Preparation and Characterization of Hydrophobin 4-Coated Liposomes for Doxorubicin Delivery to Cancer Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Physicochemical Properties of HFBs
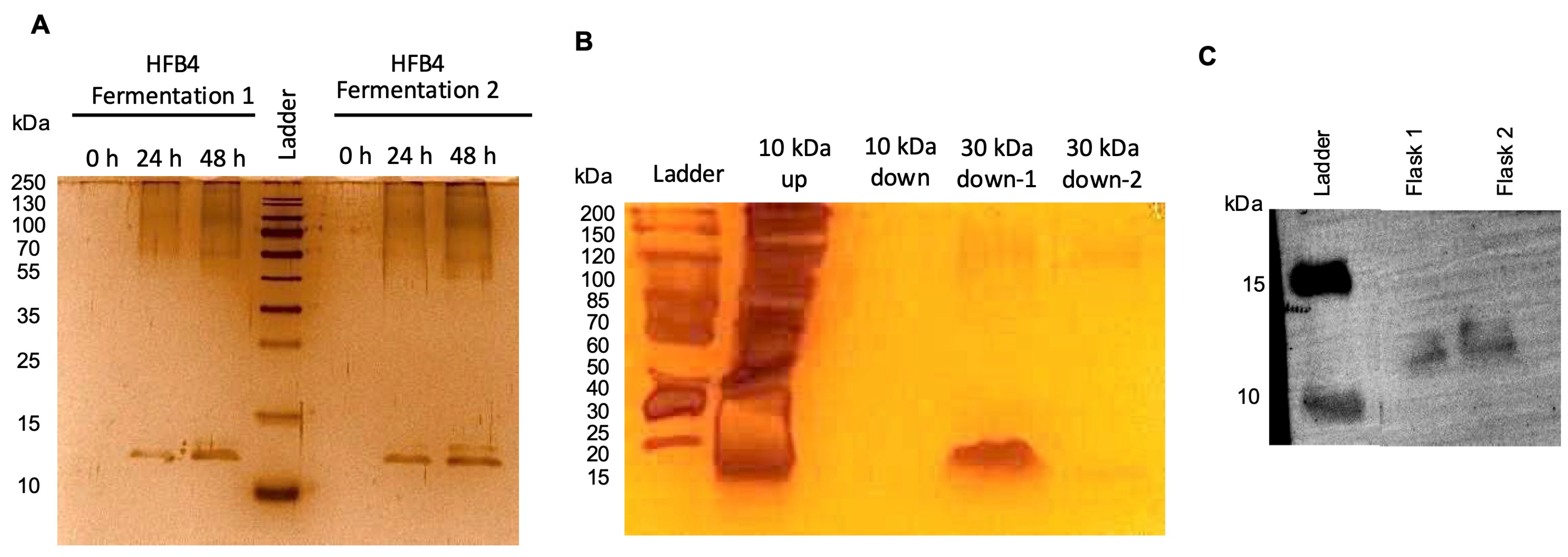
2.2. Purification of HFB4 in Pichia pastoris
2.3. Preparation and Characterization of Empty and Dox-HFB4L and Dox-PPL
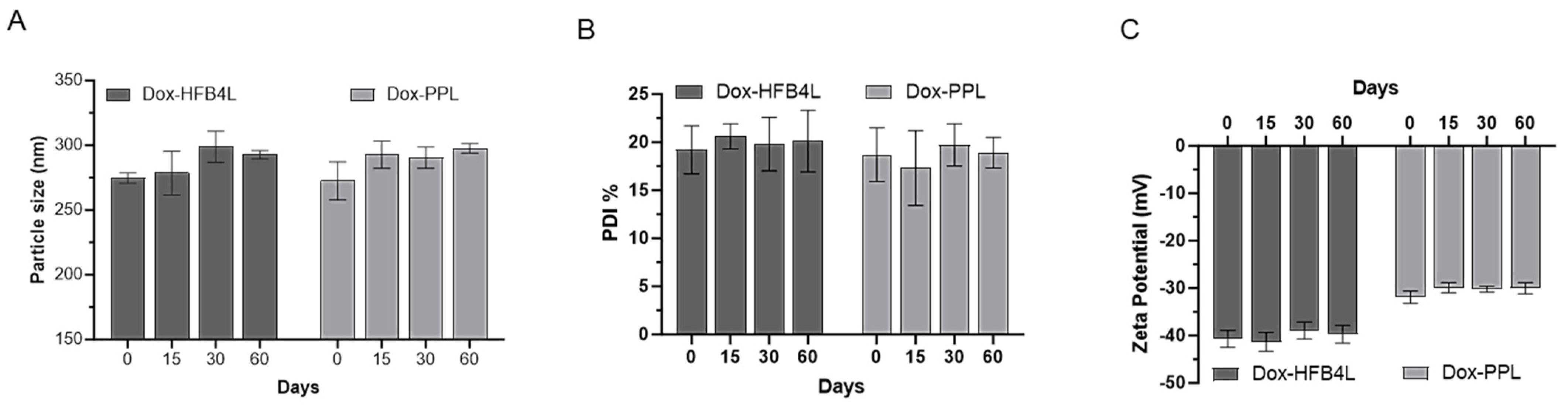
2.4. Stability of Dox-HFB4L and Dox-PPL
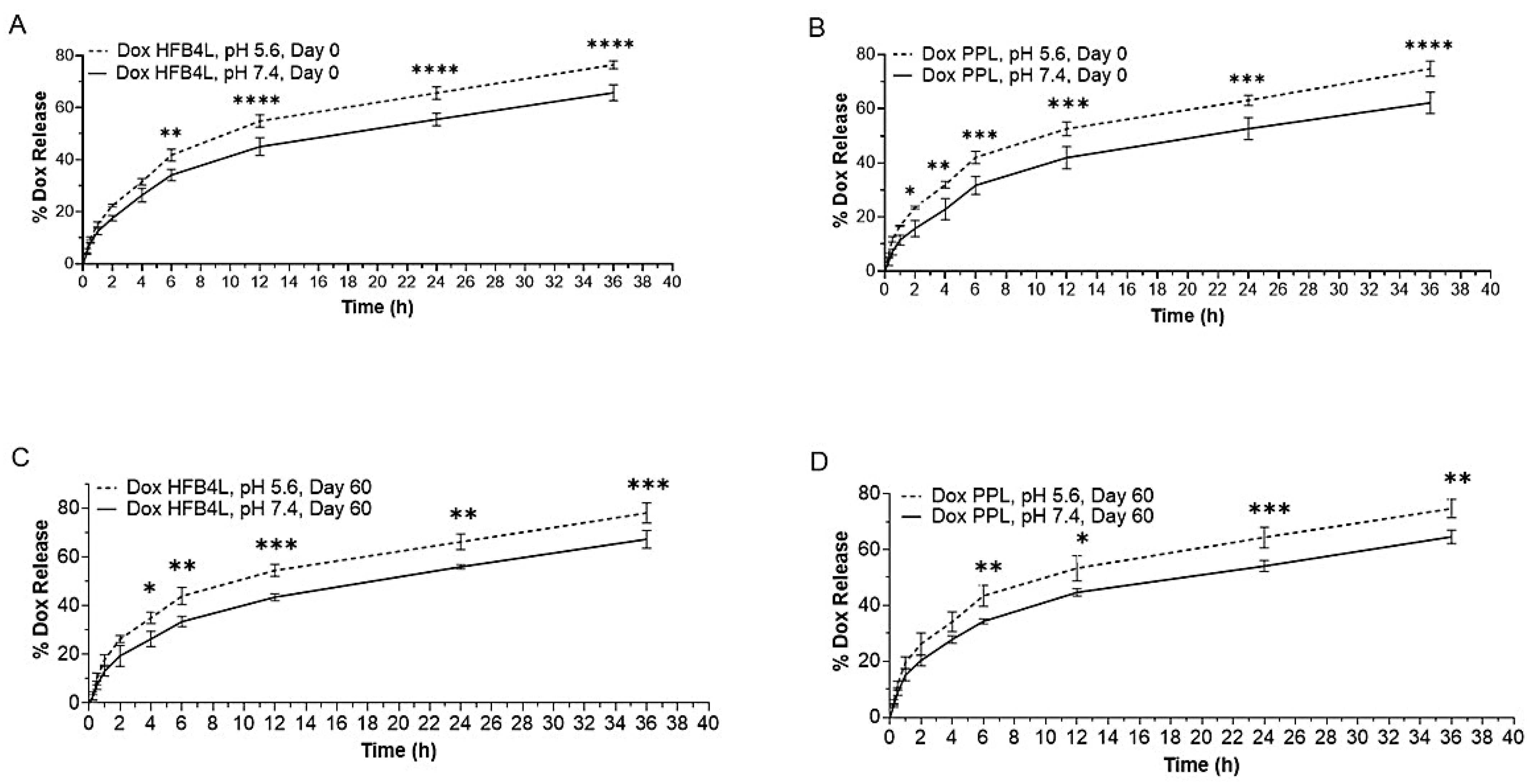
2.5. In Vitro Dox Release from Dox-HFB4L and Dox-PPL
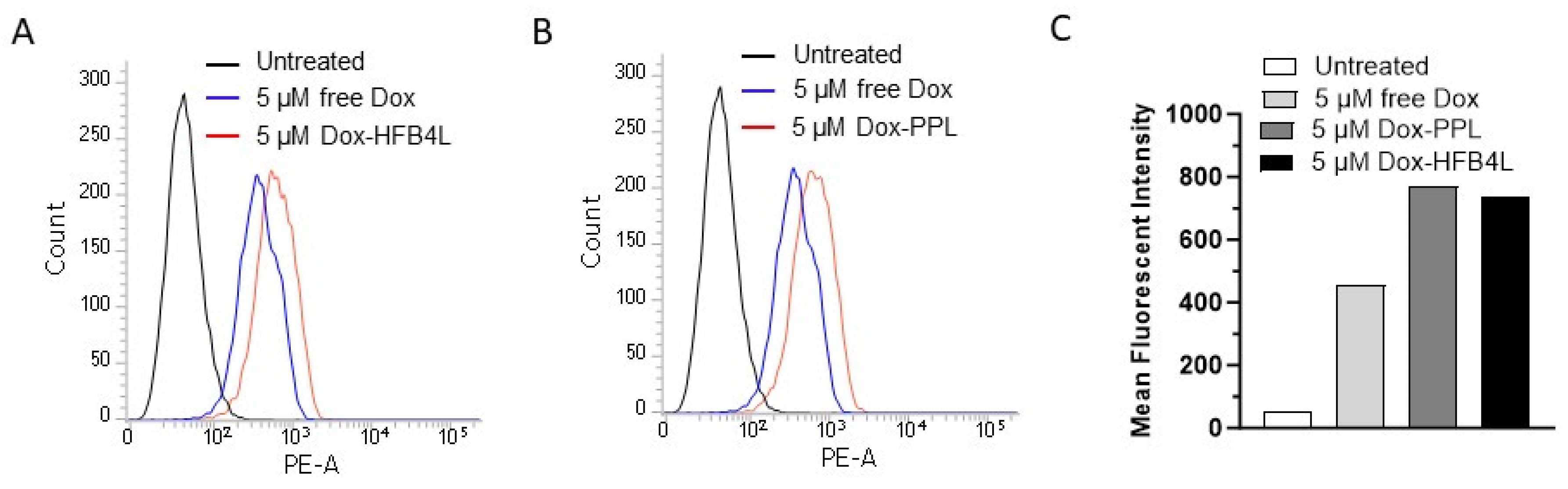
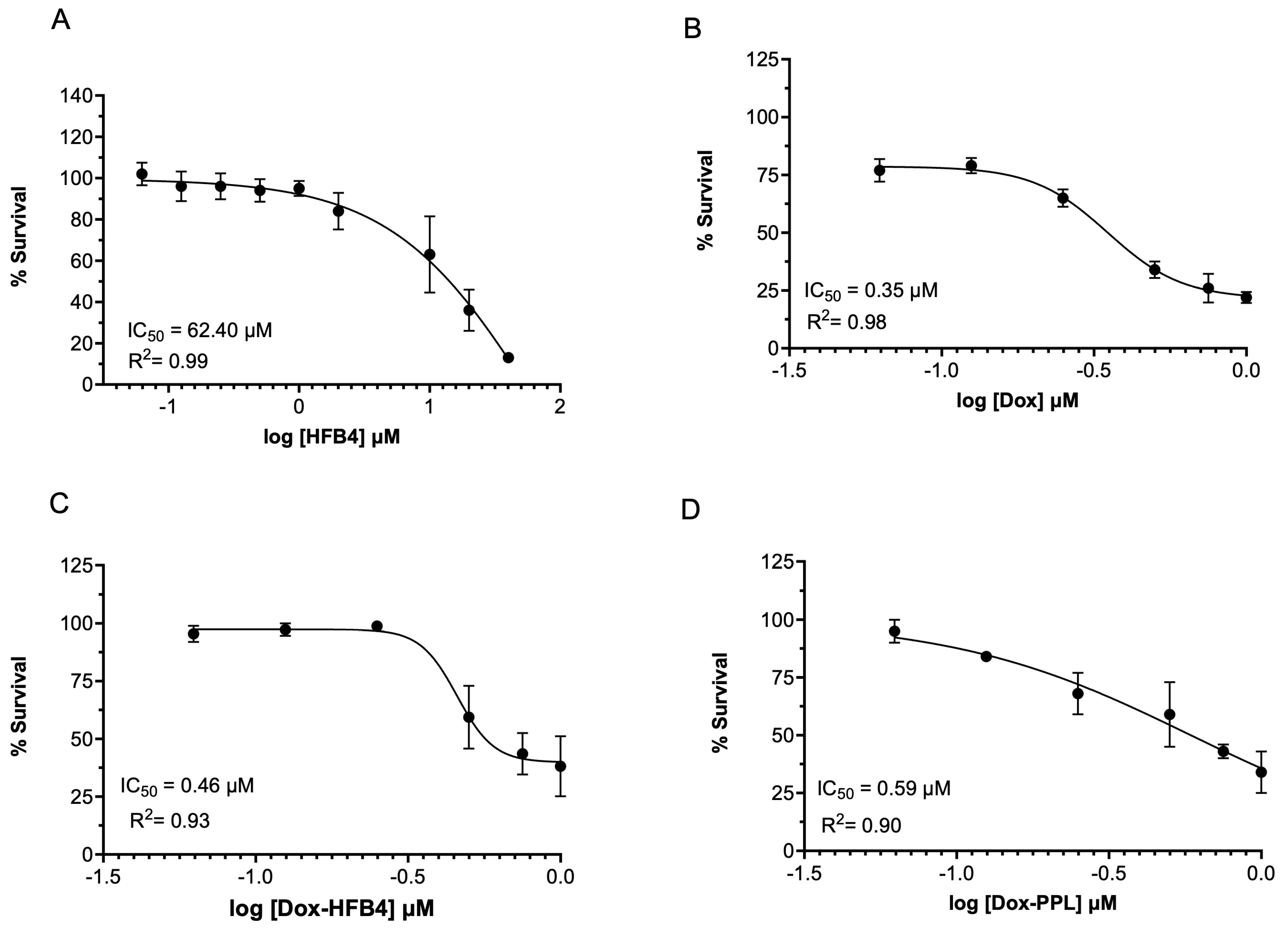
2.6. Cellular Uptake and Cytotoxicity of Free Dox, Dox-HFB4L, and Dox-PPL in MCF7 Cells
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Bioinformatics Analysis
3.3. Production and Purification of HFB4
3.4. Preparation of Empty and Dox-Loaded Liposomes Coated with HFB4 or DSPE-PEG
3.5. Characterization of Liposomes
3.6. Encapsulation Efficiency
3.7. In Vitro Drug Release
3.8. Cellular Uptake of Liposomes
3.9. In Vitro Cytotoxicity of Empty and Dox-Loaded Liposomes
3.10. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Singh, B.N.; Singh, B.R.; Gupta, V.K.; Kharwar, R.N.; Pecoraro, L. Coating with Microbial Hydrophobins: A Novel Approach to Develop Smart Drug Nanoparticles. Trends Biotechnol. 2018, 36, 1103–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, A.; Singh, S.K.; Arya, S.K.; Kundu, S.C.; Kapoor, S. Protein Nanoparticles: Promising Platforms for Drug Delivery Applications. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 4, 3939–3961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fam, S.Y.; Chee, C.F.; Yong, C.Y.; Ho, K.L.; Mariatulqabtiah, A.R.; Tan, W.S. Stealth coating of nanoparticles in drug-delivery systems. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Xu, H.; Xu, J.-H.; Wang, S.-N.; Wang, J.-W.; Zhang, H.-F.; Jia, W.-R.; Li, L.-S. Enhanced Antitumor Efficacy of Curcumin-Loaded PLGA Nanoparticles Coated with Unique Fungal Hydrophobin. AAPS PharmSciTech 2020, 21, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barani, M.; Mirzaei, M.; Torkzadeh-Mahani, M.; Lohrasbi-Nejad, A.; Nematollahi, M.H. A new formulation of hydrophobin-coated niosome as a drug carrier to cancer cells. