like Peptide. Cell Metab. 2018, 27, 740–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apperley, L.J.; Blackburn, J.; Erlandson-Parry, K.; Gait, L.; Laing, P.; Senniappan, S. Childhood obesity: A review of current and future management options. Clin. Endocrinol. 2022, 96, 288–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hampl, S.E.; Hassink, S.G.; Skinner, A.C.; Armstrong, S.C.; Barlow, S.E.; Bolling, C.F.; Avila Edwards, K.C.; Eneli, I.; Hamre, R.; Joseph, M.M.; et al. Clinical Practice Guideline for the Evaluation and Treatment of Children and Adolescents with Obesity. Pediatrics 2023, 151, e2022060640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerci, B.; Charbonnel, B.; Gourdy, P.; Hadjadj, S.; Hanaire, H.; Marre, M.; Vergès, B. Efficacy and adherence of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist treatment in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus in real-life settings. Diabetes Metab. 2019, 45, 528–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trujillo, J.M.; Nuffer, W.; Smith, B.A. GLP-1 receptor agonists: An updated review of head-to-head clinical studies. Ther. Adv. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 12, 2042018821997320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, P.M.; Seltzer, S.; Hayward, N.E.; Rodriguez, D.A.; Sless, R.T.; Hawkes, C.P. Safety and Efficacy of Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists in Children and Adolescents with Obesity: A Meta-Analysis. J. Pediatr. 2021, 236, 137–147.e113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arslanian, S.A.; Hannon, T.; Zeitler, P.; Chao, L.C.; Boucher-Berry, C.; Barrientos-Pérez, M.; Bismuth, E.; Dib, S.; Cho, J.I.; Cox, D. Once-Weekly Dulaglutide for the Treatment of Youths with Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 433–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, D.J.; Battelino, T.; Chatterjee, D.J.; Jacobsen, L.V.; Hale, P.M.; Arslanian, S. Liraglutide’s safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics in pediatric type 2 diabetes: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2014, 16, 679–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamborlane, W.V.; Barrientos-Pérez, M.; Fainberg, U.; Frimer-Larsen, H.; Hafez, M.; Hale, P.M.; Jalaludin, M.Y.; Kovarenko, M.; Libman, I.; Lynch, J.L.; et al. Liraglutide in children and adolescents with type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 637–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danne, T.; Biester, T.; Kapitzke, K.; Jacobsen, S.H.; Jacobsen, L.V.; Petri, K.C.C.; Hale, P.M.; Kordonouri, O. Liraglutide in an Adolescent Population with Obesity: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled 5-Week Trial to Assess Safety, Tolerability, and Pharmacokinetics of Liraglutide in Adolescents Aged 12–17 Years. J. Pediatr. 2017, 181, 146–153.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, A.S.; Auerbach, P.; Barrientos-Perez, M.; Gies, I.; Hale, P.M.; Marcus, C.; Mastrandrea, L.D.; Prabhu, N.; Arslanian, S. A randomized, controlled trial of liraglutide for adolescents with obesity. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 2117–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastrandrea, L.D.; Witten, L.; Carlsson Petri, K.C.; Hale, P.M.; Hedman, H.K.; Riesenberg, R.A. Liraglutide effects in a paediatric (7-11 y) population with obesity: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, short-term trial to assess safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics. Pediatr. Obes. 2019, 14, e12495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weghuber, D.; Forslund, A.; Ahlström, H.; Alderborn, A.; Bergström, K.; Brunner, S.; Cadamuro, J.; Ciba, I.; Dahlbom, M.; Heu, V.; et al. A 6-month randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of weekly exenatide in adolescents with obesity. Pediatr. Obes. 2020, 15, e12624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weghuber, D.; Barrett, T.; Barrientos-Pérez, M.; Gies, I.; Hesse, D.; Jeppesen, O.K.; Kelly, A.S.; Mastrandrea, L.D.; Sørrig, R.; Arslanian, S. Once-Weekly Semaglutide in Adolescents with Obesity. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 2245–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, A.S.; Rudser, K.D.; Nathan, B.M.; Fox, C.K.; Metzig, A.M.; Coombes, B.J.; Fitch, A.K.; Bomberg, E.M.; Abuzzahab, M.J. The effect of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist therapy on body mass index in adolescents with severe obesity: A randomized, placebo-controlled, clinical trial. JAMA Pediatr. 