Recent Advances in Potential Health Benefits of Quercetin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Review Methodology
3. Chemical Structure and Main Sources
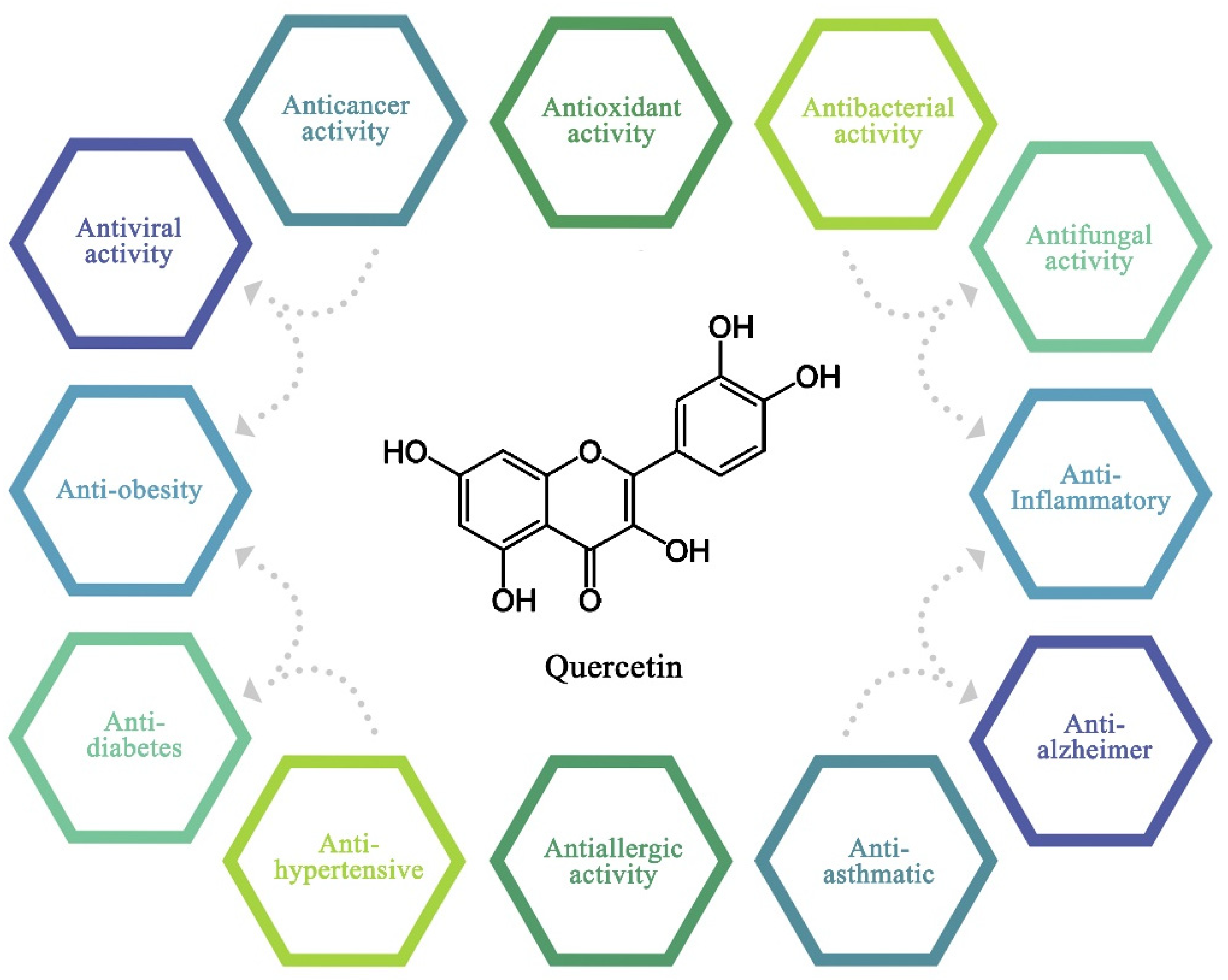
4. Biological Activities
4.1. Antioxidant Activity
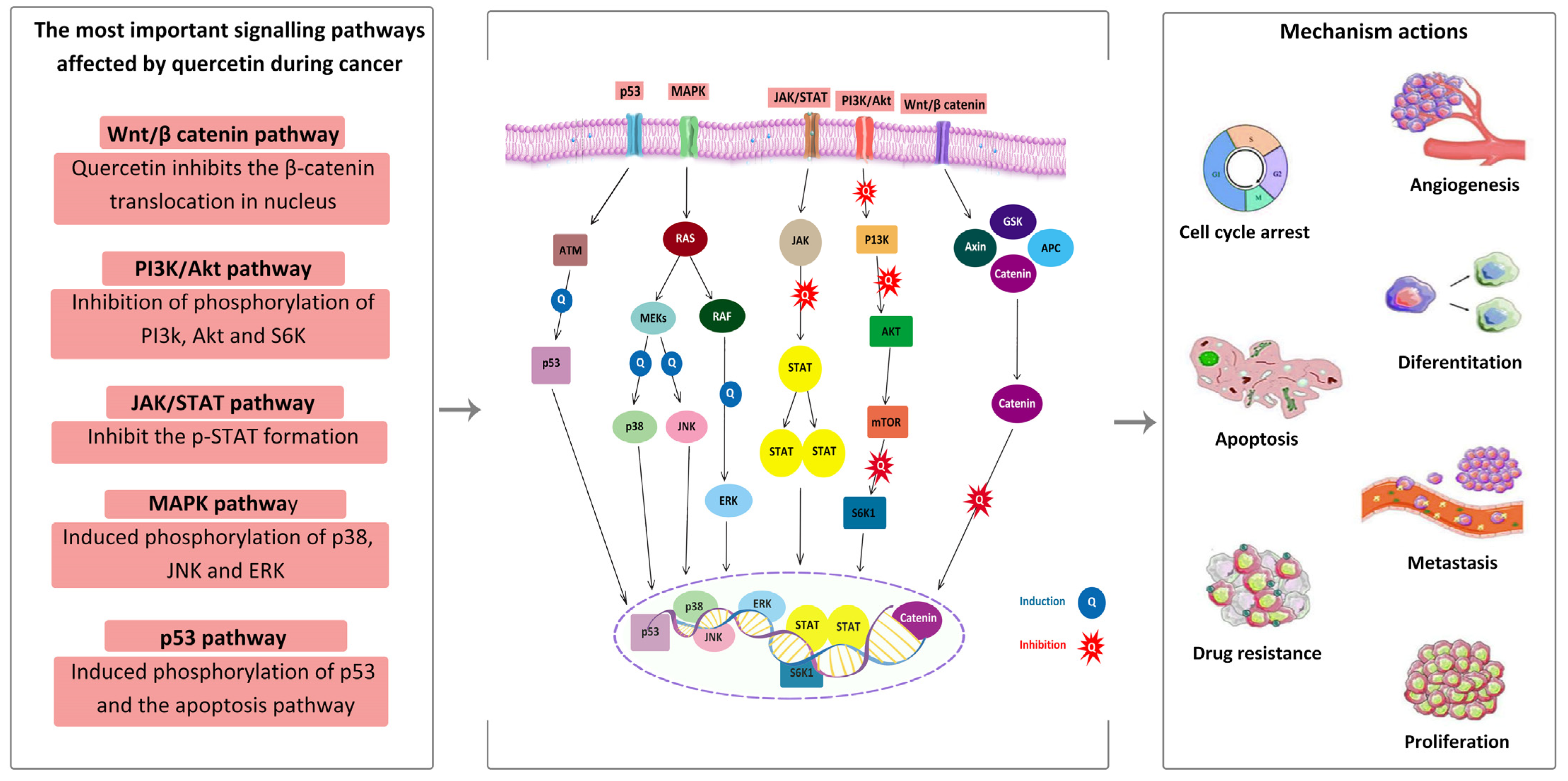
4.2. Anticancer Activity
4.3. Antibacterial Activity
4.4. Antifungal Activity
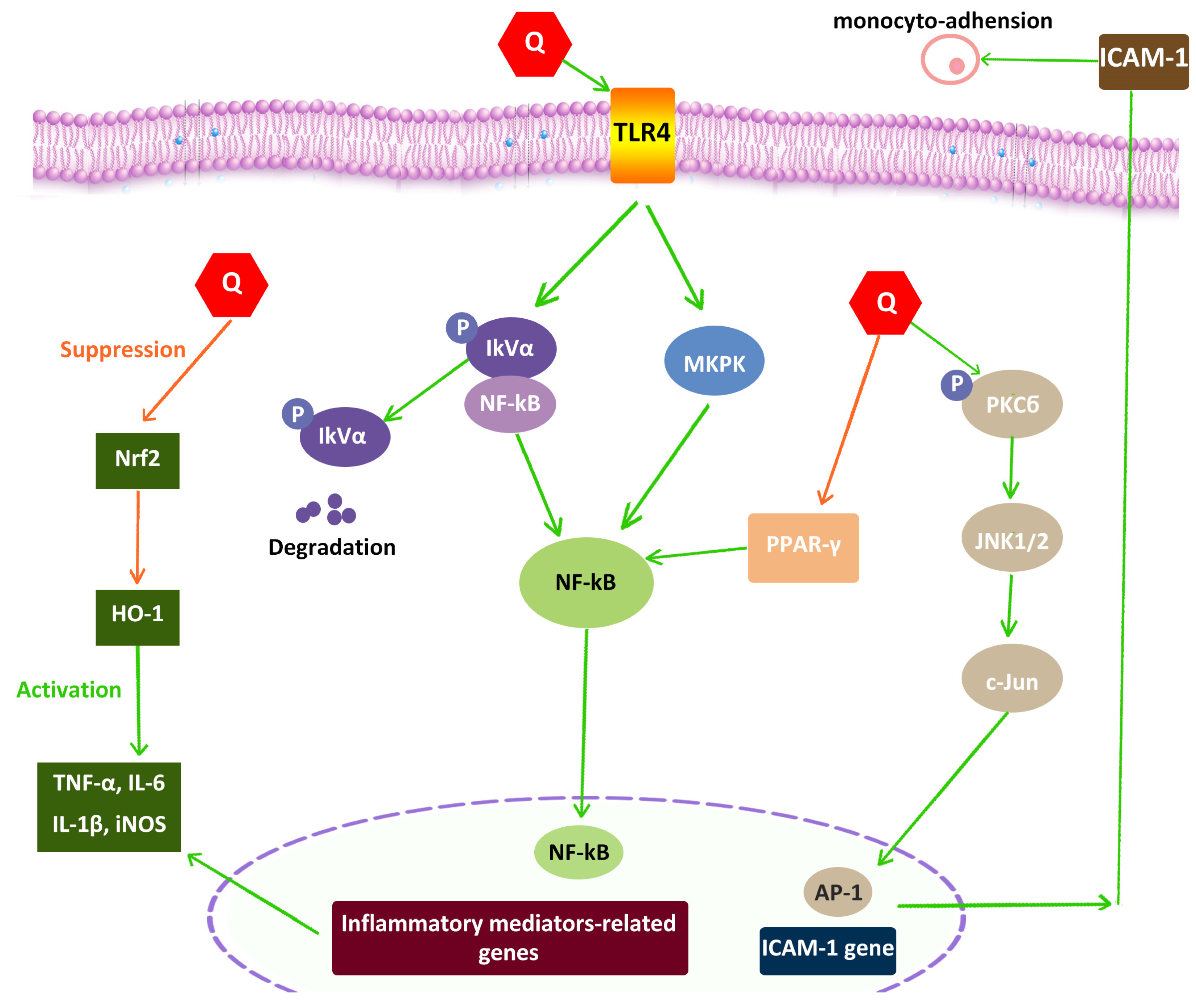
4.5. Anti-Inflammatory
| Therapeutic Agent | Biological Activity | Activity Performed | Key Findings | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quercetin | Antibacterial | S. aureus | Prevented the growth of S. aureus | [93] |
| Aspergillus niger’s transformation of rutin to quercetin | Antibacterial | S. aureus, E. coli, and P. aeruginosa | Increased activity against S. aureus was reported | [94] |
| 6 organic acids + 13 flavonoids | Antibacterial | E. faecalis, S. aureus, E. coli, and P. aeruginosa | All compounds showed activity against Gram-negative bacteria | [80] |
| Quercetin | Antibacterial | S. saprophyticus and resistant S. aureus | Antibacterial effects against MRSA, MSSA, VRSA, and VISA | [95] |
| Quercetin with kaempferol | Antifungal | C. metapsilosis, C. orthopsilosis, and C. parapsilosis | Quercetin was more effective than kaempferol as an antifungal agent | [82] |
| Quercetin/rutin and amphotericin B | Antifungal | Candida species and Cryptococcus neoformans | Evidence of synergistic antifungal action | [85] |
| Quercetin with fluconazole | Antifungal | Vulvovaginal candidiasis | Quercetin and fluconazole have a synergistic antifungal action | [86] |
| Quercetin | Antifungal | Aspergillus flavus | Against Aspergillus flavus, quercetin exhibited antifungal properties | [84] |
| Quercetin and galangin | Anti-inflammatory | Atopic dermatitis in rats | Reduced inflammation due to decreases in NF-kB, interlukin-6, and nitric oxide | [87] |
| Quercetin | Anti-inflammatory | Endothelial cell function | Alteration of HUVAC in order to prevent inflammation | [96] |
| Quercetin | Anti-inflammatory | Inflammasome NLRP3 | NLRP3 suppression results in a decrease in inflammation | [89] |
| Quercetin | Antiviral | HCV | Decreased viral load | [97] |
| Quercetin glucoside | Antiviral | Zika virus | Quercetin glucoside’s cytotoxic effects on the Zika virus | [98] |
| Quercetin | Anti-diabetes | Diabetes-induced osteopenia | Normal bone structure and blood sugar levels in the group treated with quercetin | [99] |
| Quercetin SEDDS | Anti-diabetes | Diabetes-induced streptozotocin | Antihyperglycemic effects of quercetin increased | [100] |
| Quercetin-loaded Soluplus micelles | Anti-diabetes | Rat in vivo model | Reduction in blood glucose levels due to the increased bioavailability of quercetin | [101] |
4.6. Anti-Alzheimer Activity
4.7. Antiviral Activity
4.8. Anti-Obesity
4.9. Anti-Diabetes
4.10. Anti-Hypertensive
4.11. Antiallergic
4.12. Anti-Asthmatic
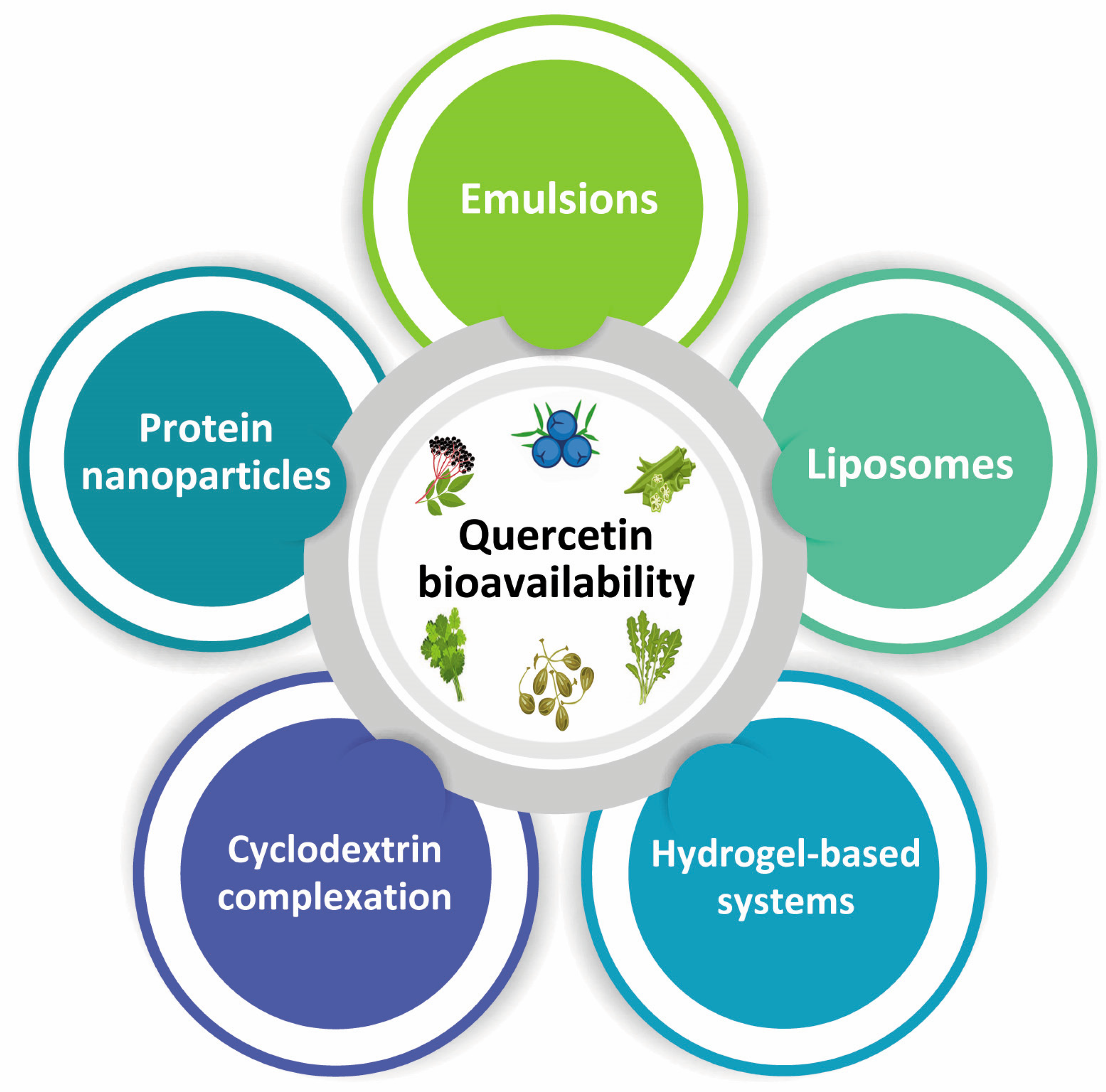
5. Bioavailability of Quercetin
Improvement of Quercetin Bioavailability
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hagde, P.; Pingle, P.; Mourya, A.; Katta, C.B.; Srivastava, S.; Sharma, R.; Singh, K.K.; Sodhi, R.K.; Madan, J. Therapeutic Potential of Quercetin in Diabetic Foot Ulcer: Mechanistic Insight, Challenges, Nanotechnology Driven Strategies and Future Prospects. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2022, 74, 103575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beshbishy, A.M.; Batiha, G.E.S.; Yokoyama, N.; Igarashi, I. Ellagic Acid Microspheres Restrict the Growth of Babesia and Theileria in Vitro and Babesia Microti in Vivo. Parasit. Vectors 2019, 12, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gueffai, A.; Gonzalez-Serrano, D.J.; Christodoulou, M.C.; Orellana-Palacios, J.C.; Ortega, M.L.S.; Ouldmoumna, A.; Kiari, F.Z.; Ioannou, G.D.; Kapnissi-Christodoulou, C.P.; Moreno, A.; et al. Phenolics from Defatted Black Cumin Seeds (Nigella sativa L.): Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction Optimization, Comparison, and Antioxidant Activity. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suganthy, N.; Devi, K.P.; Nabavi, S.F.; Braidy, N.; Nabavi, S.M. Bioactive Effects of Quercetin in the Central Nervous System: Focusing on the Mechanisms of Actions. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2016, 84, 892–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Saber Batiha, G.; Beshbishy, A.M.; Ikram, M.; Mulla, Z.S.; Abd El-Hack, M.E.; Taha, A.E.; Algammal, A.M.; Ali Elewa, Y.H. The Pharmacological Activity, Biochemical Properties, and Pharmacokinetics of the Major Natural Polyphenolic Flavonoid: Quercetin. Foods 2020, 9, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azeem, M.; Hanif, M.; Mahmood, K.; Ameer, N.; Chughtai, F.R.S.; Abid, U. An Insight into Anticancer, Antioxidant, Antimicrobial, Antidiabetic and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Quercetin: A Review. Polym. Bull. 2023, 80, 241–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozgen, S.; Kilinc, O.K.; Selamoglu, Z. Antioxidant Activity of Quercetin: A Mechanistic Review Kuersetinin Antioksidan Aktivitesi: Mekanik Bir Derleme. Turk. J. Agric.-Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 4, 1134–1138. [Google Scholar]
- Rauf, A.; Imran, M.; Khan, I.A.; ur-Rehman, M.; Gilani, S.A.; Mehmood, Z.; Mubarak, M.S. Anticancer Potential of Quercetin: A Comprehensive Review. Phytother. Res. 2018, 32, 2109–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Li, C.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, P.; Zhao, T.; Che, D.; Cao, J.; Wang, J.; Liu, R.; Zhang, T.; et al. Quercetin as a Lyn Kinase Inhibitor Inhibits IgE-Mediated Allergic Conjunctivitis. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 135, 110924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.; Gu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, L.; Meng, G.; Wu, H.; Xia, Y.; Bao, X.; Shi, H.; Sun, S.; et al. Estimated Daily Quercetin Intake and Association with the Prevalence of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Chinese Adults. Eur. J. Nutr. 2019, 58, 819–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perdicaro, D.J.; Rodriguez Lanzi, C.; Gambarte Tudela, J.; Miatello, R.M.; Oteiza, P.I.; Vazquez Prieto, M.A. Quercetin Attenuates Adipose Hypertrophy, in Part through Activation of Adipogenesis in Rats Fed a High-Fat Diet. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2020, 79, 108352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nutmakul, T. A Review on Benefits of Quercetin in Hyperuricemia and Gouty Arthritis. Saudi Pharm. J. 2022, 30, 918–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Tang, Z.G.; Lin, Y.; Qu, X.G.; Lv, W.; Wang, G.-B.; Li, C.L. Effects of Quercetin on Proliferation and Migration of Human Glioblastoma U251 Cells. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 92, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Yao, J.; Han, C.; Yang, J.; Chaudhry, M.T.; Wang, S.; Liu, H.; Yin, Y. Quercetin, Inflammation and Immunity. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2016, 8, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, J.A.; Kasum, C.M. Dietary Flavonoids: Bioavailability, Metabolic Effects, and Safety. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2002, 22, 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, H.; Peng, H.; Wu, X.; Xu, X.; Kuang, T.; Zhang, J.; Du, L.; Fan, G. The Therapeutic Effects and Mechanisms of Quercetin on Metabolic Diseases: Pharmacological Data and Clinical Evidence. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 6678662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadidi, M.; Orellana-Palacios, J.C.; Aghababaei, F.; Gonzalez-Serrano, D.J.; Moreno, A.; Lorenzo, J.M. Plant By-Product Antioxidants: Control of Protein-Lipid Oxidation in Meat and Meat Products. LWT 2022, 169, 114003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srimathi Priyanga, K.; Vijayalakshmi, K. Investigation of Antioxidant Potential of Quercetin and Hesperidin: An in vitro Approach. Asian J. Pharm. Clin. Res. 2017, 10, 83–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Serrano, D.J.; Hadidi, M.; Varcheh, M.; Jelyani, A.Z.; Moreno, A.; Lorenzo, J.M. Bioactive Peptide Fractions from Collagen Hydrolysate of Common Carp Fish Byproduct: Antioxidant and Functional Properties. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesjak, M.; Beara, I.; Simin, N.; Pintać, D.; Majkić, T.; Bekvalac, K.; Orčić, D.; Mimica-Dukić, N. Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Activities of Quercetin and Its Derivatives. J. Funct. Foods 2018, 40, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boots, A.W.; Haenen, G.R.M.M.; Bast, A. Health Effects of Quercetin: From Antioxidant to Nutraceutical. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 585, 325–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christodoulou, M.C.; Orellana Palacios, J.C.; Hesami, G.; Jafarzadeh, S.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Domínguez, R.; Moreno, A.; Hadidi, M. Spectrophotometric Methods for Measurement of Antioxidant Activity in Food and Pharmaceuticals. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suematsu, N.; Hosoda, M.; Fujimori, K. Protective Effects of Quercetin against Hydrogen Peroxide-Induced Apoptosis in Human Neuronal SH-SY5Y Cells. Neurosci. Lett. 2011, 504, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalantari, H.; Foruozandeh, H.; Khodayar, M.J.; Siahpoosh, A.; Saki, N.; Kheradmand, P. Antioxidant and Hepatoprotective Effects of Capparis spinosa L. Fractions and Quercetin on Tert-Butyl Hydroperoxide- Induced Acute Liver Damage in Mice. J. Tradit. Complement. Med. 2018, 8, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharmila, G.; Athirai, T.; Kiruthiga, B.; Senthilkumar, K.; Elumalai, P.; Arunkumar, R.; Arunakaran, J. Chemopreventive Effect of Quercetin in MNU and Testosterone Induced Prostate Cancer of Sprague-Dawley Rats. Nutr. Cancer 2014, 66, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharmila, G.; Bhat, F.A.; Arunkumar, R.; Elumalai, P.; Raja Singh, P.; Senthilkumar, K.; Arunakaran, J. Chemopreventive Effect of Quercetin, a Natural Dietary Flavonoid on Prostate Cancer in in Vivo Model. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 33, 718–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Tian, L.; Chai, G.; Wen, B.; Wang, B. Targeting Heme Oxygenase-1 by Quercetin Ameliorates Alcohol-Induced Acute Liver Injury via Inhibiting NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 4184–4193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ola, M.S.; Ahmed, M.M.; Shams, S.; Al-Rejaie, S.S. Neuroprotective Effects of Quercetin in Diabetic Rat Retina. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2017, 24, 1186–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kale, A.; Pişkin, Ö.; Baş, Y.; Aydln, B.G.; Can, M.; Elmas, Ö.; Büyükuysal, Ç. Neuroprotective Effects of Quercetin on Radiation-Induced Brain Injury in Rats. J. Radiat. Res. 2018, 59, 404–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Qian, X.; Gao, Q.; Lv, C.; Xu, J.; Jin, H.; Zhu, H. Quercetin Increases the Antioxidant Capacity of the Ovary in Menopausal Rats and in Ovarian Granulosa Cell Culture in Vitro. J. Ovarian Res. 2018, 11, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.Z.; Deng, G.; Liang, Q.; Chen, D.F.; Guo, R.; Lai, R.C. Antioxidant Activity of Quercetin and Its Glucosides from Propolis: A Theoretical Study. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 7543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, R.L.; Lyon, T.; Litwin, S.E.; Rabovsky, A.; Symons, J.D.; Jalili, T. Quercetin Reduces Blood Pressure in Hypertensive Subjects. J. Nutr. 2007, 137, 2405–2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, D.; Hu, M.J.; Wang, Y.Q.; Cui, Y.L. Antioxidant Activities of Quercetin and Its Complexes for Medicinal Application. Molecules 2019, 24, 1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X.; Wang, Y.; Gao, L. Mechanism of Antioxidant Properties of Quercetin and Quercetin-DNA Complex. J. Mol. Model. 2020, 26, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Zhao, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, C.; Bian, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, Y. Quercetin Promotes in Vitro Maturation of Oocytes from Humans and Aged Mice. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Maurya, P.K. Quercetin Mitigates Red Blood Cell Membrane Bound Na+, K+-ATPase Transporter During Human Aging. J. Membr. Biol. 2021, 254, 459–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezzati, M.; Yousefi, B.; Velaei, K.; Safa, A. A Review on Anti-Cancer Properties of Quercetin in Breast Cancer. Life Sci. 2020, 248, 117463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Nelson, K.C.; Wu, M.; Sternberg, P.; Jones, D.P. Oxidative Damage and Protection of the RPE. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2000, 19, 205–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.; Chauhan, G.; Shri, R. Anti-Depressant like Effects of Quercetin 4’-O-Glucoside from Allium Cepa via Regulation of Brain Oxidative Stress and Monoamine Levels in Mice Subjected to Unpredictable Chronic Mild Stress. Nutr. Neurosci. 2019, 24, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, T.; Cao, C.; Hou, Y.; Li, Y.; Wei, X.; Li, S.; Jia, S.; Zhao, X. Effects of Quercetin on the Alterations of Serum Elements in Chronic Unpredictable Mild Stress-Induced Depressed Rats. BioMetals 2021, 34, 589–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzmann, I.; Da Silva, L.M.; Corrêa Da Silva, J.A.; Steimbach, V.M.B.; De Souza, M.M. Antidepressant-like Effect of Quercetin in Bulbectomized Mice and Involvement of the Antioxidant Defenses, and the Glutamatergic and Oxidonitrergic Pathways. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2015, 136, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surapaneni, K.M.; Priya, V.V.; Mallika, J. Pioglitazone, Quercetin and Hydroxy Citric Acid Effect on Cytochrome P450 2E1 (CYP2E1) Enzyme Levels in Experimentally Induced Non Alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH). Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2014, 18, 2736–2741. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hanasaki, Y.; Ogawa, S.; Fukui, S. The Correlation between Active Oxygens Scavenging and Antioxidative Effects of Flavonoids. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1994, 16, 845–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van De Wier, B.; Koek, G.H.; Bast, A.; Haenen, G.R.M.M. The Potential of Flavonoids in the Treatment of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 834–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Ma, B.-l.; Xu, C.-g.; Zhou, X.-j. Dihydroquercetin Protects against Renal Fibrosis by Activating the Nrf2 Pathway. Phytomedicine 2020, 69, 153185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-González, P.D.; López-Hernández, F.J.; Dueñas, M.; Prieto, M.; Sánchez-López, E.; Thomale, J.; Ruiz-Ortega, M.; López-Novoa, J.M.; Morales, A.I. Differential Effect of Quercetin on Cisplatin-Induced Toxicity in Kidney and Tumor Tissues. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2017, 107, 226–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Yuan, P.; Zhang, Q.; Fu, Y.; Hou, Y.; Wei, Y.; Zheng, X.; Feng, W. Taxifolin Improves Disorders of Glucose Metabolism and Water-Salt Metabolism in Kidney via PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway in Metabolic Syndrome Rats. Life Sci. 2020, 263, 118713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Sun, N.; Mo, N.; Lu, S.; Song, E.; Ren, C.; Li, Z. Quercetin Inhibits Kidney Fibrosis and the Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition of the Renal Tubular System Involving Suppression of the Sonic Hedgehog Signaling Pathway. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 3782–3797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minaei, A.; Sabzichi, M.; Ramezani, F.; Hamishehkar, H. Co-Delivery with Nano-Quercetin Enhances Doxorubicin-Mediated Cytotoxicity against MCF-7 Cells. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2016, 43, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suksiriworapong, J.; Phoca, K.; Ngamsom, S.; Sripha, K.; Moongkarndi, P.; Junyaprasert, V.B. Comparison of Poly(ε-Caprolactone) Chain Lengths of Poly(ε-Caprolactone)-Co-d-α-Tocopheryl-Poly(Ethylene Glycol) 1000 Succinate Nanoparticles for Enhancement of Quercetin Delivery to SKBR3 Breast Cancer Cells. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2016, 101, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kee, J.Y.; Han, Y.H.; Kim, D.S.; Mun, J.G.; Park, J.; Jeong, M.Y.; Um, J.Y.; Hong, S.H. Inhibitory Effect of Quercetin on Colorectal Lung Metastasis through Inducing Apoptosis, and Suppression of Metastatic Ability. Phytomedicine 2016, 23, 1680–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, X.; Gao, M.; Xu, H.; Zhang, C.; Liu, H.; Lv, L.; Deng, S.; Gao, D.; Tian, Y. Quercetin-Loaded Poly (Lactic-Co-Glycolic Acid)-d-α-Tocopheryl Polyethylene Glycol 1000 Succinate Nanoparticles for the Targeted Treatment of Liver Cancer. Drug Deliv. 2016, 23, 3307–3318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Lv, Q.