Synthesis of a [18F]F Estradiol Derivative via Click Chemistry Using an Automated Synthesis Module: In Vitro Evaluation as Potential Radiopharmaceutical for Breast Cancer Imaging
Abstract
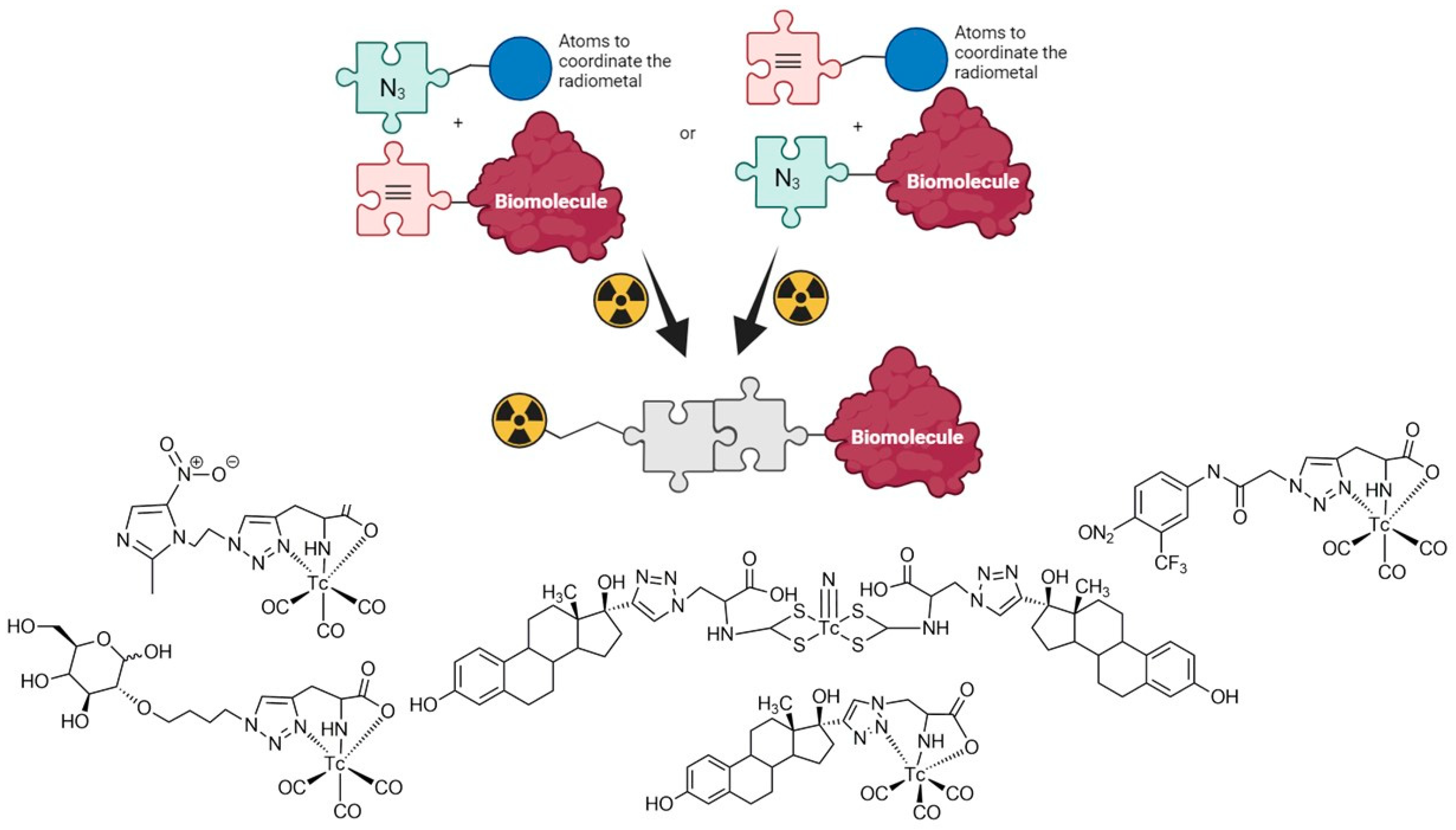
1. Introduction
2. Results
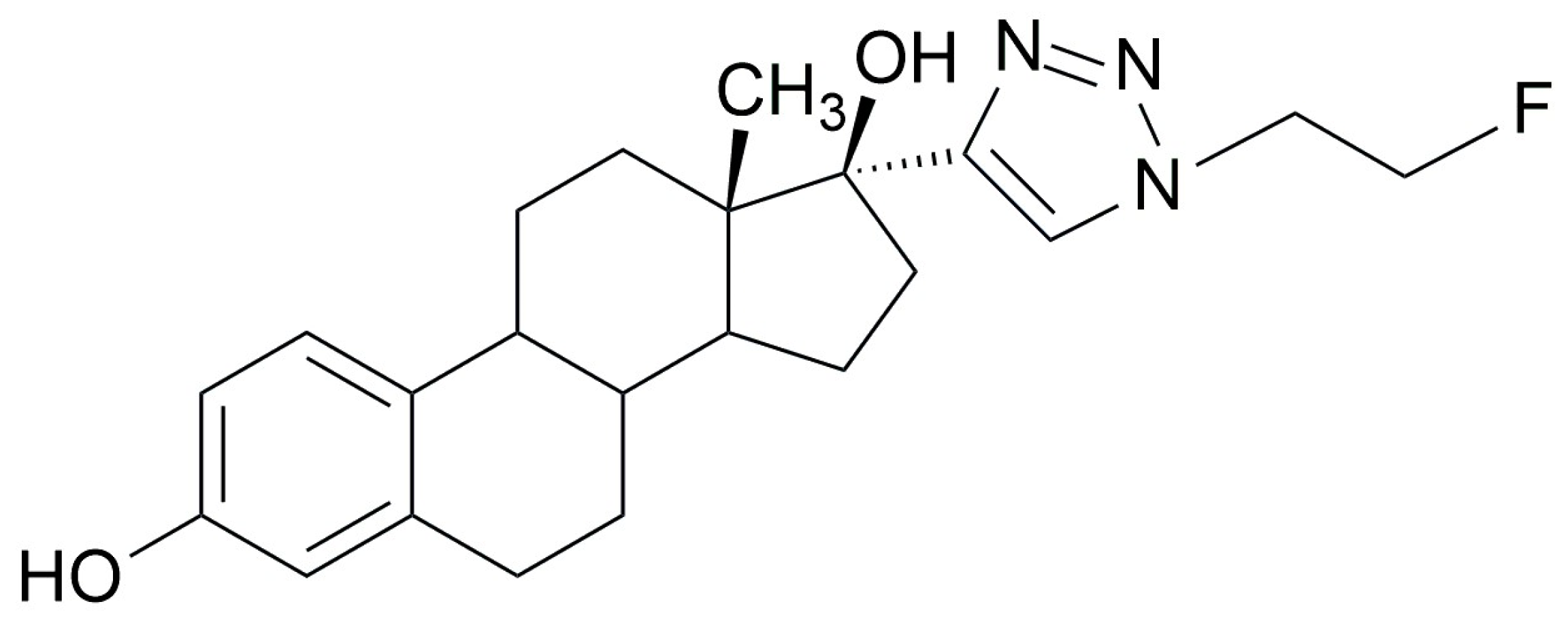
