Bioactive Molecules against Rheumatoid Arthritis by Suppressing Pyroptosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Compounds against Rheumatoid Arthritis by Suppressing Pyroptosis
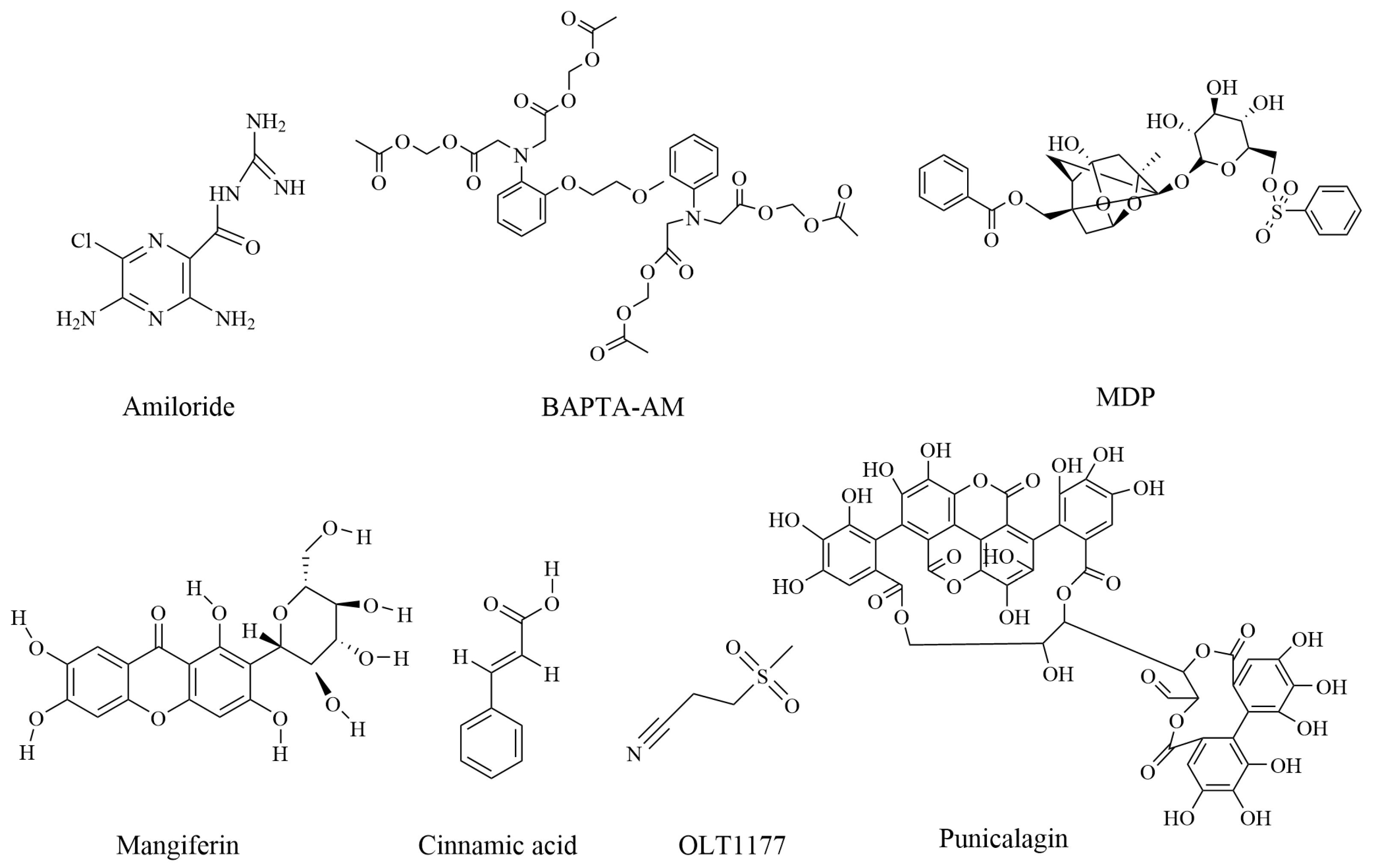
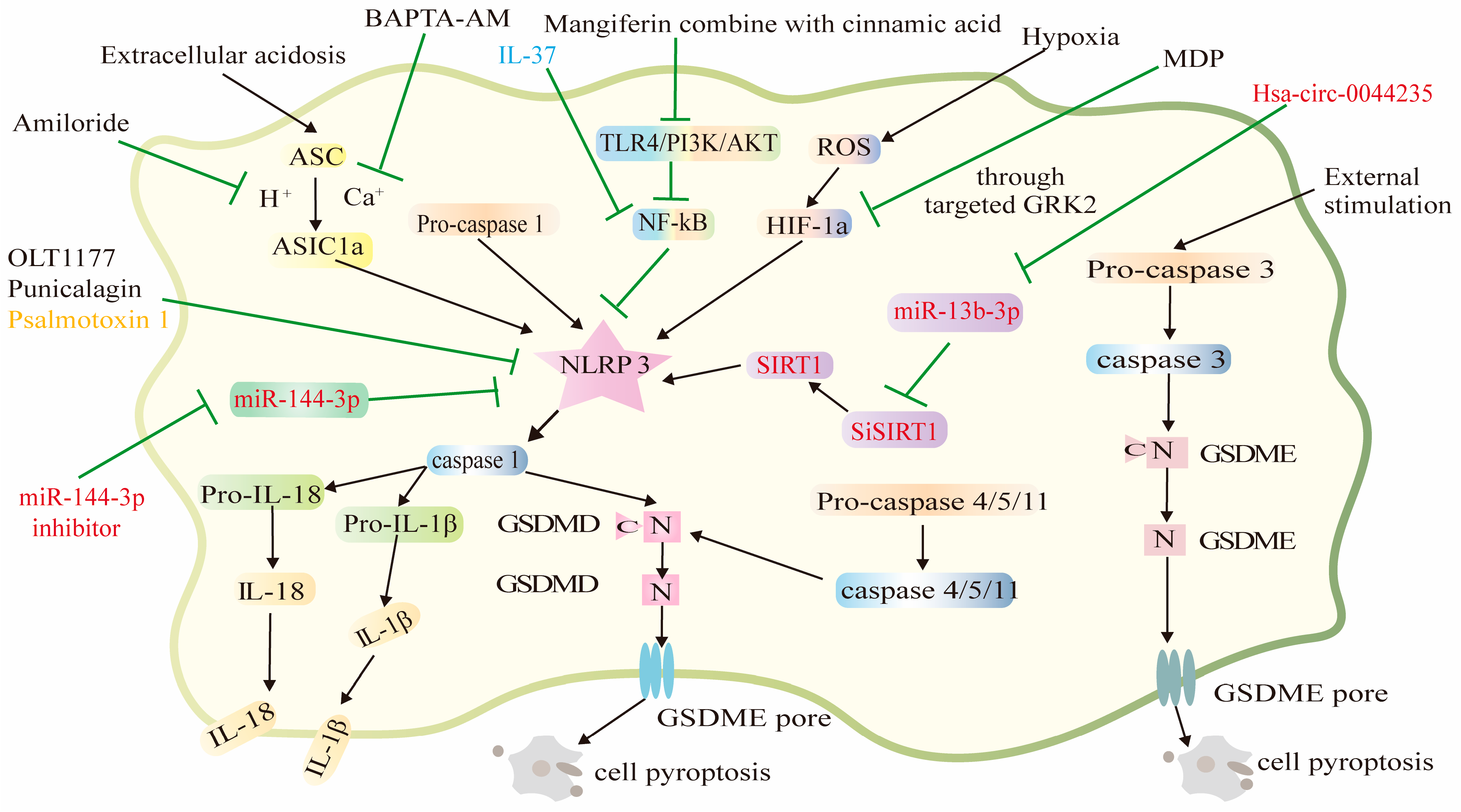
2.1. Amiloride
2.2. BAPTA-AM
2.3. Mangiferin and Cinnamic Acid
2.4. OLT1177
2.5. The Monomeric Derivatives of Paeoniflorin
2.6. Punicalagin
| No | Compounds | Influenced Proteins | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Amiloride | ASIC1a, NLRP3 | [28] |
| 2 | BAPTA-AM | ASIC1a, NLRP3 | [28] |
| 3 | Mangiferin | NF-κB, NLRP3 | [32] |
| 4 | Cinnamic acid | NF-κB, NLRP3 | [32] |
| 5 | OLT1177 | NLRP3 | [33,34] |
| 6 | The monomeric derivatives of paeoniflorin | HIF-1a, NLRP3 | [41] |
| 7 | Punicalagin | NLRP3 | [43] |
3. RNA, Peptide, and Protein against Rheumatoid Arthritis by Modulating Pyroptosis
3.1. Hsa_circ_0044235
3.2. miR-144-3p
3.3. Psalmotoxin 1
3.4. IL-37
| No | RNA or Peptide | Base Sequence (5′–3′) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | hsa_circ_0044235 | TGAGTTTGGTGATTCAGCTTGC, AACAAGGCTTCTTCTGAGTGT | [52] |
| 2 | SIRT1 | TGATTGGCACCGATCCTCG, CCACAGCGTCATATCATCCAG | [52] |
| 3 | miR-144-3p | ucauguagUAGAUAUGACAu | [53] |
| 4 | Psalmotoxin 1 | EDCIPKWKGCVNRHGDCCEGLECWKRRRSFEVCVPKTPKT (Modifications: Disulfide bonds: 3–18, 10–23, 17–33) | [56] |
4. Perspective
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tanase, D.M.; Gosav, E.M.; Petrov, D.; Teodorescu, D.-S.; Buliga-Finis, O.N.; Ouatu, A.; Tudorancea, I.; Rezus, E.; Rezus, C. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) in Cardiovascular Complications of Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA): What Is New? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matson, S.M.; Demoruelle, M.K.; Castro, M. Airway Disease in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2022, 19, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowalski, E.N.; Qian, G.; Vanni, K.M.M.; Sparks, J.A. A Roadmap for Investigating Preclinical Autoimmunity Using Patient-Oriented and Epidemiologic Study Designs: Example of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 890996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Florescu, A.; Gherghina, F.L.; Musetescu, A.E.; Padureanu, V.; Rosu, A.; Florescu, M.M.; Criveanu, C.; Florescu, L.-M.; Bobirca, A. Novel Biomarkers, Diagnostic and Therapeutic Approach in Rheumatoid Arthritis Interstitial Lung Disease-A Narrative Review. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Q.; Tian, Z.; Zhang, Y. Mechanistic and therapeutic links between rheumatoid arthritis and diabetes mellitus. Clin. Exp. Med. 2022, 23, 287–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, R.-C.; Wu, Z.-G.; Wu, Z.-Z.; Hao, M.; Wu, G.