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, D. The Critical Role of Quercetin in Autophagy and Apoptosis in HeLa Cells. Tumor Biol. 2016, 37, 925–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Henning, S.M.; Magyar, C.E.; Elshimali, Y.; Heber, D.; Vadgama, J.V. Green Tea and Quercetin Sensitize PC-3 Xenograft Prostate Tumors to Docetaxel Chemotherapy. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 35, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.H.; Lee, S.; Shin, Y.S.; Cho, M.; Kang, H.; Cho, H. Anti-Cancer Effect of Quercetin in Xenograft Models with EBV-Associated Human Gastric Carcinoma. Molecules 2016, 21, 1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Lee, J.; Kim, S.J.; Kim, J.H. Quercetin-3-O-Glucoside Suppresses Pancreatic Cancer Cell Migration Induced by Tumor-Deteriorated Growth Factors in Vitro. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 35, 2473–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klimaszewska-Wiśniewska, A.; Hałas-Wiśniewska, M.; Izdebska, M.; Gagat, M.; Grzanka, A.; Grzanka, D. Antiproliferative and Antimetastatic Action of Quercetin on A549 Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells through Its Effect on the Cytoskeleton. Acta Histochem. 2017, 119, 99–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratheeshkumar, P.; Son, Y.O.; Divya, S.P.; Wang, L.; Turcios, L.; Roy, R.V.; Hitron, J.A.; Kim, D.; Dai, J.; Asha, P.; et al. Quercetin Inhibits Cr(VI)-Induced Malignant Cell Transformation by Targeting MiR-21-PDCD4 Signaling Pathway. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 52118–52131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Tantai, J. Co-Delivery Anticancer Drug Nanoparticles for Synergistic Therapy against Lung Cancer Cells. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2020, 14, 4503–4510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, C.S.; Hou, Y.C.; Pai, M.H.; Lin, M.T.; Yeh, S.L. Effects of Quercetin Combined with Anticancer Drugs on Metastasis-Associated Factors of Gastric Cancer Cells: In Vitro and in Vivo Studies. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2018, 51, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hisaka, T.; Sakai, H.; Sato, T.; Goto, Y.; Nomura, Y.; Fukutomi, S.; Fujita, F.; Mizobe, T.; Nakashima, O.; Tanigawa, M.; et al. Quercetin Suppresses Proliferation of Liver Cancer Cell Lines in Vitro. Anticancer Res. 2020, 40, 4695–4700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, G.; Li, B.; Wang, T.; Wan, J.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, J.; Shen, Y. Enhancing the Anti-Ovarian Cancer Activity of Quercetin Using a Self-Assembling Micelle and Thermosensitive Hydrogel Drug Delivery System. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 21229–21242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Lee, J.I.; Ahn, T.G. Effect of Quercetin on the Anti-Tumor Activity of Cisplatin in EMT6 Breast Tumor-Bearing Mice. Obs. Gynecol. Sci. 2019, 62, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, L.T.; Lee, Y.H.; Sharma, A.R.; Park, J.B.; Jagga, S.; Sharma, G.; Lee, S.S.; Nam, J.S. Quercetin Induces Apoptosis and Cell Cycle Arrest in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells through Modulation of Foxo3a Activity. Korean J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2017, 21, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Fan, D.; Zheng, Z.P.; Li, E.T.S.; Chen, F.; Cheng, K.W.; Wang, M. 8-C-(E-Phenylethenyl)Quercetin from Onion/Beef Soup Induces Autophagic Cell Death in Colon Cancer Cells through ERK Activation. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2017, 61, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Liu, J.; Wei, T.; Ma, X.; Cheng, Q.; Huo, S.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Duan, X.; Liang, X.J. Quercetin-Loaded Nanomicelles to Circumvent Human Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer in Vitro and in Vivo. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 5126–5138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heeba, G.H.; Mahmoud, M.E. Dual Effects of Quercetin in Doxorubicin-Induced Nephrotoxicity in Rats and Its Modulation of the Cytotoxic Activity of Doxorubicin on Human Carcinoma Cells. Environ. Toxicol. 2016, 31, 624–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutlu Altundağ, E.; Kasaci, T.; Yilmaz, A.M.; Karademir, B.; Koçtürk, S.; Taga, Y.; Yalçin, A.S. Quercetin-Induced Cell Death in Human Papillary Thyroid Cancer (B-CPAP) Cells. J. Thyroid. Res. 2016, 2016, 9843675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quagliariello, V.; Armenia, E.; Aurilio, C.; Rosso, F.; Clemente, O.; de Sena, G.; Barbarisi, M.; Barbarisi, A. New Treatment of Medullary and Papillary Human Thyroid Cancer: Biological Effects of Hyaluronic Acid Hydrogel Loaded with Quercetin Alone or in Combination to an Inhibitor of Aurora Kinase. J. Cell. Physiol. 2016, 231, 1784–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Hollborn, M.; Grosche, A.; Reichenbach, A.; Wiedemann, P.; Bringmann, A.; Kohen, L. Effects of the Vegetable Polyphenols Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate, Luteolin, Apigenin, Myricetin, Quercetin, and Cyanidin in Primary Cultures of Human Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells. Mol. Vis. 2014, 20, 242–258. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.C.; Liang, Y.; Hu, G.R.; Tian, Y. Enhanced Therapeutic Efficacy and Amelioration of Cisplatin-Induced Nephrotoxicity by Quercetin in 1,2-Dimethyl Hydrazine-Induced Colon Cancer in Rats. Indian. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 48, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, C.Y.; Lien, C.H.; Lee, M.F.; Huang, C.Y. Quercetin Suppresses Cellular Migration and Invasion in Human Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma (HNSCC). BioMedicine 2016, 6, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baruah, M.M.; Khandwekar, A.P.; Sharma, N. Quercetin Modulates Wnt Signaling Components in Prostate Cancer Cell Line by Inhibiting Cell Viability, Migration, and Metastases. Tumor Biol. 2016, 37, 14025–14034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Kim, M.J.; Choi, K.C.; Son, J. Quercetin Sensitizes Pancreatic Cancer Cells to TRAIL-Induced Apoptosis through JNK-Mediated CFLIP Turnover. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2016, 78, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caddeo, C.; Nacher, A.; Vassallo, A.; Armentano, M.F.; Pons, R.; Fernàndez-Busquets, X.; Carbone, C.; Valenti, D.; Fadda, A.M.; Manconi, M. Effect of Quercetin and Resveratrol Co-Incorporated in Liposomes against Inflammatory/Oxidative Response Associated with Skin Cancer. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 513, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catanzaro, D.; Ragazzi, E.; Vianello, C.; Caparrotta, L.; Montopoli, M. Effect of Quercetin on Cell Cycle and Cyclin Expression in Ovarian Carcinoma and Osteosarcoma Cell Lines. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2015, 10, 1365–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, H.S.; Ku, J.M.; Choi, H.S.; Choi, Y.K.; Woo, J.K.; Kim, M.; Kim, I.; Na, C.H.; Hur, H.; Jang, B.H.; et al. Quercetin Induces Caspase-Dependent Extrinsic Apoptosis through Inhibition of Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 Signaling in HER2-Overexpressing BT-474 Breast Cancer Cells. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 36, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Yao, J.; Zhou, B.O.; Yang, J.; Chaudry, M.T.; Wang, M.I.; Xiao, F. Bacteriostatic Effect of Quercetin as an Antibiotic Alternative In Vivo and Its Antibacterial Mechanism In Vitro. J. Food Prot. 2018, 81, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osonga, F.J.; Akgul, A.; Miller, R.M.; Eshun, G.B.; Yazgan, I.; Akgul, A.; Sadik, O.A. Antimicrobial Activity of a New Class of Phosphorylated and Modi Fi Ed Flavonoids. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 12865–12871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamczak, A.; Ożarowski, M.; Karpiński, T.M. Antibacterial Activity of Some Flavonoids and Organic Acids Widely Distributed in Plants. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Jin, H.; Xiao, J.; Yin, X.; Liu, X.; Li, D.; Huang, Q. The Simultaneous Loading of Catechin and Quercetin on Chitosan-Based Nanoparticles as Effective Antioxidant and Antibacterial Agent. Food Res. Int. 2018, 111, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, M.F.G.; Sales, J.A.; da Rocha, M.G.; Galdino, L.M.; de Aguiar, L.; Pereira-Neto, W.D.; de Aguiar Cordeiro, R.; Castelo-Branco, D.D.; Sidrim, J.J.; Brilhante, R.S.N. Antifungal Effects of the Flavonoids Kaempferol and Quercetin: A Possible Alternative for the Control of Fungal Biofilms. Biofouling 2019, 35, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milanezi, F.G.; Meireles, L.M.; de Christo Scherer, M.M.; de Oliveira, J.P.; da Silva, A.R.; de Araujo, M.L.; Endringer, D.C.; Fronza, M.; Guimarães, M.C.C.; Scherer, R. Antioxidant, Antimicrobial and Cytotoxic Activities of Gold Nanoparticles Capped with Quercetin. Saudi Pharm. J. 2019, 27, 968–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shishodia, S.K.; Tiwari, S.; Hoda, S.; Vijayaraghavan, P.; Shankar, J. SEM and QRT-PCR Revealed Quercetin Inhibits Morphogenesis of Aspergillus Flavus Conidia via Modulating Calcineurin-Crz1 Signalling Pathway. Mycology 2020, 11, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, V.M.; Carraro, E.; Auler, M.E.; Khalil, N.M. Quercetina e Rutina: Potenciais Agentes Para Terapia Antifúngica. Braz. J. Biol. 2016, 76, 1029–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Wang, H.; Zhu, L. Quercetin Assists Fluconazole to Inhibit Biofilm Formations of Fluconazole-Resistant Candida Albicans in In Vitro and in Vivo Antifungal Managements of Vulvovaginal Candidiasis. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 40, 727–742. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.N.; Shin, S.A.; Choo, G.S.; Kim, H.J.; Park, Y.S.; Kim, B.S.; Kim, S.K.; Cho, S.D.; Nam, J.S.; Choi, C.S.; et al. Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Quercetin and Galangin in LPS-Stimulated RAW264.7 Macrophages and DNCB-Induced Atopic Dermatitis Animal Models. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 41, 888–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, T.B.; Ballesteros, P. Resveratrol and Quercetin, Two Natural Polyphenols, Reduce Apoptotic Neuronal Cell Death Induced by Neuroinflammation. J. Neurosci. Res. 2008, 3253, 3244–3253. [Google Scholar]
- Saeedi-Boroujeni, A.; Mahmoudian-Sani, M.R. Anti-Inflammatory Potential of Quercetin in COVID-19 Treatment. J. Inflamm. 2021, 18, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Mediavilla, V.; Crespo, I.; Collado, P.S.; Esteller, A.; Sánchez-Campos, S.; Tuñón, M.J.; González-Gallego, J. The Anti-Inflammatory Flavones Quercetin and Kaempferol Cause Inhibition of Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase, Cyclooxygenase-2 and Reactive C-Protein, and down-Regulation of the Nuclear Factor KappaB Pathway in Chang Liver Cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2007, 557, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozyel, B.; Le Gall, G.; Needs, P.W.; Kroon, P.A. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Quercetin on High-Glucose and Pro-Inflammatory Cytokine Challenged Vascular Endothelial Cell Metabolism. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2021, 65, 2000777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.F.; Leu, Y.L.; Al-Suwayeh, S.A.; Ku, M.C.; Hwang, T.L.; Fang, J.Y. Anti-Inflammatory Activity and Percutaneous Absorption of Quercetin and Its Polymethoxylated Compound and Glycosides: The Relationships to Chemical Structures. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 47, 857–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pahal, V.; Devi, U.; Swaroop Dadhich, K. Quercetin, a Secondary Metabolite Present in Methanolic Extract of Calendula Officinalis, Is a Potent Inhibitor of Peptide Deformylase, Undecaprenyl Pyrophosphate Synthase and DNA Primase Enzymes of Staphylococcus Aureus: An in Vitro and in Silico Result Analysis. MOJ Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2018, 2, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreelatha, S.; Jayachitra, A. Targeting Biofilm Inhibition Using Quercetin—Interaction with Bacterial Cell Membrane and ROS Mediated Biofilm Control. Funct. Foods Health Dis. 2018, 8, 292–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, S.; Victor, J.; Santos, D.O.; De, L.A.; Campos, A.; Pereira, M.A.; Santos, N.S.; Macário, I.; Cavalcanti, F. Antibacterial and Antibiofilm Activities of Quercetin against Clinical Isolates of Staphyloccocus Aureus and Staphylococcus Saprophyticus with Resistance Profile. Int. J. Environ. Agric. Biotechnol. (IJEAB) 2018, 3, 1948–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, H.; Yang, Y.; Chen, B. Quercetin regulates vascular endothelium function in chronic renal failure via modulation of Eph/Cav-1 signaling. Drug Dev. Res. 2022, 83, 1167–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rojas, N.; Del Campo, J.A.; Clement, S.; Lemasson, M.; García-Valdecasas, M.; Gil-Gómez, A.; Ranchal, I.; Bartosch, B.; Bautista, J.D.; Rosenberg, A.R.; et al. Effect of Quercetin on Hepatitis C Virus Life Cycle: From Viral to Host Targets. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 31777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, G.; He, S.; Siragam, V.; Bi, Y.; Mbikay, M.; Chretien, M.; Qiu, X. Antiviral Activity of Quercetin-3-β-O-D-Glucoside against Zika Virus Infection. Virol. Sin. 2017, 32, 545–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu Ayana, M.A.; Elmasry, N.A.; Shehata, F.I.; Khalil, N.M. Efficacy of Quercetin on Alveolar Bone Structure of Rats with Induced Diabetes. Alex. Dent. J. 2017, 42, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikhomar, O.A.; Bahattab, O.S. Physiological Effect of Quercetin as a Natural Flavonoid to Be Used as Hypoglycemic Agent in Diabetes Mellitus Type II Rats. Saudi J. Biomed. Res. 2021, 6, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Mittal, P.; Vasant Bonde, G.; Ajmal, G.; Mishra, B. Design, Optimization, Characterization and in-Vivo Evaluation of Quercetin Enveloped Soluplus®/P407 Micelles in Diabetes Treatment. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2018, 46, S546–S555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, V.K.; Singh, T.G. Insulin Resistance and Bioenergetic Manifestations: Targets and Approaches in Alzheimer’s Disease. Life Sci. 2020, 262, 118401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, G.N.; Kim, J.H.; Kwak, J.H.; Jeong, C.H.; Jeong, H.R.; Lee, U.; Heo, H.J. Effect of Quercetin on Learning and Memory Performance in ICR Mice under Neurotoxic Trimethyltin Exposure. Food Chem. 2012, 132, 1019–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poprac, P.; Jomova, K.; Simunkova, M.; Kollar, V.; Rhodes, C.J.; Valko, M. Targeting Free Radicals in Oxidative Stress-Related Human Diseases. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2017, 38, 592–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arlt, S. Non-Alzheimer’s Disease-Related Memory Impairment and Dementia. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2013, 15, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paez-Ribes, M.; González-Gualda, E.; Doherty, G.J.; Muñoz-Espín, D. Targeting Senescent Cells in Translational Medicine. EMBO Mol. Med. 2019, 11, e10234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saez-Atienzar, S.; Masliah, E. Cellular Senescence and Alzheimer Disease: The Egg and the Chicken Scenario. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2020, 21, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elder, G.A.; Gama Sosa, M.A.; De Gasperi, R. Mouse Models of Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2017, 57, 1171–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.W.; Chen, J.Y.; Ouyang, D.; Lu, J.H. Quercetin in Animal Models of Alzheimer’s Disease: A Systematic Review of Preclinical Studies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, P.; Li, J.; Gao, S.; Yuan, Y.; Sun, Y.; Liu, N.; Li, Y.; Wang, G.; Chen, L.; Shi, J. Network Pharmacology-Based and Experimental Identification of the Effects of Quercetin on Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2020, 12, 589588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabogal-Guáqueta, A.M.; Muñoz-Manco, J.I.; Ramírez-Pineda, J.R.; Lamprea-Rodriguez, M.; Osorio, E.; Cardona-Gómez, G.P. The Flavonoid Quercetin Ameliorates Alzheimer’s Disease Pathology and Protects Cognitive and Emotional Function in Aged Triple Transgenic Alzheimer’s Disease Model Mice. Neuropharmacology 2015, 93, 134–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denny Joseph, K.M.; Muralidhara. Combined Oral Supplementation of Fish Oil and Quercetin Enhances Neuroprotection in a Chronic Rotenone Rat Model: Relevance to Parkinson’s Disease. Neurochem. Res. 2015, 40, 894–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, R.C.; Lall, R.; Srivastava, A. Nutraceuticals: Efficacy, Safety and Toxicity; Google Books; Academic Press: London, UK, 2021; Available online: https://books.google.es/books?hl=en&lr=&id=_DUXEAAAQBAJ&oi=fnd&pg=PP1&dq=Gupta,+R.C.%3B+Lall,+R.%3B+Srivastava,+A.+&ots=sENoAPsl39&sig=88gn5r6fsJ06l5Gz0-B_YbfsfN4&redir_esc=y#v=onepage&q=Gupta%2CR.C.%3BLall%2CR.%3BSrivastava%2CA.&f=false (accessed on 28 April 2023).
