Exome Sequence Data of Eight SLC Transporters Reveal That SLC22A1 and SLC22A3 Variants Alter Metformin Pharmacokinetics and Glycemic Control
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
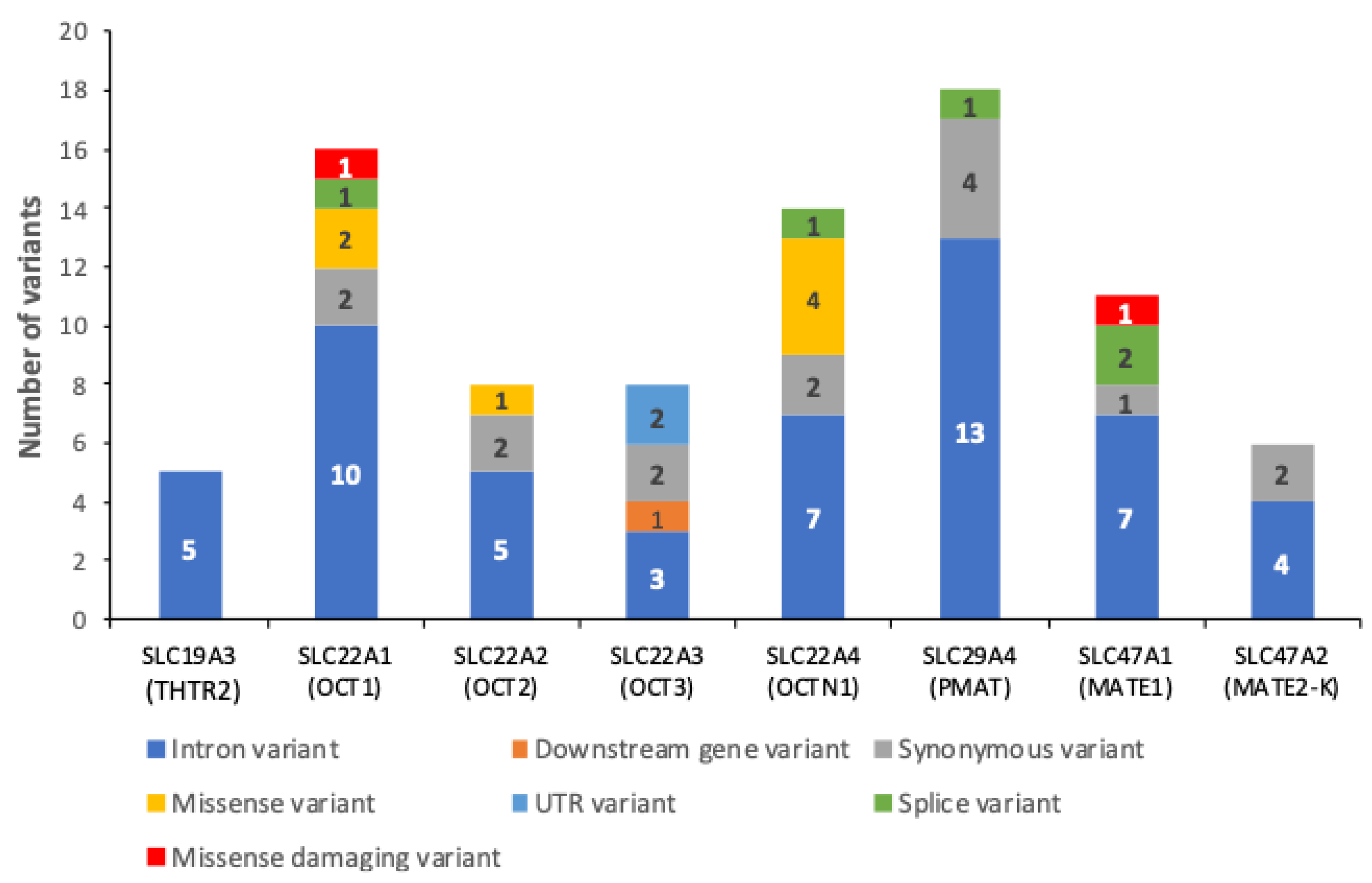
2.1. Variants on SLC Superfamily Metformin Transporters
2.2. Genetic Association with Inadequate Glycemic Control
2.3. Linkage Disequilibrium Analysis
2.4. The slc22a1 Haplotype Associated with IGC Alters Metformin Pharmacokinetics
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Populations
4.2. Genotypes
4.3. Pharmacokinetic Profiles in Pediatric Patients
4.4. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- PAHO_WHO. Diabetes. Pan American Health Organization. Available online: https://www.paho.org/en/topics/diabetes#:~:text=Diabetes%20is%20a%20major%20cause,%20these%20complications%20and%20premature%20mortality (accessed on 1 October 2024).