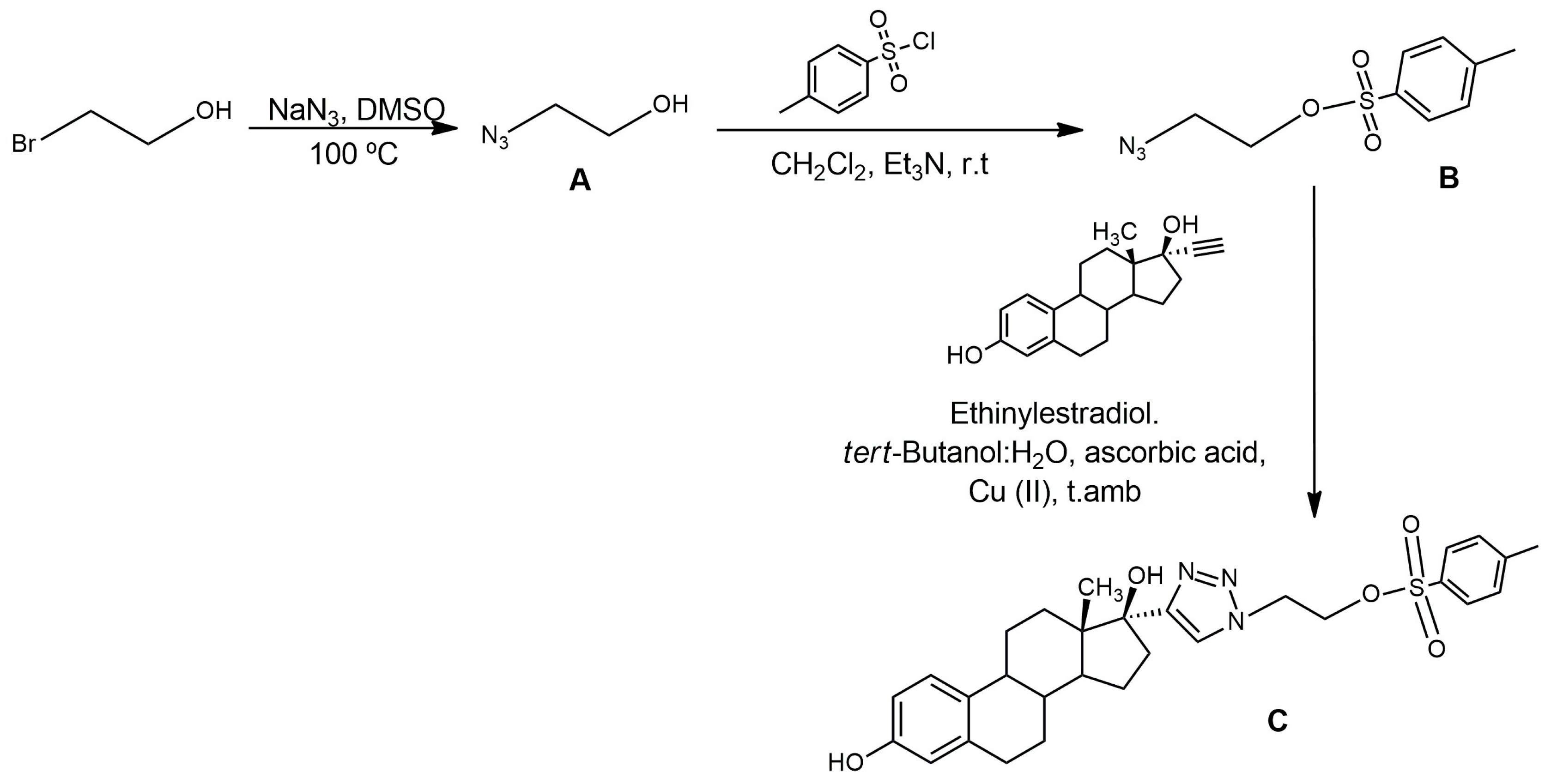
2.1. Synthesis of [18F]F-FEET- Method 1
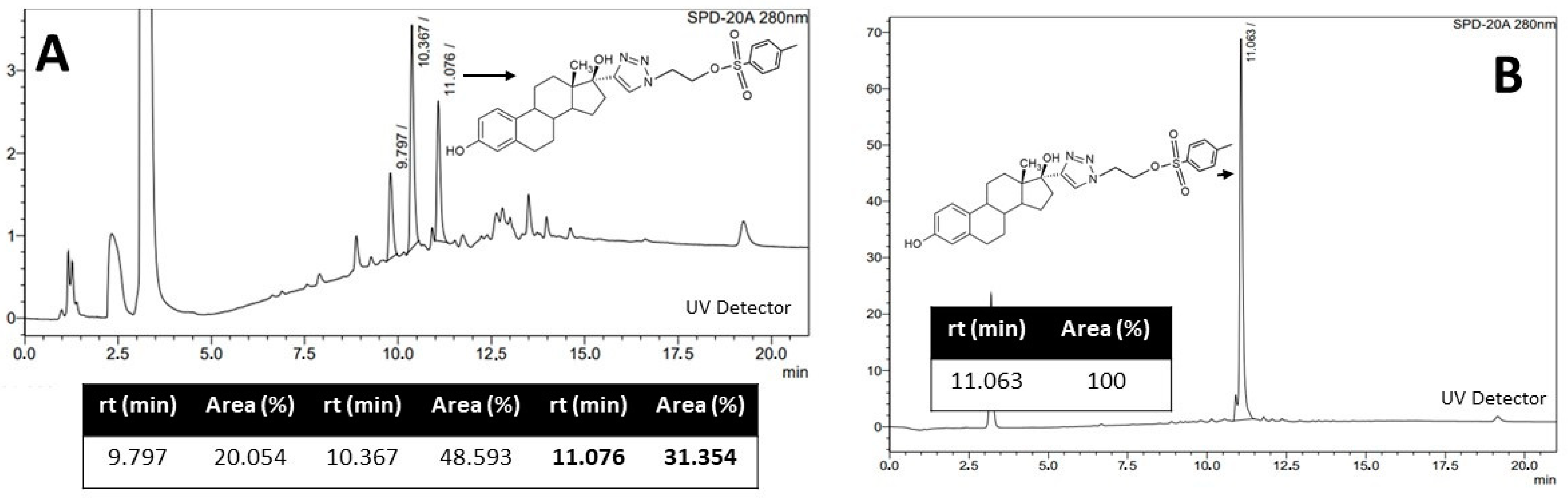
2.1.1. Synthesis of C (Precursor)
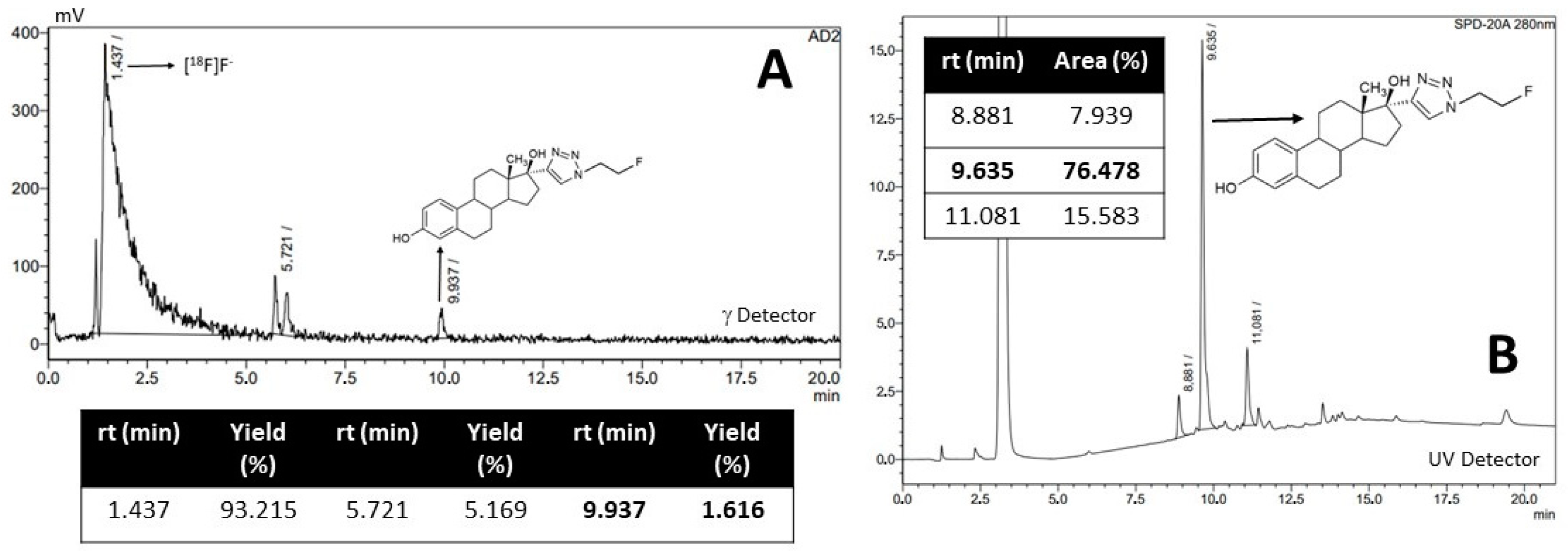
2.1.2. Radiofluorination of C to Obtain [18F]F-FEET
2.2. Synthesis of [18F]F-FEET- Method 2