- Lee, M.; McGeer, E.G.; McGeer, P.L. Quercetin, Not Caffeine, Is a Major Neuroprotective Component in Coffee. Neurobiol. Aging 2016, 46, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaplatic, E.; Bule, M.; Shah, S.Z.A.; Uddin, M.S.; Niaz, K. Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Protective Role of Quercetin in Attenuating Alzheimer’s Disease. Life Sci. 2019, 224, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewi, B.E.; Desti, H.; Ratningpoeti, E.; Sudiro, M.; Fithriyah; Angelina, M. Effectivity of Quercetin as Antiviral to Dengue Virus-2 Strain New Guinea C in Huh 7-It 1 Cell Line. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 462, 012033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johari, J.; Kianmehr, A.; Mustafa, M.R.; Abubakar, S.; Zandi, K. Antiviral Activity of Baicalein and Quercetin against the Japanese Encephalitis Virus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 16020–16045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho-dos-Reis, J.G.A.; Gomes, O.A.; Bortolini, D.E.; Martins, M.L.; Almeida, M.R.; Martins, C.S.; Carvalho, L.D.; Souza, J.G.; Vilela, J.M.C.; Andrade, M.S.; et al. Evaluation of the Effects of Quercetin and Kaempherol on the Surface of MT-2 Cells Visualized by Atomic Force Microscopy. J. Virol. Methods 2011, 174, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Son, M.; Ryu, E.; Shin, Y.S.; Kim, J.G.; Kang, B.W.; Sung, G.; Cho, H.; Kang, H. Quercetin-Induced Apoptosis Prevents EBV Infection. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 12603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colunga Biancatelli, R.M.L.; Berrill, M.; Catravas, J.D.; Marik, P.E. Quercetin and Vitamin C: An Experimental, Synergistic Therapy for the Prevention and Treatment of SARS-CoV-2 Related Disease (COVID-19). Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, D.; Zhou, X.; Zhao, C.; Chen, H.; Zhao, Y.; Gong, X. Anti-Inflammatory, Antiviral and Quantitative Study of Quercetin-3-O-β-D-Glucuronide in Polygonum perfoliatum L. Fitoterapia 2011, 82, 805–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Li, R.; Li, X.; He, J.; Jiang, S.; Liu, S.; Yang, J. Quercetin as an Antiviral Agent Inhibits Influenza a Virus (IAV) Entry. Viruses 2015, 8, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguirre, L.; Arias, N.; Macarulla, M.T.; Gracia, A.; Portillo, M.P. Beneficial Effects of Quercetin on Obesity and Diabetes. Open. Nutraceuticals J. 2011, 4, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosoda, S.; Kawazoe, Y.; Shiba, T.; Numazawa, S.; Manabe, A. Anti-Obesity Effect of Ginkgo Vinegar, a Fermented Product of Ginkgo Seed Coat, in Mice Fed a High-Fat Diet and 3T3-L1 Preadipocyte Cells. Nutrients 2020, 12, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pei, Y.; Otieno, D.; Gu, I.; Lee, S.O.; Parks, J.S.; Schimmel, K.; Kang, H.W. Effect of Quercetin on Nonshivering Thermogenesis of Brown Adipose Tissue in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Mice. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2021, 88, 108532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, H.H.; Kotob, S.E.; Abd-Rabou, A.A.; Aglan, H.A.; Elmegeed, G.A.; Mohawed, O.A. Pre-Clinical Evidence for the Anti-Obesity Potential of Quercetin and Curcumin Loaded Chitosan/PEG Blended PLGA Nanoparticles. Biomed. Pharmacol. J. 2021, 14, 1731–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabavi, S.F.; Russo, G.L.; Daglia, M.; Nabavi, S.M. Role of Quercetin as an Alternative for Obesity Treatment: You Are What You Eat! Food Chem. 2015, 179, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pangeni, R.; Kang, S.W.; Oak, M.; Park, E.Y.; Park, J.W. Oral Delivery of Quercetin in Oil-in-Water Nanoemulsion: In Vitro Characterization and in Vivo Anti-Obesity Efficacy in Mice. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 38, 571–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, M.J.; Lee, Y.J.; Hwang, J.H.; Kim, K.J.; Lee, B.Y. The Inhibitory Effects of Quercetin on Obesity and Obesity-Induced Inflammation by Regulation of MAPK Signaling. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2015, 26, 1308–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.; Zeng, Y.; Li, G.; Chen, J.; Chen, X. Quercetin Improves High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity by Modulating Gut Microbiota and Metabolites in C57BL/6J Mice. Phytother. Res. 2022, 36, 4558–4572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amanzadeh, E.; Esmaeili, A.; Rahgozar, S.; Nourbakhshnia, M. Application of Quercetin in Neurological Disorders: From Nutrition to Nanomedicine. Rev. Neurosci. 2019, 30, 555–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roshanravan, N.; Askari, S.F.; Fazelian, S.; Ayati, M.H.; Namazi, N. The roles of quercetin in diabetes mellitus and related metabolic disorders; special focus on the modulation of gut microbiota: A comprehensive review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 63, 2990–3003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, H.; Kim, C.S.; Yu, R. Quercetin Upregulates Uncoupling Protein 1 in White/Brown Adipose Tissues through Sympathetic Stimulation. J. Obes. Metab. Syndr. 2018, 27, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poznyak, A.; Grechko, A.V.; Poggio, P.; Myasoedova, V.A.; Alfieri, V.; Orekhov, A.N. The Diabetes Mellitus–Atherosclerosis Connection: The Role of Lipid and Glucose Metabolism and Chronic Inflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oboh, G.; Ademosun, A.O.; Ogunsuyi, O.B. Quercetin and Its Role in Chronic Diseases. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2016, 929, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oboh, G.; Ademosun, A.O.; Ayeni, P.O.; Omojokun, O.S.; Bello, F. Comparative Effect of Quercetin and Rutin on α-Amylase, α-Glucosidase, and Some pro-Oxidant-Induced Lipid Peroxidation in Rat Pancreas. Comp. Clin. Path. 2015, 24, 1103–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmati, M.; Mostafavi, S.E.; Zarban, A.; Hoshyar, R. Protective Effects of Quercetin on Hyperglycemia and Stress Proteins Expression in Rats with Streptozocin-Induced Diabetes. Mod. Care J. 2018, 15, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maciel, R.M.; Carvalho, F.B.; Olabiyi, A.A.; Schmatz, R.; Gutierres, J.M.; Stefanello, N.; Zanini, D.; Rosa, M.M.; Andrade, C.M.; Rubin, M.A.; et al. Neuroprotective Effects of Quercetin on Memory and Anxiogenic-like Behavior in Diabetic Rats: Role of Ectonucleotidases and Acetylcholinesterase Activities. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2016, 84, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimpour, S.; Zakeri, M.; Esmaeili, A. Crosstalk between Obesity, Diabetes, and Alzheimer’s Disease: Introducing Quercetin as an Effective Triple Herbal Medicine. Ageing Res. Rev. 2020, 62, 101095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhawan, V.; Bakshi, C.; Rather, R.A. Molecular Targets and Novel Therapeutics to Target Oxidative Stress in Cardiovascular Diseases; Springer: Singapore, 2019; ISBN 9789811382734. [Google Scholar]