2013, 167, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fox, C.K.; Clark, J.M.; Rudser, K.D.; Ryder, J.R.; Gross, A.C.; Nathan, B.M.; Sunni, M.; Dengel, D.R.; Billington, C.J.; Bensignor, M.O.; et al. Exenatide for weight-loss maintenance in adolescents with severe obesity: A randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Obesity 2022, 30, 1105–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, A.S.; Metzig, A.M.; Rudser, K.D.; Fitch, A.K.; Fox, C.K.; Nathan, B.M.; Deering, M.M.; Schwartz, B.L.; Abuzzahab, M.J.; Gandrud, L.M.; et al. Exenatide as a weight-loss therapy in extreme pediatric obesity: A randomized, controlled pilot study. Obesity 2012, 20, 364–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahapatra, M.K.; Karuppasamy, M.; Sahoo, B.M. Semaglutide, a glucagon like peptide-1 receptor agonist with cardiovascular benefits for management of type 2 diabetes. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2022, 23, 521–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holst, J.J.; Madsbad, S. Semaglutide seems to be more effective the other GLP-1Ras. Ann. Transl. Med. 2017, 5, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkhezi, O.S.; Alahmed, A.A.; Alfayez, O.M.; Alzuman, O.A.; Almutairi, A.R.; Almohammed, O.A. Comparative effectiveness of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists for the management of obesity in adults without diabetes: A network meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Obes. Rev. Mar. 2023, 24, e13543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, J.; Wu, H.; Hu, N.; Zhou, Y.; Li, L.; Xiao, F.; Wang, T.; Jiang, H.; Xu, S.; Huang, B.; et al. Effect of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists on body weight in adults with obesity without diabetes mellitus-a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized control trials. Obes. Rev. 2022, 23, e13435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, G.; Ban, B.; Li, Y.; Zhang, M. The effects of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists on adipose tissues in patients with type 2 diabetes: A meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0270899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jendle, J.; Nauck, M.A.; Matthews, D.R.; Frid, A.; Hermansen, K.; Düring, M.; Zdravkovic, M.; Strauss, B.J.; Garber, A.J.; LEAD-2 and LEAD-3 Study Groups. Weight loss with liraglutide, a once-daily human glucagon-like peptide-1 analogue for type 2 diabetes treatment as monotherapy or added to metformin, is primarily as a result of a reduction in fat tissue. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2009, 11, 1163–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunck, M.C.; Diamant, M.; Eliasson, B.; Cornér, A.; Shaginian, R.M.; Heine, R.J.; Taskinen, M.-R.; Yki-Järvinen, H.; Smith, U. Exenatide affects circulating cardiovascular risk biomarkers independently of changes in body composition. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 1734–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, F.; Wu, S.; Guo, S.; Yu, K.; Yang, Z.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Ji, L.; Zhan, S. Effect of GLP-1 receptor agonists on waist circumference among type 2 diabetes patients: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Endocrine 2015, 48, 794–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liakos, C.I.; Papadopoulos, D.P.; Sanidas, E.A.; Markou, M.I.; Hatziagelaki, E.E.; Grassos, C.A.; Velliou, M.L.; Barbetseas, J.D. Blood Pressure-Lowering Effect of Newer Antihyperglycemic Agents (SGLT-2 Inhibitors, GLP-1 Receptor Agonists, and DPP-4 Inhibitors). Am. J. Cardiovasc. Drugs 2021, 21, 123–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drozdz, D.; Alvarez-Pitti, J.; Wójcik, M.; Borghi, C.; Gabbianelli, R.; Mazur, A.; Herceg-Čavrak, V.; Lopez-Valcarcel, B.G.; Brzeziński, M.; Lurbe, E.; et al. Obesity and Cardiometabolic Risk Factors: From Childhood to Adulthood. Nutrients 2021, 13, 4176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clifton, P.M. Relationship Between Changes in Fat and Lean Depots Following Weight Loss and Changes in Cardiovascular Disease Risk Markers. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2018, 7, e008675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanderwall, C.; Randall Clark, R.; Eickhoff, J.; Carrel, A.L. BMI is a poor predictor of adiposity in young overweight and obese children. BMC Pediatr. 2017, 17, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosiborod, M.N.; Bhatta, M.; Davies, M.; Deanfield, J.E.; Garvey, W.T.; Khalid, U.; Kushner, R.; Rubino, D.M.; Zeuthen, N.; Verma, S. Semaglutide improves cardiometabolic risk factors in adults with overweight or obesity: STEP 1 and 4 exploratory analyses. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2023, 25, 468–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overgaard, R.V.; Hertz, C.L.; Ingwersen, S.H.; Navarria, A.; Drucker, D.J. Levels of circulating semaglutide determine reductions in HbA1c and body weight in people with type 2 diabetes. Cell Rep. Med. 2021, 2, 100387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, F.; Yin, S.; Xie, Y.; Liu, H. Comparison of weight loss and adverse events of obesity drugs in children and adolescents: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Expert. Rev. Clin. Pharmacol. 2022, 15, 1119–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguilar Cordero, M.J.; Ortegón Piñero, A.; Baena García, L.; Noack Segovia, J.P.; Levet Hernández, M.C.; Sánchez López, A.M. Rebound effect of intervention programs to reduce overweight and obesity in children and adolescents systematic review. Nutr. Hosp. 2015, 32, 2508–2517. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mamrot, P.; Hanć, T. The association of the executive functions with overweight and obesity indicators in children and adolescents: A literature review. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2019, 107, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, A.S. Current and future pharmacotherapies for obesity in children and adolescents. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2023, 19, 534–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, J.H.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, Y.C.; Jiang, N.; Zhang, S.X.; Huang, S.; Kakaer, A.; Chen, Y.J. Face-to-face physical activity incorporated into dietary intervention for overweight/obesity in children and adolescents: A Bayesian network meta-analysis. BMC Med. 2022, 20, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Epstein, L.H.; Wilfley, D.E.; Kilanowski, C.; Quattrin, T.; Cook, S.R.; Eneli, I.U.; Geller, N.; Lew, D.; Wallendorf, M.; Dore, P.; et al. Family-Based Behavioral Treatment for Childhood Obesity Implemented in Pediatric Primary Care: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2023, 329, 1947–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadry, S.A.; Drucker, D.J. Emerging combinatorial hormone therapies for the treatment of obesity and T2DM. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2013, 9, 425–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammoud, R.; Drucker, D.J. Beyond the pancreas: Contrasting cardiometabolic actions of GIP and GLP1. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2023, 19, 201–216. [Google Scholar]
- Jastreboff, A.M.; Aronne, L.J.; Ahmad, N.N.; Wharton, S.; Connery, L.; Alves, B.; Kiyosue, A.; Zhang, S.; Liu, B.; Bunck, M.C.; et al. Tirzepatide Once Weekly for the Treatment of Obesity. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Nahata, M.; Shi, H.; Sun, Y.; Xie, M. Efficacy and Safety of Tirzepatide in Overweight or Obese Adults without Diabetes: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Preprint (Version 1). Available online: https://www.researchsquare.com/article/rs-4184273/v1 (accessed on 1 April 2024).
- Baggio, L.L.; Drucker, D.J. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor co-agonists for treating metabolic disease. Mol. Metab. 2021, 46, 101090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravussin, E.; Smith, S.R.; Mitchell, J.A.; Shringarpure, R.; Shan, K.; Maier, H.; Koda, J.E.; Weyer, C. Enhanced weight loss with pramlintide/metreleptin: An integrated neurohormonal approach to obesity pharmacotherapy. Obesity 2009, 17, 1736–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seaquist, E.R.; Anderson, J.; Childs, B.; Cryer, P.; Dagogo-Jack, S.; Fish, L.; Heller, S.R.; Rodriguez, H.; Rosenzweig, J.; Vigersky, R. Hypoglycemia and diabetes: A report of a workgroup of the American Diabetes Association and the Endocrine Society. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 1384–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Thomas, J.; Chandler, J.; Cumpston, M.; Li, T.; Page, M.J.; Welch, V.A. (Eds.) Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Hutton, B.; Salanti, G.; Caldwell, D.M.; Chaimani, A.; Schmid, C.H.; Cameron, C.; Ioannidis, J.P.A.; Straus, S.; Thorlund, K.; Jansen, J.P.; et al. The PRISMA extension statement for reporting of systematic reviews incorporating network meta-analyses of health care interventions: Checklist and explanations. Ann. Intern. Med. 2015, 162, 777–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
 . Abbreviations: BMI, body mass index; HbA1c, hemoglobin A1C; DBP, diastolic blood pressure; SBP, systolic blood pressure; FPG, fasting plasma glucose; QOL, quality of life.