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 113, 110975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuter, L.J.; Shahbazi, M.A.; Mäkilä, E.M.; Salonen, J.J.; Saberianfar, R.; Menassa, R.; Santos, H.A.; Joensuu, J.J.; Ritala, A. Coating Nanoparticles with Plant-Produced Transferrin-Hydrophobin Fusion Protein Enhances Their Uptake in Cancer Cells. Bioconjug. Chem. 2017, 28, 1639–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiolo, D.; Pigliacelli, C.; Sánchez Moreno, P.; Violatto, M.B.; Talamini, L.; Tirotta, I.; Piccirillo, R.; Zucchetti, M.; Morosi, L.; Frapolli, R.; et al. Bioreducible Hydrophobin-Stabilized Supraparticles for Selective Intracellular Release. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 9413–9423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi, S.; Sandiford, L.; Cooper, M.; Rosca, E.V.; Ahmad Khanbeigi, R.; Fairclough, S.M.; Thanou, M.; Dailey, L.A.; Wohlleben, W.; von Vacano, B.; et al. Hydrophobin-Encapsulated Quantum Dots. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 4887–4893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wösten, H.A.; Scholtmeijer, K. Applications of hydrophobins: Current state and perspectives. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 1587–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valo, H.K.; Laaksonen, P.H.; Peltonen, L.J.; Linder, M.B.; Hirvonen, J.T.; Laaksonen, T.J. Multifunctional hydrophobin: Toward functional coatings for drug nanoparticles. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 1750–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espino-Rammer, L.; Ribitsch, D.; Przylucka, A.; Marold, A.; Greimel, K.J.; Herrero Acero, E.; Guebitz, G.M.; Kubicek, C.P.; Druzhinina, I.S. Two novel class II hydrophobins from Trichoderma spp. stimulate enzymatic hydrolysis of poly(ethylene terephthalate) when expressed as fusion proteins. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 4230–4238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Vacano, B.; Xu, R.; Hirth, S.; Herzenstiel, I.; Rückel, M.; Subkowski, T.; Baus, U. Hydrophobin can prevent secondary protein adsorption on hydrophobic substrates without exchange. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 400, 2031–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Sarparanta, M.; Bimbo, L.M.; Rytkönen, J.; Mäkilä, E.; Laaksonen, T.J.; Laaksonen, P.; Nyman, M.; Salonen, J.; Linder, M.B.; Hirvonen, J.; et al. Intravenous Delivery of Hydrophobin-Functionalized Porous Silicon Nanoparticles: Stability, Plasma Protein Adsorption and Biodistribution. Mol. Pharm. 2012, 9, 654–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aimanianda, V.; Bayry, J.; Bozza, S.; Kniemeyer, O.; Perruccio, K.; Elluru, S.R.; Clavaud, C.; Paris, S.; Brakhage, A.A.; Kaveri, S.V.; et al. Surface hydrophobin prevents immune recognition of airborne fungal spores. Nature 2009, 460, 1117–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrion Sde, J.; Leal, S.M., Jr.; Ghannoum, M.A.; Aimanianda, V.; Latgé, J.P.; Pearlman, E. The RodA hydrophobin on Aspergillus fumigatus spores masks dectin-1- and dectin-2-dependent responses and enhances fungal survival in vivo. J. Immunol. 2013, 191, 2581–2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagenais, T.R.; Giles, S.S.; Aimanianda, V.; Latgé, J.P.; Hull, C.M.; Keller, N.P. Aspergillus fumigatus LaeA-mediated phagocytosis is associated with a decreased hydrophobin layer. Infect. Immun. 2010, 78, 823–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heddergott, C.; Bruns, S.; Nietzsche, S.; Leonhardt, I.; Kurzai, O.; Kniemeyer, O.; Brakhage, A.A. The Arthroderma benhamiae hydrophobin HypA mediates hydrophobicity and influences recognition by human immune effector cells. Eukaryot. Cell 2012, 11, 673–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Han, Z.; Song, B.; Yu, L.; Ma, Z.; Xu, H.; Qiao, M. Effective drug delivery system based on hydrophobin and halloysite clay nanotubes for sustained release of doxorubicin. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 628, 127351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paslay, L.C.; Falgout, L.; Savin, D.A.; Heinhorst, S.; Cannon, G.C.; Morgan, S.E. Kinetics and Control of Self-Assembly of ABH1 Hydrophobin from the Edible White Button Mushroom. Biomacromolecules 2013, 14, 2283–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akanbi, M.H.J.; Post, E.; Meter-Arkema, A.; Rink, R.; Robillard, G.T.; Wang, X.; Wösten, H.A.; Scholtmeijer, K. Use of hydrophobins in formulation of water insoluble drugs for oral administration. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2010, 75, 526–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, G.; Tang, B.; Liu, Z.; Gou, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, H.; Tang, X. Novel hydrophobin-coated docetaxel nanoparticles for intravenous delivery: In vitro characteristics and in vivo performance. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 60, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, B.; Li, M.; Jia, J.; Zhang, C.; Fan, Y.-Y.; Li, W. Hydrophobin-enhanced stability, dispersions and release of curcumin nanoparticles in water. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2020, 31, 1793–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, D.; Wang, X.; Yang, J.; Ge, L.; Wang, B.; Xu, H.; Gong, M.; Li, Y.; Qiao, M. Hydrophobin HGFI improving the nanoparticle formation, stability and solubility of Curcumin. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 610, 125922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Song, B.; Yang, J.; Wang, B.; Ma, Z.; Yu, L.; Li, Y.; Xu, H.; Qiao, M. Curcumin-Encapsulated Fusion Protein-Based Nanocarrier Demonstrated Highly Efficient Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Targeted Treatment of Colorectal Cancer. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 15464–15473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahover, E.; Patil, Y.P.; Gabizon, A.A. Emerging delivery systems to reduce doxorubicin cardiotoxicity and improve therapeutic index: Focus on liposomes. Anticancer Drugs 2015, 26, 241–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senapati, S.; Mahanta, A.K.; Kumar, S.; Maiti, P. Controlled drug delivery vehicles for cancer treatment and their performance. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2018, 3, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schöttler, S.; Becker, G.; Winzen, S.; Steinbach, T.; Mohr, K.; Landfester, K.; Mailänder, V.; Wurm, F.R. Protein adsorption is required for stealth effect of poly(ethylene glycol)- and poly(phosphoester)-coated nanocarriers. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2016, 11, 372–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Chandaroy, P.; Hui, S.W. Grafted poly-(ethylene glycol) on lipid surfaces inhibits protein adsorption and cell adhesion. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Biomembr. 