Extracellular Matrix Stiffness-Induced Mechanotransduction of Capillarized Liver Sinusoidal Endothelial Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
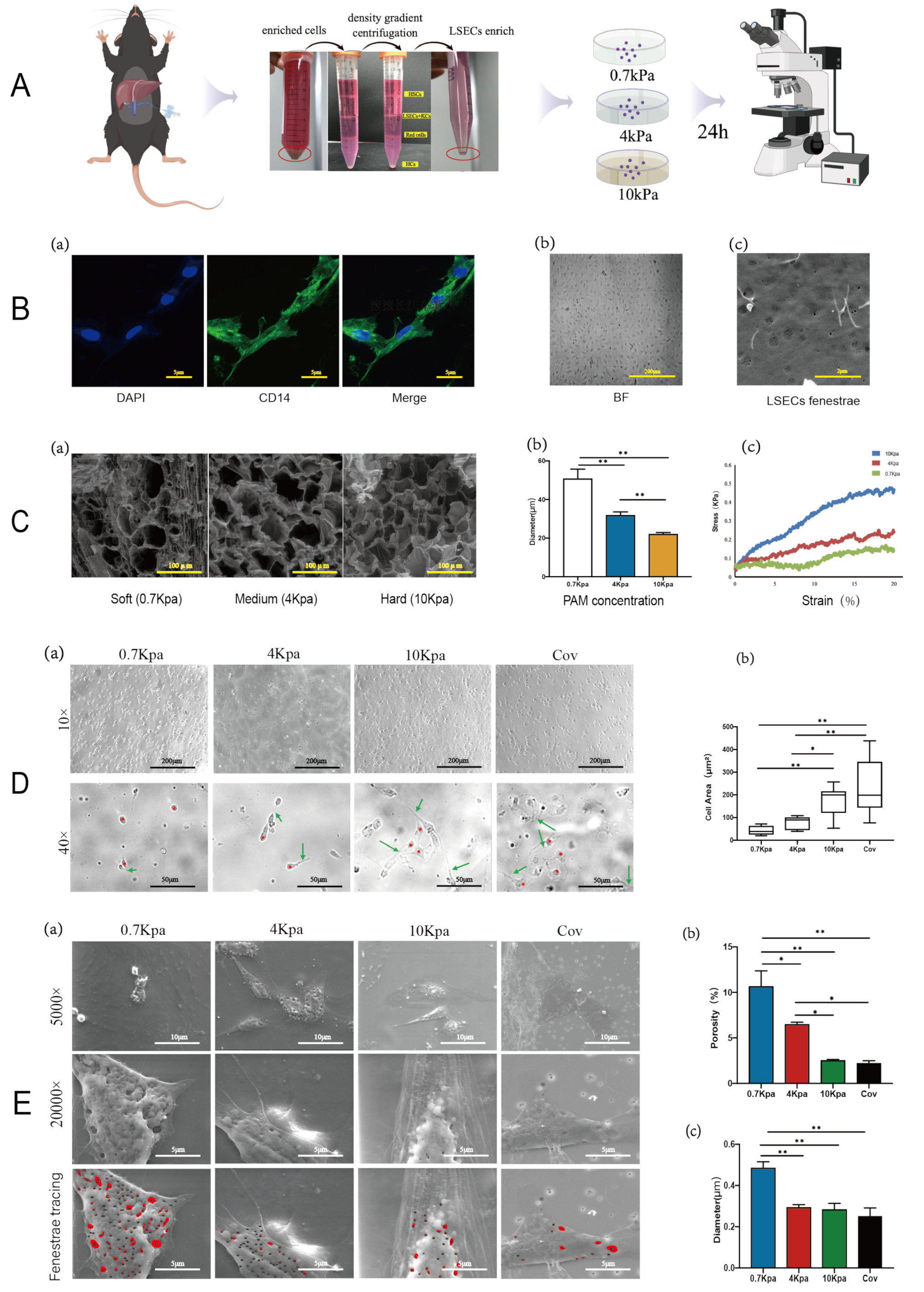
2.1. Changes in Fenestrae Phenotype Induced by Varying Substrate Stiffness
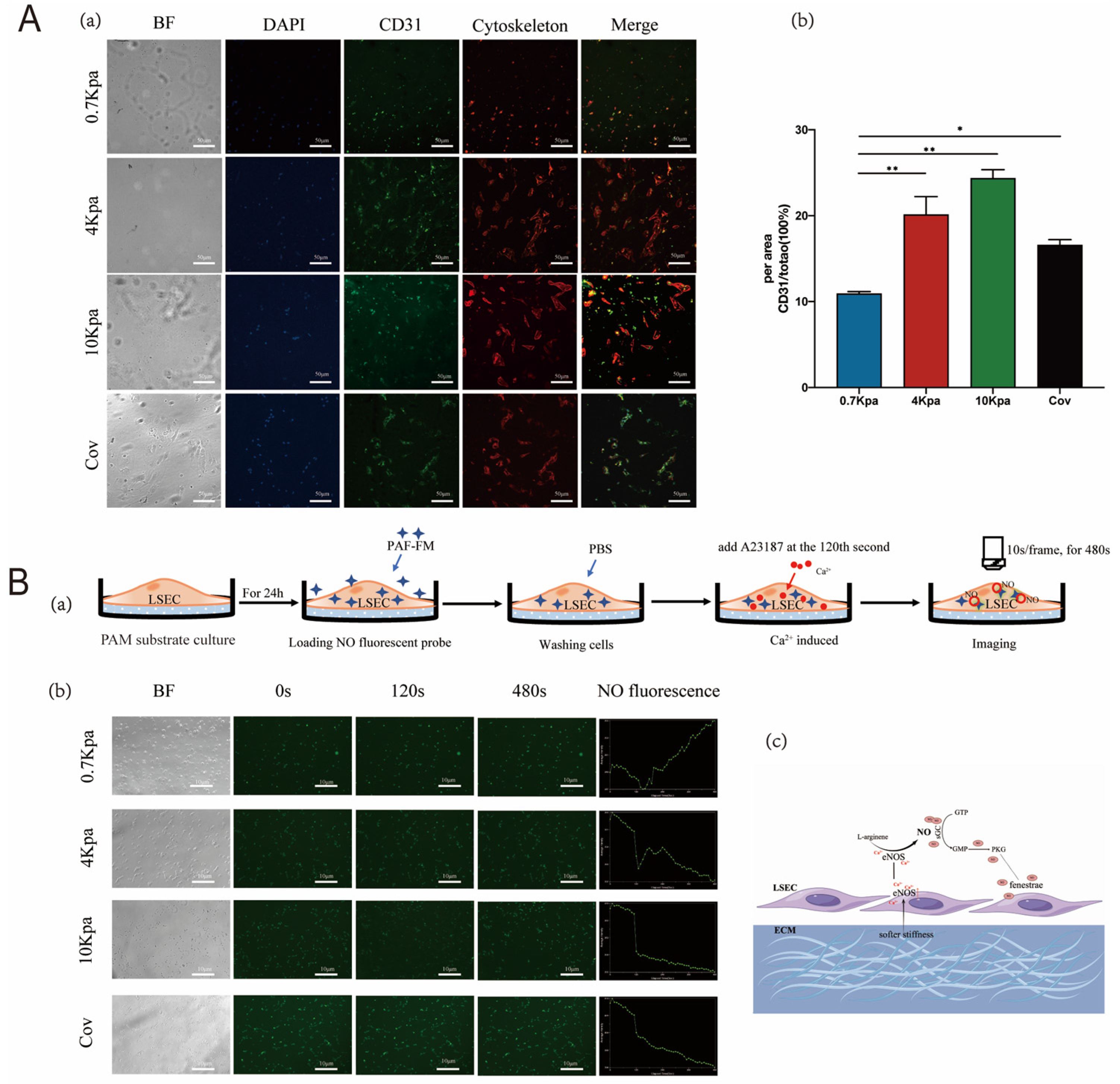
2.2. Stiffness Modulates Capillarization of LSECs by Regulating the Cytoskeleton
2.3. Stiffness Regulated Fenestrae of LSECs through the NO-Dependent Pathway
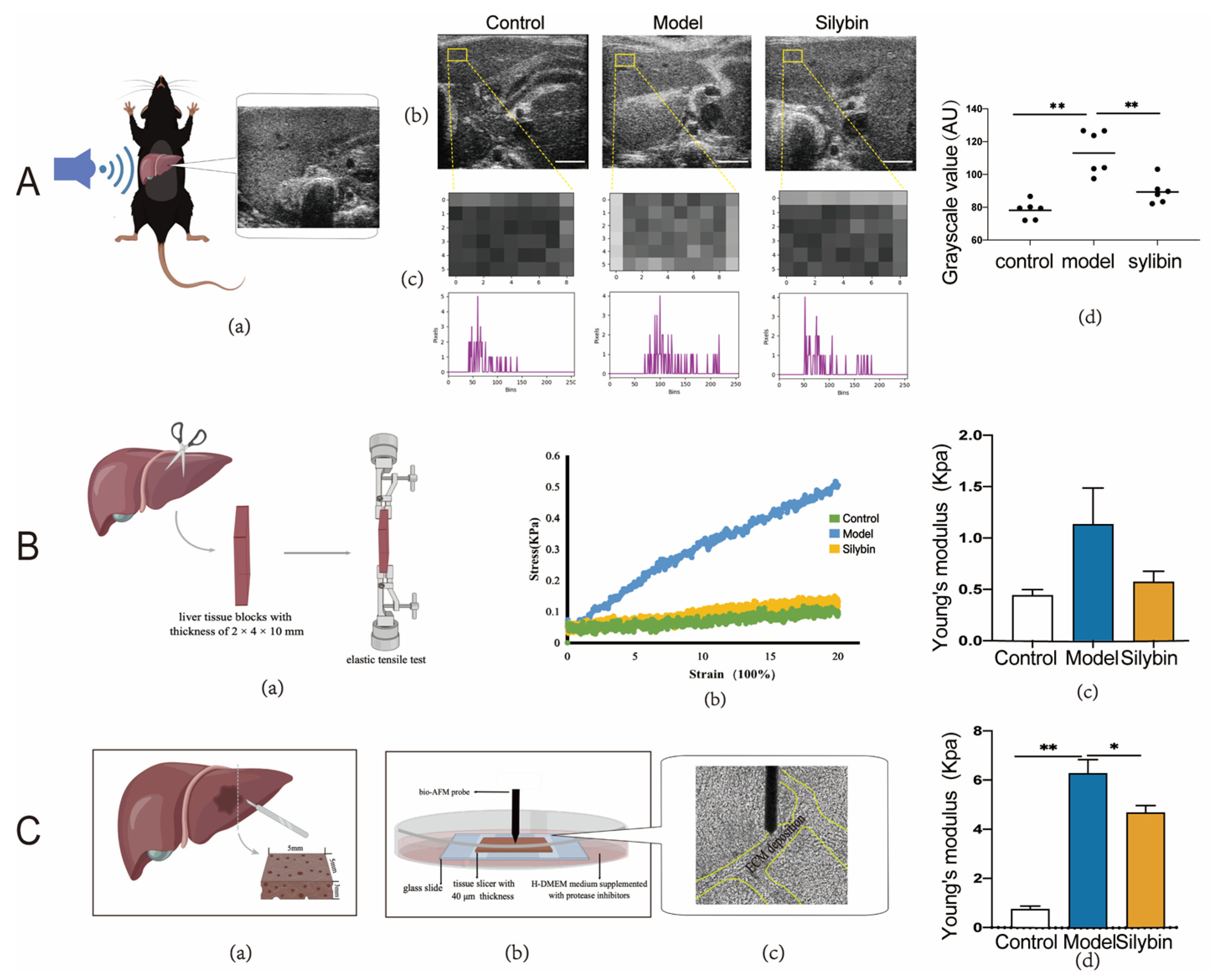
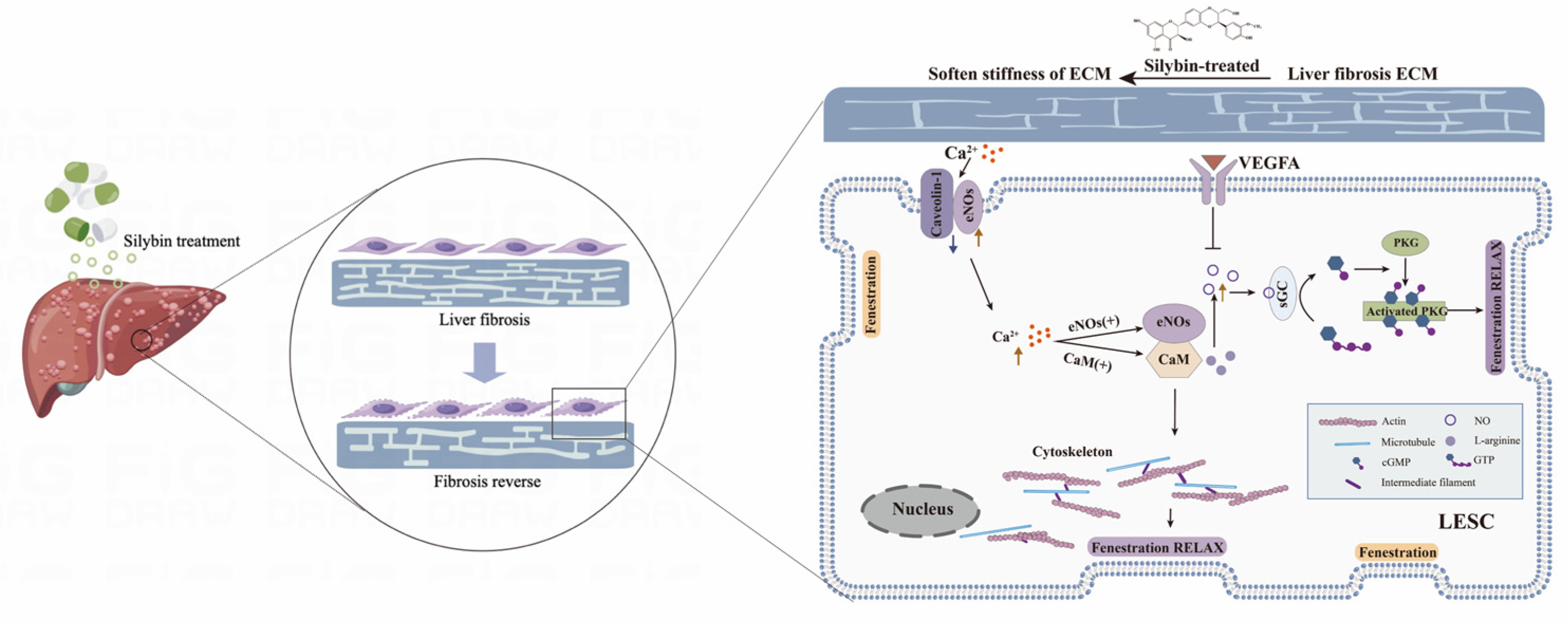
2.4. Silybin Treatment In Vivo Contributed to ECM Composition Changes
2.5. Biomechanical Alteration after Silybin-Treatment of Mice with Liver Fibrosis
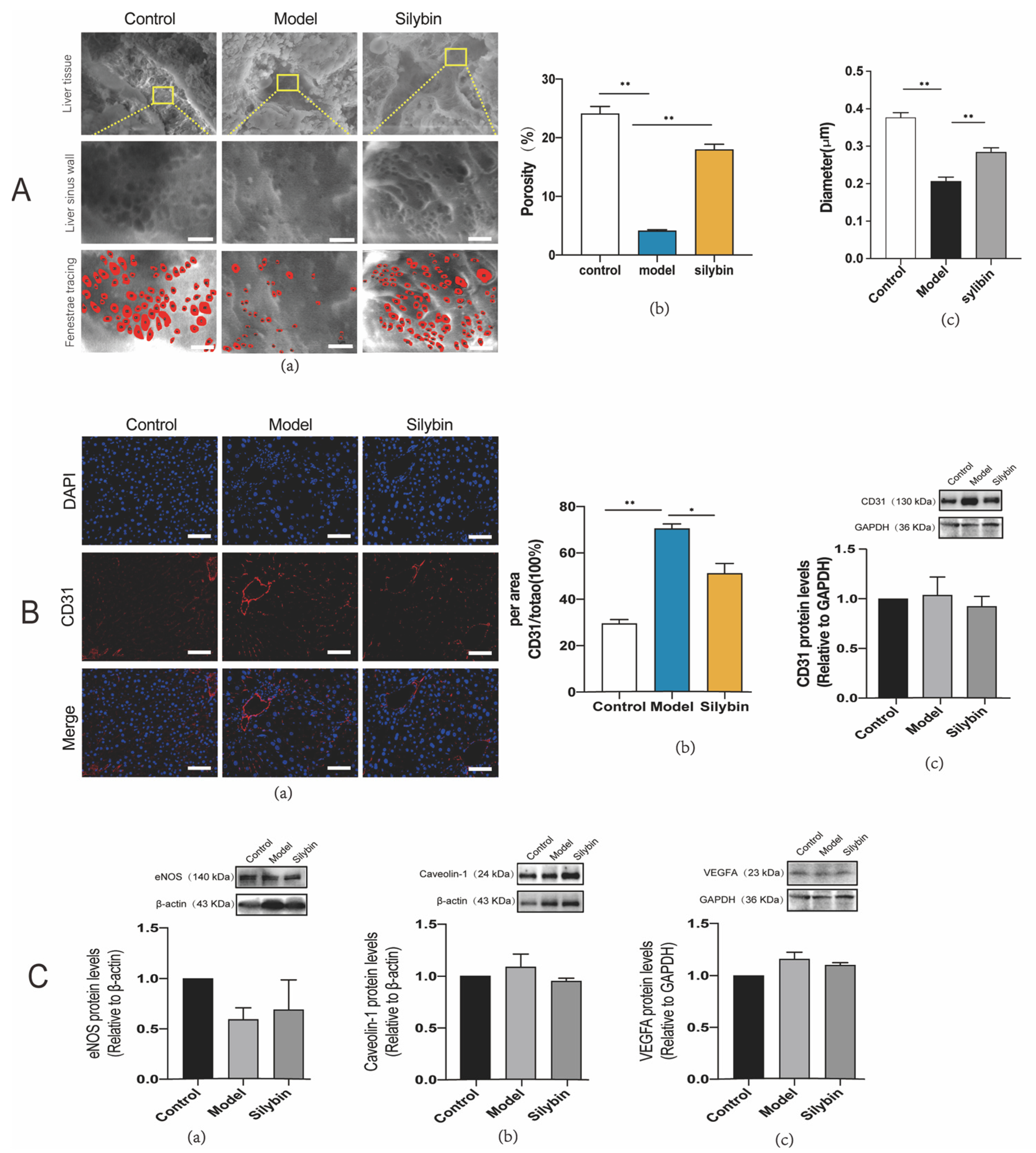
2.6. Improved Fenestration Phenotype after Silybin Treatment of Liver Fibrosis
2.7. Silybin-Induced Mechanotransduction of Anti-Capillarization by the NO-Dependent Pathway
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Polyacrylamide Hydrogel Substrates
4.2. Extraction of Primary LSECs
4.3. Ca2+ Carrier A23187 to Induce NO Release
4.4. Animal Preparation
4.5. Animal Models and Drug Intervention
4.6. Evaluation of Liver Elasticity via Ultrasound
4.7. Measurement of Young’s Modulus of Liver Tissue
4.8. Tensile Testing of Liver Tissue
4.9. Pathological Staining
4.10. Environmental Scanning Electron Microscope (ESEM) Specimen Preparation
4.11. Western Blotting
4.12. Statistical Analysis
4.13. Data Availability
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hammerich, L.; Tacke, F. Hepatic inflammatory responses in liver fibrosis. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 20, 633–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devarbhavi, H.; Asrani, S.K.; Arab, J.P.; Nartey, Y.A.; Pose, E.; Kamath, P.S. Global burden of liver disease: 2023 update. J. Hepatol. 