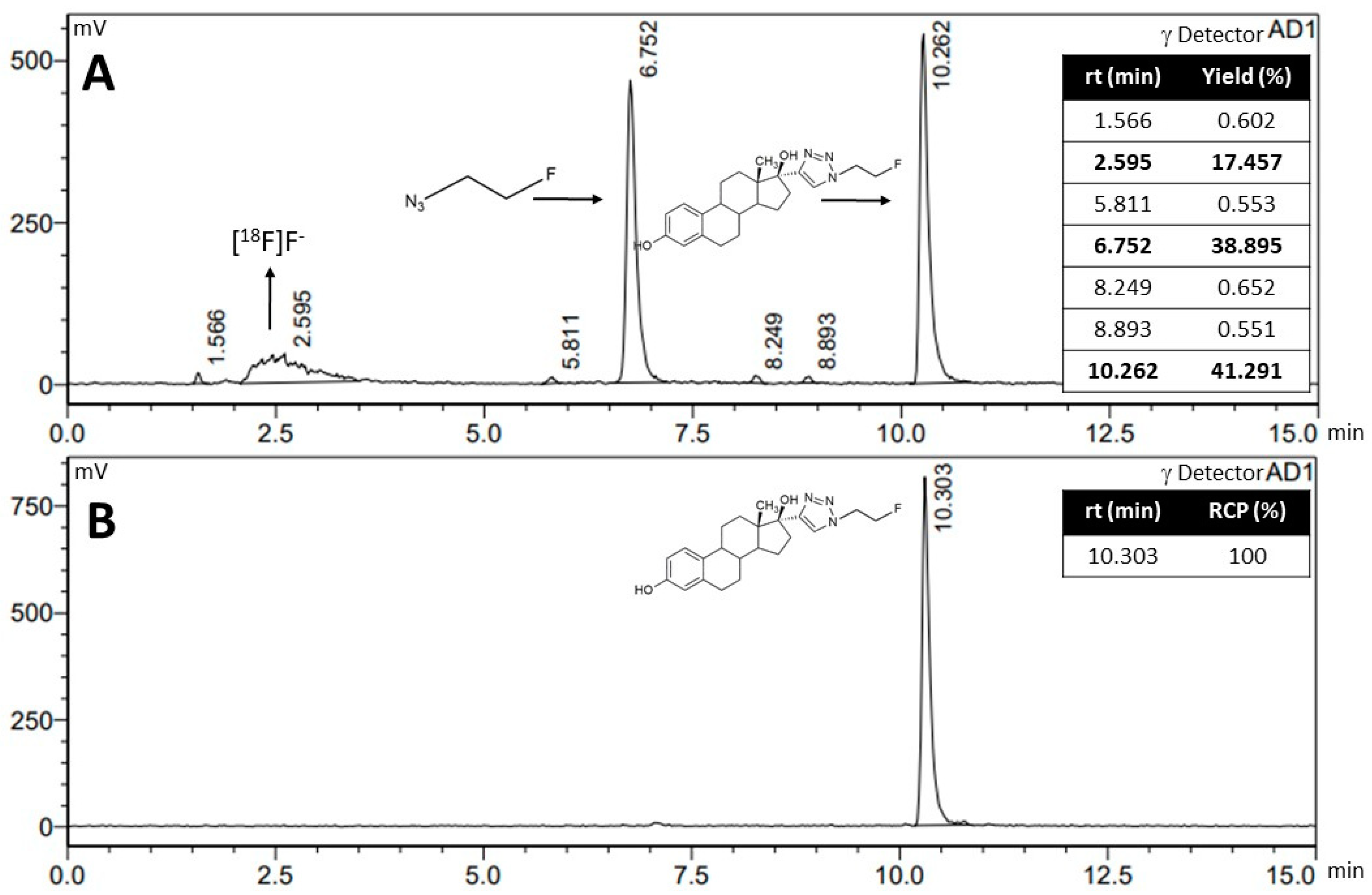
2.2.1. Radiofluorination of B to Obtain D
2.2.2. Manual Synthesis of [18F]F-FEET
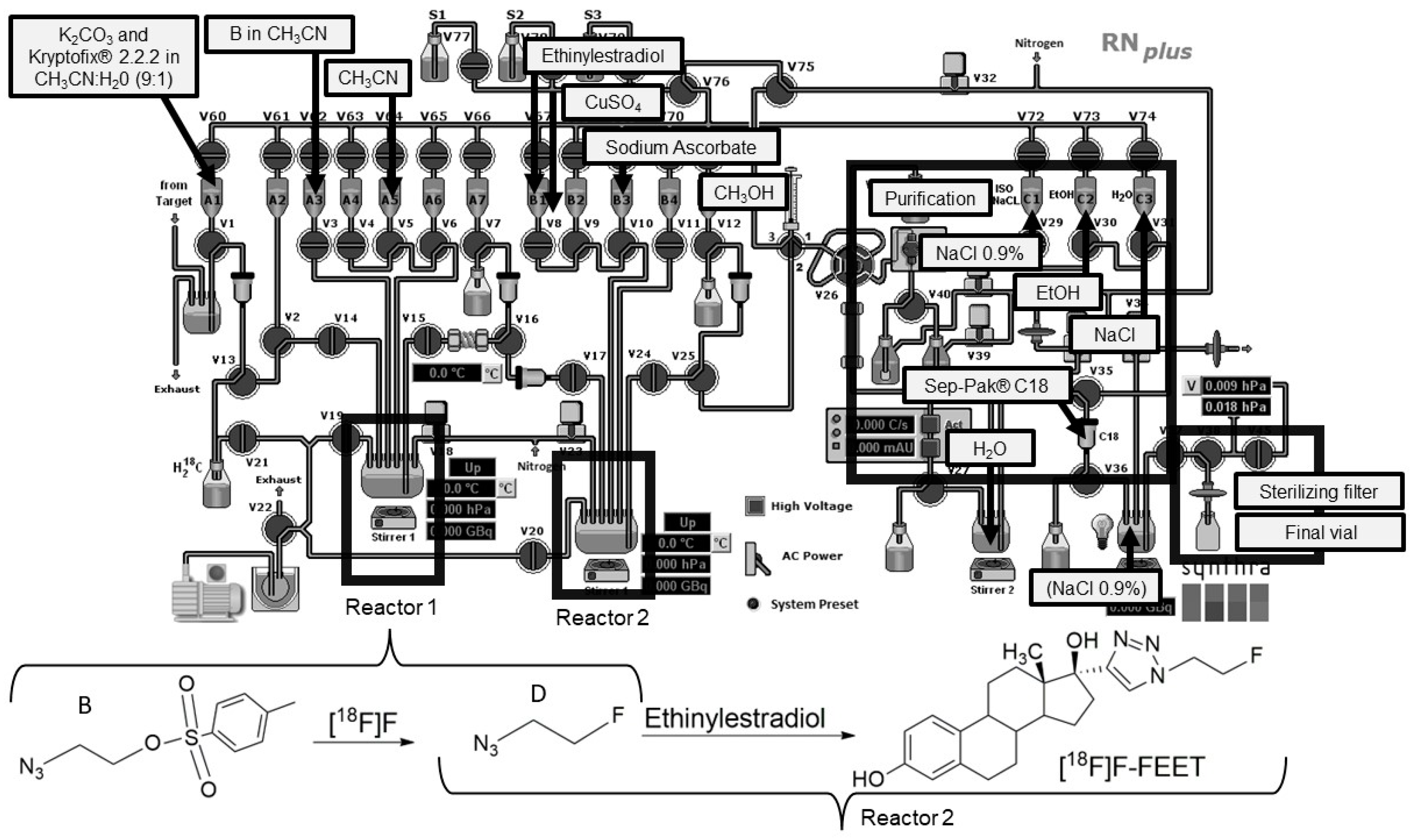
2.2.3. Complete Synthesis of [18F]F-FEET in an Automated Module
2.3. Physicochemical Studies
2.4. In Vitro Biological Studies
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. General
4.2. Synthesis
4.2.1. Synthesis of A
- NMR A 1H (400 MHz, (CDCl3) δ (ppm): 3.76 (m, 2H), 3.38 (t, 2H).
4.2.2. Synthesis of B
- NMR B 1H (400 MHz, (CDCl3) δ (ppm): 7.83 (d, 2H), 7.38 (d, 2H), 4.17 (t, 2H), 3.49 (t, 2H), 2.46 (s, 3H).
4.2.3. Synthesis of C
- NMR C 1H (400 MHz, (CDCl3) δ (ppm): 7.69 (d, 2H), 7.52 (s, 1H), 7.31(d, 2H), 7.17 (d, 1H), 7.06 (d, 1H), 6.65 (dd, 1H), 6.62 (dd, 1H), 6.57 (d, 1H), 6.55 (d, 1H), 4.66 (t, 2H), 4.42 (t, 2H), 2.80 (m, 4H), 2.61 (s, 1H), 2.40-1.25 (m, 20H), 1.05 (s, 3H), 0.88 (s, 6H).