1997, 1326, 236–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatakeyama, H.; Akita, H.; Harashima, H. A multifunctional envelope type nano device (MEND) for gene delivery to tumours based on the EPR effect: A strategy for overcoming the PEG dilemma. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2011, 63, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abouelmagd, S.A.; Sun, B.; Chang, A.C.; Ku, Y.J.; Yeo, Y. Release kinetics study of poorly water-soluble drugs from nanoparticles: Are we doing it right? Mol. Pharm. 2015, 12, 997–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, E.; Chen, B.-M.; Su, Y.-C.; Chang, Y.-C.; Cheng, T.-L.; Barenholz, Y.; Roffler, S.R. Premature Drug Release from Polyethylene Glycol (PEG)-Coated Liposomal Doxorubicin via Formation of the Membrane Attack Complex. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 7808–7822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karbalaei, M.; Rezaee, S.A.; Farsiani, H. Pichia pastoris: A highly successful expression system for optimal synthesis of heterologous proteins. J. Cell. Physiol. 2020, 235, 5867–5881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghban, R.; Farajnia, S.; Rajabibazl, M.; Ghasemi, Y.; Mafi, A.; Hoseinpoor, R.; Rahbarnia, L.; Aria, M. Yeast Expression Systems: Overview and Recent Advances. Mol. Biotechnol. 2019, 61, 365–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przylucka, A.; Akcapinar, G.B.; Bonazza, K.; Mello-de-Sousa, T.M.; Mach-Aigner, A.R.; Lobanov, V.; Grothe, H.; Kubicek, C.P.; Reimhult, E.; Druzhinina, I.S. Comparative physiochemical analysis of hydrophobins produced in Escherichia coli and Pichia pastoris. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2017, 159, 913–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, S.; Dodwadkar, N.S.; Deshpande, P.P.; Torchilin, V.P. Liposomes loaded with paclitaxel and modified with novel triphenylphosphonium-PEG-PE conjugate possess low toxicity, target mitochondria and demonstrate enhanced antitumor effects in vitro and in vivo. J. Control. Release 2012, 159, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soema, P.C.; Willems, G.-J.; Jiskoot, W.; Amorij, J.-P.; Kersten, G.F. Predicting the influence of liposomal lipid composition on liposome size, zeta potential and liposome-induced dendritic cell maturation using a design of experiments approach. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2015, 94, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andra, V.; Pammi, S.V.N.; Bhatraju, L.; Ruddaraju, L.K. A Comprehensive Review on Novel Liposomal Methodologies, Commercial Formulations, Clinical Trials and Patents. Bionanoscience 2022, 12, 274–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, A.; Narayanan, S.; Sethuraman, S.; Krishnan, U.M. Novel resveratrol and 5-fluorouracil coencapsulated in PEGylated nanoliposomes improve chemotherapeutic efficacy of combination against head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 424239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monnier, C.; Thévenaz, D.; Balog, S.; Fiore, G.; Vanhecke, D.; Rothen-Rutishauser, B.; Fink, A. A guide to investigating colloidal nanoparticles by cryogenic transmission electron microscopy: Pitfalls and benefits. AIMS Biophys. 2015, 2, 245–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannan, V.; Balabathula, P.; Thoma, L.A.; Wood, G.C. Effect of sucrose as a lyoprotectant on the integrity of paclitaxel-loaded liposomes during lyophilization. J. Liposome Res. 2015, 25, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasarin, D.; Ghizdareanu, A.I.; Enascuta, C.E.; Matei, C.B.; Bilbie, C.; Paraschiv-Palada, L.; Veres, P.A. Coating Materials to Increase the Stability of Liposomes. Polymers 2023, 15, 782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ding, L.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ping, Q. Targeted delivery of doxorubicin using stealth liposomes modified with transferrin. Int. J. Pharm. 2009, 373, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Winden, E.C.A.; Crommelin, D.J.A. Long term stability of freeze-dried, lyoprotected doxorubicin liposomes. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 1997, 43, 295–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stark, B.; Pabst, G.; Prassl, R. Long-term stability of sterically stabilized liposomes by freezing and freeze-drying: Effects of cryoprotectants on structure. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 41, 546–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Chen, Q.; Feng, L.; Liu, Z. Nanomedicine for tumor microenvironment modulation and cancer treatment enhancement. Nano Today 2018, 21, 55–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boedtkjer, E.; Pedersen, S.F. The Acidic Tumor Microenvironment as a Driver of Cancer. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2020, 82, 103–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasteiger, E.; Hoogland, C.; Gattiker, A.; Duvaud, S.; Wilkins, M.R.; Appel, R.D.; Bairoch, A. Protein Identification and Analysis Tools on the ExPASy Server; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Madeira, F.; Pearce, M.; Tivey, A.R.N.; Basutkar, P.; Lee, J.; Edbali, O.; Madhusoodanan, N.; Kolesnikov, A.; Lopez, R. Search and sequence analysis tools services from EMBL-EBI in 2022. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, W276–W279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayram Akcapinar, G.; Gul, O.; Sezerman, U.O. From in silico to in vitro: Modelling and production of Trichoderma reesei endoglucanase 1 and its mutant in Pichia pastoris. J. Biotechnol. 2012, 159, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, F.; Gao, R.; Zhao, Z.; Ding, M.; Jiang, S.; Yagtu, C.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, J.; Ebner, T.; Mayrhofer-Reinhartshuber, M.; et al. Evolutionary compromises in fungal fitness: Hydrophobins can hinder the adverse dispersal of conidiospores and challenge their survival. ISME J. 2020, 14, 2610–2624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Cui, F.-D.; Choi, M.-K.; Lin, H.; Chung, S.-J.; Shim, C.-K.; Kim, D.-D. Liposome formulation of paclitaxel with enhanced solubility and stability. Drug Deliv. 2007, 14, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzé, S.; Selmin, F.; Samaritani, E.; Minghetti, P.; Cilurzo, F. Lyophilization of liposomal formulations: Still necessary, still challenging. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonju, J.J.; Shrestha, P.; Dahal, A.; Gu, X.; Johnson, W.D.; Zhang, D.; Muthumula, C.M.R.; Meyer, S.A.; Mattheolabakis, G.; Jois, S.D. Lyophilized liposomal formulation of a peptidomimetic-Dox conjugate for HER2 positive breast and lung cancer. Int. J. Pharm. 2023, 639, 122950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nam, J.H.; Kim, S.Y.; Seong, H. Investigation on Physicochemical Characteristics of a Nanoliposome-Based System for Dual Drug Delivery. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