- World Health Organization. Diabetes Fact Sheet. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/diabetes (accessed on 6 February 2023).
- Kasznicki, J.; Sliwinska, A.; Drzewoski, J. Metformin in Cancer Prevention and Therapy. Ann. Transl. Med. 2014, 2, 7–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraei, P.; Asadi, I.; Kakar, M.A.; Moradi-Kor, N. The Beneficial Effects of Metformin on Cancer Prevention and Therapy: A Comprehensive Review of Recent Advances. Cancer Manag. Res. 2019, 11, 3295–3313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, R.; Erez, O.; Hüttemann, M.; Maymon, E.; Panaitescu, B.; Conde-Agudelo, A.; Pacora, P.; Yoon, B.H.; Grossman, L.I. Metformin, the Aspirin of the 21st Century: Its Role in Gestational Diabetes Mellitus, Prevention of Preeclampsia and Cancer, and the Promotion of Longevity. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2017, 217, 282–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pernicova, I.; Korbonits, M. Metformin—Mode of Action and Clinical Implications for Diabetes and Cancer. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2014, 10, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hur, K.Y.; Lee, M. New Mechanisms of Metformin Action: Focusing on Mitochondria and the Gut. J. Diabetes Investig. 2015, 6, 600–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diener, C.; Gibbons, S.M.; Resendis-Antonio, O. MICOM: Metagenome-Scale Modeling to Infer Metabolic Interactions in the Gut Microbiota. mSystems 2020, 5, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madiraju, A.K.; Erion, D.M.; Rahimi, Y.; Zhang, X.-M.; Braddock, D.T.; Albright, R.A.; Prigaro, B.J.; Wood, J.L.; Bhanot, S.; MacDonald, M.J.; et al. Metformin Suppresses Gluconeogenesis by Inhibiting Mitochondrial Glycerophosphate Dehydrogenase. Nature 2014, 510, 542–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, G.G.; Punt, J.; Arora, M.; Day, R.O.; Doogue, M.P.; Duong, J.K.; Furlong, T.J.; Greenfield, J.R.; Greenup, L.C.; Kirkpatrick, C.; et al. Clinical Pharmacokinetics of Metformin. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2011, 50, 81–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, L.; Goswami, S.; Giacomini, K.M.; Altman, R.B.; Klein, T.E. Metformin Pathways: Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics. Pharmacogenet Genom. 2012, 22, 820–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florez, J.C. The Pharmacogenetics of Metformin. Diabetologia 2017, 60, 1648–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamichi, N.; Shima, H.; Asano, S.; Ishimoto, T.; Sugiura, T.; Matsubara, K.; Kusuhara, H.; Sugiyama, Y.; Sai, Y.; Miyamoto, K.-I.; et al. Involvement of carnitine/organic cation transporter OCTN1/SLC22A4 in gastrointestinal absorption of metformin. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 102, 3407–3417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Chien, H.-C.; Yee, S.W.; Giacomini, M.M.; Chen, E.C.; Piao, M.; Hao, J.; Twelves, J.; Lepist, E.-I.; Ray, A.S.; et al. Metformin Is a Substrate and Inhibitor of the Human Thiamine Transporter, THTR-2 (SLC19A3). Mol. Pharm. 2015, 12, 4301–4310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bielinski, S.J.; Cardozo, L.L.Y.; Takahashi, P.Y.; Larson, N.B.; Castillo, A.; Podwika, A.; De Filippis, E.; Hernandez, V.; Mahajan, G.J.; Gonzalez, C.; et al. Predictors of Metformin Failure: Repurposing Electronic Health Record Data to Identify High-Risk Patients. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2023, 108, 1740–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TODAY Study Group. A Clinical Trial to Maintain Glycemic Control in Youth with Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 2247–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, Y.; Sheardown, S.A.; Brown, C.; Owen, R.P.; Zhang, S.; Castro, R.A.; Ianculescu, A.G.; Yue, L.; Lo, J.C.; Burchard, E.G.; et al. Effect of Genetic Variation in the Organic Cation Transporter 1 (OCT1) on Metformin Action. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 1422–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzvetkov, M.V.; Vormfelde, S.V.; Balen, D.; Meineke, I.; Schmidt, T.; Sehrt, D.; Sabolić, I.; Koepsell, H.; Brockmöller, J. The Effects of Genetic Polymorphisms in the Organic Cation Transporters OCT1, OCT2, and OCT3 on the Renal Clearance of Metformin. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2009, 86, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoro, A.B.; Botton, M.R.; Struchiner, C.J.; Suarez-Kurtz, G. Influence of Pharmacogenetic Polymorphisms and Demographic Variables on Metformin Pharmacokinetics in an Admixed Brazilian Cohort. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2018, 84, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, V.; Federico, A.; Pollastro, C.; Ziviello, C.; Cataldi, S.; Formisano, P.; Ciccodicola, A. Computational Analysis of Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms Associated with Altered Drug Responsiveness in Type 2 Diabetes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarasova, L.; Kalnina, I.; Geldnere, K.; Bumbure, A.; Ritenberga, R.; Nikitina-Zake, L.; Fridmanis, D.; Vaivade, I.; Pirags, V.; Klovins, J. Association of Genetic Variation in the Organic Cation Transporters OCT1, OCT2 and Multidrug and Toxin Extrusion 1 Transporter Protein Genes with the Gastrointestinal Side Effects and Lower BMI in Metformin-Treated Type 2 Diabetes Patients. Pharmacogenetics Genom. 2012, 22, 659–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.M.; Guan, Z.B.; Li, R.M.; Zhao, W.; Hao, G.; Yan, Y.M.; Xu, Y.; Liao, L.; Wang, H.; Gao, L.; et al. Population Pharmacokinetics and Dosing Optimization of Metformin in Chinese Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Medicine 2020, 99, e23212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diabetes Prevention Program Research Group; Jablonski, K.A.; McAteer, J.B.; Altshuler, D.; Florez, J.C.; De Bakker, P.I.; Franks, P.W.; Pollin, T.I.; Hanson, R.L.; Saxena, R.; et al. Common Variants in 40 Genes Assessed for Diabetes Incidence and Response to Metformin and Lifestyle Intervention in the Diabetes Prevention Program. Diabetes 2010, 59, 2672–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, M.M.; Brasch-Andersen, C.; Green, H.; Nielsen, F.; Damkier, P.; Beck-Nielsen, H.; Brosen, K. The Pharmacogenetics of Metformin and Its Impact on Plasma Metformin Steady-State Levels and Glycosylated Hemoglobin A1c. Pharmacogenetics Genom. 2011, 21, 837–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, S.; Brown, C.; Cheatham, S.; Castro, R.A.; Leabman, M.K.; Urban, T.J.; Chen, L.; Yee, S.W.; Choi, J.H.; et al. Effect of Genetic Variation in the Organic Cation Transporter 2 on the Renal Elimination of Metformin. Pharmacogenetics Genom. 2009, 19, 497–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajib, A.A.; Islam, T.; Paul, N.; Yeasmin, S. Interaction of Rs316019 Variants of SLC22A2 with Metformin and Other Drugs—An in Silico Analysis. J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. 