Repurposing of c-MET Inhibitor Tivantinib Inhibits Pediatric Neuroblastoma Cellular Growth
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
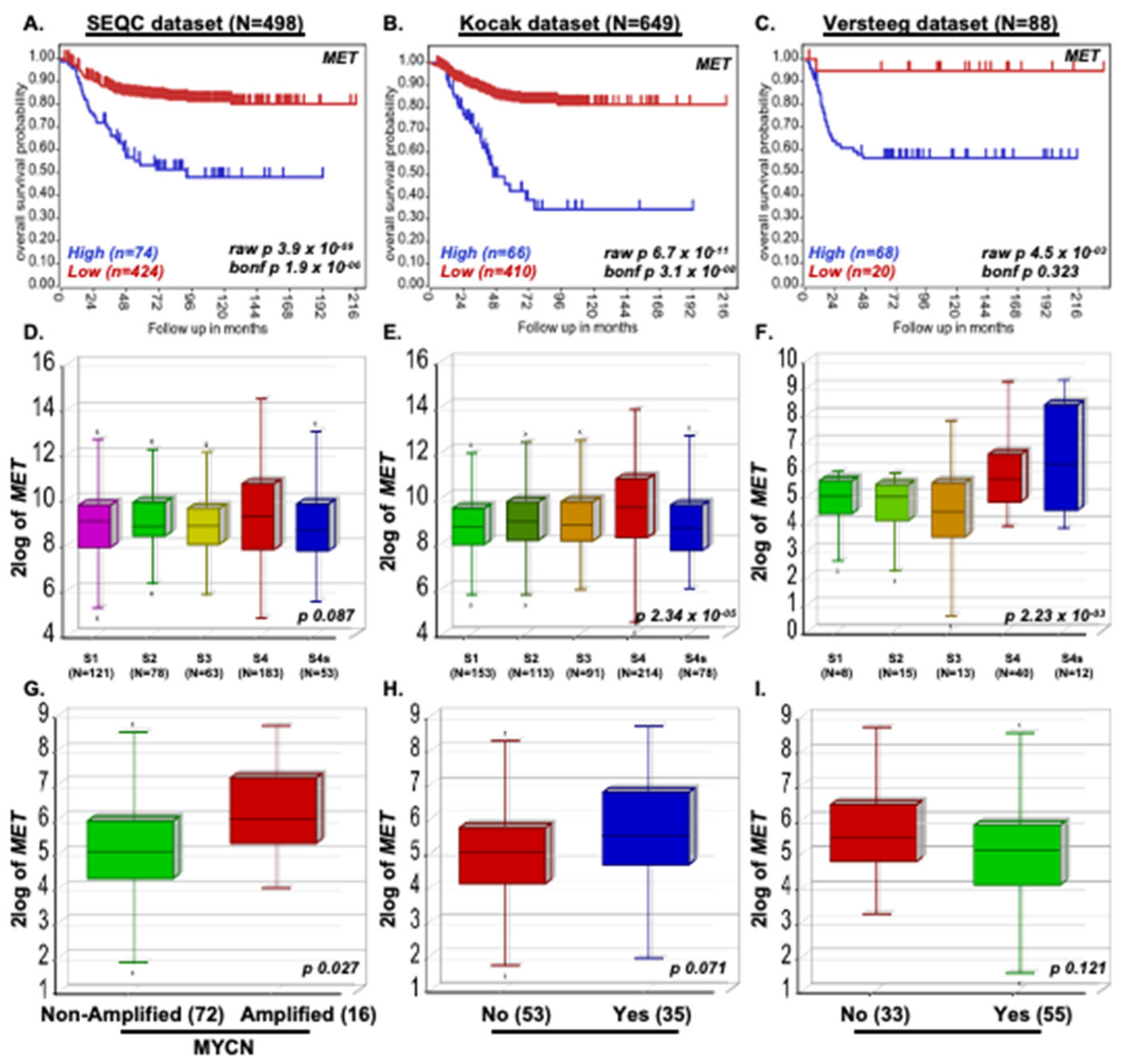
2.1. MET Promotes NB Progression
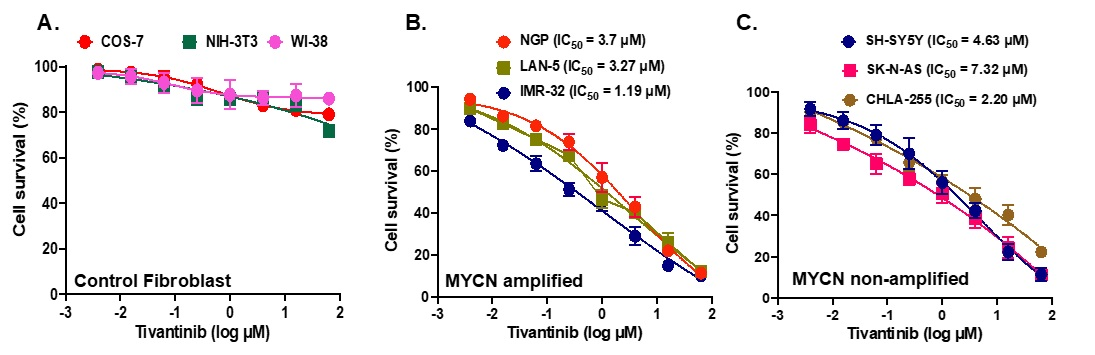
2.2. Tivantinib Inhibits NB Cell Proliferation
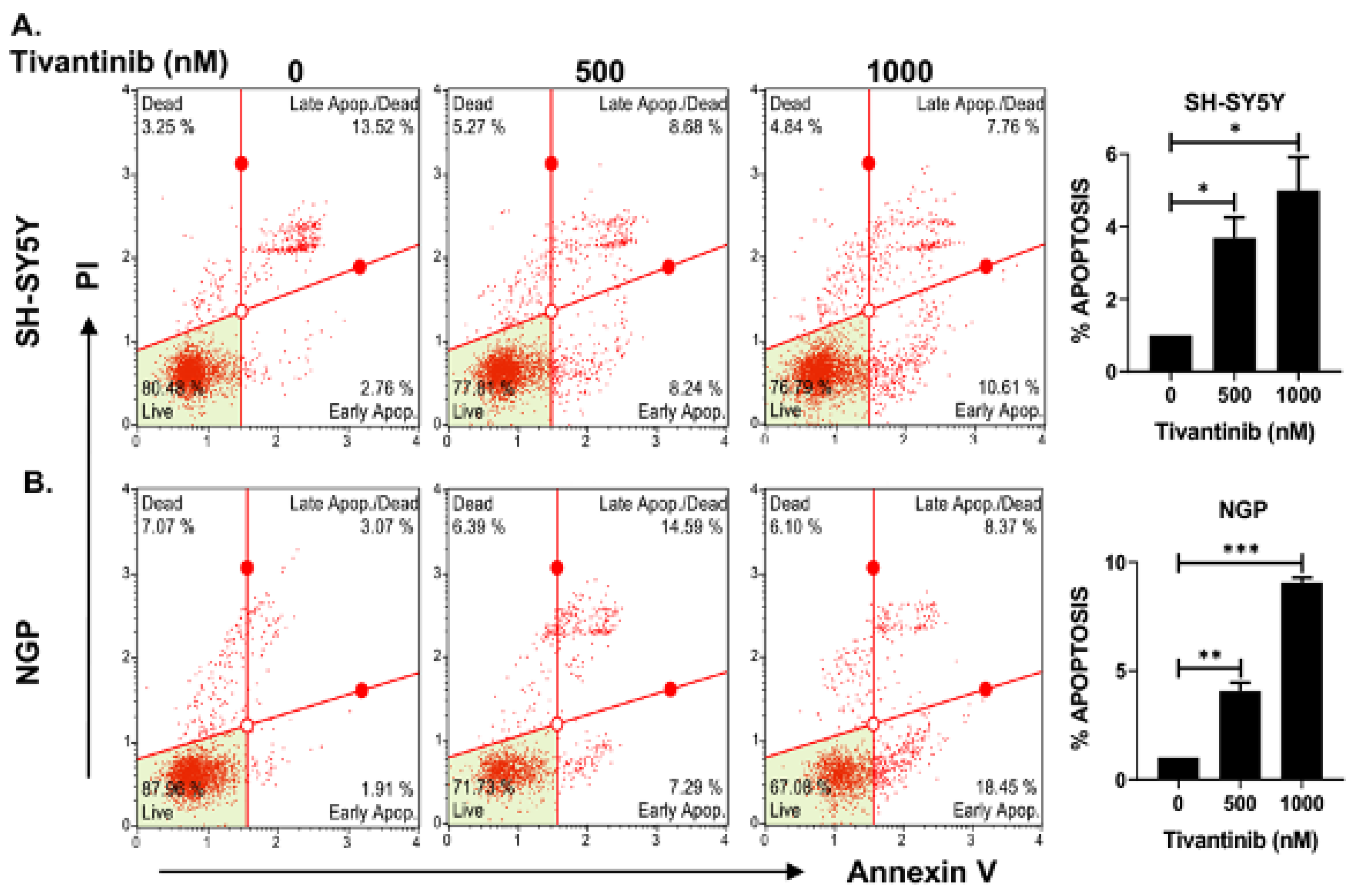
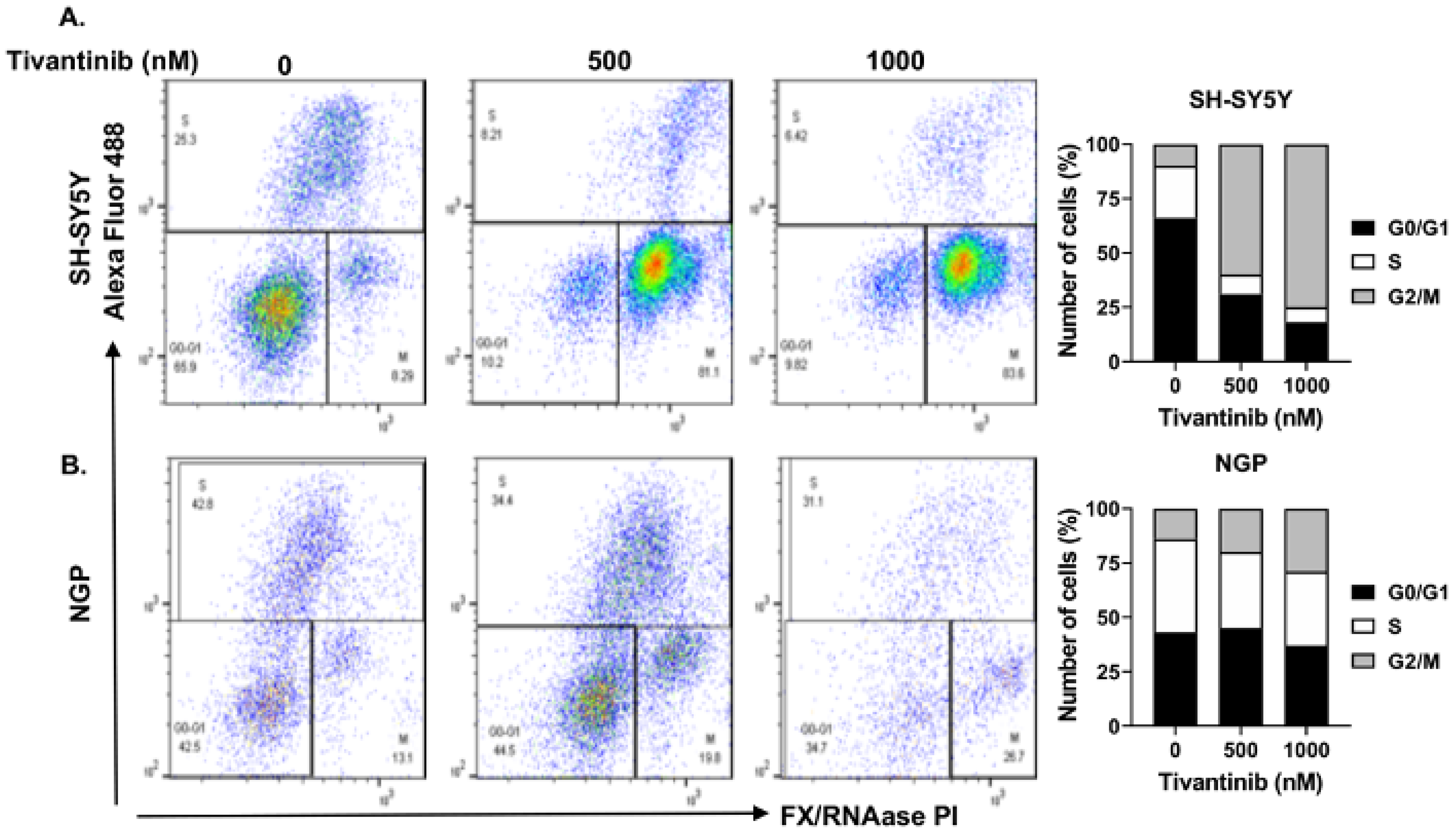
2.3. Tivantinib Triggers Apoptosis and Halts the Cell Cycle Progression in NB Cells
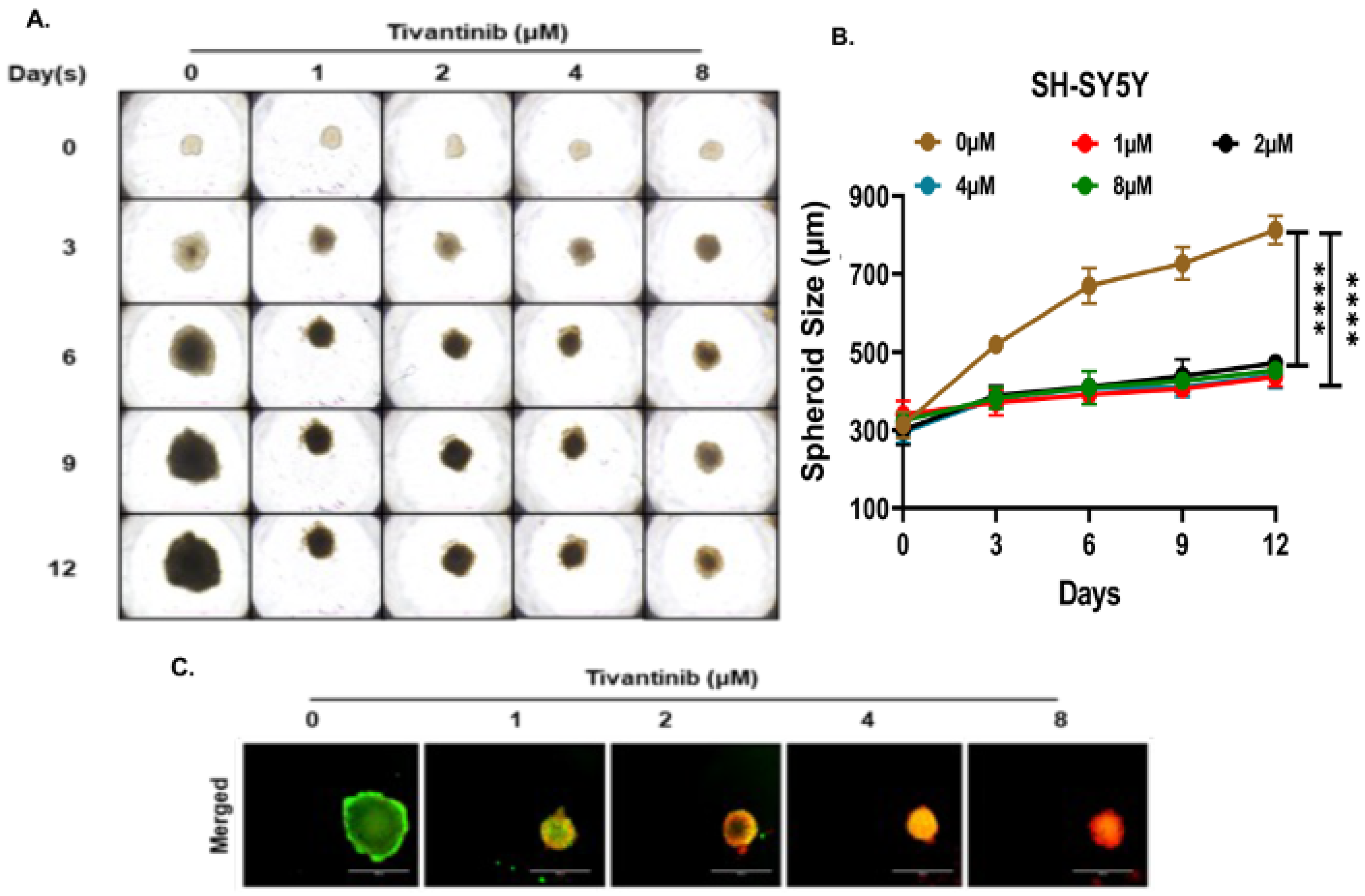
2.4. Tivantinib Inhibits NB Spheroid Tumor Growth
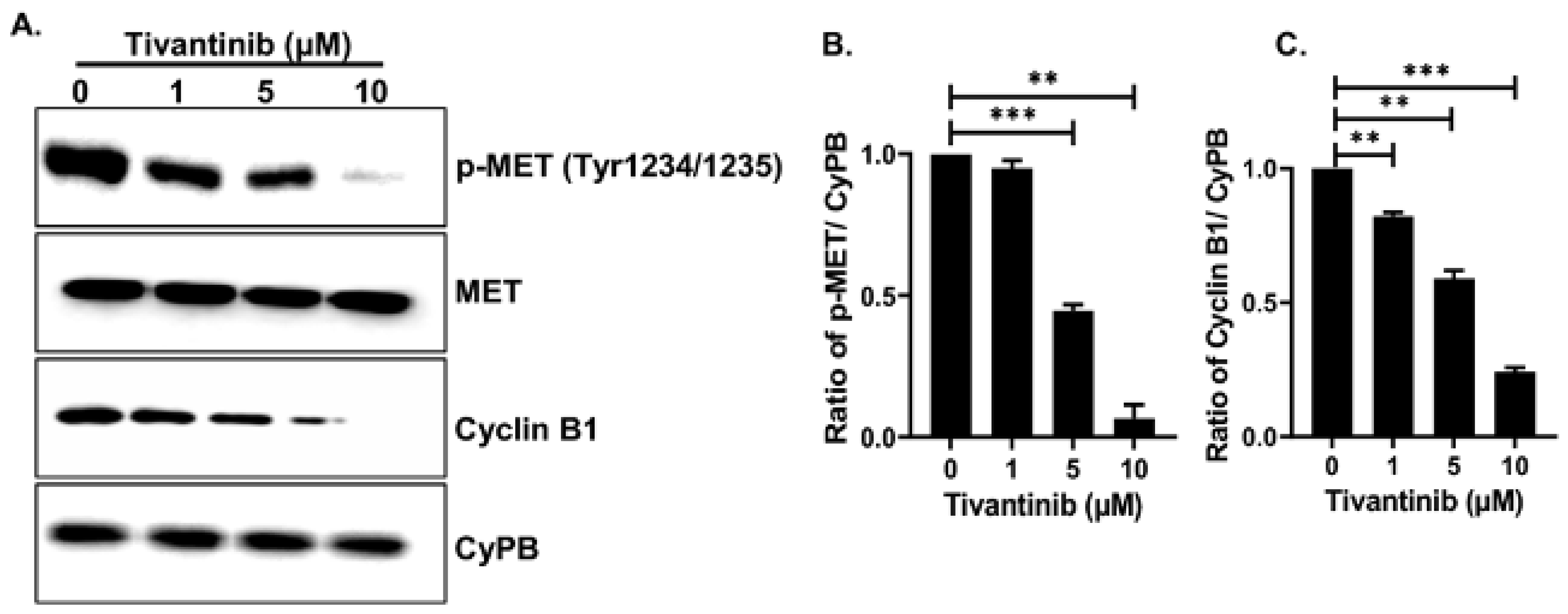
2.5. Tivantinib Suppresses the c-MET Signaling Cascade
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Cell Culture and Reagents
3.2. Dataset Analyses
3.3. Cell Proliferation and Clonogenic Assays
3.4. Cell Cycle and Apoptosis Assays
3.5. RNA Extraction and Quantitative Real-Time RT-PCR
3.6. Immunoblotting Assays
3.7. Spheroid Formation Assay
3.8. Statistical Analysis
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sonkin, D.; Thomas, A.; Teicher, B.A. Cancer treatments: Past, present, and future. Cancer Genet. 2024, 286–287, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dagogo-Jack, I.; Shaw, A.T. Tumour heterogeneity and resistance to cancer therapies. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 15, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthay, K.K.; Maris, J.M.; Schleiermacher, G.; Nakagawara, A.; Mackall, C.L.; Diller, L.; Weiss, W.A. Neuroblastoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2016, 2, 16078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esposito, M.R.; Aveic, S.; Seydel, A.; Tonini, G.P. Neuroblastoma treatment in the post-genomic era. J. Biomed. Sci. 2017, 24, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, B.; Matthay, K.K. Advancing therapy for neuroblastoma. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 19, 515–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crosswell, H.E.; Dasgupta, A.; Alvarado, C.S.; Watt, T.; Christensen, J.G.; De, P.; Durden, D.L.; Findley, H.W. PHA665752, a small-molecule inhibitor of c-Met, inhibits hepatocyte growth factor-stimulated migration and proliferation of c-Met-positive neuroblastoma cells. BMC Cancer 2009, 9, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchikawa, E.; Chen, Z.; Xiao, G.Y.; Zhang, X.; Bai, X.C. Structural basis of the activation of c-MET receptor. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xia, M.; Jin, K.; Wang, S.; Wei, H.; Fan, C.; Wu, Y.; Li, X.; Li, X.; Li, G.; et al. Function of the c-Met receptor tyrosine kinase in carcinogenesis and associated therapeutic opportunities. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, M.; Duplaquet, L.; Tulasne, D. Proteolytic cleavages of MET: The divide-and-conquer strategy of a receptor tyrosine kinase. BMB Rep. 2019, 52, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuenzi, B.M.; Remsing Rix, L.L.; Kinose, F.; Kroeger, J.L.; Lancet, J.E.; Padron, E.; Rix, U. Off-target based drug repurposing opportunities for tivantinib in acute myeloid leukemia. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, S.; Adjei, A.A. MET: A promising anticancer therapeutic target. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 9, 314–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recondo, G.; Che, J.; Janne, P.A.; Awad, M.M. Targeting MET Dysregulation in Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2020, 10, 922–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landi, L.; Minuti, G.; D’Incecco, A.; Salvini, J.; Cappuzzo, F. MET overexpression and gene amplification in NSCLC: A clinical perspective. Lung Cancer 2013, 4, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Giordano, S.; Maffe, A.; Williams, T.A.; Artigiani, S.; Gual, P.; Bardelli, A.; Basilico, C.; Michieli, P.; Comoglio, P.M. Different point mutations in the met oncogene elicit distinct biological properties. FASEB J. 2000, 14, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sierra, J.R.; Tsao, M.S. c-MET as a potential therapeutic target and biomarker in cancer. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2011, 3, S21–S35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Silva, D.M.; Roy, A.; Kato, T.; Cecchi, F.; Lee, Y.H.; Matsumoto, K.; Bottaro, D.P. Targeting the hepatocyte growth factor/Met pathway in cancer. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2017, 45, 855–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wei, L.; Wu, S.; Shen, K.; Liu, C.; Dong, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, C.; et al. ABHD5 inhibits YAP-induced c-Met overexpression and colon cancer cell stemness via suppressing YAP methylation. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hecht, M.; Papoutsi, M.; Tran, H.D.; Wilting, J.; Schweigerer, L. Hepatocyte growth factor/c-Met signaling promotes the progression of experimental human neuroblastomas. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 6109–6118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munshi, N.; Jeay, S.; Li, Y.; Chen, C.R.; France, D.S.; Ashwell, M.A.; Hill, J.; Moussa, M.M.; Leggett, D.S.; Li, C.J. ARQ 197, a novel and selective inhibitor of the human c-Met receptor tyrosine kinase with antitumor activity. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2010, 9, 1544–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eathiraj, S.; Palma, R.; Volckova, E.; Hirschi, M.; France, D.S.; Ashwell, M.A.; Chan, T.C. Discovery of a novel mode of protein kinase inhibition characterized by the mechanism of inhibition of human mesenchymal-epithelial transition factor (c-Met) protein autophosphorylation by ARQ 197. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 20666–20676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geller, J.I.; Perentesis, J.P.; Liu, X.; Minard, C.G.; Kudgus, R.A.; Reid, J.M.; Fox, E.; Blaney, S.M.; Weigel, B.J. A phase 1 study of the c-Met inhibitor, tivantinib (ARQ197) in children with relapsed or refractory solid tumors: A Children’s Oncology Group study phase 1 and pilot consortium trial (ADVL1111). Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2017, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoyama, A.; Katayama, R.; Oh-Hara, T.; Sato, S.; Okuno, Y.; Fujita, N. Tivantinib (ARQ 197) exhibits antitumor activity by directly interacting with tubulin and overcomes ABC transporter-mediated drug resistance. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2014, 13, 2978–2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katayama, R.; Aoyama, A.; Yamori, T.; Qi, J.; Oh-hara, T.; Song, Y.; Engelman, J.A.; Fujita, N. Cytotoxic activity of tivantinib (ARQ 197) is not due solely to c-MET inhibition. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 3087–3096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, Q.; Zhen, Z.; Deng, D.Y.; Wang, J.; Chen, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, F.; Chen, N.; Chen, H.; et al. Tivantinib induces G2/M arrest and apoptosis by disrupting tubulin polymerization in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 34, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanabe, K. Microtubule Depolymerization by Kinase Inhibitors: Unexpected Findings of Dual Inhibitors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, K.; Li, M.; Zoller, M.; Wang, M.; Mehrabi, A.; Hoffmann, K. Targeting