Assessment of Registered Clinical Trial Designs: Comparison of L-Arginine and/or L-Citrulline Interventions for Hypertension
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Characteristics of the Clinical Trial
2.2. Comparison of Trials with Meta-Analysis
3. Discussion
Limitations
4. Materials and Methods
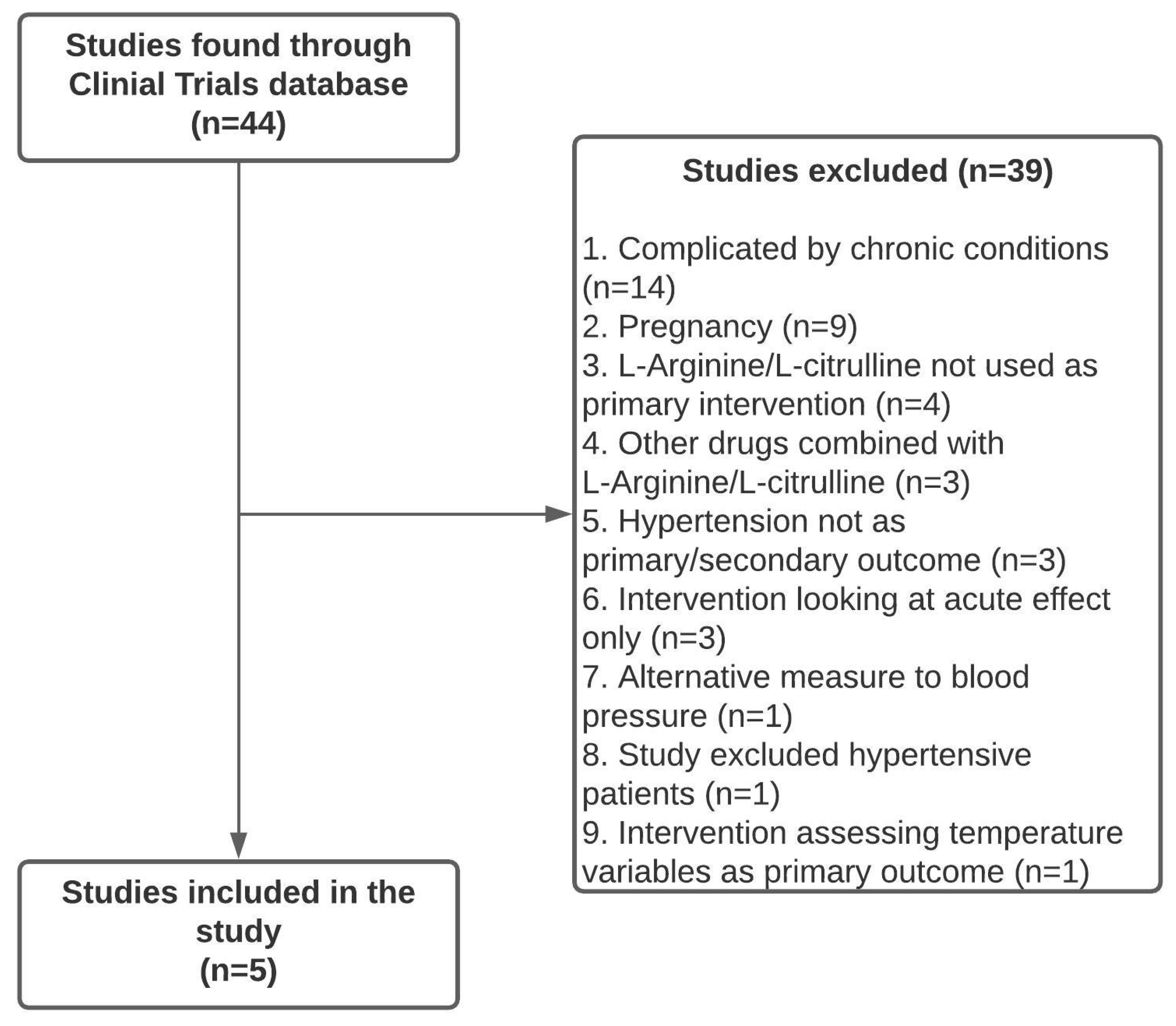
4.1. RCT Identification, Screening, and Eligibility
4.2. Comparison of Trial Elements
4.3. Comparison of Clinicaltrials.gov Trial Elements versus Those Included in Three Recent Published Meta-Analyses
4.4. Statistics
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cyr, A.R.; Huckaby, L.V.; Shiva, S.S.; Zuckerbraun, B.S. Nitric Oxide and Endothelial Dysfunction. Crit. Care Clin. 2020, 36, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryan, N.S. Nitric oxide deficiency is a primary driver of hypertension. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2022, 206, 115325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Creager, M.A.; Gallagher, S.J.; Girerd, X.J.; Coleman, S.M.; Dzau, V.J.; Cooke, J.P. L-arginine improves endothelium-dependent vasodilation in hypercholesterolemic humans. J. Clin. Investig. 1992, 90, 1248–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kajikawa, M.; Higashi, Y. Obesity and Endothelial Function. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feron, O.; Dessy, C.; Moniotte, S.; Desager, J.P.; Balligand, J.L. Hypercholesterolemia decreases nitric oxide production by promoting the interaction of caveolin and endothelial nitric oxide synthase. J. Clin. Investig. 1999, 103, 897–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Forstermann, U. Pharmacological prevention of eNOS uncoupling. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2014, 20, 3595–3606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, M.R.; Jessup, W.; Hailstones, D.; Celermajer, D.S. L-arginine reduces human monocyte adhesion to vascular endothelium and endothelial expression of cell adhesion molecules. Circulation 1997, 95, 662–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiraseb, F.; Asbaghi, O.; Bagheri, R.; Wong, A.; Figueroa, A.; Mirzaei, K. Effect