2018, 16, 769–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, M.L.; Visser, L.E.; van Schaik, R.H.; Hofman, A.; Uitterlinden, A.G.; Stricker, B.H. Genetic Variation in the Multidrug and Toxin Extrusion 1 Transporter Protein Influences the Glucose-Lowering Effect of Metformin in Patients with Diabetes: A Preliminary Study. Diabetes 2009, 58, 745–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tkáč, I.; Klimčáková, L.; Javorský, M.; Fabianová, M.; Schroner, Z.; Hermanová, H.; Babjaková, E.; Tkáčová, R. Pharmacogenomic Association between a Variant in SLC47A1 Gene and Therapeutic Response to Metformin in Type 2 Dia-betes. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2012, 15, 189–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, D.; Guo, Y.; Li, X.; Yin, J.-Y.; Zheng, W.; Qiu, X.-W.; Xiao, L.; Liu, R.-R.; Wang, S.-Y.; Gong, W.-J.; et al. The Impacts of SLC22A1 rs594709 and SLC47A1 rs2289669 Polymorphisms on Metformin Therapeutic Efficacy in Chinese Type 2 Diabetes Patients. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2016, 2016, 4350712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, S.; Kohan, L.; Yavarian, M.; Habib, A. Pharmacogenetic Variation of SLC47A1 Gene and Metformin Response in Type2 Diabetes Patients. Mol. Biol. Res. Commun. 2017, 6, 91–94. [Google Scholar]
- Stocker, S.L.; Morrissey, K.M.; Yee, S.W.; Castro, R.A.; Xu, L.; Dahlin, A.; Ramirez, A.H.; Roden, D.M.; Wilke, R.A.; McCarty, C.A.; et al. The Effect of Novel Promoter Variants in MATE1 and MATE2 on the Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Metformin. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 93, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Rivera, M.I.; Alemón-Medina, R.; Martínez-Hernández, A.; Gómez-Garduño, J.; Mirzaeicheshmeh, E.; Altamirano-Bustamante, N.F.; Ilizaliturri-Flores, I.; Mendoza-Caamal, E.C.; Pérez-Guillé, M.G.; García-Álvarez, R.; et al. The L125F MATE1 Variant Enriched in Populations of Amerindian Origin Is Associated with Increased Plasma Levels of Metformin and Lactate. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 142, 112009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatumo, S.; Chikowore, T.; Choudhury, A.; Ayub, M.; Martin, A.R.; Kuchenbaecker, K. Diversity in Genomic Studies: A Roadmap to Address the Imbalance. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flannick, J.; Mercader, J.M.; Fuchsberger, C.; Udler, M.S.; Mahajan, A.; Wessel, J.; Teslovich, T.M.; Caulkins, L.; Koesterer, R.; Barajas-Olmos, F.; et al. Exome Sequencing of 20,791 Cases of Type 2 Diabetes and 24,440 Controls. Nature 2019, 570, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The SIGMA Type 2 Diabetes Consortium; Estrada, K.; Aukrust, I.; Bjørkhaug, L.; Burtt, N.P.; Mercader, J.M.; García-Ortiz, H.; Huerta-Chagoya, A.; Moreno-Macías, H.; Walford, G.; et al. Association of a Low-Frequency Variant in HNF1A With Type 2 Diabetes in a Latino Population. JAMA 2014, 311, 2305–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas, 10th ed.; Boyko, E., Magliano, D., Karuranga, S., Piemonte, L., Riley, P., Saeedi, P., Sun, H., Eds.; 2021; Available online: https://www.diabetesatlas.org (accessed on 20 September 2024).
- Basto-Abreu, A.; López-Olmedo, N.; Rojas-Martínez, R.; Aguilar-Salinas, C.A.; Moreno-Banda, G.L.; Carnalla, M.; Rivera, J.A.; Romero-Martinez, M.; Barquera, S.; Barrientos-Gutiérrez, T. Prevalencia de prediabetes y diabetes en México: Ensanut 2022. Salud Publica De Mex. 2023, 65, s163–s168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CDC. Póngale el Freno a las Complicaciones de la Diabetes. Cdc.gob. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/spanish/resources/features/prevent-complications.html (accessed on 6 February 2023).
- COVID-19 Tablero México—CONACYT. Available online: https://datos.covid-19.conacyt.mx/ (accessed on 22 February 2024).