. Abbreviations: BMI, body mass index; HbA1c, hemoglobin A1C; DBP, diastolic blood pressure; SBP, systolic blood pressure; FPG, fasting plasma glucose; QOL, quality of life.
 . Abbreviations: BMI, body mass index; HbA1c, hemoglobin A1C; DBP, diastolic blood pressure; SBP, systolic blood pressure; FPG, fasting plasma glucose; QOL, quality of life.
. Abbreviations: BMI, body mass index; HbA1c, hemoglobin A1C; DBP, diastolic blood pressure; SBP, systolic blood pressure; FPG, fasting plasma glucose; QOL, quality of life.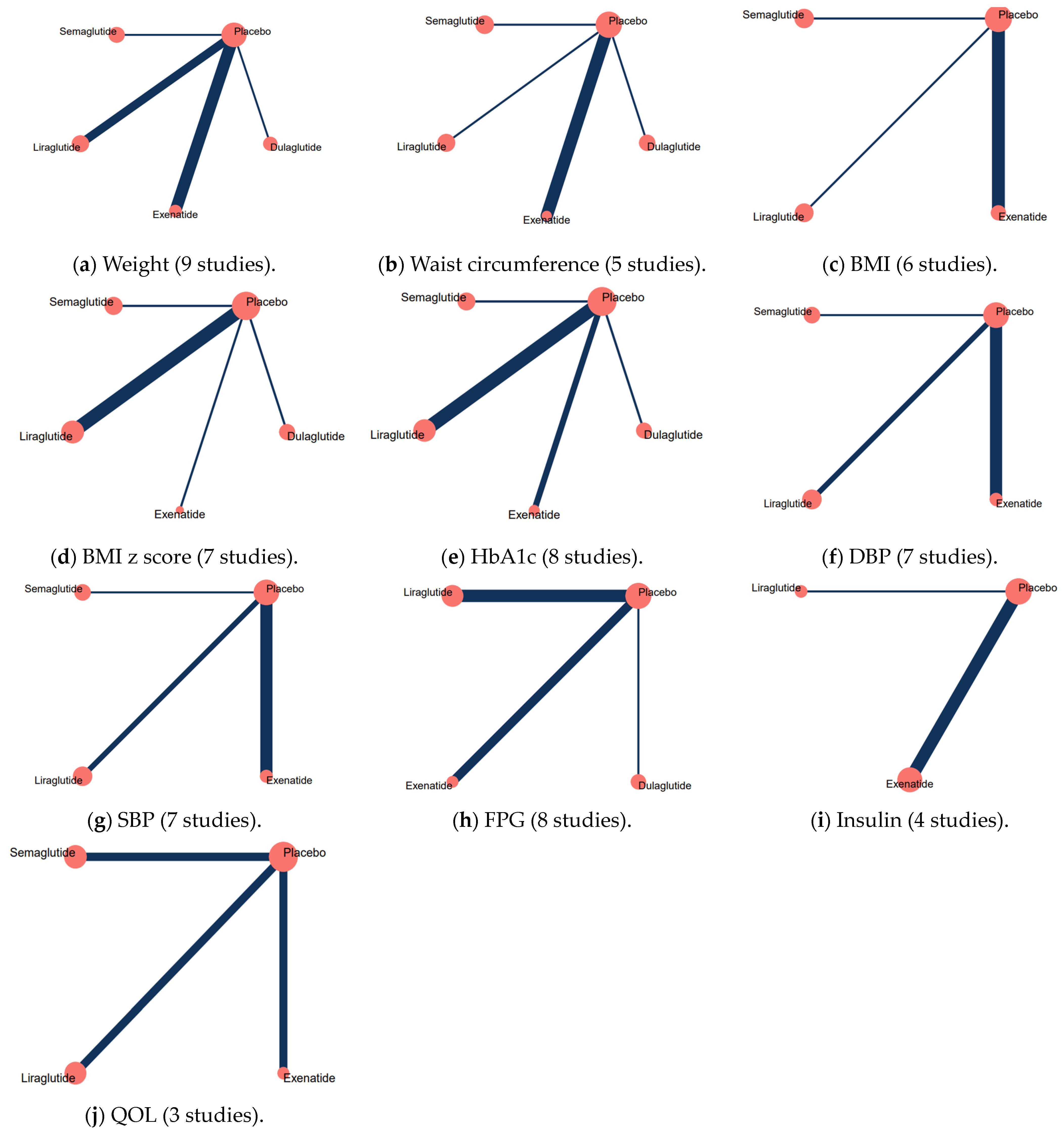
| First Author, Year | Country | Design | Population (Number of Patients) | Age (Years) | Male, (%) | Weight (Kg), | BMI (Kg/m2), | BMI z Score | Intervention | Dose Regimen | Control |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kelly, 2012 [30] | United States | Crossover RCT | Extreme obesity (N = 11) | 12.7 (2.1) | 18.2 | 93.8 (20.6) | 36.7 (4.8) | NI | 13 weeks of exenatide | Initiated at 5 mcg twice daily. After 1 month, up-titrated to 10 mcg twice daily for the remaining 2 months. | Volume-matched placebo |
| Kelly, 2013 [28] | United States | Randomized, double-blind, placebo controlled, multicenter clinical trial | Severe obesity (N = 26) | 15.2 (1.8) | 38.5 | 124 (19.3) | 42.5 (6.81) | NI | 13 weeks of exenatide | Initiated at a dose of 5 mcg twice daily. Up-titrated to 10 mcg twice daily after 1 month for the remainder of the trial. If the 10 mcg dose was not tolerated, the dose was reduced to 5 mcg. | Volume-matched placebo pen |
| Weghuber, 2020 [26] | Sweden; Austria | Parallel, double-blinded, randomized, placebo controlled two-arm trial | Obesity (N = 44) | 14.4 (2.3) | 50 | 104.4 (21.7) | 36.1 (4.9) | 3.2 (0.5) | 26 weeks of exenatide | Initiated at a dose of 0.6 mg, and was increased by 0.6 mg/week to a maximum of 3 mg/day. | Volume-matched placebo pen |
| Fox, 2022 [29] | United States | Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial | Severe obesity (N = 66) | 16 (1.5) | 53 | 108.5 (17.6) | 36.9 (4.4) | NI | 52 weeks of exenatide | Initiated at 0.3 mg daily for first week and increased weekly thereafter to 0.6 mg, 0.9 mg, 1.2 mg, and 1.8 mg. | Matching placebo devices |
| Klein, 2014 [21] | Belgium Slovenia United Kingdom US | Double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, parallel group trial | Overweight and type 2 diabetes (N = 21) | 15 (NI) | 33.3 | 113 (NI) | 40 (NI) | 3.4 (0.7) | 5 weeks of liraglutide | Escalated from 0.3 to 1.2 mg in weekly increments of 0.3 mg and then followed with 0.6 mg weekly increments to a maximum dose of 3 mg or maximum tolerated dose. | Volume-matched placebo pen |