c-MET by Tivantinib through synergistic activation of JNK/c-jun pathway in cholangiocarcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chilamakuri, R.; Rouse, D.C.; Yu, Y.; Kabir, A.S.; Muth, A.; Yang, J.; Lipton, J.M.; Agarwal, S. BX-795 inhibits neuroblastoma growth and enhances sensitivity towards chemotherapy. Transl. Oncol. 2022, 15, 101272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, H.N.; Liu, P. Targeting MET in cancer therapy. Chronic Dis. Transl. Med. 2017, 3, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, H.M.; Lee, J. MET: Roles in epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer stemness. Ann. Transl. Med. 2017, 5, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granito, A.; Guidetti, E.; Gramantieri, L. c-MET receptor tyrosine kinase as a molecular target in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatocell. Carcinoma 2015, 2, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spagnolo, C.C.; Ciappina, G.; Giovannetti, E.; Squeri, A.; Granata, B.; Lazzari, C.; Pretelli, G.; Pasello, G.; Santarpia, M. Targeting MET in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC): A New Old Story? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, C.H.; Kim, Y.; Lee, D.Y.; Choi, S.U.; Lee, H.K.; Park, C.H. c-Met-Specific Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cells Demonstrate Anti-Tumor Effect in c-Met Positive Gastric Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Gu, Y.M.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, Z.C.; Zhang, Y.T.; He, Y.D.; Wang, L.; Zhou, N.; Tang, F.T.; Liu, H.J.; et al. Construction of PD1/CD28 chimeric-switch receptor enhances anti-tumor ability of c-Met CAR-T in gastric cancer. Oncoimmunology 2021, 10, 1901434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puccini, A.; Marin-Ramos, N.I.; Bergamo, F.; Schirripa, M.; Lonardi, S.; Lenz, H.J.; Loupakis, F.; Battaglin, F. Safety and Tolerability of c-MET Inhibitors in Cancer. Drug Saf. 2019, 42, 211–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santarpia, M.; Massafra, M.; Gebbia, V.; D’Aquino, A.; Garipoli, C.; Altavilla, G.; Rosell, R. A narrative review of MET inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer with MET exon 14 skipping mutations. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2021, 10, 1536–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Xu, J.; Sun, B.