- Alonso, N.; Batule, S. COVID-19 y Diabetes Mellitus. Importancia Del Control Glucémico COVID-19. Clin. E Investig. En Arter. 2021, 33, 148–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basto-Abreu, A.C.; López-Olmedo, N.; Rojas-Martínez, R.; Aguilar-Salinas, C.A.; De la Cruz-Góngora, V.V.; Rivera-Dommarco, J.; Shamah-Levy, T.; Romero-Martínez, M.; Barquera, S.; Villalpando, S.; et al. Prevalence of Diabetes and Glycemic Control in Mexico: National Results from 2018 and 2020. Salud Publica De Mex. 2021, 63, 725–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Instituto Nacional de Salud Pública. Encuesta Nacional de Salud y Nutrición. Ensanut 2018, 1, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reséndiz-Abarca, C.A.; Flores-Alfaro, E.; Suárez-Sánchez, F.; Cruz, M.; Valladares-Salgado, A.; Alarcón-Romero, L.d.C.; Vázquez-Moreno, M.A.; Wacher-Rodarte, N.A.; Gómez-Zamudio, J.H. Altered Glycemic Control Associated with Polymorphisms in the SLC22A1 (OCT1) Gene in a Mexican Population with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Treated with Metformin: A Cohort Study. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2019, 59, 1384–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marta, M.; Sánchez-Pozos, K.; Jaimes-Santoyo, J.; Monroy-Escutia, J.; Santiago, C.R.; Granados-Silvestre, M.d.L.; Ortiz-López, M.G. Pharmacogenetic Evaluation of Metformin and Sulphonylurea Response in Mexican Mestizos with Type 2 Diabetes. Curr. Drug Metab. 2020, 21, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Covarrubias, V.; Sánchez-Ibarra, H.; Lozano-Gonzalez, K.; Villicaña, S.; Texis, T.; Rodríguez-Dorantes, M.; Cortés-Ramírez, S.; Lavalle-Gonzalez, F.; Soberón, X.; Barrera-Saldaña, H. Transporters, TBC1D4, and ARID5B Variants to Explain Glycated Hemoglobin Variability in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Pharmacology 2021, 106, 588–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Ye, W.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Meng, X.; Xiao, Q.; Zhao, Q.; Yan, J. Genetic Variants of OCT1 Influence Glycemic Re-sponse to Metformin in Han Chinese Patients with Type-2 Diabetes Mellitus in Shanghai. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 9533–9542. [Google Scholar]
- Ortega-Ayala, A.; Rodríguez-Rivera, N.S.; de Andrés, F.; Llerena, A.; Pérez-Silva, E.; Espinosa-Sánchez, A.G.; Molina-Guarneros, J.A. Pharmacogenetics of Metformin Transporters Suggests No Association with Therapeutic Inefficacy among Diabetes Type 2 Mexican Patients. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M.; Song, I. Genetic Variants of Organic Cation Transporter 1 (OCT1) and OCT2 Significantly Reduce Lamivudine Uptake. Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 2012, 33, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stegeman, S.; Amankwah, E.; Klein, K.; O'Mara, T.A.; Kim, D.; Lin, H.-Y.; Permuth-Wey, J.; Sellers, T.A.; Srinivasan, S.; Eeles, R.; et al. A Large-Scale Analysis of Genetic Variants within Putative miRNA Binding Sites in Prostate Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2015, 5, 368–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, T.A.; Machiela, M.J. LDpop: An interactive online tool to calculate and visualize geographic LD patterns. BMC Bioinform. 2020, 21, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GTEx Project. GTEx Portal. The Data Used for the Analyses Described in This Manuscript Were Obtained dbGaP Accession phs000424.v6.p1. Available online: https://gtexportal.org/home/snp/ (accessed on 1 July 2024).
