Budesonide Attains Its Wide Clinical Profile by Alternative Kinetics
Abstract
1. Development of Inhaled Corticosteroids and Pharmacological Profiles
2. Budesonide Having a Partly Different Developmental and Pharmacological Background
3. How Budesonide Made Inhaled Corticosteroids First Line Treatment of Asthma
4. Findings Enhancing Budesonide’s Clinical Profile
5. Improvements in Formulation and Lung Deposition of Budesonide
6. Further Clinical Landmarks with Budesonide
7. Budesonide/Formoterol and Guidelines
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Toogood, J.; Lefcoe, N. Dexamethasone aerosol for the treatment of steroid-dependent chronic bronchial asthmatic patients. J. Allergy 1965, 36, 321–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, H.M.; Storey, G.; George, W.H.S. Beclomethasone dipropionate: A new steroid aerosol for treatment of allergic asthma. Br. Med. J. 1972, 1, 585–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daley-Yates, P. Inhaled corticosteroids: Potency, dose equivalence and therapeutic index. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2015, 80, 372–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daley-Yates, P.; Breakey, N.; Thomas, S.; Austin, D.; Shabbir, S.; Harrisson, T.; Singh, D.; Barnes, N. Therapeutic index of inhaled corticosteroids in asthma: A dose-response comparison on airway hyperresponsiveness and adrenal axis suppression. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2021, 87, 483–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavord, I.D.; Holliday, M.; Reddel, H.K.; Braithwaite, I.; Ebmeier, S.; Hancox, R.J.; Harrison, T.; Houghton, C.; Oldfield, K.; Papi, A.; et al. Predictive value of blood eosinophils and exhaled nitric oxide in adults with mild asthma: A prespecified subgroup analysis of an open-label, parallel-group, randomized controlled trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, 671–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couillard, S.; Shrimanker, R.; Chaudhuri, R.; Mansur, A.H.; McGarvey, L.P.; Heaney, L.G.; Fowler, S.J.; Bradding, P.; Pavord, I.D.; Hinks, T.S. Fractional exhaled nitric oxide non-suppression identifies corticosteroid-resistant type 2 signaling in severe asthma. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2021, 204, 731–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brattsand, R.; Thalén, A.; Roempke, K.; Källström, L.; Gruvstad, E. Development of new glucocorticosteroids with a very high ratio between topical and systemic activities. Eur. J. Respir. Dis. 1982, 63 (Suppl. S122), 62–73. [Google Scholar]
- Johansson, S.-Å.; Andersson, K.-E.; Brattsand, R.; Gruvstad, E.; Hedner, P. Topical and systemic glucocorticoid potencies of budesonide, beclomethasone dipropionate and prednisolone in man. Eur. J. Respir. Dis. 1982, 63 (Suppl. S122), 74–82. [Google Scholar]
- Brattsand, R.; Selroos, O. May a kinetic mode explain the high efficacy/safety profile of inhaled budesonide? Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 2022, 77, 102167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, A.; Bareille, P.; Rousell, V.M. Fluticasone furoate, a novel inhaled corticosteroid, demonstrates long absorption kinetics in man compared with inhaled fluticasone propionat. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2013, 52, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tashkin, D.P.; Lipworth, B.; Brattsand, R. Beneficial profile of budesonide in obstructive airways disease. Drugs 2019, 79, 1757–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller-Larsson, A.; Mattson, H.; Hjertberg, E.; Dahlbeck, M.; Tunek, A.; Brattsand, R. Reversible fatty acid conjugation of budesonide. Novel mechanism for prolonged retention of topically applied steroid in airway tissue. Drug Metab. Dispos. 1998, 26, 623–630. [Google Scholar]