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z. MET-Targeted Therapies and Clinical Outcomes: A Systematic Literature Review. Mol. Diagn. Ther. 2022, 26, 203–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimassa, L.; Assenat, E.; Peck-Radosavljevic, M.; Pracht, M.; Zagonel, V.; Mathurin, P.; Rota Caremoli, E.; Porta, C.; Daniele, B.; Bolondi, L.; et al. Tivantinib for second-line treatment of MET-high, advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (METIV-HCC): A final analysis of a phase 3, randomised, placebo-controlled study. Lancet Oncol. 2018, 19, 682–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scorsone, K.; Zhang, L.; Woodfield, S.E.; Hicks, J.; Zage, P.E. The novel kinase inhibitor EMD1214063 is effective against neuroblastoma. Investig. New Drugs 2014, 32, 815–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Au, J.; Frenette, C. Development of Tivantinib as Treatment for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2013, 1, 75–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, K.; Higai, K.; Mukozu, T.; Matsui, D.; Amanuma, M.; Yoshimine, N.; Ogino, Y.; Matsui, T.; Wakui, N.; Shinohara, M.; et al. Tivantinib Decreases Hepatocyte Growth Factor-Induced BCRP Expression in Hepatocellular Carcinoma HepG2 Cells. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2020, 43, 1421–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.X.; Yang, Y.; Teng, Q.X.; Wang, J.Q.; Lei, Z.N.; Wang, J.Q.; Lusvarghi, S.; Ambudkar, S.V.; Yang, D.H.; Chen, Z.S. Tivantinib, A c-Met Inhibitor in Clinical Trials, Is Susceptible to ABCG2-Mediated Drug Resistance. Cancers 2020, 12, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, S.; Torok, H.P.; Gallmeier, E.; Kolligs, F.T.; Rizzani, A.; Arena, S.; Goke, B.; Gerbes, A.L.; De Toni, E.N. Tivantinib (ARQ 197) affects the apoptotic and proliferative machinery downstream of c-MET: Role of Mcl-1, Bcl-xl and Cyclin B1. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 22167–22178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Xiao, C.; Liu, H.; Huang, Y.; Dilger, J.P.; Lin, J. Effects of local anesthetics on breast cancer cell viability and migration. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Herpe, F.; Van Cutsem, E. The Role of cMET in Gastric Cancer-A Review of the Literature. Cancers 2023, 15, 1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.; Li, Y.; Xiong, L.; Wang, W.; Wu, M.; Yuan, T.; Yang, W.; Tian, C.; Miao, Z.; Wang, T.; et al. Small molecules in targeted cancer therapy: Advances, challenges, and future perspectives. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, D.; Yun, H.; Tong, J.; Liu, W.; Chai, K.; Zeng, T.; Gao, Z.; Xie, Y. Opportunities and challenges of targeting c-Met in the treatment of digestive tumors. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 923260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, B.J. MET inhibitors in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: A meta-analysis and review. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 75500–75508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menis, J.; Levra, M.G.; Novello, S. MET inhibition in lung cancer. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2013, 2, 23–39. [Google Scholar]
- Jamme, P.; Fernandes, M.; Copin, M.C.; Descarpentries, C.; Escande, F.; Morabito, A.; Gregoire, V.; Jamme, M.; Baldacci, S.; Tulasne, D.; et al. Alterations in the PI3K Pathway Drive Resistance to MET Inhibitors in NSCLC Harboring MET Exon 14 Skipping Mutations. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2020, 15, 741–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanteti, R.; Riehm, J.J.; Dhanasingh, I.; Lennon, F.E.; Mirzapoiazova, T.; Mambetsariev, B.; Kindler, H.L.; Salgia, R. PI3 Kinase Pathway and MET Inhibition is Efficacious in Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kummar, S.; Srivastava, A.K.; Navas, T.; Cecchi, F.; Lee, Y.H.; Bottaro, D.P.; Park, S.R.; Do, K.T.; Jeong, W.; Johnson, B.C.; et al. Combination therapy with pazopanib and tivantinib modulates VEGF and c-MET levels in refractory advanced solid tumors. Investig. New Drugs 2021, 39, 1577–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rotow, J.K.; Gui, P.; Wu, W.; Raymond, V.M.; Lanman, R.B.; Kaye, F.J.; Peled, N.; Fece de la Cruz, F.; Nadres, B.; Corcoran, R.B.; et al. Co-occurring Alterations in the RAS-MAPK Pathway Limit Response to MET Inhibitor Treatment in MET Exon 14 Skipping Mutation-Positive Lung Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 439–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Previdi, S.; Scolari, F.; Chila, R.; Ricci, F.; Abbadessa, G.; Broggini, M. Combination of the c-Met inhibitor tivantinib and zoledronic acid prevents tumor bone engraftment and inhibits progression of established bone metastases in a breast xenograft model. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e79101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Bian, D.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, Z. Inhibition of Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL overcomes the resistance to the third-generation EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor osimertinib in non-small cell lung cancer. Mol. Med. Rep. 2021, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calles, A.; Kwiatkowski, N.; Cammarata, B.K.; Ercan, D.; Gray, N.S.; Janne, P.A. Tivantinib (ARQ 197) efficacy is independent of MET inhibition in non-small-cell lung cancer cell lines. Mol. Oncol. 2015, 9, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, R.R.; Mishra, D.K.; Kumar, M.; Yadava, P.K. Human telomerase reverse transcriptase promotes the epithelial to mesenchymal transition in lung cancer cells by enhancing c-MET upregulation. Heliyon 2022, 8, e08673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Q.; Liang, Q.; Sun, Z.; Yuan, X.; Hou, W.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Yu, M. Development of bispecific anti-c-Met/PD-1 diabodies for the treatment of solid tumors and the effect of c-Met binding affinity on efficacy. Oncoimmunology 2021, 10, 1914954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, M.; Lee, S.; Moon, K.C. c-Met and EPHA7 Receptor Tyrosine Kinases Are Related to Prognosis in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma: Focusing on the Association with Myoferlin Expression. Cancers 2022, 14, 1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scagliotti, G.V.; Shuster, D.; Orlov, S.; von Pawel, J.; Shepherd, F.A.; Ross, J.S.; Wang, Q.; Schwartz, B.; Akerley, W. Tivantinib in Combination with Erlotinib versus Erlotinib Alone for EGFR-Mutant NSCLC: An Exploratory Analysis of the Phase 3 MARQUEE Study. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13, 849–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puzanov, I.; Sosman, J.; Santoro, A.; Saif, M.W.; Goff, L.; Dy, G.K.; Zucali, P.; Means-Powell, J.A.; Ma, W.W.; Simonelli, M.; et al. Phase 1 trial of tivantinib in combination with sorafenib in adult patients with advanced solid tumors. Investig. New Drugs 2015, 33, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.Y.; Xu, X.M.; Hong, B.; Wu, Z.G.; Qian, Y.; Weng, T.H.; Liu, Y.Z.; Tang, T.M.; Wang, M.H.; Yao, H.P. Aberrant RON and MET Co-overexpression as Novel Prognostic Biomarkers of Shortened Patient Survival and Therapeutic Targets of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Pancreatic Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lath, D.L.; Buckle, C.H.; Evans, H.R.; Fisher, M.; Down, J.M.; Lawson, M.A.; Chantry, A.D. ARQ-197, a small-molecule inhibitor of c-Met, reduces tumour burden and prevents myeloma-induced bone disease in vivo. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0199517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, B.W.; Gao, J.Q. Application of 3D cultured multicellular spheroid tumor models in tumor-targeted drug delivery system research. J. Control. Release 2018, 270, 246–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Gene | Forward Primer (5′-3′) | Reverse Primer (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| MET | AGTGGGAATTCTAGACACATTTCA | CATTCAAGAATACTGTTTGACACACTT |
| STAT3 | CCCTCAGCAGGAGGGCAGTT | TCACATGGGGGAGGTAGCACA |
| JAK2 | GCAGGCAACAGGAACAAGAT | CCATTCCCATGCAGAGTCTT |
| PI3KCA | CGCATTTCCACAGCTACACC | AGCCATTCATTCCACCTGGG |
| AKT1 | GCACAAACGAGGGGAGTACA | AAGGTGCGTTCGATGACAGT |
| MCL1 | TCGTAAGGACAAAACGGGAC | CATTCCTGATGCCACCTTCT |
| ERK2 | ACGGCATGGTTTGCTCTGCTTATG | TCATTTGCTCAATGGTTGGTGCCC |
| MAPK1 | TACACCAACCTCTCGTACATCG | CATGTCTGAAGCGCAGTAAGATT |
| MAPK2 | GGCAGCTACCTCAGGAATGAC | CCAGTGGCATGGTAAATCTCC |
| CCBN1 | AAGAGCTTTAAACTTTGGTCTGGG | CTTTGTAAGTCCTTGATTTACCATG |
| GAPDH | CACCATCTTCCAGGAGCGAG | TGATGACCCTTTTGGCTCCC |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chilamakuri, R.; Agarwal, S. Repurposing of c-MET Inhibitor Tivantinib Inhibits Pediatric Neuroblastoma Cellular Growth. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 1350. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17101350
Chilamakuri R, Agarwal S. Repurposing of c-MET Inhibitor Tivantinib Inhibits Pediatric Neuroblastoma Cellular Growth. Pharmaceuticals. 2024; 17(10):1350. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17101350
Chicago/Turabian StyleChilamakuri, Rameswari, and Saurabh Agarwal. 2024. "Repurposing of c-MET Inhibitor Tivantinib Inhibits Pediatric Neuroblastoma Cellular Growth" Pharmaceuticals 17, no. 10: 1350. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17101350
APA StyleChilamakuri, R., & Agarwal, S. (2024). Repurposing of c-MET Inhibitor Tivantinib Inhibits Pediatric Neuroblastoma Cellular Growth. Pharmaceuticals, 17(10), 1350. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17101350








