Trichostatin C Synergistically Interacts with DNMT Inhibitor to Induce Antineoplastic Effect via Inhibition of Axl in Bladder and Lung Cancer Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Isolation and Identification of TSC
2.2. TSC Exhibits Anti-Proliferation Effect in Cancer Cell Line with HDAC Inhibitory Activity
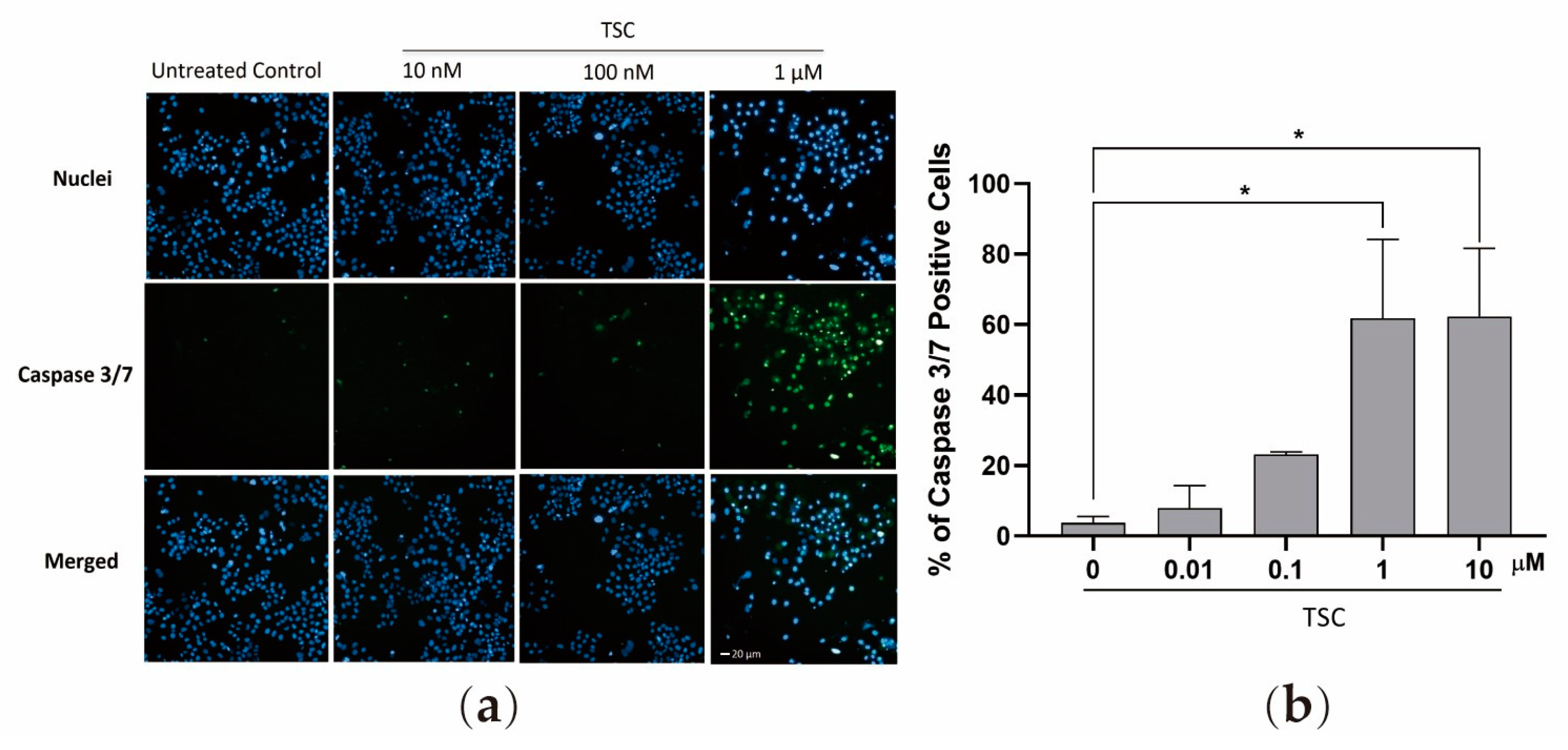
2.3. TSC Induces Apoptosis by the Activation of Caspase 3/7 Cancer Cell Line
2.4. Combining TSC and Decitabine Leads to Synergistic Cytotoxicity in Cancer Cells
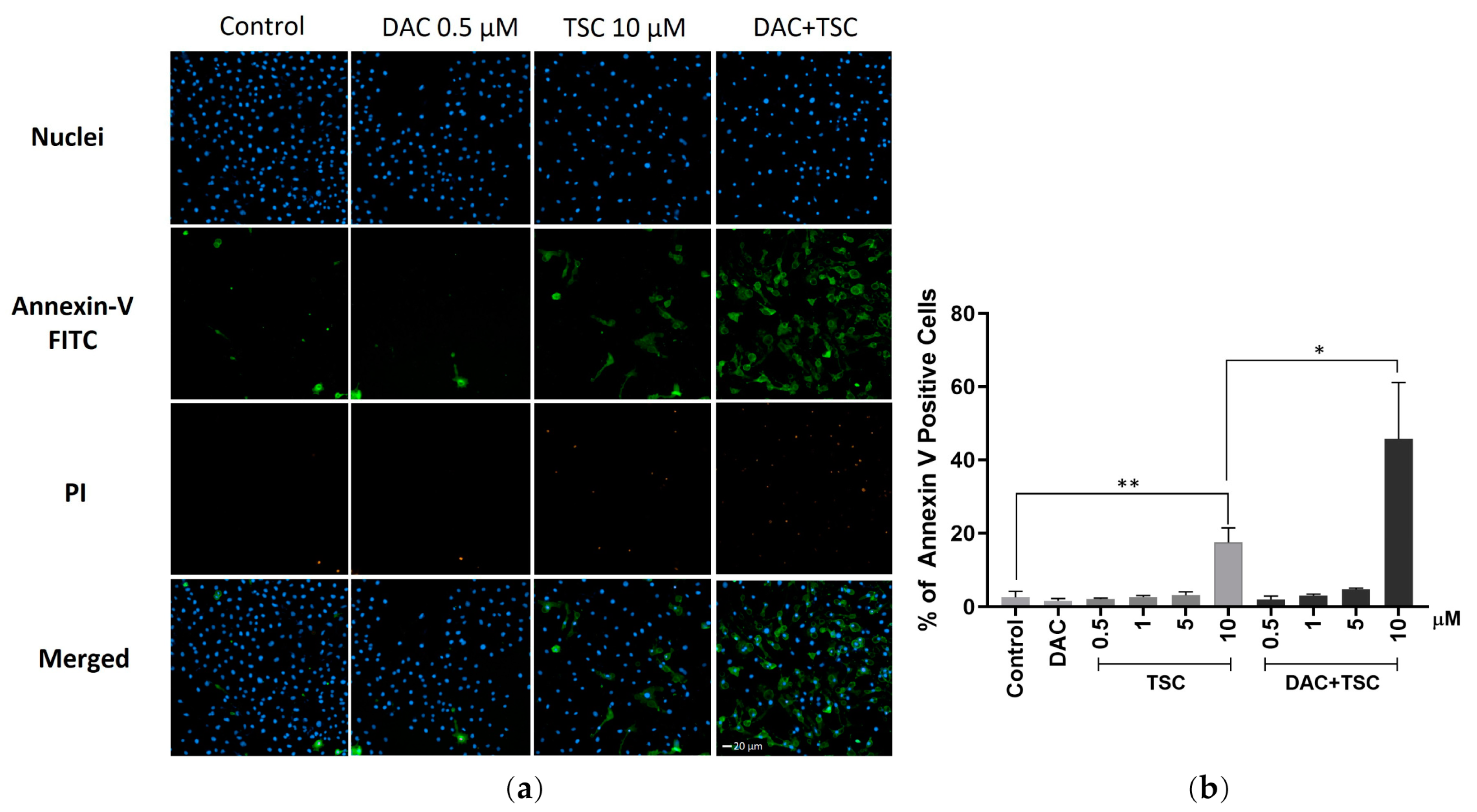
2.5. TSC and Decitabine Synergistically Induces Apoptosis
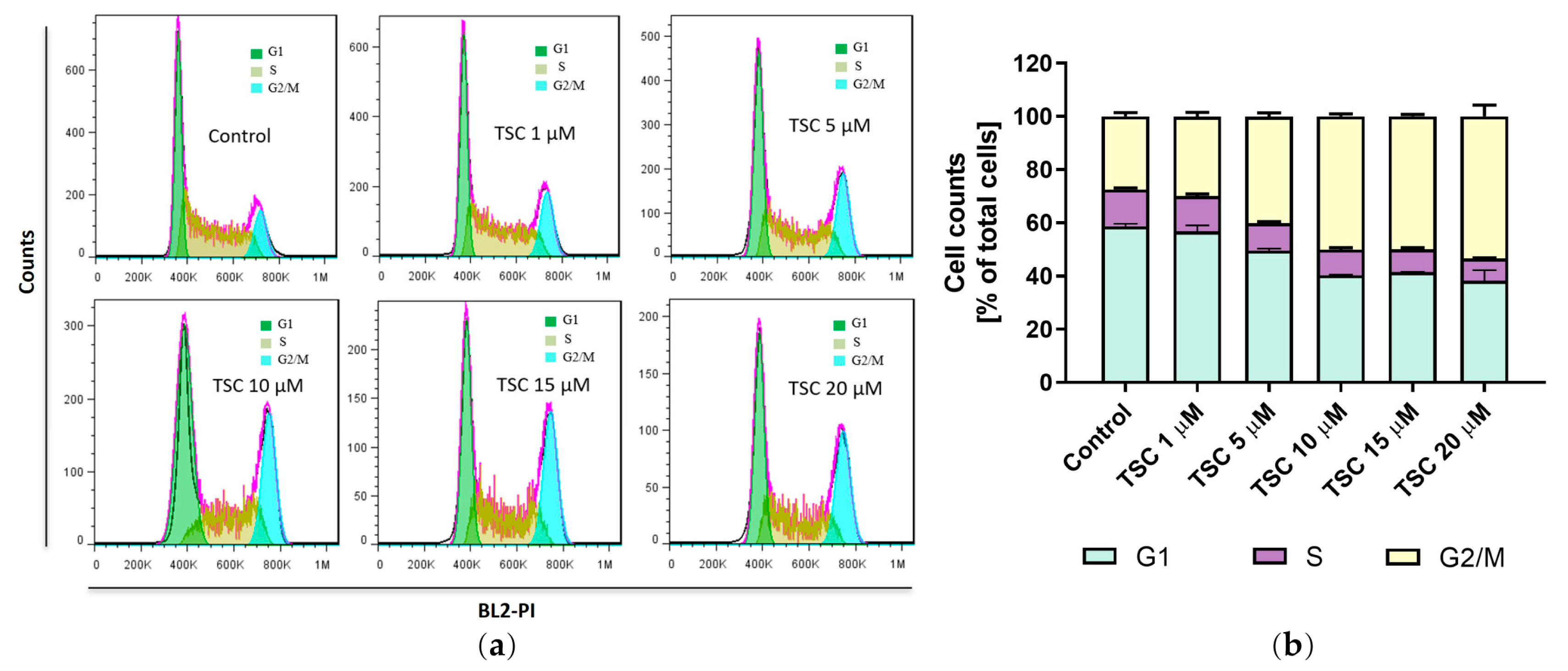
2.6. TSC Induces G2/M Phase Cell Cycle Arrest in Bladder Cancer Cells
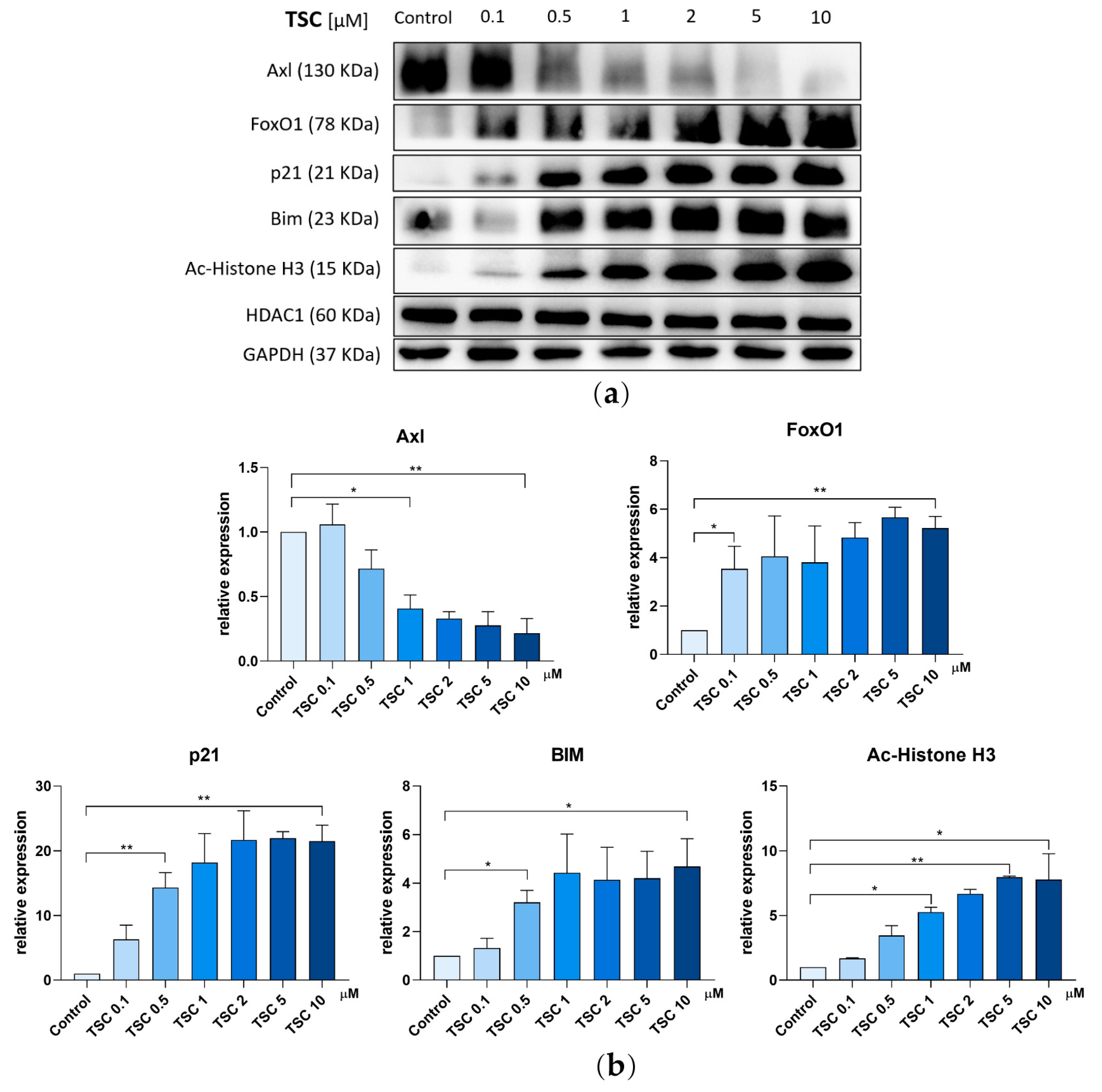
2.7. TSC Alters Expression of Axl and FoxO1 Pathway
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Fermentation of Streptomyces sp. CPCC 203909 and Isolation of TSC
4.3. Cell Culture
4.4. Cell Viability Assay
4.5. Synergistic Study
4.6. Apoptosis Assay
4.7. Cell Cycle Analysis
4.8. Caspase 3/7 Activation
4.9. Western Blot Analysis
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ho, T.C.S.; Chan, A.H.Y.; Ganesan, A. Thirty Years of HDAC Inhibitors: 2020 Insight and Hindsight. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 12460–12484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baylin, S.B. DNA methylation and gene silencing in cancer. Nat. Clin. Pract. Oncol. 2005, 2 (Suppl. 