2023, 79, 516–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Li, L. Prevalence of Liver Steatosis and Fibrosis in the General Population and Various High-Risk Populations: A Nationwide Study with 5.7 Million Adults in China. Gastroenterology 2023, 165, 1025–1040. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Rock, J.B.; Yearsley, M.M.; Ferrell, L.D.; Frankel, W.L. Different collagen types show distinct rates of increase from early to late stages of hepatitis C-related liver fibrosis. Hum. Pathol. 2014, 45, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serai, S.D.; Trout, A.T.; Miethke, A.; Diaz, E.; Xanthakos, S.A.; Dillman, J.R. Putting it all together: Established and emerging MRI techniques for detecting and measuring liver fibrosis. Pediatr. Radiol. 2018, 48, 1256–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Xia, B.; Fu, Q.; Huang, X.; Wang, F.; Chen, Z.; Lv, Y. Matrix Mechanics as Regulatory Factors and Therapeutic Targets in Hepatic Fibrosis. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2019, 15, 2509–2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poisson, J.; Lemoinne, S.; Boulanger, C.; Durand, F.; Moreau, R.; Valla, D.; Rautou, P.-E. Liver sinusoidal endothelial cells: Physiology and role in liver diseases. J. Hepatol. 2016, 66, 212–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, T.; El-Assal, O.N.; Ono, T.; Yamanoi, A.; Dhar, D.K.; Nagasue, N. Sinusoidal endothelial cell proliferation and expression of angiopoietin/Tie family in regenerating rat liver. J. Hepatol. 