- Taïlé, J.; Arcambal, A.; Clerc, P.; Gauvin-Bialecki, A.; Gonthier, M.P. Medicinal Plant Polyphenols Attenuate Oxidative Stress and Improve Inflammatory and Vasoactive Markers in Cerebral Endothelial Cells during Hyperglycemic Condition. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, R.V.; Mistry, B.M.; Shinde, S.K.; Syed, R.; Singh, V.; Shin, H.S. Therapeutic Potential of Quercetin as a Cardiovascular Agent. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 155, 889–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeinali, M.; Rezaee, S.A.; Hosseinzadeh, H. An Overview on Immunoregulatory and Anti-Inflammatory Properties of Chrysin and Flavonoids Substances. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 92, 998–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Vizcaino, F.; Bishop-Bailley, D.; Lodi, F.; Duarte, J.; Cogolludo, A.; Moreno, L.; Bosca, L.; Mitchell, J.A.; Warner, T.D. The Flavonoid Quercetin Induces Apoptosis and Inhibits JNK Activation in Intimal Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 346, 919–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marunaka, Y.; Marunaka, R.; Sun, H.; Yamamoto, T.; Kanamura, N.; Inui, T.; Taruno, A. Actions of Quercetin, a Polyphenol, on Blood Pressure. Molecules 2017, 22, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, K.; Jiang, T.; Zhao, G.J. Quercetin Induces the Selective Uptake of HDL-Cholesterol: Via Promoting SR-BI Expression and the Activation of the PPARγ/LXRα Pathway. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 624–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyagbemi, A.A.; Omobowale, T.O.; Ola-Davies, O.E.; Asenuga, E.R.; Ajibade, T.O.; Adejumobi, O.A.; Arojojoye, O.A.; Afolabi, J.M.; Ogunpolu, B.S.; Falayi, O.O.; et al. Quercetin Attenuates Hypertension Induced by Sodium Fluoride via Reduction in Oxidative Stress and Modulation of HSP 70/ERK/PPARγ Signaling Pathways. BioFactors 2018, 44, 465–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, S.; Mukai, Y. Modulation of Chronic Inflammation by Quercetin: The Beneficial Effects on Obesity. J. Inflamm. Res. 2020, 4, 421–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brüll, V.; Burak, C.; Stoffel-Wagner, B.; Wolffram, S.; Nickenig, G.; Müller, C.; Langguth, P.; Alteheld, B.; Fimmers, R.; Naaf, S.; et al. Effects of a Quercetin-Rich Onion Skin Extract on 24 h Ambulatory Blood Pressure and Endothelial Function in Overweight-to-Obese Patients with (Pre-)Hypertension: A Randomised Double-Blinded Placebo-Controlled Cross-over Trial. Br. J. Nutr. 2015, 114, 1263–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzocchella, L.; Fantini, M.; Benvenuto, M.; Masuelli, L.; Tresoldi, I.; Modesti, A.; Bei, R. Dietary Flavonoids: Molecular Mechanisms of Action as Anti- Inflammatory Agents. Recent Pat. Inflamm. Allergy Drug Discov. 2011, 5, 200–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Takahashi, R. Flavonoids and Asthma. Nutrients 2013, 5, 2128–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juríková, T. Polyphenols and Their Mechanism of Action in Allergic Immune ResponseImmune Response. Glob. J. Allergy 2015, 1, 37–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, A.; Zhang, T.; Yonekura, L.; Tamura, H. Antiallergic Activities of Eleven Onions (Allium Cepa) Were Attributed to Quercetin 4′-Glucoside Using QuEChERS Method and Pearson’s Correlation Coefficient. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 14, 581–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mlcek, J.; Jurikova, T.; Skrovankova, S.; Sochor, J. Quercetin and Its Anti-Allergic Immune Response. Molecules 2016, 21, 623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, T.T.; Campos, K.M.; Cerqueira-Lima, A.T.; Carneiro, T.C.B.; Da Silva Velozo, E.; Melo, I.C.A.R.; Figueiredo, E.A.; De Jesus Oliveira, E.; De Vasconcelos, D.F.S.A.; Pontes-De-Carvalho, L.C.; et al. Potential Therapeutic Effect of Allium cepa L. and Quercetin in a Murine Model of Blomia Tropicalis Induced Asthma. DARU J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 23, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weng, Z.; Zhang, B.; Asadi, S.; Sismanopoulos, N.; Butcher, A.; Fu, X.; Katsarou-Katsari, A.; Antoniou, C.; Theoharides, T.C. Quercetin Is More Effective than Cromolyn in Blocking Human Mast Cell Cytokine Release and Inhibits Contact Dermatitis and Photosensitivity in Humans. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izadi, N.; Luu, M.; Ong, P.Y.; Tam, J.S. The Role of Skin Barrier in the Pathogenesis of Food Allergy. Children 2015, 2, 382–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lodge, C.J.; Allen, K.J.; Lowe, A.J.; Dharmage, S.C. Overview of Evidence in Prevention and Aetiology of Food Allergy: A Review of Systematic Reviews. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2013, 10, 5781–5806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shishehbor, F.; Behroo, L.; Broujerdnia, M.G.; Namjoyan, F.; Latifi, S.M. Quercetin Effectively Quells Peanut-Induced Anaphylactic Reactions in the Peanut Sensitized Rats. Iran. J. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2010, 9, 27–34. [Google Scholar]
- Khazdair, M.R.; Anaeigoudari, A.; Kianmehr, M. Anti-Asthmatic Effects of Portulaca Oleracea and Its Constituents, a Review. J. Pharmacopunct. 2019, 22, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogerio, A.P.; Dora, C.L.; Andrade, E.L.; Chaves, J.S.; Silva, L.F.C.; Lemos-Senna, E.; Calixto, J.B. Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Quercetin-Loaded Microemulsion in the Airways Allergic Inflammatory Model in Mice. Pharmacol. Res. 2010, 61, 288–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Xu, M.; Wu, X.; Zhao, F.; Zhao, C. Quercetin Attenuates Collagen-Induced Arthritis by Restoration of Th17/Treg Balance and Activation of Heme Oxygenase 1-Mediated Anti-Inflammatory Effect. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2018, 54, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafarinia, M.; Sadat Hosseini, M.; Kasiri, N.; Fazel, N.; Fathi, F.; Ganjalikhani Hakemi, M.; Eskandari, N. Quercetin with the Potential Effect on Allergic Diseases. Allergy Asthma Clin. Immunol. 2020, 16, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Li, Q.; Zhou, X.D.; Kolosov, V.P.; Perelman, J.M. The Effect of Quercetin on Human Neutrophil Elastase-induced Mucin5AC Expression in Human Airway Epithelial Cells. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2012, 14, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.X.; Wen, L.; Zhong, W.J.; Xiong, L.; Liang, J.; Wang, H.L. Quercetin, Kaempferol and Isorhamnetin in Elaeagnus Pungens Thunb. Leaf: Pharmacological Activities and Quantitative Determination Studies. Chem. Biodivers. 2018, 15, e1800129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caglayan Sozmen, S.; Karaman, M.; Micili, S.C.; Isik, S.; Bagriyanik, A.; Arikan Ayyildiz, Z.; Uzuner, N.; Anal, O.; Karaman, O.; Sule, C.; et al. Effects of Quercetin Treatment on Epithelium-Derived Cytokines and Epithelial Cell Apoptosis in Allergic Airway Inflammation Mice Model. Iran. J. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2016, 15, 487–497. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.; Wang, H.; Zhang, J.; Yu, C.; Liu, C.; Sun, H.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Lin, X. Antiasthmatic Activity of Quercetin Glycosides in Neonatal Asthmatic Rats. 3 Biotech. 2019, 9, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Xue, L.; Xu, H.; Zhao, Q.Y.; Wang, Q.; She, Y.S.; Zang, D.A.; Shen, J.; Peng, Y.B.; Zhao, P.; et al. Polygonum aviculare L. Extract and Quercetin Attenuate Contraction in Airway Smooth Muscle. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, A.F.; Borge, G.I.A.; Piskula, M.; Tudose, A.; Tudoreanu, L.; Valentová, K.; Williamson, G.; Santos, C.N. Bioavailability of Quercetin in Humans with a Focus on Interindividual Variation. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2018, 17, 714–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabeek, W.M.; Marra, M.V. Dietary Quercetin and Kaempferol: Bioavailability and Potential Cardiovascular-Related Bioactivity in Humans. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasikci, M.B.; Bagdatlioglu, N. Bioavailability of Quercetin. Curr. Res. Nutr. Food Sci. 2016, 4, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degroote, J.; Vergauwen, H.; Van Noten, N.; Wang, W.; De Smet, S.; Van Ginneken, C.; Michiels, J. The Effect of Dietary Quercetin on the Glutathione Redox System and Small Intestinal Functionality of Weaned Piglets. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, G.; van der Hooft, J.J.J.; Crozier, A. A Comprehensive Evaluation of the [2-14C](–)-Epicatechin Metabolome in Rats. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2016, 99, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, G.; Kay, C.D.; Crozier, A. The Bioavailability, Transport, and Bioactivity of Dietary Flavonoids: A Review from a Historical Perspective. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2018, 17, 1054–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Sun, C.; Mao, L.; Ma, P.; Liu, F.; Yang, J.; Gao, Y. The Biological Activities, Chemical Stability, Metabolism and Delivery Systems of Quercetin: A Review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 56, 21–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimori, M.; Kadota, K.; Shimono, K.; Shirakawa, Y.; Sato, H.; Tozuka, Y. Enhanced Solubility of Quercetin by Forming Composite Particles with Transglycosylated Materials. J. Food Eng. 2015, 149, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vries, J.H.M.; Hollman, P.C.H.; Meyboom, S.; Buysman, M.N.C.P.; Zock, P.L.; Van Staveren, W.A.; Katan, M.B. Plasma Concentrations and Urinary Excretion of the Antioxidant Flavonols Quercetin and Kaempferol as Biomarkers for Dietary Intake. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1998, 68, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollman, P.C.H.; Van Trijp, J.M.P.; Buysman, M.N.C.P.; Martijn, M.S.; Mengelers, M.J.B.; De Vries, J.H.M.; Katan, M.B. Relative Bioavailability of the Antioxidant Flavonoid Quercetin from Various Foods in Man. FEBS Lett. 1997, 418, 152–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olthof, M.R.; Hollman, P.C.H.; Vree, T.B.; Katan, M.B. Human Nutrition and Metabolism—Research Communication Bioavailabilities of Quercetin-3- Glucoside Do Not Differ In. Hum. Nutr. Metab.-Res. Commun. 2000, 2, 1200–1203. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Mah, E.; Davis, C.G.; Jalili, T.; Ferruzzi, M.G.; Chun, O.K.; Bruno, R.S. Dietary Fat Increases Quercetin Bioavailability in Overweight Adults. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2013, 57, 896–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majidiyan, N.; Hadidi, M.; Azadikhah, D.; Moreno, A. Protein Complex Nanoparticles Reinforced with Industrial Hemp Essential Oil: Characterization and Application for Shelf-Life Extension of Rainbow Trout Fillets. Food Chem. X 2022, 13, 100202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesami, S.; Safi, S.; Larijani, K.; Badi, H.N.; Abdossi, V.; Hadidi, M. Synthesis and Characterization of Chitosan Nanoparticles Loaded with Greater Celandine (Chelidonium majus L.) Essential Oil as an Anticancer Agent on MCF-7 Cell Line. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 194, 974–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadidi, M.; Boostani, S.; Jafari, S.M. Pea Proteins as Emerging Biopolymers for the Emulsification and Encapsulation of Food Bioactives. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 126, 107474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grgić, J.; Šelo, G.; Planinić, M.; Tišma, M.; Bucić-Kojić, A. Role of the Encapsulation in Bioavailability of Phenolic Compounds. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadidi, M.; Rostamabadi, H.; Moreno, A.; Jafari, S.M. Nanoencapsulation of Essential Oils from Industrial Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) by-Products into Alfalfa Protein Nanoparticles. Food Chem. 2022, 386, 132765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadidi, M.; Majidiyan, N.; Jelyani, A.Z.; Moreno, A.; Hadian, Z.; Mousavi Khanegah, A. Alginate/Fish Gelatin-Encapsulated Lactobacillus acidophilus: A Study on Viability and Technological Quality of Bread during Baking and Storage. Foods 2021, 10, 2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasti, B.; Erfanian, A.; Selamat, J. Novel Nanoliposomal Encapsulated Omega-3 Fatty Acids and Their Applications in Food. Food Chem. 2017, 230, 690–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Kong, Y.; Ye, A.; Shen, P.; Dong, L.; Xu, X.; Hou, Y.; Wang, Y.; Jin, Y.; Han, J. Preparation, Formation Mechanism and in Vitro Dynamic Digestion Behavior of Quercetin-Loaded Liposomes in Hydrogels. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 104, 105743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caddeo, C.; Gabriele, M.; Fernàndez-Busquets, X.; Valenti, D.; Fadda, A.M.; Pucci, L.; Manconi, M. Antioxidant Activity of Quercetin in Eudragit-Coated Liposomes for Intestinal Delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 565, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Zou, M.; Ma, X.; Lv, R.; Ding, T.; Liu, D. Co-Encapsulation of EGCG and Quercetin in Liposomes for Optimum Antioxidant Activity. J. Food Sci. 2019, 84, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, M.; Han, J.; Ye, A.; Liu, W.; Xu, X.; Yao, Y.; Li, K.; Kong, Y.; Wei, F.; Zhou, W. Structural Characterization and Biological Fate of Lactoferrin-Loaded Liposomes during Simulated Infant Digestion. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2019, 99, 2677–2684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Wei, F.; Ye, A.; Tian, M.; Han, J. Kinetic Stability and Membrane Structure of Liposomes during in Vitro Infant Intestinal Digestion: Effect of Cholesterol and Lactoferrin. Food Chem. 2017, 230, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Wang, Q.; Chu, L.; Xia, Q. Liposome-Chitosan Hydrogel Bead Delivery System for the Encapsulation of Linseed Oil and Quercetin: Preparation and in Vitro Characterization Studies. LWT 2020, 117, 108615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghababaei, F.; Cano-Sarabia, M.; Trujillo, A.J.; Quevedo, J.M.; Ferragut, V. Buttermilk as Encapsulating Agent: Effect of Ultra-High-Pressure Homogenization on Chia Oil-in-Water Liquid Emulsion Formulations for Spray Drying. Foods 2021, 10, 1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.; Mcclements, D.J. Application of Advanced Emulsion Technology in the Food Industry: A Review and Critical Evaluation. Foods 2021, 10, 812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Ju, X.; Aluko, R.E.; Zou, Y.; Wang, Z.; Liu, M.; He, R. Rice Bran Protein-Based Nanoemulsion Carrier for Improving Stability and Bioavailability of Quercetin. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 108, 106042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Zheng, B.; Mcclements, D.J. In Vitro Gastrointestinal Stability of Lipophilic Polyphenols Is Dependent on Their Oil-Water Partitioning in Emulsions: Studies on Curcumin, Resveratrol, and Quercetin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 3340–3350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Zheng, B.; McClements, D.J. Encapsulation of Lipophilic Polyphenols in Plant-Based Nanoemulsions: Impact of Carrier Oil on Lipid Digestion and Curcumin, Resveratrol and Quercetin Bioaccessibility. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 3420–3432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, J.; El-Naggar, M.E. Synthesis of an Environmentally Quercetin Nanoemulsion to Ameliorate Diabetic-Induced Cardiotoxicity. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2021, 33, 101983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astray, G.; Mejuto, J.C.; Simal-Gandara, J. Latest Developments in the Application of Cyclodextrin Host-Guest Complexes in Beverage Technology Processes. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 106, 105882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paroha, S.; Dewangan, R.P.; Dubey, R.D.; Sahoo, P.K. Conventional and Nanomaterial-Based Techniques to Increase the Bioavailability of Therapeutic Natural Products: A Review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2020, 18, 1767–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashapov, R.; Lykova, A.; Kashapova, N.; Ziganshina, A.; Sergeeva, T.; Sapunova, A.; Voloshina, A.; Zakharova, L. Nanoencapsulation of Food Bioactives in Supramolecular Assemblies Based on Cyclodextrins and Surfactant. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 113, 106449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allahyari, S.; Trotta, F.; Valizadeh, H.; Jelvehgari, M.; Zakeri-Milani, P. Cyclodextrin-Based Nanosponges as Promising Carriers for Active Agents. Expert. Opin. Drug Deliv. 2019, 16, 467–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, K.H.; Choi, J.M.; Cho, E.; Jeong, D.; Shinde, V.V.; Kim, H.; Choi, Y.; Jung, S. Enhancement of Solubility and Bioavailability of Quercetin by Inclusion Complexation with the Cavity of Mono-6-Deoxy-6-Aminoethylamino-β-Cyclodextrin. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2017, 38, 880–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, R.B.; Limbhore, D.N.; Vanjari, S.S.; Chavan, M.C. Study of Solubility Enhancement of Quercetin by Inclusion Complexation with Betacyclodextrin. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2019, 11, 3102–3107. [Google Scholar]