1), S4–S11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dokmanovic, M.; Clarke, C.; Marks, P.A. Histone deacetylase inhibitors: Overview and perspectives. Mol. Cancer Res. 2007, 5, 981–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Hamacher, A.; Petzsch, P.; Kohrer, K.; Niegisch, G.; Hoffmann, M.J.; Schulz, W.A.; Kassack, M.U. Combination of Decitabine and Entinostat Synergistically Inhibits Urothelial Bladder Cancer Cells via Activation of FoxO1. Cancers 2020, 12, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bondarev, A.D.; Attwood, M.M.; Jonsson, J.; Chubarev, V.N.; Tarasov, V.V.; Schioth, H.B. Recent developments of HDAC inhibitors: Emerging indications and novel molecules. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2021, 87, 4577–4597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bieliauskas, A.V.; Pflum, M.K. Isoform-selective histone deacetylase inhibitors. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 1402–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hesham, H.M.; Lasheen, D.S.; Abouzid, K.A.M. Chimeric HDAC inhibitors: Comprehensive review on the HDAC-based strategies developed to combat cancer. Med. Res. Rev. 2018, 38, 2058–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouyahya, A.; El Omari, N.; Bakha, M.; Aanniz, T.; El Menyiy, N.; El Hachlafi, N.; El Baaboua, A.; El-Shazly, M.; Alshahrani, M.M.; Al Awadh, A.A.; et al. Pharmacological Properties of Trichostatin A, Focusing on the Anticancer Potential: A Comprehensive Review. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuji, N.; Kobayashi, M.; Nagashima, K.; Wakisaka, Y.; Koizumi, K. A new antifungal antibiotic, trichostatin. J. Antibiot. 