- Chen, J.; Akhtari, F.S.; Wagner, M.J.; Suzuki, O.; Wiltshire, T.; Motsinger-Reif, A.A.; Dumond, J.B. Pharmacogenetic Analysis of the Model-Based Pharmacokinetics of Five Anti-HIV Drugs: How Does This Influence the Effect of Aging? Clin. Transl. Sci. 2017, 11, 226–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, F.; Vranic, M.; Hetty, S.; Mathioudaki, A.; Patsoukaki, V.; Fanni, G.; Pereira, M.J.; Eriksson, J.W. Increased OCT3 Expression in Adipose Tissue with Aging: Implications for Catecholamine and Lipid Turnover and Insulin Resistance in Women. Endocrinology 2023, 165, bqad172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Wei, H.; Liu, D.; Shi, B.; Li, L.; Yan, M.; Zhang, X.; Wang, F.; Ouyang, Y. PHACTR1 and SLC22A3 Gene Polymorphisms Are Associated with Reduced Coronary Artery Disease Risk in the Male Chi-nese Han Population. Oncotarget 2016, 8, 658–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamah-Levy, T.; Gaona-Pineda, E.B.; Cuevas-Nasu, L.; Valenzuela-Bravo, D.G.; Morales-Ruan, C.; Rodríguez-Ramírez, S.; Méndez-Gómez-Humarán, I.; Ávila-Arcos, M.A.; Álvarez-Sánchez, C.; Ávila-Curiel, A.; et al. Sobrepeso y Obesidad En Población Escolar y Adolescente. Salud Publica De Mex. 2024, 66, 404–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina-Díaz, J.M.; Vargas-Terrez, B.E.; Medina-Bravo, P.G.; Martínez-Ambrosio, A.; Miranda-Lora, A.L.; Klünder-Klünder, M. Prevalence of type 2 diabetes mellitus in the pediatric population of a third-level care hospital in Mexico City in 2013 and 2018. World J. Diabetes 2023, 14, 290–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Wondisford, F.E. Metformin Action: Concentrations Matter. Cell Metab. 2015, 21, 159–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Eitan, L.N.; Almomani, B.A.; Nassar, A.M.; Elsaqa, B.Z.; Saadeh, N.A. Metformin Pharmacogenetics: Effects of SLC22A1, SLC22A2, and SLC22A3 Polymorphisms on Glycemic Control and HbA1c Levels. J. Pers. Med. 2019, 9, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweighofer, N.; Genser, B.; Maerz, W.; Kleber, M.E.; Trummer, O.; Pieber, T.R.; Obermayer-Pietsch, B. Intronic Variants in OCT1 are Associated with All-Cause and Cardiovascular Mortality in Metformin Users with Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obesity Targets Ther. 2020, 13, 2069–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurado-Camacho, P.A.; Cid-Soto, M.A.; Barajas-Olmos, F.; García-Ortíz, H.; Baca-Peynado, P.; Martínez-Hernández, A.; Centeno-Cruz, F.; Contreras-Cubas, C.; González-Villalpando, M.E.; Saldaña-Álvarez, Y.; et al. Exome Sequencing Data Analysis and a Case-Control Study in Mexican Population Reveals Lipid Trait Associations of New and Known Genetic Variants in Dyslipidemia-Associated Loci. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 807381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salud México, Secretaria de. Norma Oficial Mexicana NOM-015-SSA2 2010 Para la Prevención, Tratamiento y Control de la Diabetes. Diario Oficial de la Federación. Available online: https://www.dof.gob.mx/normasOficiales/4215/salud/salud.htm (accessed on 1 October 2024).
- American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee; ElSayed, N.A.; Aleppo, G.; Bannuru, R.R.; Bruemmer, D.; Collins, B.S.; Ekhlaspour, L.; Hilliard, M.E.; Johnson, E.L.; Khunti, K.; et al. Glycemic Goals and Hypoglycemia: Standards of Care in Diabetes—2024. Diabetes Care 2024, 47, S111–S125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaren, W.; Gil, L.; Hunt, S.E.; Riat, H.S.; Ritchie, G.R.S.; Thormann, A.; Flicek, P.; Cunningham, F. The Ensembl Variant Effect Predictor. Genome Biol. 2016, 17, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alemón-Medina, R.; Chávez-Pacheco, J.L.; Rivera-Espinosa, L.; Ramírez-Mendiola, B.; García-Álvarez, R.; Sámano-Salazar, C.; Dávila-Borja, V.M. Extemporaneous Formulations of Metformin for Pediatric Endocrinology: Physicochemical Integrity, Cytotoxicity of Sweeteners, and Quantitation of Plasma Levels. Clin. Ther. 2015, 37, 1689–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SALUD, S. NORMA Oficial Mexicana NOM-177-SSA1-2013, Que Establece las Pruebas y Procedimientos para Demostrar que un Medicamento es Intercambiable. Requisitos a que Deben Sujetarse los Terceros Autorizados que Realicen las Pruebas de Intercambiabilidad. Requisitos. Diario Oficial de la Federación. Available online: https://www.dof.gob.mx/nota_detalle.php?codigo=5314833&fecha=20/09/2013#gsc.tab=0 (accessed on 1 October 2024).