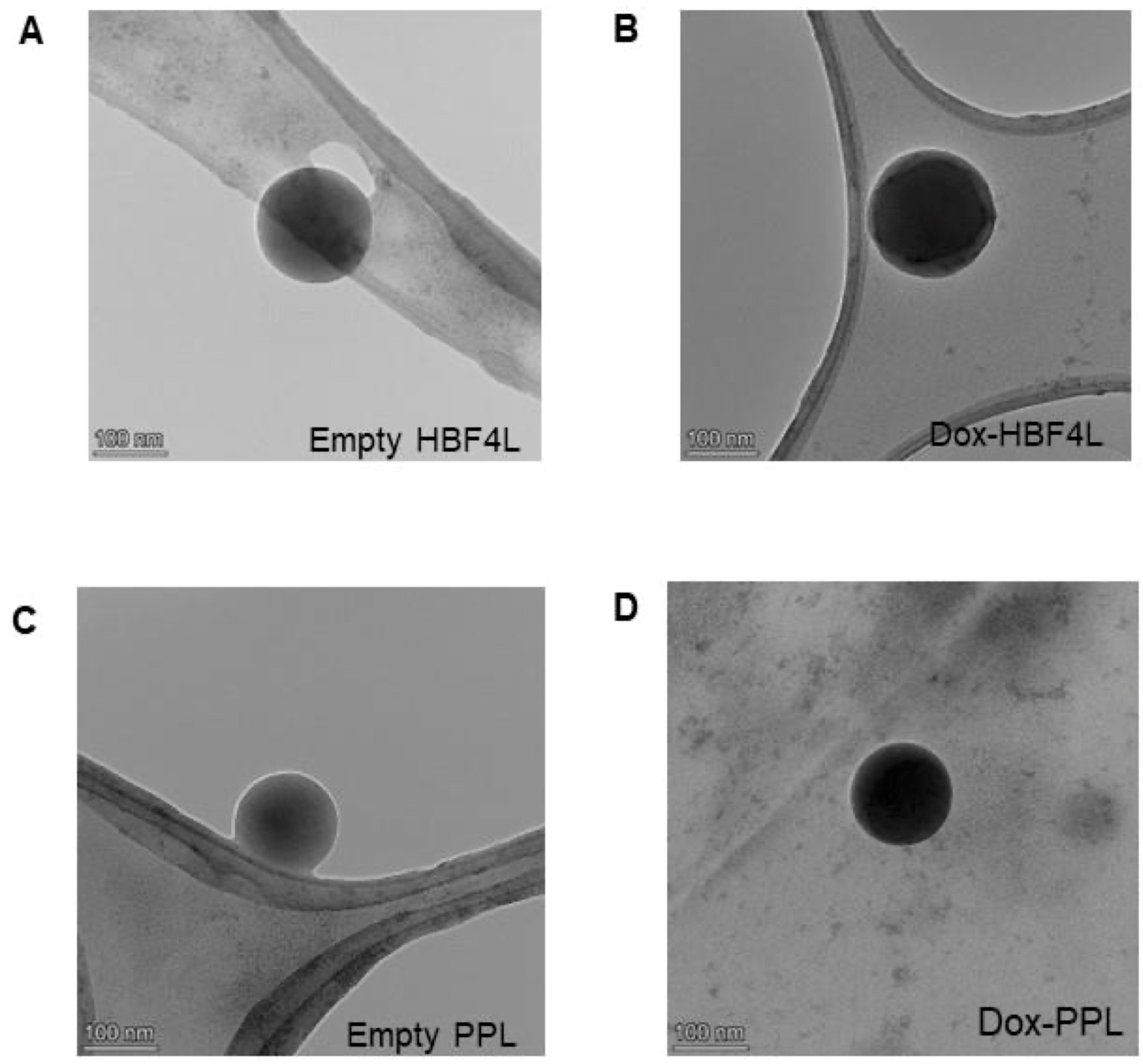
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | Theoretical pI | Total Number of Positively Charged Residues (Arg + Lys) | Instability Index | Aliphatic Index | Grand Average of Hydropathicity (GRAVY) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HFBI | 6.6 | 6.0 | 3.0 | 29.7 | 89.8 | 0.4 |
| HFBII | 6.5 | 5.4 | 3.0 | −1.3 | 102.2 | 0.8 |
| HFB4 | 6.4 | 8.2 | 4.0 | 14.2 | 97.4 | 0.5 |
| Particle Size (nm) | PDI | Zeta Potential (mV) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Empty PPL | 232.30 ± 2.97 | 0.20 ± 0.04 | −9.91 ± 0.70 |
| Dox-PPL | 260.15 ± 4.63 | 0.19 ± 0.03 | −36.13 ± 3.71 |
| Empty HFB4L | 233.10 ± 3.29 | 0.20 ± 0.01 | −40.93 ± 0.33 |
| Dox-HFB4L | 253.40 ± 8.33 | 0.19 ± 0.02 | −41.63 ± 1.58 |
| Dox-PPL (-Sucrose) | 252.60 ± 0.31 | 0.16 ± 0.07 | −34.85 ± 577 |
| Dox-HFB4L (-Sucrose) | 252.95 ± 14.11 | 0.18 ± 0.05 | −42.73 ± 2.14 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Osmanagaoglu, F.H.; Ekmekcioglu, A.; Ozcan, B.; Bayram Akcapinar, G.; Muftuoglu, M. Preparation and Characterization of Hydrophobin 4-Coated Liposomes for Doxorubicin Delivery to Cancer Cells. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 1422. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17111422
Osmanagaoglu FH, Ekmekcioglu A, Ozcan B, Bayram Akcapinar G, Muftuoglu M. Preparation and Characterization of Hydrophobin 4-Coated Liposomes for Doxorubicin Delivery to Cancer Cells. Pharmaceuticals. 2024; 17(11):1422. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17111422
Chicago/Turabian StyleOsmanagaoglu, Fatma Hande, Aysegul Ekmekcioglu, Busel Ozcan, Gunseli Bayram Akcapinar, and Meltem Muftuoglu. 2024. "Preparation and Characterization of Hydrophobin 4-Coated Liposomes for Doxorubicin Delivery to Cancer Cells" Pharmaceuticals 17, no. 11: 1422. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17111422
APA StyleOsmanagaoglu, F. H., Ekmekcioglu, A., Ozcan, B., Bayram Akcapinar, G., & Muftuoglu, M. (2024). Preparation and Characterization of Hydrophobin 4-Coated Liposomes for Doxorubicin Delivery to Cancer Cells. Pharmaceuticals, 17(11), 1422. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17111422