-C. Frailty in rheumatoid arthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Jt. Bone Spine 2022, 89, 105343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giollo, A.; Fuzzi, E.; Doria, A. Methotrexate in early rheumatoid arthritis: Is the anchor drug still holding? Autoimmun. Rev. 2022, 21, 103031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorantla, S.; Batra, U.; Samshritha, R.N.; Puppala, E.R.; Waghule, T.; Naidu, V.G.M.; Singhvi, G. Emerging trends in microneedle-based drug delivery strategies for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2022, 19, 395–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aloke, C.; Ohanenye, I.C.; Aja, P.M.; Ejike, C.E.C.C. Phytochemicals from medicinal plants from African forests with potentials in rheumatoid arthritis management. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2022, 74, 1205–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arunsi, U.O.; Chioma, O.E.; Etusim, P.E.; Owumi, S.E. Indigenous Nigeria medicinal herbal remedies: A potential source for therapeutic against rheumatoid arthritis. Exp. Biol. Med. 2022, 247, 1148–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moura, R.A.; Fonseca, J.E. JAK Inhibitors and Modulation of B Cell Immune Responses in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front. Med. 2021, 7, 607725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.-Y.; Zhang, W.; Rao, G.-W. Targeting Janus Kinase (JAK) for Fighting Diseases: The Research of JAK Inhibitor Drugs. Curr. Med. Chem. 2022, 29, 5010–5040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harigai, M. Growing evidence of the safety of JAK inhibitors in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology 2019, 58, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, S.; Ogata, F.; Tsunoda, R. Risk of venous thromboembolism associated with Janus kinase inhibitors for rheumatoid arthritis: Case presentation and literature review. Clin. Rheumatol. 2021, 40, 4457–4471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, I.C.; Hider, S.L.; Scott, D.L. Thromboembolism with Janus Kinase (JAK) Inhibitors for Rheumatoid Arthritis: How Real is the Risk? Drug Saf. 2018, 41, 645–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, P.; Chen, Z.; Xia, Y.; Qiao, C.; Liu, W.; Deng, H.; Li, J.; Ning, P.; et al. Pyroptosis in inflammatory diseases and cancer. Theranostics 2022, 12, 4310–4329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Bettadapura, S.N.; Smeltzer, M.S.; Zhu, H.; Wang, S. Pyroptosis and pyroptosis-inducing cancer drugs. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2022, 43, 2462–2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, R.; Xue, W.; Shi, S.; Zhou, Y.; Du, Y.; Li, Y.; Song, Q.; Wu, H.; Hu, Y. Cardiac Remodeling in Heart Failure: Role of Pyroptosis and Its Therapeutic Implications. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 870924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Liu, H.; Yang, Y.; Wang, H. The Role of Autophagy and Pyroptosis in Liver Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chadha, S.; Behl, T.; Bungau, S.; Kumar, A.; Arora, R.; Gupta, A.; Uddin, M.S.; Zengin, G.; Aleya, L.; Setia, D.; et al. Mechanistic insights into the role of pyroptosis in rheumatoid arthritis. Curr. Res. Transl. Med. 2020, 68, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinarello, C.A.; Novick, D.; Kim, S.; Kaplanski, G. Interleukin-18 and IL-18 binding protein. Front. Immunol. 