of l-Arginine Supplementation on Blood Pressure in Adults: A Systematic Review and Dose-Response Meta-analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials. Adv. Nutr. 2022, 13, 1226–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Y. Regulation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase activity by protein-protein interaction. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2014, 20, 3514–3520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böger, R.H. The pharmacodynamics of L-arginine. Altern. Ther. Health Med. 2014, 20, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio-Ruiz, M.E.; Pérez-Torres, I.; Soto, M.E.; Pastelín, G.; Guarner-Lans, V. Aging in blood vessels. Medicinal agents FOR systemic arterial hypertension in the elderly. Ageing Res. Rev. 2014, 18, 132–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacolley, P.; Regnault, V.; Segers, P.; Laurent, S. Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells and Arterial Stiffening: Relevance in Development, Aging, and Disease. Physiol. Rev. 2017, 97, 1555–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, D.G.; Coffman, T.M.; Wilcox, C.S. Pathophysiology of Hypertension: The Mosaic Theory and Beyond. Circ. Res. 2021, 128, 847–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- George, M.; Selvarajan, S.; Suresh-Kumar, S.; Dkhar, S.A.; Chandrasekaran, A. Globalization of clinical trials–Where are we heading? Curr. Clin. Pharmacol. 2013, 8, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-González, L. Registering transparency: The making of the international clinical trial registry platform by the world health organization (2004–2006). Glob. Health 2023, 19, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, J.Y.; Qin, L.Q.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, J.; Arigoni, F.; Zhang, W. Effect of oral L-arginine supplementation on blood pressure: A meta-analysis of randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials. Am Heart J. 2011, 162, 959–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barkhidarian, B.; Khorshidi, M.; Shab-Bidar, S.; Hashemi, B. Effects of L-citrulline supplementation on blood pressure: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Avicenna J. Phytomed. 