| Danne, 2017 [23] | Germany | Randomized, double-blind, parallel-group, placebo-controlled trial | Obesity (N = 21) | 14.9 (1.3) | 33.3 | 105.5 (20.5) | 36 (4.0) | 3.2 (0.59) | 5 weeks of liraglutide | Initiated at the 0.75 mg dose for the first 4 weeks and then escalated to the 1.5 mg dose if the participant did not have unacceptable side effects with the lower dose. | Volume-matched placebo pen |
| Mastrandrea, 2019 [25] | United States | Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial | Obesity (N = 24) | 9.9 (1.1) | 37.5 | 71.5 (15.4) | NI | 3.9 (0.9) | 7 to 13 weeks of liraglutide | Weekly subcutaneous injections of exenatide; 2 mg | Equal volume of placebo |
| Tamborlane, 2019 [22] | 84 sites in 25 countries | Randomized, parallel-group, placebo-controlled trial | Overweight and type 2 diabetes (N = 134) | 14.6 (1.7) | 38.1 | 91.5 (26.8) | 33.90 (9.25) | 2.94 (1.30) | 52 weeks liraglutide | liraglutide was initiated at a dose of 0.6 mg per day and was escalated in both groups in increments of approximately 0.6 mg each week over the course of 2 to 3 weeks. | Visually identical prefilled pen injectors |
| Kelly, 2020 [24] | Belgium | Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial | Obesity (N = 251) | 14.6 (1.6) | 40.6 | 100.75 (20.95) | 35.55 (5.44) | 3.17 (0.71) | 56 weeks of liraglutide | Initiated and maintained at a dose of 2 mg weekly. | Volume-matched placebo pen |
| Arslanian, 2022 [20] | Nine countries | Phase 3, randomized, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, superiority trial | Overweight and type 2 diabetes (N = 154) | 14.5 (2.0) | 29 | 90.5 (26.5) | 34.1 (8.8) | 2.94 (NI) | 26 weeks of dulaglutide | Initiated at a dose of 0.6 mg daily for 1 week; increased weekly thereafter until the maximum tolerated dose or 3 mg daily. | Visually identical, single-use, single-dose pen devices |
| Weghuber, 2022 [27] | Austria, Belgium, Croatia, Ireland, Mexico, Russian Federation, United Kingdom, United States | Multinational, double-blind, parallel-group, randomized, placebo-controlled, phase 3a trial | Obesity (N = 201) | 15.4 (1.6) | 38 | 107.5 (24.5) | 37.0 (6.4) | 3.31 (0.86) | 68 weeks of semaglutide | Initiated at a dose of 0.25 mg once weekly for the first 4 weeks, followed by escalation every 4 weeks to 0.5, 1.0, 1.7, and 2.4 mg. | Matching placebo |
| Dulaglutide | Exenatide | Liraglutide | Semaglutide | Placebo | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weight | 15.47% | 68.65% | 52.41% | 99.95% | 13.52% |