2001, 34, 690–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, B.D.; Grashoff, C.; Schwartz, M.A. Dynamic molecular processes mediate cellular mechanotransduction. Nature 2011, 475, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeLeve, L.D.; Wang, X.; Kanel, G.C.; Atkinson, R.D.; McCuskey, R.S. Prevention of hepatic fibrosis in a murine model of metabolic syndrome with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Am. J. Pathol. 2008, 173, 993–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwakiri, Y.; Kim, M. Nitric oxide in liver diseases. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2015, 36, 524–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wohl, B.M.; Smith, A.A.; Kryger, M.B.; Zelikin, A.N. Narrow therapeutic window of ribavirin as an inhibitor of nitric oxide synthesis is broadened by macromolecular prodrugs. Biomacromolecules 2013, 14, 3916–3926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marrone, G.; Russo, L.; Rosado, E.; Hide, D.; García-Cardeña, G.; García-Pagán, J.C.; Bosch, J.; Gracia-Sancho, J. The transcription factor KLF2 mediates hepatic endothelial protection and paracrine endothelial-stellate cell deactivation induced by statins. J. Hepatol. 2013, 58, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, Y.; Niu, Y.; Liang, K.; Du, Y. Mechanical communication in fibrosis progression. Trends Cell Biol. 2022, 32, 70–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shetty, S.; Lalor, P.F.; Adams, D.H. Liver sinusoidal endothelial cells—Gatekeepers of hepatic immunity. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 15, 555–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, T.; Tan, B.; Zhu, L.; Wang, Y.; Liao, J. A Review on the Design of Hydrogels with Different Stiffness and Their Effects on Tissue Repair. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 817391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, O.; Kim, T.H.; Alsberg, E. Reversible dynamic mechanics of hydrogels for regulation of cellular behavior. Acta Biomater. 2021, 136, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanton, A.E.; Tong, X.; Yang, F. Extracellular matrix type modulates mechanotransduction of stem cells. Acta Biomater. 2019, 96, 310–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandow, C.E.; Georges, P.C.; Janmey, P.A.; Beningo, K.A. Polyacrylamide hydrogels for cell mechanics: Steps toward optimization and alternative uses. Methods Cell Biol. 2007, 83, 29–46. [Google Scholar]
- Ware, B.R.; Durham, M.J.; Monckton, C.P.; Khetani, S.R. A Cell Culture Platform to Maintain Long-term Phenotype of Primary Human Hepatocytes and Endothelial Cells. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 5, 187–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLeve, L. Liver sinusoidal endothelial cells in hepatic fibrosis. Hepatology 2015, 61, 1740–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, W.P.; Mittal, C.K.; Katsuki, S.; Murad, F. Nitric oxide activates guanylate cyclase and increases guanosine 3’:5’-cyclic monophosphate levels in various tissue preparations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1977, 74, 3203–3207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Xu, H.H.; Lin, Y.; Sun, X.; Wang, L.J.; Fang, Z.P.; Su, X.H.; Liang, X.J.; Hu, Y.; Liu, Z.M.; et al. LECT2, a Ligand for Tie1, Plays a Crucial Role in Liver Fibrogenesis. Cell 2019, 178, 1478–1492.e20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swift, J.; Ivanovska, I.L.; Buxboim, A.; Harada, T.; Dingal, P.C.; Pinter, J.; Pajerowski, J.D.; Spinler, K.R.; Shin, J.W.; Tewari, M.; et al. Nuclear lamin-A scales with tissue stiffness and enhances