2019, 9, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mirenayat, M.S.; Moradi, S.; Mohammadi, H.; Rouhani, M.H. Effect of L-Citrulline Supplementation on Blood Pressure: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Clinical Trials. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2018, 20, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahboobi, S.; Tsang, C.; Rezaei, S.; Jafarnejad, S. Effect of L-citrulline supplementation on blood pressure: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2019, 33, 10–21, Retracted in: J. Hum. Hypertens. 2021, 35, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Rourke, M.F.; Staessen, J.A.; Vlachopoulos, C.; Duprez, D.; Plante, G.E. Clinical applications of arterial stiffness; definitions and reference values. Am. J. Hypertens. 2002, 15, 426–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legerer, C.; Almsherqi, Z.A.; Dokos, S.; McLachlan, C.S. Computational evaluation of an extra-aortic elastic-wrap applied to simulated aging anisotropic human aorta models. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 20109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrova, M.; Kiat, H.; Gavino, A.; McLachlan, C.S. Carotid Ultrasound Screening Programs in Rural Communities: A Systematic Review. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobrino, A.; Vallejo, S.; Novella, S.; Lázaro-Franco, M.; Mompeón, A.; Bueno-Betí, C.; Walther, T.; Sánchez-Ferrer, C.; Peiró, C.; Hermenegildo, C. Mas receptor is involved in the estrogen-receptor induced nitric oxide-dependent vasorelaxation. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2017, 129, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chambliss, K.L.; Shaul, P.W. Estrogen modulation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase. Endocr. Rev. 2002, 23, 665–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klawitter, J.; Hildreth, K.L.; Christians, U.; Kohrt, W.M.; Moreau, K.L. A relative L-arginine deficiency contributes to endothelial dysfunction across the stages of the menopausal transition. Physiol. Rep. 2017, 5, e13409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tikhonoff, V.; Casiglia, E.; Gasparotti, F.; Spinella, P. The uncertain effect of menopause on blood pressure. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2019, 33, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawecka-Jaszcz, K.; Czarnecka, D.; Olszanecka, A.; Rajzer, M.; Jankowski, P. The effect of hormone replacement therapy on arterial blood pressure and vascular compliance in postmenopausal women with arterial hypertension. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2002, 16, 509–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samargandy, S.; Matthews, K.A.; Brooks, M.M.; Barinas-Mitchell, E.; Magnani, J.W.; Thurston, R.C.; El Khoudary, S.R. Trajectories of Blood Pressure in Midlife Women: Does Menopause Matter? Circ. Res. 2022, 130, 312–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reckelhoff, J.F.; Kellum, J.A.; Blanchard, E.J.; Bacon, E.E.; Wesley, A.J.; Kruckeberg, W.C. Changes in nitric oxide precursor, L-arginine, and metabolites, nitrate and nitrite, with aging. Life Sci. 1994, 55, 1895–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epstein, B.J.; Anderson, S. Discordant effects of beta-blockade on central aortic systolic and brachial systolic blood pressure: Considerations beyond the cuff. Pharmacotherapy 2007, 27, 1322–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, I.B.; Franklin, S.S.; Cockcroft, J.R. Nitric oxide and the regulation of large artery stiffness: From physiology to pharmacology. Hypertension 2004, 44, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giles, T.D. Aspects of nitric oxide in health and disease: A focus on hypertension and cardiovascular disease. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2006, 8 (Suppl. 