| BMI z score | 27.45% | 46.04% | 57.75% | 98.94% | 19.82% |
| BMI | NI | 44.97% | 53.06% | 98.03% | 3.95% |
| Waist circumference | 34.04% | 48.26% | 54.57% | 93.00% | 20.13% |
| HbA1c | 93.74% | 27.03% | 61.63% | 48.48% | 19.13% |
| SBP | NI | 81.48% | 45.44% | 56.64% | 16.44% |
| DBP | NI | 72.40% | 32.38% | 55.98% | 39.24% |
| FPG | 78.94% | 23.32% | 77.88% | NI | 19.86% |
| Insulin | NI | 67.03% | 61.55% | NI | 21.43% |
| QOL | NI | 11.12% | 59.44% | 88.48% | 40.97% |
| Dulaglutide | Exenatide | Liraglutide | Semaglutide | Placebo | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nausea | 44.72% | 56.95% | 76.82% | 63.40% | 8.11% |
| Vomiting | 58.51% | 62.90% | 66.37% | 55.23% | 6.99% |
| Diarrhea | 54.48% | 39.21% | 81.48% | 43.45% | 31.39% |
| Abdominal pain | 35.31% | 29.25% | 73.54% | 77.28% | 34.63% |
| Headache | 69.80% | 48.79% | 45.39% | 45.13% | 40.89% |
| Injection-site reaction | 34.96% | 49.81% | 99.56% | 27.99% | 37.69% |
| Hypoglycemia | 19.42% | 74.93% | 73.00% | NI | 32.65% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, L.; Shi, H.; Shi, Y.; Wang, A.; Guo, N.; Tao, H.; Nahata, M.C. Comparative Efficacy and Safety of Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists in Children and Adolescents with Obesity or Overweight: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 828. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17070828
Liu L, Shi H, Shi Y, Wang A, Guo N, Tao H, Nahata MC. Comparative Efficacy and Safety of Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists in Children and Adolescents with Obesity or Overweight: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. Pharmaceuticals. 2024; 17(7):828. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17070828
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Ligang, Hekai Shi, Yufei Shi, Anlin Wang, Nuojin Guo, Heqing Tao, and Milap C. Nahata. 2024. "Comparative Efficacy and Safety of Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists in Children and Adolescents with Obesity or Overweight: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis" Pharmaceuticals 17, no. 7: 828. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17070828
APA StyleLiu, L., Shi, H., Shi, Y., Wang, A., Guo, N., Tao, H., & Nahata, M. C. (2024). Comparative Efficacy and Safety of Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists in Children and Adolescents with Obesity or Overweight: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. Pharmaceuticals, 17(7), 828. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17070828