2013, 4, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulze-Koops, H.; Kalden, J.K. The balance of Th1/Th2 cytokines in rheumatoid arthritis. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2001, 15, 677–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, C.; Chen, F.-H.; Jiang, S.; Hu, W.; Wu, F.-R.; Chen, T.-Y.; Yuan, F.-L. Inhibition of acid-sensing ion channels by amiloride protects rat articular chondrocytes from acid-induced apoptosis via a mitochondrial-mediated pathway. Cell Biol. Int. 2012, 36, 635–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Inchauspe, C.; Urbano, F.J.; Di Guilmi, M.N.; Uchitel, O.D. Acid-Sensing Ion Channels Activated by Evoked Released Protons Modulate Synaptic Transmission at the Mouse Calyx of Held Synapse. J. Neurosci. 2017, 37, 2589–2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhowmick, S.; Moore, J.T.; Kirschner, D.L.; Curry, M.C.; Westbrook, E.G.; Rasley, B.T.; Drew, K.L. Acidotoxicity via ASIC1a Mediates Cell Death during Oxygen Glucose Deprivation and Abolishes Excitotoxicity. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2017, 8, 1204–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, F.-L.; Chen, F.-H.; Lu, W.-G.; Li, X.; Wu, F.-R.; Li, J.-P.; Li, C.-W.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, T.-Y.; Hu, W. Acid-sensing ion channel 1a mediates acid-induced increases in intracellular calcium in rat articular chondrocytes. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2010, 340, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, W.; Chen, F.-H.; Yuan, F.-L.; Zhang, T.-Y.; Wu, F.-R.; Rong, C.; Jiang, S.; Tang, J.; Zhang, C.-C.; Lin, M.-Y. Blockade of acid-sensing ion channels protects articular chondrocytes from acid-induced apoptotic injury. Inflamm. Res. 2012, 61, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Ren, G.; Zhou, R.; Ge, J.; Chen, F.-H. The role of Ca2+ in acid-sensing ion channel 1a-mediated chondrocyte pyroptosis in rat adjuvant arthritis. Lab. Investig. 2019, 99, 499–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Canisso, I.F.; Yang, W.; Ul Haq, I.; Liu, Q.; Han, Y.; Zeng, S. Intracellular calcium chelating agent (BAPTA-AM) aids stallion semen cooling and freezing-thawing. Reprod. Domest. Anim. 2018, 53, 1235–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.-Y.; Chen, Y.-J.; Liu, C.-A.; Gong, J.-H.; Xu, X.-S. STING Induces Liver Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury by Promoting Calcium-Dependent Caspase 1-GSDMD Processing in Macrophages. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2022, 2022, 8123157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Mao, X.