4), 2–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craig, A.; Mels, C.M.C.; Schutte, A.E.; Tsikas, D.; Kruger, R. Nitric oxide-related markers link inversely to blood pressure in black boys and men: The ASOS and African-PREDICT studies. Amino Acids 2020, 52, 639–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasan, R.S.; Pan, S.; Xanthakis, V.; Beiser, A.; Larson, M.G.; Seshadri, S.; Mitchell, G.F. Arterial Stiffness and Long-Term Risk of Health Outcomes: The Framingham Heart Study. Hypertension 2022, 79, 1045–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durante, W.; Johnson, F.K.; Johnson, R.A. Arginase: A critical regulator of nitric oxide synthesis and vascular function. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2007, 34, 906–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillsley, A.; Chin, V.; Li, A.; McLachlan, C.S. Resveratrol for Weight Loss in Obesity: An Assessment of Randomized Control Trial Designs in ClinicalTrials.gov. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
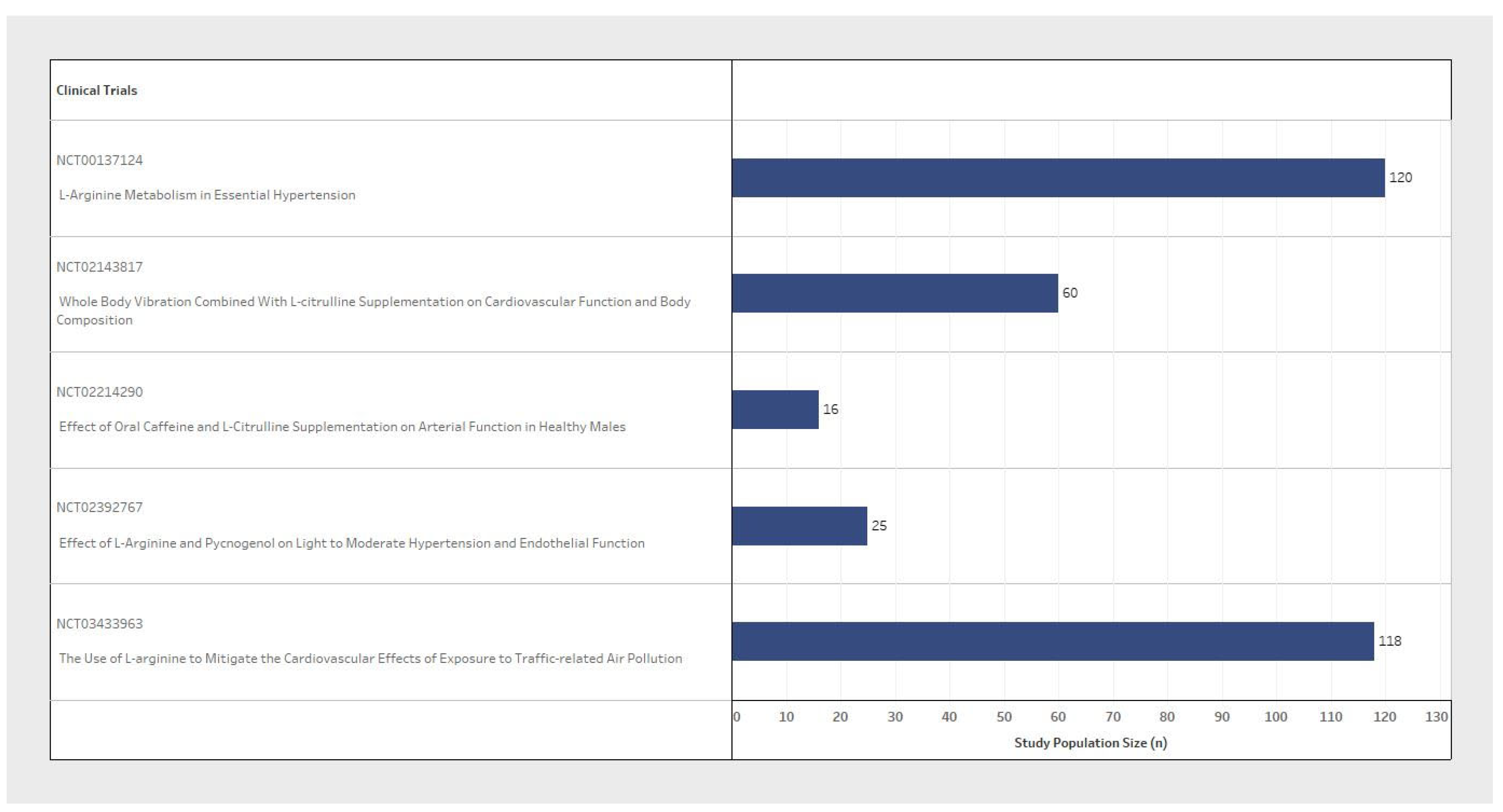
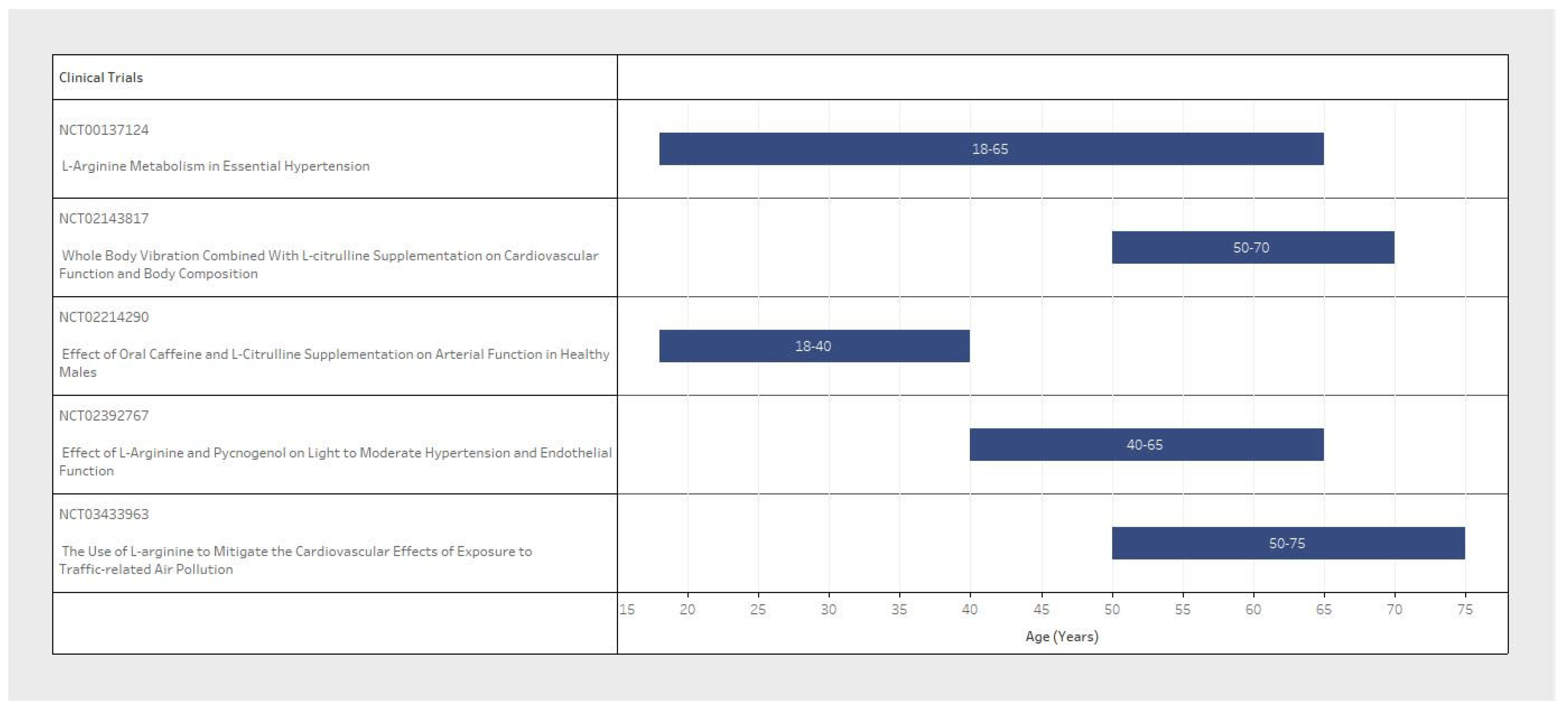

| NCT Number | n (Study Population Size) | Inclusion Criteria | Exclusion Criteria | L-Arginine/L-Citrulline | BP Measure | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | Age Range (Years) | Systolic BP (mmHg) | Diastolic BP (mmHg) | Population | L-Arginine/ L-Citrulline Dosage (Per Dose) | Interval | Outcome Measures | Type of BP Measures | Timing/Interval of Measures | ||
| NCT03433963 | 118 | Female/ Male | 50–75 | 120–160 | 65–100 | Cardiovascular Diseases/Coagulopathy Neurological Diseases/Pulmonary Diseases Gastrointestinal Diseases/Liver or Kidney Diseases/Cancer | L-Arg supplement 3 g | 3 times/day for 2 weeks | Primary: Systolic and diastolic BP/ambulatory BP. Secondary: Endothelial nitric oxide synthase/Plasma L-Arg or L-citrulline and ornithine in L-arg metabolic pathway | Systolic and diastolic BP/Ambulatory BP | Baseline twice on the 14th day, and end point on 15th day |
| NCT02214290 | 16 | Male | 18–40 | <160 | <99 | Cardiovascular Diseases | L-citrulline capsule 0.75 g | 8 times/day for 1 week | Primary: Brachial, ankle, and central BP. Secondary: Aeriel Stiffness (PWV) and wave reflection | Brachial, ankle, and central BP | Baseline and end point at 1 week |
