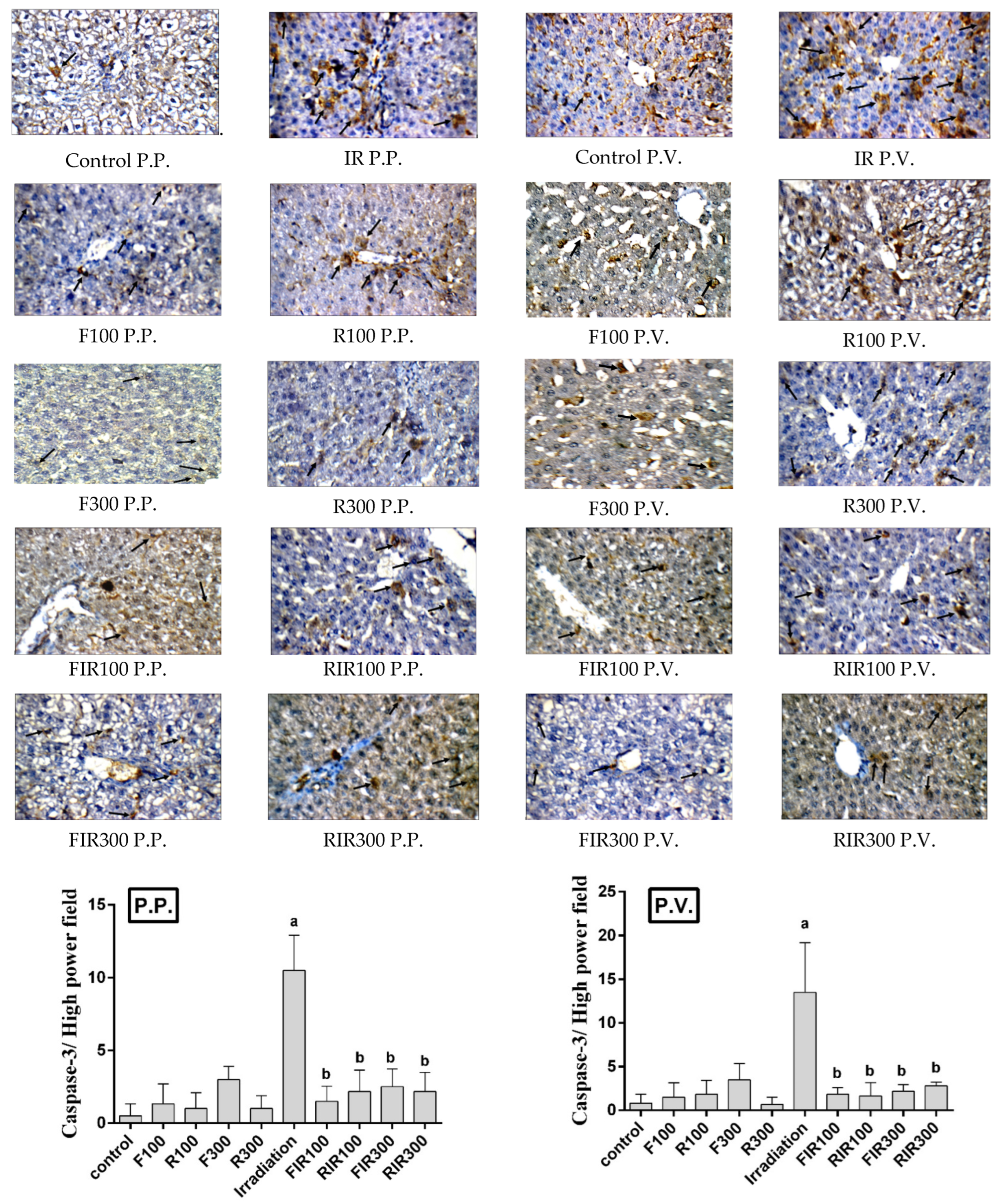
Correction: Selim et al. Impact of Washingtonia robusta Leaves on Gamma Irradiation-Induced Hepatotoxicity in Rats and Correlation with STING Pathway and Phenolic Composition. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 320
Error in Figure
Reference
- Selim, N.M.; El-Hawary, S.S.; El Zalabani, S.M.; Shamma, R.N.; Mahdy, N.E.S.; Sherif, N.H.; Fahmy, H.A.; Mekkawy, M.H.; Yasri, A.; Sobeh, M. Impact of Washingtonia robusta Leaves on Gamma Irradiation-Induced Hepatotoxicity in Rats and Correlation with STING Pathway and Phenolic Composition. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Selim, N.M.; El-Hawary, S.S.; El Zalabani, S.M.; Shamma, R.N.; Mahdy, N.E.S.; Sherif, N.H.; Fahmy, H.A.; Mekkawy, M.H.; Yasri, A.; Sobeh, M. Correction: Selim et al. Impact of Washingtonia robusta Leaves on Gamma Irradiation-Induced Hepatotoxicity in Rats and Correlation with STING Pathway and Phenolic Composition. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 320. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 1481. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17111481
Selim NM, El-Hawary SS, El Zalabani SM, Shamma RN, Mahdy NES, Sherif NH, Fahmy HA, Mekkawy MH, Yasri A, Sobeh M. Correction: Selim et al. Impact of Washingtonia robusta Leaves on Gamma Irradiation-Induced Hepatotoxicity in Rats and Correlation with STING Pathway and Phenolic Composition. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 320. Pharmaceuticals. 2024; 17(11):1481. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17111481
Chicago/Turabian StyleSelim, Nabil M., Seham S. El-Hawary, Soheir M. El Zalabani, Rehab Nabil Shamma, Nariman El Sayed Mahdy, Noheir H. Sherif, Hanan A. Fahmy, Mai H. Mekkawy, Abdelaziz Yasri, and Mansour Sobeh. 2024. "Correction: Selim et al. Impact of Washingtonia robusta Leaves on Gamma Irradiation-Induced Hepatotoxicity in Rats and Correlation with STING Pathway and Phenolic Composition. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 320" Pharmaceuticals 17, no. 11: 1481. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17111481
APA StyleSelim, N. M., El-Hawary, S. S., El Zalabani, S. M., Shamma, R. N., Mahdy, N. E. S., Sherif, N. H., Fahmy, H. A., Mekkawy, M. H., Yasri, A., & Sobeh, M. (2024). Correction: Selim et al. Impact of Washingtonia robusta Leaves on Gamma Irradiation-Induced Hepatotoxicity in Rats and Correlation with STING Pathway and Phenolic Composition. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 320. Pharmaceuticals, 17(11), 1481. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17111481