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, K.; Li, C.; Li, T.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, N. Disease-Modifying Anti-rheumatic Drug Prescription Baihu-Guizhi Decoction Attenuates Rheumatoid Arthritis via Suppressing Toll-Like Receptor 4-mediated NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 743086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Wang, K.; Liu, Y.; Wu, H.; He, Y.; Li, C.; Wang, Q.; Su, X.; Yan, S.; Su, W.; et al. A Novel Drug Combination of Mangiferin and Cinnamic Acid Alleviates Rheumatoid Arthritis by Inhibiting TLR4/NF kappa B/NLRP3 Activation-Induced Pyroptosis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 912933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchetti, C.; Swartzwelter, B.; Gamboni, F.; Neff, C.P.; Richter, K.; Azam, T.; Carta, S.; Tengesdal, I.; Nemkov, T.; D’Alessandro, A.; et al. OLT1177, a ss-sulfonyl nitrile compound, safe in humans, inhibits the NLRP3 inflammasome and reverses the metabolic cost of inflammation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E1530–E1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchetti, C.; Swartzwelter, B.; Koenders, M.I.; Azam, T.; Tengesdal, I.W.; Powers, N.; de Graaf, D.M.; Dinarello, C.A.; Joosten, L.A.B. NLRP3 inflammasome inhibitor OLT1177 suppresses joint inflammation in murine models of acute arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2018, 20, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fearon, U.; Canavan, M.; Biniecka, M.; Veale, D.J. Hypoxia, mitochondrial dysfunction and synovial invasiveness in rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2016, 12, 385–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phull, A.-R.; Nasir, B.; ul Haq, I.; Kim, S.J. Oxidative stress, consequences and ROS mediated cellular signaling in rheumatoid arthritis. Chem. -Biol. Interact. 2018, 281, 121–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittal, M.; Siddiqui, M.R.; Tran, K.; Reddy, S.P.; Malik, A.B. Reactive Oxygen Species in Inflammation and Tissue Injury. Antioxidants & Redox Signaling 2014, 20, 1126–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reglero, C.; Lafarga, V.; Rivas, V.; Albitre, A.; Ramos, P.; Berciano, S.R.; Tapia, O.; Martinez-Chantar, M.L.; Mayor, F., Jr.; Penela, P. GRK2-Dependent HuR Phosphorylation Regulates HIF1 alpha Activation under Hypoxia or Adrenergic Stress. Cancers 2020, 12, 1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Huang, Z.; Xing, R.; Li, X.; Yu, S.; Mao, J.; Zhang, N.; Mei, W.; Ding, L.; Wang, P. Increased HIF-1 alpha in Knee Osteoarthritis Aggravate Synovial Fibrosis via Fibroblast-Like Synoviocyte Pyroptosis. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 6326517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wei, W. Anti-inflammatory and immunoregulatory effects of paeoniflorin and total glucosides of paeony. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 207, 107452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, T.; Hu, L.; Liu, R.; Wang, P.; Wang, H.; Yu, Q.; Mei, D.; Xue, Z.; et al. The ROS/GRK2/HIF-1alpha/NLRP3 Pathway Mediates Pyroptosis of Fibroblast-Like Synoviocytes and the Regulation of Monomer Derivatives of Paeoniflorin. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2022, 2022, 4566851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.F.; Shi, C.; Wu, Q.; Zheng, Z.W.; Liu, P.F.; Li, G.H.; Peng, X.L.; Xia, X.D. Antimicrobial Activity of Punicalagin Against Staphylococcus aureus and Its Effect on Biofilm Formation. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2017, 14, 282–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, G.; Bai, J.; Wang, Q.; Liang, X.; Tao, H.; Chen, H.; Wei, M.; Niu, J.; Yang, H.; Xu, Y.; et al. Punicalagin ameliorates collagen-induced arthritis by downregulating M1 macrophage and pyroptosis via NF-kappa B signaling pathway. Sci. China Life Sci. 2022, 65, 588–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Funes, S.C.; Rios, M.; Escobar-Vera, J.; Kalergis, A.M. Implications of macrophage polarization in autoimmunity. Immunology 2018, 154, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alunno, A.; Carubbi, F.; Giacomelli, R.; Gerli, R. Cytokines in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis: New players and therapeutic targets. BMC Rheumatol. 2017, 1, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.; Pang, H.-B.; Kang, J.; Park, J.-H.; Ruoslahti, E.; Sailor, M.J. Immunogene therapy with fusogenic nanoparticles modulates macrophage response to Staphylococcus aureus. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laria, A.; Lurati, A.; Marrazza, M.; Mazzocchi, D.; Re, K.A.; Scarpellini, M. The macrophages in rheumatic diseases. J. Inflamm. Res. 2016, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, K.-Y.; Sun, H.S.; Tsai, S.-J. Circular RNA—New member of noncoding RNA with novel functions. Exp. Biol. Med. 2017, 242, 1136–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Zhang, L.; Li, X.; Fu, B.; Deng, Z.; Qing, C.; Su, R.; Xu, J.; Guo, Y.; Huang, Z.; et al. Identification of circular RNAs hsa_circ_0044235 in peripheral blood as novel biomarkers for rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2018, 194, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.-W.; Yang, P.; Zhao, L.-L. Chlorpyrifos activates cell pyroptosis and increases susceptibility on oxidative stress-induced toxicity by miR-181/SIRT1/PGC-1 alpha/Nrf2 signaling pathway in human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells: Implication for association between chlorpyrifos and Parkinson’s disease. Environ. Toxicol. 2019, 34, 699–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Xia, Z.; Liu, Y.; Meng, F.; Wu, X.; Fang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Liu, D. SIRT1 inhibits rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocyte aggressiveness and inflammatory response via suppressing NF-kappa B pathway. Biosci. Rep. 2018, 38, BSR20180541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Luo, Z.; Chen, X. Hsa_circ_0044235 regulates the pyroptosis of rheumatoid arthritis via MiR-135b-5p-SIRT1 axis. Cell Cycle 2021, 20, 1107–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.