matrix-directed differentiation. Science 2013, 341, 1240104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swift, J.; Discher, D.E. The nuclear lamina is mechano-responsive to ECM elasticity in mature tissue. J. Cell Sci. 2014, 127 Pt 14, 3005–3015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jabłońska-Trypuć, A.; Matejczyk, M.; Rosochacki, S. Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), the main extracellular matrix (ECM) enzymes in collagen degradation, as a target for anticancer drugs. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2016, 31 (Suppl. 1), 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corpechot, C.; Barbu, V.; Wendum, D.; Kinnman, N.; Rey, C.; Poupon, R.; Housset, C.; Rosmorduc, O. Hypoxia-induced VEGF and collagen I expressions are associated with angiogenesis and fibrogenesis in experimental cirrhosis. Hepatology 2002, 35, 1010–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, G.; Wang, X.; Wang, L.; Wang, L.; Atkinson, R.D.; Kanel, G.C.; Gaarde, W.A.; Deleve, L.D. Role of differentiation of liver sinusoidal endothelial cells in progression and regression of hepatic fibrosis in rats. Gastroenterology 2012, 142, 918–927e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangwung, P.; Greco, T.M.; Wang, Y.; Ischiropoulos, H.; Sessa, W.C.; Iwakiri, Y. Proteomic identification of S-nitrosylated Golgi proteins: New insights into endothelial cell regulation by eNOS-derived NO. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e315642012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doulias, P.T.; Tenopoulou, M.; Greene, J.L.; Raju, K.; Ischiropoulos, H. Nitric oxide regulates mitochondrial fatty acid metabolism through reversible protein S-nitrosylation. Sci. Signal 2013, 