| NCT00137124 | 120 | Female/ Male | 18–65 | Not Specified | Not Specified | Cardiovascular Diseases/Neurological Diseases/Liver or Kidney Diseases | Not Specified | Not Specified | Primary: L-arginine transport and metabolism on endothelial function | Not Specified | 4 week timeframe, interval not specified |
| NCT02392767 | 25 | Female/ Male | 40–65 | 130–149 | Not Specified | Cardiovascular Diseases/Underweight/Obese | L-arginine 2.4 g | 2 times/day for 4 weeks | Primary: Endothelial Function. Secondary: Systolic and diastolic BP/Asymmetric dimethyl arginine (ADMA) Level. Other: Prothrombin Time | Systolic and diastolic BP | Daily during the 4th (final) week |
| NCT02143817 | 60 | Female | 50–70 | Not Specified | Not Specified | Diabetes | L-citrulline supplementation 3 g | 2 times/day for 8 weeks | Primary: Brachial and aortic BP. Secondary: Arterial Stiffness and pressure wave reflection/Endothelial and autonomic functions. Other: Body Composition/Muscle Strength | Brachial and aortic BP | 8 week timeframe, interval not specified |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hillsley, A.B.; McLachlan, C.S. Assessment of Registered Clinical Trial Designs: Comparison of L-Arginine and/or L-Citrulline Interventions for Hypertension. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 477. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17040477
Hillsley AB, McLachlan CS. Assessment of Registered Clinical Trial Designs: Comparison of L-Arginine and/or L-Citrulline Interventions for Hypertension. Pharmaceuticals. 2024; 17(4):477. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17040477
Chicago/Turabian StyleHillsley, Ashley Brett, and Craig Steven McLachlan. 2024. "Assessment of Registered Clinical Trial Designs: Comparison of L-Arginine and/or L-Citrulline Interventions for Hypertension" Pharmaceuticals 17, no. 4: 477. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17040477
APA StyleHillsley, A. B., & McLachlan, C. S. (2024). Assessment of Registered Clinical Trial Designs: Comparison of L-Arginine and/or L-Citrulline Interventions for Hypertension. Pharmaceuticals, 17(4), 477. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17040477