-M.; Mo, M.-L.; Long, X.-P.; Xie, L.-H. MiR-144-3p induced by SP1 promotes IL-1 beta-induced pyroptosis in chondrocytes via PTEN/PINK1/Parkin axis. Autoimmunity 2022, 55, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cristofori-Armstrong, B.; Saez, N.J.; Chassagnon, I.R.; King, G.F.; Rash, L.D. The modulation of acid-sensing ion channel 1 by PcTx1 is pH-, subtype- and species-dependent: Importance of interactions at the channel subunit interface and potential for engineering selective analogues. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2019, 163, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Chen, F. Acid-Sensing Ion Channel-1a in Articular Chondrocytes and Synovial Fibroblasts: A Novel Therapeutic Target for Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front. Immunol. 2021, 11, 580936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, R.; Hang, X.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Qian, X.; Song, S.; Wang, C.; Tao, J.; Peng, X.; Chen, F. ASIC1a promotes synovial invasion of rheumatoid arthritis via Ca2+/Rac1 pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 79, 106089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Qian, X.; Yang, X.; Niu, R.; Song, S.; Zhu, F.; Zhu, C.; Peng, X.; Chen, F. ASIC1a induces synovial inflammation via the Ca2+/NFATc3/ RANTES pathway. Theranostics 2020, 10, 247–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhu, C.-J.; Zhu, F.; Dai, B.-B.; Song, S.-J.; Wang, Z.-Q.; Feng, Y.-B.; Ge, J.-F.; Zhou, R.-P.; Chen, F.-H. Necrostatin-1 ameliorates adjuvant arthritis rat articular chondrocyte injury via inhibiting ASIC1a-mediated necroptosis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 504, 843–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Shen, H.; Lu, J. Elevated serum and synovial fluid levels of interleukin-37 in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: Attenuated the production of inflammatory cytokines. Cytokine 2015, 76, 553–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busfield, S.J.; Comrack, C.A.; Yu, G.; Chickering, T.W.; Smutko, J.S.; Zhou, H.; Leiby, K.R.; Holmgren, L.M.; Gearing, D.P.; Pan, Y. Identification and gene organization of three novel members of the IL-1 family on human chromosome 2. Genomics 2000, 66, 213–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalli, G.; Koenders, M.; Kalabokis, V.; Kim, J.; Tan, A.C.; Garlanda, C.; Mantovani, A.; Dagna, L.; Joosten, L.A.B.; Dinarello, C.A. Treating experimental arthritis with the innate immune inhibitor interleukin-37 reduces joint and systemic inflammation. Rheumatology 2016, 55, 2220–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, T.; Sun, X.; Zhu, J.; Hon, K.-L.; Jiang, P.; Chu, I.M.-T.; Tsango, M.S.