4.2.4. Synthesis of [19F]F-FEET
4.3. Radiolabeling
4.3.1. Production of [18F]F−
4.3.2. Conditioning of 18F
4.3.3. Radiofluorination of C to Obtain [18F]F-FEET
4.3.4. Radiofluorination of B to Obtain D
4.3.5. Complete Synthesis of [18F]F-FEET in an Automated Module
4.4. Physicochemical Studies
4.4.1. Stability in the Labeling Milieu
4.4.2. Stability in Human Plasma
4.4.3. Lipophilicity
4.4.4. Plasma Protein Binding
4.5. In Vitro Studies
4.5.1. Uptake Assay Dependent on the Activity of the Radiotracer
4.5.2. Uptake Assay Dependent on the Time of Incubation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kolb, H.C.; Finn, M.G.; Sharpless, K.B. Click Chemistry: Diverse Chemical Function from a Few Good Reactions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2001, 40, 2004–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Liu, X.; Shen, J.; Zhao, G.; Wang, P.G. The impact of click chemistry in medicinal chemistry. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2012, 6, 489–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Hao, X.; Jing, L.; Wu, G.; Kang, D.; Liu, X.; Zhan, P. Recent applications of click chemistry in drug discovery. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2019, 14, 779–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawon, Y.; Son, J.; Yoo, J.; Park, C.; Koo, H. Application of click chemistry in nanoparticle modification and its targeted delivery. Biomater. Res. 2018, 22, 13. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, J.Y.; Lee, B.C. Click Reaction: An Applicable Radiolabeling Method for Molecular Imaging. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2015, 49, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, D.; Cornejo, M.A.; Hoang, T.T.; Lewis, J.J.; Zeglis, B.M. Click Chemistry and Radiochemistry: An Update. Bioconjugate Chem. 2023, 34, 1925–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mindt, T.L.; Struthers, H.; Brans, L.; Anguelov, T.; Schweinsberg, C.; Maes, V.; Tourwe, D.; Schibli, R. “Click to Chelate”: Sythesis and Installation of Metal Chelates into Biomolecules in a Single Step. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 15096–15097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kluba, C.A.; Mindt, T.M. Click-to-Chelate: Development of Technetium and Rhenium-Tricarbonyl Labeled Radiopharmaceutical. Molecules 2013, 18, 3206–3226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Notni, J.; Wester, H.J. A Practical Guide on the Synthesis of Metal Chelates for Molecular Imaging and Therapy by Means of Click Chemistry. Chem. Eur. J. 2016, 22, 11500–11508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferro-Flores, G.; Rivero, I.; Santos-Cuevas, C.; Sarmiento, J.; Arteaga de Murphy, C.; Ocampo-García, B.; García-Becerra, R.; Ordaz-Rosado, D. Click chemistry for [Tc-99m(CO)3] labeling of Lys(3)-bombesin. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2010, 68, 2274–2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández, S.; Crócamo, N.; Incerti, M.; Giglio, J.; Scarone, L.; Rey, A. Preparation and preliminary bioevaluation of a 99mTc(CO)3-glucose derivative prepared by a click chemistry route. J. Label. Compd. Radiopharm. 2012, 55, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, S.; Giglio, J.; Rey, A.M.; Cerecetto, H. Influence of ligand denticity on the properties of novel 99mTc(I)–carbonyl complexes. Application to the development of radiopharmaceuticals for imaging hypoxic tissue. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2012, 20, 4040–4048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejería, M.E.; Giglio, J.; Dematteis, S.; Rey, A. Development and characterization of a 99mTc-tricarbonyl–labelled estradiol derivative obtained by “Click Chemistry” with potential application in estrogen receptors imaging. J. Label. Comp. Radiopharm. 2017, 60, 521–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejería, E.; Giglio, J.; Fernández, L.; Rey, A. Development and evaluation of a 99mTc(V)-nitrido complex derived from estradiol for breast cancer imaging. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2019, 154, 108854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colibri UdelaR. Available online: https://www.colibri.udelar.edu.uy/jspui/handle/20.500.12008/32120 (accessed on 15 December 2023).
- Cardoso, M.E.; Decuadra, P.; Zeni, M.; Delfino, A.; Tejería, M.E.; Coppe, F.; Mesa, J.M.; Daher, G.; Giglio, J.; Carrau, G.; et al. Development and Evaluation of 99mTc Tricarbonyl Complexes Derived from Flutamide with Affinity for Androgen Receptor. Molecules 2023, 28, 820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobson, O.; Kiesewetter, D.O.; Chen, X. Fluorine-18 Radiochemistry, Labeling Strategies and Synthetic Routes. Bioconjugate Chem. 2015, 26, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, L.; Cheng, Z.; Shi, L.; Li, J.; Wang, C.; Jiang, D.; Zhou, W.; Meng, H.; Qi, Y.; Cheng, D.; et al. Fluorine-18 labeling by click chemistry: Multiple probes in one pot. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2013, 75, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pretze, M.; Mamat, C. Automated preparation of [18F]AFP and [18F]BFP: Two novel bifunctional 18F-labeling building blocks for Huisgen-click. J. Fluorine Chem. 2013, 150, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Jacobson, O.; Zhu, G.; Chen, Z.; Liang, S.H.; Tian, R.; Yang, Z.; Niu, G.; Zhu, X.; Chen, X. PET imaging of EGFR expression using an 18F-labeled RNA aptamer. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2019, 46, 948–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Kruchten, M.; de Vries, E.G.E.; Brown, M.; de Vries, E.F.J.; Glaudemans, A.W.J.M.; Dierckx, R.A.J.O.; Schröder, C.P.; Hospers, G.A.P. PET imaging of estrogen receptors in patients with breast cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2013, 14, 465–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- François, B.; Mavi, A. Receptor Imaging in Patients with Breast Cancer. PET Clin. 2009, 4, 329–341. [Google Scholar]
- Hanstein, B.; Djahansouzi, S.; Dall, P.; Beckmann, M.W.; Bender, H.G. Insights into the molecular biology of the estrogen receptor define novel therapeutic targets for breast cancer. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2004, 150, 243–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, S.; Fuqua, S.A.W. Estrogen receptor and breast cancer. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2001, 11, 339–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurdziel, K.A.; Ravizzini, G.; Croft, B.Y.; Tatum, J.L.; Choyke, P.L.; Kobayashi, H. The evolving role of nuclear molecular imaging in cancer. Expert Opin. Med. Diagn. 2008, 7, 829–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiesewetter, D.O.; Kilbourn, M.R.; Landvatter, S.W.; Heiman, D.F.; Katzenellenbogen, J.A.; Welch, M.J. Preparation of four fluorine-18-labeled estrogens and their selective uptakes in target tissues of immature rats. J. Nucl. Med. 1984, 25, 1212–1221. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Scott, P.J.H.; Hockley, B.G. Radiochemical Syntheses: Radiopharmaceuticals for Positron Emission Tomography; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011; Volume 1, pp. 69–80. [Google Scholar]
- Mintun, M.A.; Welch, M.J.; Siegel, B.A.; Mathias, C.J.; James, M.S.S.; Brodack, W.; McGuire, A.H.; Katzenellenbogen, J.A. Breast Cancer: PET Imaging of Estrogen Receptors. Radiology 1988, 69, 45–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundararajan, L.; Linden, H.M.; Link, J.M.; Krohn, K.A.; Mankoff, D.A. 18F-Fluoroestradiol. Semin. Nucl. Med. 2007, 37, 470–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckelman, W. The Application of Receptor Theory to Receptor-binding and Enzyme-binding Oncologic Radiopharmaceuticals. Nucl. Med. Biol. 1994, 21, 759–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heesch, A.; Maurer, J.; Stickeler, E.; Beheshti, M.; Mottaghy, F.M.; Morgenroth, A. Development of Radiotracers for Breast Cancer—The Tumor Microenvironment as an Emerging Target. Cells 2020, 9, 2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ZIONEXA. Available online: https://www.zionexa.com/2020/05/27/zionexa-usa-and-petnet-solutions-announce-fdaapproval-of-cerianna-fluoroestradiol-f18/ (accessed on 15 December 2023).