6, rs1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Underbakke, E.S.; Iavarone, A.T.; Chalmers, M.J.; Pascal, B.D.; Novick, S.; Griffin, P.R.; Marletta, M.A. Nitric oxide-induced conformational changes in soluble guanylate cyclase. Structure 2014, 22, 602–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.P.; He, P.N. Endothelial Ca2+ (i) and caveolin-1 antagonistically regulate eNOS activity and microvessel permeability in rat venules. Cardiovasc. Res. 2010, 87, 340–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Wu, K.; Geng, J.; Chi, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhi, P.; Zhang, M.; Xiao, B. Ion Permeation and Mechanotransduction Mechanisms of Mechanosensitive Piezo Channels. Neuron 2016, 89, 1248–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kechagia, J.Z.; Ivaska, J.; Roca-Cusachs, P. Integrins as biomechanical sensors of the microenvironment. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 20, 457–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, A.S.; Duszyc, K.; Viasnoff, V. Mechanosensing and Mechanotransduction at Cell-Cell Junctions. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2018, 10, a028761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romani, P.; Valcarcel-Jimenez, L.; Frezza, C.; Dupont, S. Crosstalk between mechanotransduction and metabolism. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2021, 22, 22–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; You, Z.; Yu, H.; Zhou, L.; Zhao, H.; Yan, X.; Li, D.; Wang, B.; Zhu, L.; Xu, Y.; et al. Mechanotransduction-modulated fibrotic microniches reveal the contribution of angiogenesis in liver fibrosis. Nat. Mater 2017, 16, 1252–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Z.; Xian, C.; Yuan, Q.; Liu, G.; Wu, J. Natural