-M.; Lam, C.W.-K.; Zeng, H.; Wongo, C.-K. IL-37 Ameliorating Allergic Inflammation in Atopic Dermatitis Through Regulating Microbiota and AMPK-mTOR Signaling Pathway-Modulated Autophagy Mechanism. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Yan, M.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wu, J.; Fu, L.; Yu, J. Extracellular IL-37 promotes osteogenic and odontogenic differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells via autophagy. Exp. Cell Res. 2021, 407, 112780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Lai, C.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, M.; Liu, X.; Peng, S.; Guo, W.; Xu, Q.; Chen, S.; Chen, G.-X. Chloroquine and Rapamycin Augment Interleukin-37 Expression via the LC3, ERK, and AP-1 Axis in the Presence of Lipopolysaccharides. J. Immunol. Res. 2020, 2020, 6457879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, C.; Chen, J.; Che, Q.; Jia, Q.; Lu, H.; Qi, X.; Zhang, X.; Shu, Q. IL-37 alleviates TNF-alpha-induced pyroptosis of rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes by inhibiting the NF-kappa B/GSDMD signaling pathway. Immunobiology 2023, 228, 152382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kim, H.Y.; Song, S.Y.; Go, S.-h.; Sohn, H.S.; Baik, S.; Soh, M.; Kim, K.; Kim, D.; Kim, H.-C.; et al. Synergistic Oxygen Generation and Reactive Oxygen Species Scavenging by Manganese Ferrite/Ceria Co-decorated Nanoparticles for Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 3206–3217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; McCormick, J.; Connolly, M.; Balogh, E.; Veale, D.J.; Fearon, U. Hypoxia and STAT3 signalling interactions regulate pro-inflammatory pathways in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 74, 1275–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Chen, Z.; Fan, X.; Li, W.; Qu, J.; Dong, C.; Wang, Z.; Ji, Z.; Li, Y. Inhibition of DNM1L and mitochondrial fission attenuates inflammatory response in fibroblast-like synoviocytes of rheumatoid arthritis. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 1516–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Zheng, L.; Wang, Y.; Tao, M.; Xie, Z.; Xia, C.; Gu, C.; Chen, J.; Qiu, P.; Mei, S.; et al. Desktop-stereolithography 3D printing of a radially oriented extracellular matrix/mesenchymal stem cell exosome bioink for osteochondral defect regeneration. Theranostics 2019, 9, 2439–2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, N.; Sahu, A.; Prabhakar, A.; Chatterjee, T.; Tyagi, T.; Kumari, B.; Khan, N.; Nair, V.; Bajaj, N.; Sharma, M.; et al. Activation of NLRP3 inflammasome complex potentiates venous thrombosis in response to hypoxia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. United States Am. 2017, 114, 4763–4768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laghlali, G.; Lawlor, K.E.; Tate, M.D. Die Another Way: Interplay between Influenza A Virus, Inflammation and Cell Death. Viruses 2020, 12, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Torres, J.; Angelica Martinez-Nava, G.; Concepcion Gutierrez-Ruiz, M.; Enrique Gomez-Quiroz, L.; Gutierrez, M. Role of HIF-1 alpha signaling pathway in osteoarthritis: A systematic review. Rev. Bras. Reumatol. 