- Brzozowski, A.M.; Pike, A.C.W.; Dauter, Z.; Hubbard, R.E.; Bonn, T.; Engström, O.; Öhman, L.; Greene, G.; Gustafsson, J.; Carlquist, M. Molecular basis of agonism and antagonism in the oestrogen receptor. Nature 1997, 389, 753–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dessislava, J.; Frateva, F.; Tsakovska, I.; Alova, P.; Pencheva, T.; Pajeva, I. Molecular dynamics simulation of the human estrogen receptor alpha: Contribution to the pharmacophore of the agonists. Math. Comput. Simul. 2015, 133, 124–134. [Google Scholar]
- Kreimerman, I.; Porcal, W.; Olivera, S.; Oliver, P.; Savio, E.; Engler, H. Synthesis of [18F]2B-SRF101: A Sulfonamide Derivative of the Fluorescent Dye Sulforhodamine 101. Curr. Radiopharm. 2017, 10, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Berta, M.; Dancsó, A.; Nemes, A.; Pathó, Z.; Szabó, D.; Rábai, J. Convenient Synthesis of Pure Fluorous Alkyl Azides at Multigram Scale. J. Fluor. Chem. 2016, 16, 30240–30248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hay, M.P.; Wilson, W.R.; Moselen, J.W.; Palmer, B.D.; Denny, W.A. Hypoxia-Selective Antitumor Agents. 8. Bis(nitroimidazoly1)alkanecarboxamides: A New Class of Hypoxia-Selective Cytotoxins and Hypoxic Cell Radiosensitisers. J. Med. Chem. 1994, 37, 381–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, M.P.; Tejería, M.E.; Zeni, M.; Gambini, J.P.; Duarte, P.; Rey, A.; Giglio, J. Radiosynthesis and validation of [18F]fluoroestradiol in a Synthra plus research platform for use in routine clinical practic. J. Label. Comp. Radiopharm. 2022, 65, 292–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hausner, S.H.; Marik, J.; Gagnon, M.K.J.; Sutcliffe, J.L. In Vivo Positron Emission Tomography (PET) Imaging with an αvβ6 Specific Peptide Radiolabeled using 18F-“Click” Chemistry: Evaluation and Comparison with the Corresponding 4-[18F]Fluorobenzoyl- and 2-[18F]Fluoropropionyl-Peptides. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 5901–5904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marik, J.; Sutcliffe, J.L. Click for PET: Rapid preparation of [18F]fluoropeptides using CuI catalyzed 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition. Tetrahedron Lett. 2006, 47, 6681–6684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, H.L.; Carroll, L.; Aboagye, E.O.; Spivey, A.C. Bioorthogonal chemistry for 68Ga radiolabeling of DOTA-containing compounds. J. Label. Comp. Radiopharm. 2014, 57, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glaser, M.; Arstad, E. “Click Labeling” with 2-[18F]Fluoroethylazide for Positron Emission Tomography. Bioconjugate Chem. 2007, 18, 989–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ATCC. Available online: https://www.atcc.org/Products/All/HTB-22.aspx#characteristics (accessed on 15 December 2023).
- Xia, X.; Feng, H.; Li, C.; Qin, C.; Song, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Lan, X. 99mTc-labeled estradiol as an estrogen receptor probe: Preparation and preclinical evaluation. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2016, 43, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banister, S.; Roeda, D.; Dolle, D.; Kassiou, M. Fluorine 18- Chemistry for PET: A concise introduction. Curr. Radiopharm. 2010, 3, 68–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannone, M.N.; Stucchi, S.; Turolla, E.A.; Beretta, C.; Ciceri, S.; Chinello, C.; Pagani, L.; Todde, S.; Ferraboschi, P. Synthesis and automated fluorine-18 radiolabeling of new PSMA-617 derivatives with a CuAAC radiosynthetic approach. J. Label. Compd. Radiopharm. 2021, 65, 48–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Cai, Z.; Li, L.; Ropchan, J.; Lim, K.; Boutagy, N.E.; Wu, J.; Stendahl, J.C.; Chu, W.; Gropler, R.; et al. Optimized and Automated Radiosynthesis of [18F]DHMT for Translational Imaging of Reactive Oxygen Species with Positron Emission Tomography. Molecules 2016, 21, 1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Testa, B.; Fahr, A. Lipophilicity and Its Relationship with Passive Drug Permeation. Pharm. Res. 2011, 28, 962–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnott, J.A.; Planey, S.L. The influence of lipophilicity in drug discovery and design. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2012, 7, 909–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estradiol Catalog NoS1709 Selleckchem. Houston, Texas. Available online: http://www.selleckchem.com/datasheet/Estradiol-DataSheet.html (accessed on 2 February 2024).