- Edsbäcker, S.; Brattsand, R. Budesonide fatty-acid esterification: A novel mechanism prolonging binding to airway tissue. Review of available data. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2022, 88, 609–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maassen van den Brink, K.I.; Boorsma, M.; Staal-van den Brekel, A.J.; Edsbäcker, S.; Wouters, E.F.; Thorson, L. Evidence of the in vitro esterification of budesonide in human airways. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2008, 66, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller-Larsson, A.; Jansson, P.; Runström, A.; Brattsand, R. Prolonged airway activity and improved selectivity of budesonide possibly due to esterification. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2000, 162, 1455–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selroos, O.; Edsbäcker, S.; Hultquist, C. Once-daily inhaled budesonide for the treatment of asthma: Clinical evidence and pharmacokinetic explanation. J. Asthma 2004, 41, 771–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
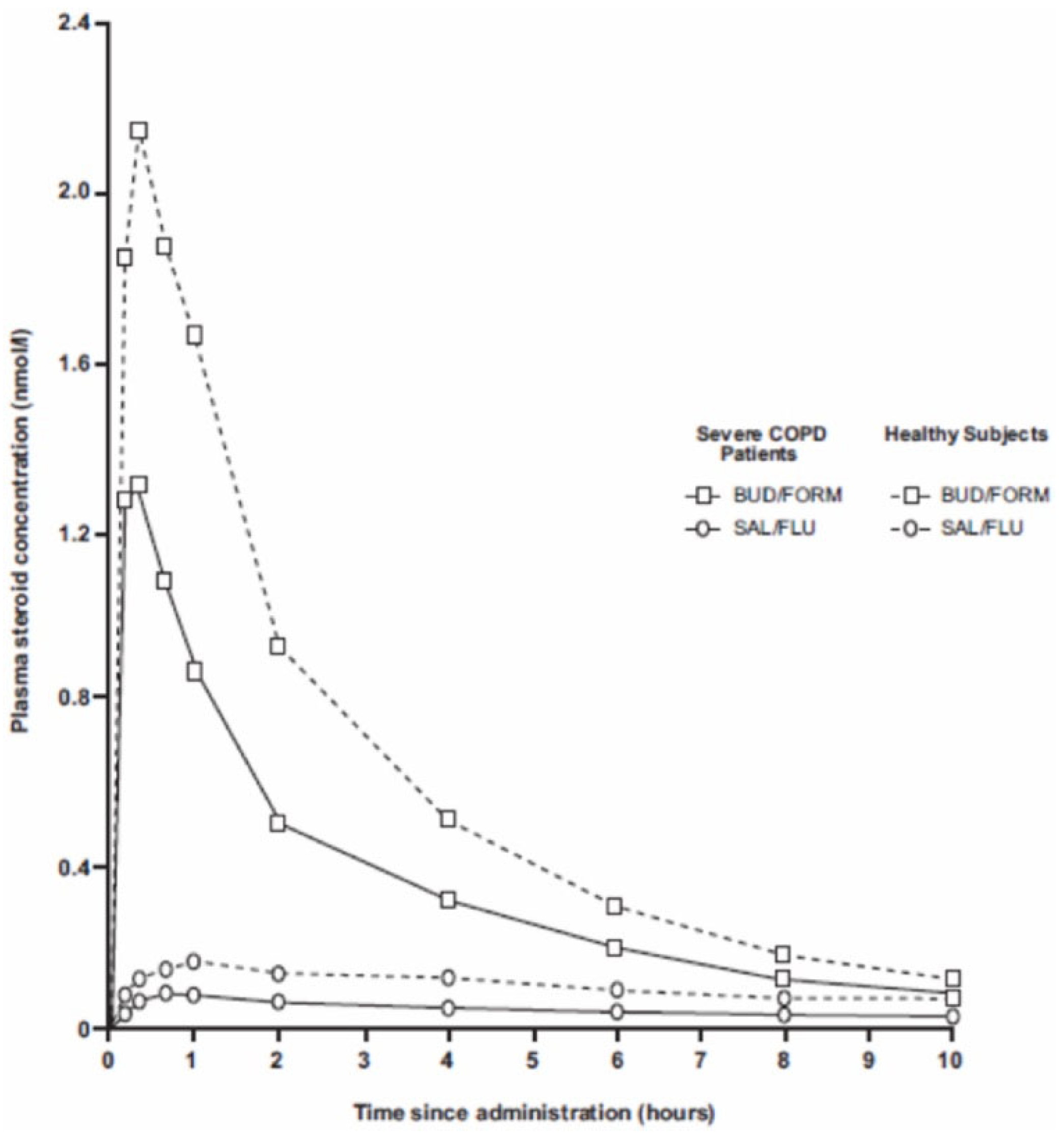
- Dalby, C.; Polanowski, T.; Larsson, T.; Borgström, L.; Edsbäcker, S.; Harrison, T. The bioavailability and airway clearance of the steroid component of budesonide/formoterol and salmeterol/fluticasone propionate after inhaled administration in patients with COPD and healthy subjects: A randomized controlled study. Respir. Res. 2009, 10, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rüdiger, J.J.; Gencay, M.; Yang, J.Q.; Bihl, M.; Tamm, M.; Roth, M. Fast beneficial systemic anti-inflammatory effects of budesonide and formoterol on circulating lymphocytes in asthma. Respirology 2013, 18, 840–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denburg, J.; Inman, M.D.; Sehmi, R.; O’Byrne, P.M.; Gauvreau, G.M.; Wook, L.J. Extrapulmonary effects of inhaled corticosteroids. In Inhaled Steroids in Asthma. Optimizing Effects in the Airways; Schleimer, R.P., O’Byrne, P.M., Szefler, S.J., Brattsand, R., Eds.; Marcel Dekker, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2002; pp. 273–281. [Google Scholar]
- Fokkens, V.J.; van de Merwe, J.P.; Braat, J.P.; Overbeek, S.E.; Hooijkaas, H. The effect of intranasal and inhaled corticosteroids in healthy volunteers on the number of circulating lymphocytes and lymphocyte subsets. Allergy 1999, 54, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christenssen, C.; Thoren, A.; Lindberg, B. Safety of inhaled budesonide: Clinical manifestations of systemic corticosteroid-related adverse effects. Drug Saf. 2008, 31, 965–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahrami-Nejad, Z.; Zhao, M.L.; Tholen, S.; van Schie, S.; Chung, M.; Teuel, M.N. A transcriptual circuit filters oscillating circadian hormonal inputs to regulate fat cell differentiation. Cell Metab. 2018, 27, 854–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, P.J.; Pedersen, S. Efficacy and safety of inhaled corticosteroids in asthma. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1993, 148, S1–S26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, S. Efficacy and safety of inhaled corticosteroids in children. In Inhaled Glucocorticoids in Asthma: Mechanisms and Clinical Actions; Schleimer, R.P., Busse, W.W., O’Byrne, P.M., Eds.; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1997; pp. 551–606. [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen, S.; O’Byrne, P. A comparison of the efficacy and safety of inhaled corticosteroids in asthma. Allergy 1997, 39 (Suppl. S52), 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, P.J.; Pedersen, S.; Busse, W.W. Efficacy and safety of inhaled corticosteroids. New developments. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1998, 157, S1–S53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laitinen, L.A.; Heino, M.; Laitinen, A.; Kava, T.; Haahtela, T. Damage of the airway epithelium and bronchial reactivity in patients with asthma. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1985, 131, 599–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haahtela, T.; Järvinen, M.; Kava, T.; Kiviranta, K.; Koskinen, S.; Lehtonen, K.; Nikander, K.; Persson, T.; Reinikainen, K.; Selroos, O.; et al. Comparison of a β2-agonist, terbutaline, with an inhaled corticosteroid, budesonide, in newly detected asthma. N. Engl. J. Med. 1991, 325, 388–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haahtela, T.; Järvinen, M.; Kava, T.; Kiviranta, K.; Koskinen, S.; Lehtonen, K.; Nikander, K.; Persson, T.; Selroos, O.; Sovijärvi, A.; et al. Effects of reducing or discontinuating inhaled budesonide in patients with mild asthma. N. Engl. J. Med. 1994, 331, 700–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selroos, O.; Pietinalho, A.; Löfroos, A.-B.; Riska, H. Effect of early vs late intervention with inhaled corticosteroids in asthma. Chest 1995, 108, 1228–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selroos, O.; Löfroos, A.-B.; Pietinalho, A.; Riska, H. Asthma control and steroid doses 5 years after early or delayed introduction of inhaled corticosteroids in asthma: A real-life study. Respir. Med. 2004, 98, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haahtela, T.; Selroos, O.; O’Byrne, P.M. Revisiting early intervention in adult asthma. ERJ Open Res. 2016, 1, 00022–02015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bel, E.H.; Timmers, M.C.; Zwinderman, A.H.; Dijkman, J.H.; Sterk, P.J. The effect of inhaled corticosteroids on the maximal degree of airway narrowing to methacholine in asthmatic subjects. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1991, 143, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahl, R.; Johansson, S.-Å. Importance of duration of treatment with inhaled budesonide on the immediate and late bronchial reaction. Eur. J. Respir. Dis. 1982, 63 (Suppl. S122), 167–175. [Google Scholar]
- Henriksen, J.M.; Dahl, R. Effects of inhaled budesonide alone and in combination with low-dose terbutaline in children with exercise-induced asthma. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1983, 128, 993–997. [Google Scholar]
- Crompton, G.K. Problems patients having using pressurized aerosol in halers. Eur. J. Respir. Dis. Suppl. 1982, 119, 101–104. [Google Scholar]
- Pauwels, R.; Newman, S.; Borgström, L. Airway deposition and airway effects of antiasthma drugs delivered from metered dose inhaler. Eur. Respir. J. 1997, 10, 2127–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selroos, O. Some aspects on comparative efficacy studies with inhaled corticosteroids in asthma. Curr. Drug Ther. 2007, 2, 57–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorsson, L.; Edsbäcker, S. Lung deposition of budesonide from a pressurized metered-dose inhaler attached to a spacer. Eur. Respir. J. 1998, 12, 1340–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorsson, L.; Edsbäcker, S.; Conradson, T.-B. Lung deposition of budesonide from Turbuhaler is twice that from a pressurized metered dose in haler (pMDI). Eur. Respir. J. 1994, 7, 1839–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitcairn, G.; Reader, S.; Pavia, D.; Newman, S. Deposition of corticosteroid aerosol in human lung by Respimat® Soft MistTM inhaler compared to deposition by metered dose inhaler or by Turbuhaler® dry powder inhaler. J. Aerosol Med. 2005, 18, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgström, L.; Bondesson, E.; Morén, F.; Trofast, E.; Newman, S. Lung deposition of budesonide via Turbuhaler: A comparison with terbutaline sulphate in normal subjects. Eur. Respir. J. 1994, 7, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauwels, R.A.; Hargreave, F.E.; Camus, P.; Bukoski, M.; Ståhl, E. A 1-year comparison of turbuhaler vs pressurized metered-dose inhaler in asthmatic patients. Chest 1996, 110, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, T.; Takahashi, T.; Nakajima, S.; Makino, S.; Yamakido, M.; Mano, K.; Nakashima, M.; Tollemar, U.; Selroos, O. Efficacy of budesonide Turbuhaler compared with that of beclomethasone dipropionate pMDI in Japanese patients with moderately persistent asthma. Respirology 2001, 6, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahlström, K.; Thorsson, L.; Larsson, P.; Nikander, K. Systemic availability and lung deposition of budesonide via three different nebulizers in adults. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2003, 90, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agertoft, L.; Andersen, A.; Weibull, E.; Pedersen, S. Systemic availability and pharmacokinetics of nebulized budesonide in preschool children. Arch. Dis. Child. 1999, 80, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, J.W.; Mellon, M.; Wald, J.; Welsh, M.; Cruz-Rivera, M.; Walton-Bowen, K. A multiple-dosing, placebo-controlled study of budesonide inhalation suspension given once or twice daily for treatment of persistent asthma in young children and infants. Pediatrics 1999, 103, 414–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ädelroth, E.; Rosenhall, L.; Glennow, C. High dose inhaled budesonide in the treatment of severe steroid-dependent asthmatics—A 2-year study. Allergy 1985, 40, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, H.S.; Bernstein, I.L.; Fink, J.; Edwards, T.B.; Spector, S.L.; Storms, W.W.; Tashkin, D.P.; Pulmicort Turbuhaler Study Group. Oral glucocorticosteroid-sparing effect of budesonide administered by Turbuhaler: A double-blind, placebo-controlled study in adults with moderate-to-severe chronic asthma. Chest 1998, 113, 1264–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toogood, J.H. Comparisons between inhaled and oral corticosteroids in patients with chronic asthma. In Advances in the Use of Inhaled Corticosteroids; Ellul-Micallef, R., Lam, W.K., Toogood, J.H., Eds.; Excerpta Medica: Hong Kong, China, 1987; pp. 140–149. [Google Scholar]
- Toogood, J.H.; Baskerville, J.; Jennings, B.; Lefcoe, N.; Johansson, S.-Å. Bioequivalent doses of budesonide and prednisone in moderate to severe asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1989, 84, 688–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haahtela, T.; Tamminen, K.; Kava, T.; Malmberg, P.; Rytilä, P.; Nikander, K.; Persson, T.; Selroos, O. Thirteen-year follow-up of early intervention with an inhaled corticosteroid in patients with asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2009, 124, 1180–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agertoft, L.; Pedersen, S. Effects of long-term treatment with an inhaled corticosteroid on growth and pulmonary function in asthmatic children. Respir. Med. 1994, 88, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauwels, R.A.; Pedersen, S.; Busse, W.W.; Tan, W.C.; Chen, Y.Z.; Ohlsson, S.V.; Ullman, A.; Lamm, C.J.; O’Byrne, P.M. Early intervention with budesonid in mild persistent asthma: A randomised, double-blind trial. Lancet 2003, 361, 1071–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haahtela, T.; Tuomisto, L.E.; Pietinalho, A.; Klaukka, T.; Erhola, M.; Kaila, M.; Nieminen, M.M.; Kontula, E.; Laitinen, L.A. A 10 year asthma programme in Finland: Major change for the better. Thorax 2006, 61, 663–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haahtela, T.; Herse, F.; Karjalainen, J.; Klaukka, T.; Linna, M.; Leskelä, R.L.; Selroos, O.; Reissell, E. The Finnish experience to save asthma costs by improving care in 1987–2013. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 139, 408–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selroos, O.; Kupczyk, M.; Kuna, P.; Lacwik, P.; Bousquet, J.; Brennan, D.; Palkonen, S.; Contreras, J.; FitzGerald, M.; Hedlin, G.; et al. National and regional asthma programmes in Europe. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2015, 24, 474–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, T.; Takahashi, T.; Nakajima, S.; Makino, S.; Yamakido, M.; Mano, K.; Nakashima, M.; Selroos, O. A double-blind placebo-controlled dose-response study with budesonide Turbuhaler in Japanese asthma patients. Respirology 2000, 5, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busse, W.W.; Chervinsky, P.; Condemi, J.; Lumry, W.R.; Petty, T.L.; Rennard, S.; Townley, R.G. Budesonide delivered by Turbuhaler is effective in a dose-dependent fashion when used in the treatment of adult patients with chronic asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1998, 101, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, M.T.; Laippala, P.; Lenko, H.L. Growth of asthmatic children is slower during than before treatment with inhaled glucocorticoids. Acta Paediatr. 1997, 86, 138–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Childhood Asthma Management Program Research Group; Szefler, S.; Weiss, S.; Tonascia, J.; Adkinson, N.F.; Bender, B.; Cherniack, R.; Donithan, M.; Kelly, H.W.; Reisman, J.; et al. Long-term effects on budesonide or nedocromil in children with asthma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 343, 1054–1063. [Google Scholar]
- Turpeinen, M.; Nikander, K.; Pelkonen, A.S.; Syvänen, P.; Sorva, R.; Raitio, H.; Malmberg, P.; Juntunen-Backman, K.; Haahtela, T. Daily versus as-needed inhaled corticosteroid for mild persistent asthma. The Helsinki early intervention childhood asthma study. Arch. Dis. Child. 2008, 93, 654–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringdal, N.; Derom, E.; Wåhlin-Boll, E.; Pauwels, R. Onset and duration of action of single doses of formoterol inhaled via Turbuhaler®. Respir. Med. 1998, 92, 1017–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selroos, O. Oxis (formoterol) Turbuhaler®: Its pharmacological and clinical properties. Eur. Respir. Rev. 1998, 8, 216–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aalbers, R.; Vogelmeier, C.; Kuna, P. Achieving asthma control with ICS/LABA: A review of strategies for asthma management and prevention. Respir. Med. 2016, 111, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pauwels, R.A.; Löfdahl, C.G.; Postma, D.S.; Tattersfield, A.E.; O’Byrne, P.; Barnes, P.J.; Ullman, A. Effect of inhaled formoterol and budesonide on exacerbations of asthma. Formoterol and corticosteroid establishing therapy (FACET) international study group. N. Engl. J. Med. 1997, 337, 1405–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Byrne, P.M.; Barnes, P.J.; Rodriguez-Roisin, R.; Runnerstrom, E.; Sandstrom, T.; Svensson, K.; Tattersfield, A. Low dose inhaled budesonide and formoterol in mild persistent asthma: The OPTIMA randomized trial. Am. I Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2001, 164, 1392–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Averell, C.M.; Laliberté, F.; Germain, G.; Sheng Duh, M.; Lima, R.; Mahendran, M.; Slade, D.J. Symptom control in patients with asthma using inhaled corticosteroid/long-acting β2-agonists (fluticasone furoate/vilanterol or budesonide/formoterol) in the US: A retrospective matched cohort study. J. Asthma 2022, 59, 1805–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beasley, R.; Harrison, T.; Peterson, S.; Gustafson, P.; Hamblin, A.; Bengtsson, T.; Fagerås, M. Maintenance and reliever therapy among patients with poorly controlled asthma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Netw. Open 2022, 5, e220615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hozawa, S.; Terada, M.; Haruta, Y.; Hozawa, M. Comparison of early effects of budesonide/formoterol maintenance and reliever therapy with fluticasone furoate/vilanterol for asthma patients requiring step-up from inhaled corticosteroid monotherapy. Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 37, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Byrne, P.M.; FitzGerald, J.M.; Bateman, E.D.; Barns, P.J.; Zhong, N.; Keen, C.; Jorup, C.; Lamarca, R.; Ivanov, S.; Reddel, H.K. Inhaled budesonide-formoterol as needed in mild asthma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 1865–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bateman, E.D.; Reddel, H.K.; O’Byrne, P.M.; Barnes, P.J.; Zhong, N.; Keen, C.; Jorup, C.; Lamarca, R.; Siwek-Posluszna, A.; FitzGerald, J.M. As-needed budesonide-formoterol versus maintenance budesonide in mild asthma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 1877–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FitzGerald, J.M.; O’Byrne, P.M.; Bateman, E.D.; Barnes, P.J.; Zheng, J.; Ivanov, S.; Lamarca, R.; Larsdotter, U.; Emerath, U.; Jansen, G.; et al. Safety of as-needed budesonide-formoterol in mild asthma. Data from the two phase III Sygma studies. Drug Saf. 2021, 44, 467–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddel, H.K.; O’Byrne, P.M.; FitzGerald, J.M.; Barnes, P.J.; Zheng, J.; Ivanov, S.; Lamarca, R.; Puu, M.; Alagappan, V.K.; Bateman, E.D. Efficacy and safety as-needed budesonide-formoterol in adolescents with mild asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2021, 9, 3069–3077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddel, H.K.; FitzGerald, J.M.; Bateman, E.D.; Bacharier, L.B.; Becker, A.; Brusselle, G.; Buhl, R.; Cruz, A.A.; Fleming, L.; Inoue, H.; et al. GINA 2019: A fundamental change in asthma management: Treatment of asthma with short-acting bronchodilators alone is no longer recommended for adults and adolescents. Eur. Respir. J. 2019, 53, 1901046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daley-Yates, P.; Aggarwal, B.; Lulic, Z.; Fulmali, S.; Cruz, A.; Singh, D. Pharmacology versus convenience: A benefit/risk analysis of regular maintenance versus infrequent or as-needed inhaled corticosteroid use in mild asthma. Adv. Ther. 2022, 39, 706–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daley-Yates, P.; Singh, D.; Igea, J.; Macchia, L.; Verma, M.; Berend, N.; Plank, M. Assessing the effects of changing patterns of inhaled corticosteroid dosing and adherence with fluticasone furoate and budesonide on asthma management. Adv. Ther. 2023, 40, 4042–4059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global Initiative for Asthma. Global Strategy for Asthma Management and Prevention. 2023. Updated July 2023. Available online: www.ginasthma.org (accessed on 10 February 2024).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Brattsand, R.; Selroos, O. Budesonide Attains Its Wide Clinical Profile by Alternative Kinetics. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 503. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17040503
Brattsand R, Selroos O. Budesonide Attains Its Wide Clinical Profile by Alternative Kinetics. Pharmaceuticals. 2024; 17(4):503. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17040503
Chicago/Turabian StyleBrattsand, Ralph, and Olof Selroos. 2024. "Budesonide Attains Its Wide Clinical Profile by Alternative Kinetics" Pharmaceuticals 17, no. 4: 503. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17040503
APA StyleBrattsand, R., & Selroos, O. (2024). Budesonide Attains Its Wide Clinical Profile by Alternative Kinetics. Pharmaceuticals, 17(4), 503. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17040503