2017, 57, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muz, B.; Khan, M.N.; Kiriakidis, S.; Paleolog, E.M. Hypoxia The role of hypoxia and HIF-dependent signalling events in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2009, 11, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, S.; Zou, H.; Chen, G.; Huang, G. Synthesis and Biological Activities of Chemical Drugs for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Top. Curr. Chem. 2019, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harty, T.; O’Shaughnessy, M.; Harney, S. Therapeutics in rheumatology and the kidney. Rheumatology 2022, 62, 1009–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulla, J.; Katti, R.; Scott, M.J.J. The Role of Gasdermin-D-Mediated Pryoptosis in Organ Injury and Its Therapeutic Implications. Organogenesis 2023, 19, 2177484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Yang, L.; Pandeya, A.; Cui, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z. Pyroptosis-Induced Inflammation and Tissue Damage. J. Mol. Biol. 2022, 434, 167301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; Liu, W.-C.; Chen, X.-Y.; Wang, X.; Li, J.-L.; Zhang, X. Gasdermin D-mediated pyroptosis: Mechanisms, diseases, and inhibitors. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1178662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Wang, X.; Deng, Y.; Li, S.; Xu, X.; Qin, Y.; Peng, L. Pyroptosis Provides New Strategies for the Treatment of Cancer. J. Cancer 2023, 14, 140–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, W.; Qian, Z.; Mao, X.; Li, J. T lymphocyte-mediated pyroptosis: A new regulatory mechanism in non-viral liver disease. Clin. Res. Hepatol. Gastroenterol. 2023, 47, 102070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, Q.; Li, T.; Fang, G.; Pang, Y.; Wang, X. Bioactive Molecules against Rheumatoid Arthritis by Suppressing Pyroptosis. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 952. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16070952
Zhou Q, Li T, Fang G, Pang Y, Wang X. Bioactive Molecules against Rheumatoid Arthritis by Suppressing Pyroptosis. Pharmaceuticals. 2023; 16(7):952. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16070952
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Qian, Tian Li, Gang Fang, Yuzhou Pang, and Xueni Wang. 2023. "Bioactive Molecules against Rheumatoid Arthritis by Suppressing Pyroptosis" Pharmaceuticals 16, no. 7: 952. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16070952
APA StyleZhou, Q., Li, T., Fang, G., Pang, Y., & Wang, X. (2023). Bioactive Molecules against Rheumatoid Arthritis by Suppressing Pyroptosis. Pharmaceuticals, 16(7), 952. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16070952







