Synergistic Combination of Letrozole and Berberine in Ascorbic Acid-Stabilized AuNPs: A Promising Solution for Breast Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Preparation and Fourier Transform Infrared Analysis of LTZ-BBR@AA-AuNPs
2.2. Drug Capping
2.3. Shape, Particle Size, Polydispersity Index, and Zeta Potential
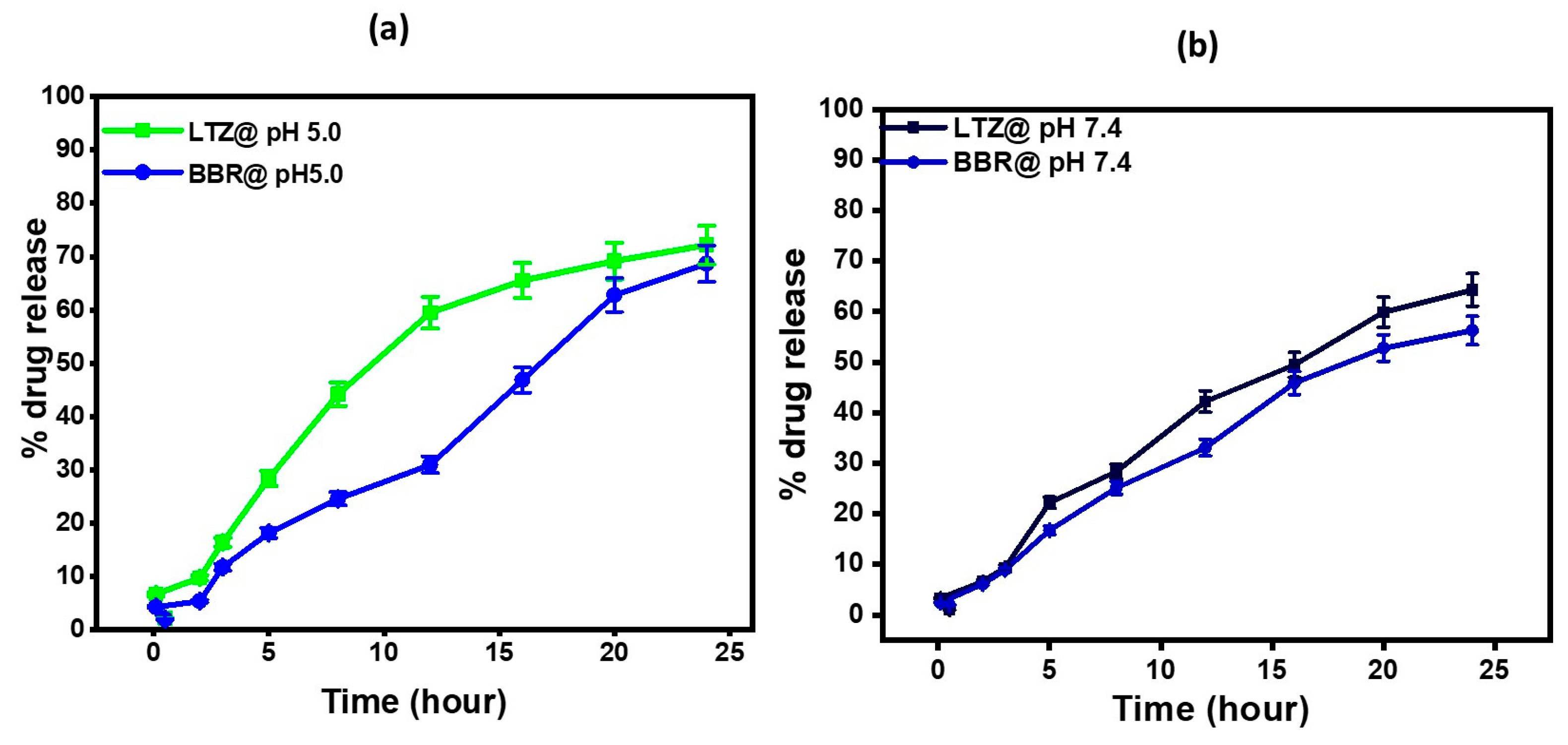
2.4. In Vitro Drug Release Studies
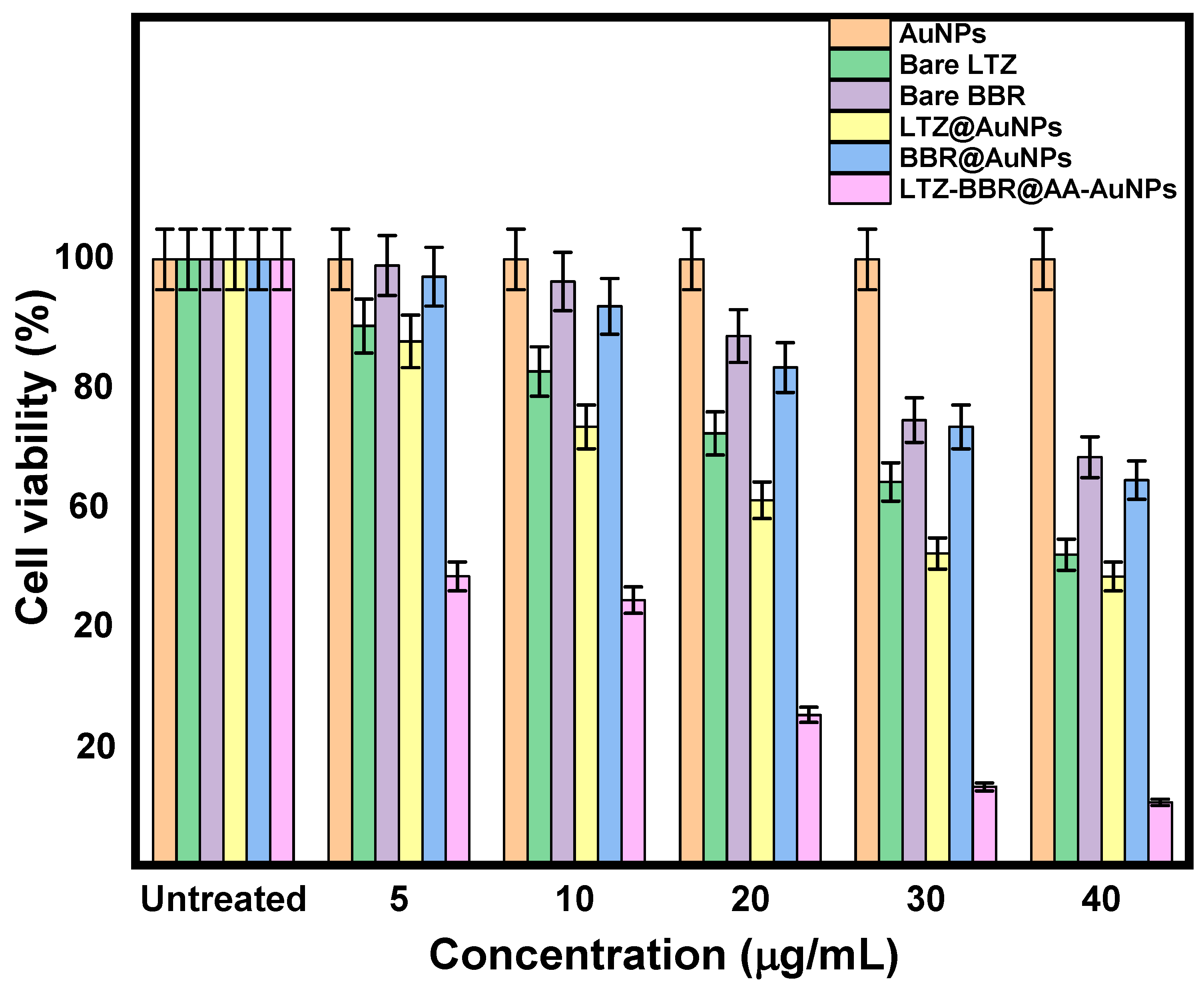
2.5. Anticancer Activity
2.6. Estimation of Intracellular ROS by ELISA
2.7. Cell Cycle Analysis by Flow Cytometry
2.8. Stability Study
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Preparation of Ascorbic Acid Solution (AA)
4.3. Preparation of Gold Chloride Solution
4.4. Synthesis and Optimization of Gold Nanoparticles (AuNPs)
4.5. Drug Capping
- Capping of BBR and LTZ separately
- Capping of BBR and LTZ altogether
4.6. Characterization of Nanoparticles
- Hydrodynamic diameter and surface charges measurement
- Fourier Transform Infrared analysis
4.7. Morphology Study
4.8. In Vitro Drug Release Rtudies
4.9. Anticancer Activity of Test Compounds In Vitro by MTT Assay
4.10. Estimation of Intracellular Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS)
4.11. Cell Cycle Analysis by Flow Cytometry
4.12. Stability Studies
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aldawsari, H.M.; Singh, S.; Alhakamy, N.A.; Bakhaidar, R.B.; Halwani, A.A.; Badr-Eldin, S.M. Gum Acacia Functionalized Colloidal Gold Nanoparticles of Letrozole as Biocompatible Drug Delivery Carrier for Treatment of Breast Cancer. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhushan, A.; Gonsalves, A.; Menon, J.U. Current state of breast cancer diagnosis, treatment, and theranostics. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hooshyar, S.P.; Panahi, H.A.; Moniri, E.; Farsadrooh, M. Tailoring a new hyperbranched PEGylated dendrimer nano-polymer as a super-adsorbent for magnetic solid-phase extraction and determination of letrozole in biological and pharmaceutical samples. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 338, 116772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubovszky, G.; Kocsis, J.; Boér, K.; Chilingirova, N.; Dank, M.; Kahán, Z.; Kaidarova, D.; Kövér, E.; Krakovská, B.V.; Máhr, K.; et al. Systemic Treatment of Breast Cancer. 1st Central-Eastern European Professional Consensus Statement on Breast Cancer. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2022, 28, 1610383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mátrai, Z.; Kelemen, P.; Kósa, C.; Maráz, R.; Paszt, A.; Pavlovics, G.; Sávolt, Á.; Simonka, Z.; Tóth, D.; Kásler, M.; et al. Modern Breast Cancer Surgery 1st Central-Eastern European Professional Consensus Statement on Breast Cancer. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2022, 28, 1610377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, B.; Amorim, I.; Gärtner, F.; Vale, N. Understanding Breast cancer: From conventional therapies to repurposed drugs. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 151, 105401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Xu, X.; Fang, L.; Liu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Wang, M.; Zhao, N.; He, Z. The transdermal patches for site-specific delivery of letrozole: A new option for breast cancer therapy. AAPS PharmSciTech 2010, 11, 1054–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- McDonnell, D.P.; Wardell, S.E.; Norris, J.D. Oral Selective Estrogen Receptor Downregulators (SERDs), a Breakthrough Endocrine Therapy for Breast Cancer. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 4883–4887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, H.B.; Huffman, S.; Veerapaneni, P.; Kirma, N.B.; Binkley, P.; Perla, R.P.; Evans, D.B.; Tekmal, R.R. Hyaluronic acid-bound letrozole nanoparticles restore sensitivity to letrozole-resistant xenograft tumors in mice. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2011, 11, 3789–3799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaban, M.; Ghaffary, S.; Hanaee, J.; Karbakhshzadeh, A.; Soltani, S. Synthesis and characterization of new surface modified magnetic nanoparticles and application for the extraction of letrozole from human plasma and analysis with HPLC-fluorescence. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2021, 193, 113659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Undevia, S.D.; Gomez-Abuin, G.; Ratain, M.J. Pharmacokinetic variability of anticancer agents. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2005, 5, 447–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbarzadeh, I.; Saremi Poor, A.; Khodarahmi, M.; Abdihaji, M.; Moammeri, A.; Jafari, S.; Salehi Moghaddam, Z.; Seif, M.; Moghtaderi, M.; Lalami, Z.A.; et al. Gingerol/letrozole-loaded mesoporous silica nanoparticles for breast cancer therapy: In-silico and in-vitro studies. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2022, 337, 111919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Housman, G.; Byler, S.; Heerboth, S.; Lapinska, K.; Longacre, M.; Snyder, N.; Sarkar, S. Drug resistance in cancer: An overview. Cancers 2014, 6, 1769–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.; Zhu, F.; Ma, X.; Cao, Z.W.; Li, Y.X.; Chen, Y.Z. Mechanisms of drug combinations: Interaction and network perspectives. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2009, 8, 111–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, F.; Kovács, I.A.; Barabási, A.L. Network-based prediction of drug combinations. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaei, M.; Evers, T.M.J.; Shokri, F.; Altucci, L.; de Lange, E.C.M.; Mashaghi, A. Biochemical reaction network topology defines dose-dependent Drug–Drug interactions. Comput. Biol. Med. 2023, 155, 106584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagga, A.S.; Sanzgiry, S.M. Chemotherapy of pulmonary tuberculosis. Tuberc. Respir. Dis. 1982, 29, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, A.-K.; He, S.-M.; Liu, L.; Liu, J.-P.; Qian Wei, M.; Zhou, S.-F. Herbal Interactions with Anticancer Drugs: Mechanistic and Clinical Considerations. Curr. Med. Chem. 2010, 17, 1635–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atallah, M.A.; Sallam, M.A.; Abdelmoneem, M.A.; Teleb, M.; Elkhodairy, K.A.; Bekhit, A.A.; Khafaga, A.F.; Noreldin, A.E.; Elzoghby, A.O.; Khattab, S.N. Green self-assembled lactoferrin carboxymethyl cellulose nanogels for synergistic chemo/herbal breast cancer therapy. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2022, 217, 112657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.; Joshi, G.; Nakhate, K.T.; Ajazuddin; Kumar, R.; Gupta, U. Nano-Co-Delivery of Berberine and Anticancer Drug Using PLGA Nanoparticles: Exploration of Better Anticancer Activity and In Vivo Kinetics. Pharm. Res. 2019, 36, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, S.Y.; Wei, W.C.; Jian, F.Y.; Yang, N.S. Therapeutic applications of herbal medicines for cancer patients. Evid. -Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 2013, 302426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bazrafshani, M.S.; Khandani, B.K.; Pardakhty, A.; Tajadini, H.; Pour Afshar, R.M.; Moazed, V.; Nemati, A.; Nasiri, N.; Sharifi, H. The prevalence and predictors of using herbal medicines among Iranian cancer patients. Complement. Ther. Clin. Pract. 2019, 35, 368–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.; Jeong, D.; Song, M.; Kim, B. Recent advances in anti-metastatic approaches of herbal medicines in 5 major cancers: From traditional medicine to modern drug discovery. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vemuri, S.K.; Banala, R.R.; Mukherjee, S.; Uppula, P.; GPV, S.; Gurava, G.R.; Malarvilli, T. Novel biosynthesized gold nanoparticles as anti-cancer agents against breast cancer: Synthesis, biological evaluation, molecular modelling studies. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 99, 417–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Shang, Y.; Han, Z.; Wang, T.; Wang, Z.G.; Ding, B. Fabrication of Metal Nanostructures on DNA Templates. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 13835–13852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, L.; Gupta, R.; Jain, S.K.; Singh, S.; Kesharwani, P. Synthesis, characterization and in vitro assessment of colloidal gold nanoparticles of Gemcitabine with natural polysaccharides for treatment of breast cancer. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 56, 101565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, T.; Zeng, J.; Wang, X.; Yang, X.; Yang, J.; McQuarrie, S.; McEwan, A.; Roa, W.; Chen, J.; Xing, J.Z. Enhancement of radiation cytotoxicity in breast-cancer cells by localized attachment of gold nanoparticles. Small 2008, 4, 1537–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosn, Y.; Kamareddine, M.H.; Tawk, A.; Elia, C.; El Mahmoud, A.; Terro, K.; El Harake, N.; El-Baba, B.; Makdessi, J.; Farhat, S. Inorganic Nanoparticles as Drug Delivery Systems and Their Potential Role in the Treatment of Chronic Myelogenous Leukaemia. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2019, 18, 1533033819853241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazarus, G.G.; Singh, M. In vitro cytotoxic activity and transfection efficiency of polyethyleneimine functionalized gold nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2016, 145, 906–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, K.-I.; Hyeon, G.L. Stability of chitosan nanoparticles for L-ascorbic acid during heat treatment in aqueous solution. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 1936–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Chen, K.; Cheng, H.; Chen, X.; Feng, S.; Song, Y.; Liang, L. Chemical Stability of Ascorbic Acid Integrated into Commercial Products: A Review on Bioactivity and Delivery Technology. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, M.P.; Bayir, H.; Belousov, V.; Chang, C.J.; Davies, K.J.A.; Davies, M.J.; Dick, T.P.; Finkel, T.; Forman, H.J.; Janssen-Heininger, Y.; et al. Guidelines for measuring reactive oxygen species and oxidative damage in cells and in vivo. Nat. Metab. 2022, 4, 651–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto-Bermejo, R.; Romo-González, M.; Pérez-Fernández, A.; Ijurko, C.; Hernández-Hernández, Á. Reactive oxygen species in haematopoiesis: Leukaemic cells take a walk on the wild side. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 37, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perillo, B.; Di Donato, M.; Pezone, A.; Di Zazzo, E.; Giovannelli, P.; Galasso, G.; Castoria, G.; Migliaccio, A. ROS in cancer therapy: The bright side of the moon. Exp. Mol. Med. 2020, 52, 192–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alemrayat, B.; Elhissi, A.; Younes, H.M. Preparation and characterization of letrozole-loaded poly(d,l-lactide) nanoparticles for drug delivery in breast cancer therapy. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2019, 24, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coates, A.S.; Keshaviah, A.; Thürlimann, B.; Mouridsen, H.; Mauriac, L.; Forbes, J.F.; Paridaens, R.; Castiglione-Gertsch, M.; Gelber, R.D.; Colleoni, M.; et al. Five years of letrozole compared with tamoxifen as initial adjuvant therapy for postmenopausal women with endocrine-responsive early breast cancer: Update of study BIG 1-98. J. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 25, 486–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alemrayat, B.; Elhissi, A.; Younes, H. Preparation and Characterization of Letrozole-Loaded Poly (D,L-Lactide) Nanoparticles for Breast Cancer Therapy. In Qatar Foundation Annual Research Conference Proceedings; Hamad bin Khalifa University Press (HBKU Press): Doha, Qatar, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Muhamad, N.; Plengsuriyakarn, T.; Na-Bangchang, K. Application of active targeting nanoparticle delivery system for chemotherapeutic drugs and traditional/herbal medicines in cancer therapy: A systematic review. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 3921–3935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdulridha, M.K.; Al-Marzoqi, A.H.; Al-awsi, G.R.L.; Mubarak, S.M.H.; Heidarifard, M.; Ghasemian, A. Anticancer Effects of Herbal Medicine Compounds and Novel Formulations: A Literature Review. J. Gastrointest. Cancer 2020, 51, 765–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majidzadeh, H.; Araj-Khodaei, M.; Ghaffari, M.; Torbati, M.; Ezzati Nazhad Dolatabadi, J.; Hamblin, M.R. Nano-based delivery systems for berberine: A modern anti-cancer herbal medicine. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2020, 194, 111188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mughees, M.; Wajid, S. Herbal Based Polymeric Nanoparticles as a Therapeutic Remedy for Breast Cancer. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2020, 21, 433–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibellini, L.; Pinti, M.; Nasi, M.; de Biasi, S.; Roat, E.; Bertoncelli, L.; Cossarizza, A. Interfering with ROS metabolism in cancer cells: The potential role of quercetin. Cancers 2010, 2, 1288–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, A.; Doshi, S. The role of oxidative stress in menopause. J. Midlife Health 2013, 4, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourgonje, A.R.; Abdulle, A.E.; Al-Rawas, A.M.; Al-Maqbali, M.; Al-Saleh, M.; Enriquez, M.B.; Al-Siyabi, S.; Al-Hashmi, K.; Al-Lawati, I.; Bulthuis, M.L.C.; et al. Systemic oxidative stress is increased in postmenopausal women and independently associates with homocysteine levels. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, B.; Zhang, S.-Y.; Chan, K.I.; Zhong, Z.-F.; Wang, Y.-T. Novel Anti-Cancer Products Targeting AMPK: Natural Herbal Medicine against Breast Cancer. Molecules 2023, 28, 740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, W.; Wei, J.; Abidi, P.; Lin, M.; Inaba, S.; Li, C.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Si, S.; Pan, H.; et al. Berberine is a novel cholesterol-lowering drug working through a unique mechanism distinct from statins. Nat. Med. 2004, 10, 1344–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Feng, X.; Chai, L.; Cao, S.; Qiu, F. The metabolism of berberine and its contribution to the pharmacological effects. Drug Metab. Rev. 2017, 49, 139–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.C.; Wang, J.; Chen, H.; Tang, J.; Bian, A.W.; Liu, T.; Yu, L.F.; Yi, Z.; Yang, F. Synthesis and anticancer activity of novel 9,13-disubstituted berberine derivatives. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2020, 30, 126821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauf, A.; Abu-Izneid, T.; Khalil, A.A.; Imran, M.; Shah, Z.A.; Bin Emran, T.; Mitra, S.; Khan, Z.; Alhumaydhi, F.A.; Aljohani, A.S.M.; et al. Berberine as a potential anticancer agent: A comprehensive review. Molecules 2021, 26, 7368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, C.F.; Fu, R.H.; Hsu, S.H.; Yu, Y.H.; Yang, S.F.; Tsao, T.C.Y.; Chang, K.B.; Yeh, C.A.; Tang, C.M.; Huang, S.C.; et al. Delivery capacity and anticancer ability of the berberine-loaded gold nanoparticles to promote the apoptosis effect in breast cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 5317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed Iqbal, M.; Quispe, C.; Javed, Z.; Sadia, H.; Qadri, Q.R.; Raza, S.; Salehi, B.; Cruz-Martins, N.; Abdulwanis Mohamed, Z.; Sani Jaafaru, M.; et al. Nanotechnology-Based Strategies for Berberine Delivery System in Cancer Treatment: Pulling Strings to Keep Berberine in Power. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 7, 624494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqarni, M.H.; Foudah, A.I.; Alam, A.; Salkini, M.A.; Muharram, M.M.; Labrou, N.E.; Kumar, P. Development of Gum-Acacia-Stabilized Silver Nanoparticles Gel of Rutin against Candida albicans. Gels 2022, 8, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Yu, P.; Tang, J. Characterization of triple-negative breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cell spheroid model. Onco Targets Ther. 2020, 13, 5395–5405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekkawy, A.I.; Eleraky, N.E.; Soliman, G.M.; Elnaggar, M.G.; Elnaggar, M.G. Combinatorial Therapy of Letrozole- and Quercetin-Loaded Spanlastics for Enhanced Cytotoxicity against MCF-7 Breast Cancer Cells. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
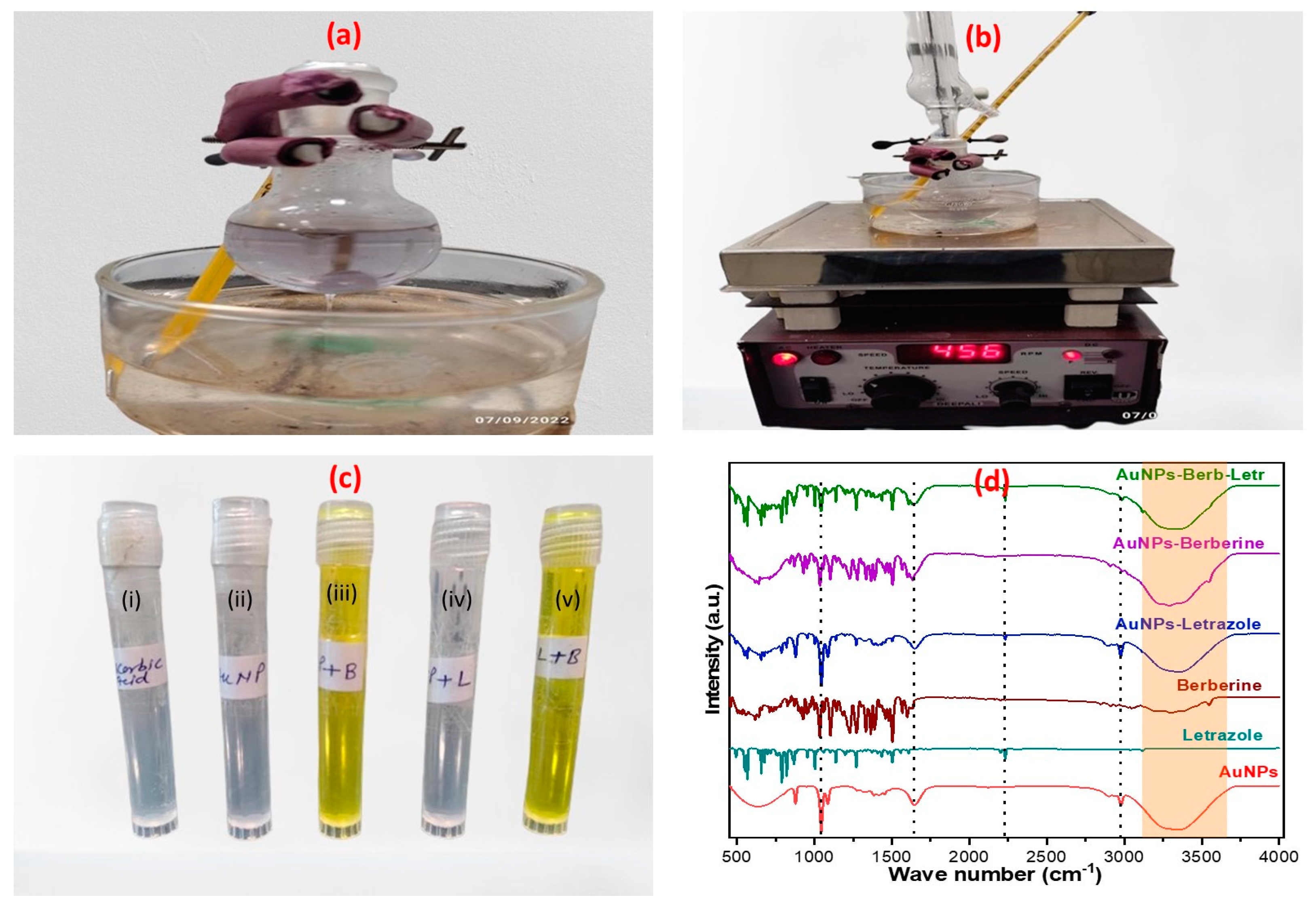



| Days | Colour | Transparency | Drug Capping @BBR | Drug Capping @LTZ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Yellow | Transparent | 54.33 ± 0.47 | 58.13 ± 2.28 |
| 15 | Yellow | Transparent | 54.87 ± 0.17 | 56.65 ± 1.06 |
| 30 | Yellow | Transparent | 56.14 ± 0.65 | 59.54 ± 0.33 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Foudah, A.I.; Alam, A.; Salkini, M.A.; Ross, S.A.; Kumar, P.; Aldawsari, M.F.; Alqarni, M.H.; Sweilam, S.H. Synergistic Combination of Letrozole and Berberine in Ascorbic Acid-Stabilized AuNPs: A Promising Solution for Breast Cancer. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1099. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16081099
Foudah AI, Alam A, Salkini MA, Ross SA, Kumar P, Aldawsari MF, Alqarni MH, Sweilam SH. Synergistic Combination of Letrozole and Berberine in Ascorbic Acid-Stabilized AuNPs: A Promising Solution for Breast Cancer. Pharmaceuticals. 2023; 16(8):1099. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16081099
Chicago/Turabian StyleFoudah, Ahmed I., Aftab Alam, Mohammad Ayman Salkini, Samir A. Ross, Piyush Kumar, Mohammed F. Aldawsari, Mohammed H. Alqarni, and Sherouk Hussein Sweilam. 2023. "Synergistic Combination of Letrozole and Berberine in Ascorbic Acid-Stabilized AuNPs: A Promising Solution for Breast Cancer" Pharmaceuticals 16, no. 8: 1099. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16081099
APA StyleFoudah, A. I., Alam, A., Salkini, M. A., Ross, S. A., Kumar, P., Aldawsari, M. F., Alqarni, M. H., & Sweilam, S. H. (2023). Synergistic Combination of Letrozole and Berberine in Ascorbic Acid-Stabilized AuNPs: A Promising Solution for Breast Cancer. Pharmaceuticals, 16(8), 1099. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16081099