- Freshney, R.I. Culture of Animal Cells: A Manual of Basic Technique; John Wiley and Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, D.; Zhuang, R.; You, L.; Guo, Z.; Wang, X.; Peng, C.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, P.; Wu, H.; Pan, W.; et al. 18F–labeled estradiol derivative for targeting estrogen receptor-expressing breast cancer. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2018, 59, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Entry | Reagents (eq) | Time (min) | Temperature | Yield (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D | Ethinylestradiol | Ascorbic Acid | CuI | DIPEA | ||||
| 1 | 0.1 | 1 | 31 | 3 | 31 | 10 | r.t | 31.1 |
| 2 | 0.1 | 1 | 31 | 3 | 31 | 45 | r.t | 81.2 |
| 3 | 0.1 | 1 | 31 | 3 | 31 | 65 | r.t | 98.7 |
| 4 | 0.1 | 0.5 | 31 | 3 | 31 | 15 | 80 °C | 69.3 |
| 5 | 0.1 | 0.5 | 31 | 3 | 31 | 30 | 80 °C | 94.0 |
| 6 | 0.03 | 1 | 10 | 1 | 10 | 30 | r.t | 84.8 |
| 7 | 1 | 1.6 | - | 1.2 | 3.6 | 20 | 60 °C | 4.2 |
| 8 | 1 | 1.6 | - | 1.2 | 3.6 | 30 | 60 °C | 3.9 |
| Entry | Reagents (eq) | Time (min) | Yield (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D | Ethinylestradiol | CuSO4 (0.45 M) | Ascorbic Acid (1.5 M) | |||
| 1 | 1 | 6 | 9 | 30 | 15 | 5.7 |
| 2 | 1 | 6 | 30 | 300 | 15 | 54.8 |
| 3 | 1 | 6 | 30 | 300 | 30 | 84.8 |
| 4 | 1 | 2 | 30 | 300 | 15 | 35.3 |
| 5 | 1 | 2 | 30 | 300 | 30 | 73.0 |
| 6 | 1 | 2 | 30 | 30 | 15 | 3.8 |
| 7 | 1 | 2 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 6.2 |
| 8 | 1 | 2 | 30 | 100 | 15 | 15.2 |
| 9 | 1 | 2 | 30 | 100 | 30 | 41.2 |
| 10 | 1 | 2 | 30 | 50 | 15 | 20.1 |
| 11 | 1 | 2 | 30 | 50 | 30 | 41.7 |
| [18F]F-FEET | |
| Stability in labeling milieu at 4 h | RCP > 95% |
| Stability in human plasma at 4 h | RCP > 95% |
| Log P (o/aq) | 1.8 ± 0.1 |
| PPB | (58 ± 7)%. |
| (MBq) | % Uptake |
|---|---|
| 0.37 | 1.0 ± 0.2 |
| 0.74 | 1.3 ± 0.4 |
| 1.85 | 1.3 ± 0.2 |
| 3.7 | 1.0 ± 0.2 |
| % Uptake | |
|---|---|
| 30 min | 0.60 ± 0.04 |
| 1 h | 0.6 ± 0.1 |
| 2 h | 1.0 ± 0.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tejería, M.E.; Pereira, M.P.; Gambini, J.P.; Duarte, P.; Giglio, J.G.; Rey, A.M. Synthesis of a [18F]F Estradiol Derivative via Click Chemistry Using an Automated Synthesis Module: In Vitro Evaluation as Potential Radiopharmaceutical for Breast Cancer Imaging. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 388. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17030388
Tejería ME, Pereira MP, Gambini JP, Duarte P, Giglio JG, Rey AM. Synthesis of a [18F]F Estradiol Derivative via Click Chemistry Using an Automated Synthesis Module: In Vitro Evaluation as Potential Radiopharmaceutical for Breast Cancer Imaging. Pharmaceuticals. 2024; 17(3):388. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17030388
Chicago/Turabian StyleTejería, María Emilia, María Pía Pereira, Juan Pablo Gambini, Pablo Duarte, Javier Gabriel Giglio, and Ana María Rey. 2024. "Synthesis of a [18F]F Estradiol Derivative via Click Chemistry Using an Automated Synthesis Module: In Vitro Evaluation as Potential Radiopharmaceutical for Breast Cancer Imaging" Pharmaceuticals 17, no. 3: 388. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17030388
APA StyleTejería, M. E., Pereira, M. P., Gambini, J. P., Duarte, P., Giglio, J. G., & Rey, A. M. (2024). Synthesis of a [18F]F Estradiol Derivative via Click Chemistry Using an Automated Synthesis Module: In Vitro Evaluation as Potential Radiopharmaceutical for Breast Cancer Imaging. Pharmaceuticals, 17(3), 388. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17030388