- Peñalva, R.; Esparza, I.; Morales-Gracia, J.; González-Navarro, C.J.; Larrañeta, E.; Irache, J.M. Casein Nanoparticles in Combination with 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-Cyclodextrin Improves the Oral Bioavailability of Quercetin. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 570, 118652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penalva, R.; González-Navarro, C.J.; Gamazo, C.; Esparza, I.; Irache, J.M. Zein Nanoparticles for Oral Delivery of Quercetin: Pharmacokinetic Studies and Preventive Anti-Inflammatory Effects in a Mouse Model of Endotoxemia. Nanomedicine 2017, 13, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirpoor, S.F.; Hosseini, S.M.H.; Nekoei, A.R. Efficient Delivery of Quercetin after Binding to Beta-Lactoglobulin Followed by Formation Soft-Condensed Core-Shell Nanostructures. Food Chem. 2017, 233, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caló, E.; Khutoryanskiy, V.V. Biomedical Applications of Hydrogels: A Review of Patents and Commercial Products. Eur. Polym. J. 2015, 65, 252–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadidi, M.; Tan, C.; Assadpour, E.; Kharazmi, M.S.; Jafari, S.M. Emerging Plant Proteins as Nanocarriers of Bioactive Compounds. J. Control. Release 2023, 355, 327–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandemir, K.; Tomas, M.; McClements, D.J.; Capanoglu, E. Recent Advances on the Improvement of Quercetin Bioavailability. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 119, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, M.; Ghosh, B.; Giri, T.K. Enhanced Intestinal Stability and PH Sensitive Release of Quercetin in GIT through Gellan Gum Hydrogels. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2020, 196, 111341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Huang, R.L.; Zha, X.Q.; Li, Q.M.; Pan, L.H.; Luo, J.P. Encapsulation and Sustained Release of Curcumin by a Composite Hydrogel of Lotus Root Amylopectin and Chitosan. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 232, 115810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, T.; Chang, Y.H. Structural, Physicochemical, and in-Vitro Release Properties of Hydrogel Beads Produced by Oligochitosan and de-Esterified Pectin from Yuzu (Citrus junos) Peel as a Quercetin Delivery System for Colon Target. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 108, 106086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
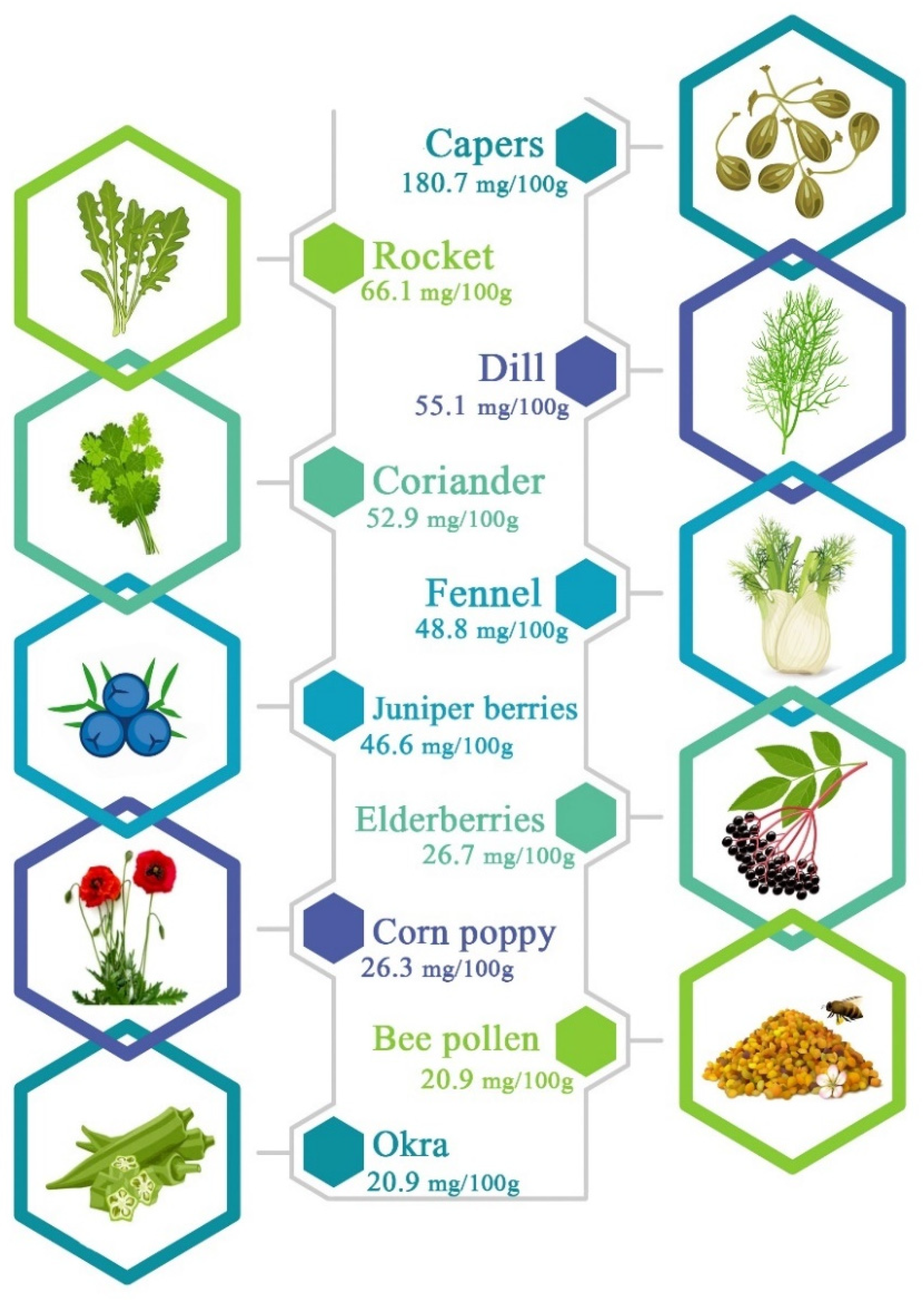
| Antioxidant Agent | Activity Carried Out | Key Findings | Study Models | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quercetin | Aging ovary-oxidative stress | Related genes are more prevalent | Animal models/in vivo | [30] |
| Quercetin | H2O2 | Quercetin has neuroprotective properties in addition to reducing the cytotoxicity of H2O2 | Clinical trial/in vitro | [23] |
| Onion extract plus six different types of quercetin | DPPH | There was an increase in the antioxidant activity of quercetin-3-O-glucuronide, isorhamnetin, tamarixetin, and quercetin | In vitro | [19] |
| Quercetin with Hesperidin | Hydrogen peroxide radical, DPPH, hydroxyl radical, nitric oxide, reducing power assay, and superoxide | Enhanced effectiveness of both substances against DPPH | In vitro | [18] |
| Quercetin and its glucosides | Hydroxyl groups’ function in DFT | The antioxidative exercises are predominantly OH, groups in the C-ring and B-ring | In vitro | [31] |
| Quercetin | Oxidative stress and BP in factors in urine and blood | No effects on oxidative stress; BP reduction | Clinical trial/ex vivo | [32] |
| Quercetin | Anti-reactive oxygen species (ROS) | GSH level regulated; decreases MDA levels while increasing SOD activity | Animal model/in vivo | [33] |
| Quercetin | Anti-free radical | Scavenging DNA from the free radicals | In vitro | [34] |
| Quercetin | Anti-aging | Reduced the severity of mouse senescence and lengthened the life of C. elegans by 15% | Animal model/in vivo | [35] |
| Quercetin with Na+, K+-ATPase | Anti-aging in humans | Influences the activity of ATP-dependent protein transporter | Clinical trial/in vitro | [36] |
| Quercetin | Cancer treatment | The antioxidant activity of quercetin caused inhibition of tumor growth | Milad | [37] |
| Quercetin | Anti-aging | Prevention of developing eye diseases such as macular degeneration and cataracts | Clinical trial/in vitro | [38] |
| Quercetin | Antidepressant activity | Increased 5-HT levels and prevented MAO-A levels in brain | Animal model | [39] |
| Quercetin | Antidepressant activity | Quercetin treatment with a concentration of 50 mg/kg for 8 weeks restored the levels of serum elements | Animal model | [40] |
| Quercetin | Antidepressant activity | Lipid hydroperoxide levels in the hippocampus rose after olfactory bulbectomy, proving improved depression in rats | Animal model | [41] |
| Quercetin | Anti-non-alcoholic liver | Liver protection from NASH by decreasing the levels of CYP2E1 | Animal model | [42] |
| Quercetin | Anti-free radical | Maintains homeostasis in the human body by removing free radicals | In vivo | [43] |
| Quercetin | Fatty liver treatment in non-alcoholics | Prevention of NAFLD and liver steatosis | In vivo | [44] |
| Dihydroquercetin | Renal protection | Regulating the nuclear factor 2 (Nrf2) signaling pathways connected to erythroid 2 (Nrf2). | Animal model/in vivo and in vitro | [45] |
| Quercetin | Quercetin treatment in kidney and tumor tissues | Regulated mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAP kinases) | Animal model/in vivo | [46] |
| Quercetin | Kidney disorder | Negatively regulated the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K/Akt). | Animal model/in vitro | [47] |
| Quercetin | kidney fibrosis treatment | Activated B-cell nuclear factor kappa light-chain enhancer hedgehog | Animal model/in vivo and in vitro | [48] |
| Quercetin | Anti-inflammatory | Participated in the overall biological activity of a quercetin-rich diet | Ex vivo | [20] |
| Cancer Type | Mechanisms | References |
|---|---|---|
| Lung cancer | BCL2/BAX-mediated necrosis, apoptosis, and mitotic catastrophe are all triggered Inhibits the ability of A549 cells to migrate; | [57] |
| Lung cancer | increases miR-21 expression and inhibits [Cr(VI)] | [58] |
| Lung cancer | In nanoparticle form, improved antitumor effect | [59] |
| Gastric cancer cell lines | Combination treatment results in improved anticancer effects | [60] |
| 13 HCC liver cancer cell line | Both substances’ combined anticancer effects | [61] |
| Ovarian cancer mouse model | Hydrogel of quercetin demonstrates improved apoptosis | [62] |
| EMT6 breast cancer cell line | In combined form, synergistic antitumor effects | [63] |
| Breast cancer | Slows cell cycle progression and increases cell apoptosis; p51, p21, and GADD45 signaling activity are upregulated, as is FasL mRNA expression | [64] |
| Colon cancer | ERK activation triggers G2 phase arrest and autophagic cell death | [65,66] |
| Kidney cancer | Increases the cytotoxic effects of DOX and guards against nephrotoxicity caused by DOX; reduces the expression of TNF, IL1B, iNOS, and caspase-3 in the kidneys | [67] |
| Thyroid cancer | Reduces chymotrypsin-like proteasome activity; raises the rate of apoptosis and decreases the rate of cell proliferation via activating caspases; reduces the concentration of Hsp90 | [68,69] |
| Eye cancer | Reduces the secretion of VEGF, RPE cell proliferation, and migration dose-dependently; VEGF production generated by CoCl2’s hypoxia is prevented | [70] |
| Brain cancer | Hsp27 inhibition reduces COX2 expression and serves as both a COX2 and Hsp27 inhibitor | [71] |
| Neck and head cancer | HSC3 cell colony growth is reduced; retards MMP2 and MMP9 levels | [72] |
| Gastric cancer | EBNA1 and LMP2 protein expression from EBV is inhibited | [55] |
| Prostate cancer | Prevents vimentin and N-cadherin expression that is stimulated by TGF-β; reduces Twist, Snail, and Slug expression when TGF-β is present in the prostate cancer 3 cell line | [73] |
| Pancreatic cancer | Cellular FLICE-like inhibitory protein expression is decreased | [74] |
| Skin cancer | Blocks the NF-kB activation and COX-2 up-regulation caused by UVB light in the Hacat cell line | [75] |
| Bone cancer | Reduces the expression of cyclin D1 in U2OSPt and SKOV3 cells | [76] |
| Liver cancer | Induces apoptosis | [52] |
| Breast cancer | Increases the amounts of cleaved caspases 8 and 3; inhibits the manufacture of phosphorylated JAK1 and STAT3; -reduces the activity of the STAT3-dependent luciferase reporter gene in BT474 cells. | [77] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aghababaei, F.; Hadidi, M. Recent Advances in Potential Health Benefits of Quercetin. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1020. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16071020
Aghababaei F, Hadidi M. Recent Advances in Potential Health Benefits of Quercetin. Pharmaceuticals. 2023; 16(7):1020. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16071020
Chicago/Turabian StyleAghababaei, Fatemeh, and Milad Hadidi. 2023. "Recent Advances in Potential Health Benefits of Quercetin" Pharmaceuticals 16, no. 7: 1020. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16071020
APA StyleAghababaei, F., & Hadidi, M. (2023). Recent Advances in Potential Health Benefits of Quercetin. Pharmaceuticals, 16(7), 1020. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16071020