Polymer-Based Hydrogels with Enhanced Mechanical Performances: Preparation, Structure, and Property. Adv. Healthc Mater 2018, 17, e1900670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, A.; Haag, R.; Schedler, U. Hydrogels and Their Role in Biosensing Applications. Adv. Healthc Mater 2021, 10, e2100062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tse, J.R.; Engler, A.J. Preparation of hydrogel substrates with tunable mechanical properties. Curr. Protoc. Cell Biol. 2010, 47, 10.16.1–10.16.16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, Q.; Sun, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, N.; Lv, W.; Han, D. Extracellular Matrix Stiffness-Induced Mechanotransduction of Capillarized Liver Sinusoidal Endothelial Cells. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 644. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17050644
Wu Q, Sun Q, Zhang Q, Wang N, Lv W, Han D. Extracellular Matrix Stiffness-Induced Mechanotransduction of Capillarized Liver Sinusoidal Endothelial Cells. Pharmaceuticals. 2024; 17(5):644. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17050644
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Qingjuan, Quanmei Sun, Qiang Zhang, Ning Wang, Wenliang Lv, and Dong Han. 2024. "Extracellular Matrix Stiffness-Induced Mechanotransduction of Capillarized Liver Sinusoidal Endothelial Cells" Pharmaceuticals 17, no. 5: 644. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17050644
APA StyleWu, Q., Sun, Q., Zhang, Q., Wang, N., Lv, W., & Han, D. (2024). Extracellular Matrix Stiffness-Induced Mechanotransduction of Capillarized Liver Sinusoidal Endothelial Cells. Pharmaceuticals, 17(5), 644. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17050644