1976, 29, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlando, E.; Aebersold, D.M.; Medova, M.; Zimmer, Y. Oncogene addiction as a foundation of targeted cancer therapy: The paradigm of the MET receptor tyrosine kinase. Cancer Lett. 2019, 443, 189–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Marrocco, I.; Yarden, Y. Roles for receptor tyrosine kinases in tumor progression and implications for cancer treatment. Adv. Cancer Res. 2020, 147, 1–57. [Google Scholar]
- Du, Z.; Lovly, C.M. Mechanisms of receptor tyrosine kinase activation in cancer. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regad, T. Targeting RTK Signaling Pathways in Cancer. Cancers 2015, 7, 1758–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, C.; Wei, Y.; Wei, X. AXL receptor tyrosine kinase as a promising anti-cancer approach: Functions, molecular mechanisms and clinical applications. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spangle, J.M.; Roberts, T.M. Epigenetic regulation of RTK signaling. J. Mol. Med. 2017, 95, 791–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, C.W.; Wu, M.S.; Huang, W.C.; Chen, C.C. HDAC inhibition decreases the expression of EGFR in colorectal cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e18087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinogradova, M.; Gehling, V.S.; Gustafson, A.; Arora, S.; Tindell, C.A.; Wilson, C.; Williamson, K.E.; Guler, G.D.; Gangurde, P.; Manieri, W.; et al. An inhibitor of KDM5 demethylases reduces survival of drug-tolerant cancer cells. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2016, 12, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, L.; Chen, M.; Wang, C.; Jiang, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, W.; Li, S.; Zhao, L.; Sheng, R.; Han, J.; et al. Trichostatin D as a Novel KLF2 Activator Attenuates TNFalpha-Induced Endothelial Inflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 13477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuji, N.; Kobayashi, M. Trichostatin C, a glucopyranosyl hydroxamate. J. Antibiot. 1978, 31, 939–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connolly, R.M.; Rudek, M.A.; Piekarz, R. Entinostat: A promising treatment option for patients with advanced breast cancer. Future Oncol. 2017, 13, 1137–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slee, E.A.; Adrain, C.; Martin, S.J. Executioner caspase-3, -6, and -7 perform distinct, non-redundant roles during the demolition phase of apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 7320–7326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.V.; Varma, M.; Rai, M.; Pratap Singh, S.; Bansod, G.; Laux, P.; Luch, A. Advancing Predictive Risk Assessment of Chemicals via Integrating Machine Learning, Computational Modeling, and Chemical/Nano-Quantitative Structure-Activity Relationship Approaches. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2024, 2300366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bose, P.; Dai, Y.; Grant, S. Histone deacetylase inhibitor (HDACI) mechanisms of action: Emerging insights. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 143, 323–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asfaha, Y.; Schrenk, C.; Alves Avelar, L.A.; Hamacher, A.; Pflieger, M.; Kassack, M.U.; Kurz, T. Recent advances in class IIa histone deacetylases research. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2019, 27, 115087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marks, P.A.; Xu, W.S. Histone deacetylase inhibitors: Potential in cancer therapy. J. Cell Biochem. 2009, 107, 600–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byers, L.A.; Diao, L.; Wang, J.; Saintigny, P.; Girard, L.; Peyton, M.; Shen, L.; Fan, Y.; Giri, U.; Tumula, P.K.; et al. An epithelial-mesenchymal transition gene signature predicts resistance to EGFR and PI3K inhibitors and identifies Axl as a therapeutic target for overcoming EGFR inhibitor resistance. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vajkoczy, P.; Knyazev, P.; Kunkel, A.; Capelle, H.H.; Behrndt, S.; von Tengg-Kobligk, H.; Kiessling, F.; Eichelsbacher, U.; Essig, M.; Read, T.A.; et al. Dominant-negative inhibition of the Axl receptor tyrosine kinase suppresses brain tumor cell growth and invasion and prolongs survival. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 5799–5804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanczky, A.; Gyorffy, B. Web-Based Survival Analysis Tool Tailored for Medical Research (KMplot): Development and Implementation. J. Med. Internet Res. 2021, 23, e27633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.V.; Shelar, A.; Rai, M.; Laux, P.; Thakur, M.; Dosnkyi, I.; Santomauro, G.; Singh, A.K.; Luch, A.; Patil, R.; et al. Harmonization Risks and Rewards: Nano-QSAR for Agricultural Nanomaterials. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 2835–2852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, T.-C. The combination index (CI < 1) as the definition of synergism and of synergy claims. Synergy 2018, 7, 49–50. [Google Scholar]