- Yang, J.; Ferreira, T.; Morris, A.P.; Medland, S.E.; Madden, P.A.F.; Heath, A.C.; Martin, N.G.; Montgomery, G.W.; Weedon, M.N.; Loos, R.J.; et al. Conditional and Joint Multiple-SNP Analysis of GWAS Summary Statistics Identifies Additional Variants Influencing Complex Traits. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purcell, S.; Neale, B.; Todd-Brown, K.; Thomas, L.; Ferreira, M.A.R.; Bender, D.; Maller, J.; Sklar, P.; de Bakker, P.I.W.; Daly, M.; et al. PLINK: Whole Genome Data Analysis Toolset. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2007, 81, 559–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, J.C.; Fry, B.; Maller, J.; Daly, M.J. Haploview: Analysis and Visualization of LD and Haplotype Maps. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 263–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Population | Adult Patients | Pediatric Patients | |
|---|---|---|---|
| n | 375 | 23 | |
| Female | 71.7 (269) | 36.7 (11) | |
| %(n) | Male | 28.3 (106) | 63.3 (19) |
| AGC | 26.9 (101) | - | |
| IGC | 73.1 (274) | - | |
| Age (years) | 58 ± 12.6 | 13 ± 2.6 | |
| Diagnostic time (years) | 9.4 ± 8.1 | - | |
| Mean ± S.D. | BMI (Kg/m2) | 28.3 ± 5.3 | 28.1 ± 4.5 |
| Fasting glycemia (mg/dL) | 144.5 ± 70.9 | 126.1 ± 69.4 | |
| HbA1c (%) | 8.2 ± 2.33 | 6.5 ± 2.5 |
| Gene (Transporter) | SNV | Allele Associated with IGC | Allele Frequency IGC Group | Allele Frequency AGC Group | OR | CI 95% | p-Value 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs4646272 | T | 0.53 | 0.45 | 1.56 | 1.09–2.23 | 0.016 | |
| SLC22A1 | rs4646273 | G | 0.59 | 0.51 | 1.51 | 1.06–2.16 | 0.022 |
| (OCT1) | rs4646276 | G | 0.57 | 0.49 | 1.63 | 1.13–2.32 | 0.008 |
| rs622591 | C | 0.49 | 0.39 | 1.66 | 1.17–2.39 | 0.006 | |
| SLC22A3 | rs668871 | C | 0.75 | 0.64 | 1.51 | 1.04–2.18 | 0.028 |
| (OCT3) | rs1810126 | T | 0.67 | 0.56 | 1.49 | 1.04–2.15 | 0.028 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Morales-Rivera, M.I.; Alemón-Medina, R.; Martínez-Hernández, A.; Contreras-Cubas, C.; Altamirano-Bustamante, N.F.; Gómez-Garduño, J.; Mendoza-Caamal, E.C.; Nuñez-González, J.O.; García-Álvarez, R.; Revilla-Monsalve, C.; et al. Exome Sequence Data of Eight SLC Transporters Reveal That SLC22A1 and SLC22A3 Variants Alter Metformin Pharmacokinetics and Glycemic Control. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 1385. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17101385
Morales-Rivera MI, Alemón-Medina R, Martínez-Hernández A, Contreras-Cubas C, Altamirano-Bustamante NF, Gómez-Garduño J, Mendoza-Caamal EC, Nuñez-González JO, García-Álvarez R, Revilla-Monsalve C, et al. Exome Sequence Data of Eight SLC Transporters Reveal That SLC22A1 and SLC22A3 Variants Alter Metformin Pharmacokinetics and Glycemic Control. Pharmaceuticals. 2024; 17(10):1385. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17101385
Chicago/Turabian StyleMorales-Rivera, Monserrat I., Radamés Alemón-Medina, Angélica Martínez-Hernández, Cecilia Contreras-Cubas, Nelly F. Altamirano-Bustamante, Josefina Gómez-Garduño, Elvia C. Mendoza-Caamal, J. Orlando Nuñez-González, Raquel García-Álvarez, Cristina Revilla-Monsalve, and et al. 2024. "Exome Sequence Data of Eight SLC Transporters Reveal That SLC22A1 and SLC22A3 Variants Alter Metformin Pharmacokinetics and Glycemic Control" Pharmaceuticals 17, no. 10: 1385. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17101385
APA StyleMorales-Rivera, M. I., Alemón-Medina, R., Martínez-Hernández, A., Contreras-Cubas, C., Altamirano-Bustamante, N. F., Gómez-Garduño, J., Mendoza-Caamal, E. C., Nuñez-González, J. O., García-Álvarez, R., Revilla-Monsalve, C., Valcarcel-Gamiño, J. A., Villafan-Bernal, J. R., Centeno-Cruz, F., García-Ortiz, H., Barajas-Olmos, F., & Orozco, L. (2024). Exome Sequence Data of Eight SLC Transporters Reveal That SLC22A1 and SLC22A3 Variants Alter Metformin Pharmacokinetics and Glycemic Control. Pharmaceuticals, 17(10), 1385. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17101385