- Gohr, K.; Hamacher, A.; Engelke, L.H.; Kassack, M.U. Inhibition of PI3K/Akt/mTOR overcomes cisplatin resistance in the triple negative breast cancer cell line HCC38. BMC Cancer 2017, 17, 711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, C.; Lei, L.; Xu, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Xu, Y.; Si, S. Trichostatin C Synergistically Interacts with DNMT Inhibitor to Induce Antineoplastic Effect via Inhibition of Axl in Bladder and Lung Cancer Cells. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 425. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17040425
Wang C, Lei L, Xu Y, Li Y, Zhang J, Xu Y, Si S. Trichostatin C Synergistically Interacts with DNMT Inhibitor to Induce Antineoplastic Effect via Inhibition of Axl in Bladder and Lung Cancer Cells. Pharmaceuticals. 2024; 17(4):425. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17040425
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Chenyin, Lijuan Lei, Yang Xu, Yan Li, Jing Zhang, Yanni Xu, and Shuyi Si. 2024. "Trichostatin C Synergistically Interacts with DNMT Inhibitor to Induce Antineoplastic Effect via Inhibition of Axl in Bladder and Lung Cancer Cells" Pharmaceuticals 17, no. 4: 425. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17040425
APA StyleWang, C., Lei, L., Xu, Y., Li, Y., Zhang, J., Xu, Y., & Si, S. (2024). Trichostatin C Synergistically Interacts with DNMT Inhibitor to Induce Antineoplastic Effect via Inhibition of Axl in Bladder and Lung Cancer Cells. Pharmaceuticals, 17(4), 425. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17040425





